Pneumocystis jiroveci: Epidemiology and diagnosis
|
|
|
- Malcolm Geoffrey Ball
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 122 Pneumocystis jiroveci: Epidemiology and diagnosis Zineb Tlamçani 1, Mohammed Er-Rami 2 1 Laboratory of Peripheral Hospital Center, Taroudant, Morocco. 2 Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy of Fes, Morocco. Corresponding Author Zineb Tlamcani E mail: Tzineb@hotmail.fr Key words: Pneumocystis jiroveci, Pneumocystis pneumonia, immunodeficiency. The Pneumocystis organism was initially described in 1909 by Chagas. Pneumocystis jiroveci is an uncommon opportunistic organism, which induces a severe and mostly fatal pneumonia in immunocompromised people. Pneumocystosis comes from reactivation of latent infection acquired while childhood or active acquisition while immunosuppression state. The epidemiology of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) has changed considerably through the course of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. The establishments of PCP prophylaxis in 1989 and effective combination antiretroviral therapy in 1996, have resulted in substantial reduces INTRODUCTION Pneumocystis jiroveci is an uncommon opportunistic organism, which induces a severe and mostly fatal pneumonia in immunocompromised people [1]. The Pneumocystis organism was initially described in 1909 by Chagas in Guinea pigs, and after that by Carini in rat lung [2]. Until 1980 Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) was unusual and primarily noticed in association with syndromes of immunodeficiency or intensive immunosuppression, particularly cancer chemotherapy. With the HIV-1 pandemic, however, PCP become the major AIDS defining disease in developed countries[3]. Pneumocystis jiroveci, consequently, continues to be an organism of clinical significance in today's practice [4] ORGANISM Pneumocystis organisms were primarily known and named Pneumocystis carinii at the beginning of last century [5]. In 2002, human Pneumocystis organism was recalled in the incidence of PCP. Due to the insufficient specificity of clinical symptoms as well as the possibility of toxicity with therapy, the affirmation of PCP is important details for correct patient management. The traditional method for diagnosis of PCP depends on the microscopic visualization of organisms in respiratory samples. PCR diagnosis of P. jiroveci was introduced experimentally in Molecular methods, could detect P jirovecii DNA in respiratory samples from patients without clinically apparent PCP. In this review both epidemiology and diagnosis of Pneumocystis jiroveci will be discussed. Pneumocystis jiroveci by the identification of its genetic and functional distinctness, in honour of Otto Jirovec, who is recognized for identifying the microbe in humans [6,7]. Pneumocystis was for an extended time defined as a protozoe according to morphologic features and the resistance to classical antifungal agents. Then again, in the late eighties, P. carinii was positioned in the fungal kingdom depending on phylogenetic analysis of ribosomal RNA (rrna) sequences and observations of genome size. [8]. The organism has currently been fixed in a group of fungi entitled the Archiascomycetes. [9] In the lung, two main forms of the organism could be identified by microscopy: They are usually called cystic form (cysts) and trophic form (trophozoites), however they more appropriately, considering the fungal reclassification, might be defined as sporangium and yeast cells[10].
2 123 The cystic form (sporangium) is usually thickwalled oval, about 5 to 8 μ in diameter and include approximately eight daughter forms (spores or endospores, initially called intracystic bodies or sporozoites), which will eventually become trophic forms after excystation. The trophic form (yeast, previously trophozoite) is small (2 to 5μm), thin-walled, pleomorphic and commonly has an eccentric nucleus. The trophic forms are usually seen in clusters. A third form, the precyst, is infrequently encountered, but is believed to constitute an intermediate stage. There is no precise knowledge of the lifecycle as well as the mode of replication has not been absolutely demonstrated, but both asexual and sexual life cycles have been suggested according to electromicrographic observations of synaptonemal complexes [11,12] TRANSMISSION Reactivation of Latency Traditional concepts have retained that pneumocystosis comes from reactivation of latent infection acquired while childhood. Detectable antibodies are found in most of children by four years of age. Moreover, presence of P. jiroveci in respiratory samples from clinically normal population sustains the reactivation theory [13,14]. Besides, host immune evasion by variation of major suface glycoprotein (MSG), species specificity of P. jiroveci and complicated in vitro cultivation are constant with extended carriage or latency in the host 15,16]. Active Acquisition Almost all attempts to transfer P. jiroveci from one animal species to another have been failed. In natural environment, P. jiroveci deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) has been found in water, air and in soil samples, however, whole organism has been practically never recognized from these sources. Navin et al [17] discovered that patients with P. jiroveci were usually have history of recent gardening, therefore suggesting soil exposure. Outbreaks in oncology and transplant units have increased the possibility of person to person transmission. Besides clinical cases, sub-clinical cases and a few number of immunocompetent persons with no evidence of clinical disease accommodate P. jiroveci, forming the reservoir. This source should not be disregarded without the presence of other evidences. In any case, the transmission occurs via an airborne route as alveolus is the site of infection. The vertical transmission is rarely reported and it couldn't be demonstrated by animal experiments [18]. EPIDEMIOLOGY The epidemiology of PCP has changed considerably through the course of the HIV/AIDS epidemic. In the 1980s, PCP was the AIDS defining disease for about two-thirds of adults and adolescents with AIDS in the United States, and it was supposed that 75% of HIVinfected persons would acquire PCP through their lifetime [19]. At the beginning of the epidemic, the incidence of Pneumocystis pneumonia was approximately 20 cases per100 person-years in HIV-infected persons with CD4+ cell counts under 200 cells/l [20]. The establishments of PCP prophylaxis in 1989 and effective combination antiretroviral therapy in 1996 have resulted in substantial reduces in the incidence of Pneumocystis pneumonia. In the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Adult and Adolescent Spectrum of Disease (ASD) Project, the incidence of Pneumocystis pneumonia declined 3.4% per year for the period from 1992 to 1995 and then decreased 21.5% annually during 1996 to 1998, a time when effective combinations of antiretroviral therapy were starting to be applied [21]. In the Euro SIDA study, the incidence of Pneumocystis pneumonia reduced from 4.9 cases per 100 person-years before March 1995 to 0.3 cases per 100 person-years after March 1998 [22]. Even with its decreased incidence, PCP continues to be the common serious opportunistic infection among HIV-infected persons, and a considerable proportion of persons who develop Pneumocystis pneumonia are unconscious of their HIV infection or are outside of medical care, consequently minimizing opportunities for additional reductions in the incidence of the disease. A consideration, Pneumocystis pneumonia has been significantly reported in low- or middle-income countries (LMIC). One clinical study from Uganda observed that 38.6% of 83 HIV-infected patients who were admitted to the hospital with pneumonia and who had three expectorated sputum smears which were negative for acidfast bacilli had Pneumocystis pneumonia detected on bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) [23,24].
3 124 DIAGNOSIS CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS The fungal pathogen Pneumocystis jirovecii is the source of PCP in humans [25]. Patients with PCP generally present non-specific respiratory symptoms, such as dyspnea, cough, and fever. Immunocompromised hosts commonly present a triad of progressive dyspnoea of many weeks, non-productive cough or with clear sputum and low-grade fever. They are more apt to be in respiratory distress coupled with severe hypoxemia [4]. On medical exam, tachypnoea, tachycardia, cyanosis and fine dry rales can be present [2]. While extrapulmonary involvement is exceptional, eye, ear, spleen, bone marrow, lymph node, liver, and meningeal involvement, have been mentioned [4]. Chest X-ray generally reveals diffuse interstitial or peri-hilar reticulonodular infiltrates but could be normal in one-third of cases. Other findings, including spontaneous pneumothorax, effusions or cavitary lesions may be seen in few numbers of cases [26]. BIOLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS Due to the insufficient specificity of clinical symptoms as well as the possibility of toxicity with therapy, affirmation of PCP is important an essential details for correct evidence-based patient management [1]. Diagnosis of P jirovecii infection is hampered by the lack of a sustainable in vitro culture method. Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) > 460 IU/L has been noticed to be a sensitive test for this disease, but a variety of pathological conditions involving lungs indicate increased serum LDH level. Measurement of partial pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2) gives a perfect negative predictive value for exemption of P. jiroveci infection as PaO2 < 75 mmhg correlates with the illness [27, 28]. Conventional methods The traditional method for diagnosis of PCP depends on the microscopic visualization of P. jiroveci organisms in respiratory samples. Given that only a few organisms can be found within the upper respiratory tract, lower respiratory secretions are often essential for certain diagnosis. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) coupled with colorimetric as well as an immunofluorescent stain of BAL fluid is recognized as the technique of choice with sensitivity and specificity more than 95%. A different option is evaluation of material gotten by induced sputum. In spite of this, the sensitivity of that method is much more based on the experience of the personnel executing the procedure and checking the samples, with elevated variation in the diagnostic sensitivity noted (between 50 to 90%) [29,30,31,32]. The usage of cytochemical stains for diagnosis is very slow process, and it could be complicated to preserve laboratory diagnostic expertise due to the reduced incidence of PCP after the introduction of significantly active antiretroviral therapy [33,34]. PCR methods Since BAL is an invasive and irritating procedure that is not without risk, other noninvasive test were approved. PCR diagnosis of P. jiroveci was introduced experimentally in 1990 once Wakefield et al first identified DNA amplification of the multicopy mitochondrial ribosomal RNA gene. Since that time, numerous studies have evaluated PCR detection of Pneumocystis DNA in respiratory samples from HIV-1 positive and negative patients. To improve the diagnostic sensitivity of non-bal specimens, distinct PCR methods have been considered, such as different gene targets and the use of nested PCR, during which a second round of PCR reamplifies the primary PCR product [1]. Molecular methods, on the other hand, could detect P jirovecii DNA in respiratory samples from patients without clinically apparent PCP [35,36] advocating asymptomatic carriage or colonisation. Real-time PCR permits appropriate quantification of DNA as well as possibility to discriminate between asymptomatic carriage of P jirovecii and clinical disease depending on pathogen load. CONCLUSION P jirovecii is pathogen fungal organism witch continues to be an organism of clinical significance in today's practice and should not be disregarded because of the close link between this disease and HIV-infected persons. An earlier diagnosis with appropriate method could improve the prognosis of PCP and the correct patient therapy management.
4 125 REFERENCES 1. Helweg-Larsen J. Pneumocystis jiroveci Applied molecular microbiology, epidemiology and diagnosis.dan Med Bull 2004;51: Redhead SA, Cushion MT, Frenkel JK, Stringer JR. Pneumocystis and Trypanosoma cruzi: nomenclature and typifications. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2006;53: Chaisson RE, Keruly J, Richman DD, Moore RD. Pneumocystis prophylaxis and survival in patients with advanced human immunodeficiency virus infection treated with zidovudine. The Zidovudine Epidemiology Group. Arch Intern Med 1992; 152(10): Juliana Li, Andrew McIvor, Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia: Not a Disease of the Past; MUMJ 2012 ; 9 : Delanoe P, Delanoe M. Sur les supports des kystes Pneumocystis carinii du poumon des rats avec Tryponosoma lewisi. C R Acad Sci (Paris)1912; 155: Frenkel JK. Pneumocystis pneumonia, an immunodeficiency-dependent disease (IDD): a critical historical overview. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1999; 46(5):89S-92S. 7. Stringer JR, Beard CB, Miller RF, Wakefield AE. A New Name (Pneumocystis jiroveci) for Pneumocystis from Humans. Emerg Infect Dis,2002; 8(9): Lundgren B, Cotton R, Lundgren JD, Edman JC, Kovacs JA. Identification of Pneumocystis carinii chromosomes and mapping of five genes. Infect Immun 1990; 58(6): Haase G. Pneumocystis carinii Delanoe and Delanoe (1912) has been placed in the Archiascomycetales, a class of the Ascomycota. Infection and Immunity 1997; 65(10): Schuh JC, Harrington KA, Fanslow WC. Terminology changes needed for descriptions of Pneumocystis carinii infection. Infect Immun 1997; 65(3): Cushion MT, Ruffolo JJ, Walzer PD. Analysis of the developmentalstages of Pneumocystis carinii, in vitro. Lab Invest 1988; 58(3): Matsumoto Y, Yoshida Y. Sporogony in Pneumocystis carinii: synaptonemal complexes and meiotic nuclear divisions observed in precysts. J Protozool 1984; 31(3): Morris A, Beard CB, Huang L. Update on epidemiology and transmission of Pneumocystis carinii. Microbes Infect 2002; 4: Peglow SL, Smulian AG, Linke MJ, Pogue CL, Nurre S, Crisler J, et al. Serological responses to Pneumocystis carinii antigens in health and disease. J Infect Dis 1990; 161: Gigliotti F. Host species-specific antigenic variation of a mannosylated surface glycoprotein of Pneumocystis carinii. J Infect Dis 1992; 165: Gigliotti F, Harmsen AG, Haidaris CG, Haidaris PJ. Pneumocystis carinii is not universally transmissible between mammalian species. Infect Immun 1993; 61: Kaplan JE,Masur H, Holmes KK. Guidelines for preventing opportunistic infections among HIVinfected persons Recommendations of the U.S. Public Health Service and the Infectious Diseases Society of America. MMWR Recomm Rep 2002;51: R. Singhal, B.R. Mirdha and R. Guleria,Human Pneumocystosis.The Indian Journal of Chest Diseases & Allied Sciences 2005; 47: Hay JW, Osmond DH, Jacobson MA. Projecting the medical costs of AIDS and ARC in the United States. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1988;1: Phair J, Munoz A, Detels R, Kaslow R, Rinaldo C, Saah A. The risk of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia among men infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study Group. N Engl J Med 1990; 322: Kaplan JE, Hanson D, Dworkin MS, Frederick T, Bertolli J, Lindegren ML,et al. Epidemiology of human immunodeficiency virus-associated opportunistic infections in the United States in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 30:S Weverling GJ, Mocroft A, Ledergerber B, Kirk O, Gonzales-Lahoz J, d Arminio Monforte A, et al. Discontinuation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia prophylaxis after start of highly active antiretroviral therapy in HIV-1 infection. EuroSIDA Study Group. Lancet 1999;353: Worodria W, Okot-Nwang M, Yoo SD, Aisu T. Causes of lower respiratory infection in HIVinfected Ugandan adults who are sputum AFB smear-negative. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2003;7:
5 Laurence Huang, Alison Morris, Andrew H. Limper, and James M. Beck. Recent Advances and Future Directions in Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP).American Thoracic Society Documents 2006(3): Wilkin A, Fienberg J. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: a clinical review. Am Fam Physician 1999; 60: Opravil M, Marincek B, Walter AF, Weber R, Speich R, Battegay M, et al. Shortcomings of chest radiography in detecting Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 1994; 7: Quist J, Hill AR. Serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, tuberculosis and bacterial pneumonia. Chest 1995; 108: Thomas CF, Limper AH. Pneumocystis pneumonia: clinical presentation and diagnosis in patients with and without acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Semin Respir Infect 1998; 13: Elvin KM, Bjorkman A, Linder E, Heurlin N, Hjerpe A. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: detection of parasites in sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid by monoclonal antibodies. BMJ 1988; 297(6645): Huang L, Hecht FM, Stansell JD, Montanti R, Hadley WK, Hopewell PC. Suspected Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with negative induced sputum examination: Is early bronchoscopy useful? American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 1995; 151: Kovacs JA, Ng VL, Masur H, Leoung G, Hadley WK, Evans G et al. Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia: improved detection in sputum with use of monoclonal antibodies. N Engl J Med 1988; 318(10): Metersky ML, Aslenzadeh J, Stelmach P. A comparison of induced and expectorated sputum for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Chest 1998; 113(6): Wakefield AE, Pixley FJ, Banerji S, Sinclair K, Miller RF, Moxon ER, et al. Detection of Pneumocystis carinii with DNA amplification. Lancet 1990;336: Caliendo AM, Hewitt PL, Allega JM, Keen A, Ruoff KL, Ferraro MJ. Performance of a PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis carinii from respiratory specimens. J Clin Microbiol 1998;36: Helweg-Larsen J, Jensen JS, Dohn B, Benfield TL, Lundgren B. Detection of Pneumocystis DNA in samples from patients suspected of bacterial pneumonia: a case-control study. BMC Infect Dis 2002;2: Wakefield AE, Lindley AR, Ambrose HE, Denis CM, Miller RF. Limited asymptomatic carriage of Pneumocystis jiroveci in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J Infect Dis 2003;187: Peer reviewer :Hamed Suliman: Professor of Tropical Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt. Editor : Tarik Zaher: Professor of Tropical Medicine, Zagazig University.
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
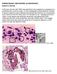 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
OCCURRENCE OF PNEUMOCYSTIS PNEUMONIA IN HIV-INFECTED PATIENTS AND THE INTERFERENCE OF THE HIGHLY ACTIVE ANTIRETROVIRAL THERAPY
 Received: August 24, 2007 Accepted: December 6, 2007 Abstract published online: December 17, 2007 Full paper published online: March 8, 2008 J. Venom. Anim. Toxins incl. Trop. Dis. V.14, n.1, p.152-160,
Received: August 24, 2007 Accepted: December 6, 2007 Abstract published online: December 17, 2007 Full paper published online: March 8, 2008 J. Venom. Anim. Toxins incl. Trop. Dis. V.14, n.1, p.152-160,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients with Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine ISSN 1681-6579 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-nahrain.edu.iq Detection of Pneumocystis carinii (jiroveci) from Iraqi Patients
Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia M. Olsson 1, K. Strålin 2 and H. Holmberg 2 1 Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical significance of nested polymerase chain reaction and immunofluorescence for detection of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia M. Olsson 1, K. Strålin 2 and H. Holmberg 2 1 Department
Pneumocystis colonisation is common among hospitalised HIV infected patients with non- Pneumocystis pneumonia
 1 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, San Francisco General Hospital, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA; 2 HIV/AIDS Division, San Francisco General Hospital,
1 Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, San Francisco General Hospital, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, California, USA; 2 HIV/AIDS Division, San Francisco General Hospital,
Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine
 Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
PNEUMOCYSTIS PNEUMONIA AMONG HIV PATIENTS IN MALAYSIA
 PNEUMOCYSTIS PNEUMONIA AMONG HIV PATIENTS IN MALAYSIA H Siti Asma 1, Mahiran Mustafa 5, Shukri Abdullah 2, AR Zaidah 1, AR Nurhaslindawati 4, A Sarimah 3, YY Chan 1 and M Ravichandran 1 1 Department of
PNEUMOCYSTIS PNEUMONIA AMONG HIV PATIENTS IN MALAYSIA H Siti Asma 1, Mahiran Mustafa 5, Shukri Abdullah 2, AR Zaidah 1, AR Nurhaslindawati 4, A Sarimah 3, YY Chan 1 and M Ravichandran 1 1 Department of
Geographical variation in serological responses to recombinant Pneumocystis jirovecii major surface glycoprotein antigens
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02716.x Geographical variation in serological responses to recombinant Pneumocystis jirovecii major surface glycoprotein antigens K. Daly 1,2, J. Koch 1,2, N.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2009.02716.x Geographical variation in serological responses to recombinant Pneumocystis jirovecii major surface glycoprotein antigens K. Daly 1,2, J. Koch 1,2, N.
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii
 141 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients with Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Blinded Comparison to Standard Methods Juan Torres, 1,a Mitchell Goldman,
141 Diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients with Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Blinded Comparison to Standard Methods Juan Torres, 1,a Mitchell Goldman,
Characteristics of Mycobacterium
 Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Mycobacterium Characteristics of Mycobacterium Very thin, rod shape. Culture: Aerobic, need high levels of oxygen to grow. Very slow in grow compared to other bacteria (colonies may be visible in up to
Pierre Flori, 1 Bahrie Bellete, 1 Fabrice Durand, 1 Hélène Raberin, 1 Céline Cazorla, 2 Jamal Hafid, 1 Frédéric Lucht 2 and Roger Tran Manh Sung 1
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 603 607 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45528-0 Comparison between real-time PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2004), 53, 603 607 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.45528-0 Comparison between real-time PCR, conventional PCR and different staining techniques for diagnosing Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia
ORIGINAL ARTICLE /j x
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01367.x Endemic fungal infections caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and Penicillium marneffei in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus and treated
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01367.x Endemic fungal infections caused by Cryptococcus neoformans and Penicillium marneffei in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus and treated
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection
 Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Diagnosis and Medical Management of Latent TB Infection Marsha Majors, RN September 7, 2017 TB Contact Investigation 101 September 6 7, 2017 Little Rock, AR EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Marsha Majors,
Outline. Cryptococcosis Pneumocystosis Diarrhea. Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015
 AU Edited: 05/06/15 Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015 Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Bethesda, Maryland Washington,
AU Edited: 05/06/15 Case Histories: HIV Related- Opportunistic Infections in 2015 Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University School of Medicine Bethesda, Maryland Washington,
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System
 Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Fungal Diseases of the Respiratory System Histoplasmosis(cave disease) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Histoplasma capsulatum, is usually
Jundishapur Journal of. Rate of Pneumocystis pneumonia in Iranian HIV+ Patients with Pulmonary Infiltrates
 KOWSAR Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology www.jjmicrobiol.com Rate of Pneumocystis pneumonia in Iranian HIV+ Patients with Pulmonary Infiltrates Fatemeh Maryam Sheikholeslami 1, Javid Sadraei 1, *, Parissa
KOWSAR Jundishapur Journal of Microbiology www.jjmicrobiol.com Rate of Pneumocystis pneumonia in Iranian HIV+ Patients with Pulmonary Infiltrates Fatemeh Maryam Sheikholeslami 1, Javid Sadraei 1, *, Parissa
Outcomes of Moderate-to-Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia Treated with Adjunctive Steroid in Non-HIV-Infected Patients
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017
 Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures
Pediatric Tuberculosis Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Lisa Y. Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Use of Different Primer Directed Sequence Amplification by Polymerase Chain Reaction for Identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Clinical Samples
 Original Article Use of Different Primer Directed Sequence Amplification by Polymerase Chain Reaction for Identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Clinical Samples Rashmi Gupta 1, Bijay Ranjan Mirdha
Original Article Use of Different Primer Directed Sequence Amplification by Polymerase Chain Reaction for Identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii in Clinical Samples Rashmi Gupta 1, Bijay Ranjan Mirdha
Opportunistic infections
 Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection. Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA
 Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
TB In Detroit 2011* Early TB: Smudge Sign. Who is at risk for exposure to or infection with TB? Who is at risk for TB after exposure or infection?
 Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Those oral antibiotics are just not working! Inpatient Standards of Care & Discharge Planning S/He s in the Hospital: Now What Do I Do? Dana G. Kissner, MD TB Intensive Workshop, Lansing, MI 2012 Objectives:
Prevalent opportunistic infections associated with HIV-positive children 0-5 years in Benin city, Nigeria
 Malaysian Journal of Microbiology, Vol 4(2) 2008, pp. 11-14 http://dx.doi.org/10.21161/mjm.11508 Prevalent opportunistic infections associated with HIV-positive children 0-5 years in Benin city, Nigeria
Malaysian Journal of Microbiology, Vol 4(2) 2008, pp. 11-14 http://dx.doi.org/10.21161/mjm.11508 Prevalent opportunistic infections associated with HIV-positive children 0-5 years in Benin city, Nigeria
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN. Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012
 TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
TB & HIV CO-INFECTION IN CHILDREN Reené Naidoo Paediatric Infectious Diseases Broadreach Healthcare 19 April 2012 Introduction TB & HIV are two of the leading causes of morbidity & mortality in children
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Disease Under Surveillance Management Guidelines March 2011
 March 2011 Histoplasmosis Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical illness [1] with laboratory confirmation of infection: Isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from an appropriate clinical specimen (tissue
March 2011 Histoplasmosis Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical illness [1] with laboratory confirmation of infection: Isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from an appropriate clinical specimen (tissue
HIV-related respiratory conditions
 HIV-related respiratory conditions 3 Rossana A. Ditangco Head, AIDS Research Group Department of Health, Research Institute for Tropical Medicine, Philippines The respiratory system is one of the most
HIV-related respiratory conditions 3 Rossana A. Ditangco Head, AIDS Research Group Department of Health, Research Institute for Tropical Medicine, Philippines The respiratory system is one of the most
COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
 COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Ong CK 1, Tan WC 2, Leong KN 2, Abdul Razak M 1, Chow TS 2 1 Respiratory Unit, Penang
COHORT STUDY OF HIV POSITIVE AND HIV NEGATIVE TUBERCULOSIS in PENANG HOSPITAL: COMPARISON OF CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS Ong CK 1, Tan WC 2, Leong KN 2, Abdul Razak M 1, Chow TS 2 1 Respiratory Unit, Penang
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis
 PARA 317331 Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Microspora A group of organisms: small single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites belonging to Phylum Microspora Early-
PARA 317331 Microspora, Pneumocystis & Blastocystis hominis Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Microspora A group of organisms: small single-celled, obligate intracellular parasites belonging to Phylum Microspora Early-
Notice of Decision Not to Designate Pneumocystis Pneumonia as a Tropical Disease
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 08/24/2018 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2018-18313, and on govinfo.gov 4164-01-P DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 08/24/2018 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2018-18313, and on govinfo.gov 4164-01-P DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND
Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I
 BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
BIOL 4849 Medical Mycology Summer 2006 Histoplasmosis Lecture 7: Mycoses Caused by Dimorphic Fungi, Part I u Most common endemic mycotic disease in the United States u Two different varieties (actually
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP. Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital
 Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al.
 Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) processing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods The BAL procedure was performed following a standardized protocol by an experienced
Supplementary Material. Mühlethaler et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) processing and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) methods The BAL procedure was performed following a standardized protocol by an experienced
Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients
 DOI 10.1007/s10096-013-1960-3 ARTICLE Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients M. Maillet & D. Maubon & J. P. Brion
DOI 10.1007/s10096-013-1960-3 ARTICLE Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pj) quantitative PCR to differentiate Pj pneumonia from Pj colonization in immunocompromised patients M. Maillet & D. Maubon & J. P. Brion
Limited Asymptomatic Carriage of Pneumocystis jiroveci in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients
 MAJOR ARTICLE Limited Asymptomatic Carriage of Pneumocystis jiroveci in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients Ann E. Wakefield, 1,a Austin R. Lindley, 1 Helen E. Ambrose, 1 Cecile-Marie Denis,
MAJOR ARTICLE Limited Asymptomatic Carriage of Pneumocystis jiroveci in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients Ann E. Wakefield, 1,a Austin R. Lindley, 1 Helen E. Ambrose, 1 Cecile-Marie Denis,
TB Intensive Houston, Texas. Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith. November 12, 2009
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 10-12, 12 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 Childhood Tuberculosis Kim Connelly Smith MD, MPH November 12, 2009 1 OUTLINE Stages
A comparison of capillary electrophoresis and direct sequencing in upstream conserved sequence region analysis of Pneumocystis jirovecii strains
 Journal of Medical Microbiology (2013), 62, 560 564 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.045336-0 A comparison of capillary electrophoresis and direct sequencing in upstream conserved sequence region analysis of Pneumocystis
Journal of Medical Microbiology (2013), 62, 560 564 DOI 10.1099/jmm.0.045336-0 A comparison of capillary electrophoresis and direct sequencing in upstream conserved sequence region analysis of Pneumocystis
AIDS at 25. Epidemiology and Clinical Management MID 37
 AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
AIDS at 25 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Regional HIV and
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 03 Page March 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i3.50 Original Article A Study on the Incidence of Pneumocystis
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i3.50 Original Article A Study on the Incidence of Pneumocystis
To interrupt or not to interrupt Are we SMART enough?
 SMART To interrupt or not to interrupt Are we SMART enough? highly active antiretroviral therapy 5 1996 1997 10 25 43 45 35 metabolism 50 copies/ml lipodystrophy [fat redistribution syndrome] lactic acidosis
SMART To interrupt or not to interrupt Are we SMART enough? highly active antiretroviral therapy 5 1996 1997 10 25 43 45 35 metabolism 50 copies/ml lipodystrophy [fat redistribution syndrome] lactic acidosis
Title: Role of Interferon-gamma Release Assays in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Patients with Advanced HIV infection
 Author's response to reviews Title: Role of Interferon-gamma Release Assays in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Patients with Advanced HIV infection Authors: Adithya Cattamanchi (acattamanchi@medsfgh.ucsf.edu)
Author's response to reviews Title: Role of Interferon-gamma Release Assays in the Diagnosis of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Patients with Advanced HIV infection Authors: Adithya Cattamanchi (acattamanchi@medsfgh.ucsf.edu)
Geographic Clustering of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Patients with HIV Infection
 Geographic Clustering of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Patients with HIV Infection MICHAEL N. DOHN*, MICHAEL L. WHITE, ELLEN M. VIGDORTH, C. RALPH BUNCHER, VICKI S. HERTZBERG, ROBERT P. BAUGHMAN, A.
Geographic Clustering of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Patients with HIV Infection MICHAEL N. DOHN*, MICHAEL L. WHITE, ELLEN M. VIGDORTH, C. RALPH BUNCHER, VICKI S. HERTZBERG, ROBERT P. BAUGHMAN, A.
Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study
 MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study J. R. Zahar, 1,a M. Robin, 1 E. Azoulay, 2 F. Fieux, 2 G. Nitenberg, 1 and B. Schlemmer 2 1
MAJOR ARTICLE Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients with Malignancy: A Descriptive Study J. R. Zahar, 1,a M. Robin, 1 E. Azoulay, 2 F. Fieux, 2 G. Nitenberg, 1 and B. Schlemmer 2 1
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
New Insights Into Transmission, Diagnosis, and Drug Treatment of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia
 GRAND ROUNDS At the Clinical Center of the National Institutes of Health New Insights Into Transmission, Diagnosis, and Drug Treatment of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia Joseph A. Kovacs, MD Vee J. Gill,
GRAND ROUNDS At the Clinical Center of the National Institutes of Health New Insights Into Transmission, Diagnosis, and Drug Treatment of Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia Joseph A. Kovacs, MD Vee J. Gill,
Clinical and Public Health Impact of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) for Tuberculosis
 Clinical and Public Health Impact of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) for Tuberculosis Amit S. Chitnis, MD, MPH; Pennan M. Barry, MD, MPH; Jennifer M. Flood, MD, MPH. California Tuberculosis Controllers
Clinical and Public Health Impact of Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs) for Tuberculosis Amit S. Chitnis, MD, MPH; Pennan M. Barry, MD, MPH; Jennifer M. Flood, MD, MPH. California Tuberculosis Controllers
HIV-associated Pulmonary Disease. Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond QUESTION: HIV-associated Pulmonary Diseases
 Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
5/15/2017. What Does HIV/AIDS Look Like in DC in Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections
 Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
Potpourri of Challenges With Opportunistic Infections Henry Masur, MD Clinical Professor of Medicine George Washington University Washington, DC FORMATTED: 4/28/217 Learning Objectives After attending
Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome AIDS
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome AIDS Sudden outbreak in USA of opportunistic infections and cancers in young men in 1981 Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), Kaposi s
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome AIDS Sudden outbreak in USA of opportunistic infections and cancers in young men in 1981 Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), Kaposi s
Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011
 TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
TB Nurse Case Management Davenport, Iowa September 27 28, 2011 Pediatric TB Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD September 28, 2011 Lisa Armitige, MD, PhD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interest.
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Epidemiology and Management MID 37
 AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Adults and children
AIDS at 30 Epidemiology and Clinical Management Blood HIV Transmission transfusion injection drug use Sexual Intercourse heterosexual male to male Perinatal intrapartum breast feeding Adults and children
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author. CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel
 CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis
 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH May 12, 2015 TB for Community Providers May 12, 2015 Phoenix, Arizona EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Renuka Khurana, MD, MPH has the following disclosures
medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests
 medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests Purpose of monitoring Check on the physical, psychological and emotional condition of the patient Detect other treatable conditions Identify
medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests Purpose of monitoring Check on the physical, psychological and emotional condition of the patient Detect other treatable conditions Identify
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Quantitative and qualitative comparison of DNA
 1404 JClin Pathol 1993;46: 140-144 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Westminster Hospital, Horseferry Road, London SWIP 2AP T R Leigh J V Collins Department of HIV Medicine B G Gazzard Protein Reference
1404 JClin Pathol 1993;46: 140-144 Department of Respiratory Medicine, Westminster Hospital, Horseferry Road, London SWIP 2AP T R Leigh J V Collins Department of HIV Medicine B G Gazzard Protein Reference
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS
 Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
Immunodeficiencies HIV/AIDS Immunodeficiencies Due to impaired function of one or more components of the immune or inflammatory responses. Problem may be with: B cells T cells phagocytes or complement
ORIGINAL ARTICLE /j x
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01944.x Pneumocystis jirovecii multilocus genotyping profiles in patients from Portugal and Spain F. Esteves 1, M. A. Montes-Cano 2, C. de la Horra 2, M. C. Costa
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2007.01944.x Pneumocystis jirovecii multilocus genotyping profiles in patients from Portugal and Spain F. Esteves 1, M. A. Montes-Cano 2, C. de la Horra 2, M. C. Costa
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012
 TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Smith, MD, MPH July 19, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
TB Nurse Case Management San Antonio, Texas July 18 20, 2012 Pediatric TB Kim Smith, MD, MPH July 19, 2012 Kim Smith, MD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Philippine General Hospital
 Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Albert B. Albay Jr., MD Jemylyn Garcia, MD Joel Santiaguel, MD UP- TB in the Philippines 6 th leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Profile of Tuberculosis Infection among Current HIV+ Patients at the Albert B. Albay Jr., MD Jemylyn Garcia, MD Joel Santiaguel, MD UP- TB in the Philippines 6 th leading cause of morbidity and mortality
Laboratory investigation of Pneumocystis carinii
 336 Department of Microbiology, Raigmore Hospital, Inverness 1V2 3UJ, UK J M W Chatterton Genitourin Med 1992;68:336-341 Laboratory investigation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia JMW Chatterton, D O Ho
336 Department of Microbiology, Raigmore Hospital, Inverness 1V2 3UJ, UK J M W Chatterton Genitourin Med 1992;68:336-341 Laboratory investigation of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia JMW Chatterton, D O Ho
Contact Investigation San Antonio, Texas January 14-15, 2013
 Contact Investigation San Antonio, Texas January 14-15, 2013 Assigning Priorities to Contacts Patrick Moonan, PhD, MPH January 14, 2013 Patrick Moonan, PhD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No
Contact Investigation San Antonio, Texas January 14-15, 2013 Assigning Priorities to Contacts Patrick Moonan, PhD, MPH January 14, 2013 Patrick Moonan, PhD, MPH has the following disclosures to make: No
Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data
 Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data David Ebler, MD David Skarupa, MD Andrew J. Kerwin, MD, FACS Jhun de Villa, MD Michael S. Nussbaum, MD, FACS J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS
Accurate Diagnosis Of Postoperative Pneumonia Requires Objective Data David Ebler, MD David Skarupa, MD Andrew J. Kerwin, MD, FACS Jhun de Villa, MD Michael S. Nussbaum, MD, FACS J.J. Tepas III, MD, FACS
MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
 MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSP There are no translations available. MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSP There are no translations available. MANAGEMENT OF FEVER IN PEDIATRIC PATIENTS FOLLOWING HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL TRANSPLANTATION
PCR Diagnosis of Pneumocystis Pneumonia: A Bivariate Meta-analysis
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 October 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06066-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 October 2011 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.06066-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016
 TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD
 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
J F Huggett, 1 M S Taylor, 2 G Kocjan, 3 H E Evans, 4 S Morris-Jones, 5 V Gant, 5 T Novak, 1 A M Costello, 6 A Zumla, 1 R F Miller 4,7
 1 Centre for Infectious Diseases and International Health, Windeyer Institute for Medical Sciences, University College London, London, UK; 2 Welcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford,
1 Centre for Infectious Diseases and International Health, Windeyer Institute for Medical Sciences, University College London, London, UK; 2 Welcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics, University of Oxford,
Case 1. Background. Presenting Symptoms. Schecter Case1 Differential Diagnosis of TB 1
 TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
TB or Not TB? Case 1 Gisela Schecter, M.D., M.P.H. California Department of Public Health Background 26 year old African American male Born and raised in Bay Area of California Convicted of cocaine trafficking
GAFFI Fact Sheet. Disseminated histoplasmosis
 F GAFFI Fact Sheet Disseminated histoplasmosis ION NS ACT ALOR ECTIO B O F F L G ND L IN FU NGA FU Disseminated histoplasmosis is a sub- acute infection that may be diagnosed in patients with impaired
F GAFFI Fact Sheet Disseminated histoplasmosis ION NS ACT ALOR ECTIO B O F F L G ND L IN FU NGA FU Disseminated histoplasmosis is a sub- acute infection that may be diagnosed in patients with impaired
P neumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) continues to be a
 716 RESPIRATORY INFECTION Improved survival for HIV infected patients with severe Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is independent of highly active antiretroviral therapy R F Miller, E Allen, A Copas, M
716 RESPIRATORY INFECTION Improved survival for HIV infected patients with severe Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is independent of highly active antiretroviral therapy R F Miller, E Allen, A Copas, M
Prognostic Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Patients with Non-HIV Pneumocystis Pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Patients with Non-HIV Pneumocystis Pneumonia Koji Tamai, Ryo Tachikawa, Keisuke Tomii, Kazuma Nagata, Kojiro Otsuka, Atsushi Nakagawa, Kyoko
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Value of Bronchoalveolar Lavage in Patients with Non-HIV Pneumocystis Pneumonia Koji Tamai, Ryo Tachikawa, Keisuke Tomii, Kazuma Nagata, Kojiro Otsuka, Atsushi Nakagawa, Kyoko
Tuberculosis Intensive
 Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Tuberculosis Intensive San Antonio, Texas April 3 6, 2012 Tuberculosis Pathogenesis Lynn Horvath, MD April 3, 2012 Lynn Horvath, MD has the following disclosures to make: No conflict of interests No relevant
Making the Right Call With. Pneumonia. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a. Community-Acquired. What exactly is CAP?
 Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics
 Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit
 MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit Topics to be covered What is Tuberculosis? TB bacteria and what is unique about it. How is TB different from HIV? How is TB
MODULE ONE" TB Basic Science" Treatment Action Group TB/HIV Advocacy Toolkit Topics to be covered What is Tuberculosis? TB bacteria and what is unique about it. How is TB different from HIV? How is TB
Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal transplant
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10683-10689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050944 Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):10683-10689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0050944 Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
What are the clinical indicators of PCP?
 International Child Health Review Collaboration What are the clinical indicators of PCP? Primary Reviewers: Savini Wijesingha 1 Secondary Reviewer: Stephen Graham 2 1 University of Edinburgh,Scotland 2
International Child Health Review Collaboration What are the clinical indicators of PCP? Primary Reviewers: Savini Wijesingha 1 Secondary Reviewer: Stephen Graham 2 1 University of Edinburgh,Scotland 2
Influenza. Giovanni Maciocia
 Influenza Giovanni Maciocia Zhang Zhong Jing (about 150-219AD) Ye Tian Shi (1667-1746) Wu Ju Tong (1758-1836) 1. WESTERN MEDICINE VIEW a) INFLUENZA INFLUENZA IN CHINESE MEDICINE Epidemiologists predict
Influenza Giovanni Maciocia Zhang Zhong Jing (about 150-219AD) Ye Tian Shi (1667-1746) Wu Ju Tong (1758-1836) 1. WESTERN MEDICINE VIEW a) INFLUENZA INFLUENZA IN CHINESE MEDICINE Epidemiologists predict
Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease
 Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease Assist Prof. Somnuek Sungkanuparph Division of Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol
Cryptococcosis of the Central Nervous System: Classical and Immune-Reconstitution Disease Assist Prof. Somnuek Sungkanuparph Division of Infectious Diseases Faculty of Medicine Ramathibodi Hospital Mahidol
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update
 Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
Tuberculosis Tools: A Clinical Update CAPA Conference 2014 JoAnn Deasy, PA-C. MPH, DFAAPA jadeasy@sbcglobal.net Adjunct Faculty Touro PA Program Learning Objectives Outline the pathogenesis of active pulmonary
A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients T. Tia 1, C. Putaporntip 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE MYCOLOGY A highly sensitive novel PCR assay for detection of Pneumocystis jirovecii DNA in bronchoalveloar lavage specimens from immunocompromised patients T. Tia 1, C. Putaporntip 1,
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION
 MHD II, Session XII, STUDENT Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION Session XII MHD II April 21, 2014 STUDENT COPY Helpful Resource: ACP Medicine online available through LUHS Library Infectious
MHD II, Session XII, STUDENT Copy Page 1 CASE-BASED SMALL GROUP DISCUSSION Session XII MHD II April 21, 2014 STUDENT COPY Helpful Resource: ACP Medicine online available through LUHS Library Infectious
Before the talk. Have you encountered opportunistic infection? Have you ever prescribed biologic agents?
 Is prophylaxis of Pneumocystis jiroveci necessary during use of biologic agents in HIV-uninfected patients? Kai-Che Wei, MD. Department of Dermatology, Kaohsiung, Taiwan Before the talk Have you ever prescribed
Is prophylaxis of Pneumocystis jiroveci necessary during use of biologic agents in HIV-uninfected patients? Kai-Che Wei, MD. Department of Dermatology, Kaohsiung, Taiwan Before the talk Have you ever prescribed
This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017.
 This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017. 0 There is good evidence to suggest that patients eventually diagnosed with HIV infection have had contact with medical services, with symptoms
This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017. 0 There is good evidence to suggest that patients eventually diagnosed with HIV infection have had contact with medical services, with symptoms
Tuberculosis. Impact of TB. Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH)
 Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 20 Tuberculosis Learning Objectives 1. Describe the biologic characteristics of the agent 2. Determine the epidemiologic characteristics
Infectious Disease Epidemiology BMTRY 713 (A. Selassie, DrPH) Lecture 20 Tuberculosis Learning Objectives 1. Describe the biologic characteristics of the agent 2. Determine the epidemiologic characteristics
Introduction to HIV/AIDS
 HIV/AIDS Seminar 5 Welcome Back Introduction to HIV/AIDS History of HIV/AIDS It is now thought that HIV came from a similar virus found in chimpanzees - SIV. HIV probably entered North America around 1970
HIV/AIDS Seminar 5 Welcome Back Introduction to HIV/AIDS History of HIV/AIDS It is now thought that HIV came from a similar virus found in chimpanzees - SIV. HIV probably entered North America around 1970
Risk factors for active tuberculosis following antiretroviral treatment initiation in Abidjan
 Risk factors for active tuberculosis following antiretroviral treatment initiation in Abidjan Catherine Seyler, Siaka Toure, Eugène Messou, Dominique Bonard, Delphine Gabillard, Xavier Anglaret Online
Risk factors for active tuberculosis following antiretroviral treatment initiation in Abidjan Catherine Seyler, Siaka Toure, Eugène Messou, Dominique Bonard, Delphine Gabillard, Xavier Anglaret Online
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016
 Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
Latent Tuberculosis Infections Controversies in Diagnosis and Management Update 2016 Randy Culpepper, MD, MPH Deputy Heath Officer/Medical Director Frederick County Health Department March 16, 2016 2 No
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:478-485 Clinical significance of positive Pneumocystis jirovecii polymerase chain reaction in non-human immunodeficiency virus immunocompromised patients in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:478-485 Clinical significance of positive Pneumocystis jirovecii polymerase chain reaction in non-human immunodeficiency virus immunocompromised patients in
