ACUPUNCTURE AND GI TRACT DISORDERS
|
|
|
- Elaine Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACUPUNCTURE AND GI TRACT DISORDERS About GI tract disorders Around 2 4 in 1,000 people in Northern Europe have ulcerative colitis or Crohn s disease (Rubin 2000). Both are chronic, relapsing, inflammatory disorders of the gastrointestinal tract with several shared clinical features, but with largely distinct risk factors, genetic, immunological, anatomical and histological features, and response to therapy (DTB 2003). Their treatment, which includes medical and surgical approaches, is usually considered in two phases: the induction of remission in an acute attack, and the long-term maintenance of remission (DTB 2003). Gastritis is an inflammation, irritation, or erosion of the lining of the stomach, which can be acute or chronic. Causes include irritation due to excessive alcohol use, chronic vomiting, stress, or the use of certain drugs (e.g. NSAIDs), Helicobacter pylori infection and pernicious anaemia. Symptoms of gastritis vary among individuals, and many have no symptoms. However, the most common symptoms include nausea, vomiting (possibly with blood), abdominal pain and bloating, indigestion, loss of appetite, and blood in the stools. Treatment usually involves drug therapy. Gastro-oesophageal reflux is a common (affecting up to 25% of adults) relapsing condition caused by repeated exposure of the lower oesophagus to refluxed gastric contents (Moayyedi 2007). It presents in various ways: some patients just have symptoms, some have endoscopic evidence of mucosal damage (oesophagitis), with or without symptoms, and an important minority have complications such as bleeding, stricture or columnar epithelial (Barrett s) transformation of the lower oesophageal mucosa which predisposes to adenocarcinoma. Conventional treatment options include drugs and surgery. About 20% of people in the UK have functional gastrointestinal disorders such as functional dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome (Jones 1990; Jones 1992). The latter condition is the subject of another professional information backgrounder, and will not be discussed further here. Functional gastrointestinal disorders are characterised by persisting gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g. pain, bloating) in the absence of any identifiable underlying structural or biochemical explanation (Drossman 2000). They are conventionally treated with drugs or with psychological treatments such as cognitive behavioural therapy, brief psychotherapy and gutdirected hypnotherapy (DTB 2005). November 2014 page 1
2 References Drossman DA (Ed). Diagnostic Criteria for the Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. Second edition. Kansas: Degnon Associates, 2000: Hypnotherapy for functional gastrointestinal disorders. DTB 2005; 43: Inducing remission in inflammatory bowel disease. DTB 2003; 41: Jones RH et al. Dyspepsia in England and Scotland. Gut 1990; 31: Jones R, Lydeard S. Irritable bowel syndrome in the general population. BMJ 1992; 304: Moayyedi P, Delaney B. GORD in adults. Clinical Evidence. Search date July Rubin GP et al. Inflammatory bowel disease: epidemiology and management in an English general practice population. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2000; 14: How acupuncture can help Acupuncture has been found superior to sham acupuncture for disease activity scores in Chrohns Disease and Ulcerative Colitis (Joos 2006; Joos 2006; Schneider 2007). Other placebo comparisons have tended to show no statistical effect; however, there is as yet no satisfactory placebo intervention for acupuncture so the interpretation of such data is difficult and controversial. In comparisons with Western drug treatments acupuncture has been found beneficial for a variety of gastrointestinal diseases: dyspepsia (Chen 2005), gastritis (Ren 2009; Gu 2009), ulcerative colitis (Mu 2007; Lee 2009), reflux (Journal of the National Medical Association 2008; Zhang 2010) and pancreatitis (Wang 2007). Nevertheless most systematic reviews have been reluctant to endorse acupuncture because of the generally poor quality, and hence unreliability, of the studies to date (Schneider 2007; Lee 2009). (see Table overleaf). Acupuncture may help in the treatment of GI tract disorders, by: inhibiting gastric and duodenal motility by activating sympathetic nerves via spinal reflexes, and increasing motility via the vagus nerve and supraspinal reflexes (Chang 2001; Takahashi 2006; Sehn 2006; Yao 2006; Noguchi 2008); altering acid secretion, and visceral pain (Takahashi 2006) improving delayed gastric emptying (Xu 2006) reducing inflammation, by promoting release of vascular and immunomodulatory factors (Zijlstra 2003) stimulating areas in the brain that are involved in gastric perception (Zeng 2009) inhibiting stress-induced pro-opiomelanocortin expression in the hypothalamus (Sun 2008) increasing vasoactive intestinal peptide and nitric oxide in plasma, gastric mucosal and bulb tissues, and elevating expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide in antral smooth muscle (Shen 2006); decreasing permeability of intestinal mucosa in patients with acute pancreatitis, and reducing accumulation of endogenous inflammatory mediators and vascular active substance in intestinal mucosa (Wang 2007). November 2014 page 2
3 About traditional acupuncture Acupuncture is a tried and tested system of traditional medicine, which has been used in China and other eastern cultures for thousands of years to restore, promote and maintain good health. Its benefits are now widely acknowledged all over the world, and in the past decade traditional acupuncture has begun to feature more prominently in mainstream healthcare in the UK. In conjunction with needling, the practitioner may use techniques such as moxibustion, cupping, massage or electroacupuncture. They may also suggest dietary or lifestyle changes. Traditional acupuncture takes a holistic approach to health and regards illness as a sign that the body is out of balance. The exact pattern and degree of imbalance is unique to each individual. The traditional acupuncturist s skill lies in identifying the precise nature of the underlying disharmony and selecting the most effective treatment. The choice of acupuncture points will be specific to each patient s needs. Traditional acupuncture can also be used as a preventive measure to strengthen the constitution and promote general wellbeing. An increasing weight of evidence from Western scientific research (see overleaf) is demonstrating the effectiveness of acupuncture for treating a wide variety of conditions. From a biomedical viewpoint, acupuncture is believed to stimulate the nervous system, influencing the production of the body s communication substances - hormones and neurotransmitters. The resulting biochemical changes activate the body's self-regulating homeostatic systems, stimulating its natural healing abilities and promoting physical and emotional wellbeing. About the British Acupuncture Council With over 3000 members, the British Acupuncture Council (BAcC) is the UK s largest professional body for traditional acupuncturists. Membership of the BAcC guarantees excellence in training, safe practice and professional conduct. To find a qualified traditional acupuncturist, contact the BAcC on or visit November 2014 page 3
4 ACUPUNCTURE AND GI TRACT DISORDERS The evidence Research Conclusion Systematic reviews Lee D-H et al. Moxibustion for ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterology 2009; 10, Article Number: 36. A systematic review and meta-analysis that assessed the clinical evidence for moxibustion as a treatment for ulcerative colitis. Five randomised controlled trials with a total of 407 patients were included (published up to February 10, 2010). All the trials were considered to be of low methodological quality. They all compared the effects of moxibustion with conventional drug therapy. Three tested moxibustion against sulfasalazine and two against sulfasalazine plus other drugs. Meta-analysis of the five trials showed favourable effects of moxibustion on response rate compared to conventional drug therapy (n = 407; risk ratio = 1.24, 95% CI = 1.11 to 1.38; P < ). However, the reviewers concluded that current evidence is insufficient to show that moxibustion is an effective treatment of ulcerative colitis because most of included trials had a high risk of bias. Mu JP et al. Meta-analysis on acupuncture and moxibustion for treatment of ulcerative colitis. [Chinese]. Zhongguo Zhenjiu 2007; 27: A meta-analysis that assessed the effectiveness and safety of acupuncture and moxibustion for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. A total of 11 randomised controlled trials or clinical controlled were included (all published within 10 years). Statistical analysis indicated the odds ratio in favour of acupuncture and moxibustion was 3.82 (95% CI 2.65 to 5.52). The therapeutic effect and the cure rate in the treatment group were significantly higher than those of the control group (p<0.01). The reviewers concluded that the therapeutic effect and safety of acupuncture and moxibustion on ulcerative colitis is superior to that of western medicine. Schneider A et al. Acupuncture treatment in gastrointestinal diseases: A systematic review. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2007; 13: Clinical studies Functional dyspepsia: A systematic review that assessed the evidence for effectiveness of acupuncture treatment in gastrointestinal diseases. A total of 18 clinical studies (published up to May 2006) were included; two for irritable bowel syndrome, one for Crohn's disease and one for ulcerative colitis were randomised controlled trials. For other gastrointestinal disorders, study quality was poor. In all trials, quality of life improved significantly, but this was independent of the kind of acupuncture used (i.e. real or sham). Real acupuncture was significantly superior to sham acupuncture with regard to disease activity scores in the Crohn s and ulcerative colitis trials. The reviewers concluded that further trials of acupuncture for inflammatory bowel disease are necessary to evaluate the efficacy of acupuncture treatment. Park Y-C et al. Evaluation of manual acupuncture at classical and A single-blind randomised controlled trial that looked at the efficacy of acupuncture as a treatment in 68 patients with November 2014 page 4
5 nondefined points for treatment of functional dyspepsia: A randomizedcontrolled trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2009; 15: , functional dyspepsia. Acupuncture was given three times a week for 2 weeks. Patients were either given acupuncture at classical points or undefined points Symptoms and quality of life were scored according to the Nepean Dyspepsia Index before and after treatments. Acupuncture treatment significantly decreased dyspepsia symptoms and improved the quality of life, but there was no difference between the two acupuncture groups. The researchers concluded that acupuncture at both classical points and undefined points improved the symptoms of patients with functional dyspepsia, but that a placebo effect could not be ruled out. Chen JY et al. Effects of acupuncture on the gastric motivity in patients with functional dyspepsia. [Chinese]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi/Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional & Western Medicine/Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Hui, Zhongguo Zhong Yi Yan Jiu Yuan Zhu Ban 2005; 25: Gastritis: Ren R, Zhuang LX. Effect of acupuncture and moxibustion of Shu- and Mu-acupoints on the quality of life in patients chronic superficial gastritis. [Zhongguo yi xue ke xue yuan Yi xue qing bao yan jiu suo bian ji] 2009; 34: A randomised controlled trial that looked at the effects of the acupuncture on the gastric motivity in patients with functional dyspepsia. Ninety patients were randomly allocated to acupuncture treatment, cisapride (withdrawn in the UK because of adverse effects) or granules containing azulene sulfonate sodium and L-glutamine. Symptoms, gastro-electric frequency and rhythm, and gastric emptying time and plasma motilin improved in the acupuncture and cisapride groups, and more so than in the azulene group (p<0.05). The researchers concluded that acupuncture could significantly improve the gastric motivity of patients with functional dyspepsia. A 4-week randomised controlled trial that compared electroacupuncture plus moxibustion with omeprazole (20 mg four times daily) on the symptoms and quality of daily life in 60 patients with chronic superficial gastritis. Overall, the effective rates were 90% with acupuncture and 67% with medication (p<0.05). Self-comparison showed a marked improvement in the quality of life including physical function, bodily pain, general health, vitality, social function, and mental health in both groups after the treatment. The researchers concluded that electroacupuncture plus moxibustion can effectively relieve clinical symptoms and improve quality of life in patients with chronic superficial gastritis. Gu W. Hu QC. Clinical observation on acupuncture for treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis. [Chinese]. Zhongguo Zhenjiu 2009; 29: A randomised controlled trial to compare the therapeutic effects of acupuncture and western medicine for the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis. Eighty patients were randomly divided into an observation group treated with acupuncture and a control group given western medicine (e.g. omeprazole, amoxicillin etc.). Evaluation was carried out before treatment and after 4 and 8 weeks of treatment. The total effective rate was 92.5% in the acupuncture group and 75% in the control group (p<0.05). For pathologic changes in the gastric mucosa assessed by gastroscopic inspection, the total effective rate was 85% in the acupuncture group and 65% in the control group (p<0.05). For histopathologic improvement, the total effective rate was 87.5% in the acupuncture group and 65% in the control group (p<0.05). The researchers concluded that acupuncture therapy can significantly improve the clinical symptoms, gastroscopic expression and histopathologic situation in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis, and its therapeutic effect is better than that of November 2014 page 5
6 the western medicine. Gao X et al. Clinical research on acupuncture and moxibustion treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2007; 27: A 2-month randomised controlled trial that looked at the clinical therapeutic effects of acupuncture and moxibustion in treating chronic atrophic gastritis. A total of 88 patients allocated to acupuncture, acupuncture plus moxibustion or a control group. The active treatment groups had significantly greater improvement in symptoms compared with controls, and the acupuncture plus moxibustion group had the greatest improvement. Improvement in glandular atrophy and intestinal metaplasia was also greater with acupuncture plus moxibustion (total effective rate 67%). All three groups had marked improvement in the level of serum gastrin, with the acupuncturemoxibustion group showing the best effects. The researchers concluded that acupuncture and moxibustion have definite therapeutic effects in the treatment of chronic atrophic gastritis, especially in improving the symptoms. Peptic ulceration: Niu HY et al. Multicentral randomized controlled trials of acupuncture at Zhongwan (CV 12) for treatment of peptic ulcer. [Chinese]. Zhongguo Zhenjiu 2007; 27: A 6-week randomised controlled trial that evaluated the efficacy and safety of acupuncture for treatment of peptic ulcers in 276 patients compared with cimetidine. The therapeutic effects were evaluated by clinical symptoms and gastroscopy. The symptoms improved significantly in both groups (p<0.01), but with no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05). The acupuncture group was better than the control group in terms of rapid alleviation of stomachache and improvement of appetite (p<0.05). However, there was no difference between the groups in terms of the total effective rate (91% in the acupuncture group vs. 88% in the control group, p>0.05), or in terms of the therapeutic effect of gastroscopy (p>0.05). The researchers concluded that acupuncture has a reliable therapeutic effect on peptic ulcer. Gastro-oesophageal reflux: Zhang CX, Qin YM, Guo BR. Clinical study on the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux by acupuncture. Chin J Integr Med Aug;16(4): Acupuncture may have value in treating gastroesophageal reflux. Journal of the National Medical Association 2008; 100: 350. Sixty patients with confirmed diagnosis of gastro-oesophageal reflux (GER) were randomly assigned to an acupuncture group (once a day, for 1 week, with 2-3 days between courses) or a control group taking omeprazole (20 mg twice a day) and mosapride (20 mg thrice a day). Treatment lasted 6 weeks hr intra-oesophageal ph and bile reflux, endoscopic grading score and symptom score were all decreased significantly at the end of treatment in both groups (P<0.01), with insignificant difference between them (P>0.05). Four weeks later the symptom scores had reverted to a high level in the control group (P<0.05), but this did not occur in the treatment group (P>0.05). Acupuncture can effectively inhibit the intraesophageal acid and bile reflux in GER patients to alleviate patients' symptoms with good safety and is well accepted by patients A randomised controlled trial that compared acupuncture plus a standard dose of omeprazole with a double dose of omeprazole in 30 adult patients with a 3-month history of symptoms related to gastro-oesophageal reflux disease despite taking a standard- November 2014 page 6
7 dose of omeprazole (20 mg daily).. The addition of acupuncture to standard-dose omeprazole therapy significantly decreased symptoms of daytime and nighttime heartburn, acid regurgitation, dysphagia and chest pain, whereas there was no change in symptoms with double-dose omeprazole. Quality of life, assessed at the end of the study using the SF-36 general health scale, was significantly improved in the acupuncture group as compared with the increased dose group. Ulcerative colitis: Joos S et al. Acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled study. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2006; 41: A randomised controlled trial that investigated the efficacy of acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of mild to moderately active ulcerative colitis in 29 patients compared with sham acupuncture. The main outcome measure was the change in the Colitis Activity Index (CAI) after treatment; secondary outcome measures were changes in quality of life, general wellbeing and serum markers of inflammation. In the acupuncture plus moxa group, the CAI decreased from 8.0 to 4.2 points and in the control group from 6.5 to 4.8 points (p=0.048). In both groups these changes were associated with significant improvements in general well-being (from 3.0 to 1.8 and from 3.2 to 2.2, respectively) and quality of life (from 146 to 182 and from 157 to 183, respectively). No significant differences between the groups were found regarding these secondary outcome measures. The researchers concluded that differences in efficacy between traditional acupuncture and sham acupuncture were small but significant for CAI as the main outcome measure. Both traditional and sham acupuncture seem to offer an additional therapeutic benefit in patients with mild to moderately active ulcerative colitis. Crohn s disease: Joos S et al. Acupuncture and moxibustion in the treatment of active Crohn's disease: A randomized controlled study. Digestion 2004; 69: Acute Pancreitis: Wang XY. [Electroacupuncture for treatment of acute pancreatitis and its effect on the intestinal permeability of the A randomised controlled trial that investigated the efficacy of traditional Chinese acupuncture in the treatment of mild to moderately active Crohn's disease in 51 patients compared with sham acupuncture. The primary outcome measure was the change in the Crohn s disease activity index (CDAI). Changes in quality of life and general well-being, and serum markers of inflammation were secondary outcome measures. In the real acupuncture group the CDAI decreased from 250 to 163 points as compared with a mean decrease from 220 to 181 in the sham group (p = 0.003). In both groups these changes were associated with improvements in general well-being and quality of life. With regard to general well-being, traditional acupuncture was superior to control treatment (p = 0.045). Alpha 1-acid glycoprotein concentration fell significantly only in the acupuncture group (p = 0.046). The researchers concluded that traditional acupuncture offers an additional therapeutic benefit in patients with mild to moderately active Crohn s disease. A randomised controlled trial that looked at the mechanism and effects of electroacupuncture added to medication on intestinal permeability in 68 patients with acute pancreatitis. Compared to medication only (the control group), the total effective rate was greater in the acupuncture group (86.7% vs. 76.3%, p<0.05). November 2014 page 7
8 patient [Article in Chinese]. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 2007;27: After treatment, changes in endothelin, nitric oxide, tumour necrosis factor and the lactulose/mannose ratio were significantly greater in the acupuncture group than in Research on mechanisms of action Human studies the control group (p<0.05). The researchers concluded that electroacupuncture can significantly decrease permeability of intestinal mucosa in patients with acute pancreatitis, and reduce accumulation of endogenous inflammatory mediators and vascular active substance in intestinal mucosa, so as to alleviate necrosis of intestinal epithelial cells and protect the barrier of gastro-intestinal mucosa. Wu Q et al. 1H NMR-based metabonomic study on the metabolic changes in the plasma of patients with functional dyspepsia and the effect of acupuncture. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2010; 51: A study that investigated the biological effects of function dyspepsia and the effect of acupuncture on metabolism. It used nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomic techniques to compare the plasma metabolic profiles of six patients with functional dyspepsia before and after acupuncture treatment and six healthy controls. The results found relatively higher levels of glucose, acetate, high-density lipoprotein, and phosphatidylcholine, and lower levels of lactate, leucine/isoleucine, N-acetyl glycoprotein, and low-density lipoprotein/very low-density lipoprotein in the patients compared with the controls. Acupuncture treatment significantly changed the levels of leucine/isoleucine, lactate and glucose, and slightly changed lipid levels towards those of the healthy controls. Zeng F et al. Brain areas involved in acupuncture treatment on functional dyspepsia patients: A PET-CT study. Neuroscience Letters 2009; 456: A study that aimed to investigate the influence of acupuncture stimulation on brain activities in eight patients with functional dyspepsia and eight health controls. Each control received a PET-CT scan at baseline, while each patient received scans at baseline and after acupuncture stimulation. Compared to the controls, the patients showed a lower glycometabolism in the right orbital gyrus, the left caudate tail and the cingulate gyrus, and a higher glycometabolism in the left inferior temporal gyrus (p<0.005). After acupuncture, the patients showed a decrease in glycometabolism in the postcentral gyrus and the cerebella, and an increase in the visual-related cortices (p<0.005). The results suggest that the anterior cingulate cortex, the prefrontal cortices and the caudate tail are involved in processing gastric perceptions in patients with functional dyspepsia, and that acupuncture stimulation contributes to deactivation of the primary somatosensory area and the cerebella, and activation of the visual-related cortex. Yao X-M et al. Effect of acupuncture on proximal gastric motility in patients with functional dyspepsia. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2006; 14: Xu S et al. Electroacupuncture A study that looked at the effect of acupuncture on the proximal gastric motility in 60 patients with functional dyspepsia induced by mechanical gastric distension. Half the patients were given acupuncture with electrical stimulation and half served as the controlled group. The initial volume and pressure, the maximal tolerable volume and pressure, and the compliance were significantly higher in the acupuncture group than the control group (p<0.05). A study that investigated the effects of electroacupuncture on November 2014 page 8
9 accelerates solid gastric emptying and improves dyspeptic symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia. Digestive Diseases & Sciences 2006; 51: solid gastric emptying and dyspeptic symptoms in 19 patients with functional dyspepsia. Ten patients showed delayed gastric emptying of solids, and acute electroacupuncture significantly improved delayed gastric emptying (p=0.007). In the nine patients with normal gastric emptying, electroacupuncture significantly decreased symptom score (p<0.001). Chang X et al. The affects of acupuncture at Sibai and Neiting acupoints on gastric peristalsis. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine 2001; 21: A study that found the frequency and amplitude of gastric peristaltic waves were significantly changed in 15 patients given acupuncture. Animal studies Sun JP et al. Effect of acupuncturing at the acupoint ST 36 on substance P and proopiomelanocortin expression in hypothalamus and adrenal in rats with cold-restraint stress-induced ulcer. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2008; 16: Shen GM et al. Role of vasoactive intestinal peptide and nitric oxide in the modulation of electroacupucture on gastric motility in stressed rats. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2006; 12: A study that assessed the protective effect of acupuncture against cold-restraint stress-induced ulcer, and the expression of substance P and proopiomelanocortin associated with stress in the hypothalamus and adrenals in rats. Twenty-two rats were randomised into 3 groups: the normal control group, the stress group, and the acupuncture. The ulcer index and serum cortisol levels in the acupuncture group were significantly lower than those in the stress group (p<0.01). The expression of substance P was up-regulated in the hypothalamus (p<0.05) but downregulated in adrenals (p<0.05) in the acupuncture group compared with the stress group. Acupuncture inhibited stressinduced proopiomelanocortin expression in the hypothalamus (p<0.01). An investigation into the effects and mechanisms of vasoactive intestinal peptide and nitric oxide in the modulation of electroacupuncture on gastric motility in restrained, cold-stressed rats. Gastric myoelectric activities were recorded by electrogastroenterography, and were initially found to be disordered and irregular. Following electroacupuncture, the frequency and amplitude of gastric motility were obviously lowered (p<0.01), while the levels of vasoactive intestinal peptide and nitric oxide in plasma, gastric mucosal and bulb tissues increased strikingly (p<0.01 and p<0.05, respectively) and expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide in antral smooth muscle was elevated significantly (p<0.01) in comparison with those of model group. Reviews of mechanisms for acupuncture in GI tract disorders Noguchi E. Mechanism of reflex regulation of the gastroduodenal function by acupuncture. Evidencebased Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2008; 5: Takahashi T. Acupuncture for A review of recent experimental work on the mechanism of acupuncture for reflex regulation of gastroduodenal function. It explains that acupuncture to the abdomen of anaesthetised rats has been found to excite sympathetic nerves via spinal reflexes, causing inhibition of gut motility. It also explains that acupuncture to the limbs of anaesthetised rats has been found to excite the vagus nerve via supraspinal reflexes, causing an increase in gut motility. As well as such reflexes the underlying mechanism of acupuncture in gastro-intestinal disorders may include the limbic system, the hypothalamus and the brain stem. A review discussing how acupuncture might work in the November 2014 page 9
10 functional gastrointestinal disorders. Journal of Gastroenterology 2006; 41: Zijlstra FJ et al. Anti-inflammatory actions of acupuncture. Mediators Inflamm 2003;12: treatment of functional gastrointestinal symptoms. It suggests that acupuncture may be effective because it has been shown to alter acid secretion, gastrointestinal motility, and visceral pain. Acupuncture on the lower limbs causes muscle contractions (i.e. stimulates motility) via the somatoparasympathetic pathway, which could be beneficial in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease, functional dyspepsia and constipation associated with irritable bowel syndrome, in whom peristalsis and gastric motility are impaired. Acupuncture on the upper abdomen causes muscle relaxation via the somatosympathetic pathway (i.e. inhibits motility), which could be beneficial in patients with diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome, in whom colonic motility is enhanced and colonic transit is accelerated. A review that suggests a hypothesis for the anti-inflammatory action of acupuncture. Insertion of acupuncture needle initially stimulates production of beta-endorphins, calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P, leading to further stimulation of cytokines and nitric oxide (NO). While high levels of CGRP have been shown to be pro-inflammatory, CGRP in low concentrations exerts potent anti-inflammatory actions. Therefore, a frequently applied 'low-dose' treatment of acupuncture could provoke a sustained release of CGRP with anti-inflammatory activity, without stimulation of pro-inflammatory cells. Terms and conditions The use of this fact sheet is for the use of British Acupuncture Council members and is subject to the strict conditions imposed by the British Acupuncture Council details of which can be found in the members area of its website November 2014 page 10
 ACUPUNCTURE AND OBESITY About obesity Around 60% of adults in England are either overweight or obese (DOH 2011), and 2% are morbidly obese (Body Mass Index (BMI) above 40kg/m2) (Information Centre 2008).
ACUPUNCTURE AND OBESITY About obesity Around 60% of adults in England are either overweight or obese (DOH 2011), and 2% are morbidly obese (Body Mass Index (BMI) above 40kg/m2) (Information Centre 2008).
Chen JC, Mannino DM. Worldwide epidemiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Curr Opin Pulm Med 1999; 5: 93 9.
 ACUPUNCTURE AND COPD About COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is thought to be the fourth most common cause of death worldwide, and the World Health Organisation anticipates that by 2020
ACUPUNCTURE AND COPD About COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is thought to be the fourth most common cause of death worldwide, and the World Health Organisation anticipates that by 2020
ACUPUNCTURE AND OSTEOARTHRITIS
 ACUPUNCTURE AND OSTEOARTHRITIS About osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis involves damage to articular cartilage and other structures in and around joints, with variable levels of inflammation.(hunter 2006) The
ACUPUNCTURE AND OSTEOARTHRITIS About osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis involves damage to articular cartilage and other structures in and around joints, with variable levels of inflammation.(hunter 2006) The
ACUPUNCTURE AND NECK PAIN
 ACUPUNCTURE AND NECK PAIN About neck pain Neck pain is one of the three most frequently reported complaints of the musculoskeletal system. Twenty-six to 71% of the adult population can recall experiencing
ACUPUNCTURE AND NECK PAIN About neck pain Neck pain is one of the three most frequently reported complaints of the musculoskeletal system. Twenty-six to 71% of the adult population can recall experiencing
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University
 CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
CHAPTER 11 Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (FGID) Mr. Ashok Kumar Dept of Pharmacy Practice SRM College of Pharmacy SRM University 1 Definition of FGID Chronic and recurrent symptoms of the gastrointestinal
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection
 Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
Management of dyspepsia and of Helicobacter pylori infection The University of Nottingham John Atherton Wolfson Digestive Diseases Centre University of Nottingham, UK Community management of dyspepsia
ACUPUNCTURE AND ENDOMETRIOSIS
 ACUPUNCTURE AND ENDOMETRIOSIS About endometriosis Endometriosis is a chronic condition characterised by growth of endometrial tissue in sites other than the uterus, most commonly in the pelvic cavity,
ACUPUNCTURE AND ENDOMETRIOSIS About endometriosis Endometriosis is a chronic condition characterised by growth of endometrial tissue in sites other than the uterus, most commonly in the pelvic cavity,
Disclosures. GI Motility Disorders. Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome
 Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
Gastrointestinal Motility Disorders & Irritable Bowel Syndrome None Disclosures Jasmine Zia, MD Acting Assistant Professor Division of Gastroenterology, University of Washington 6 th Asian Health Symposium
References Coronary heart disease. NHS Choices. Available:
 ACUPUNCTURE AND CORONARY HEART DISEASE About coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease (sometimes called ischaemic heart disease) occurs when cholesterol builds up in the coronary arteries and atherosclerotic
ACUPUNCTURE AND CORONARY HEART DISEASE About coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease (sometimes called ischaemic heart disease) occurs when cholesterol builds up in the coronary arteries and atherosclerotic
ACUPUNCTURE AND DYSMENORRHOEA
 ACUPUNCTURE AND DYSMENORRHOEA About dysmenorrhoea Dysmenorrhoea is painful cramps originating in the uterus just prior to or during menstruation. It can be primary (i.e. without any organic pathology)
ACUPUNCTURE AND DYSMENORRHOEA About dysmenorrhoea Dysmenorrhoea is painful cramps originating in the uterus just prior to or during menstruation. It can be primary (i.e. without any organic pathology)
Acupuncture Found Effective For IBS-D
 Acupuncture Found Effective For IBS-D Published by HealthCMI on 26 February 2018. Investigators find acupuncture effective for the treatment of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). In a controlled study, Yiwu
Acupuncture Found Effective For IBS-D Published by HealthCMI on 26 February 2018. Investigators find acupuncture effective for the treatment of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). In a controlled study, Yiwu
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
ACUPUNCTURE AND URINARY INCONTINENCE
 ACUPUNCTURE AND URINARY INCONTINENCE About urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence affects around 3.5 million people of all ages in the UK (DoH 2000; the Continence Foundation 2000). For many, urinary
ACUPUNCTURE AND URINARY INCONTINENCE About urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence affects around 3.5 million people of all ages in the UK (DoH 2000; the Continence Foundation 2000). For many, urinary
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
ACUPUNCTURE AND VERTIGO. About vertigo
 ACUPUNCTURE AND VERTIGO About vertigo People with vertigo have the illusion that the environment is moving about them, or that they are moving with respect to the environment.(dtb 2009) The condition usually
ACUPUNCTURE AND VERTIGO About vertigo People with vertigo have the illusion that the environment is moving about them, or that they are moving with respect to the environment.(dtb 2009) The condition usually
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
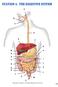
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
ACUPUNCTURE AND MALE INFERTILITY
 ACUPUNCTURE AND MALE INFERTILITY About male infertility The clinical definition of male infertility is the presence of abnormal semen parameters in the male partner of a couple who have been unable to
ACUPUNCTURE AND MALE INFERTILITY About male infertility The clinical definition of male infertility is the presence of abnormal semen parameters in the male partner of a couple who have been unable to
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders. TERRAGASTRO - Good health starts in the gut
 Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Clinically proven to quickly relieve symptoms of common gastrointestinal disorders GASTROINTESTINAL DISEASE Referred to as gastrointestinal diseases, they are common disorders which affect the esophagus,
Helicobacter Pylori Testing HELICOBACTER PYLORI TESTING HS-131. Policy Number: HS-131. Original Effective Date: 9/17/2009
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Inc. Ohana Health Plan, a plan offered by WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc. WellCare Health Insurance of Illinois,
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS...
 ... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
... SELECTED ABSTRACTS... The following abstracts, from medical journals containing literature on irritable bowel syndrome, were selected for their relevance to this supplement. A Technical Review for
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus
 Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Peptic ulcer disease Disorders of the esophagus Peptic ulcer disease Burning epigastric pain Exacerbated by fasting Improved with meals Ulcer: disruption of mucosal integrity >5 mm in size, with depth
Functional Dyspepsia. Norbert Welkovics Heine van der Walt
 Norbert Welkovics Heine van der Walt Characteristics: Central abdomen Pain or discomfort Not associated with bowel movements No structural or biochemical abnormalty Definition Part of Gastroduodenal disorders
Norbert Welkovics Heine van der Walt Characteristics: Central abdomen Pain or discomfort Not associated with bowel movements No structural or biochemical abnormalty Definition Part of Gastroduodenal disorders
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540
 Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
Electrical stimulation of the lower oesophageal sphincter for treating gastro-oesophageal reflux disease Interventional procedures guidance Published: 16 December 2015 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg540 Your
The usual dose is 40 mg daily with amoxycillin 1.5 g (750 mg b.d.) for 2 weeks. Up to 2 g/day of amoxycillin has been used in clinical trials.
 Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Name Gasec - 2 Gastrocaps Composition Gasec-20 Gastrocaps Each Gastrocaps contains: Omeprazole 20 mg (in the form of enteric-coated pellets) Properties, effects Proton Pump Inhibitor Omeprazole belongs
Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
Key concepts in Digestion. Our gut reactions to food or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl Swallowing
ACUPUNCTURE AND MALE INFERTILITY
 ACUPUNCTURE AND MALE INFERTILITY About male infertility The clinical definition of male infertility is the presence of abnormal semen parameters in the male partner of a couple who have been unable to
ACUPUNCTURE AND MALE INFERTILITY About male infertility The clinical definition of male infertility is the presence of abnormal semen parameters in the male partner of a couple who have been unable to
Motility Conference Ghrelin
 Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
6/25/ % 20% 50% 19% Functional Dyspepsia Peptic Ulcer GERD Cancer Other
 Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
Peptic Ulcer Disease and Dyspepsia John M. Inadomi, MD Professor of Medicine UCSF Chief, Clinical Gastroenterology San Francisco General Hospital Case History 49 y/o woman complains of several months of
ACUPUNCTURE AND THE PUERPERIUM
 ACUPUNCTURE AND THE PUERPERIUM About puerperium The puerperium covers the 6-week period following birth, during which time the various physiological changes that occurred during pregnancy revert to the
ACUPUNCTURE AND THE PUERPERIUM About puerperium The puerperium covers the 6-week period following birth, during which time the various physiological changes that occurred during pregnancy revert to the
June By: Reza Gholami
 ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
ACG/CAG guideline on Management of Dyspepsia June 2017 By: Reza Gholami DEFINITION OF DYSPEPSIA AND SCOPE OF THE GUIDELINE Dyspepsia was originally defined as any symptoms referable to the upper gastrointestinal
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS
 INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
INVESTIGATIONS OF GASTROINTESTINAL DISEAS Lecture 1 and 2 دز اسماعيل داود فرع الطب كلية طب الموصل Radiological tests of structure (imaging) Plain X-ray: May shows soft tissue outlines like liver, spleen,
ACUPUNCTURE AND INSOMNIA
 ACUPUNCTURE AND INSOMNIA About Insomnia According to a survey by the Office of National Statistics (ONS 2000), around 29% of adults reported experiencing sleep problems the week before interview. Such
ACUPUNCTURE AND INSOMNIA About Insomnia According to a survey by the Office of National Statistics (ONS 2000), around 29% of adults reported experiencing sleep problems the week before interview. Such
ACUPUNCTURE AND FEMALE INFERTILITY
 ACUPUNCTURE AND FEMALE INFERTILITY About infertility Infertility is the inability of a couple to get pregnant despite having regular unprotected sex. A couple is regarded as infertile if, after regular
ACUPUNCTURE AND FEMALE INFERTILITY About infertility Infertility is the inability of a couple to get pregnant despite having regular unprotected sex. A couple is regarded as infertile if, after regular
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS
 1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
Gastrointestinal Disorders. Disorders of the Esophagus 3/7/2013. Congenital Abnormalities. Achalasia. Not an easy repair. Types
 Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
Gastrointestinal Disorders Congenital Abnormalities Disorders of the Esophagus Types Stenosis Atresia Fistula Newborn aspirates while feeding. Pneumonia Not an easy repair Achalasia Lack of relaxation
MCDERMOTT WELLNESS CENTER NEURO ACUPUNCTURE
 Urinary Incontinence Incontinence is sometimes called a silent epidemic because people struggling with the condition often do not talk about it to others or their physicians. Researchers estimate that
Urinary Incontinence Incontinence is sometimes called a silent epidemic because people struggling with the condition often do not talk about it to others or their physicians. Researchers estimate that
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA o Patients of any age with ALARM signs should be referred through the 2-week referral system o Routine endoscopic investigation
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA o Patients of any age with ALARM signs should be referred through the 2-week referral system o Routine endoscopic investigation
National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Gastritis National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH What is gastritis? Gastritis is a condition in which the stomach
Functional Dyspepsia
 Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Functional Dyspepsia American College of Gastroenterology Boston Massachusetts, June 2015 Brian E. Lacy, PhD, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth Chief, Section of Gastroenterology
Barrett s Oesophagus Information Leaflet THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM. gutscharity.org.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM http://healthfavo.com/digestive-system-for-kids.html This factsheet is about Barrett s Oesophagus Barrett s Oesophagus is the term used for a pre-cancerous condition where the normal
Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia: what is it? What can we do with these patients? Overview. Dyspepsia Definition. Functional Dyspepsia. Dyspepsia the Basics
 Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Non-Ulcer : what is it? What can we do with these patients? Temporal Changes and Geographic Variations in Developing Peptic Ulcer Disease Gastric Cancer 1900 Eamonn M M Quigley MD FACG Alimentary Pharmabiotic
Indigestion (dyspepsia)
 Commissioning pathways Indigestion (dyspepsia) Supplementary information to be read in conjunction with the pathway Reference Supplementary Information 1.1 Symptom Description Annual incidence 40%. Prevalence
Commissioning pathways Indigestion (dyspepsia) Supplementary information to be read in conjunction with the pathway Reference Supplementary Information 1.1 Symptom Description Annual incidence 40%. Prevalence
Fecal incontinence causes 196 epidemiology 8 treatment 196
 Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Subject Index Achalasia course 93 differential diagnosis 93 esophageal dysphagia 92 95 etiology 92, 93 treatment 93 95 work-up 93 Aminosalicylates, pharmacokinetics and aging effects 36 Antibiotics diarrhea
Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD. Gastroenterology/ Acute Adult Governance. Drugs and Therapeutics Committee
 Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD Document type: Version: 3.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Prescribing Dr. G. Lipscomb Date validated October 2015 Ratified by: Date
Guidelines for the Management of Dyspepsia and GORD Document type: Version: 3.0 Author (name): Author (designation): Validated by Prescribing Dr. G. Lipscomb Date validated October 2015 Ratified by: Date
STRESS AND THE HEALTH OF THE BODY
 Slide 1 STRESS AND THE HEALTH OF THE BODY Slide 2 What is Stress It is a physical response that occurs in our body when we are stressed Physiologically, it is a series of actions in the body that are regulated
Slide 1 STRESS AND THE HEALTH OF THE BODY Slide 2 What is Stress It is a physical response that occurs in our body when we are stressed Physiologically, it is a series of actions in the body that are regulated
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts
 Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Physiological processes in the GI tract:
 Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE)
 Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
Eosinophilic Esophagitis (EoE) 01.06.2016 EoE: immune-mediated disorder food or environmental antigens => Th2 inflammatory response. Key cytokines: IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 stimulate the production of eotaxin-3
190 Index Case studies, abdominal pain, 2 Crohn s disease, 2 3, cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS), 2 fecal incontinence (FI), 2 medical c
 Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
Index Abdominal pain, case study, 2 Achalasia, 75 Acupuncture 108 American Academy of Pediatrics, 49 Anxiety, 8 9, 98 Autism, GI disorders and, 25 27 BASC. See Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD)
 DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA AND GASTRO-OESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE (GORD) Routine endoscopic investigation of patients of any age, presenting with dyspepsia
Subject Index. ATP, see Mucosal energy metabolism Autophagy gastric adenocarcinoma 208, 209 gastric carcinoid
 Subject Index Acetic acid ulcer model gastric cancer removal 38, 39 healing studies 33 36 overview 32, 33 treatment studies 36 38 Achillea millefolium, acetic acid ulcer Adrenergic receptors, gastroprotection
Subject Index Acetic acid ulcer model gastric cancer removal 38, 39 healing studies 33 36 overview 32, 33 treatment studies 36 38 Achillea millefolium, acetic acid ulcer Adrenergic receptors, gastroprotection
5. Which component of the duodenal contents entering the stomach causes the most severe changes to gastric mucosa:
 Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Gastro-intestinal disorders 1. Which are the most common causes of chronic gastritis? 1. Toxic substances 2. Chronic stress 3. Alimentary factors 4. Endogenous noxious stimuli 5. Genetic factors 2. Chronic
Number of studies. Endoscopic finding. Number of subjects. Pooled prevalence 95% CI
 Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
Clinical Approach to the Patient t with Dyspepsia William D. Chey, MD, FACG Professor of Medicine University of Michigan Prevalence of Endoscopic Findings in Individuals with Dyspepsia Systematic Review
PRESCRIBING SUPPORT TEAM AUDIT: PROTON PUMP INHIBITOR PRESCRIBING REVIEW
 PRESCRIBING SUPPORT TEAM AUDIT: PROTON PUMP INHIBITOR PRESCRIBING REVIEW DATE OF AUTHORISATION: AUTHORISING GP: PRESCRIBING SUPPORT TECHNICIAN: SUMMARY Dyspepsia refers to a broad range of symptoms related
PRESCRIBING SUPPORT TEAM AUDIT: PROTON PUMP INHIBITOR PRESCRIBING REVIEW DATE OF AUTHORISATION: AUTHORISING GP: PRESCRIBING SUPPORT TECHNICIAN: SUMMARY Dyspepsia refers to a broad range of symptoms related
Second term/
 Second term/ 2015-2016 L. 1 Dr Mohammed AL-Zobaidy Learning objectives GIT pharmacology After completing this chapter the student will be able to: Recognise pathophysiological factors implicated in acid-peptic
Second term/ 2015-2016 L. 1 Dr Mohammed AL-Zobaidy Learning objectives GIT pharmacology After completing this chapter the student will be able to: Recognise pathophysiological factors implicated in acid-peptic
Overview of digestion
 Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
Key concepts in Digestion. Overview of digestion introduction to the GI system Prof. Barry Campbell Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl DIGESTION
Can erythropoietin treatment during antiviral drug treatment for hepatitis C be cost effective?
 Below Are Selected Good Abstracts from Digestive Disease Week 2006 Meeting Published in Gut. 2006 April; 55(Suppl 2): A1 A119. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc1859999/?tool=pmcentrez Can erythropoietin
Below Are Selected Good Abstracts from Digestive Disease Week 2006 Meeting Published in Gut. 2006 April; 55(Suppl 2): A1 A119. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc1859999/?tool=pmcentrez Can erythropoietin
Setting The setting was secondary care. The economic study was carried out in Hong Kong, China.
 Cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori "test and treat" for patients with typical reflux symptoms in a population with a high prevalence of H. pylori infection: a Markov model analysis You J H, Wong
Cost-effectiveness of Helicobacter pylori "test and treat" for patients with typical reflux symptoms in a population with a high prevalence of H. pylori infection: a Markov model analysis You J H, Wong
QUICK QUERIES. Topical Questions, Sound Answers
 QUICK QUERIES Topical Questions, Sound Answers Dyspepsia: An Evidence-Based Approach Alan B. R. Thomson, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG Presented at the University of Alberta s Medical Grand Rounds, University
QUICK QUERIES Topical Questions, Sound Answers Dyspepsia: An Evidence-Based Approach Alan B. R. Thomson, MD, PhD, FRCPC, FACP, FACG Presented at the University of Alberta s Medical Grand Rounds, University
F A M N O P R S ! D !
 A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
A B C D E F A M N O P Q G H I J R S T U V 595 W http://www.encognitive.com/images/digestive-system-2.jpg K L M A N B C O P D E F G D Q R H S I J K http://apbrwww5.apsu.edu/thompsonj/anatomy%20&%20physiology/2020/2020%20exam%20reviews/exam%203/colon%20diagram.jpgd
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
Paraoesophageal Hernia
 Paraoesophageal Hernia Grand Round Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar Paraoesophageal Hernia Type of hiatal hernia Transdiaphragmatic migration of abdominal content gastric fundus gastric body pylorus colon
Paraoesophageal Hernia Grand Round Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar Paraoesophageal Hernia Type of hiatal hernia Transdiaphragmatic migration of abdominal content gastric fundus gastric body pylorus colon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis. Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada
 Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Update on the pathological classification of gastritis Hala El-Zimaity, M.D. M.S. Epidemiology McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario Canada CLASSIFICATION GASTRITIS GASTROPATHY 1. Acute 2. Chronic 3. Uncommon
Chronic Fatigue Recovery With Acupuncture
 Chronic Fatigue Recovery With Acupuncture Published by HealthCMi on August 2017 Shenzhen Hospital of Chinese Medicine researchers determined that acupuncture is safe and effective for the alleviation of
Chronic Fatigue Recovery With Acupuncture Published by HealthCMi on August 2017 Shenzhen Hospital of Chinese Medicine researchers determined that acupuncture is safe and effective for the alleviation of
About arrhythmias and heart failure
 ACUPUNCTURE AND ARRHYTHMIAS AND HEART FAILURE About arrhythmias and heart failure A cardiac arrhythmia is a problem with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat: the heart can beat too fast (tachycardia),
ACUPUNCTURE AND ARRHYTHMIAS AND HEART FAILURE About arrhythmias and heart failure A cardiac arrhythmia is a problem with the rate or rhythm of the heartbeat: the heart can beat too fast (tachycardia),
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/48400
Esophageal Disorders. Learning Objectives. Introduction. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T.
 Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
Esophageal Disorders Reza Shaker, MD, and Benson T. Massey, MD, FACP Learning Objectives AFTER COMPLETING THIS CHAPTER, THE LEARNER SHOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Recognize the typical and atypical presentations
KEYWORDS Dyspepsia, Acid Peptic Disease, Helicobacter Pylori, Urease, Giemsa, Peptic Ulcer, Non-Ulcer Dyspepsia.
 INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
INCIDENCE OF HELICOBACTER PYLORI WITH ACID PEPTIC DISEASE AND MALIGNANT CONDITIONS OF UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT IN A TERTIARY CENTRE - A PROSPECTIVE STUDY Karunamoorthy Rajachidambaram 1, Dinkaran Kaarthesan
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
 Gastroenter oenterology 2005 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Screening and surveillance for upper and lower gastrointestinal cancer JN Plevris Consultant Gastroenterologist and Honorary Senior
Gastroenter oenterology 2005 Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh Screening and surveillance for upper and lower gastrointestinal cancer JN Plevris Consultant Gastroenterologist and Honorary Senior
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS
 Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
Original Article Efficiency of gastroscopy in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract diseases: a retrospective of 442 pediatric patients
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):12140-12144 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0020969 Original Article Efficiency of gastroscopy in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract diseases: a retrospective of 442
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):12140-12144 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0020969 Original Article Efficiency of gastroscopy in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract diseases: a retrospective of 442
Western Health Specialist Clinics Access & Referral Guidelines
 Gastroenterology Specialist Clinics at Western Health: Western Health provides the following Specialist Clinics for patients who require assessment and management of Gastroenterology / Hepatology conditions.
Gastroenterology Specialist Clinics at Western Health: Western Health provides the following Specialist Clinics for patients who require assessment and management of Gastroenterology / Hepatology conditions.
Helicobacter 2008;13:1-6. Am J Gastroent 2007;102: Am J of Med 2004;117:31-35.
 An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
An Update on Helicobacter pylori and Its Treatment Trenika Mitchell, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Assistant Professor University of Kentucky College of Pharmacy October 18, 2008 Objectives Review the epidemiology
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
GASTROENTEROLOGY Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examination Blueprint ABIM invites diplomates to help develop the Gastroenterology MOC exam blueprint Based on feedback from physicians that MOC assessments
Article: Min, T and Ford, AC (2016) Efficacy of mesalazine in IBS. Gut, 65 (1). pp ISSN
 This is a repository copy of Efficacy of mesalazine in IBS. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/97338/ Version: Accepted Version Article: Min, T and Ford, AC (2016)
This is a repository copy of Efficacy of mesalazine in IBS. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/97338/ Version: Accepted Version Article: Min, T and Ford, AC (2016)
ACUPUNCTURE AND OBSTETRICS
 ACUPUNCTURE AND OBSTETRICS About Obstetrics Pregnancy is a physiological state, but even when a woman has an uncomplicated pregnancy she may suffer with back and pelvic pain, nausea, indigestion or emotional
ACUPUNCTURE AND OBSTETRICS About Obstetrics Pregnancy is a physiological state, but even when a woman has an uncomplicated pregnancy she may suffer with back and pelvic pain, nausea, indigestion or emotional
Setting The setting was primary care. The economic study was conducted in Canada.
 Treating Helicobacter pylori infection in primary care patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia: the Canadian adult dyspepsia empiric treatment - Helicobacter pylori positive (CADET-Hp) randomised controlled
Treating Helicobacter pylori infection in primary care patients with uninvestigated dyspepsia: the Canadian adult dyspepsia empiric treatment - Helicobacter pylori positive (CADET-Hp) randomised controlled
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Helicobacter and gastritis
 1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
1 Helicobacter and gastritis Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Helicobacter pylori is a spiral-shaped gram-negative rod. H. pylori is associated with antral gastritis, duodenal (peptic) ulcer disease, gastric ulcers,
HOW TO NATURALLY TREAT INDIGESTION YOGI CAMERON
 HOW TO NATURALLY TREAT INDIGESTION YOGI CAMERON Indigestion is a condition that is often a symptom of another, underlying condition and is associated with various forms of discomfort in the stomach including
HOW TO NATURALLY TREAT INDIGESTION YOGI CAMERON Indigestion is a condition that is often a symptom of another, underlying condition and is associated with various forms of discomfort in the stomach including
Acupuncture Found Effective for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
 Acupuncture Found Effective for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Published by HealthCMi on 07 June 2018 Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Researchers at the Beijing
Acupuncture Found Effective for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Published by HealthCMi on 07 June 2018 Acupuncture is effective for the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). Researchers at the Beijing
Diarrhea may be: Acute (short-term, usually lasting several days), which is usually related to bacterial or viral infections.
 Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
Pediatric Gastroenterology Conditions Evaluated and Treated Having a child suffer with abdominal pain, chronic eating problems, or other gastrointestinal disorders can be a very trying time for a parent.
GI update. Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about
 GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
GI update Common conditions and concerns my patients frequently asked about Specific conditions I ll try to cover today 1. Colon polyps, colorectal cancer and colonoscopy 2. Crohn s disease 3. Peptic ulcer
The Clinical Efficacy, Evaluation and Central Mechanism Study on Acupuncture for Treating Functional Dyspepsia
 Section 2 08 Physical Methods The Clinical Efficacy, Evaluation and Central Mechanism Study on Acupuncture for Treating Functional Dyspepsia China Fanrong Liang, Ying Li, Fang Zeng, Tingting Ma, Lei Lan,
Section 2 08 Physical Methods The Clinical Efficacy, Evaluation and Central Mechanism Study on Acupuncture for Treating Functional Dyspepsia China Fanrong Liang, Ying Li, Fang Zeng, Tingting Ma, Lei Lan,
SUMMARY REPORT OF ACUPUNCTURE SESSION
 SUMMARY REPORT OF ACUPUNCTURE SESSION 1 Presenter: Jaung-Geng Lin 2 Introduction to acupuncture session In this session, we had 26 posters and 12 posters were selected for presentation and discussion.
SUMMARY REPORT OF ACUPUNCTURE SESSION 1 Presenter: Jaung-Geng Lin 2 Introduction to acupuncture session In this session, we had 26 posters and 12 posters were selected for presentation and discussion.
UNDERSTANDING CROHN S DISEASE
 UNDERSTANDING CROHN S DISEASE START YOUR JOURNEY TOWARD UNDERSTANDING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 4 WHAT IS CROHN S DISEASE? 6 Symptoms of Crohn s disease 6 WHAT CAUSES CROHN S DISEASE?
UNDERSTANDING CROHN S DISEASE START YOUR JOURNEY TOWARD UNDERSTANDING INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 4 WHAT IS CROHN S DISEASE? 6 Symptoms of Crohn s disease 6 WHAT CAUSES CROHN S DISEASE?
Oesophageal Disorders
 Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Oesophageal Disorders Anatomy Upper sphincter Oesophageal body Diaphragm Lower sphincter Gastric Cardia Symptoms Of Oesophageal Disorders Dysphagia Odynophagia Heartburn Atypical Chest Pain Regurgitation
Outline. Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology Management With an emphasis on recent developments
 Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
Chronic Dyspepsia Eamonn M M Quigley MD FRCP FACP MACG FRCPI Lynda K and David M Underwood Center for Digestive Disorders Houston Methodist Hospital Houston, Texas Outline Definition (s) Epidemiology Pathophysiology
GI Pharmacology. Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018
 GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
GI Pharmacology Dr. Alia Shatanawi 5/4/2018 Drugs Used in Gastrointestinal Diseases Drugs used in Peptic Ulcer Diseases. Drugs Stimulating Gastrointestinal Motility &Laxatives. Antidiarrheal Agents. Drugs
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA
 GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA MANAGEMENT Dyspepsia refers to a spectrum of usually intermittent upper gastrointestinal symptoms, including epigastric pain and heartburn. For the majority
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM MANAGEMENT OF DYSPEPSIA MANAGEMENT Dyspepsia refers to a spectrum of usually intermittent upper gastrointestinal symptoms, including epigastric pain and heartburn. For the majority
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus. Barbora Konečná
 Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
Gastric ulcer Duodenal ulcer Pancreatitis Ileus Barbora Konečná basa.konecna@gmail.com Peptic ulcers of stomach and duodenum (PUD) Ulcers are chronic, often solitary lesions, that occur in any part of
Complementary & Alternative Therapies in IBD
 Complementary & Alternative Therapies in IBD Laurie Rosales, APRN-CNP OSU Wexner Medical Center Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Complementary & Alternative Probiotics Cannabis Fish
Complementary & Alternative Therapies in IBD Laurie Rosales, APRN-CNP OSU Wexner Medical Center Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Complementary & Alternative Probiotics Cannabis Fish
fever a persistent unexplained change in bowel habit in somebody over 50 years of age a family history of bowel or ovarian cancer.
 If you have had these symptoms for some time, if they come and go but never completely go away, then go and see your doctor. In practice, IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion. There is no test or marker that
If you have had these symptoms for some time, if they come and go but never completely go away, then go and see your doctor. In practice, IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion. There is no test or marker that
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease
 Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Management of Dyspepsia
 MPharm Programme Management of Dyspepsia Slide 1 of 28 Learning Objectives Understand the principles and wider implications underpinning evidence based therapeutics in the key clinical specialities Objectively
MPharm Programme Management of Dyspepsia Slide 1 of 28 Learning Objectives Understand the principles and wider implications underpinning evidence based therapeutics in the key clinical specialities Objectively
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 15: The Autonomic Nervous System Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements is correct about the component of the autonomic nervous system identified
