'A new road paved towards a factual science of Vital Force.' 'Vital Force is Oxygen' Dr. Amarsinha Dattatray Nikam
|
|
|
- Philomena Norton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VITAL FORCE IS OXYGEN
2 Vital Force is Oxygen An Enlightening Research in Vital Force Dr Amarsinha D. Nikam B. Jain Publishers (P) Ltd. An ISO 9001 : 2000 Certified Company USA EUROPE INDIA
3 Contents v Preface The vital force is an interesting concept of utmost importance in Homeopathic science. But, the theoretical rather an unscientific explanation of vital force was very confusing for homeopathic students and doctors. The subject of vital force (vital energy) is a scientific and an important document of Homeopathy which was put forth by Master Hahnemann. But, it has been transformed into an unperceivable, an unexplainable, and an unscientific philosophy which has made homeopathic science a target for criticism in the medical world by other pathies. Since, I was enrolled in first year in homeopathic college, I was eager to understand this interesting subject of vital force. But I was not being guided enthusiastically on this subject. My father was a homeopathic consultant. I had seen the tremendous recovery and results. Since my childhood I had developed full faith on this science as I had been born and brought up with homeopathy. It compelled me to become a follower of this wonderful science. The keen interest for understanding the science kept me enthusiastic and my efforts helped me to perceive the concepts without any guidance.
4 vi Vital Force is Oxygen After completing my college curriculum I continued with my study and practice. A continuous reading of Dr Hahnemann s philosophy and following his methods and principles of prescription gave me good results. This enhanced my knowledge and confidence in our pathy. As I started practising, I came up with good results and witnessed amazing recoveries of patients. This success was giving me happiness. But, I wasn t satisfied with it, for me these results were of no use until they had a scientific explanation. This allowed other people to criticize me, call me a fluke and even a non-homeopathic method prescriber. This criticism made me aware of the truth and with acceptance I continued my journey. I had done enormous readings of the books of Philosophies of our pioneers Dr Hahnemann, Dr Kent s, Dr H.A. Roberts and Dr Stuart Close and many more. This brought me to a conclusion that Yes, our homeopathic philosophy has a solid scientific foundation! Today, nearly after three decades of my practice, I have established an 80 beded homeopathic hospital which only works on a standard homeopathic prescription of 30 potency. Also, I have delivered many seminars through which I have put forth my classical and scientific way of homeopathic practice and understanding of homeopathic philosophy by different angles. For the first time, I introduced this concept of vital force in 2005 at Singapore. The concept was greatly appreciated and the crowd was eager to know the subject in deep. This also inspired me to write a book on this concept. To write a book was a very difficult task, I required a proper data to put forth my thoughts. This took me four
5 Contents Preface vii years of hard & heart work to complete each matter in a scientific manner. My only aim is to establish Homeopathy as a firm science; so that no one can ever criticize or underestimate it. To fulfill this purpose erasing the wrong concepts and inculcate the basic scientific concepts on the mind of newly emerging generation of Homeopaths is a necessity. It will strengthen their faith and dedication to the pathy. This will result in wide spread of the pathy from richest to the commonest and to all corners of this world. This book is a humble attempt made by me for better understanding and development of our pathy. This is my request to the readers, take help of this book to make their concepts clearer regarding vital force and erase all the doubts in their mind; as in my previous books - The manifestation of Miasm and Thermal Materia Medica. Dr Amarsinha D. Nikam
6 Contents ix Acknowledgements For the first time, I explored my deeper understanding of Vital Force and shared my thoughts in the year 2005, at Singapore Seminar. Dr Rangachari, the Principal of Singapore Homeopathic Faculty, and graduate and Post-Graduate students were astonished with my lecture on the Vital Force. Everybody appreciated and requested me to write a book on this scientific subject. That s why firstly I am expressing my sense of gratitude to all the students and especially Dr Rangachari. Special thanks to Dr Rakhi Subhash Munot and Dr Neeta Kiran Jain who wrote down my delivered speech and helped me in writing this book. They have given me their precious time for writing this book. And my heartiest thanks to my daughter, Dr Suchitra and Dr Pallavi Bub for giving me full time support in completing this book. I convey my heartiest thanks to my loving nephew Dr Rohit Deshmukh for helping and supporting me in every book. It would not have been possible for me to complete the book within time, without the help of my students (mentioned above) prompt and perfect work following action, under my guidance.
7 x Vital Force is Oxygen My special thanks to Dr Bharat B. Kale, who is Ph.D. (Scientist-E) who helped me with the scientific references. Also his student, Mr Yogesh Sonawane, who provided me the required and needed information. My special thanks to Dr Vijay Satav, (M.D. Pathology), Chinchwad, Pune, who gave me valuable information about Pathology for this book. All my thanks to my budding students Dr Sneha, Dr Sona and all my students and many budding students from B. V. P. Medical College, and other colleges whose great efforts made this task easy. Difficult task of computerized formatting and composing of this book was done by Ms Vandana Kale by giving her valuable efforts to fulfill this task within time. Special thanks to my close friend and colleague Dr Arun Jadhav, Principal, Bharati Vidyapeeth Homeopathic Medical College, Pune. Mr Mahendra Konde, P.R.O. in my hospital who is always busy with Hospital activities and has always treasured the moments of special events by his excellent photography. My mother who not only loves me but gives me encouragement, affection and blessings in every moment of my life. Thanks to my wife, Sudha who is sacrificing her life for me and always encourages me in every moment of my life. She also gives attention towards Hospital Management and makes my task easy. My son Dr Vijaysinha and Dr Manish who helped me a lot for this book. My brother, Mr Mahesh and his wife Mrs Rajashree look after my patients and are doing excellent service in Aditya Cafe.
8 Acknowledgements Contents xi My sisters and their family members always supported me in my mission. My staff members who are tirelessly working day-night for my hospital in maintaining the rigors and serving my patients promptly to make this organization a unique picture of human service. I want to thank lots of people who have always influenced and inspired me in my progressive work and whenever I remember them, I thank them in my heart.
9 Contents xiii Special Thanks and Gratitude My special thanks to Hon.Cabinet Minister Mr Prithviraj Chauhan, Hon. Ex-Minister, Central Government, India, Mrs Suryakanta Patil, Mr Vilasrao Deshmukh (Heavy Industry, Cabinet Minister), Mr Govindrao Adik, Mr Vijaysinha Mohite-Patil, Mr Prataprao Bhosale and Mr Ulhasrao Pawar, Mr Sadakant (I.A.S. Joint Secretary, Home Ministry), Dr Patangrao Kadam (Hon. Minister, Maharashtra State), Mr Laxman Jagtap (M.L.A.), Mr Vilas Lande (M.L.A.), Mr Gajanan Babar (M.L.A.), Mr Prabhakar Deshmukh (Ex-Collector, Pune), Mr Gulabrao Pol (D.I.G. Police, Maharashtra State), Mr Dilip Band (Divisional Commissionar, Maharashtra State), Mr Anil Diggikar (Deputy-Comissionar, Mumbai) and Mr Pravinsinha Pardeshi (Ex-Commissionar, P.C.M.C. & Pune), Mr Shengaonkar, D.C.P., Pune (Commissioner Office) My special thanks to Mr Shivajirao Kadam, Vice Chancellor of Bharati Vidyapeeth, Mr Uttamrao Bhoite (Executive Director) B. V. P, Pune, Mr S.F. Patil, Ex-Vice Chancellor, Principal Mr K. D. Jadhav, Director audit and Law, B. V.P. Pune.
10 xiv Vital Force is Oxygen My friend Mr Umeshchandra Upadhyay, Mr Umesh Chandgude (Social worker), Mr Hasan Tamboli (Industrialist, Satara), Mr Gaikwad Mama, Mr Amol Prabhu, Mr G. M. Mahale, Advocate Mr Mukundrao Awate. My thanks to Principal and staff of Bharati Vidyapeeth Homeopathic Medical College, Pune, who honoured me with a post of Honorary Professor as well as Homeopathic Faculty member and encouraged me to share my work with budding Homeopaths. Padmashree Dr D.Y. Patil and Mrs Patil (D.Y. Patil University), and Mr Arun Chopra, Ex-Comd. N.D.A., always inspire me. Dr Mrs Dehalani Madam, Vice Principal, Foster Hom. Med. College, Aurangabad. I.I.H.P. (Mumbai) the biggest group of classical Homeopathy taking tremendous efforts to spread Homeopathy in practitioners and students, always invited me every year to conduct a Seminar on Homeopathy. Study Circle Group from Mumbai which is also popular among the practitioners and students, conducting lots of my Seminars at Mumbai to share my experiences in Homeopathy. UHA, Classical Homeopathic Group from Nagpur Dr Ashish, Dr Shilpa, Dr Yadnik and other students who are doing good work for spreading Classical Homeopathy. To various Homeopathic colleges from all over India which have regularly invited me to deliver a speech on Classical Homeopathy and Homeopathic Hospital practice. Editor of Homeopathic Community Journal, Dr Neelam Avtar Singh and Association for Scientific
11 Special Thanks and Gratitude Contents xv Research in Homeopathy Group who arranged my seminar at Patiala Dr Amar Singh Maan, Dr Avtar Singh and Dr H.S. Matharoo who comes all the way from Punjab to observe Classical Homeopathic work at my hospital. Editor of Homeopathic Mind Journals Dr Ashok Gupta, who always spends his valuable time for me, writing articles on my hospital cases. Now, he is enjoying Classical Homeopathy at Baithia, Bihar. He has also arranged video seminar of my cases at Bihar. The Organizer of The Research Society of Homeopathy Dr C.P.Singh, Dr Anurudh Verma, Dr Jitendra Verma and other students from U.P. who invited me for - National Seminar on Applied Homeopathy at Lucknow. I would also like to forward my gratitude to the editor of H-pathy Dr. Manish Bhatia. I also thank my friends Mr Faizy Dalal and Mr Lalit Fulfagar for bringing critical cases to me. I am also thankful to B. Jain Publishers, Dr. Geeta Rani Arora and all editorial staff of B. Jain Publishers.
12 Contents xvii Contents Dedication Preface Acknowledgements Special Thanks and Gratitude iii v ix xiii CHAPTERS 1. Introduction 1 2. Different Concepts of Vital Force 7 APHORISMS RELATED TO VITAL FORCE CONCEPT BY Dr KENT SIMPLE SUBSTANCE CONCEPT BY Dr HERBERT ROBERTS CONCEPT BY STUART CLOSE VITAL PRINCIPLE CONCEPT BY VITHOULKAS CONCEPT OF RESONANCE, ELECTRO-DYNAMIC IELD F 3. Oxygen 19 OXYGEN HISTORY 18th ntury ce 19th ntury ce 20th ntury ce STRUCTURE PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OCCURRENCE BIOLOGICAL ROLE ALLOTROPES OF OXYGEN Dioxygen Singlet xygen o Ozone Tetraoxygen ISOTOPES OXIDES AND OTHER INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
13 xviii Vital Force is Oxygen 4. Oxygen Energy is Nothing but the Vital Energy How the Vital Force (Oxygen) enters the Human Body? 31 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM EXCHANGE OF RESPIRATORY GASES BETWEEN BLOOD AND LVEOLI A DIFFUSION OF OXYGEN From atmosphere to the alveoli From alveoli into the blood Diffusion of oxygen from blood into the tissues TRANSPORT OF OXYGEN IN BLOOD As simple physical solution In combination with haemoglobin ROLE OF OXYGEN IN RESPIRATORY CONTROL 6. Cell and Oxygen Physiology 41 MAJOR CELL STRUCTURES AND ITS FUNCTIONS Cell membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm and organelles - cytoskeleton, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus or complex, lysosomes, centrioles and centrosomes, flagella and cilia Mitochondrion Origin Structure Functions Dysfunction d an isease d NORMAL CELLULAR AGEING AND DEATH Cellular eing ag Cell eath D 7. Role of Oxygen (Vital Energy) in Metabolism 53 PHOSPHORYLATION KREBS CYCLE OR CITRIC ACID CYCLE CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM FAT METABOLISM PROTEIN METABOLISM EFFECTS OF INTRACELLULAR Po 2 ON RATE OF OXYGEN USAGE EFFECTS OF BLOOD FLOW ON METABOLIC USE OF OXYGEN Functions of ATP in cells FATE OF ANAEROBIC METABOLISM 8. Exercise and Oxygen 67 CLASSIFICATION OF EXERCISE Severe exercise/violent exercise
14 Contents xix Moderate xercise e Mild exercise/non-violent exercise FACTORS INVOLVED IN INCREASING THE PULMONARY VENTILATION DURING EXERCISE 9. How Symptoms Manifest in Human Body? 73 SYMPTOMS SENSATIONS DISEASE ISCHAEMIA - CAUSE OF PAIN 10. Relation of Oxygen to Disease State 79 FREE RADICALS-MEDIATED CELL INJURY CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Hypoxia and Ischaemia Reversible cell injury Irreversible ll ce njury i The Most Important Cause of Vital Energy Derangement: Hypo xia Types of hypoxia Local effects of hypoxia Response ypoxia to h Effect of hypoxia on synaptic transmission The relation of vital force with hypoxia Effects of fetal hypoxia Physical & Chemical injuries Physical njuries i Chemical njuries i Microbial agents Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites Immunologic agents Nutritional derangements Genetic factors Psychological factors 11. Mapping of Vital Energy Damages (Investigations and its use) 106 USE OF INVESTIGATIONS FROM HOMEOPATHIC POINT OF VIEW PULSE-OXIMETRY 12. Oxygen (Vital Force) and its Relation to Miasm 109 PSORA
15 xx Vital Force is Oxygen SYCOSIS TUBERCULAR SYPHILIS 13. Oxygen (Vital Force) and its Relation to Emotions 115 EMOTIONS STRESS AND DISEASE Neuroendocrine regulation of stress Catecholamines Cortisol EMOTIONAL DYSPNOEA 14. Vital Energy Derangement Origin of Pathology 12 INTRODUCTION ACUTE DISEASES CHRONIC DISEASES Inflammation Stages of the inflammatory response Acute nflammation i Chronic nflammation i Haemodynamic Disturbances Disturbances in the volume of the circulating blood Circulatory disturbances of obstructive nature Infectious and Parasitic Diseases Environmental and Nutritional Diseases Environmental iseases D Nutritional iseases D Effect of blood flow on gastrointestinal absorption Neoplasia Immunopathology Genetic seases di 15. Oxygen and its Relation with Homeopathic Medicine 153 NERVOUS SYSTEM DIVISIONS Receptors METHOD OF PREPARATION OF DYNAMIC MEDICINE DRUG PROVING / ACTION OF HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINE ON HEALTHY HUMAN BEING ACTION OF HOMEOPATHIC MEDICINE ON DISEASED PERSON 16. Importance of Vital Force (Oxygen) 165 Bibliography 171
16 74 Vital Force is Oxygen CHAPTER9 How Symptoms Manifest in Human Body? When the body is in equilibrium, the functions and the sensations in the body and mind are in normally active and balanced state. This is the state where the human being feels contentment. The body feels at ease, weightless, trouble-free along with complete physical, mental, & social harmony. Usually, if any changes occur in the body or its function, it is perceived by the patient. Symptoms represent subjective experience of the disease, which is narrated by the patient in their complaints or history of present illness. The various aspects of general symptom analysis includes mode of onset, progress (gradual or sudden), duration and precipitating factors, characteristics, location, radiation, severity, timing aggravation [<] & amelioration [>] factors. These symptoms are expressed by various kinds of abnormal sensations. Sensation means a feeling or awareness of the conditions within the body resulting from the stimulation of sensory receptors. The word disease is produced by mixture of two words
17 How Symptoms Manifest in Human Introduction Body? 75 i.e. dis + ease. The man, who is not at ease, is in disease. The concept of disease and illness differs in that disease is usually measurable whereas illness is highly individual and personal. Thus, a person may have a serious but symptom free disease i.e. hypertension, diabetes mellitus and even myocardial infarction. As from the homeopathic point of view, when we are treating the sick i.e. the unwell-being of the person, the homeopathic physician must consider the physical generals and characteristic symptoms along with mental symptoms (i.e. patient as a whole). Usually the symptoms and the abnormal sensations indicate that there is some dysfunction in the human body. Whenever there is less oxygen supply, at that time the cells start their abnormal behavior and at the same time changes occur in aerobic metabolism. The indication of this abnormal behavior of the cell is received by the different receptors and they give information through the nerves to the brain. So the lack of oxygen is most probably responsible for all kinds of symptoms. Whenever the body is in well being state, each and every cell receives appropriate amount of oxygen via the respiratory system. Lack of oxygen leads to cell injury which depends on the duration of hypoxia and every physician make an effort to find out the cause for the oxygen lack in human body. Disease occurs due to lack of ease in the cellular metabolic process. Multiple biochemical disturbances occur in metabolic pathway leading to various diseases; for example - atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia etc. for which again disturbance in oxygen energy or vital
18 76 Vital Force is Oxygen force is responsible. The symptoms, abnormal sensations, and dysfunction in the body occur due to inappropriate oxygen supply. Example, pain occurs whenever any tissues are being damaged, and it causes the individual to react to remove the pain stimulus. Even such simple activities as sitting for a long time on the ischia can cause tissue destruction because of lack of blood flow to the skin where it is compressed by the weight of the body. When skin becomes painful as a result of the ischaemia, the person normally shifts body weight subconsciously. When blood flow to a tissue is blocked, (ischaemia) the tissue often becomes very painful within a few minutes. The greater the rate of metabolism of the tissue, the more rapidly the pain appears. One of the suggested causes of pain during ischaemia is accumulation of large amounts of lactic acid in the tissues formed as a consequence of anaerobic metabolism. Probably, other chemical agents, such as bradykinin and proteolytic enzymes, are formed in the tissues because of cell damage and these stimulate the pain nerve endings.
19 How Symptoms Manifest in Human Introduction Body? 77 Fig. 9.1: Transmission of pain signals into the brain stem, thalamus, and cerebral cortex by way of the fast pricking pain pathway and the slow burning pain pathway The physiology behind the pain is ischemic condition of the affected tissue which releases the pain stimulation through the receptor to the neuron and message is sent through hypothalamus and cerebral cortex. It indicates alarming situation to the body and the central nervous system takes appropriate decision according to pain stimulation. Here, again it is important indication that pain is a manifestation of lack of oxygen (vital force) to the body.
20 Introduction 79 CHAPTER10 Relation of Oxygen to Disease State FREE RADICALS-MEDIATED CELL INJURY CAUSES OF CELL INJURY Hypoxia and ischaemia Reversible cell injury Irreversible cell injury The most important cause of vital energy derangement: hypoxia Types of hypoxia Local effects of hypoxia Effect of hypoxia on synaptic transmission The relation of vital force with hypoxia Effects of foetal hypoxia Physical & chemical injuries Physical injuries Chemical injuries Microbial agents Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites Immunologic agents Nutritional derangements Genetic factors Psychological factor
21 80 Vital Force is Oxygen CHAPTER10 Relation of Oxygen to Disease State In health, all expressions of vital force may be expressed by perfect functioning of all parts of the body and by a sense of general well-being. In disease, this expression is vastly changed. There is a sense of discomfort. The mental expressions are vastly altered according to the degree of disturbance. The signs and symptoms appear and all because of the disturbed vital functions, either from external impressions having a depressing effect, and the consequent reaction of the vital force or from some hidden miasm coming into its full expression in its impression on the vital force. Thus, disease is a disturbed vital process. Because of the impacts of these external impressions and the miasms, each and every cell of our body undergoes severe stress. This stressful situation affects the functioning of whole body and its microcellular organelles. Every disease is born through this process. Most of the disease states begin with cell injury and consequent loss of cellular function. Cell injury is defined as
22 Relation of Oxygen to Introduction Disease State 81 a variety of stress a cell encounters as a result of changes in its internal and external environment. In this chapter, I would like to specify the relation between the disturbed oxygen energy (vital energy) and disease process at the cellular level (cell organelle especially mitochondria). Cells need an adequate and constant supply of oxygen. Without this, they cannot generate enough amount of energy to maintain the metabolism and mechanisms (example, ion pumps) that move some of the essential substances across the cell membrane. Initially lack of oxygen affects the cellular function temporarily but with time irreversible damage is done and revitalization is impossible. Absence of vital force for just few minutes in the body creates a great hazard in each and every cell of living organism and obviously the result will be hypoxia, instant cell injury, and death. The cell cannot survive without this vital energy i.e. oxygen. Free radicals-mediated cell injury Within every cell there are small micro organelle called mitochondria. It is a power house of every cell which reduces oxygen by the transfer of electrons to create energy in the form of ATP and also produces a byproduct of water. This process goes without any hitch at least 90 to 98 percent. Generation of oxygen radicals begins within mitochondrial inner membrane when cytochrome oxidase catalyses the four electron reduction of oxygen (O 2 ) to water (H 2 O). Intermediate between reactions of oxygen to water, three partially reduced species of oxygen are generated depending upon the number of electrons transferred. These are:
23 82 Vital Force is Oxygen 1. Superoxide oxygen (O' 2 ): one electron 2. Hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ): two electrons 3. Hydroxyl radical (OH - ): three electrons Free radicals are electrically charged molecules that have an unpaired electron. Such molecules are unstable and highly reactive. When an oxygen free radical takes an electron from one molecule, that molecule becomes unstable and borrows an electron from another molecule, which, in turn, becomes unstable. These chain reactions lead to cellular damage and death. Among the molecules attacked by oxygen free radicals are proteins (such as enzymes), neurotransmitters, nucleic acid, and phospholipids of plasma membranes. These free radicals are responsible for most of the life threatening diseases in our life. Whichever part of body receives the most free radicals damage, are the first to wear out and this results in degenerative diseases. If this process is developed in eyes, it causes macular degeneration or cataract and glaucoma type of diseases. In a blood vessel atherosclerosis develops which is responsible for infarction, in joints it leads to arthritis, in brain it causes Alzheimer s or Parkinson s disease, and in kidneys or liver the physiological function of that organ undergo damage and pathology develops. When oxygen molecules maintain their strength there is energy and life, but the breakdown of oxygen create hazards in the life through the free radicals and this is called oxidative stress. This oxidative stress is underlying cause of almost all degenerative diseases. The aging process itself is an oxidative stress that is caused due to free radicals. The free radicals set off a chain reaction leading to potentially
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury.
 Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
Chemical and Biochemical Mechanism Of Cell Injury. Professor Dr. M. Tariq Javed Dept. of Pathology Faculty of Vet. Science The University Of Agriculture Faisalabad Cell Injury When the cell is exposed
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Editorial for the month of June 2011
 Editorial for the month of June 2011 Clinical Implications of Second prescription or the Follow up Management of acute and chronic disease chiefly depends on first and second prescription, This knowledge
Editorial for the month of June 2011 Clinical Implications of Second prescription or the Follow up Management of acute and chronic disease chiefly depends on first and second prescription, This knowledge
Name: Block: Date: PACKET #8 Unit 3: Energy Transfer, Part II: Cellular Respiration
 Name: Block: Date: PACKET #8 Unit 3: Energy Transfer, Part II: Cellular Respiration Reading: BSCS Text chapters 4, 5, and 2.8. Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit the student will be able to: Topic
Name: Block: Date: PACKET #8 Unit 3: Energy Transfer, Part II: Cellular Respiration Reading: BSCS Text chapters 4, 5, and 2.8. Objectives: By the conclusion of this unit the student will be able to: Topic
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
CELL INJURY. Severity of Cell Injury
 GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
GENERAL PATHOLOGY LECTURE - 3 DR. M. TARIQ JAVED Professor Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, Pakistan. 9/11/2009 1 CELL INJURY No adaptive response
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Robertson Ward, MD. theredoxdoc.com
 Robertson Ward, MD theredoxdoc.com Cell Anatomy = Human Anatomy Cell Membrane = Kidney Nucleus = Brain Endoplasmic Reticulum = Liver Mitochondrion = Lung Vacuole = Colon Lysosome = Stomach Golgi Apparatus
Robertson Ward, MD theredoxdoc.com Cell Anatomy = Human Anatomy Cell Membrane = Kidney Nucleus = Brain Endoplasmic Reticulum = Liver Mitochondrion = Lung Vacuole = Colon Lysosome = Stomach Golgi Apparatus
Polar Density (solid vs. liquid water) Cohesion Surface tension Adhesion Capillary Action
 GT Biology Midterm Study Guide Make sure that you are familiar with the following. You do not need to write notes for bold items: I. Scientific method Independent variable vs. Dependent variable Experimental
GT Biology Midterm Study Guide Make sure that you are familiar with the following. You do not need to write notes for bold items: I. Scientific method Independent variable vs. Dependent variable Experimental
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
KEY CONCEPT VOCABULARY
 SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development
SECTION 3.1 KEY CONCEPT CELL THEORY Study Guide Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development
Dr. V. PUSHPALATHA, M.D.(HOM) Asst. Professor, JSPS GOVT. HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICAL COLLEGE, RAMANTHAPUR, HYDERABAD (A.P) INDIA
 ORGANON FROM THE PRECURSOR TO THE LATEST Dr. V. PUSHPALATHA, M.D.(HOM) Asst. Professor, JSPS GOVT. HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICAL COLLEGE, RAMANTHAPUR, HYDERABAD 500013 (A.P) INDIA Exactly 200 years back, Hahnemann
ORGANON FROM THE PRECURSOR TO THE LATEST Dr. V. PUSHPALATHA, M.D.(HOM) Asst. Professor, JSPS GOVT. HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICAL COLLEGE, RAMANTHAPUR, HYDERABAD 500013 (A.P) INDIA Exactly 200 years back, Hahnemann
Biology Chapter-7 Cellular Respiration
 Biology-1406 Chapter-7 Cellular Respiration Energy is stored in Chemicals Catabolism- the breaking down of complex molecules, such as glucose, to release their stored energy. Catabolism may or may not
Biology-1406 Chapter-7 Cellular Respiration Energy is stored in Chemicals Catabolism- the breaking down of complex molecules, such as glucose, to release their stored energy. Catabolism may or may not
Raghad El-massri. Omar Fahed. Mohammad Khatatbeh
 1 Raghad El-massri Omar Fahed Mohammad Khatatbeh introductory lecture The first slide contains the syllabus of Dr.Khatatbah's material - We have different type of cells in our body so a group of cells
1 Raghad El-massri Omar Fahed Mohammad Khatatbeh introductory lecture The first slide contains the syllabus of Dr.Khatatbah's material - We have different type of cells in our body so a group of cells
MIDDLETOWN HIGH SCHOOL SOUTH BIOLOGY
 MIDDLETOWN HIGH SCHOOL SOUTH BIOLOGY BOOKLET 10 NAME: CLASS: 1 S.Tagore Middletown South High School March 2013 LEARNING OUTCOMES The role and production of ATP (a) Importance, role and structure of ATP
MIDDLETOWN HIGH SCHOOL SOUTH BIOLOGY BOOKLET 10 NAME: CLASS: 1 S.Tagore Middletown South High School March 2013 LEARNING OUTCOMES The role and production of ATP (a) Importance, role and structure of ATP
FulvicForce offers an ideal replacement for. creatine. FulvicForce boosts immune system and fights. inflammation. FulvicForce is effective in weight
 FulvicForce fulvic acid in Sport and Training Research confirms that fulvic acid possesses truly remarkable biological, nutritional and remedial properties. It is these same properties, which make FulvicForce
FulvicForce fulvic acid in Sport and Training Research confirms that fulvic acid possesses truly remarkable biological, nutritional and remedial properties. It is these same properties, which make FulvicForce
International Journal of Homoeopathic Sciences 2018; 2(4): Dr. Skandhan S Kumar and Dr. Shivaprasad K
 2018; 2(4): 23-27 E-ISSN: 2616-4493 P-ISSN: 2616-4485 IJHS 2018; 2(4): 23-27 Received: 14-08-2018 Accepted: 18-09-2018 Dr. Skandhan S Kumar Assistant Professor Homoeopathic Medical College, Mangaluru,
2018; 2(4): 23-27 E-ISSN: 2616-4493 P-ISSN: 2616-4485 IJHS 2018; 2(4): 23-27 Received: 14-08-2018 Accepted: 18-09-2018 Dr. Skandhan S Kumar Assistant Professor Homoeopathic Medical College, Mangaluru,
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
The Brain & Homeostasis. The Brain & Technology. CAT, PET, and MRI Scans
 The Brain & Homeostasis Today, scientists have a lot of information about what happens in the different parts of the brain; however they are still trying to understand how the brain functions. We know
The Brain & Homeostasis Today, scientists have a lot of information about what happens in the different parts of the brain; however they are still trying to understand how the brain functions. We know
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport
 Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Title: Sep 10 7:59 PM (1 of 36) Ch 3 Cell Organelles and Transport Title: Sep 10 8:02 PM (2 of 36) Cell organelles Nucleus: contains DNA Title: Sep 10 8:03 PM (3 of 36) Nuclear envelope double membrane
Introduction. Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters).
 Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Introduction Biochemistry: It is the chemistry of living things (matters). Biochemistry provides fundamental understanding of the molecular basis for the function and malfunction of living things. Biochemistry
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
PEMF Therapy. Content Source: PEMF 5 th Element of Health, by Bryan Meyers.
 PEMF Therapy BENEFITS OF PEMF THERAPY Content Source: PEMF 5 th Element of Health, by Bryan Meyers. Top 8 Benefits 1. Stronger Bones 2. Endorphins and Pain Relief 3. Better Sleep and HGH secretion 4. More
PEMF Therapy BENEFITS OF PEMF THERAPY Content Source: PEMF 5 th Element of Health, by Bryan Meyers. Top 8 Benefits 1. Stronger Bones 2. Endorphins and Pain Relief 3. Better Sleep and HGH secretion 4. More
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function
 Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
Lab 3: Cellular Structure and Function What is the basic unit of life? The simplest form of life is the cell! All living things are either: unicellular (only one cell) multicellular (many cells make one
8/7/18. UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function. I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory
 8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
8/7/18 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function
 UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
UNIT 2: Cells Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function I. Cell Theory (3.1) A. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory 1. Discovery of Cells a. Robert Hooke (1665)-Used compound microscope
CHAPTER 3 1/21/2016. Typical Bacteria Cell. The Cell
 CHAPTER 3 The Cell Chapter 3 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain why surface area-to-volume ratios constrain cell size. Contrast light microscopy
CHAPTER 3 The Cell Chapter 3 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the features of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Explain why surface area-to-volume ratios constrain cell size. Contrast light microscopy
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
g) Cellular Respiration Higher Human Biology
 g) Cellular Respiration Higher Human Biology What can you remember about respiration? 1. What is respiration? 2. What are the raw materials? 3. What are the products? 4. Where does it occur? 5. Why does
g) Cellular Respiration Higher Human Biology What can you remember about respiration? 1. What is respiration? 2. What are the raw materials? 3. What are the products? 4. Where does it occur? 5. Why does
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Overview. Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions. The Cell. Key Terms. Microscopes. Microscopes. Cytology The study of cells
 Overview Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Key Terms The Cell active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic
Overview Chapter 3: Cells and Their Functions Key Terms The Cell active transport filtration mitochondria cancer gene mitosis carcinogen hemolysis mutation chromosome hypertonic nucleus cytology hypotonic
Cellular Respiration Assignment
 I. MULTIPLE CHOICES. Select the best answer. Write the letter of your choice on the space provided. 1. Electron transport chain allows the electron to. a) transfer from grana to stroma. b) transfer from
I. MULTIPLE CHOICES. Select the best answer. Write the letter of your choice on the space provided. 1. Electron transport chain allows the electron to. a) transfer from grana to stroma. b) transfer from
Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Functions Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 62-107 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 527) 1. 2. 3. 4. 9. What
Cellular Respiration- -conversion of stored energy in glucose to usable energy for the cell -energy in cells is stored in the form of ATP
 Cellular Respiration Notes Chapter 7 How Cells Make ATP Energy Releasing Pathways Cellular Respiration- -conversion of stored energy in glucose to usable energy for the cell -energy in cells is stored
Cellular Respiration Notes Chapter 7 How Cells Make ATP Energy Releasing Pathways Cellular Respiration- -conversion of stored energy in glucose to usable energy for the cell -energy in cells is stored
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Name Class Date. cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell. MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
 Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
The Cell. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 3 The Cell Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Review. Respiration. Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the decomposition (lysis) of glucose (glyco) to pyruvate (or pyruvic acid).
 Review Photosynthesis is the process of incorporating energy from light into energy-rich molecules like glucose. Respiration is the opposite process extracting that stored energy from glucose to form ATP
Review Photosynthesis is the process of incorporating energy from light into energy-rich molecules like glucose. Respiration is the opposite process extracting that stored energy from glucose to form ATP
THE CELL Cells: Part 1
 THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
THE CELL Cells: Part 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lesson you should be able to: State the 2 types of cells Relate the structure to function for all the organelles TYPES OF CELLS There are two types of
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam
 Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
Name: Class: Date: Cell Structure and Transport Take Home Exam 1. Which is found in the nucleus? (1.) ribosome (2.) centrosome (3.) vacuole (4.) lysosome (5.) chromosome 2. Which structure composed mainly
CELLULAR RESPIRATION. Chapter 7
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chapter 7 7.1 GLYCOLYSIS AND FERMENTATION If I have a $10.00 bill and a $10.00 check, which is better? ATP is like cash in the cell Glucose, NADH, FADH2 are like checks in a cell.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION Chapter 7 7.1 GLYCOLYSIS AND FERMENTATION If I have a $10.00 bill and a $10.00 check, which is better? ATP is like cash in the cell Glucose, NADH, FADH2 are like checks in a cell.
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Background knowledge
 Background knowledge This is the required background knowledge: State three uses of energy in living things Give an example of an energy conversion in a living organism State that fats and oils contain
Background knowledge This is the required background knowledge: State three uses of energy in living things Give an example of an energy conversion in a living organism State that fats and oils contain
Cells. Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function. Cells. Plasma Membrane
 Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Understanding Parkinson s Disease
 Understanding Parkinson s Disease Professor Tony Schapira Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute
Understanding Parkinson s Disease Professor Tony Schapira Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson 3.2: True or False. Lesson 3.2: Critical Reading
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson 3.2: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. The water-hating hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer face the outside
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson 3.2: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. The water-hating hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer face the outside
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock. Dr Than Kyaw March 2012
 Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
Cardiovascular System L-5 Special Circulations, hemorrhage and shock Dr Than Kyaw March 2012 Special circulation (Coronary, Pulmonary, and Cerebral circulations) Introduction Special attention to circulation
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Pyruvate + NADH + H + ==== Lactate + NAD +
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR ANAEROBIC METABOLISM - An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR ANAEROBIC METABOLISM - An Overview
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY
 Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
Cell Injury MECHANISMS OF CELL INJURY The cellular response to injurious stimuli depends on the following factors: Type of injury, Its duration, and Its severity. Thus, low doses of toxins or a brief duration
CELLS CELL THEORY. There are two types of cells: 9/26/2016 CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES. Which is more complicated? REMEMBER YOU ARE EUKARYOTIC!
 CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
CELLS CELLULAR COMPONENTS & PROCESES CELL THEORY 1. All living things are made up of one or more cells 2. The cell is the smallest unit of life. 3. All new cells come from pre-existing cells. There are
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology
 3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
3- Cell Structure and Function How do things move in and out of cells? A Quick Review Taft College Human Physiology How do things move in and out of cells? Things may move through cell membranes by Passive
RESPIRATION IN PLANTS
 7777 CHAPTER 14 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is: a Cytochrome b Oxygen c Hydrogen d Glucose 2. Phosphorylation
7777 CHAPTER 14 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is: a Cytochrome b Oxygen c Hydrogen d Glucose 2. Phosphorylation
Speech by HRH Crown Princess Mary at WHO s 62nd Regional Committee Malta, September 10, 2012
 Speech by HRH Crown Princess Mary at WHO s 62nd Regional Committee Malta, September 10, 2012 Your Excellency Prime Minister, Honourable Ministers, Madam Director-General, Mr. Commissioner, Mr. Deputy Secretary-General,
Speech by HRH Crown Princess Mary at WHO s 62nd Regional Committee Malta, September 10, 2012 Your Excellency Prime Minister, Honourable Ministers, Madam Director-General, Mr. Commissioner, Mr. Deputy Secretary-General,
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Cell Respiration. Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration
 Cell Respiration Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration Understandings/Objectives 2.8.U1: Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP. Define cell respiration State
Cell Respiration Anaerobic & Aerobic Respiration Understandings/Objectives 2.8.U1: Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP. Define cell respiration State
1. Prokaryotic (Bacteria) Eukaryotic (all other living things)
 AP BIOLOGY CONCEPT 2 CELLS (Review for Exam 3 on Nov. 30) 1. Prokaryotic (Bacteria) Eukaryotic (all other living things) no membrane-bound organelles m.b.o, ex. Chloroplasts and nucleus no nucleus(single;
AP BIOLOGY CONCEPT 2 CELLS (Review for Exam 3 on Nov. 30) 1. Prokaryotic (Bacteria) Eukaryotic (all other living things) no membrane-bound organelles m.b.o, ex. Chloroplasts and nucleus no nucleus(single;
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 9 How animal cells work Pack Code: EBS9 This pack you will help you to: Identify the main components of an animal cell Describe the functions of the main cell components
Equine biological systems Pack 9 How animal cells work Pack Code: EBS9 This pack you will help you to: Identify the main components of an animal cell Describe the functions of the main cell components
[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology
![[General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology [General Pathology] Introduction to Pathology](/thumbs/73/69585662.jpg) Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
Introduction to Pathology Pathology: Literally translated, pathology is the study (logos) of disease (pathos, suffering). It involves the investigation of the causes of disease and the associated changes
1- Which of the following statements is TRUE in regards to eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
 Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Resp & Cell Comm Review
 Resp & Cell Comm Review Two main catabolic processes: fermentation: partial degradation of sugars in the absence of oxygen. cellular respiration: uses oxygen to complete the breakdown of many organic molecules.
Resp & Cell Comm Review Two main catabolic processes: fermentation: partial degradation of sugars in the absence of oxygen. cellular respiration: uses oxygen to complete the breakdown of many organic molecules.
Objectives. To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles.
 Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
ROLE OF BDNF IN ENRICHED ENVIRONMENT MEDIATED AMELIORATION OF HYPOBARIC HYPOXIA INDUCED MEMORY IMPAIRMENT
 ROLE OF BDNF IN ENRICHED ENVIRONMENT MEDIATED AMELIORATION OF HYPOBARIC HYPOXIA INDUCED MEMORY IMPAIRMENT THESIS SUBMITTED TO BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE, INDIA FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
ROLE OF BDNF IN ENRICHED ENVIRONMENT MEDIATED AMELIORATION OF HYPOBARIC HYPOXIA INDUCED MEMORY IMPAIRMENT THESIS SUBMITTED TO BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE, INDIA FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
1. The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is: Cytochrome Oxygen Hydrogen Glucose
 7777 CHAPTER 14 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is: a b c d Cytochrome Oxygen Hydrogen Glucose 2. Phosphorylation
7777 CHAPTER 14 RESPIRATION IN PLANTS MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. The ultimate electron acceptor of respiration in an aerobic organisms is: a b c d Cytochrome Oxygen Hydrogen Glucose 2. Phosphorylation
Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
 Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology,
Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology,
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment
 Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
Chapter 3: Cell Structure and Function Assignment Provide full detail and be specific for full marks. 1. How do these organelles work together? 2 marks each = 10 marks a. lysosomes and vacuoles When material
The Cell. The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes.
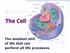 The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
The Cell The smallest unit of life that can perform all life processes. Life is macromolecules that can perform unique functions because they are enclosed in a structural compartment that is separate from
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation*
 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Life Is Work
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Life Is Work
Cellular Structure and Function
 7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
7 Cellular Structure and Function section 2 The Plasma Membrane A cell s plasma membrane helps maintain homeostasis. What You ll Learn how the cell s plasma membrane functions the role of proteins, carbohydrates,
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Biology and Society: Marathoners versus Sprinters Sprinters do not usually compete at short and long distances. Natural differences in the muscles of these athletes favor
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Biology and Society: Marathoners versus Sprinters Sprinters do not usually compete at short and long distances. Natural differences in the muscles of these athletes favor
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Different Methods of Prescribing
 Different Methods of Prescribing Hahnemann Organon The striking, singular, uncommon and peculiar( characteristic) S/S should correspond to the selected medicine for cure. Not the general undefined ones
Different Methods of Prescribing Hahnemann Organon The striking, singular, uncommon and peculiar( characteristic) S/S should correspond to the selected medicine for cure. Not the general undefined ones
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
National Homoeopathic Seminar Satara 2018 At D.C.C. Hall, Satara 22 April 2018
 National Homoeopathic Seminar Satara 2018 At D.C.C. Hall, Satara 22 April 2018 RANGOLI OF DR HAHNEMANN DELEGATES TEAM OF HOMOEOAPATHIC PRASAR MANDAL, Satara RECIEVING DR. MANOJ PATEL SIR BY ICR TEAM SATARA
National Homoeopathic Seminar Satara 2018 At D.C.C. Hall, Satara 22 April 2018 RANGOLI OF DR HAHNEMANN DELEGATES TEAM OF HOMOEOAPATHIC PRASAR MANDAL, Satara RECIEVING DR. MANOJ PATEL SIR BY ICR TEAM SATARA
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles. Hüseyin Çağsın
 Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7
 Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
Cellular Structure and Function. Chapter 7 Cell Discovery and Theory. A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. The human body is made of trillions of cells that are too
This is a large part of coaching presence as it helps create a special and strong bond between coach and client.
 Page 1 Confidence People have presence when their outer behavior and appearance conveys confidence and authenticity and is in sync with their intent. It is about being comfortable and confident with who
Page 1 Confidence People have presence when their outer behavior and appearance conveys confidence and authenticity and is in sync with their intent. It is about being comfortable and confident with who
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration I. The Importance of Food A. Food provides living things with the: B. Food serves as a source of: C. Food serves as a source of: II. Chemical Energy and ATP A. Inside living cells,
Cellular Respiration I. The Importance of Food A. Food provides living things with the: B. Food serves as a source of: C. Food serves as a source of: II. Chemical Energy and ATP A. Inside living cells,
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
First discovered in 1665 since then every organism observed with microscopes shows cells
 The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
The Cell Cell theory (1838): 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell morphology. Cell organelles structure and function. Chapter 1: UNIT 1. Dr. Charushila Rukadikar
 UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
UNIT 1 Cell morphology Cell organelles structure and function Chapter 1: Dr. Charushila Rukadikar Assistant Professor Department Of Physiology ZMCH, Dahod Physiology The science that is concerned with
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 1 1/30/15
 Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 1 1/30/15 Answer each of the following short- and long- answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each of the multiple choice
Name: TRASK Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 1 1/30/15 Answer each of the following short- and long- answer questions in the space provided; circle the BEST answer or answers for each of the multiple choice
Cell Transport Unit Test
 Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
 Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon,
Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon,
HIGH DILUTION EFFECTS: PHYSICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL BASIS
 HIGH DILUTION EFFECTS: PHYSICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL BASIS High Dilution Effects: Physical and Biochemical Basis by Nirmal C. Sukul Department of Zoology, Visva-Bharati University and Anirban Sukul Department
HIGH DILUTION EFFECTS: PHYSICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL BASIS High Dilution Effects: Physical and Biochemical Basis by Nirmal C. Sukul Department of Zoology, Visva-Bharati University and Anirban Sukul Department
Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food
 Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon,
Chapter 6 Cellular Respiration: Obtaining Energy from Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon,
Plant Cells. Chapter 3
 Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
Plant Cells Chapter 3 Major Learning Objectives Contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Describe the functions of 10 parts of a plant cell Summarize the similarities and differences between plant cells
