Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography. Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears
|
|
|
- Homer Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fosbury Flop Tear of the Rotator Cuff: Diagnostic Assessment with Magnetic Resonance Arthrography Running Title: Fosbury Flop Tears FC Kolo, 1 AJP Schwitzguébel, 2 A Kourhani, 1 PJ Denard, 3 C Charbonnier, 4 A Lädermann. 1,5,6 1) Rive Droite Radiology Center, Switzerland 2) Division of Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery, La Tour Hospital, Rue J.-D. Maillard 3, 1217 Meyrin, Switzerland. 3) Southern Oregon Orthopedics, Medford, Oregon, USA; and Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, Oregon, USA. 4) Medical Research Department, Artanim Foundation, 40 chemin du Grand-Puits, 1217 Meyrin, Switzerland. 5) Faculty of Medicine, University of Geneva, Rue Michel-Servet 1, 1211 Geneva 4, Switzerland. 6) Division of Orthopaedics and Trauma Surgery, Department of Surgery, Geneva University Hospitals, Rue Gabrielle-Perret-Gentil 4, CH-1211 Geneva 14, Switzerland. Page 1/21
2 Abstract Objectives The aim was to assess the diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA) of the shoulder for the detection of "Fosbury flop" tears. Methods All patients undergoing arthroscopic rotator cuff repair were considered as potentially eligible for inclusion in this prospective case series. Preoperative MRAs were consecutively performed and compared with intraoperative findings being the gold standard control. Two experienced musculoskeletal radiologists, blinded to the arthroscopic findings, independently analyzed all MRAs for the presence of typical signs of Fosbury flop tears. Results 423 patients were included. Among this group, 11 presented a Fosbury flop tear with a prevalence of 2.6 %. Inter-observer agreement was considered as excellent for thickened tendon, tendon stump, fluid accumulation, abnormal fibers orientation, and adherences between tendon and bursa. The most sensitive and specific criterion was the tendon thickness (90.9%; CI: % and 97.1% CI: %, respectively). Conclusions Fosbury flop tear is an uncommon condition that should be recognized to allow optimal anatomic repair. MRA is a valuable tool in making the diagnosing of this lesser recognized type of rotator cuff tear. An abnormally thickened supraspinatus tendon tear should especially raise suspicion for a Fosbury flop tear of the posterosuperior rotator cuff. Page 2/21
3 Advances in knowledge MRA is a valuable tool in making the diagnosing of Fosbury flop tears. An abnormally thickened supraspinatus tendon tear should especially raise suspicion for such lesion. Keywords: Shoulder arthroscopy; Magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA); Rotator cuff lesion; Fosbury flop tear; New tear pattern. Abbreviations and acronyms: None Page 3/21
4 Introduction Shoulder pain and dysfunction is a common musculoskeletal problem with rotator cuff tears being one of the most common causes [1]. Rotator cuff lesions have substantial variability in location, tear pattern, functional impairment, and reparability. They can be categorized into four major groups based on involvement of the bone (Type A), tendon (Type B), musculotendinous junction (Type C) and muscle (Type D) [2]. Tearing of the tendon from the bone is the most common [2]. Full-thickness tears come in a variety of patterns often classified as crescent tears, L-shaped tears, reverse L-shaped tears, and U-shaped tears [3]. Recognizing the tear pattern is important in understanding the pathology in order to propose an adapted treatment and repair plan. A new full thickness tear pattern of the posterosuperior rotator cuff associated with reversal healing of the supraspinatus on its bursal side has been recently recognized [4, 5] and described as B3 lesions according to Lädermann et al. [2]. This unusual avulsion of the posterosuperior rotator cuff has been termed the Fosbury flop tear (Figure 1) [4]. The two series that analyzed specifically Fosbury flop tears both found a prevalence of 5% [4, 5]. Nevertheless, other large series of MRI or MRA analysis on the prevalence of posterosuperior rotator cuff lesions did not reported this particular pattern [6]. The purpose of this study was to assess the diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance arthrography (MRA) of the shoulder for the detection of Fosbury flop tear pattern of the rotator cuff with an arthroscopic correlation. The hypothesis was that MRA was a valuable tool in making the diagnosis of this lesser recognized type of rotator cuff tear. Page 4/21
5 Figure 1: Illustration of a Fosbury flop tear. Page 5/21
6 Material and methods Patients selection Between March 2012 and September 2015, all patients undergoing arthroscopic rotator cuff repair by an experienced orthopedic shoulder surgeon (AL) were considered as potentially eligible for inclusion in this prospective case series. The only exclusion criterion was whether the patients in which diagnosis was performed without MRA. Some patients have been previously reported [4]. This prior article dealt with the description of this new full-thickness tear pattern, the associated specific radiological signs and the arthroscopic rotator cuff repair technique, whereas in this manuscript we report on the diagnostic performance of MRA for the detection of Fosbury flop tear pattern. The study protocol was approved by our institutional Ethics Committee (AMG: 12-26) and all patients gave written informed consent. MRA procedure After local anesthesia, 2 ml (300 mg iodine per milliliter) of ionic contrast media (Lopamiro 300, Bracco, Plan-les-Ouates, Switzerland), followed by 10 ml of diluted gadopentate dimeglumine (Magnevist, Bayer, Basel, Switzerland) with a concentration of 2 mmol/l were injected inside the shoulder joint under fluoroscopic guidance. MRAs were performed with a 1.5T system (MR450 W, General Electrics, Milwaukee, USA) or a 3T system (Philips Achieva, Eindhoven, Netherlands). A dedicated shoulder coil was used. Imaging parameters are detailed in Tables 1 and 2. Image analysis Preoperative MRAs were consecutively performed and compared with intraoperative findings being the gold standard control. All MRAs were independently analyzed by Page 6/21
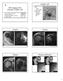
7 two experienced musculoskeletal radiologists (KFC and KA). They were blinded to the arthroscopic findings. The rotator cuff morphology was assessed qualitatively. The presence of MRA findings that seem to typically describe the Fosbury flop tear [4] were systematically evaluated by each reader: the maximum thickness of the full torn tendon was measured in millimeters in the coronal plane (Figure 2), the presence of adherences between the bursal tendon side and the wall of the subacromial bursa (Figure 3), the presence of fluid accumulation in the superomedial part of the subacromial bursa and the visualization of a tendon stump with superomedial orientation (Figure 4) were reported. Finally, the presence of an abnormal orientation of the fibers in the tendon stump in the coronal plane (see Figures 3 and 4) was also reported. Figure 2: Coronal T2 weighted MRA image with fat saturation of a right shoulder. A complete tear and retracted supraspinatus tendon is observed. The tendon stump is abnormally thickened (9 mm) which should raise suspicion for a Fosbury flop tear. Page 7/21
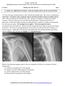
8 Figure 3: Coronal T1 weighted MRA image with fat saturation of a right shoulder demonstrates adhesions between the bursal side of the tendon and the wall of the subacromial bursa (red arrow), and abnormal orientation of the fibers stump (yellow arrow). Sample size calculation Because a Fosbury flop tear is a rare condition described with a prevalence of 5% [4], the sample size will be important for specificity, but quite low for sensitivity. An expected sensitivity of 80% was estimated from a pilot analysis (unpublished results). The sample size was thus estimated upon the determination of the acceptable width of the confidence interval of sensitivity, which was fixed at 12% for each arm. A sample size of 11 patients with a Fosbury flop tear was calculated with epitools online calculator (epitools.ausvet.com.au/). It was therefore decided to stop the patient s recruitment when the quota of 11 was reached. Page 8/21
9 Figure 4: Coronal intermediate weighted MRA image without fat saturation of a right shoulder demonstrates the tendon stump projecting on the top of the superomedial part of the subacromial bursa (arrow). A two-layered structure and the stump is readily identifiable. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed with R v3.2.2 Portable (Free Software Foundation Inc, Vienna, Austria). Agreement between the two experienced radiologists verifying the presence of radiological signs was assessed using Cohen s Kappa (К) and intraclass correlation coefficients, which were interpreted as described by Landis and Koch [7]. In the case of a discordant observation, consensus was made between the two radiologists. Then, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value and accuracy were calculated for each radiological criterion, as well as their corresponding confidence intervals. ROC curve was plotted for each combination of radiological criteria. Page 9/21
10 Results From the 500 patients meeting inclusion criteria, 77 were excluded because MRA was not performed (i.e., rotator cuff tear evaluation was performed with MRI, ultrasound or computed tomography arthrogram). Therefore, 423 patients (202 females and 221 males) with a mean age of 56 ± 10 years old (range, 21 to 82 years) were selected for analysis. The median timing between MRA and surgery was 82 days (range, 2 to 337 days). Among this group, 11 presented a Fosbury flop tear with a prevalence of 2.6 ± 1.5 %. Two of the 11 patients have been previously reported [4]. Inter-observer agreement Inter-observer agreement was considered as excellent for tendon thickness (К=0.81), tendon stump (К=0.93), fluid accumulation (К=0.89), fiber orientation (К=0.89), and adhesion between tendon and bursa (К=0.87). While reviewing the 423 patients, consensus was necessary in 12 cases for tendon thickness, 4 cases for tendon stump, 22 cases for fluid accumulation, 6 cases for fiber orientation, and 22 cases for adhesion between tendon and bursa. Prevalence of radiological criteria Table 3 shows the prevalence of Fosbury signs in the whole patients sample, as well as in the subgroups of patients with and without arthroscopically recognized Fosbury flop tear. Mean tendon thickness for the patients without Fosbury flop tear was 5.4 ± 1.3 mm, mean thickness in patients with a Fosbury flop tear was 9.1 ± 2.2 mm. Sensitivity analysis In the sensitivity analysis of the five described radiological criteria, most sensitive Page 10/21
11 isolated criteria for diagnosing a Fosbury flop tear were tendon thickness (90.9%; CI: %) and tendon stump (90.9%; CI: %) (Table 4). Note that the sensitivities are equivalent because the proportion of those two criteria are identical into the Fosbury flop tear subgroup (see Table 3). However, the most specific criterion was tendon thickness (97.1% CI: %). Even if the presence of one of the five criteria showed a sensitivity of 100% (CI: %) and the presence of five of the five criteria showed a specificity of 98.5% (CI: %), no combination of radiological criteria showed both sensitivity and specificity as performant as the tendon thickness. Indeed, as illustrated in the ROC curve (Figure 5), the tendon thickness criterion is closest to the upper left corner of the plot than the presence of any other criteria. Figure 5: ROC curve, depending on the number of positive radiological criteria. Single point, tendon thickness 9 mm. Curve, combination of the five radiological signs. Page 11/21
12 Discussion While the Fosbury flop tear is an uncommon rotator cuff tear, radiologists and orthopedic surgeons must be aware of this tear pattern. Failure to recognize this type of tear will lead to a non-anatomic repair or even the inability to achieve repair. Among the five different radiological criteria reviewed by the two musculoskeletal radiologists, the sensitivity analysis showed that tendon thickness is the most accurate MRA sign for diagnosing a Fosbury flop tear. In the present study, the mean tendon thickness for the patients without Fosbury flop tear was 5.4 ± 1.3 mm. Similar values have been found in other studies. Aktuk et al. found a mean supraspinatus thickness of 4.9 ± 0.4 mm in a control group [8]. In our study, the mean thickness in patients with a Fosbury flop tear was 9.1 ± 2.2 mm. The effect of pathologies on tendon thickness is not well known. Theoretically, it could be related to tear, tendinopathy, diabetes in relation to retraction, edema or structural changes in tendon collagen. Meyer et al. demonstrated that musculotendinous retraction in chronic tears results mainly from shortening without thickening [9]. Another study reported that diabetes increased tendon thickness up to 6.6 ± 1.2 mm compared to a control group [8]. To our best knowledge, Fosbury flop tears are consequently the only condition that creates such an increase in tendon thickness. Compared to tendon thickness only, the most efficient combination of radiological signs, including the presence of all five signs, allows an increase of specificity from 97.8 to 98.5, but the cost is a decrease of sensitivity from 90.9 to 54.5 (Figure 5). The sensitivity analysis shows an excellent sensitivity (90.9, CI: ) and an excellent negative predictive value (99.8, CI: ) for tendon thickness. However, false- Page 12/21
13 positive events are not uncommon, as the positive predictive value (45.5, CI: ) is quite low. The excellent interobserver reliability shows that all radiological signs of interest are reproducible, especially tendon thickness. Strength and limitations The major strength of this study is the prospective design comparing patients with and without Fosbury flop tear with arthroscopic correlation. Furthermore, it has been shown that MRA is highly accurate in the diagnosis of full-thickness rotator cuff tears using arthroscopy as the gold standard [1]. Moreover, the sample size is relatively large in relation to an uncommon pathology. However, we acknowledge several limitations in our study. First, the confidence intervals for sensitivity remain quite wide due to the limited number of patients having a Fosbury flop tear. Second, MRIs were performed with arthrography and with different systems (1.5T vs. 3T). Conventional MRI [1, 10] and particularly 3D MRI may improve the accuracy of rotator cuff tear shape characterization. [11] Nonethess, MRI remains a sensitive and specific tool for the diagnosis of full-thickness tear of the rotator cuff and in our experience Fosbury flop tears can be diagnosed accurately without arthrography. Third, nearly one year could have passed between the MRA and the surgery, leading to a potential evolution of the rotator cuff tears. Conclusion Fosbury flop tear is an uncommon rotator cuff tear pattern that should be recognized to achieve anatomic rotator cuff repair. MRA is a valuable tool in the preoperative recognition of this tear pattern. An abnormally thickened supraspinatus tendon tear should especially raise suspicion for a Fosbury flop tear of the posterosuperior rotator Page 13/21
14 cuff. Source of funding None Conflict of interest None Page 14/21
15 References 1. Waldt S, Bruegel M, Mueller D, Holzapfel K, Imhoff AB, Rummeny EJ, et al. Rotator cuff tears: assessment with MR arthrography in 275 patients with arthroscopic correlation. European radiology. 2007;17(2): Lädermann A, Burkhart SS, Hoffmeyer P, Neyton L, Collin P, Yates E, et al. Classification of full-thickness rotator cuff lesions: a review. EFORT Open Rev. 2016;1(12): Davidson J, Burkhart SS. The geometric classification of rotator cuff tears: a system linking tear pattern to treatment and prognosis. Arthroscopy. 2010;26(3): Lädermann A, Denard PJ, Kolo FC. A new tear pattern of the rotator cuff and its treatment: Fosbury flop tears. International journal of shoulder surgery. 2015;9(1): Nakamizo H. Arthroscopic repair for subacromial incarceration of a torn rotator cuff. AP-SMART. 2015;2: Choo HJ, Lee SJ, Kim JH, Kim DW, Park YM, Kim OH, et al. Delaminated tears of the rotator cuff: prevalence, characteristics, and diagnostic accuracy using indirect MR arthrography. AJR American journal of roentgenology. 2015;204(2): Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977;33(1): Akturk M, Karaahmetoglu S, Kacar M, Muftuoglu O. Thickness of the supraspinatus and biceps tendons in diabetic patients. Diabetes care. 2002;25(2): Meyer DC, Farshad M, Amacker NA, Gerber C, Wieser K. Quantitative analysis of muscle and tendon retraction in chronic rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med. 2012;40(3): Page 15/21
16 10. Smith TO, Daniell H, Geere JA, Toms AP, Hing CB. The diagnostic accuracy of MRI for the detection of partial- and full-thickness rotator cuff tears in adults. Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;30(3): Gyftopoulos S, Beltran LS, Gibbs K, Jazrawi L, Berman P, Babb J, et al. Rotator cuff tear shape characterization: a comparison of two-dimensional imaging and three-dimensional magnetic resonance reconstructions. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2016;25(1): Page 16/21
17 Table 1: MRI sequences with their imaging parameters acquired on the 1.5T system (GE MR450W). MRI Sequences Imaging Parameters Coronal T2 weighted propeller fast spin-echo with fat saturation Section thickness 3.5 mm; gap 0.5 mm; TR/TE msec 4045/103; field of view, 16x16 cm; matrix ; 3 signal acquired Sagittal T2 weighted propeller fast spin-echo with fat saturation Section thickness 3.5 mm; gap 0.5 mm; TR/TE msec 4934/96; field of view, 16x16 cm; matrix ; 3 signal acquired Coronal intermediate weighted propeller fast spin-echo with fat saturation Section thickness 3.5 mm; gap 0.5 mm; TR/TE msec 2099/47; field of view 16x16 cm; matrix ; 3 signals acquired Coronal T1 weighted fast spin echo with fat saturation Section thickness 3.5 mm; TR/TE msec 643/9; field of view, 16x16 cm; matrix ; 2 signal acquired Transverse T1 weighted fast spin echo with fat saturation Section thickness 3.5 mm; gap 0.5 mm; TR/TE msec 641/9; field of view, 16x16 cm; matrix ; 2 signal acquired Sagittal T1 weighted fast spin-echo without fat saturation Section thickness 3.5mm; TR/TE msec 562/10; field of view 16x16 cm; matrix ; 1 signal acquired Transverse 3D MERGE* Section thickness 2 mm; no intersection gap; TR/TE msec 40/18; flip angle 7 ; field of view, 19x19 cm; matrix ; 2 signal acquired * Multiple Echo Recombined Gradient Echo Page 17/21
18 Table 2: MRI sequences with their imaging parameters acquired on the 3T system (Philips Achieva). MRI Sequences Coronal intermediate weighted fast spin-echo with fat saturation Transverse intermediate weighted fast spin echo with fat saturation Sagittal T1 weighted fast spin-echo without fat saturation Coronal T1 fast spin-echo with fat saturation Ultrafast isovoxel spoiled gradient echo (Thrive) Imaging Parameters Section thickness 3 mm; gap 0.8 mm; TR/TE msec 2679/35; field of view, 13x13 cm; matrix ; 4 signal acquired Section thickness 3 mm; gap 0.8mm; TR/TE msec 3613/30; field of view, 13x13 cm; matrix ; 3 signal acquired Section thickness 3 mm; gap 0.8 mm; TR/TE msec 694/20; field of view, 14x14 cm; matrix ; 2 signal acquired Section thickness 3 mm; gap 0.7 mm; TR/TE msec 687/8,9; field of view 13x13 cm; matrix 672x672; 3 signals acquired Section thickness 0.7 mm; TR/TE msec 11,2/5; field of view 18x18 cm; matrix ; 1 signal acquired Page 18/21
19 Table 3: Prevalence of Fosbury flop tear MRA signs. Patients diagnosed with Fosbury flop tear (n = 11) Patients with other rotator cuff tears (n = 412) Whole patients sample (n = 423) Thickened tendon (> 9mm) 10 (91%) 8 (2%) 18 (4%) Tendon Stump 10 (91%) 15 (4%) 25 (6%) Fluid accumulation 9 (82%) 111 (27%) 120 (28%) Abnormal fibers orientation 9 (82%) 14 (3%) 23 (5%) Adherences between tendon and bursa 7 (64%) 78 (19%) 85 (20%) Page 19/21
20 Table 4: Sensitivity analysis for the radiologic assessment of supraspinatus Fosbury tear. Sensitivity Specificity PPV NPV Accuracy Thickened tendon (> 9mm) (A) 90.9 ( ) 97.1 ( ) 45.5 ( ) 99.8 ( ) 96.9 ( ) Tendon stump (B) 90.9 ( ) 94.7 ( ) 31.2 ( ) 99.7 ( ) 94.6 ( ) Fluid accumulation (C) 81.8 ( ) 58.5 ( ) 5 ( ) 99.2 ( ) 59.1 ( ) Abnormal fibers orientation (D) 81.8 ( ) 94.9 ( ) 30 ( ) 99.5 ( ) 94.6 ( ) Adherences between tendon and bursa (E) 63.6 ( ) 70.6 ( ) 5.5 ( ) 98.6 ( ) 70.4 ( ) One of A, B, C, D, and E 100 ( ) 54.9 ( ) 5.6 ( ) 100 ( ) 56 ( ) Two of A, B, C, D, and E 90.9 ( ) 72.1 ( ) 8 ( ) 99.7 ( ) 72.6 ( ) Three of A, B, C, D, and E 90.9 ( ) 94.4 ( ) 30.3 ( ) 99.7 ( ) 94.3 ( ) Four of A, B, C, D, and E 72.7 ( ) 95.9 ( ) 32 ( ) 99.2 ( ) 95.3 ( ) All of A, B, C, D, and E 54.5 ( ) 98.5 ( ) 50 ( ) 98.8 ( ) 97.4 ( ) In parenthesis: 95% confidence intervals. PPV, positive predictive value; NPV, negative predictive value. Page 20/21
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Diagnostic Accuracy Using Indirect MR Arthrography
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Choo et al. MR Arthrography of Delaminated Tears of the Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hye Jung Choo 1 Sun Joo Lee 1 Jung-Han Kim 2 Dong
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP MR arthrography
 Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Skeletal Radiol (2010) 39:473 480 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0844-1 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Articular cartilage and labral lesions of the glenohumeral joint: diagnostic performance of 3D water-excitation true FISP
Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative MRI
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR Arthrography and Arthroscopic Correlation
 Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Comparisons of the Various Partial- Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears on MR rthrography and rthroscopic Correlation Kyung h Chun, MD Min Sung Kim, MD Young Joo Kim, MD Index terms: Shoulder MR arthrography
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
3/9/2018. Algorithm for Massive RCT s. Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option?
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears: When is Reverse TSA the only option? Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Team Physician, Chicago White Sox
Hugo C. van der Veen James P. M. Collins Paul C. Rijk
 DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
DOI 10.1007/s00402-011-1423-1 ARTHROSCOPY AND SPORTS MEDICINE Value of magnetic resonance arthrography in post-traumatic anterior shoulder instability prior to arthroscopy: a prospective evaluation of
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
MR rthrography fter Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 186:237 241 0361 803X/06/1861 237 merican Roentgen Ray Society Y Sylvain R.
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS
 DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN ACUTE AND CHRONIC ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES IN WORKERS COMPENSATION PATIENTS Lyndon B. Gross M.D. Ph.D. The Orthopedic Center of St. Louis SHOULDER PAIN Third most common musculoskeletal
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff Tears. University of Medical Sciences, Iran. Medical Sciences, Iran.
 Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
Comparative Study of MRI and Operative Findings in Rotator Cuff s Mohammad Hossein Daghighi 1, Alireza Rouhani 2, Masoud oureisa 3, Ali Sadighi 4, Farnaz Hafez Quran 5 *, Masoumeh Ahmadi Mohtasham 5 1.
MRI Evaluation of Bipolar Bone Loss Using the On-Track Off-Track Method: A Feasibility Study
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Bipolar Bone Loss Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Soterios Gyftopoulos 1 Luis S. Beltran 1 Jared Bookman 2 Andrew Rokito 3
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes
 Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
Partial Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears: All-Inside Repair of PASTA Lesions in Athletes Thomas M. DeBerardino, MD Associate Professor, UConn Health Center Team Physician, Orthopaedic Consultant UConn Huskie
Rotator Cable: MRI Study of Its Appearance in the Intact Rotator Cuff With Anatomic and Histologic Correlation
 Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Gyftopoulos et al. MRI of Rotator Cable in Intact Rotator Cuff Musculoskeletal Research Original Research Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging
 MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
MRI of the Shoulder What to look for and how to find it? Dr. Eric Handley Musculoskeletal Radiologist Cherry Creek Imaging MRI of the Shoulder Benefits of Ultrasound: * Dynamic * Interactive real time
Detection and Measurement of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography: Analysis of Diagnostic Errors
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Teefey et al. Detection of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography Sharlene A. Teefey 1 William D. Middleton 1 William T. Payne 2 Ken Yamaguchi 3 Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Payne WT, Yamaguchi
Musculoskeletal Imaging Teefey et al. Detection of Rotator Cuff Tears with Sonography Sharlene A. Teefey 1 William D. Middleton 1 William T. Payne 2 Ken Yamaguchi 3 Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Payne WT, Yamaguchi
Quantitative analysis of muscle and tendon retraction in chronic rotator cuff tears
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Quantitative analysis of muscle and tendon retraction in chronic rotator
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Quantitative analysis of muscle and tendon retraction in chronic rotator
Comparison of Three-dimensional Isotropic T1-weighted Fast Spin-Echo MR Arthrography with Two-dimensional MR Arthrography of the Shoulder 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Hye Jung Choo, MD
Rotator cuff. MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff. Trauma. Trauma. Trauma. Tendon calcification. Acute. Degenerative. Trauma Calcific tendinitis
 Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Rotator cuff MR Imaging of the Shoulder: Rotator Cuff Dr. Mini N. Pathria M.D., FRCP(C) Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California Acute Trauma Calcific tendinitis
Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations
 MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
MRI of Internal Impingement of the Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Eddie L. Giaroli 1 Nancy M. Major Laurence D. Higgins Giaroli EL, Major NM, Higgins LD DOI:10.2214/AJR.04.0971
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference. Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16
 Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Arthroscopy / MRI Correlation Conference Department of Radiology, Section of MSK Imaging Department of Orthopedic Surgery 7/19/16 Case 1: 29 YOM with recurrent shoulder dislocations Glenoid Axial T1FS
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis
 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis Lloyd W. Taylor Resident Award: Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI in SLAP Tears: A Retrospective Review of 444 Patients Utilizing Musculoskeletal
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery University of California, Davis Lloyd W. Taylor Resident Award: Diagnostic Accuracy of MRI in SLAP Tears: A Retrospective Review of 444 Patients Utilizing Musculoskeletal
Intramuscular Rotator Cuff Cysts: Association with Tendon Tears on MRI and Arthroscopy
 Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Kassarjian et al. MRI of Rotator Cuff Cysts and Tendon Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations Ara Kassarjian 1 Martin Torriani Hugue Ouellette William E. Palmer Kassarjian A, Torriani M, Ouellette
Post-injury painful and locked knee
 H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
H R J Post-injury painful and locked knee, p. 54-59 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Musculoskeletal Imaging Post-injury painful and locked knee Ioannis I. Daskalakis 1, 2, Apostolos H. Karantanas 1, 2 1
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease
 Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
Shoulder Ultrasonography as a Diagnostic Tool for Rotator Cuff Disease Jay D Keener, MD Associate Professor Shoulder and Elbow Service Washington University Disclosure No relevant financial disclosures
Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
Original Article pissn / eissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2016;75(6): https://doi.org/ /jksr
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.6.480 Discrepancy between Fluoroscopic Arthrography and Magnetic Resonance Arthrography in Patients with Arthroscopically
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Shoulder AUC 05/22/2018 Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with shoulder pain and the following clinical presentations: *Including
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears
 Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
Sonographic Differences in the Appearance of Acute and Chronic Full-Thickness Rotator Cuff Tears Sharlene A. Teefey, MD, William D. Middleton, MD, Gregory S. Bauer, MD, Charles F. Hildebolt, DDS, PhD,
Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY
 Diagnosis Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY Degenerative muscular changes associated with rotator cuff tears include fatty infiltration and atrophy. Increased
Diagnosis Diagnosis: Significant atrophy of supraspinatus FATTY INFILTRATION AND CUFF ATROPHY Degenerative muscular changes associated with rotator cuff tears include fatty infiltration and atrophy. Increased
Considerations 3/9/2018. Asheesh Bedi, MD. I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest related to the content of this presentation.
 Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
Radiological Assessment of the Rotator Cuff What predicts outcomes? Asheesh Bedi, MD Harold and Helen W. Gehring Professor Chief, Sports Medicine & Shoulder Surgery MedSport, Department of Orthopedic Surgery
Introduction & Question 1
 Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Page 1 of 7 www.medscape.com To Print: Click your browser's PRINT button. NOTE: To view the article with Web enhancements, go to: http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/424981 Case Q & A Shoulder Pain, Part
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.320 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):320-327 Evaluation of the Subscapularis Tendon Tears on 3T
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.2.320 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(2):320-327 Evaluation of the Subscapularis Tendon Tears on 3T
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019
 AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
AMSER Case of the Month January 2019 55 yo female presenting with 1 year of shoulder pain without prior trauma Nicholas Bertha, MS4 Drexel University College of Medicine Brandon Schooley, MD Allegheny
The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience
 The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience Poster No.: C-0596 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. A. Ahyad, Z.
The use of Ultrasound of the shoulder as a screening method for rotator cuff tear; A single institution experience Poster No.: C-0596 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. A. Ahyad, Z.
Arthroscopic Evaluation of Subluxation of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon and Its Relationship with Subscapularis Tears
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:332-339 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.3.332 Arthroscopic Evaluation of Subluxation of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon and Its Relationship
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:332-339 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.3.332 Arthroscopic Evaluation of Subluxation of the Long Head of the Biceps Tendon and Its Relationship
Impingement syndrome. Clinical features. Management. Rotator cuff tear diagnosed. Go to rotator cuff tear
 Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Impingement syndrome Clinical features Management Poor response Good response Refer to orthopaedic surgery R Review as appropriate Investigations Rotator cuff tear diagnosed Go to rotator cuff tear Consider
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
11/13/2017. Disclosures: The Irreparable Rotator Cuff. I am a consultant for Arhtrex, Inc and Endo Pharmaceuticals.
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears without Arthritis THE CASE FOR SUPERIOR CAPSULAR RECONSTRUCTION MICHAEL GARCIA, MD NOVEMBER 4, 2017 FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE Disclosures: I am a consultant for Arhtrex,
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography. Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System
 Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Sports Medicine: Shoulder Arthrography Christine B. Chung, M.D. Professor of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division UCSD and VA Healthcare System Disclosure Off-label use for gadolinium Pediatric Sports Injuries
Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears ABSTRACT
 1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
1 Iran J Nucl Med 2005; 23 Accuracy of SPECT bone scintigraphy in diagnosis of meniscal tears M. Saghari 1, M. Moslehi 1, J. Esmaeili 2, M.N. Tahmasebi 3, A. Radmehr 4, M. Eftekhari 1,2, A. Fard-Esfahani
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 9/22/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 91 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
What can Imaging tell us?
 What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
What can Imaging tell us? David Connell FRANZCR, FFSEM (UK) Assoc Professor Dept of Medicine, Nursing & Healthcare Monash University, Melbourne, Australia Assoc Professor Sport & Exercise Medicine Research
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology
 Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
Rotator Cuff and Biceps Pathology Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Board:
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Meniscal Tears: Role of Axial MRI Alone and in Combination with Other Imaging Planes
 Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
Nefise Cagla Tarhan 1,2 Christine. Chung 1 urea Valeria Rosa Mohana-orges 1 Tudor Hughes 1 Donald Resnick 1 Received September 30, 2003; accepted after revision February 2, 2004. 1 Department of Radiology,
MR measurements of subcoracoid impingement using a new method and its relationship to rotator cuff pathology at MR arthrography
 MR measurements of subcoracoid impingement using a new method and its relationship to rotator cuff pathology at MR arthrography Poster No.: P-0055 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
MR measurements of subcoracoid impingement using a new method and its relationship to rotator cuff pathology at MR arthrography Poster No.: P-0055 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study of Rotator Cuff Disorders by Ultrasound with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Hemanth Purigali Naganna 1, Shashikumar Mysore Rangaswamy 2, Jaganathan 3, Nanjaraj Chakenalli
Original Research Article Study of Rotator Cuff Disorders by Ultrasound with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Hemanth Purigali Naganna 1, Shashikumar Mysore Rangaswamy 2, Jaganathan 3, Nanjaraj Chakenalli
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE
 MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MRI SHOULDER WHAT TO SEE DR SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr. Consultant- Knee & Shoulder Arthroscopy Sant Parmanand Hospital Normal Anatomy Normal Shoulder MRI Coronal Oblique Sagital Oblique Axial Cuts Normal Coronal
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder
 MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
MR imaging features of paralabral ganglion cyst of the shoulder Poster No.: C-1482 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Bartocci, C. Dell'atti, E. Federici, D. Beomonte Zobel, V. Martinelli,
Normalization of the subscapularis belly-press test
 Normalization of the subscapularis belly-press test Brian Gilmer, a Thomas Bradley Edwards, MD, a Gary Gartsman, MD, a Daniel P. O Connor, PhD, b and Hussein Elkousy, MD, a Houston, TX The purpose of this
Normalization of the subscapularis belly-press test Brian Gilmer, a Thomas Bradley Edwards, MD, a Gary Gartsman, MD, a Daniel P. O Connor, PhD, b and Hussein Elkousy, MD, a Houston, TX The purpose of this
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping
 The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
MRI Diagnosis of Tears of the Hip Abductor Tendons (Gluteus Medius and Gluteus Minimus)
 Oliver Cvitanic 1 Gregory Henzie 1 Nicholas Skezas 2 Jack Lyons 2 Jon Minter 3 Received October 2, 2002; accepted after revision July 10, 2003. 1 Southwest Oklahoma MRI, 13301 N Meridian Ave., Ste. 600A,
Oliver Cvitanic 1 Gregory Henzie 1 Nicholas Skezas 2 Jack Lyons 2 Jon Minter 3 Received October 2, 2002; accepted after revision July 10, 2003. 1 Southwest Oklahoma MRI, 13301 N Meridian Ave., Ste. 600A,
Variant origin of the bifurcated long head of biceps tendon - the case for supraspinatus.
 Variant origin of the bifurcated long head of biceps tendon - the case for supraspinatus. Poster No.: P-0066 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster H. Madani 1, C. G. Boulet
Variant origin of the bifurcated long head of biceps tendon - the case for supraspinatus. Poster No.: P-0066 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster H. Madani 1, C. G. Boulet
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in 99 subjects
 Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in subjects Masaki Shin, M.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Hitoshi Hirata, M.D., Shukuki Koh, M.D., Takaaki Shinohara, M.D. Department of Hand
Reliability of Lichtman s classification for Kienböck s disease in subjects Masaki Shin, M.D., Masahiro Tatebe, M.D., Hitoshi Hirata, M.D., Shukuki Koh, M.D., Takaaki Shinohara, M.D. Department of Hand
Multidetector CT arthrography in shoulder instability and its comparison with MR arthrography and arthroscopy
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kumar V et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1189-1194 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174712
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Kumar V et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1189-1194 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174712
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
imri 2018;22:
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:229-239 Diagnosis of Rotator Cuff Tears with Non-Arthrographic MR Imaging: 3D Fat-Suppressed Isotropic Intermediate-Weighted Turbo Spin-Echo Sequence versus
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Case study # 6 Sharon P
 Patient is a morbidly obese 70 year old female presenting with left shoulder pain after a severe fall. Patient is in moderate to severe pain with extremely limited range of motion due to extensive shoulder
Patient is a morbidly obese 70 year old female presenting with left shoulder pain after a severe fall. Patient is in moderate to severe pain with extremely limited range of motion due to extensive shoulder
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders
 Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Ultrasound assessment of most frequent shoulder disorders Poster No.: C-2026 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. P. Ivanoski; Ohrid/MK Keywords: Trauma, Athletic injuries, Arthritides,
Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
10.5005/jp-journals-10017-1017 Ankur M Manvar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Distinguishing Superior Labral Tears from Normal Meniscoid Insertions with Magnetic Resonance Imaging Ankur M Manvar BS, Sheetal M
Part II: Rotator Cuff Repair, Day of Surgery and Postoperative Course
 Part II: Rotator Cuff Repair, Day of Surgery and Postoperative Course Benjamin W. Sears, MD 303-321-1333 western-ortho.com denvershoulder.com Day of Surgery Most patients will undergo outpatient surgery
Part II: Rotator Cuff Repair, Day of Surgery and Postoperative Course Benjamin W. Sears, MD 303-321-1333 western-ortho.com denvershoulder.com Day of Surgery Most patients will undergo outpatient surgery
Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:669 674 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0677-y SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff Jan E. Vandevenne & Filip Vanhoenacker & Jestinah
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:669 674 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0677-y SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Fast MR arthrography using VIBE sequences to evaluate the rotator cuff Jan E. Vandevenne & Filip Vanhoenacker & Jestinah
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears
 Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
Management of Massive/Revision Rotator Cuff Tears Nikhil N. Verma MD, Director Sports Medicine, Rush University Medical Center, Midwest Orthopedics at Rush, Chicago, IL nverma@rushortho.com I. Anatomy
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Shoulder Arthroscopy. Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij. NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Muscle fatty infiltration in rotator cuff tears: Descriptive analysis of 1688 cases
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2009) 95, 319 324 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Muscle fatty infiltration in rotator cuff tears: Descriptive analysis of 1688 cases B. Melis a, C. Nemoz b,c,d, G. Walch
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2009) 95, 319 324 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Muscle fatty infiltration in rotator cuff tears: Descriptive analysis of 1688 cases B. Melis a, C. Nemoz b,c,d, G. Walch
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI
 Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI Frank Kolo C. MD, Caecilia Charbonnier* PhD, Christian W.A. Pfirrmann ** MD, Sylvain R. Duc MD, Anne Lubbeke
Extreme Hip Motion in Professional Ballet Dancers: Dynamic and Morphologic Evaluation Based on MRI Frank Kolo C. MD, Caecilia Charbonnier* PhD, Christian W.A. Pfirrmann ** MD, Sylvain R. Duc MD, Anne Lubbeke
Variant origin of the bifurcated long head of biceps tendon - the case for supraspinatus.
 Variant origin of the bifurcated long head of biceps tendon - the case for supraspinatus. Poster No.: P-0066 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster H. Madani 1, C. G. Boulet
Variant origin of the bifurcated long head of biceps tendon - the case for supraspinatus. Poster No.: P-0066 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Poster H. Madani 1, C. G. Boulet
Arthroscopic Treatment of Anterosuperior Rotator Cuff Tears
 Arthroscopic Treatment of Anterosuperior Rotator Cuff Tears Erik Schnaser, MD; Bruno Toussaint, MD; Robert Gillespie, MD; Yves Lefebvre, MD; Reuben Gobezie, MD abstract Full article available online at
Arthroscopic Treatment of Anterosuperior Rotator Cuff Tears Erik Schnaser, MD; Bruno Toussaint, MD; Robert Gillespie, MD; Yves Lefebvre, MD; Reuben Gobezie, MD abstract Full article available online at
PROPELLER Technique to Improve Image Quality of MRI of the Shoulder
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Dietrich et al. PROPELLER Technique in MRI of Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Tobias J. Dietrich 1 Erika J. Ulbrich 1 Marco Zanetti 1 Sandro
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Dietrich et al. PROPELLER Technique in MRI of Shoulder Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Tobias J. Dietrich 1 Erika J. Ulbrich 1 Marco Zanetti 1 Sandro
Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Shoulder Disorders
 Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Shoulder Disorders NAOEM Oct 14 th, 2017 Michael Codsi, M.D. www.drcodsi.com Learning Objectives SLAP tears diagnosis, imaging and treatment How to diagnose rotator cuff
Diagnosis and Treatment of Common Shoulder Disorders NAOEM Oct 14 th, 2017 Michael Codsi, M.D. www.drcodsi.com Learning Objectives SLAP tears diagnosis, imaging and treatment How to diagnose rotator cuff
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 185 189 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acromioclavicular joint, MR imaging findings concerning, 161 Acromion, types of, 77 79
SSA13-01 The Detour Sign on MR Image for Subluxation of the Long Head of Biceps Tendon with Arthroscopic Correlation
 Musculoskeletal (Shoulder I) Sunday, 10:45 AM - 12:15 PM E451A MR MK SSA13 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit :1.5 ARRT Category A+ Credit:1.5 Moderator Michael J Tuite, MD Moderator Kirkland W Davis, MD Back to
Musculoskeletal (Shoulder I) Sunday, 10:45 AM - 12:15 PM E451A MR MK SSA13 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit :1.5 ARRT Category A+ Credit:1.5 Moderator Michael J Tuite, MD Moderator Kirkland W Davis, MD Back to
Lesions of the Menisci of the Knee: Value of MR Imaging Criteria for Recognition of Unstable Lesions
 B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
B. C. Vande Berg 1 P. Poilvache 2 F. Duchateau 1 F. E. Lecouvet 1 J. E. Dubuc 2 B. Maldague 1 J. Malghem 1 Received June 12, 2000; accepted after revision August 24, 2000. 1 Department of Radiology, Cliniques
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of
 Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
Adress correspondence and reprint requests to Hyun Seok Song, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, St.Paul s Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea 620-56 Jeonnong-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul, Korea
HAGL lesion of the shoulder
 HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
HAGL lesion of the shoulder A 24 year old rugby player presented to an orthopaedic surgeon with a history of dislocation of the left shoulder. It reduced spontaneously and again later during the same match.
Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when?
 Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when? Kolo Frank Lesions to scapholunate ligament(sl) Most frequent cause of carpal instability Traumatic tears of SL ligament = most common ligament injury
Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when? Kolo Frank Lesions to scapholunate ligament(sl) Most frequent cause of carpal instability Traumatic tears of SL ligament = most common ligament injury
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries
 MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
MRI grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate ligament injuries Poster No.: C-2533 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Lopes Dias, J. A. Sousa Pereira, L. Fernandes,
Case Report Supraspinatus Intramuscular Calcified Hematoma or Necrosis Associated with Tendon Tear
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 496313, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/496313 Case Report Supraspinatus Intramuscular Calcified Hematoma or Necrosis Associated with Tendon Tear
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 496313, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/496313 Case Report Supraspinatus Intramuscular Calcified Hematoma or Necrosis Associated with Tendon Tear
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation
 Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Superior Labrum Anterior Posterior lesions: ultrasound evaluation Poster No.: C-0472 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Belyaev; Yaroslavl/RU Keywords: Trauma, Arthrography, Ultrasound,
Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder instability
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0027-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2008) 9:187 193 DOI 10.1007/s10195-008-0027-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Virtual MR arthroscopy of the shoulder: image gallery with arthroscopic correlation of major pathologies in shoulder
Sensitivity of Physical Examination Versus Arthroscopy in Diagnosing Subscapularis Tendon Injury
 Sensitivity of Physical Examination Versus Arthroscopy in Diagnosing Subscapularis Tendon Injury Sami Faruqui, BS; Coen Wijdicks, PhD; Abdullah Foad, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
Sensitivity of Physical Examination Versus Arthroscopy in Diagnosing Subscapularis Tendon Injury Sami Faruqui, BS; Coen Wijdicks, PhD; Abdullah Foad, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries
 What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
What is the most effective MRI specific findings for lateral meniscus posterior root tear in ACL injuries Kazuki Asai 1), Junsuke Nakase 1), Kengo Shimozaki 1), Kazu Toyooka 1), Hiroyuki Tsuchiya 1) 1)
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears. Rafael M. Williams, MD
 Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Massive Rotator Cuff Tears Rafael M. Williams, MD Rotator Cuff MRI MRI Small / Partial Thickness Medium Tear Arthroscopic View Massive Tear Fatty Atrophy Arthroscopic View MassiveTears Tear is > 5cm
Is ultrasonographic evaluation of rotator interval useful in diagnosis of adhesive capsulitis of shoulder?
 Is ultrasonographic evaluation rotator interval useful in diagnosis adhesive capsulitis shoulder? Poster No.: C-2230 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: Y. C. Yoon, J. M. Seo, H. S. Kim,
Is ultrasonographic evaluation rotator interval useful in diagnosis adhesive capsulitis shoulder? Poster No.: C-2230 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: Y. C. Yoon, J. M. Seo, H. S. Kim,
Temporal Evolution of MRI Findings After Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Crim et al. MRI of Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Julia Crim 1,2 Robert Burks 2 Betty J. Manaster 1 Christopher Hanrahan
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Crim et al. MRI of Arthroscopic Rotator Cuff Repair Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Julia Crim 1,2 Robert Burks 2 Betty J. Manaster 1 Christopher Hanrahan
