Microbial recognition and the immune response Dr. Dana Philpott
|
|
|
- Virgil Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection Link between innate and adaptive immunity 2 Innate immunity Innate vs. adaptive immunity Adaptive immunity Conserved throughout evolution Evolved 500 million yrs ago? In all multicellular organisms Unique to vertebrates Organisms possess a set Infinite number of recognition number of recognition molecules molecules (antibodies) Cells are immediately active Cells require priming Has no memory Provides memory of infection 3 1
2 The discovery of the innate immune system Metchnikoff first described role of phagocytes in invertebrates (star fish) 4 How can our cells tell that something is foreign? Recognition of exogenous microbial products Recognition of endogenous danger signals Dr. Charles Janeway Dr. Polly Matzinger 5 Turns out they are both right! Innate immunity depends upon the recognition of: MAMPs (microbial-associated molecular patterns) Signatures of microbial infection - pieces of microbes DAMPs (danger-associated molecular patterns) Danger signals released from dead or dying cells 6 2
3 Overview of innate immunity Recognition of a: MAMP/DAMP (Danger signal) By a : PRM (Pattern recognition molecule) To induce: Signal transduction (Changes in gene expression) Destruction of microbes 7 What are MAMPs? Also known as PAMPs (pathogen-associated molecular patterns) Represent structural components of microorganisms unable to be modified d Include LPS, peptidoglycan, protein (flagellin) and nucleic acid 8 What are DAMPs? End or by-products of cell death or stress ATP, uric acid Xenogenous compounds Alum, silica, asbestos, amyloid fibers Common denominator of these factors: ROS, K+ efflux, lysosomal damage 9 3
4 MAMPs and DAMPs are the sensees, what are the sensors? PRM - pattern recognition molecules Soluble PRMs Collectins (e.g.: g: surfactant, mannose-binding lectin), Ficolins Cell signaling PRMS Toll-like receptors (TLR), Nod-like receptors (NLR), RIG-like helicase receptors (RLR), Dectin 10 Cell-signaling PRMs Membrane-associated TLR Cytoplasmic NLRs Membrane NLRs : Bruno Lemaitre and Jules Hoffmann: Drosophila use Toll to defend from infection with fungus Toll was first shown to be a protein involved in embryonic development Toll-deficient flies infected with Aspergillus fumigatus succumb to infection Flies use Toll to defend from fungi and also Gram + bacteria Lemaitre et al., Cell
5 Toll-like receptors - outside-in signalling Extracellular stimulation MAMP MAMP TLR3,7-9 TLR1,2,4-6 TLR1: BLP (with TLR2) TLR2: PGN, BLP, LTA TLR3: dsrna TLR4: LPS, taxol TLR5: Flagellin TLR6: BLP (With TLR2) TLR7: Anti-virals, ssrna TLR8: Anti-viral, ssrna TLR9: CpG DNA TLR10:? TLR11 (mouse): Toxoplasma NF-κB JNK Inflammation 13 Two distinct systems to detect microbialassociated molecular patterns? Intracellular Extracellular MAMP TLRs MAMP? NF-κB JNK Inflammation Clearance NF-κB JNK 14 Keeping peace with the intestine LPS Lack or low TLR expression Expression of TLR modulating proteins that interfere with signaling: MyD88s 15 5
6 Keeping peace with the intestine (2) LPS Pathogen NF-κB JNK Inflammation IL-8 16 Shigella flexneri Gram-negative bacteria Induces uptake into epithelial cells lives free in cytoplasm (actin comet tail) Causes intestinal inflammation bacteria Eukaryotic cell Philippe Sansonetti s laboratory 17 NFκB is activated in epithelial cells by invasive Shigella Non-invasive Shigella Shigella NFκB in cytoplasm NFκB in nucleus 18 6
7 Invasive S. flexneri induces NF-κB activation non invasive Shigella Invasive Shigella Electromobility shift assay: nuclear extracts P 32 -labeled DNA probe specific for NF-κB binding p50 p65 P 32 PAGE NF-κB 19 Cytoplasmic exposure of Shigella soluble factors activates NF-κB Supernatant of Shigella + FITC-dextran Medium anti p65 supernatant Immunofluorescence microscopy FITC dextran NF-κB 20 Microflora vs. pathogen Presentation of bacterial products to the intracellular compartment is sufficient to initiate a defensive Intracellular surveillance system of host defence 21 7
8 NLRs are related to plant R proteins involved in disease resistance NOD1 CARD NBS Tobacco N TIR NBS Arabidopsis RPS5 LZ NBS 22 NLR family (Nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat) CIITA (NLRA) (CARD) AD NACHT NAD NAIP (NLRB) BIR BIR BIR NACHT NOD1 NOD2 NLRC3 NLRC4 NLRC5 CARD NACHT NAD CARD CARD NACHT NAD (CARD) NACHT NAD CARD NACHT (CARD) NACHT NAD NLRX1 X NACHT NLRP1 PYD NACHT NAD FIIND CARD NLRP2-14 PYD NACHT NAD Modified from Fritz J.H. & Philpott D.J., Nat. Immunol. 2006;7(12): NLRs NOD2 Crohn s disease Blau syndrome NOD1 Asthma / IBD? Vitiligo NLRP1 NLRP3/Pypaf1/CIAS1/ Cryopyrin: NLRP 2-14 Muckle-Wells syndrome Cold stress syndrome CINCA syndrome NLRB/NAIP/Birc1 Susceptibility to Legionella infection (mice) NLRC4 Bare lymphocyte syndrome CIITA Leucine-rich repeats NBS CARD BIR (baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis) Pyrin DNA interaction domain 24 8
9 NLRs - detectors of MAMPs AND danger signals NOD1 NOD2 NLRP1 NLRP2-14 NLRC4 NAIP CIITA? Nalp3 Peptidoglycan MDP = Nod2 Tri-dap = Nod1 ROS K+ efflux Flagellin ATP Toxins Uric acid Asbestos 25 Nod proteins detect peptidoglycan from the bacterial cell wall Gram-positive Gram-negative From Perry et al., 2002 Microbial Life, Sinauer Associated ed. 26 Nod1 is an intracellular sensor for Gramnegative-specific peptidoglycan AU 205 nm HPLC analysis of peptidoglycan monomers from Neisseria Retention time (min) Only 2 fractions activate Nod1 Stimulation of Nod1 with each fraction NF-κB activation (fold synergy) Girardin et al., Science 2003 HPLC fraction 27 9
10 Nod1 HO O MurNAc O NH O O HN L-Ala O O NH D-Glu HO O Meso DAP HN O O NH 2 OH OH Microbial recognition and the immune Nod proteins detect peptidoglycan from the bacterial cell wall Tri-DAP Nod2 HO O MurNAc HO O NH O O MDP HN L-Ala O O NH D-Glu HO O HO MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu Minimal structure detected by Nod2 MurNAc-L-Ala-D-Glu-mesoDAP Minimal structure detected by Nod1 Nod1 recognizes DAP-type peptidoglycan - mostly Gram-negative Nod2 recognizes muramyl dipeptide - both types Inohara et al., J.B.C Girardin et al., J.B.C Girardin et al., Science 2003 Chamaillard et al., Nat. Immunol Proposed mechanism for Nod protein activation by a MAMP (PG) 2. Intracellular bacteria release PG PG 3. Nod1 unfolds and oligomerizes 1. Nod1 is folded in inactive state Nod1 PG 4. Nod1 oligomers provide a focal point for the recruitment of adaptors and kinases (Rip2) Rip2 29 Alerting the cell: Nod1 activates NFκB PG Nod1 IκB Rip2 IKK Nucleus NFκB Defense 30 10
11 Nod1 and Nod2 are intracellular PRMs hpept1 SLC15A4 Shigella flexneri Enteroinvasive E. coli Nod2 PG Nod1 PG H. pylori Rip2 P. aeruginosa IKK Girardin et al., EMBO Reports 2001 Kim et al., IAI 2004 Viala et al., Nat. Immunol Travassos et al., JBC 2005 Pro-inflammatory cytokines 31 Nod1 is recruited to the site of bacterial entry Shigella Actin Nod1 Shigella entry focus Thomas Kufer, University of Cologne 32 Critical role of Nod1 in infected intestinal epithelial cells WT Nod1 -/- NF-κB p65 DAPI Villin NF-κB p65 DAPI Villin Non infected Non Invasive S.flexneri Invasive S.flexneri 33 11
12 NLRs cytoplasmic sensors of MAMPs AND DAMPs Nod proteins and NLRC4 - MAMPs Nod1 and Nod2 detect fragments of peptidoglycan NLRC4 detects flagellin (therefore 2 sensors of flagellin - inside and outside through TLR5) NLRPs - DAMPs K+ and ROS trigger NLRP1 and NLRP3 34 Proposed mechanism for NLRP protein activation by a DAMP Asbestos fibre ROS ROS ROS NLRP3 1. NLRP3 is folded in inactive state 2. Frustrated phagocytosis and generation of ROS; Lysosomal leakage; K+ efflux 3. NLRP3 is triggered (?), unfolds allowing oligomerization 4.NLRP3 oligomers provide a focal point for the recruitment of adaptors and kinases ASC 35 Bacterial-induced inflammasomes Salmonella, Shigella, Legionella Francisella Shigella Salmonella Francisella Legionella NLRC4 ASC Casp-1 ASC Casp
13 Alerting the cell: the inflammasome DAMPs NLRP3 ASC Secretion of IL-1β & IL-18 from the cell Pyroptosis (in some cases) 37 How do innate immune signals translate into adaptive immune s? Detection of microbial constituents Detection of danger Appropriate adaptive (Th1 Th2 Th17) Antigen-specificity 38 Antigen + peptidoglycan Implication of Nod1 and Nod2 in adaptive immune s NLRs Mature DC Immature DC Antigen processing Cytokines/chemokines Co-stimulatory molecules Migration Th1 What kind of pathogen-specific? Naïve T cell Th2 Th
14 s / 10 6 splenocytes Cytokine producing cells No IFNγ a * 200 IL * IL-5 * Nod2 stimulation drives Th2 polarization profile * Microbial recognition and the immune IgG1 (mg/ml) OVA-specific b prime boost * No IgG2c WT Nod2-/- WT Nod2-/- WT Nod2-/- 1 WT Nod2-/- WT Nod2-/- WT Nod2-/- OVA OVA+MDP OVA+FK156 OVA OVA+MDP OVA+FK156 medium control Ovalbumin Magalhaes et al., Journal of Immunology, 2008 MHC class I peptide OVA MHC class II peptide OVA * 40 Overview: TLRS vs. Nods LPS Flagellin Profilin dsrna ssrna Unmethylated CpG DNA Peptidoglycan (Gram + bacteria)? Lipoproteins Lipoarabinomannan (Mycobacteria) LPS (Leptospira) LPS (Porphyromonas) Glycophosphatylinositol - (T. cruzi) Zymosan (Yeast) Tri-DAP MDP Alum CD D14 MD-2 TLR 4 TLR 5 TLR 11 TLR 3 TLR 8 TLR 7 TLR 9 TLR 2 TLR 1 TLR 6 TLR 2 Nod1 Nod2 Nlrp3 High IL-12p70 IFN-a High IL-12p70 IL-12p70 IFN-a IFN-a Low level IL-12p70 Some ligands induce IL-10 or IL-12p35 MCP-1 IL-1b no IL-12p70 IL-18 Th1 Th0/Th2/Treg Th2 41 What happens when TLRs and NLRs are co-activated? 42 14
15 Nod1 is critical for priming adaptive immunity Immunizations with CFA ne producing cells 0 6 splenocytes cytokin per 1 (pg/ml) T cell frequency 600 IFN-γ IL IL-17A /+ -/- OVA +/+ -/- OVA/CFA control CD4 + /CD8 + CD8 + CD4 + globulin (mg/ml) OVA-specific Immunog Antibody titers Fritz et al., Immunity, * IgG1 +/+ -/- +/+ -/- OVA IgG2c * OVA/CFA 43 Nod1 is required for priming adaptive immunity Infections with Helicobacter pylori ri load e Intra-gastric H. pylor Log CFU/g tissue Altered bacterial clearance day 7 day 30 +/+ -/- +/+ -/- H. pylori urease-specific Imm munoglobulin OD value (A 450n m) Lower antigen-specific antibody titers /+ -/- * IgG1 IgG2c Viala et al., Nature Immunology, 2004 Fritz et al., Immunity, What is the compartment that carries Nod1-specific function? Bone marrow Wild-type Nod1-deficient Adaptive immune? 45 15
16 / 10 6 splenocytes Cytokine producing cells / Wild-type hematopoietic cells cannot rescue Nod1-deficent mice for Th2 Therefore, signaling within stromal compartment is required for driving Th2 immunity by Nod proteins Fritz et al., Immunity, Nod-mediated microbial recognition regulates innate and adaptive antimicrobial immunity Summary Nod1 stimulation Injection of the Nod1 agonist Nod1 stimulation + TLRs Infection or Immunization models Nod1 Nod1 Inflammation Inflammation Nod1 expression in radioresistant, non-hematopoietic is essential DC T H1 T H17 T H2 T IL-4 H2 IL-5 Priming of T H 2 Priming of T H 1/T H 17/ T H 2 IFN-γ IL-17A IL-4 IL-17F IL-5 47 Acknowledgements Present lab members: Joao Magalhaes Leonardo Travassos Kaoru Geddes Seamus Hussey Thirumahal Selvanantham Previous lab members: Lionel Le Bourhis Jorg Fritz Thomas Kufer Girardin lab members: Leticia Carneiro Ivan Tattoli Szilvia Benko Kavi Ramjeet Stephen Rubino Fraser Soares Jooeun Lee Arthur Ling 48 16
17 Funding:
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Inflammation - Molecular events
 Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 25 July 2017 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Innate Immunity. Jan 8 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
Innate Immunity Jan 8 th 2018. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Adaptive Innate 2 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription (-) TLR2 PGN MDP. MyD88 IRAK ECSIT TRAF6 NIK. Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IKK.
 D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
NOD-like Receptors (NLRs) and Inflammasomes
 International Edition NOD-like Receptors (NLRs) and Inflammasomes In mammals, germ-line encoded pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect the presence of pathogens through recognition of pathogen-associated
International Edition NOD-like Receptors (NLRs) and Inflammasomes In mammals, germ-line encoded pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect the presence of pathogens through recognition of pathogen-associated
Basic immunology. Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
Basic immunology Lecture 7. Innate immunity, pattern recognition Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of the innate immunity The levels of host defense Anatomical
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
How Toll-like receptors and Nod-like receptors contribute to innate immunity in mammals
 Proceedings How Toll-like receptors and Nod-like receptors contribute to innate immunity in mammals Jörg H. Fritz 1, Stephen E. Girardin 2 1 Immunité Innée et Signalisation Laboratoire, and 2 Pathogénie
Proceedings How Toll-like receptors and Nod-like receptors contribute to innate immunity in mammals Jörg H. Fritz 1, Stephen E. Girardin 2 1 Immunité Innée et Signalisation Laboratoire, and 2 Pathogénie
Relative sizes of infectious agents
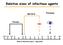 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No
 Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS
 Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
NOD-LIKE RECEPTORS: VERSATILE CYTOSOLIC SENTINELS
 Physiol Rev 95: 149 178, 2015 doi:10.1152/physrev.00009.2014 NOD-LIKE RECEPTORS: VERSATILE CYTOSOLIC SENTINELS Vinicius Motta, Fraser Soares, Tian Sun, and Dana J. Philpott Departments of Immunology and
Physiol Rev 95: 149 178, 2015 doi:10.1152/physrev.00009.2014 NOD-LIKE RECEPTORS: VERSATILE CYTOSOLIC SENTINELS Vinicius Motta, Fraser Soares, Tian Sun, and Dana J. Philpott Departments of Immunology and
Pathogen Recognition and Inflammatory Signaling in Innate Immune Defenses
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
3rd International Conference on Neurology & Therapeutics.
 3rd International Conference on Neurology & Therapeutics www.neuroimmunology.ca Multiple sclerosis is a devastating disease The first description of the disease was mentioned in 14th century In 1838 Dr.
3rd International Conference on Neurology & Therapeutics www.neuroimmunology.ca Multiple sclerosis is a devastating disease The first description of the disease was mentioned in 14th century In 1838 Dr.
State of the Art. Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung CONTENTS AT A GLANCE COMMENTARY 1.
 State of the Art Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung Bastian Opitz 1, Vincent van Laak 1, Julia Eitel 1, and Norbert Suttorp 1 1 Department of Internal Medicine/Infectious
State of the Art Innate Immune Recognition in Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Lung Bastian Opitz 1, Vincent van Laak 1, Julia Eitel 1, and Norbert Suttorp 1 1 Department of Internal Medicine/Infectious
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER. Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma
 INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury. Journal Club December 16, 2004
 Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Commensal Bacteria, Toll-like Receptors and Intestinal Injury Journal Club December 16, 2004 Gut-Commensal Interactions Nutrient metabolism Tissue development Resistance to colonization with pathogens
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
New Insights into the Regulation of Intestinal Immunity by Nod1 and Nod2
 New Insights into the Regulation of Intestinal Immunity by Nod1 and Nod2 by Stephen J. Rubino A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of a Doctorate of Philosophy Laborartory
New Insights into the Regulation of Intestinal Immunity by Nod1 and Nod2 by Stephen J. Rubino A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of a Doctorate of Philosophy Laborartory
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
11/25/2017. THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS BARRIER DEFENSES INNATE IMMUNITY OF VERTEBRATES
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 43 IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY EXAMPLE IN INSECTS Exoskeleton made of chitin forms the first barrier to pathogens Digestive system is protected by a chitin-based barrier and lysozyme,
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
Immune receptors Y Y. Multiple immune responses CLR TLR NLR ITAM RLR. C-type lectin. ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif
 C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
C Immune receptors Innate immunity Acquired immunity TLR CLR FcR BCR TCR C-type lectin Y Y Ig Ig NLR ITAM ITAM ITAM RLR Multiple immune responses ITAM: Immunoreceptor Tyrosine-based Activation Motif Immune
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire d Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr 1 Contents 1. General features and specificity
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
The Innate Immune Response
 The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
The Innate Immune Response FUNCTIONS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM: Recognize, destroy and clear a diversity of pathogens. Initiate tissue and wound healing processes. Recognize and clear damaged self components.
Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity
 Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
Noah W. Palm Ruslan Medzhitov Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity Authors address Noah W. Palm 1, Ruslan Medzhitov 1 1 Howard Hughes Medical Institute and Department of Immunobiology,
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide. The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition
 Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout volution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition.coli ell wall organization Lipid A Lipopolysaccharide Outer
The roles of TLRs, RLRs and NLRs in pathogen recognition
 International Immunology, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 317 337 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxp017 ª The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2009. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
International Immunology, Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 317 337 doi:10.1093/intimm/dxp017 ª The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2009. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org
Within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, innate immune REVIEWS IN BASIC AND CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;141:1986 1999 IN BASIC CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY HEPATOLOGY Robert F. Schwabe and John W. Wiley, Section Editors Inflammasomes in Intestinal Inflammation and Cancer GRACE Y. CHEN*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;141:1986 1999 IN BASIC CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY HEPATOLOGY Robert F. Schwabe and John W. Wiley, Section Editors Inflammasomes in Intestinal Inflammation and Cancer GRACE Y. CHEN*
Innate Immunity. Natural or native immunity
 Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Innate Immunity 1 Innate Immunity Natural or native immunity 2 When microbes enter in the body 3 Secondly, it also stimulates the adaptive immune system 4 Immunologic memory 5 Components of Innate Immunity
Two signal models in innate immunity
 Mary F. Fontana Russell E. Vance Two signal models in innate immunity Authors address Mary F. Fontana 1, Russell E. Vance 1 1 Division of Immunology & Pathogenesis, Department of Molecular & Cell Biology,
Mary F. Fontana Russell E. Vance Two signal models in innate immunity Authors address Mary F. Fontana 1, Russell E. Vance 1 1 Division of Immunology & Pathogenesis, Department of Molecular & Cell Biology,
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis
 The Open Inflammation Journal, 2011, 4, (Suppl 1-M5) 31-48 31 Open Access Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis Lesley Doughty* Division of Critical
The Open Inflammation Journal, 2011, 4, (Suppl 1-M5) 31-48 31 Open Access Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns, Pattern Recognition Receptors and Pediatric Sepsis Lesley Doughty* Division of Critical
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Role of TLR- / NLR-signaling and the associated cytokines involved in recruitment of neutrophils in murine models of Staphylococcus aureus infection
 Virulence ISSN: 2150-5594 (Print) 2150-5608 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/kvir20 Role of TLR- / NLR-signaling and the associated cytokines involved in recruitment of neutrophils
Virulence ISSN: 2150-5594 (Print) 2150-5608 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/kvir20 Role of TLR- / NLR-signaling and the associated cytokines involved in recruitment of neutrophils
Review Articles. Advances in Immunology INNATE IMMUNITY
 Review Articles Advances in Immunology I AN MACKAY, M.D., AND FRED S. ROSEN, M.D., Editors INNATE IMMUNITY RUSLAN MEDZHITOV, PH.D., AND CHARLES JANEWAY, JR., M.D. THE immune system has traditionally been
Review Articles Advances in Immunology I AN MACKAY, M.D., AND FRED S. ROSEN, M.D., Editors INNATE IMMUNITY RUSLAN MEDZHITOV, PH.D., AND CHARLES JANEWAY, JR., M.D. THE immune system has traditionally been
Innate Immunity. By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik
 Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Innate Immunity By Dr. Gouse Mohiddin Shaik Types of immunity Immunity Innate / inborn Non-specific Acquired / adaptive Specific 3rd line of defense Physical barriers Skin, Saliva, Mucous, Stomach acid,
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells
 Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
Basic immunology. Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration. Péter Engelmann
 Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Basic immunology Lecture 9. Innate immunity: inflammation, leukocyte migration Péter Engelmann Different levels of the immune response Recognition molecules of innate immunity Initiation of local and systemic
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD. Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany
 Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
Innate immunity as a therapeutic target in IBD Elke Cario Division of Gastroenterology & Hepatology University Hospital of Essen Essen, Germany The intestinal mucosa must rapidly recognize luminal pathogens
Understanding basic immunology. Dr Mary Nowlan
 Understanding basic immunology Dr Mary Nowlan 1 Immunology Immunology the study of how the body fights disease and infection Immunity State of being able to resist a particular infection or toxin 2 Overview
Understanding basic immunology Dr Mary Nowlan 1 Immunology Immunology the study of how the body fights disease and infection Immunity State of being able to resist a particular infection or toxin 2 Overview
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections
 ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
MICR2209. Innate Immunity. Dr Allison Imrie
 MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The Immune System All animals have innate immunity, a defense active immediately upon infection Vertebrates also have adaptive immunity Figure 43.2 In innate immunity, recognition and
Chapter 22: The Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Bio40C schedule Lecture Immune system Lab Quiz 2 this week; bring a scantron! Study guide on my website (see lab assignments) Extra credit Critical thinking questions at end of chapters 5 pts/chapter Due
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官. The Immune System. KE, Yuehai 柯越海. Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院
 生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官 The Immune System KE, Yuehai 柯越海 Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院 Outlines The Immune System 1. Innate immunity 2. Adaptive immunity 3. Immune
生命科学基础 (21)- 动物的免疫器官 The Immune System KE, Yuehai 柯越海 Zhejiang University, School of Basic Medical Sciences (BMS-ZJU) 浙江大学基础医学院 Outlines The Immune System 1. Innate immunity 2. Adaptive immunity 3. Immune
Innate Immunity. Jan 9 th Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1
 Innate Immunity Jan 9 th 2017. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid cells, anemicrobial
Innate Immunity Jan 9 th 2017. Prof. dr. sc. Ivana Novak Nakir 1 Immune system overview 1 st line of defense skin (2m 2 ) and mucosal membranes (~400m 2 ): physical barrier, lymphoid cells, anemicrobial
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases
 محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
Innate immunity. Monika Raulf. Lecture Tasks of the immune system. Body protection against damaging influences
 Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
NALP12, a gene responsible for periodic fever syndromes. Isabelle Jéru INSERM U.654, Paris, FRANCE
 NALP12, a gene responsible for periodic fever syndromes Isabelle Jéru INSERM U.654, Paris, FRANCE Hereditary periodic fever syndromes (HPFs) Phenotype 6 clinical entities Fever episodes Abdominal pain
NALP12, a gene responsible for periodic fever syndromes Isabelle Jéru INSERM U.654, Paris, FRANCE Hereditary periodic fever syndromes (HPFs) Phenotype 6 clinical entities Fever episodes Abdominal pain
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH THE IMMUNE SYSTEM.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF HOST DEFENSES The human body contains three lines of against infectious agents (pathogens) 1. Mechanical and chemical boundaries (part of the innate immune system)
Fc receptors, phagocytosis role 128
 Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Subject Index Adaptive immunity dependence on innate immunity 9, 10 evolution 10 Aging anti-inflammatory agents in counteraction 202 beneficial polymorphisms 199 201 definition 18, 189 innate immunity
Innate Immunity in Transplantation. Innate and Adapative Immunity
 Innate Immunity in Transplantation M. Sue Leffell, PhD Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Innate and Adapative Immunity Innate or natural defense mechanisms phylogenetically older; present in
Innate Immunity in Transplantation M. Sue Leffell, PhD Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Innate and Adapative Immunity Innate or natural defense mechanisms phylogenetically older; present in
Structure-function analysis of Nlrp1b reveals a link. between metabolism and inflammation: energy stress. triggers inflammasome activation
 Structure-function analysis of Nlrp1b reveals a link between metabolism and inflammation: energy stress triggers inflammasome activation by Kuo-Chieh Liao A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements
Structure-function analysis of Nlrp1b reveals a link between metabolism and inflammation: energy stress triggers inflammasome activation by Kuo-Chieh Liao A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements
Regulation of the Antimicrobial Response by NLR Proteins
 Regulation of the Antimicrobial Response by NLR Proteins Eran Elinav, 1,3 Till Strowig, 1,3 Jorge Henao-Mejia, 1,3 and Richard A. Flavell 1,2, * 1 Department of Immunobiology, Yale University School of
Regulation of the Antimicrobial Response by NLR Proteins Eran Elinav, 1,3 Till Strowig, 1,3 Jorge Henao-Mejia, 1,3 and Richard A. Flavell 1,2, * 1 Department of Immunobiology, Yale University School of
A. Incorrect! The resistance that an individual acquires during life is known as specific immunity.
 Microbiology - Problem Drill 13: Innate Immunity No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of immunity is attributed to the Anatomic, Physiologic, Phagocytic and inflammatory barriers? A. Specific Immunity B. Adaptive
Microbiology - Problem Drill 13: Innate Immunity No. 1 of 10 1. Which type of immunity is attributed to the Anatomic, Physiologic, Phagocytic and inflammatory barriers? A. Specific Immunity B. Adaptive
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release. Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation. Neutrophils & Innate Defense
 Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
Macrophage Activation & Cytokine Release Dendritic Cells & Antigen Presentation Neutrophils & Innate Defense Neutrophils Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) are recruited to the site of infection where they
Inflammasoma e malattie
 Inflammasoma e malattie Ferrara, Novembre 2017 The rediscovery of inflammation Body Defense Dummy arm Smart arm Inflammation Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity tumor, calor, dolor, rubor Very smart Control
Inflammasoma e malattie Ferrara, Novembre 2017 The rediscovery of inflammation Body Defense Dummy arm Smart arm Inflammation Innate Immunity Adaptive Immunity tumor, calor, dolor, rubor Very smart Control
NOD2 Activation promotes anti-inflammatory activity of human Umbilical cord blood MSCs against Inflammatory bowel disease
 NOD2 Activation promotes anti-inflammatory activity of human Umbilical cord blood MSCs against Inflammatory bowel disease Prof. Kyung-Sun Kang, DVM, PhD. Adult Stem Cell Research Center Seoul National
NOD2 Activation promotes anti-inflammatory activity of human Umbilical cord blood MSCs against Inflammatory bowel disease Prof. Kyung-Sun Kang, DVM, PhD. Adult Stem Cell Research Center Seoul National
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Toll-like Receptor Signaling During Infection and Inflammation Prof. Luke O Neill
 Toll-like Receptor Signalling 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology Trinity College Dublin Ireland Inflammatory diseases: the facts 2 Overall incidence: 25% Major pathologies: Infectious diseases Rheumatoid
Toll-like Receptor Signalling 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology Trinity College Dublin Ireland Inflammatory diseases: the facts 2 Overall incidence: 25% Major pathologies: Infectious diseases Rheumatoid
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 35 Active Reading Guide The Immune System Section 1 Phagocytosis plays an important role in the immune systems of both invertebrates and vertebrates. Review the process
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Functional cross talk between NOD1 and NOD2 with SOCS proteins in regulating immunity
 Functional cross talk between NOD1 and NOD2 with SOCS proteins in regulating immunity Marc J. Ouellette Department of Physiology McGill University Montreal, Quebec December 15 A thesis submitted to McGill
Functional cross talk between NOD1 and NOD2 with SOCS proteins in regulating immunity Marc J. Ouellette Department of Physiology McGill University Montreal, Quebec December 15 A thesis submitted to McGill
immunity defenses invertebrates vertebrates chapter 48 Animal defenses --
 defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
defenses Animal defenses -- immunity chapter 48 invertebrates coelomocytes, amoebocytes, hemocytes sponges, cnidarians, etc. annelids basophilic amoebocytes, acidophilic granulocytes arthropod immune systems
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Innate Immunity II. Integration. Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2
 Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
Innate Immunity II Integration Lindsay Nicholson Advanced Immunology L2 l.nicholson@bristol.ac.uk Lecture 1 Defining Innate Immunity Recognition and effector mechanisms (I) Lecture 2 Recognition and effector
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
