The innate immune system: Contributions to Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins
|
|
|
- Kory Lewis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The innate immune system: Contributions to Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins Daniela Verthelyi, M.D., Ph.D. Laboratory of Immunology Division of Therapeu8c Proteins OBP, CDER, FDA
2 Map to the talk: Innate immune system Innate immune response modulating impurities (IIRMI) Ø Can impurities that activate the innate immune system impact the immunogenicity of therapeutic products? Ø What level of impurities may impact the immunogenicity of therapeutic products? Synergy? Ø Can we devise methods of testing for the presence of unidentified impurities that may affect product immunogenicity?
3 Immune system: CLR TLR NLR RLR SR Gene encoded Respond to PAMPs and DAMPs
4 INNATE ADAPTIVE Innate immune receptors are key to initiate and augment immune responses Protein Antigen Adjuvant PAMPs Evolutionary conserved Non-specific (?) No memory(?) Adjuvant PAMPs Polyreactive IgM Abs B cell Cytok. Ag Presentation Antigen specific Abs B cell B cell B cell Clonal Specific Memory * Cytokines T cell IFNs CD4T T Phagoc. * Chemokines T cell T cell cytokines APC activation T cell CD8T
5 TLR : pattern-recognition receptors The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still appears, you may have to delete the image and then insert it again. The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still appears, you may have to delete the image and then insert it again. ssrna TLR7 TLR8 Virus dsrna TLR3 CpG DNA The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still appears, you may have to delete the image and then insert it again. TLR9 Gram+ Flagellin TLR5 TLR6 TLR2 Lipoproteins Peptidoglycan Zymosan Lipoteichoic Ac Phospholipomannans Viral envelope proteins TLR4 Gram- TLR TLR Parasites Profilin Uropathogenic bacteria? LPS TLR Triacyl lipoproteins The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still appears, you may have to delete the image and then insert it again. LPS Mannan Fibrinogen Glycoinositolphospholipids Taxol The image cannot be displayed. Your computer may not have enough memory to open the image, or the image may have been corrupted. Restart your computer, and then open the file again. If the red x still appears, you may have to delete the image and then insert it again.
6 TLR agonists in optimal concentrations: Microbial DNA agonists activate the immune response in splenocytes (Klinman 995) Secreting cell number Fold increase E. coli DNA Mammalian DNA IgM IL-6 IL-2 IFNγ
7 Small amounts of TLR agonist induce Dendritic Cell Maturation and Activation (Gursel 23) CD4 CD8 CD86 HLA-DR CD69 Control b DNA (2ug/ml) CpG ODN (3uM)
8 Fold Change in Gene expression in skin of rhesus macaques injected s.c. with TLR9 agonist (5ug/kg) CAMP CCL CCL7 CCL9 CCL2 CCL2 SOCS5 FASLG IFNA8 CXCL9 IFNa2 IL2RA IL22 IFNG IL-2A CCL5 IFNb PRF PRF CCR5 TLR9 IL6 TLR4 SELE IL- ICOS CXCL3 CXCL CTLA-4 CD4LG VEGFA TNF-ALPHA TLR8 CD8 TLR7 SOCS2 SOCS TLR3 OAS SELP SA6 SA MX 24hrs after injection with TLR9 agonist MAMU-B MAMU-DRB IRF8 CCL8 CD83 IRF7 CD86 GZMB CD94 TGFB CD69 MAMU-A CD9 CD3E CD4 CD4 CD8 CTSC CXCL2 DAD FAS foxp3 HLA-DMA,HLA-DMB HLA-DPA HLA-DQA,HLA-DQA2 IKBKB IL5 IL8 ILA ILB IRF IRF3 CCL8=MIP4 CXCL9=MIG CCL5=Rantes CXCL= IP-
9 TLR agonists enhance ab. responses to protein antigens IgG Titers OVA + DNA (25ug) OVA WEEKS Accelerate IgG responses. Four macaques/group Verthelyi, J.Immunol, 22
10 Therapeutic proteins?
11 Biotechnology Process Natural source **Impurities can come from all steps** Host cells Adventitious agents Harvest Protein mixture Bioburden Down stream purification Chromatography Columns Formulation Filling Container/closure Mammalian Bacteria Yeast Insect Plant Fermentor/ Bioreactor Immunogenicity Complex Drug Product Impurities * Narrow definition of impurity
12 Can trace PAMPs can enhance ab. to proteins? Antigen PAMP Polyreactive IgM Abs PAMP Antigen specific B cell Abs B cell B cell B cell cell B cell Cytokines Phagoc. APC activation Cytokines IFNs Chemokines T cell T cell T cell T cell cytokines innate adaptive
13 TLR : pattern-recognition receptors ssrna TLR7 TLR8 Virus CpG DNA TLR9 TLR TLR Parasites Profilin Uropathogenic bacteria? dsrna TLR3 TLR4 Gram- LPS Flagellin TLR5 TLR6 Gram+ TLR2 TLR Triacyl lipoproteins
14 Models: LPS and CpG ODN on mouse splenocytes Splenocytes: 48hr supernatants (ng/ml) IFNγ IL-6 LPS IFNγ IL-6 CpG ODN LPS pg/ml ng/ml ng/ml ug/ml CpG ODN 2.5 nm 5 nm µm ' '. '. '. LPS ng/ml CpG ODN (nm) LPS: ~ ng (~ -, fold less than adjuvant studies) CpG DNA ~-5nM (~ - fold less than adjuvant studies
15 Low levels of Innate Immune Response Modulating Impurities induce low levels of mrna transcription LPS DNA 5 ccl3-5 cox2 nos2 - cxcl cxcl 6 il-6 ifnγ gzmb 3 nm CpG ODN ng/ml LPS
16 Hematocrit Hematocrit * EPO untreated * * ** * DAYS EPO EPO + LPS.ng EPO + LPS ng Hematocrit Hematocrit EPO EPO + CpG 5ng EPO + CpG 5ng Low levels of TLR agonists induce antibody response in * EPO EPO + CpG 5 ng + LPS.ng EPO + CpG 5 ng + LPS *** *** DAYS vivo * ***
17 Low levels of IIRMI can: Activate immune cells Activate local immune response at drug delivery/depot site Facilitate an antigen-specific immune response to exogenous proteins. Facilitate neutralizing responses that cross-react with endogenous proteins. Change the quality of the response (IgG) Therefore
18 Impurities that activate the innate immune system are a critical product attributes 22 that impact on the immunogenicity of therapeutic products. Current routine characterization of most therapeutic proteins (regardless of expression system): Endotoxin DNA Shouldn t we do better?
19 Screening system should be: sensitive to wide spectrum of IIRMIs. suited to the specific manufacturing process. Not trivial! Several issues to contemplate when designing an assay to control for unidentified impurities that may affect product immunogenicity
20 Challenges and Criteria for a good assay system to detect IIRMIs. Impurities are complex Cover a wide spectrum of IIRMIs Sensitive enough to detect minute amount of impurities How minute? 2. IIRMI synergize 3. No specific biomarkers for any one impurity or receptor 4. Reliable reference standard Differential expression pattern of gene activation in sigma LPS versus ultra pure LPS (List) on RAW cells (Rutledge et al 22). Source Bacteria Virus Yeast Mammalia n cells PAMP LPS Lipoproteins, LTA, PGN Flagellin DNA RNA DNA RNA Structural prot. Zymosan, β glycan Mannan DNA RNA HMGB HSP S DNA RNA TLR TLR4 TLR2/ TLR2/6 TLR5 TLR9 TLR7 TLR9 TLR, TLR7,TLR8 TLR2, TLR4 TLR2,TLR6 TLR2, TLR4 TLR9 TLR7 TLR2, TLR4, TLR2,TLR4, TLR9 TLR3 PRR NOD, NOD2, NALP3, NALP IPAF, NAIP5 AIM2 NALP3 AIM2, DAI,IFI6 RIG-I, MDA-5, NALP3 Dectin-, NALP-3 RAGE, CD24 CD9,CD24,CD4,CD4 RAGE AIM2
21 Sensitivity of testing system Human PBMC Dose response to LPS Macaque skin IFN γ ng/ml. LPS (pg/ml) IL-6 relative expression vs saline pg~. EU. Saline LPS pg LPS pg LPS pg Macaques injected with LPS SC. Skin biopsies at 6h. Gene expression by qpcr.
22 Exposure to lower level of IIRMIs in vivo results in induction of inflammatory genes IL-6 Fold vs saline IP fold vs saline. Saline LPS pg LPS pg LPS pg. Saline CPG 5ng CPG 5ug CPG 5ug IL-6 fold vs saline IL-6 Fold vs saline. Saline Flagellin ng Flagellin ug Flagellin ug. Saline FSL- ng FSL- ug FSL- ug
23 Screening: Sensitive to wide spectrum of unknown IIRMIs. Adequate to the specific manufacturing process. LAL and pyrogenicity tests are limited PBMC (technically demanding & high variability)
24 Multi cell line platform
25 Combined Sensitivity of monocyte/macrophage cell lines to Impurities TLR Cell Cell 2 Cell 3 LPS pg/ml pg/ml pg/ml Pam3CSK4 5pg/mL 5pg/mL pg/ml PolyI:C negative negative 2.5 ug/ml Flagellin negative negative ng/ml FSL- pg/ml 5pg/mL pg/ml Imiquimod 5ng/mL negative negative CLO75 5ng/mL Negative negative CPG 2.5nM (6ng/mL) negative negative Zymosan ug/ml ng/ml ng/ml MDP negative ug/ml negative
26 Dose response. IL-6 relative expression verus media treated Endotoxin (EU/mL) Cells were treated with USP-reference standard endotoxin (RSE)-Lonza for 24h and gene expression is quantified by qpcr for mrna expression.
27 Cell line should be relevant OD OD with out product EPO IFNb Omonyts OD LPS (pg/ml) OD Pam 3 CSK 4 (ng/ml) 5 Test products should not impact the detection IFNb of Omonyts impurities by cell lines.... FSL- (ng/ml) Zymosan (ug/ml)
28 NF-kB activation (OD 62) Lack of interference by Products on detection of impurities EPO (IU/mL) pg/ml LPS.ng/mL LPS ng/ml LPS ng/ml LPS NF-kB activation (OD 62) EPO (IU/mL) pg/ml FSL-.ng/mL FSL- ng/ml FSL- ng/ml FSL- NF-kB activation (OD 62) IFNβ (IU/mL) pg/ml LPS.ng/mL LPS ng/ml LPS ng/ml LPS NF-kB activation (OD 62) IFNβ (IU/mL) pg/ml FSL-.ng/mL FSL- ng/ml FSL- ng/ml FSL-
29 IL-6 Fold expression media IFNβ IL-6 Fold expression media IFNβ LPS (Pg/mL) 5 FSL- (Pg/mL) IL-8 Fold expression 5 5 media IFNβ IL-8 Fold expression media IFNβ LPS (Pg/mL) 5 FSL- (Pg/mL)
30 Summary Individual cell lines are not optimal for the detection of unidentified impurity, but combination of cells lines serve as a good system to detect a wide range of lower level impurities. Low or no product interference Dose response
31 Gene activation pattern by IIRMI IL2 IL3 IL4 IL5 TNF LTA COL4A5 C3 AGTR2 AGTR CD34 VEGF ACE EDN ILα ILβ IL6 IL8 IL7 8S IL IL2A IL2B IL3 IL5 IL7 IL8 media LPS Pam 3 CSK 4 Zymosan FN SKI CCL9 SMAD7 CCL2 SMAD3. CCL5 TGFB CCR2 FASLG CCR4 FAS GNLY CYPA2 RPL3L CCR7 CXCL CXCL CCR5 CXCR3 MYH6 LRP2 SELE REN HMOX PTGS2 SELP ICAM BAX BCL2L BCL2 NOS2A ICOS TNFRSF8 HLA-DRA CD4LG CTLA4 CD8 CD86 CD4 CD68 PTPRC NFKB2 CSF3 CD3E CD4 CD8A CD9 IL2RA CD28 CD38 IKBKB STAT3 CSF CSF2
32 Distinct gene signatures induced by minute level of impurities in macrophages Media TNF EDN ILα ILβ IL6 pg/ml LPS pg/ml LPS FN IL8 ng/ml LPS HMOX IL2b CYP7A IL3 ICAM IL5 TNFRSF8 CCL3 HLA-DRA CCL9 CD8 CCL2 CD4 CCL5 CD38 CCR5 IL2RA CCR7 NFKB2 CXCL CSF3 CSF2 CSF CXCL
33 Products induce a gene expression profile REN C3 ILβ ILα IL6 Omontys # Omontys # 2 Omontys # 3 Buffer control PTGS2 IL8 HMOX. IL ICAM CCR5 CD8 CCR7 CD4 CXCL NFKB2 CSF3 CSF
34 Pattern of gene signature doesn t vary between different lots of same product IL-6 relative expression versus media treated. Pg/mL LPS Pg/mL LPS Pg/mL LPS IL-8 relatve expression verus media treated buffer Lot# Lot # 2 Lot # 3 Lot # 4 Lot # 5. Pg/mL LPS Pg/mL LPS Pg/mL LPS buffer Lot# Lot # 2 Lot # 3 Lot # 4 Lot # 5
35 Different lots of the same product induce similar gene expression profiles PTGS2 REN C3 ILβ ILα IL6 IL8 omontys # omontys # 2 omontys # 3 Buffer control omontys # + LPS omontys # 2 + LPS omontys # 3 + LPS buffer + LPS HMOX. IL ICAM CCR5 CD8 CCR7 CD4 CXCL NFKB2 CSF3 CSF
36 Gene expression profiling of licensed products for impurities using cell lines Erythropoetin Erythropoetin + Endotoxin ICAM HMOX C3 IL-α IL-β IL-6 IL-8 media EPO ICAM HMOX C3 IL-α IL-β IL-6 IL-8 media EPO EPO + Endotoxin Endotoxin CD8. IL- CD8. IL- CD4 CCL3 CD4 CCL3 NFKB2 CCL2 NFKB2 CCL2 CSF-3 CXCL CXCL CCR7 CSF-3 CXCL CXCL CCR7
37 Products have gene expression patterns IFNβ (Avonex) IFNβ (Avonex) + Endotoxin ICAM HMOX C3 IL-α IL-β IL-6 IL-8 media IFNβ ICAM HMOX C3 IL-α IL-β IL-6 IL-8 media IFNβ IFNβ + Endotoxin Endotoxin CD8 IL- CD8 IL- CD4 CCL3 CD4 CCL3 NFKB2 CCL2 NFKB2 CCL2 CSF-3 CXCL CXCL CCR7 CSF-3 CXCL CXCL CCR7
38 Summary Low levels of impurities (microbial or mammalian) that are recognized by receptors of the innate immune system can : Activate the innate immune system Induce an antigen-specific immune response to exogenous proteins. Induce antibodies that cross-neutralize endogenous proteins.
39 Summary-2. Platform based on multiple cell lines can detect a broad spectrum of IIRMI in therapeutic products 2. IIRMIs induce predictable gene profile expression 3. Products induce specific finger print of genes can be utilized to detect contaminating IIRMIs. Immunogenicity risk in comparability studies.
40 THANK YOU Lydia Haile Montserrat Puig Vivian Wang Amy Rosenberg Susan Kirshner Joao Pedras-Vasconcelos
41 IL-6 I J A 25 2 B C H D G E F
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription (-) TLR2 PGN MDP. MyD88 IRAK ECSIT TRAF6 NIK. Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IKK.
 D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
D2 inhibits TLR2- initiated 12p40 transcription CARD CARD NOD2 LRR RICK/Rip2 NIK MDP TRAF6 PGN TLR2 MyD88 IRAK ECSIT (-) IKK Smallest unit of PGN muramyl dipeptide IκB NF-κB atanabe et al, 2004 NF-κB IL-12p40
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS
 1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
1 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATIONS Figure S1 Cumulative ZIKV production by testis explants over a 9 day-culture period. Viral titer values presented in Figure 1B (viral release over a 3 day-culture period measured
Interferon-gamma pathway is activated in a chronically HBV infected chimpanzee that controls HBV following ARC-520 RNAi treatment
 Interferon-gamma pathway is activated in a chronically HBV infected chimpanzee that controls HBV following ARC-520 RNAi treatment Zhao Xu, Deborah Chavez, Jason E. Goetzmann, Robert E. Lanford and Christine
Interferon-gamma pathway is activated in a chronically HBV infected chimpanzee that controls HBV following ARC-520 RNAi treatment Zhao Xu, Deborah Chavez, Jason E. Goetzmann, Robert E. Lanford and Christine
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk
 Contact Technical Support BRCsupport@QIAGEN.COM 1-800-362-7737 Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk Jesse Liang, Ph.D. Legal disclaimer QIAGEN products shown here are intended for molecular biology
Contact Technical Support BRCsupport@QIAGEN.COM 1-800-362-7737 Cancer, inflammation, and immunity crosstalk Jesse Liang, Ph.D. Legal disclaimer QIAGEN products shown here are intended for molecular biology
TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity. Kingston H.G. Mills
 TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity Kingston H.G. Mills Immunology Research Centre and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland Abstract Autoimmune disease can
TLR-dependent T cell activation in autoimmunity Kingston H.G. Mills Immunology Research Centre and School of Biochemistry and Immunology, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland Abstract Autoimmune disease can
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy
 Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate Immunity and the Paradoxes of Viral Pathogens and Tissue Injury in Gene Therapy Daniel R. Salomon, M.D. Department of Molecular and Experimental Medicine The Scripps Research Institute Tissue and
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
DISCOVER MORE WITH LESS SAMPLE. nanostring.com/3d
 nanostring.com/3d DISCOVER MORE WITH LESS SAMPLE. WHY COMPROMISE? ncounter Vantage ASSAYS POWERED BY 3D BIOLOGY TECHNOLOGY Don t let sample volume limit your analytical aspirations. Quantify DNA, RNA,
nanostring.com/3d DISCOVER MORE WITH LESS SAMPLE. WHY COMPROMISE? ncounter Vantage ASSAYS POWERED BY 3D BIOLOGY TECHNOLOGY Don t let sample volume limit your analytical aspirations. Quantify DNA, RNA,
Eosinophils! 40! 30! 20! 10! 0! NS!
 A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
A Macrophages Lymphocytes Eosinophils Neutrophils Percentage (%) 1 ** 4 * 1 1 MMA SA B C Baseline FEV1, % predicted 15 p = 1.11 X 10-9 5 CD4:CD8 ratio 1 Supplemental Figure 1. Cellular infiltrate in the
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli Cell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
qpcr-array Analysis Service
 qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
qpcr-array Analysis Service Customer Name Institute Telephone Address E-mail PO Number Service Code Report Date Service Laboratory Department Phalanx Biotech Group, Inc 6 Floor, No.6, Technology Road 5,
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Development of a Novel IL-12 DNA-based Immunotherapy in Combination with Chemotherapy for Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer
 Development of a Novel IL-12 DNA-based Immunotherapy in Combination with Chemotherapy for Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer Khursheed Anwer, Ph.D. Executive Vice President and CSO Molecular Medicine
Development of a Novel IL-12 DNA-based Immunotherapy in Combination with Chemotherapy for Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer Khursheed Anwer, Ph.D. Executive Vice President and CSO Molecular Medicine
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL).
 Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL). (b) Depiction of a MTZ array generated by NAFL. (c-e) IgG production
Supplementary Figure 1. NAFL enhanced immunity of other vaccines (a) An over-the-counter, hand-held non-ablative fractional laser (NAFL). (b) Depiction of a MTZ array generated by NAFL. (c-e) IgG production
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Innate immunity. Monika Raulf. Lecture Tasks of the immune system. Body protection against damaging influences
 Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
Innate immunity Monika Raulf Lecture 20.04.2016 Tasks of the immune system Body protection against damaging influences Deployment of a strong defense 2 The line of defence Skin Mucosa Sweat Digestive fluids
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections
 ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
ABIMMUNE Repurposing disused antibiotics with immune modulators as antimicrobial strategy for respiratory tract infections Jean-Claude Sirard Christophe Carnoy Fiordiligie Casilag Delphine Cayet The partners
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
TCR, MHC and coreceptors
 Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Cooperation In Immune Responses Antigen processing how peptides get into MHC Antigen processing involves the intracellular proteolytic generation of MHC binding proteins Protein antigens may be processed
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Relative sizes of infectious agents
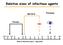 Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Relative sizes of infectious agents Bacteria Protozoa Viruses RBC 0.005 0.01 0.03 01 03 05 1 3 5 10 30 50 100 300 Size in microns ( µm ) - log scale Immunity to Infection Principle 1 Every clinical infection
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
Pathogen Recognition and Inflammatory Signaling in Innate Immune Defenses
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2009, p. 240 273 Vol. 22, No. 2 0893-8512/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00046-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Pathogen Recognition
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF)
 F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF) Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus, Department of
F12 Sorbent Based and Hybrid Therapies for Extracorporeal Support Continuous Hemodiafiltration with Cytokine-Adsorbing Hemofilters (CAH-CHDF) Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor Emeritus, Department of
Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer - TLR9 as a therapeutic target -
 Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer - TLR9 as a therapeutic target - Wilfried Eberhardt,, MD Head of Outpatient Unit, Dept. of Internal Medicine (Cancer Research) West German Cancer Centre Essen University Hospital
Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer - TLR9 as a therapeutic target - Wilfried Eberhardt,, MD Head of Outpatient Unit, Dept. of Internal Medicine (Cancer Research) West German Cancer Centre Essen University Hospital
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
Supplementary Information An orally available, small-molecule interferon inhibits viral replication Hideyuki Konishi 1, Koichi Okamoto 1, Yusuke Ohmori 1, Hitoshi Yoshino 2, Hiroshi Ohmori 1, Motooki Ashihara
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis. Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University
 Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Synergy of radiotherapy and PD-1 blockade in Kras-mutant lung cancer
 Supplementary Information Synergy of radiotherapy and PD-1 blockade in Kras-mutant lung cancer Grit S. Herter-Sprie, Shohei Koyama, Houari Korideck, Josephine Hai, Jiehui Deng, Yvonne Y. Li, Kevin A. Buczkowski,
Supplementary Information Synergy of radiotherapy and PD-1 blockade in Kras-mutant lung cancer Grit S. Herter-Sprie, Shohei Koyama, Houari Korideck, Josephine Hai, Jiehui Deng, Yvonne Y. Li, Kevin A. Buczkowski,
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Life Sciences. Cytokine assays
 Life Sciences Cytokine assays A full range of cytokines Cisbio s kits cover the full range of cytokines: interleukins, interferons (IFN), chemokines, TNF and lymphokines. All our assays are cell based
Life Sciences Cytokine assays A full range of cytokines Cisbio s kits cover the full range of cytokines: interleukins, interferons (IFN), chemokines, TNF and lymphokines. All our assays are cell based
Cationic Liposome-DNA Complexes as Immunomodulators and Vaccine Adjuvants
 Cationic Liposome-DNA Complexes as Immunomodulators and Vaccine Adjuvants September 29, 28 Platform Technology Proprietary Cationic Lipid-DNA Complexes Cationic/Neutral Lipid + DNA = JVRS-1 JVRS-1 + Antigen
Cationic Liposome-DNA Complexes as Immunomodulators and Vaccine Adjuvants September 29, 28 Platform Technology Proprietary Cationic Lipid-DNA Complexes Cationic/Neutral Lipid + DNA = JVRS-1 JVRS-1 + Antigen
HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER
 OncoPept TM HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER OncoPept identifies and delivers priortized T-cell neo-epitopes from the patient's tumor mutanome 2 What is OncoPept? OncoPept is an integrated
OncoPept TM HARNESS THE POWER OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM TO FIGHT CANCER OncoPept identifies and delivers priortized T-cell neo-epitopes from the patient's tumor mutanome 2 What is OncoPept? OncoPept is an integrated
Blood Purification for Sepsis - Which Molecules Should We Remove Endotoxin or Cytokines?
 Plenary 5 MINI SYMPOSIA Challenges and Controversies in Renal Support and CRRT Blood Purification for Sepsis - Which Molecules Should We Remove Endotoxin or Cytokines? Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor
Plenary 5 MINI SYMPOSIA Challenges and Controversies in Renal Support and CRRT Blood Purification for Sepsis - Which Molecules Should We Remove Endotoxin or Cytokines? Hiroyuki Hirasawa, MD, PhD Professor
TLR Ligands Set I [Toll-like Receptors Ligands Set I ]
![TLR Ligands Set I [Toll-like Receptors Ligands Set I ] TLR Ligands Set I [Toll-like Receptors Ligands Set I ]](/thumbs/73/69044669.jpg) Manual TLR Ligands Set I [Toll-like Receptors Ligands Set I ] For Research Use Only APO-54N-018-KI01 Version 3 (12-Jun-08) 1. CONTENT The TLR Ligands Set I contains a comprehensive sterile, ready-to-use
Manual TLR Ligands Set I [Toll-like Receptors Ligands Set I ] For Research Use Only APO-54N-018-KI01 Version 3 (12-Jun-08) 1. CONTENT The TLR Ligands Set I contains a comprehensive sterile, ready-to-use
Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 *** Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Pten pc-/- ;Zbtb7a pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Pml pc-/- Pten pc-/- ;Trp53 pc-/-
 Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Gr-1 Gr-1 Gr-1 Bezzi et al., Supplementary Figure 1 a Gr1-CD11b 3 months Spleen T cells 3 months Spleen B cells 3 months Spleen Macrophages 3 months Spleen 15 4 8 6 c CD11b+/Gr1+ cells [%] 1 5 b T cells
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
INTERLEUKIN-10 RECEPTOR DYSFUNCTION IN PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES BY TOLL-LIKE RECEPTOR LIGANDS
 University of Kentucky UKnowledge University of Kentucky Master's Theses Graduate School 2005 INTERLEUKIN-10 RECEPTOR DYSFUNCTION IN PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES BY TOLL-LIKE RECEPTOR LIGANDS Surjya Bhattacharyya
University of Kentucky UKnowledge University of Kentucky Master's Theses Graduate School 2005 INTERLEUKIN-10 RECEPTOR DYSFUNCTION IN PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES BY TOLL-LIKE RECEPTOR LIGANDS Surjya Bhattacharyya
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
The Innate Immune Response is Conserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition. Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide
 The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
The Innate Immune Response is onserved Throughout Evolution and is Triggered by Pattern Recognition Lipopolysaccharide = Lipid + Polysaccharide E.coli ell wall organization Lipopolysaccharide Outer membrane
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
doi: 1.138/nature89 IFN- (ng ml ) 5 4 3 1 Splenocytes NS IFN- (ng ml ) 6 4 Lymph node cells NS Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / Nfkbiz / IL- (ng ml ) 3 1 Splenocytes IL- (ng ml ) 1 8 6 4 *** ** Lymph node cells
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No
 Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Adenovirus engineered human dendritic cell vaccine induces natural killer cell chemotaxis
 Adenovirus engineered human dendritic cell vaccine induces natural killer cell chemotaxis via CXCL8/IL 8 and CXCL10/IP 10 chemokines Lazar Vujanović, Ph.D. Research Instructor P.I. Lisa H. Butterfield,
Adenovirus engineered human dendritic cell vaccine induces natural killer cell chemotaxis via CXCL8/IL 8 and CXCL10/IP 10 chemokines Lazar Vujanović, Ph.D. Research Instructor P.I. Lisa H. Butterfield,
Toll-like receptors in health and disease in the brain: mechanisms and therapeutic potential
 Clinical Science (2011) 121, 367 387 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/cs20110164 367 R E V I E W Toll-like receptors in health and disease in the brain: mechanisms and therapeutic potential Mark
Clinical Science (2011) 121, 367 387 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/cs20110164 367 R E V I E W Toll-like receptors in health and disease in the brain: mechanisms and therapeutic potential Mark
Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity. Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada
 Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Early Goal-Directed Therapy Rivers E et al. NEJM 345:1368-77,
Inflammatory Pathways in Sepsis: TLRs and Innate Immunity Keith R. Walley, MD St. Paul s Hospital University of British Columbia Vancouver, Canada Early Goal-Directed Therapy Rivers E et al. NEJM 345:1368-77,
The Use of Human Dendritic Cell
 The Use of Human Dendritic Cell Subsets in Cancer Vaccines Jolien Sweere Student #: 3145298 Master Thesis Infection and Immunity Supervisor: Dr. Jeanette Leusen Immunotherapy University Medical Centre
The Use of Human Dendritic Cell Subsets in Cancer Vaccines Jolien Sweere Student #: 3145298 Master Thesis Infection and Immunity Supervisor: Dr. Jeanette Leusen Immunotherapy University Medical Centre
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
Horizon 2020 Programme. SFS-01b Tackling losses from terrestrial animal diseases
 Horizon 2020 Programme SFS-01b-2014 Tackling losses from terrestrial animal diseases Strengthening Animal Production and Health through the Immune Response Project ID: 633184 D12.1 Age related innate responses
Horizon 2020 Programme SFS-01b-2014 Tackling losses from terrestrial animal diseases Strengthening Animal Production and Health through the Immune Response Project ID: 633184 D12.1 Age related innate responses
7/6/2009. The study of the immune system and of diseases that occur as a result of inappropriate or inadequate actions of the immune system.
 Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
Diseases of Immunity 2009 CL Davis General Pathology Paul W. Snyder, DVM, PhD Purdue University Acknowledgements Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease, 4 th Ed Veterinary Immunology, An Introduction 8
CPM (x 10-3 ) Tregs +Teffs. Tregs alone ICOS CLTA-4
 A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
ACTIVATION OF INNATE IMMUNITY BY HUMAN VACCINE ADJUVANTS AT INJECTION SITE
 Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna DOTTORATO DI RICERCA in Biologia Funzionale dei Sistemi Cellulari e Molecolari Ciclo XX Settore Scientifico Disciplinare: BIO/11 ACTIVATION OF INNATE IMMUNITY
Alma Mater Studiorum Università di Bologna DOTTORATO DI RICERCA in Biologia Funzionale dei Sistemi Cellulari e Molecolari Ciclo XX Settore Scientifico Disciplinare: BIO/11 ACTIVATION OF INNATE IMMUNITY
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Microbial recognition and the immune response Dr. Dana Philpott
 Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1: Ex[Ca 2+ ]-induced IL-1ß production of monocytes primed with different TLR ligands IL-1ß release of CD14+ monocytes in response to stimulation for 16
Supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1: Ex[Ca 2+ ]-induced IL-1ß production of monocytes primed with different TLR ligands IL-1ß release of CD14+ monocytes in response to stimulation for 16
MICR2209. Innate Immunity. Dr Allison Imrie
 MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
MICR2209 Innate Immunity Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au Synopsis: In this lecture we will review the different mechanisms which consbtute the innate immune response, and examine the major cells
Interferon-dependent IL-10 production by Tregs limits tumor Th17 inflammation
 Interferon-dependent IL-10 production by Tregs limits tumor Th17 inflammation C. Andrew Stewart,, Werner Müller, Giorgio Trinchieri J Clin Invest. 2013;123(11):4859-4874. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci65180.
Interferon-dependent IL-10 production by Tregs limits tumor Th17 inflammation C. Andrew Stewart,, Werner Müller, Giorgio Trinchieri J Clin Invest. 2013;123(11):4859-4874. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci65180.
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences
 The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
The Case of the Spring Break Consequences Hazel reluctantly opened her eyes when her alarm went off. Spring Break was over, and she was definitely NOT ready for the second half of the semester. However,
4. Th1-related gene expression in infected versus mock-infected controls from Fig. 2 with gene annotation.
 List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS
 Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS MS disease course histologic features Courtesy of Samuel Ludwin I ACUTE CHRONIC s ACTIVE CHRONIC Clinical Course Intra CNS Extra CNS Imaging
Contribution of microglia to tissue injury and repair in MS MS disease course histologic features Courtesy of Samuel Ludwin I ACUTE CHRONIC s ACTIVE CHRONIC Clinical Course Intra CNS Extra CNS Imaging
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection
 Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Your Partner in Proteomics. Reporter System Luciferase Reporter Stable Cell Lines One-Step Luc Assay Kit Stable Cell Lines.
 Reporter System Luciferase Reporter Stable Cell Lines One-Step Luc Assay Kit Stable Cell Lines www.abeomics.com Reporter Cell Lines Reporter cell lines are used for cell-based assays for screening of drugs/compounds
Reporter System Luciferase Reporter Stable Cell Lines One-Step Luc Assay Kit Stable Cell Lines www.abeomics.com Reporter Cell Lines Reporter cell lines are used for cell-based assays for screening of drugs/compounds
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells
 Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
Innate immunity and Antigen presenting cells Sanipa Suradhat, D.V.M., Ph.D. Dept. of Veterinary Microbiology Faculty of Veterinary Science Chulalongkorn University Innate & specific immune responses Innate
TLR agonists: our best frenemy in cancer immunotherapy
 Review TLR agonists: our best frenemy in cancer immunotherapy Sabina Kaczanowska,* Ann Mary Joseph,* and Eduardo Davila*,,,1 *Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Cancer
Review TLR agonists: our best frenemy in cancer immunotherapy Sabina Kaczanowska,* Ann Mary Joseph,* and Eduardo Davila*,,,1 *Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Cancer
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D.
 Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Regulation of anti-tumor immunity through migration of immune cell subsets within the tumor microenvironment Thomas F. Gajewski, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Medicine Program Leader,
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel:
 Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Title. CitationCancer science, 109(4): Issue Date Doc URL. Rights(URL)
 Title Toll-like receptor 3 signal augments radiation-induc Yoshida, Sumito; Shime, Hiroaki; Takeda, Yohei; Nam, Author(s) Hiroki; Kasahara, Masanori; Seya, Tsukasa CitationCancer science, 19(): 956-965
Title Toll-like receptor 3 signal augments radiation-induc Yoshida, Sumito; Shime, Hiroaki; Takeda, Yohei; Nam, Author(s) Hiroki; Kasahara, Masanori; Seya, Tsukasa CitationCancer science, 19(): 956-965
Anti-infectious Immunity
 Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Anti-infectious Immunity innate immunity barrier structures Secretory molecules Phagocytes NK cells Anatomical barriers 1. Skin and mucosa barrier 2.hemo-Spinal Fluid barrier 3. placental barrier Phagocytic
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D.
 Treatment of established tumors with peritumoral injections of CD40 ligand (CD40L), CpG, poly(i:c), and extracellular ATP in murine models Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure: Richard Kornbluth
Treatment of established tumors with peritumoral injections of CD40 ligand (CD40L), CpG, poly(i:c), and extracellular ATP in murine models Richard S. Kornbluth, M.D., Ph.D. Disclosure: Richard Kornbluth
Measles virus vaccine induces oncolysis of tumor cells and activates immune responses.
 Measles virus vaccine induces oncolysis of tumor cells and activates immune responses. Marc Grégoire*, J.-F. Fonteneau, N. Boisgerault, J.-B. Guillerme and F. Tangy. * INSERM, Nantes, F-44, France. Pasteur
Measles virus vaccine induces oncolysis of tumor cells and activates immune responses. Marc Grégoire*, J.-F. Fonteneau, N. Boisgerault, J.-B. Guillerme and F. Tangy. * INSERM, Nantes, F-44, France. Pasteur
Chapter 10 (pages ): Differentiation and Functions of CD4+ Effector T Cells Prepared by Kristen Dazy, MD, Scripps Clinic Medical Group
 FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
FIT Board Review Corner September 2015 Welcome to the FIT Board Review Corner, prepared by Andrew Nickels, MD, and Sarah Spriet, DO, senior and junior representatives of ACAAI's Fellows-In-Training (FITs)
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
