To evaluate the role of high resolution ultrasonography in diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis
|
|
|
- Kory Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2018; 4(1): ISSN: IJOS 2018; 4(1): IJOS Received: Accepted: Ravikant Jain HOD and Prof, Dept of orthopaedics, SAMC & PGI, Indore, Madhya Pradesh, India Aamir Johar Junior Resident, Dept of orthopaedics, SAMC & PGI, Indore, Madhya Pradesh, India To evaluate the role of high resolution ultrasonography in diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis Ravikant Jain and Aamir Johar DOI: Abstract Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive and disabling joint disease. It is one of the most frequently occurring health problems for middle-aged and older people. [1, 2] OA can occur in every synovial joint, but is most common in hip, knee, hand, foot and spine. [3] It is characterized by joint pain and limited function of the joint. In a synovial joint several structures can cause these clinical symptoms. The Kellgren and Lawrence (K&L) classification criteria are the most widely used radiographic classification criteria to identify and grade OA. Objectives: To evaluate the role of High Resolution Ultrasonography in knee osteoarthritis. Material and Methods: Fifty patients attending the outpatient orthopaedics department of our institute with unilateral or bilateral knee pain were included. 32 patients had bilateral symptomatic knee OA and 18 patients had unilateral symptomatic OA. All knees were subjected to radiographic examination and HRUS assessment. Conclusion: HRUS plays a significant role in early diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis, as well as its progression and therapy monitoring. It is desirable as a quick and easy method of screening for articular cartilage abnormalities and extra-articular abnormalities. Its cost effectiveness, dynamic scanning capabilities and therapeutic guidance providing abilities make it valuable in all settings. Keywords: Osteoarthritis, HRUS, K&L Classification Correspondence Ravikant Jain HOD and Prof, Dept of orthopaedics, SAMC & PGI, Indore, Madhya Pradesh, India Introduction Osteoarthritis (OA) is a progressive and disabling joint disease. It is one of the most frequently occurring health problems for middle-aged and older people. [1,2] OA can occur in every synovial joint, but is most common in hip, knee, hand, foot and spine. [3] It is characterized by joint pain and limited function of the joint. In a synovial joint several structures can cause these clinical symptoms. Bone, cartilage, synovial fluid, ligaments and also the muscles around the joint are tissues that change with OA and affect the function of the joint. [4] Several tissues might be a starting point for pathways that lead to OA. Cartilage might be a tissue in which the patho-physiological process of OA starts, but biochemical and imaging studies have shown that synovium and bone can also be starting points. A diagnosis of OA is mainly based on symptoms. Recommendations for the diagnosis of knee OA were published in [5] They include three main symptoms: knee pain, short-lived morning stiffness, and functional limitation in combination with three signs on physical examination (crepitus, restricted movement and bony enlargement). In all joints, the prevalence of OA increases with age. In addition, the elderly population continues to increase, resulting in an even higher clinical and economic burden of OA. [6] Worldwide estimates are that 9.6% of men and 18.0% of women aged 60 years and over have symptomatic OA. For radiological knee OA these estimates are somewhat higher, even at a younger age (45 years and over): 14.1% for men and 22.8% for women. [2] When a patient presents in healthcare with symptoms of OA, it is likely that there is already pathological damage in the knee, perhaps for a long period. Symptomatic treatment (e.g. exercise and mechanical interventions, like insoles) might be more effective at an earlier clinical stage; the same probably applies to disease-modifying treatment. In a pre-clinical stage with early pathological damage of the knee joint, such disease-modifying treatment might be even more promising. ~ 69 ~
2 Radiographs have for long been the most frequently used and the standard images for visualizing OA. But as mentioned above there is lack of agreement between clinical and radiographic knee OA. And also it is not useful in predicting preclinical OA. MRI has the advantage of direct assessment of the cartilage, which is still thought to be an important tissue in OA, as well as the advantage of visualizing all the other important tissues of the joint. MRI has another important potential advantage compared to radiographs: it can show structural damage or lesions earlier than can be seen clinically or on radiographs. Therefore, identifying OA features at a pre-clinical stage with MRI makes it to be a test of choice. But it is not cost effective. Knee high resolution ultrsonography (HRUS) is desirable as a quick and easy method of screening for articular cartilage abnormalities and extra-articular abnormalities. Its cost effectiveness, dynamic scanning capabilities and therapeutic guidance providing abilities make it useful in our settings. In addition, for some patients sonography may be the test of choice, because of the presence of a pacemaker or other absolute or relative contraindication to MRI. By this study we want to evaluate role of HRUS in knee osteoarthritis as a early diagnostic tool. Aims & objectives To evaluate the role of High Resolution Ultrasonography in knee osteoarthritis. Materials & methods The present study, To Evaluate the Role of High Resolution Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis was carried out in the Department of Orthopaedics, Sri Aurobindo Medical College & P.G. Institute, Indore from 1 st January, 2016 to 30 th September, 2017 after approval from institutional research and ethical committee with main objective to evaluate the role of High Resolution Ultrasonography (HRUS) in knee osteoarthritis. Study population will comprise of patients above 40 years of age. The exclusion criteria include all patients with history of recent trauma, mechanical knee derangement, fibromyalgia, inflammatory arthritis, microcrystalline arthropathy, recent surgery and known cases of malignancies around knee. Fifty patients attending the outpatient orthopaedics department of our institute with unilateral or bilateral knee pain were included. No patient has received arthrocentesis and/or intraarticular steroid injection during the last 3 months. 32 patients had bilateral symptomatic knee OA and 18 patients had unilateral symptomatic OA. Thus total of 82 symptomatic knees and 18 asymptomatic knees constituted part of our study. All symptomatic and asymptomatic knees were subjected to radiographic examination and HRUS assessment. Weight-bearing anteroposterior (AP) and lateral knee radiographs were read by radiologist blinded to the clinical and US findings who assessed the severity of OA on the AP view using the Kellgren and Lawrence (K-L) scale (scores 0-4) and for the presence of patello-femoral (PF) degenerative signs. A written informed consent was obtained from all patients prior to the clinical, US and radiographic evaluation. An HRUS examination of both the knees was performed on Philips iu22 machine using a high frequency linear probe of 5-12 MHz.US examination was performed according to standardized scanning method Findings were recorded on a proforma for the study and statistical was analysis done. Articular cartilage of the femur is clearly depicted by sonography. The synovial membrane is carefully studied by sonography. In fact, it is possible to measure its thickness and show the presence of villi and septa. In this way the episodic synovitis that may appear in OA is easily detected and useful information is obtained for disease and therapy monitoring. In a normal knee its thickness is between 2 and 3 mm. In an osteoarthritic joint the synovial membrane is usually thickened when synovitis is present Synovial fluid is very well evaluated, sonography may detect the quantity of this fluid, revealing the presence of joint effusion with very high sensitivity. [7] The physiological amount of synovial fluid in a normal knee is between 3 and 3.5 ml. Hydrarthrosis is demonstrated by the evidence of anechoic or hypoechoic collection within the joint cavity. It is possible to evaluate the regularity of the bone surfaces of the femur and the tibia. Osteophytes are easily detected, their presence being demonstrated by the finding of irregularity at the joint margins. Another frequent alteration in OA is capsular fibrosis. [8] Sonography shows the thickening of the capsule. Evaluation of the calf may show the presence of Baker s cysts. They are frequently found in OA, especially when effusion is present and the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa communicates with the joint cavity. Classification Criteria: The Kellgren and Lawrence (K&L) classification criteria are the most widely used radiographic classification criteria to identify and grade OA Review of literature Keen et al. (2009) did a study to undertake a systematic review of the published literature evaluating ultrasonography as an assessment tool in osteoarthritis. Results: Forty-seven studies were identified that utilized ultrasonography to assess structural pathology in osteoarthritis. Doppler function was only assessed in 10 studies and contrast agents in one. There was heterogeneity with regard to the pathology examined, the definition of pathology, quantification and the reporting of these factors. There was also a lack of construct and criterion validity and data demonstrating reliability and sensitivity to change. Whereas there is increasing evidence of the validity of ultrasonography in detecting structural pathology in inflammatory arthritis, more work is required to develop standardized definitions of pathology and to demonstrate the validity of ultrasonography in osteoarthritis. [9] Study was conducted by Abraham et al. (2011) to measure the inter-rater reliability and validity of ultrasound imaging in the detection of features of knee OA and found that Reliability for osteophyte presence was 0.77(right femur), 0.65(left femur) and 0.88 for both tibia. ICCs for effusion size were 0.70(right) and 0.85(left). Moderate to substantial agreement was found in cartilage thickness measurements. And Validity for osteophytes, was moderate to excellent at 0.52(right) and 0.75(left). Concluded that excellent agreement was found between ultrasound observers for the presence of osteophytes and measurement of effusion size; it was moderate to substantial for femoral cartilage thickness. Moderate to substantial agreement was observed between ultrasound and radiographs for osteophyte presence. [10] Kazam et al. (2011) did a sonographic evaluation of femoral trochlear cartilage in patients with knee pain. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether routine clinical sonographic evaluation of femoral trochlear cartilage can ~ 70 ~
3 identify abnormalities in patients with knee pain. Using repeated measures analysis of variance, there were significant differences (P=.02) for both decreased cartilage clarity (df=1/28; F=5.76) and increased grade (df=1/28; F=5.77) in patients. There was also a non-significant (P>.05) trend toward more frequent calcifications, osteophytes, and bony irregularity in patients. Routine clinical sonography can identify femoral trochlear cartilage abnormalities in patients with knee pain and therefore can be a useful adjunct to other imaging tests for identifying arthritic changes in the knee. [11] Hammer et al. (2016) did a study to assess whether ultrasonography (US) is reliable for the evaluation of inflammatory and structural abnormalities in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). Intra- and interobserver reliability scores were moderate to good for synovitis (mean κ 0.67 and 0.52, respectively) as well as moderate to good for the global synovitis (0.70 and 0.50, respectively). Mean intra- and interobserver reliability κ for cartilage damage, medial meniscal damage and osteophytes ranged from fair to good (0.55 and 0.34, 0.75 and 0.56, 0.73 and 0.60, respectively).using a standardized protocol, dichotomous and semi quantitative US scoring of pathological changes in knee OA can be reliable. [12] Observations and Results There were 6 (12%) in the age group years, 24 (48%) were in the age group years, 13 (26%) were in the age group years and 7 (14%) were in the age group years. There were 35 (70%) females and 15 (30%) males in the study. There was a female preponderance in the study. Table 1: Distribution of patients according to BMI grading (N=50) S. No. BMI Grading No. % 1. Underweight (< 18.5 kg/m 2 ) Normal ( kg/m 2 ) Overweight (> kg/m 2 ) Obese (> kg/m 2 ) Total The above table shows the distribution of patients according to BMI grading. There were 4 (8%) patients who were underweight, 6 (12%) patients who were normal, 33 (66%) patients were overweight and 7 (14%) patients were obese. Majority of the patients were overweight. Table 2: Distribution of patients according to laterality (N=50) S. No. Laterality of involvement No. % 1. Unilateral Bilateral Total The above table shows the distribution of patients according to laterality. 18 (36%) of the patients had shown unilateral involvement and 32 (64%) of the patients had shown bilateral involvement. Table 3: Distribution of patients according to presenting symptoms (N=50) S. No. Presenting Symptoms No. % 1. Pain on walking Pain on stair climbing Pain on lying Pain on sitting Pain on standing The above table shows the distribution of patients according to presenting symptoms. The most common presenting symptom was pain on walking 40 (80%), followed by pain on lying in 35 (70%) of the patients, 20 (40%) patients had pain on stair climbing, 6 (12%) patients had pain on sitting and 4 (8%) of the patients had pain on standing. (N=100) S. No. Table 8, Fig 24: X-ray Findings in Patients Symptomatic (n=82) Asymptomatic (n=18) X-ray Findings No. % No. % 1. Joint space reduction Osteophytes formation Subarticular sclerosis Geode formation Loose bodies Deformity of both ends Normal The above table shows the distribution of knees according to X-ray findings. There were 82 symptomatic and 18 asymptomatic knees of the 50 patients. In symptomatic knees, 28 (34.1%) knees had joint space reduction, 20 (24.4%) knees had osteophytes formation, 14 (17.1%) knees had subarticular sclerosis, 6 (7.3%), 6 (7.3%) knees had Geode formation, 8 (9.8%) knees had loose bodies, 6 (7.3%) knees had deformity of the both ends as seen on the x-ray. In the asymptomatic knees, 10 (55.6%) knees had joint space reduction, 5 (27.8%) knees had osteophytes formation, 4 (22.2%) knees had subarticular sclerosis, 2 (11.1%) knees had Geode formation, 2 (11.1%) knees had loose bodies and 6 (33.3%) knees had shown normal findings on x-ray. Joint space reduction, osteophytes formation and subarticular sclerosis were the commonest findings on x-ray in both the symptomatic as well as asymptomatic knees. ~ 71 ~
4 Fig 24 Table 9: K & L Grading (N=100) S. No. K&L Grading Symptomatic (n=82) Asymptomatic (n=18) No. % No. % 1. Grade I Grade II Grade III Grade IV Total The above table shows the distribution of knees according to various K & L Grading. In the symptomatic knees, 28 (21.0%) knees had Grade I, 21 (30.6%) had Grade II, 18 (24.2%) had Grade III and 15 (24.2%) had Grade IV K&L Grading. In the asymptomatic knees, 10 (73.7%) knees had Grade I, 7 (18.4%) had Grade II, 1 (7.9%) had Grade III K&L Grading, while there were none in Grade IV. In the asymptomatic group, the distribution of knees was nearly similar in all the grades, while in the asymptomatic knees, majority of the knees were in the Grade I K&L grading. ~ 72 ~
5 Fig 25: K & L Grading Table No. 10, Fig. 26: Ultrasonographic Findings in Knees (N=100) Symptomatic Asymptomatic S. No. Ultrasonographic Findings (n=82) (n=18) No. % No. % 1. Articular cartilage thinning Loss of cartilage interface Osteophyte formation Medial meniscal protrusion Lateral meniscal protrusion Joint effusion Popliteal cyst The above table shows the distribution according to ultrasonographic findings. In the asymptomatic group, 80 (97.6%) knees had shown articular cartilage thinning, 78 (95.1%) had shown loss of cartilage interface, 75 (91.5%) had shown osteophyte formation, 75 (91.5%) had shown medial meniscal protrusion, 70 (85.4%) had shown lateral meniscal protrusion, 20 (24.4%) had shown joint effusion and 15 (18.3%) had shown popliteal cyst on ultrasonography. In the symptomatic group, 10 (55.6%) had shown articular cartilage thinning, 8 (44.4%) had shown loss of cartilage interface, 6 (33.3%) had shown osteophyte formation, 4 (22.2%) had shown medial meniscal protrusion, 3 (16.7%) had shown lateral meniscal protrusion, 1 (5.6%) had shown joint effusion and one had shown popliteal cyst on ultrasonography. ~ 73 ~
6 Discussion *Osteoarthritis (OA) is one of the most common medical conditions in elderly people. [1] Worldwide estimates suggested that 9.6% of men and 18.0% of women aged 60 years have symptomatic OA of the hips or knees. [2] It is also the most common reason for restricted daily activity [3] with significantly impact on the quality of life among affected people. [4] Pain is the predominant symptom of OA knee and is the main reason for medical consultation; besides, it the main reason of disability especially during painful episodes. [5 7] Fig 26 group years (48%), followed by years (26%) and 14% in the age group years. Gender In our study, female (70%) preponderance was seen in comparison to male (30%). Body Mass Index (BMI) Majority of the patients in our study were overweight (66%), followed by 14% obese and 12% normal, while 8% of the patients were underweight. Age Group In our study, the higher the KL grading was associated with In the present study, majority of the patients were in the age more pain in general. The finding is in line with a recent ~ 74 ~
7 systematic review that higher grade of osteoarthritis (K/L 3 or above) is a stronger predictor of pain than lower grades (K/L 2 or less). [8] Synovitis is a sign of joint inflammation and its association with pain when sitting and not with walking or stair climbing suggests that the resting OA knee pain during sitting is more likely inflammatory pain. This study showed that knee effusion has positive correlation with symptoms upon walking and climbing, but not with sitting. Similar findings are found in other overseas studies. [13, 14] This suggests that the knee effusion among OA knee patients relates more to mechanical rather than inflammatory pain. Knee effusion has been shown to affect knee mechanics and muscle activity during gait in individuals with knee osteoarthritis and therefore can be a cause of the mechanical pain by itself. [15] The knee joint is a complex joint consisting of a patellofemoral joint (PFJ) articulating the patella with the femoral condyle and two tibiofemoral joints, one medial and one lateral (medial and lateral TFJs), articulating the medial and lateral tibial plateau with the corresponding femoral condyles. Although X-rays measure mainly bony pathologies and ultrasound on soft tissue pathologies, both the X-ray and ultrasound findings in our study showed two trends in common (1) walking pain is related to pathologies of the either the lateral or medial TFJ; (2) stair climbing pain is related to both TFJ pathologies and also to the PFJ pathology. Meniscus subluxation was highly associated with painful OA knee. [26] Our HRUS studies showed that lateral meniscal extrusion was associated with increased pain on walking. X- ray studies, on the other hand, showed pain on walking was associated with the narrowing of the medial TFJ at mid-point. When stair climbing, pathologies from both the medial and lateral TFJ are implicated. The US findings showed that stair climbing pain has a positive correlation to both medial meniscal protrusion and lateral meniscus protrusion; whereas on X-rays, the narrower the medial TFJ at midpoint and the wider the lateral TFJ at midpoint, more the pain. Both of these X-rays findings are commonly found among bow knees (Genu Varus) which are commonly found among OA knee patients. Pain with stair climbing, especially on descending stairs is a well-known feature with OA knee involving the PFJs. [16] Our X-ray studies found that the narrower the lateral facet joint, the more the pain on stair climbing. However, our US finding showed that the thickness of the lateral femoral condyle cartilage, which is a measurement of the lateral PFJ, has no association with stair climbing. Such finding is expected because ultrasound can only measure, through the sky view, the cartilage of the upper part of the femoral condyle. Some limitations of our study should be mentioned. Firstly, we used the conventional standing AP knee radiograph whereas a semi flexion AP view would be more accurate for studying the FT space. Moreover, we did not use an axial view for evaluating the PF space. Nevertheless, we performed the routine views mostly used in daily clinical practice for radiologically assessing severity and progression of knee OA. Secondly, the US inter-observer reliability was not studied. HRUS has been viewed as one of the most operatordependent imaging technique. This fact is partly due to the intrinsic real time nature of US images acquisition. However, in our study all the HRUS examinations were performed by the same radiologist who has 9 years of experience in MSK US. In addition, the recent study by Scheel et al. has revealed an excellent inter-observer reliability (kappa value of 1) between 14 experts in MSK US for the US detection of knee pathological findings including effusion, bone surface abnormalities, tendon lesions, bursitis and Baker s cyst. In the same study, the overall sensitivity and specificity of US compared with MRI for diagnosing knee abnormalities were 90.5% and 87.5%, respectively. In Indian population there is habit of squatting and sitting cross legged, which leads to more incidence of knee OA than Hip OA. Conclusion Knee sonography is desirable as a quick and easy method of screening for articular cartilage abnormalities and extraarticular abnormalities. Its cost effectiveness, dynamic scanning capabilities and therapeutic guidance providing abilities make it useful in our settings. In addition, for some patients sonography may be the test of choice, because of the presence of a pacemaker or other absolute or relative contraindication to MRI. High resolution ultra-sonography can identify femoral trochlear cartilage abnormalities in patients with knee pain and therefore can be a useful adjunct to other imaging tests for identifying arthritic changes in the knee this diagnostic imaging method makes it possible to evaluate most of the structures involved in this disease, carefully revealing the possible changes produced. This method assures the repeatability of the technique so that both the disease and therapy monitoring is possible., sonography may detect the quantity of synovial fluid, revealing the presence of joint effusion with very high sensitivity. Hence, HRUS plays a significant role in early diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis, as well as its progression and therapy monitoring. References 1. Buckwalter JA, Martin JA. Osteoarthritis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2006; 58: Woolf AD, P$eger B. Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ. 2003; 81: Buckwalter JA, Saltzman C, Brown T. The impact of osteoarthritis: implications for research. ClinOrthopRelat Res. 2004; (427 Suppl):S Andriacchi TP, Koo S, Scanlan SF. Gait mechanics in$uence healthy cartilage morphology andosteoarthritis of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009; 91Suppl 1: Samuels J, Krasnokutsky S, Abramson SB. Osteoarthritis: a tale of three tissues. Bull NYU HospJt Dis. 2008; 66: Zhang W, Doherty M, Peat G, Bierma-Zeinstra MA, Arden NK, Bresnihan B, et al. EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69: Hunter DJ. Pharmacologic therapy for osteoarthritis--the era of disease modification. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7: Reginster JY. The prevalence and burden of arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002; 41Supp 1: Keen HI, Wakefield RJ, Conaghan PG. A systematic review of ultrasonography in osteoarthritis Ann Rheum Dis 2009; 68: Abraham. Reliability and validity of ultrasound imaging of features of knee osteoarthritis in the community BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2011; 12: Kazam JK, Nazarian LN, Miller TT, Sofka CM, Parker L, Adler RS. ~ 75 ~
8 12. Hammer HB, Bruyn GA, Naredo E, Damjanov N on behalf of the Ultrasound Task Force, et alan OMERACT reliability exercise of inflammatory and structural abnormalities in patients with knee osteoarthritis using ultrasound assessmentannals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2016; 75: Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957; 16: Lawrence JS. Rheumatism in populations. London, UK: William Heinemann Medica Books Ltd, 1977, Kellgren JH, Jeffrey MR, Ball J. The epidemiology of chronic rheumatism.atlas of standard radiographsof arthritis. Oxford, UK: Blackwell Scientific Publications, 1963, Neustadt D, Caldwell J, Bell M. Clinical Effects of Intraarticular Injection of High Molecular Weight Hyaluronan (Orthovisc) in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, controlled, multicenter trial. J Rheumatol 2005; 32: Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1957; 16: ~ 76 ~
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN. David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging
 MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
MY PATIENT HAS KNEE PAIN David Levi, MD Chief, Division of Musculoskeletal l limaging Atlantic Medical Imaging Causes of knee pain Non traumatic Trauma Osteoarthritis Patellofemoral pain Menisci or ligaments
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping
 Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas
 ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
ELENI ANDIPA General Hospital of Athens G. Gennimatas Technological advances over the last years have caused a dramatic improvement in ultrasound quality and resolution An established imaging modality
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Diagnosis & Nonoperative Treatment of the Osteoarthritic Knee. Randall R Wroble MD Orthopedic One Columbus OH
 Diagnosis & Nonoperative Treatment of the Osteoarthritic Knee Randall R Wroble MD Orthopedic One Columbus OH There are 2 things a good doctor does First Step: Finds out what's wrong Second step Makes the
Diagnosis & Nonoperative Treatment of the Osteoarthritic Knee Randall R Wroble MD Orthopedic One Columbus OH There are 2 things a good doctor does First Step: Finds out what's wrong Second step Makes the
Cristal Castellanos 1, Abelardo Camacho 2, Klaus Mieth 3, Gamal Zayed 3, German Carrillo 3, Oscar Rivero 4, Rafael Gómez 4, Sara Jaimes 4
 Inter- And Intra-Observer Concordance Of The Modified Kellgren And Lawrence Scale For Knee Osteoarthritis By Compartments In Patients Of The University Hospital Fundación Santa Fe De Bogotá, Colombia.
Inter- And Intra-Observer Concordance Of The Modified Kellgren And Lawrence Scale For Knee Osteoarthritis By Compartments In Patients Of The University Hospital Fundación Santa Fe De Bogotá, Colombia.
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer Research Institute for Primary Care & Health Sciences, Keele University Department of Rheumatology, Cannock Hospital, Royal Wolverhampton
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit. Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care
 Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when?
 Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
Chronic knee pain in adults - a multimodality approach or which modality to choose and when? Poster No.: P-0157 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E. Ilieva, V. Tasseva,
Clinical Presentation. Medial or Lateral Focal Swelling Consider meniscal Cysts. Click for more info. Osteoarthritis confirmed. Osteoarthritis pathway
 Focal Knee Swelling Information for GPs who refer into PAH Spinal and knee MRIs should only be requested as a pre-cursor to surgery. Clinical Presentation If you think a patient requires an MRI as there
Focal Knee Swelling Information for GPs who refer into PAH Spinal and knee MRIs should only be requested as a pre-cursor to surgery. Clinical Presentation If you think a patient requires an MRI as there
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis
 Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210972, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210972 Research Article Relationship between Pain and Medial Meniscal Extrusion in Knee Osteoarthritis Hiroaki
Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS
 Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS Objective Outline some clinical features that are not well appreciated in OA patients Recent advances in knowledge and management of OA
Osteoarthritis What is new? Dr Peter Cheung, Rheumatologist, NUHS Objective Outline some clinical features that are not well appreciated in OA patients Recent advances in knowledge and management of OA
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research
 New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
American College of Physicians 2013 Ohio Chapter Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 11, 2013
 American College of Physicians 2013 Ohio Chapter Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 11, 2013 Paul J. Gubanich, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine/Sports Medicine Team Physician, Ohio
American College of Physicians 2013 Ohio Chapter Scientific Meeting Columbus, OH October 11, 2013 Paul J. Gubanich, MD, MPH Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine/Sports Medicine Team Physician, Ohio
SCALENE ASIA PACIFIC SDN BHD ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN TREATMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE JOINT
 SCALENE ASIA PACIFIC SDN BHD ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN TREATMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE JOINT ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN
SCALENE ASIA PACIFIC SDN BHD ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN TREATMENT OF OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE JOINT ROTATIONAL FIELD QUANTUM NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (RFQMR) IN
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT. Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology
 PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
PRE & POST OPERATIVE RADIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. Divya Rani K 2 nd Year Resident Dept. of Radiology PRE OPERATIVE ASSESSMENT RADIOGRAPHS Radiographs are used for assessment and
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes
 Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
Clinical Evaluation and Imaging of the Patellofemoral Joint Common clinical syndromes A. Panagopoulos Lecturer in Orthopaedics Medical School, Patras University Objectives Anatomy of patellofemoral joint
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis Classification of Knee Arthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis of Knee
 1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
Osteoarthritis. Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow
 Osteoarthritis Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Das S.K. Osteoarthritis In Wagh S. (Ed). Rheumatology
Osteoarthritis Dr. Siddharth Kumar Das M. D. Professor and Head, Department of Rheumatology, Chhatrapati Shahu Maharaj Medical University, Lucknow Das S.K. Osteoarthritis In Wagh S. (Ed). Rheumatology
BRIEF REPORT. KENNETH D. BRANDT, ROSE S. FIFE, ETHAN M. BRAUNSTEIN, and BARRY KATZ. From the Department of Medicine, the Department of
 1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
POPLITEAL CYST FILLED WITH HEMATOMA AT THE LOWER CALF: A CASE REPORT
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, No 4, pp 411-414, 2016 Copyright 2016 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) doi:10.15547/tjs.2016.04.019
Trakia Journal of Sciences, No 4, pp 411-414, 2016 Copyright 2016 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1313-7050 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) doi:10.15547/tjs.2016.04.019
Arthritis & Rheumatism
 ~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people develop during middle age or older. Osteoarthritis of the hip causes pain and
The examination of the painful knee. Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University
 The examination of the painful knee Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University Objectives of the talk By the end of this talk you will know The important anatomy
The examination of the painful knee Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University Objectives of the talk By the end of this talk you will know The important anatomy
DISCLOSURES. T. McAlindon: Samumed, grant/research support; Astellas, Flexion, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samumed,and Seikugaku, consulting
 Radiographic Outcomes from a Randomized, Double- Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of a Novel, Intra-Articular, Wnt Pathway Inhibitor (SM04690) for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Week
Radiographic Outcomes from a Randomized, Double- Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2 Study of a Novel, Intra-Articular, Wnt Pathway Inhibitor (SM04690) for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis of the Knee: Week
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Case study #12 Left knee
 The patient is a 55 year old female who presents with bilateral knee pain. Patient is a collegiate softball coach and has a very active lifestyle and career that is hampered by her chronic knee pain. She
The patient is a 55 year old female who presents with bilateral knee pain. Patient is a collegiate softball coach and has a very active lifestyle and career that is hampered by her chronic knee pain. She
Knee Conditions and Disability
 Knee Conditions and Disability Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal August 2013 Prepared by: Dr. John Cameron M.D., F.R.C.S. (C) Orthopaedic Surgeon Contributing
Knee Conditions and Disability Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal August 2013 Prepared by: Dr. John Cameron M.D., F.R.C.S. (C) Orthopaedic Surgeon Contributing
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES
 A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
A NEW CONCEPT IN FUNCTIONAL ORTHOSES THE KNEE in movement! Climbing stairs, walking and running are everyday actions that we can perform thanks to our knees. The knee joint is one of the most exposed and
Sonographic Imaging of Meniscal Subluxation in Patients with Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sonographic Imaging of Meniscal Subluxation in Patients with Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis Chun-Hung Ko, 1 Kam-Kong Chan, 1 Hui-Ling Peng 2 Background/Purpose: This study was undertaken
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sonographic Imaging of Meniscal Subluxation in Patients with Radiographic Knee Osteoarthritis Chun-Hung Ko, 1 Kam-Kong Chan, 1 Hui-Ling Peng 2 Background/Purpose: This study was undertaken
"EULAR endorsed course"
 MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE InterMediate Level 15 17 September, 2017 Dubai, UAE Organizing Office: Compass Conferences "EULAR endorsed course" Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer) Esperanza
MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE InterMediate Level 15 17 September, 2017 Dubai, UAE Organizing Office: Compass Conferences "EULAR endorsed course" Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer) Esperanza
Scoring and Grading B-Mode Synovitis and Doppler findings in pediatric MSKUS. Johannes Roth MD PhD FRCPC RhMSUS
 Scoring and Grading B-Mode Synovitis and Doppler findings in pediatric MSKUS Johannes Roth MD PhD FRCPC RhMSUS Pathology - Definition Synovitis Synovitis on ultrasonography in children B-mode and Doppler
Scoring and Grading B-Mode Synovitis and Doppler findings in pediatric MSKUS Johannes Roth MD PhD FRCPC RhMSUS Pathology - Definition Synovitis Synovitis on ultrasonography in children B-mode and Doppler
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: 07/26/17 Page 1 of 9
 Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: Relation to a Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis
 International Journal of Chinese Medicine 2017; 1(3): 102-107 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcm doi: 10.11648/j.ijcm.20170103.15 Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis
International Journal of Chinese Medicine 2017; 1(3): 102-107 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcm doi: 10.11648/j.ijcm.20170103.15 Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling
 KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
KNEE VASU PAI Arthritic history is similar to that of the hip. Add history of give way and locking, swelling INJURY MECHANISM When How Sequence Progress Disability IKDC Activity I - Strenuous activity
The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the
 The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
Case Report Synostosis of the Proximal Tibiofibular Joint
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 794594, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/794594 Case Report Synostosis of the Proximal Tibiofibular Joint Nikolaos K. Sferopoulos
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2010, Article ID 794594, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2010/794594 Case Report Synostosis of the Proximal Tibiofibular Joint Nikolaos K. Sferopoulos
Unusual Lateral Presentation of Popliteal Cyst
 Unusual Lateral Presentation of Popliteal Cyst Tarek Hemmali,* Abstract: The most common cyst occurs in the popliteal region is the popliteal cyst and over the past years it has been received much clinical
Unusual Lateral Presentation of Popliteal Cyst Tarek Hemmali,* Abstract: The most common cyst occurs in the popliteal region is the popliteal cyst and over the past years it has been received much clinical
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE Basic Level 4 6 November, 2016 Manama, Kingdom of Bahrain Organizing Office: Compass Conferences ENDORSED
 MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE Basic Level 4 6 November, 2016 Manama, Kingdom of Bahrain Organizing Office: Compass Conferences ENDORSED Organizers Möller (Scientific Organizer) Ayman Fahim (Organizer)
MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE Basic Level 4 6 November, 2016 Manama, Kingdom of Bahrain Organizing Office: Compass Conferences ENDORSED Organizers Möller (Scientific Organizer) Ayman Fahim (Organizer)
Focal Knee Swelling Clinical Presentation
 Focal Knee Swelling Clinical Presentation referral for MSK Triage History and Examination Baker's Cyst Medial or Lateral Focal Swelling Consider meniscal Cysts Bursitis Refer for Weight Bearing X-ray AP
Focal Knee Swelling Clinical Presentation referral for MSK Triage History and Examination Baker's Cyst Medial or Lateral Focal Swelling Consider meniscal Cysts Bursitis Refer for Weight Bearing X-ray AP
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Page 1 of 8 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis
Page 1 of 8 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear-and-tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis. RA Hughes
 Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Role of High Resolution Diagnostic Ultrasound in Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy
 Role of High Resolution Diagnostic Ultrasound in Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy Dr.Amandeep Singh* *Professor, Department of Physiotherapy, Chandigarh University, Gharuan. Email ID: aman_ruby@yahoo.com
Role of High Resolution Diagnostic Ultrasound in Musculoskeletal Physiotherapy Dr.Amandeep Singh* *Professor, Department of Physiotherapy, Chandigarh University, Gharuan. Email ID: aman_ruby@yahoo.com
Osteoarthritis of the Hip
 Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Osteoarthritis of the Hip Information on hip osteoarthritis is also available in Spanish: Osteoartritis de cadera (topic.cfm?topic=a00608). Sometimes called "wear and tear" arthritis, osteoarthritis is
Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
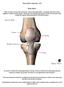 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis
 the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans
 Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
Appendix 1 Primary care referral criteria for musculoskeletal MRI scans Accepted Criteria for Direct Access MRI Body Part Symptoms Imaging indicated Lumbar Spine Low Back Pain with adverse symptoms or
Diagnosis and Management of Knee Conditions. Jenny Love / Lynn Robertson AFLAR Oct 2009
 Diagnosis and Management of Knee Conditions Jenny Love / Lynn Robertson AFLAR Oct 2009 AIMS Review 4 common Knee Conditions: Anterior knee pain Meniscal Injuries Ligament injuries ACL Osteoarthritis Discuss
Diagnosis and Management of Knee Conditions Jenny Love / Lynn Robertson AFLAR Oct 2009 AIMS Review 4 common Knee Conditions: Anterior knee pain Meniscal Injuries Ligament injuries ACL Osteoarthritis Discuss
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (October 2017) Vol. 69 (4), Page 2294-2300 Role of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonography in Diagnosis and Follow Up Rheumatoid Arthritis in Hand and Wrist
David Bong (Spain), MD Faculty member of the EULAR MSUS courses since 2011.
 MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE Intermediate Level Sept 30 & Oct 1 & 2, 2016 Dubai, United Arab Emirates Organizing Office: Compass Conferences ENDORSED Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer)
MUSCULOSKELTAL SONOGRAPHY COURSE Intermediate Level Sept 30 & Oct 1 & 2, 2016 Dubai, United Arab Emirates Organizing Office: Compass Conferences ENDORSED Organizers Ingrid Möller (Scientific Organizer)
Summary. Introduction
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1999) 7, 526 532 1999 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/99/060526+07 $12.00/0 Article No. joca.1999.0256, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1999) 7, 526 532 1999 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/99/060526+07 $12.00/0 Article No. joca.1999.0256, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Standardised. knee. scanning of the. Basic pathology. Nemanja Damjanov. University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology
 Standardised scanning of the Nemanja Damjanov University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology knee Basic pathology Disclosure Lecturer: Pfizer, Abbvie, Roche, MSD, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gedeon Richter,
Standardised scanning of the Nemanja Damjanov University of Belgrade Institute of Rheumatology knee Basic pathology Disclosure Lecturer: Pfizer, Abbvie, Roche, MSD, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Gedeon Richter,
Viscosupplementation VISCOSUPPLEMENTATION AND CANALOSTOMY HS-270. Policy Number: HS-270. Original Effective Date: 1/8/2015. Revised Date(s): 1/7/2016
 Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Exactus Pharmacy Solutions, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Incorporated WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc., operating in Hawai i as Ohana
Easy Choice Health Plan, Inc. Exactus Pharmacy Solutions, Inc. Harmony Health Plan of Illinois, Inc. Missouri Care, Incorporated WellCare Health Insurance of Arizona, Inc., operating in Hawai i as Ohana
International Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Course MITOS
 Basic and Intermediate Levels th International Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Course MITOS Final Course Program 30 November - 2 December 2017 Wyndham Grand Athens Hotel Athens Greece www.synthesispco.com/mitoscourse2017
Basic and Intermediate Levels th International Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Course MITOS Final Course Program 30 November - 2 December 2017 Wyndham Grand Athens Hotel Athens Greece www.synthesispco.com/mitoscourse2017
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
The factors which affect the cartilage thickness of ankle joint
 The factors which affect the cartilage thickness of ankle joint Fei Chang, YunLong Jia, Yao Fu, HanYang Zhang, Zhuan Zhong,QuanYu Dong The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China Declaration
The factors which affect the cartilage thickness of ankle joint Fei Chang, YunLong Jia, Yao Fu, HanYang Zhang, Zhuan Zhong,QuanYu Dong The Second Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, China Declaration
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy. Stephanie E. Siegrist, MD, LLC
 A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
A Patient s Guide to Knee Anatomy Hands, shoulders, knees and toes (and elbows and ankles, too!) Most bone and joint conditions have several treatment options. The best treatment for you is based on your
What is Medial Plica Syndrome?
 What is Medial Plica Syndrome? It is a congenital disorder in which the thin wall of fibrous tissue extends from the synovial capsule of the knee. Pain usually occurs when the synovial capsule becomes
What is Medial Plica Syndrome? It is a congenital disorder in which the thin wall of fibrous tissue extends from the synovial capsule of the knee. Pain usually occurs when the synovial capsule becomes
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques
 Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
Meniscal Root Tears: Evaluation, Imaging, and Repair Techniques R O B E R T N A S C I M E N TO, M D, M S C H I E F OF S P O RT S M E D I C I N E & SH O U L D E R S U R G E RY N E W TO N- W E L L E S L
DECREASE JOINT PAIN IMPROVE JOINT FUNCTION Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Ostenil
 PATIENT - INFORMATION DECREASE JOINT PAIN IMPROVE JOINT FUNCTION Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Ostenil What is osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that mainly occurs due to
PATIENT - INFORMATION DECREASE JOINT PAIN IMPROVE JOINT FUNCTION Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Ostenil What is osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that mainly occurs due to
The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates!
 7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
7th Advanced Course on Knee Surgery - 2018: Imaging assessment of Unicomp candidates! Presenter: Anders Troelsen, MD, ph.d., dr.med., Professor Distribution of the basic primary OA patterns Medial FT:
Bulgarian Association for Musculoskeletal Ultrasound
 MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE INTERMEDIATE LEVEL ORGANIZATION AND COMMITTEE Scientific Organiser Prof. Annamaria Iagnocco Local Organisers Prof Anastas Batalov Dr Rodina Nestorova Dr Plamen Todorov
MUSCULOSKELETAL ULTRASOUND COURSE INTERMEDIATE LEVEL ORGANIZATION AND COMMITTEE Scientific Organiser Prof. Annamaria Iagnocco Local Organisers Prof Anastas Batalov Dr Rodina Nestorova Dr Plamen Todorov
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Evaluation of the Hip and Knee
 Evaluation of the Hip and Knee Causes of hip pain RA Osteoarthritis Psoriatic arthritis Septic arthritis Bursitis Hip fx Labral tear Tendinitis Referred back pain Cancer AVN Legg-Calve-Perthes Paget's
Evaluation of the Hip and Knee Causes of hip pain RA Osteoarthritis Psoriatic arthritis Septic arthritis Bursitis Hip fx Labral tear Tendinitis Referred back pain Cancer AVN Legg-Calve-Perthes Paget's
Osteoarthritis - suspected
 Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians Red flags - Septic arthritis - Fracture Clinical presentation and history Examination -Pain on movement of the joint is a critical finding
Care map information Resources for patients, carers and clinicians Red flags - Septic arthritis - Fracture Clinical presentation and history Examination -Pain on movement of the joint is a critical finding
Prevention Diagnosis Assessment Prescription and /or application of wide range of interventions and PRM program management
 OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
OA PATHOLOGY Characterized by progressive deterioration and ultimate loss of articular cartilage Reactive changes of joint margins and joint thickening of the capsule When OA symptomatic leads to: Pain
Arthritis. What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available?
 Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only
 Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only นพ. ส หธ ช งามอ โฆษ ภาคว ชา ออร โธป ด กส คณะแพทย ศาสตร จ ฬาลงกรณ มหาว ทยาล ย Knee anatomy Femur Pathophysiology Symptoms
Some illustrations are from the internet and intended for educational purpose only นพ. ส หธ ช งามอ โฆษ ภาคว ชา ออร โธป ด กส คณะแพทย ศาสตร จ ฬาลงกรณ มหาว ทยาล ย Knee anatomy Femur Pathophysiology Symptoms
Total Joint Replacement. Hip and Knee Pain Lawrence P. Johnson, MD Merrimack Valley Orthopedic Associates Lowell General Hospital
 Hip and Knee Pain Lawrence P. Johnson, MD Merrimack Valley Orthopedic Associates Lowell General Hospital This talk will touch upon the following topics: Understanding the Causes of Hip and Knee pain Treatment
Hip and Knee Pain Lawrence P. Johnson, MD Merrimack Valley Orthopedic Associates Lowell General Hospital This talk will touch upon the following topics: Understanding the Causes of Hip and Knee pain Treatment
Ankle Arthritis PATIENT INFORMATION. The ankle joint. What is ankle arthritis?
 PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
PATIENT INFORMATION Ankle Arthritis The ankle joint The ankle is a very complex joint. It is actually made up of two joints: the true ankle joint and the subtalar ankle joint. The ankle joint consists
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Peggers Super Summaries: PFJ
 Patellofemoral Joint: ANATOMY: Largest sesamoid ossifying at 3-5 years of age Multiple foci having a sec ossification centre SUPEROLATERAL Helps increase moment arm PATELLOFEMORAL OA Incidence 10% of knee
Patellofemoral Joint: ANATOMY: Largest sesamoid ossifying at 3-5 years of age Multiple foci having a sec ossification centre SUPEROLATERAL Helps increase moment arm PATELLOFEMORAL OA Incidence 10% of knee
