Lamellated Hyperintense Synovitis: Potential MR Imaging Sign of an Infected Knee Arthroplasty 1
|
|
|
- Hubert Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at Original Research n Musculoskeletal Imaging Andrew J. Plodkowski, MD Catherine L. Hayter, MBBS Theodore T. Miller, MD Joseph T. Nguyen, MPH Hollis G. Potter, MD Lamellated Hyperintense Synovitis: Potential MR Imaging Sign of an Infected Knee Arthroplasty 1 Purpose: Materials and Methods: To determine the sensitivity and specificity of lamellated hyperintense synovitis for infection following knee arthroplasty and to determine the inter- and intraobserver variability of this sign at magnetic resonance (MR) imaging. The purpose of the retrospective case control study was approved by the hospital s institutional review board. MR images from 28 patients with proved infected total knee arthroplasty and 28 patients with noninfected arthroplasty were reviewed by two musculoskeletal radiologists for the presence of lamellated hyperintense synovitis. Cases were rereviewed 2 weeks later by each reader. The sensitivity and specificity were calculated with the initial reads. The k statistic was used to assess inter- and intraobserver reliability. Results: Conclusion: The sensitivity of lamellated hyperintense synovitis for infection was (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.75, 0.97) and the specificity was (95% CI: 0.74, 0.94). There was almost perfect interobserver agreement (k = 0.82; 95% CI: 0.72, 0.93; P,.001) and intraobserver agreement (for reader 1, k = 0.89 [95% CI: 0.78, 1.00; P,.001] and for reader 2, k = 0.89 [95% CI: 0.77, 1.00; P,.001]) in the classification of the synovial pattern. In this selected series of patients, the presence of lamellated hyperintense synovitis at MR imaging of knee arthroplasty had a high sensitivity and specificity for infection. This sign had high inter- and intraobserver reliability. q RSNA, From the Department of Radiology and Imaging, Hospital for Special Surgery, 535 E 70th St, New York, NY Received January 16, 2012; revision requested March 19; final revision received May 30; accepted June 14; final version accepted July 11. Address correspondence to A.J.P. ( Plodkowski@yahoo.com). q RSNA, radiology.rsna.org n Radiology: Volume 266: Number 1 January 2013
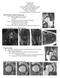
2 Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging is an increasingly used modality to investigate patients presenting with pain following arthroplasty (1,2). Some studies indicate that MR imaging is the most accurate imaging modality to detect and quantify osteolysis (3,4) and that MR imaging findings may be used to distinguish different patterns of wear-induced synovitis (5). Infection, which has been reported in less than 1% of arthroplasties (6), may be a cause of synovitis. We have previously reported anecdotally that a lamellated hyperintense synovium is suggestive of an infected arthroplasty (7). Thus the purpose of this retrospective case control study was to determine the sensitivity and specificity of lamellated hyperintense synovitis as an MR sign of an infected knee arthroplasty and to determine the inter- and intraobserver reliability of this sign. Materials and Methods Subject Cohort The project was approved by the institutional review board at the Hospital for Special Surgery (New York, NY). A total of 1425 patients with painful total knee arthroplasty who underwent MR imaging at our institution between January 2008 and July 2011 were identified through the picture archiving and communication system. The clinical and laboratory notes were reviewed to determine which patients underwent knee joint aspiration or revision surgery within 3 months of the MR imaging. A total of 213 patients met these inclusion criteria. Of the 213 patients, there were 29 (cohort 1) who were ultimately clinically considered to have an infection, and infection was defined as a culture positive for bacterial organisms at aspiration Advance in Knowledge nn A lamellated hyperintense synovial pattern in the setting of a total knee arthroplasty is suggestive of infection. and/or histopathologic findings positive for bacterial infection (8) at revision surgery, with subsequent long-term intravenous antibiotic treatment. We then arbitrarily selected 29 patients from the remaining 184 patients who showed no evidence of infection at either aspiration or histopathologic examination to serve as controls (cohort 2). One patient from each cohort was excluded from analysis because of motion artifact that degraded the diagnostic quality of the MR images. Therefore, each cohort consisted of 28 patients. Data, including patient age, sex, side of arthroplasty, duration of knee arthroplasty placement, indication for performing the MR imaging, and type of bacterial infection, were recorded. The control cohort was not matched for body mass index or sex. MR Image Acquisition Imaging was performed with 1.5-T clinical imaging units (GE Healthcare, Waukesha, Wis) by using eight-channel phased-array transmit-receive knee coils (In Vivo, Orlando, Fla). Images were optimized to minimize susceptibility artifact by using commercially available protocols (7). Two-dimensional fast spin-echo (SE) imaging was performed in three orthogonal planes with the following parameters: repetition time msec/echo time msec, /24 34; bandwidth, 6 83 to 100 khz ( Hz/pixel); field of view, cm; number of signals acquired, four to six; acquisition matrix, 512 (frequency) (phase); section thickness, mm; echo train length, A short-tau fast inversion recovery sequence was obtained in the sagittal plane with the parameters: repetition time msec/echo time msec/inversion time msec, 6000/17/150; receiver bandwidth, 6 83 to 100 khz ( Hz/pixel); field of view, 18 cm; number of Implication for Patient Care nn The finding of lamellated hyperintense synovitis at MR imaging of the knee arthroplasty should alert the radiologist to the possibility of infection. signals acquired, two; acquisition matrix, 256 (frequency) (phase); section thickness, 4 mm; echo train length, 12. Total acquisition time was 30 minutes. MR Image Analysis The two-dimensional fast SE images in the axial plane were used for the assessment of the synovium. The images were evaluated independently by two musculoskeletal radiologists who were blinded to the indication for performing the MR imaging and the results of subsequent aspiration and histopathologic examination. One of the readers was a senior musculoskeletal radiologist with 12 years of experience in MR imaging of arthroplasty (T.T.M., reader 1); the other was a dedicated musculoskeletal MR imaging fellow with 18 months of experience in MR imaging of arthroplasty (C.L.H., reader 2). Images were assessed for the presence of lamellated hyperintense synovitis. Lamellated synovium was defined as a thickened synovium composed of multiple layers. The synovium was characterized as hyperintense if the signal intensity of the synovium was higher than that of skeletal muscle on the intermediate echo time fast SE images (Fig 1). Any other synovial pattern was designated as not lamellated (Fig 2). No training session was given. The images were not assessed for secondary signs of infection such as extracapsular soft-tissue edema, extracapsular collections, bone destruction, Published online before print /radiol Content code: Radiology 2013; 266: Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval SE = spin echo Author contributions: Guarantors of integrity of entire study, all authors; study concepts/study design or data acquisition or data analysis/interpretation, all authors; manuscript drafting or manuscript revision for important intellectual content, all authors; approval of final version of submitted manuscript, all authors; literature research, A.J.P., C.L.H., H.G.P.; clinical studies, A.J.P., C.L.H., T.T.M., H.G.P.; statistical analysis, A.J.P., J.T.N., H.G.P.; and manuscript editing, all authors Conflicts of interest are listed at the end of this article. Radiology: Volume 266: Number 1 January 2013 n radiology.rsna.org 257
3 or reactive lymphadenopathy. Because the presence of these secondary signs of infection might have subconsciously biased the reader, only the non fatsuppressed axial images were used in this study, because marrow edema and soft-tissue collections are not as conspicuous in these sequences. The readers classified findings on MR images in each case as lamellated or not lamellated. The data from this first read were used to calculate the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of the sign. Blinded to the results of the original read, the observers reread images in each case 2 weeks later to determine intraobserver reliability. To further assess interobserver reproducibility, a musculoskeletal fellow with limited experience in MR imaging of arthroplasty was given a training session, including 20 knee arthroplasty cases, some of which were from the patient cohorts. After a 1-week wait, this fellow then read images in each case in the study for the presence of lamellated hyperintense synovitis by using the criteria above. Statistical Analysis The k statistic was used to assess interrater reliability between the readers. Additional reliability analyses were conducted for each reader to evaluate intraobserver reliability. Overall interpretations of the k statistic were based on criteria described by Landis and Koch (9), with calculated 95% confidence intervals (CIs) used to assess the precision of our estimates. The level of agreement was defined as follows: k statistic of was considered to represent almost perfect agreement; k statistic of , substantial agreement; k statistic of , moderate agreement; k statistic of , fair agreement; and k statistic of , slight agreement. All P values reported were results from two-sided tests, with significance set as a of.05. All statistical tests were conducted by using statistical analysis software (SAS software, version 9.2; SAS Institute, Cary, NC). Figure 1 Figure 1: Axial intermediate echo-time fast SE MR image demonstrates the criteria used to denote the presence of lamellated hyperintense synovitis. The lamellated synovium is thickened and composed of multiple layers (white arrows). The synovium is hyperintense when compared with skeletal muscle (black arrow). The synovium was read as lamellated by both readers. Subsequent cultures revealed a Staphylococcus aureus infection. Results Cohort 1 (infected) comprised 12 women (mean age, 64.2 years [standard deviation]) and 16 men (mean age, 67.1 years ), with a combined mean age of 65.8 years The left knee was imaged in 13 patients, and the right knee in 15 patients. The mean duration of knee arthroplasty placement was 80.7 months, with a range of months. In 11 patients, the arthroplasty was revision surgery. The indication for performing the MR imaging was that a patient was suspected of having infection (17 cases), loosening (three cases), quadriceps tendon rupture (two cases), neuroma, Baker cyst, polyethylene wear, component position, patella-backing integrity, and hemarthrosis. The bacteria isolated after culture for these patients consisted of Staphylococcus epidermidis (seven cases), Staph aureus (five cases), Enterococcus faecalis (two cases), methicillin-resistant Staph aureus (two cases), Streptococcus viridans (two cases), Propionibacterium acnes (two cases), Staphylococcus haemolyticus, beta-hemolytic Streptococcus group G, coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species, Figure 2 Figure 2: Axial intermediate echo-time fast SE MR image demonstrates a nonlamellated synovitis. The synovium is thickened and is of low signal intensity (white arrows) when compared with skeletal muscle (black arrow). The synovium was read as not lamellated by both readers. This patient eventually was determined to have wear-induced synovitis. Peptostreptococcus micros, Escherichia coli, Streptococcus intermedius, Bacteroides fragilis, Enterobacter cloacae, and Diphtheroids species. In four patients, two isolated bacteria were observed, and in two patients, no bacteria were identified but infection was confirmed at histologic examination. Overall, infection was confirmed in 20 patients with histologic examination and culture, in six patients with culture only, and in two patients with histologic examination only. Cohort 2 (control) comprised 15 women (mean age, 66.4 years 6 8.0) and 13 men (mean age, 64.8 years ), with a combined mean age of 65.7 years The left knee was imaged in 15 patients, and the right knee in 13 patients. The mean duration of knee arthroplasty placement was 67 months, with a range of months. In three patients, the arthroplasty was revision surgery. The indication for performing the MR imaging was pain (nine cases), the patient was suspected of having infection (four cases), loosening (four cases), polyethylene wear (two cases), osteolysis (two cases), scar tissue (two cases), popliteal aneurysm (one case), patellar fracture (one case), instability (one case), stiffness (one case), and alignment (one case). 258 radiology.rsna.org n Radiology: Volume 266: Number 1 January 2013
4 Figure 3 Statistical Analysis Results for MR Interpretation of Lamellated Hyperintense Synovitis as Sign of Infection Statistic Reader 1 Reader 2 Sensitivity 0.86 (0.75, 0.93) 0.92 (0.82, 0.97) Specificity 0.87 (0.76, 0.94) 0.85 (0.74, 0.92) Positive predictive value 0.88 (0.79, 0.96) 0.84 (0.74, 0.94) Negative predictive value 0.86 (0.77, 0.95) 0.93 (0.86, 0.99) Note. Data in parentheses are the 95% CIs. Figure 4 Figure 3: Axial intermediate echo-time fast SE MR image in a 67-year-old woman referred for MR imaging to evaluate for patellar component loosening. The synovium is mildly thickened and hyperintense but does not appear lamellated (arrow). The synovium was read as not lamellated by both readers. Subsequent culture revealed methicillinresistant Staph aureus infection that was confirmed at histopathologic examination after surgery for removal of the arthroplasty. Figure 4: A, B, Axial intermediate echo-time fast SE MR images in a 69-year-old woman referred for MR imaging to evaluate for infection. A, The synovium is lamellated and hyperintense to skeletal muscle (arrows). The synovium was read as lamellated by both readers. B, Subsequent diagnostic arthroscopy was performed, and a piece of extruded cement was removed. Cultures were negative for infection, and the patient s symptoms resolved following arthroscopy. In retrospect, the piece of extruded cement was visible in the lateral aspect of the suprapatellar pouch (arrow). intraobserver agreement for the musculoskeletal fellow between the two reads (k = 0.75; 95% CI: 0.58, 0.92; P,.001). Using the musculoskeletal fellow s first set of data after the training session, the sensitivity for infection for the musculoskeletal fellow s read was 0.78 (95% CI: 0.66, 0.87). The specificity for infection for the musculoskeletal fellow s read was 0.81 (95% CI: 0.69, 0.89). The results of analysis for readers 1 and 2 are outlined in the Table. The sensitivity of lamellated hyperintense synovitis for infection was (95% CI: 0.75, 0.97). The specificity of lamellated hyperintense synovitis for infection was (95% CI: 0.74, 0.94). In the infected cohort, images in three cases were read as not lamellated by both readers (Fig 3). In the noninfected cohort, the image in one case was read as lamellated by both readers. This patient underwent diagnostic arthroscopy following MR imaging, and a piece of extruded cement was removed (Fig 4). There was almost perfect interobserver agreement between the two readers in the classification of the synovial pattern (k = 0.82; 95% CI: 0.72, 0.93; P,.001). There was almost perfect intraobserver agreement for each reader in their classification of the synovial pattern between the two reads. For reader 1, the k statistic was 0.89 (95% CI: 0.78, 1.00; P,.001). For reader 2, the k statistic was 0.89 (95% CI: 0.77, 1.00; P,.001). There was moderate to substantial interobserver agreement between the first read of the musculoskeletal fellow and the first read of readers 1 and 2 in the classification of the synovial pattern (k = ; 95% CI: 0.50, 0.90; P,.001). There was moderate Discussion While the best diagnostic algorithm for diagnosis of infection relies on histologic and microbiological studies of several tissue specimens (10), other studies such as amplification of the 16S rrna gene have been recently introduced to improve detection of infection (11). Secondary clinical parameters such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level are nonspecific and have limited predictive values in certain patient cohorts (12). Radionuclide bone scanning is sensitive but not specific, (13) and indium 111 white blood cell scans are not universally available and may present technical challenges with labeling (14,15). Radiology: Volume 266: Number 1 January 2013 n radiology.rsna.org 259
5 We previously reported, using a different cohort of patients, that the positive predictive value of lamellated hyperintense synovitis alone for infection was 0.47, which increased to 0.83 when it was combined with extracapsular softtissue edema, extracapsular collections, or reactive lymphadenopathy (16). In this current study we found a high positive predictive value of lamellated synovitis alone, along with a high sensitivity and specificity for infection. The finding of lamellated hyperintense synovitis should therefore alert the radiologist to the possibility of infection. We have also anecdotally seen lamellated hyperintense synovitis in infected native knees but not in inflammatory arthritides such as rheumatoid arthritis. There was one case in which the image was read as lamellated by both readers and the knee was, in fact, not infected. This patient subsequently underwent arthroscopy, and a piece of extruded cement was removed. Following arthroscopy, the patient s symptoms resolved. It is possible that the mechanical irritation of the intraarticular body generated a synovial inflammation pattern similar to that of infection, resulting in the lamellated hyperintense pattern observed at MR imaging. There were some limitations to this study. There were a small number of patients in each cohort. This, however, reflects the fact that infection is an uncommon complication following arthroplasty. We found 29 cases of confirmed infection of 1425 MR images obtained during a 3-year period; this finding represents an infection rate of approximately 2% in this select group and an overall infection rate of less than 1% at our institution (17). Both readers in this study were musculoskeletal radiologists who were experienced with reading MR images of arthroplasty. This may have also affected our results. For this reason, we undertook a brief training session with a musculoskeletal fellow with little experience in MR imaging of arthroplasty. Although inter- and intraobserver reproducibility was lower for the musculoskeletal fellow, using the results of the first read, he also had a high sensitivity and specificity for determining infection by using the MR imaging sign of lamellated hyperintense synovitis. Finally, because of the retrospective nature of this study, we do not have a histologic explanation of what is the lamellated synovium. We speculate that the lamellated hyperintense appearance of the synovium is caused by a combination of inflammatory edema and cellular infiltration. In conclusion, the presence of lamellated hyperintense synovitis at MR imaging of knee arthroplasty is highly suggestive of infection. This sign is reproducible, with high inter- and intraobserver reliability. Disclosures of Conflicts of Interest: A.J.P. No relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. C.L.H. No relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. T.T.M. Financial activities related to the present article: none to disclose. Financial activities not related to the present article: received royalties from Amirsys Publishers for an anatomy chapter. Other relationships: none to disclose. J.T.N. No relevant conflicts of interest to disclose. H.G.P. Financial activities related to the present article: none to disclose. Financial activities not related to the present article: receive payment for advisory board membership from Kensey Nash; received consultancy fees from Biomet, BioMimetic Therapeutics, and Smith & Nephew; author and institution received institutional research support from GE Healthcare. Other relationships: none to disclose. References 1. Kosy JD, Eyres KS, Toms AD. The value of magnetic resonance imaging in investigating a painful total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2011;26(6):977.e9 977.e S Published October 29, Accessed December 1, Mallo GC, Stanat SJ, Jones JA, Capozzi JD, Luchs JS. Catastrophic polyethylene failure diagnosed with magnetic resonance imaging in a painful total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2011;26(3):505.e e15. S %2810% /abstract. Published March 23, Accessed December 1, Walde TA, Weiland DE, Leung SB, et al. Comparison of CT, MRI, and radiographs in assessing pelvic osteolysis: a cadaveric study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005;(437): Weiland DE, Walde TA, Leung SB, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of periprosthetic acetabular osteolysis: a cadaveric study. J Orthop Res 2005;23(4): Hayter CL, Koff MF, Potter HG. Magnetic resonance imaging of the postoperative hip. J Magn Reson Imaging 2012;35(5): Meehan JP, Danielsen B, Tancredi DJ, Kim S, Jamali AA, White RH. A population-based comparison of the incidence of adverse outcomes after simultaneous-bilateral and stagedbilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2011;93(23): Potter HG, Foo LF. Magnetic resonance imaging of joint arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 2006;37(3): Morawietz L, Classen RA, Schröder JH, et al. Proposal for a histopathological consensus classification of the periprosthetic interface membrane. J Clin Pathol 2006;59(6): Landis JR, Koch GG. An application of hierarchical kappa-type statistics in the assessment of majority agreement among multiple observers. Biometrics 1977;33(2): Zimmerli W, Ochsner PE. Management of infection associated with prosthetic joints. Infection 2003;31(2): Ince A, Rupp J, Frommelt L, Katzer A, Gille J, Löhr JF. Is aseptic loosening of the prosthetic cup after total hip replacement due to nonculturable bacterial pathogens in patients with low-grade infection? Clin Infect Dis 2004;39(11): Accessed December 1, Spangehl MJ, Masri BA, O Connell JX, Duncan CP. Prospective analysis of preoperative and intraoperative investigations for the diagnosis of infection at the sites of two hundred and two revision total hip arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1999;81(5): Love C, Marwin SE, Palestro CJ. Nuclear medicine and the infected joint replacement. Semin Nucl Med 2009;39(1): Love C, Tomas MB, Marwin SE, Pugliese PV, Palestro CJ. Role of nuclear medicine in diagnosis of the infected joint replacement. RadioGraphics 2001;21(5): Love C, Palestro CJ. Radionuclide imaging of infection. J Nucl Med Technol 2004;32(2):47 57; quiz Hayter CL, Miller TT, Bogner EA, Potter HG. MR imaging findings of infection following knee arthroplasty: the positive predictive value of a lamellated synovitis [abstr]. Skeletal Radiol 2011;40(8): Ranawat AS. Revision total knee replacement: frequently asked questions (FAQs). Hospital for Special Surgery Web site. Published April 14, Accessed April 9, radiology.rsna.org n Radiology: Volume 266: Number 1 January 2013
MRI Findings in Painful Metal-on- Metal Hip Arthroplasty
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hayter et al. MRI of Painful Metal-on-Metal Hip Prostheses Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Catherine L. Hayter 1 Stephanie L. Gold 1 Matthew F. Koff
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hayter et al. MRI of Painful Metal-on-Metal Hip Prostheses Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Catherine L. Hayter 1 Stephanie L. Gold 1 Matthew F. Koff
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Percutaneous Fluoroscopic Synovial Biopsy as a New Diagnostic Test for Periprosthetic Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Feasibility Study
 Percutaneous Fluoroscopic Synovial Biopsy as a New Diagnostic Test for Periprosthetic Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Feasibility Study J Quon, K Hynes, P Lapner, A Sheikh The Ottawa Hospital
Percutaneous Fluoroscopic Synovial Biopsy as a New Diagnostic Test for Periprosthetic Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Feasibility Study J Quon, K Hynes, P Lapner, A Sheikh The Ottawa Hospital
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections
 Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Nuclear medicine and Prosthetic Joint Infections Christophe Van de Wiele, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Orthopedic prostheses: world market 1996 Prosthetic
Soft Tissue Imaging in. Total Hip Arthroplasty
 FDA Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Devices Panel Medical Devices Advisory Committee Meeting Thursday June 28th 2012 Soft Tissue Imaging in Metal-on on-metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Young-Min Kwon MD, PhD, FRCS,
FDA Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Devices Panel Medical Devices Advisory Committee Meeting Thursday June 28th 2012 Soft Tissue Imaging in Metal-on on-metal Total Hip Arthroplasty Young-Min Kwon MD, PhD, FRCS,
Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures
 Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures Collin, David; Dunker, Dennis; Gothlin, Jan H.; Geijer, Mats Published in: Acta Radiologica
Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures Collin, David; Dunker, Dennis; Gothlin, Jan H.; Geijer, Mats Published in: Acta Radiologica
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Dr. Ashish Shah MD Dr. John Kirchner MD Dr. Sameer Naranje MD
 Dr. Ashish Shah MD Dr. John Kirchner MD Dr. Sameer Naranje MD Assistant Professor, UAB Orthopaedic Surgery, Foot & Ankle Section, 1313 13th Street South, Birmingham, AL 35205 Clinical Instructor Fellow,
Dr. Ashish Shah MD Dr. John Kirchner MD Dr. Sameer Naranje MD Assistant Professor, UAB Orthopaedic Surgery, Foot & Ankle Section, 1313 13th Street South, Birmingham, AL 35205 Clinical Instructor Fellow,
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Imaging After Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Revised 2017 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Imaging After Total Knee Arthroplasty Variant 1: Follow-up of the asymptomatic patient with a total knee arthroplasty. Radiologic
Revised 2017 American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria Imaging After Total Knee Arthroplasty Variant 1: Follow-up of the asymptomatic patient with a total knee arthroplasty. Radiologic
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Complex Fractures and Hip Dislocations
 IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
Total Hip Arthroplasty: MR Imaging of Complications Unrelated to Metal Wear
 31 Total Hip Arthroplasty: MR Imaging of Complications Unrelated to Metal Wear Alissa J. Burge, MD 1,2,3 1 Department of Radiology and Imaging, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, New York 2 Department
31 Total Hip Arthroplasty: MR Imaging of Complications Unrelated to Metal Wear Alissa J. Burge, MD 1,2,3 1 Department of Radiology and Imaging, Hospital for Special Surgery, New York, New York 2 Department
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist
 Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist Poster No.: B-0950 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. Dunker, J. H. Göthlin, M. Geijer ; Gothenburg/SE, Lund/SE Keywords:
Seemingly isolated greater trochanter fractures do not exist Poster No.: B-0950 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: D. Dunker, J. H. Göthlin, M. Geijer ; Gothenburg/SE, Lund/SE Keywords:
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Imaging features of complications following hip replacement: A pictorial assay
 Imaging features of complications following hip replacement: A pictorial assay Poster No.: C-2041 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Pilania, B. Jankharia ; Mumbai, maharashtra/in,
Imaging features of complications following hip replacement: A pictorial assay Poster No.: C-2041 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Pilania, B. Jankharia ; Mumbai, maharashtra/in,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
 SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1873 1878 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Christian W. A. Pfirrmann, MD,* Alexander
SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1873 1878 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Christian W. A. Pfirrmann, MD,* Alexander
Oak foundation for donating the 3T Siemens Verio scanner. Board of directors BBH and Frh Hospitals for supporting the
 Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty
 Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty John W. Sperling, MD, MS, a Hollis G. Potter, MD, b Edward V. Craig, MD, a Evan Flatow, MD, c and Russell F. Warren, MD, a New York, NY Specialized
Magnetic resonance imaging of painful shoulder arthroplasty John W. Sperling, MD, MS, a Hollis G. Potter, MD, b Edward V. Craig, MD, a Evan Flatow, MD, c and Russell F. Warren, MD, a New York, NY Specialized
Coffey et al ND 6 HA, 5 TSA, and 5 other MRSA (3) and Staphylococcus epidermidis (3)
 Page 1 of 6 TABLE E-1 Outcomes of the Treatment of Periprosthetic Shoulder Infections* ä Study No. Presentation Prosthesis Most Common Pathogens Braman et al. 68 7 1 acute, 2 subacute, 2 HA and 5 TSA Staphylococcus
Page 1 of 6 TABLE E-1 Outcomes of the Treatment of Periprosthetic Shoulder Infections* ä Study No. Presentation Prosthesis Most Common Pathogens Braman et al. 68 7 1 acute, 2 subacute, 2 HA and 5 TSA Staphylococcus
H.P. Teng, Y.J. Chou, L.C. Lin, and C.Y. Wong Under general or spinal anesthesia, the knee was flexed gently. In the cases of limited ROM, gentle and
 THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
Power Doppler evaluation of joint effusions: investigation in a rabbit model
 Pediatr Radiol (1999) 29: 617±623 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Peter J. Strouse Michael A. DiPietro Eu-Leong H. J. Teo Kei Doi Clarence E. Chrisp Power Doppler evaluation of joint effusions: investigation in
Pediatr Radiol (1999) 29: 617±623 Ó Springer-Verlag 1999 Peter J. Strouse Michael A. DiPietro Eu-Leong H. J. Teo Kei Doi Clarence E. Chrisp Power Doppler evaluation of joint effusions: investigation in
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Adverse reaction metal debris (ARMD) after metal-on-metal (MOM) hip replacement: magnetic resonance imaging features with surgical feedback
 Adverse reaction metal debris (ARMD) after metal-on-metal (MOM) hip replacement: magnetic resonance imaging features with surgical feedback Poster No.: C-0533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper
Adverse reaction metal debris (ARMD) after metal-on-metal (MOM) hip replacement: magnetic resonance imaging features with surgical feedback Poster No.: C-0533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper
Metal Artifact Reduction With MAVRIC SL at 3-T MRI in Patients With Hip Arthroplasty
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choi et al. Metal rtifact Reduction on 3-T MRI of H Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soo-Jung Choi 1 Kevin M. Koch 2 rian. Hargreaves 3 Kathryn J. Stevens
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choi et al. Metal rtifact Reduction on 3-T MRI of H Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soo-Jung Choi 1 Kevin M. Koch 2 rian. Hargreaves 3 Kathryn J. Stevens
For Commercial products, please refer to the following policy: Preauthorization via Web-Based Tool for Procedures
 Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Medical Coverage Policy Total Joint Arthroplasty Hip and Knee EFFECTIVE DATE: 08/01/2017 POLICY LAST UPDATED: 06/06/2017 OVERVIEW Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, has proved to be
Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
Bone and prosthetic joint infections: what the ID specialist needs?
 Bone and prosthetic joint infections: what the ID specialist needs? Andrej Trampuz Charité University Medicine Berlin Center for Septic Surgery Hip and knee replacements in Europe Germany Austria Belgium
Bone and prosthetic joint infections: what the ID specialist needs? Andrej Trampuz Charité University Medicine Berlin Center for Septic Surgery Hip and knee replacements in Europe Germany Austria Belgium
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
ASJ. Magnification Error in Digital Radiographs of the Cervical Spine Against Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER 2: RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF THE KNEE Radiographic Evaluation of the Knee Presented by: R. Michael Meneghini, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE KNEE SOCIETY Disclosures
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Leucocytscintigraphy. Lene Rørdam Senior Consultant DMSci Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine Bispebjerg University Hospital
 Leucocytscintigraphy Lene Rørdam Senior Consultant DMSci Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine Bispebjerg University Hospital Indications for leucocytscintigraphy in the past Inflammatory
Leucocytscintigraphy Lene Rørdam Senior Consultant DMSci Department of Clinical Physiology and Nuclear Medicine Bispebjerg University Hospital Indications for leucocytscintigraphy in the past Inflammatory
Disclosures! Infection & Nonunions. Infection workup. Skip early infection. Culture (+) fractures. Gross Infection
 The Infected Nonunion Paul Tornetta III, MD Professor Boston Medical Center Disclosures! Publications: Rockwood and Green, Tornetta and Ricci TIFS, Tornetta and Einhorn; Subspecialty series, Court-Brown,
The Infected Nonunion Paul Tornetta III, MD Professor Boston Medical Center Disclosures! Publications: Rockwood and Green, Tornetta and Ricci TIFS, Tornetta and Einhorn; Subspecialty series, Court-Brown,
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, cont
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Correspondence should be addressed to Thomas Kurien;
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 6043497, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6043497 Case Report Resection and Resolution of Bone Marrow Lesions Associated with an Improvement of
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 6043497, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6043497 Case Report Resection and Resolution of Bone Marrow Lesions Associated with an Improvement of
Interesting Case Series. Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus
 Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
Interesting Case Series Ganglion Cyst of the Peroneus Longus Andrew A. Marano, BA, Paul J. Therattil, MD, Dare V. Ajibade, MD, PhD, MPH, and Ramazi O. Datiashvili, MD, PhD Division of Plastic and Reconstructive
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
The Painful Prosthetic Joint: Role of Nuclear Medicine
 The Painful Prosthetic Joint: Role of Nuclear Medicine Christopher J. Palestro, M.D. Professor of Radiology Hofstra North Shore-LIJ of Medicine Chief Division of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging North
The Painful Prosthetic Joint: Role of Nuclear Medicine Christopher J. Palestro, M.D. Professor of Radiology Hofstra North Shore-LIJ of Medicine Chief Division of Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging North
21 year-old collegiate rower: R/O labral tear
 Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Relieving Arthritis Knee Pain Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics
 Arthritis is COMMON Relieving Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-622-3172 More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the number of
Arthritis is COMMON Relieving Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-622-3172 More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the number of
Unified Classification System (UCS) for peri-prosthetic fractures (PPFx)
 Unified Classification System (UCS) for peri-prosthetic fractures (PPFx) Waleed A Abdulwahid Consultant surgeon Medical City, Iraq 6th Emirates International Orthopedic Congress Dubai, UAE May 3-5, 2018
Unified Classification System (UCS) for peri-prosthetic fractures (PPFx) Waleed A Abdulwahid Consultant surgeon Medical City, Iraq 6th Emirates International Orthopedic Congress Dubai, UAE May 3-5, 2018
A Validated Classification for External Immobilization of the Cervical Spine
 72 Original Research A Validated Classification for External Immobilization of the Cervical Spine Micha Holla 1 Joske M. R. Huisman 1 Allard J. F. Hosman 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Radboud University
72 Original Research A Validated Classification for External Immobilization of the Cervical Spine Micha Holla 1 Joske M. R. Huisman 1 Allard J. F. Hosman 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Radboud University
Comparison of Three-dimensional Isotropic T1-weighted Fast Spin-Echo MR Arthrography with Two-dimensional MR Arthrography of the Shoulder 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Balgrist Shoulder Course 2017
 Diagnosis and Management of Infection in Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflict
Diagnosis and Management of Infection in Revision Shoulder Arthroplasty Joseph P. Iannotti MD, PhD Maynard Madden Professor and Chairman Orthopaedic and Rheumatologic Institute Cleveland Clinic Conflict
Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
 Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty in the Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections. Can Spacer Be a Source of Reinfection?
 Dwuetapowa endoprotezoplastyka rewizyjna w leczeniu zakażeń okołoprotezowych. Czy spacer może stanowić źródło reinfekcji? Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty in the Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections.
Dwuetapowa endoprotezoplastyka rewizyjna w leczeniu zakażeń okołoprotezowych. Czy spacer może stanowić źródło reinfekcji? Two-Stage Revision Arthroplasty in the Management of Periprosthetic Joint Infections.
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in 99 subjects
 Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in subjects Masaki Shin, M.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Hitoshi Hirata, M.D., Shukuki Koh, M.D., Takaaki Shinohara, M.D. Department of Hand
Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in subjects Masaki Shin, M.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Hitoshi Hirata, M.D., Shukuki Koh, M.D., Takaaki Shinohara, M.D. Department of Hand
PI-RADS classification: prognostic value for prostate cancer grading
 PI-RADS classification: prognostic value for prostate cancer grading Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Platzek, A. Borkowetz, T. Paulus, T. Brauer, M. Wirth, M.
PI-RADS classification: prognostic value for prostate cancer grading Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Platzek, A. Borkowetz, T. Paulus, T. Brauer, M. Wirth, M.
Obturator Externus Bursa: Anatomic Origin and MR Imaging Features of Pathologic Involvement 1
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Philip Robinson, MB, ChB 2 Lawrence M. White, MD Anne Agur, MD Jay Wunder, MD Robert S. Bell, MD Index terms: Hip, abnormalities, 44.4843 Hip, anatomy, Hip, arthrography,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Radiology Philip Robinson, MB, ChB 2 Lawrence M. White, MD Anne Agur, MD Jay Wunder, MD Robert S. Bell, MD Index terms: Hip, abnormalities, 44.4843 Hip, anatomy, Hip, arthrography,
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography. Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears
 Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier,
CASE 56 Hip Pain. ? Diagnosis
 CSE 56 Hip Pain PIN IN THE HIP: 1. 50-year-old female who had undergone total hip arthroplasty [Metal on metal] of the right hip 3.4 years earlier. Shee had a tingling sensation in the trochanteric region
CSE 56 Hip Pain PIN IN THE HIP: 1. 50-year-old female who had undergone total hip arthroplasty [Metal on metal] of the right hip 3.4 years earlier. Shee had a tingling sensation in the trochanteric region
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation. Disclosures. Outline. Joint Effusion. Suprapatellar recess
 Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, cont
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Peter Beddy, FFRRCSI,
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Peter Beddy, FFRRCSI,
The value of weight-bearing functional CT scans
 The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
The value of weight-bearing functional scans In musculoskeletal medicine, advanced imaging like computed axial tomography () scanning, has become invaluable to the evaluation and management of patients
A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis of the Knee Joint
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 84, No. 3, December: 97-, www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net A Comparative Study of Ultrasonographic Findings with Clinical and Radiological Findings of Painful Osteoarthritis
Prosthetic liner wear in total hip replacement: a longitudinal 13-year study with computed tomography
 Skeletal Radiology (2018) 47:883 887 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-2878-8 CASE REPORT Prosthetic liner wear in total hip replacement: a longitudinal 13-year study with computed tomography Lars Weidenhielm
Skeletal Radiology (2018) 47:883 887 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-018-2878-8 CASE REPORT Prosthetic liner wear in total hip replacement: a longitudinal 13-year study with computed tomography Lars Weidenhielm
MRI Features of Lyme Arthritis in Children
 Pediatric Imaging Ecklund et al. MRI of Lyme Arthritis in Children Kirsten Ecklund 1 Sigella Vargas 1 David Zurakowski 2 Robert P. Sundel 3 Ecklund K, Vargas S, Zurakowski D, Sundel RP Received June 30,
Pediatric Imaging Ecklund et al. MRI of Lyme Arthritis in Children Kirsten Ecklund 1 Sigella Vargas 1 David Zurakowski 2 Robert P. Sundel 3 Ecklund K, Vargas S, Zurakowski D, Sundel RP Received June 30,
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
Digital tomosynthesis (DT) has been well described as a
 Case Report The Usefulness of Digital Tomosynthesis (DT) in Assisting in Cases of Doubtful Routine Radiography and/or Computed Tomography (CT) Image. Abstract Digital tomosynthesis is useful in assisting
Case Report The Usefulness of Digital Tomosynthesis (DT) in Assisting in Cases of Doubtful Routine Radiography and/or Computed Tomography (CT) Image. Abstract Digital tomosynthesis is useful in assisting
Introduction. Disclosure. Biomet-Royalties. Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty. Infection. John W. Sperling MD, MBA
 Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty John W. Sperling MD, MBA Biomet-Royalties Disclosure Introduction Infection Rare, but devastating complication Reported incidence ranges from 0% to 4% Coste et al.
Infection after Shoulder Arthroplasty John W. Sperling MD, MBA Biomet-Royalties Disclosure Introduction Infection Rare, but devastating complication Reported incidence ranges from 0% to 4% Coste et al.
Personalized Solutions. MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides
 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Case Report: Arthroscopic Treatment of Psoas Abscess Concurrent with Septic Arthritis of the Hip Joint
 Case Report: Arthroscopic Treatment of Psoas Abscess Concurrent with Septic Arthritis of the Hip Joint Pil Whan Yoon, MD*, Jeong Joon Yoo, MD, Hee Joong Kim, MD, and Kang Sup Yoon, MD* Department of Orthopedic
Case Report: Arthroscopic Treatment of Psoas Abscess Concurrent with Septic Arthritis of the Hip Joint Pil Whan Yoon, MD*, Jeong Joon Yoo, MD, Hee Joong Kim, MD, and Kang Sup Yoon, MD* Department of Orthopedic
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Is Aseptic Loosening of the Prosthetic Cup after Total Hip Replacement Due to Nonculturable Bacterial Pathogens in Patients with Low-Grade Infection?
 MAJOR ARTICLE Is Aseptic Loosening of the Prosthetic Cup after Total Hip Replacement Due to Nonculturable Bacterial Pathogens in Patients with Low-Grade Infection? A. Ince, 1 J. Rupp, 3 L. Frommelt, 2
MAJOR ARTICLE Is Aseptic Loosening of the Prosthetic Cup after Total Hip Replacement Due to Nonculturable Bacterial Pathogens in Patients with Low-Grade Infection? A. Ince, 1 J. Rupp, 3 L. Frommelt, 2
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP
 THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER IX PARTIAL KNEE: MEDIAL, LATERAL AND PFR Revision of Failed Unicompartmental to Total Knee Arthroplasty Presented by: Keith R. Berend, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE
THE KNEE SOCIETY VIRTUAL FELLOWSHIP CHAPTER IX PARTIAL KNEE: MEDIAL, LATERAL AND PFR Revision of Failed Unicompartmental to Total Knee Arthroplasty Presented by: Keith R. Berend, MD COPYRIGHT 2016 THE
Available online at
 Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Original Research Article Evaluation of knee joint by MRI in 65 patients Gulamus sibtain asad *, Himanshu Singla, Ankit vasoya, P. J. Jhala 2 2 nd year Resident, 2 Professor Radiology Department, SBKS
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Radiologic Imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 Radiologic Imaging X-ray has always been the golden rule in diagnosing and treating podiatric patients. Unfortunately, for some patients the diagnosis is not as evident. That is when we need to utilize
Radiologic Imaging X-ray has always been the golden rule in diagnosing and treating podiatric patients. Unfortunately, for some patients the diagnosis is not as evident. That is when we need to utilize
Sonography of the Acetabular Labrum
 Case Series Visualization of Labral Injuries During Intra-Articular Injections Carolyn M. Sofka, MD, Ronald S. Adler, PhD, MD, Martha A. Danon, MD Objective. The purpose of this series was to describe
Case Series Visualization of Labral Injuries During Intra-Articular Injections Carolyn M. Sofka, MD, Ronald S. Adler, PhD, MD, Martha A. Danon, MD Objective. The purpose of this series was to describe
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
The use of CRP within a clinical prediction algorithm for the differentiation of septic arthritis and transient synovitis in children
 CHILDREN S ORTHOPAEDICS The use of CRP within a clinical prediction algorithm for the differentiation of septic arthritis and transient synovitis in children R. Singhal, D. C. Perry, F. N. Khan, D. Cohen,
CHILDREN S ORTHOPAEDICS The use of CRP within a clinical prediction algorithm for the differentiation of septic arthritis and transient synovitis in children R. Singhal, D. C. Perry, F. N. Khan, D. Cohen,
Marcin Borowski, Przemysław Bereza, Damian Kusz, Katedra i Klinika Ortopedii i Traumatologii Narządu Ruchu Śląski Uniwersytet Medyczny w Katowicach
 Spacer as a source of re-infection? Comparison of cultures and 16s r-rna sequencing for identification for bacteria in 2-stage revision knee arthroplasty Marcin Borowski, Przemysław Bereza, Damian Kusz,
Spacer as a source of re-infection? Comparison of cultures and 16s r-rna sequencing for identification for bacteria in 2-stage revision knee arthroplasty Marcin Borowski, Przemysław Bereza, Damian Kusz,
Pathological plain-film findings related to patellar resurfacing in total knee replacement
 Pathological plain-film findings related to patellar resurfacing in total knee replacement Poster No.: P-0010 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster P. Melloni, M. T. Veintemillas,
Pathological plain-film findings related to patellar resurfacing in total knee replacement Poster No.: P-0010 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster P. Melloni, M. T. Veintemillas,
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
The role of histopathology: Diagnostics of PJI
 The role of histopathology: Diagnostics of PJI BSc. Vincent Krenn Sigmund Freud PrivatUniversität Wien ZHZMD Trier 2011 In joint replacement operations a histopathological diagnosis is generally advised
The role of histopathology: Diagnostics of PJI BSc. Vincent Krenn Sigmund Freud PrivatUniversität Wien ZHZMD Trier 2011 In joint replacement operations a histopathological diagnosis is generally advised
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Antibiotic Prophylaxis in Joint Arthroplasty: Do we get it right?
 International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences ISSN: 2167-0447 Vol. 2 (4), pp. 088-091, April, 2012. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full
International Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences ISSN: 2167-0447 Vol. 2 (4), pp. 088-091, April, 2012. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full
Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability.
 Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability. Satoshi Yamaguchi, M.D. 1, Hiroshi Matsumoto, R.T. 2, Atsuya Watanabe, M.D.
Depiction of Lateral Ligament Complex of the Ankle using 3D MRI in Healthy Subjects and Patients with Chronic Ankle Instability. Satoshi Yamaguchi, M.D. 1, Hiroshi Matsumoto, R.T. 2, Atsuya Watanabe, M.D.
a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report
 Haematogenous Infection of a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER 5 5.1. Introduction In orthopaedic surgery, an infection of a prosthesis is a very serious,
Haematogenous Infection of a Total Hip Prosthesis by Clostridum perfringens. A Case Report CHAPTER 5 CHAPTER 5 5.1. Introduction In orthopaedic surgery, an infection of a prosthesis is a very serious,
Latest Treatments for Hip Arthritis. Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics You re Not Alone
 Latest Treatments for Hip Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-502-9404 You re Not Alone More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the
Latest Treatments for Hip Arthritis Michael J. Repine MD Boulder Medical Center Orthopedics 303-502-9404 You re Not Alone More than 43 million people have some form of arthritis. It is estimated that the
