Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging
|
|
|
- Daniel Carpenter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Demonstration of evolution of hemispherical spondysclerosis by contrast enhanced Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging Vladimir Jevtič 1, Natalija Majcen 2 1 Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical Centre Ljubljana, Slovenia; 2 Radiologica Department, General Hospital Ptuj, Slovenia Background. The purpose of the study was to estimate the value of Gd-DTPA magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in demonstrating the evolution of hemispherical spondylosclerosis (HSS). Patients and methods. In eighteen patients with chronic low back pain and typical radiographic findings of HSS seen on plain films, Gd-DTPA MRI of the lumbar spine was performed. MRI morphological and signal intensity appearances of HSS were analysed and compared with radiographic changes. Results. On the basis of MRI features, three distinct groups of cases were identifiable. Within the first group the region of dome-shaped osteosclerosis demonstrated low signal intensity on T1-weighted precontrast spin-echo images, high signal intensity on T2-weighted images and diffuse contrast enhancement on T1-weighted postcontrast images, findings compatible with bone marrow oedema and hyperaemia. The second group showed high signal intensity vertebral body corners surrounded by low signal intensity area, which indicated the combination of fat accumulation and the sclerotic bone. In the third intermediate group anterior disco-vertebral junctions revealed a mixture of MRI appearances characteristic of the first and the second group. Conclusions. Gd-DTPA MRI is capable of demonstrating a spectrum of features which reflect the evolution of HSS. These typical appearances showed by MRI could be of eventual clinical relevance in following the progression of HSS. Key words: spinal diseases; magnetic resonance imaging; gadolinium DTPA; osteosclerosis Introduction The term HSS was used by Dihlmann 1 to describe a peculiar form of localised erosive Received 3 November 2004 Accepted 18 November 2004 Correspondence to: Prof. Vladimir Jevtič, MD, Clinical Radiology Institute, University Clinical Centre, Zaloška 7, SI-1525 Ljubljana, Slovenia; Phone/Fax: ; vladimir.jevtic@mf.uni-lj.si spondylopathy with well defined radiographic findings. The most typical features include dome-shaped osteosclerosis which usually affects the anteroinferior portion of the vertebral body with the base at the endplate. Commonly, similar appearances are seen in the neighbouring vertebra. Narrowing of the corresponding disc space indicating disc degeneration is present in the majority of cases. There is a predilection for L4, L5 and L3 vertebral bodies and the toracolumbar junction.
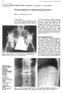
2 276 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis HSS mainly affects middle-aged women and is clinically characterized by chronic low back pain. Since its first description in literature as nonneoplastic scleroses, 2 different terms like traumatic lesion of the disco-vertebral junction, 3 discogenic vertebral scleroses, 4 idiopathic segmental sclerosis 5 have been used to indicate the possible aetiology of the disease entity. However, the exact aetiology and pathogenesis of HSS still remains uncertain. Experience with MRI of this condition, especially with the use of paramagnetic contrast agents is limited. 6,7 The purpose of this study was to investigate the morphological and signal intensity MRI appearances of HSS, to compare these features with the conventional radiography and to estimate the value of Gd-DTPA MRI in demonstrating the evolution of HSS. Patients and methods 18 patients (12 women, 6 men, mean age 45 years) with radiographic findings typical of HSS seen on AP and lateral plain films of the lumbar spine were selected for the study. In 5 patients, lateral conventional tomograms were also available. In order to be included in the study, the radiographs were required to demonstrate dome-shaped osteosclerosis with the base at the intervertebral disc affecting the anterior part of the vertebral body. Other radiographic findings which were also noted included bone erosions of the endplate at the base of sclerosis, new bone production along the anterior vertebral body contour, the presence of an anterior ostephyte and the disc space narrowing. 1 Additional inclusion criteria were chronic low back pain and normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate. In six patients, the exacerbation of low back pain was registered during the last several weeks. MRI of the lumbar spine was performed on a 1.5 T superconducting scanner (Magnetom, Siemens) one to three weeks after plain films. A spin-echo sequence with T1W images (TR 500 ms, TE 15 ms, 2 averages) and T2W images (TR 1900 ms, TE 80 ms, 2 averages) was used, followed by the postcontrast examination immediately after Gd-DTPA (0.1 mmol / kg body weight) was injected intravenously as a bolus through a cannula. The field of view was 28 cm with a data acquisition matrix of 256 x 256. The region of the lumbar spine was presented in a sagittal plane with 5 mm thick consecutive slices. The axial images of the intervertebral discs and the neighbouring parts of the vertebral bodies were obtained at the levels of HSS seen on plain films. Conventional radiographs and MR images were analysed in a qualitative fashion for morphological and signal intensity differences between normal and pathological disco-vertebral junctions. On the basis of MRI features, an attempt has been made to reconstruct the eventual evolution of HSS. Results Three distinct MRI patterns of disco-vertebral junction abnormalities were found at the levels of HSS seen on the plain film radiography. Within the first group of three patients the region of dome-shaped osteosclerosis demonstrated low signal intensity on T1-weighted precontrast images, high signal intensity on T2-weighted images and a diffuse intense contrast enhancement on T1-weighted postcontrast images. There was also focal Gd-DT- PA accumulation within the endplate erosions at the base of sclerosis. In one of the patients, these typical MRI appearances were seen at the anterosuperior part of the vertebral body L5 while the neighbouring anteroinferior part of the vertebral body of L4 showed MRI findings characteristic of the second group (Figures 1a, 1b, 1c). The second group comprised five patients with MRI features of high signal intensity an-
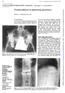
3 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis 277 Figure 1a. Initial HSS of the vertebral bodies L4 and L5. Lateral conventional tomography shows discrete osteosclerosis of the vertebral body L4 and typical erosions affecting the anterior thirds of the endplates at the levels of L4 and L5 (big arrow heads). terior portions of the vertebral bodies on T1- weighted precontrast and T2- weighted images surrounded by a band-like low signal intensity area. No contrast enhancement could be registered within the region HSS of (Figures 2a, 2b, 2c). The accumulation of paramagnetic contrast agent within the endplate erosions was seen in four of these patients. In one of the cases, typical MRI changes developed during the six months following a disc surgery. In the remainder of the twelve patients, disco-vertebral junctions demonstrated heterogenous MRI appearances which represented a mixture of signal intensity changes and morphological findings from the first and the second group (Figure 3). A focal contrast enhancement was seen within the erosions of Figure 1b. T1 - weighted sagittal (TR 500 ms, TE 15 ms) precontrast image reveals high signal intensity anteroinferior part of the vertebral body L4, findings consistent with fat accumulation (big arrow head) and low signal intensity anterosuperior part of the vertebral body L5 indicating bone marrow oedema (small arrow heads). Note also that the erosion of the vertebral body L4 is sharply corticated while the erosion at the level of L5 shows indistinct contour. the vertebral body endplates. In two of the patients from this intermediate group, MRI showed the posterior disc herniation and in one the presence of ischemic spondylolysis localised at the same level as HSS. The erosions of the vertebral body endplates typically localised at the anterior junctions of the peripheral bone rim and the cartilaginous endplate (Figures 3a, 3b, 3c, 3d, 3e) were identified by MRI in all of the patients. In three cases the erosions were not seen on the plain films. With the exception of six patients belonging to the first and the third group, in whom indistinct cortical bone was
4 278 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis Figure 1c. T1-weighted sagittal postcontrast image demonstrates contrast accumulation within the region of bone marrow oedema of the vertebral body L5 and within the endplate erosions (small arrow heads). revealed (Figure 1); in the rest of the vertebral bodies the erosions were clearly corticated. Additional erosions localised more dorsally were demonstrated in two patients from the second and six from the third group (Figures 4a, 4b, 4c). Varying amounts of new bone production along the anterior vertebral body contour contiguous with the anterior ostephytes (Figure 4) were revealed on the plain films in patients from all three groups. However, the signal intensity MRI appearances of the periosteal apposition differed between the groups. Within the first and the second group new bone production was of low signal intensity on T1-weighted precontrast images and of high signal intensity on T2-weighted and T1- weighted postcontrast images (Figures 3, 4). Figure 2a. HSS following disc surgery at the level of L4-L5. Lateral plain film with typical radiographic findings. Similar findings were revealed in one case from the third group, while the rest demonstrated the linear high signal intensity area along the anterior surface of the vertebral bodies on all MRI sequences (Figure 2). The anterior ostephytes were more pronounced in patients from the second and the third group. Their signal intensity characteristics were similar to MRI features of the neighbouring vertebral body bone marrow. At the level of HSS an absence of normal high signal intensity on T2-weighted images affecting the anterior part or the whole disc space indicating disc degeneration was revealed in all of our patients with the exception of focally increased signal intensity within the bone erosions.
5 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis 279 Figure 2b. T1-weighted sagittal (TR 500 ms, TE 15 ms) image reveals high signal intensity fat conversion within the bone marrow and the ostephytes (big arrow heads) surrounded by low signal intensity sclerotic bone (small arrow heads). Discussion The exact aetiology and evolution of HSS is not completely clear. Therefore, different terms indicating possible aetiology or radiographic features have been applied to this entity. 1-5 In comparison to other radiological techniques, MRI proved to have a unique ability not only to present an excellent anatomical image but also to reflect closely pathophysiological and pathoanatomical changes in different osteoarticular diseases. The experience with MRI of HSS is limited 6,7 especially with the use of paramagnetic contrast agent GD-DTPA and no detailed description of the eventual evolution of MRI changes has been made. Figure 2c. T1-weighted postcontrast sagittal image shows minute contrast enhancement within the endplate erosion (small arrow head). There is no contrast accumulation within the vertebral bodies and the ostephytes. MRI findings of low signal intensity on T1- weighted spin-echo images and of high signal intensity on T2-weighted images within the area of bone sclerosis seen in the patients from the first group (Figure 1) have already been reported. 6,7 In addition we were able to demonstrate a marked contrast enhancement affecting the same region. These MRI features were compatible with the presence of bone marrow oedema and hyperaemia. With the exception of different distribution, which has been focal in HSS and widespread in early degenerative disc disease, there was an obvious resemblance in MRI appearances between described changes in HSS and Modic I lesions 8 in which the existence of fibrovascular tissue below the vertebral body endplates was
6 280 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis Figure 3a. HSS at the level of L4-L5 disc. Lateral radiograph shows osteosclerosis affecting the anterior parts of the vertebral bodies (small arrow heads), erosions of the endplates (big arrow heads) and periosteal apposition at the anterior contour of the vertebral body L4 (arrow). proved histologically. Furthermore, we showed similar focal MRI findings at the anterior disco-vertebral junctions in patients with ankylosing spondylitis, having early Romanus lesions. 9 Some histological studies proved that the bone erosions of the vertebral bodies at the attachment of the annulus fibrosus in spondylitis anterior were occupied by the vascularised granulation tissue. 10,11 Within the so-called Type a localised discovertebral destructive lesions, which radiographically resemble HSS, Cawley et al 12 revealed a peripheral focal infiltration by cartilaginous and fibrous tissue, new bone deposition with thickened trabeculae and oedematous bone marrow, histological evidence of trauma with persistent pressure. These similar histological and MRI appearances seen in various disco-vertebral lesions are evidently nonspecific phenomena and reflect the limited reactive abilities of the osteoarticular system to etiologically different joint diseases. Figure 3b. T1-weighted sagittal (TR 500 ms, TE 15 ms) precontrast image reveals nonhomogenous low signal intensity anterior parts of the vertebral bodies L3, L4 and L5 and the erosions of the endplates (small arrow heads). Within the second group of patients, high signal intensity anterior portions of the vertebral bodies on T1-weighted precontrast and T2-weighted images, surrounded by a bandlike low signal intensity area without contrast enhancement on T1-weighted postcontrast images indicated a bone marrow fat conversion combined with a sclerotic bone (Figure 2) nonspecific reaction which has also been described in longstanding disc degeneration 8 or advanced nonactive sacroiliitis. 13 The most numerous was the third intermediate group of cases in which a combination of signal intensity changes and varying degrees of contrast enhancement represented a mixture of MRI appearances characteristic of the first and the second group. MRI features within the anterior parts of the vertebral bodies were compatible with a combination of
7 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis 281 Figure 3c. T2-weighted sagittal (TR 1900 ms, TE 80 ms) image demonstrates widespread high signal intensity bone marrow oedema (big arrow heads) surrounding low signal intensity osteosclerosis (small arrow heads). Figure 3d. T1-weighted sagittal postcontrast image shows diffuse contrast enhancement within the vertebral bodies (big arrow heads) and linear enhancement within the endplate erosions and along the anterior surface of the vertebral body L4 (small arrow heads). bone marrow oedema and hyperaemia, fat accumulation and sclerotic bone (Figure 3). The distribution of these changes within the individual vertebral bodies suggested the possibility that the initial bone marrow oedema at the vertebral body margins has been progressively replaced by fatty and sclerotic bone marrow, findings similar to those seen in progressive disc degeneration. 8 The reported incidence of the endplate erosions in HSS varies. 1,4 In three of our patients the erosions were not identified on the plain films. However, with the use of MRI as a tomographic method, they were demonstrated in all the cases. This finding supports the opinion of some authors that the anterior defect of the vertebral body endplate represents the initial lesion 1,14 and that the common feature in HSS is the herniation of disc material into the vertebral body 4 which might be provoked by the subclinical endplate trauma. 3 The fact that the erosions were not clearly corticated in several of the patients from the first and the third group while the majority of cases from the third and all from the second group showed corticated erosions, suggests the possibility of advancing process of cortical healing. Gd-DTPA contrast accumulation within the erosion was consistent with the histological findings of the focal replacement of the disc and the disc-bone border by vascularised fibrous tissue in peripheral disco-vertebral destructive lesions reported by Cawley et al. 12 The frequent location of HSS at the lumbosacral and the toracolumbar junctions has
8 282 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis Figure 3e. T1-weighted axial postcontrast image at the level of the lower endplate of L4 demonstrates distribution of bone erosions (big arrow heads) at the border between the epiphyseal ring and the cartilage endplate. been attributed to the increased stress at these levels produced by the transition of a mobile to a fixed part of the axial skeleton. It has been postulated that the increase in the segmental mobility due to tears affecting the periphery of the intervertebral disc causes the overstretching of the anterior longitudinal ligament and provoke the osteoblastic production of the marginal osteophytes. 1 Indeed high signal intensity of the new bone production and of the contiguous ostephytes on T2- weighted and T1-weighted postcontrast images (Figures 3, 4) consistent with the presence of oedema and hyperaemia may indicate the instability of the corresponding vertebral dynamic segment. On the other hand, the organized periosteal apposition and marginal ostephytes of high signal intensity on all MRI sequences (Figure 2), due to a fat transformation, presumably represent the end stage of Figure 4a. Disc degeneration at the level of L4-L5 with HSS affecting the anteroinferior part of the vertebral body L4. Lateral radiograph shows dome-shaped osteosclerosis (small arrow heads), an anterior erosion of the endplate (big arrow head) and periosteal apposition along the anterior surface of the vertebral body (arrow). stabilization of abnormally mobile vertebral segments at the level of HSS. The clinical relevance of different MRI features in HSS is not clear. Modic et al 8 suggested the possibility that early disc degenerative changes with the presence of subchondral bone marrow oedema might be symptomatic. Stäbler et al 15 showed that the Schmorl s nodes with adjacent bone marrow oedema were seen more frequently in symptomatic than in asymptomatic patients. It would seem therefore that the cases of HSS surrounded by widespread bone marrow oedema could eventually represent symptomatic or»active«lesions. It is of interest to note that all six patients with recent exacer-
9 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis 283 Figure 4b. T1-weighted sagittal (TR 450 ms, TE 15 ms) precontrast image demonstrates high signal intensity fat accumulation within the region of sclerosis seen on the plain film (small arrow heads). Note several erosions of the lower endplate of L4 (big arrow heads). Figure 4c. T1-weighted Gd-DTPA postcontrast sagittal image reveals linear contrast enhancement at the anterior contour of vertebral body L4, the anterior part of the annulus fibrosus L4-L5 (small arrow heads) and within the endplate erosions (big arrow heads). There is no contrast accumulation in the region of osteosclerosis. bation of low back pain belonged to the first and the second groups in which varying amounts of bone marrow oedema and hyperaemia were demonstrated by MRI. Analogously, it can be assumed that the cases of HSS similar to Modic II lesions 8 seen within the second group of our patients are presumably less symptomatic or»nonactive«. Although the lack of histology in our study precludes definite conclusions on the basis of the histological results of others 3,4,7,8,10-12 and according to MRI appearances in our patients the eventual evolution of HSS could be postulated. The findings are in favour of the theory that the initial lesion could be anterior erosion at the junction between the epiphyseal ring and the cartilage endplate 1,3,4,14 followed by the instability of the corresponding vertebral dynamic segment. Due to a compromised vertebral body integrity and resulting instability, the bone underlying erosion is exposed to a persistent pressure, which similarly to the initial disc degeneration provokes bone marrow oedema and hyperemia. 8 The process of repair resembling healing of the fracture 12 ensues, characterized by the ingrowth of vascular fibrous tissue into the erosion and the vertebral body and consecutive new bone production within the bone and along its anterior surface. A favourable outcome may eventually result in which the cortication of the endplate erosion, the reinforcement of the vertebral body in the form of bone sclerosis and the anterior disco-vertebral junction shown as the organized periosteal apposition and marginal osteophytes lead ultimately to the spontaneous stabilization of the corresponding vertebral dynamic segment. In cases with an unfavourable outcome the instability persists and may eventually be followed by new bone erosions and the progressive disc degeneration. In our study, MRI proved to be a sensitive indicator of these complex dynamic changes. It is concluded that GD-DTPA MRI is capable of demonstrating the evolution of HSS. It seems to enable the differentiation of a spectrum, including the initial phase characterized by a compromised integrity of the anterior endplate, followed by the intermediate phase of reactive changes, leading finally to the stabilization of the abnormally mobile vertebral dynamic segment. MRI appearances could be of eventual clinical relevance in following the progression of HSS.
10 284 Jevtič V and Majcen N / MRI of hemispherical spondylosclerosis References 1. Dihlmann W. Hemispherical spondylosclerosis-a polyetiologic syndrome. Skeletal Radiol 1981; 7: Ackerman W, Schwarz GS. Nonneoplastic sclerosis in vertebral bodies. Cancer 1958; 11: Stäbler A, Bellan M, Weiss M, Gartner C, Brossmann J, Reiser MF. MR imaging of enhacing intraosseous disk herniations (Shmorl s nodes). AJR 1997; 168: Herbsthofer B, Eysel P, Eckardt A, Humke T. Diagnostik und therapie der erosiven osteochondrosis intervertebralis. Zeitschrift fur Orthopadie und Ihre Grenzgebiete 1996; 134(5): Martel W, Seeger JF, Wicks JD, Washburn RL. Traumatic lesions of the discovertebral junction in the lumbar spine. Am J Roentgenol 1976; 127: Sauser DD, Godman AB, Kaye JJ. Discogenic vertebral sclerosis. J Can Assoc Radiol 1978; 29: McCarthy EF, Dorfman HD. Idiopathic segmental sclerosis of vertebral bodies. Skeletal Radiol 1982; 9: Sobel DF, Zyroff J, Thorne RP. Discogenic vertebral sclerosis: MR imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1987; 11(5): Jensen ME, Hayes CW, DeBlois GG, Laine FJ. Hemispherical spondylosclerosis: MR appearance. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1989; 13(3): Modic MT, Masaryk TJ, Ross JS, Carter RJ. Imaging of degenerative disc disease. Radiology 1988; 168: Jevtic V, Rozman B, Kos-Golja M, Watt I. MR- Bildgebung bei Seronegativen Spondyloarthritiden. Radiologe 1996; 36: Baggenstoss AH, Bickel WH, Ward LE. Rheumatoid granulomatous nodules as destructive lesions of vertebrae. J Bone Joint Surg 1952; 34A: Ball J. Entheshopathy of rheumatoid and ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Disease 1971; 30: Cawley MID, Chalmers TM, Kellgren JH, Ball J. Destructive lesions of vertebral bodies in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Disease 1972; 31: Ahlström H, Feltelius N, Nyman R, Hšllgreen R. Magnetic resonance imaging of sacroiliac joint inflammation. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1990; 33: Resnick D, Niwayama G. Segmental sclerosis of vertebral bodies. In: Resnick D,editor. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. Philadelphia: W. B. Saundres; p
Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 984; 43, 3-37 Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine R. C. HILTON AND J. BALL From the Department of Rheumatology, Hope Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY The frequency,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 984; 43, 3-37 Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine R. C. HILTON AND J. BALL From the Department of Rheumatology, Hope Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY The frequency,
Vertebral sclerosis in adults
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist. Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation
 Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
Vacuum phenomenon in computed tomography - fluid signal in MRI: a correlative study of degenerative disc disease
 Vacuum phenomenon in computed tomography - fluid signal in MRI: a correlative study of degenerative disc disease Poster No.: C-1570 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. D'Anastasi, C.
Vacuum phenomenon in computed tomography - fluid signal in MRI: a correlative study of degenerative disc disease Poster No.: C-1570 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: M. D'Anastasi, C.
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PREVALENCE OF MODIC DEGENERATIVE MARROW CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PREVALENCE OF MODIC DEGENERATIVE MARROW CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 prevalence of modic degenerative marrow changes in the cervical spine prevalence
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PREVALENCE OF MODIC DEGENERATIVE MARROW CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 prevalence of modic degenerative marrow changes in the cervical spine prevalence
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
8/4/2012. Causes and Cures. Nucleus pulposus. Annulus fibrosis. Vertebral end plate % water. Deforms under pressure
 Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Contiguous Spinal Metastasis Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Spinal infection. Outline ANATOMY 6/2/2017. Anatomy Pathogen
 Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate
 Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache
 Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
End Plate Heat Injury after Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD) in the Lumbar Spine: MR imaging and Pathological Correlation
 End Plate Heat Injury after Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD) in the Lumbar Spine: MR imaging and Pathological Correlation Kosaka, Riya 1 ; Kobayashi, Shigeru 2, ; Yonezawa, Takumi 3 Orthopedic
End Plate Heat Injury after Percutaneous Laser Disc Decompression (PLDD) in the Lumbar Spine: MR imaging and Pathological Correlation Kosaka, Riya 1 ; Kobayashi, Shigeru 2, ; Yonezawa, Takumi 3 Orthopedic
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
MR Imaging of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine. Acknowledgements 3/3/2016 MRI
 MR Imaging of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine Gina A. Ciavarra Assistant Professor of Radiology NYU-Langone Medical Center 4/1/2016 Acknowledgements Thank you to Leon Rybak, M.D. and Michael Mechlin, M.D.,
MR Imaging of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine Gina A. Ciavarra Assistant Professor of Radiology NYU-Langone Medical Center 4/1/2016 Acknowledgements Thank you to Leon Rybak, M.D. and Michael Mechlin, M.D.,
Facet Joint Arthrosis Disc Degeneration and Lumbago. Dr.Ruchira Sethi Dr. Vishram Singh Department of Anatomy Santosh University, India
 Facet Joint Arthrosis Disc Degeneration and Lumbago Dr.Ruchira Sethi Dr. Vishram Singh Department of Anatomy Santosh University, India INTRODUCTION The initial division of spine into three columns for
Facet Joint Arthrosis Disc Degeneration and Lumbago Dr.Ruchira Sethi Dr. Vishram Singh Department of Anatomy Santosh University, India INTRODUCTION The initial division of spine into three columns for
Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002
 Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002 MICHAEL D. MARTIN, M.D., CHRISTOPHER M. BOXELL, M.D., F.A.C.S., AND DAVID G. MALONE, M.D. FROM
Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002 MICHAEL D. MARTIN, M.D., CHRISTOPHER M. BOXELL, M.D., F.A.C.S., AND DAVID G. MALONE, M.D. FROM
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior Endplate Lesion after Recurrent Disc Herniation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after competition
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:72 76 International Skeletal Society 2001 ARTICLE W. Krampla R. Mayrhofer J. Malcher K.H. Kristen M. Urban W. Hruby MR imaging of the knee in marathon runners before and after
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004?
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS: WHAT REMAINS OF THE STANDARD RADIO- GRAPHY ANNO 2004? V. Lambrecht, F.M. Vanhoenacker, P. Van Dyck, J. Gielen, P.M. Parizel 1 In this review, the radiographic features of ankylosing
Artificial intervertebral disc
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Artificial intervertebral disc Vikas Ghai Medical University of Ohio Follow this and additional works
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Artificial intervertebral disc Vikas Ghai Medical University of Ohio Follow this and additional works
Case Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case.
 Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
709 BRIEF REPORT RHEUMATOID NODULES OF THE SPINE: CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE MARK E. PEARSON, MARY KOSCO, WILLIAM HUFFER, WILLIAM WINTER, JAMES A. ENGELBRECHT, and JAMES C. STEIGERWALD We
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when?
 Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when? Kolo Frank Lesions to scapholunate ligament(sl) Most frequent cause of carpal instability Traumatic tears of SL ligament = most common ligament injury
Scapholunate Ligament Lesions Imaging Which and when? Kolo Frank Lesions to scapholunate ligament(sl) Most frequent cause of carpal instability Traumatic tears of SL ligament = most common ligament injury
RETROLISTHESIS. Retrolisthesis. is found mainly in the cervical spine and lumbar region but can also be often seen in the thoracic spine
 RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications
 Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury
 Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
The spinal vacuum sign or vacuum phenomenon. Is a Persistent Vacuum Phenomenon a Sign of Pseudarthrosis After Posterolateral Spinal Fusion?
 An Original Study Is a Persistent Vacuum Phenomenon a Sign of Pseudarthrosis After Posterolateral Spinal Fusion? Arjun A. Dhawale, MD, Steven Falcone, MD, Barth A. Green, MD, and Nathan H. Lebwohl, MD
An Original Study Is a Persistent Vacuum Phenomenon a Sign of Pseudarthrosis After Posterolateral Spinal Fusion? Arjun A. Dhawale, MD, Steven Falcone, MD, Barth A. Green, MD, and Nathan H. Lebwohl, MD
Outline. Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures
 C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
C-Spine Plain Films Outline Epidemiology Indications for C-spine imaging Modalities Interpretation Types of fractures Epidemiology 7000-10000 c-spine injuries treated each year Additional 5000 die at the
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings
 Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging
 Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Assissment of Extradural Degenerative Disease with Gd DTPA-Enhanced MR Imaging: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Findings
 1243 ssissment of Extradural Degenerative Disease with Gd DTP-Enhanced MR Imaging: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Findings - - ' \. l JeffreyS. Ross 1 Michael T. Modic 1 Thomas J. Masaryk 1 John
1243 ssissment of Extradural Degenerative Disease with Gd DTP-Enhanced MR Imaging: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Findings - - ' \. l JeffreyS. Ross 1 Michael T. Modic 1 Thomas J. Masaryk 1 John
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Zi-Xuan Wang 1* and You-Gu Hu 2
 Wang and Hu Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:307 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1010-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Factors associated with lumbar disc highintensity zone (HIZ)
Wang and Hu Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2018) 13:307 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-1010-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Factors associated with lumbar disc highintensity zone (HIZ)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary?
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Ross JS, Brant-Zawadzki M, et al. Diagnostic Imaging: Spine 2004; V-1-5. Greenspan A. Orthopedic Radiology: A Practical Approach 1997; V-19-3
 MR Imaging of Spinal Infections 台大醫院 台大醫學院 影像醫學部 放射線科 許昭禹醫師 / 施庭芳主任 2009/02/14 Risk factors of spinal infections Advanced age > 50 Intravenous drug abuse Immunosuppression or immune deficiency Long-term
MR Imaging of Spinal Infections 台大醫院 台大醫學院 影像醫學部 放射線科 許昭禹醫師 / 施庭芳主任 2009/02/14 Risk factors of spinal infections Advanced age > 50 Intravenous drug abuse Immunosuppression or immune deficiency Long-term
Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography
 Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Correlation Between Vacuum Phenomenon on CT and Fluid on MRI in Degenerative Disks
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research D Anastasi et al. Vacuum Phenomenon on CT and Fluid on MRI of Degenerative Disks Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Melvin D Anastasi 1 Christof Birkenmaier
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research D Anastasi et al. Vacuum Phenomenon on CT and Fluid on MRI of Degenerative Disks Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Melvin D Anastasi 1 Christof Birkenmaier
Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients
 Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
Dynamic Chiropractic October 21, 2010, Vol. 28, Issue 22 Musculoskeletal Development and Sports Injuries in Pediatric Patients By Deborah Pate, DC, DACBR Physical activity is extremely important for everyone,
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis
 SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
 SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1873 1878 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Christian W. A. Pfirrmann, MD,* Alexander
SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1873 1878 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Christian W. A. Pfirrmann, MD,* Alexander
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
The Role of Two-Dimensional Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Protrusion of Cervical Intervertebral Discs in Adolescents
 American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2017; 5(5): 176-180 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajcem doi: 10.11648/j.ajcem.20170505.14 ISSN: 2330-8125 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8133 (Online)
American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2017; 5(5): 176-180 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajcem doi: 10.11648/j.ajcem.20170505.14 ISSN: 2330-8125 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8133 (Online)
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Lumbosacral Transitional Vertebrae
 Lumbosacral Transitional Vertebrae Poster No.: C-073 Congress: ECR 206 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Mustapic, R. Vukojevi#, M. Gulin, D. Marjan, I. Boric ; 2 2 Zagreb/HR, Zabok/HR Keywords: Congenital,
Lumbosacral Transitional Vertebrae Poster No.: C-073 Congress: ECR 206 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Mustapic, R. Vukojevi#, M. Gulin, D. Marjan, I. Boric ; 2 2 Zagreb/HR, Zabok/HR Keywords: Congenital,
3 Sternoclavicular Joints
 3 Sternoclavicular Joints Anne Grethe Jurik and Flemming Brandt Soerensen 29 Contents 3.1 Introduction.......................................................... 29 3.2 Macroscopic Anatomy.................................................
3 Sternoclavicular Joints Anne Grethe Jurik and Flemming Brandt Soerensen 29 Contents 3.1 Introduction.......................................................... 29 3.2 Macroscopic Anatomy.................................................
Sciatica in degenerative spondylolisthesis of the
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 539-543 539 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series editor: V N Cassar-Pullicino* Sciatica in degenerative spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine S Maheshwaran,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 539-543 539 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series editor: V N Cassar-Pullicino* Sciatica in degenerative spondylolisthesis of the lumbar spine S Maheshwaran,
IMAGING FINDINGS OF GAUCHER DISEASE IN ALL OVER THE BODY
 IMAGING FINDINGS OF GAUCHER DISEASE IN ALL OVER THE BODY V. Katsaros 1, P. Lampropoulou 2, M. Mitropoulou 1, A. Nikolaou 1, C. Drossos 2 Departments of CT and MRI 1 IKA Oncology Hospital and 2 Athens General
IMAGING FINDINGS OF GAUCHER DISEASE IN ALL OVER THE BODY V. Katsaros 1, P. Lampropoulou 2, M. Mitropoulou 1, A. Nikolaou 1, C. Drossos 2 Departments of CT and MRI 1 IKA Oncology Hospital and 2 Athens General
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging
 Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic resonance imaging study evidence
 See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
See the Editorial and the Response in this issue, p 1. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 100:2 6, 2004 Accelerated spondylotic changes adjacent to the fused segment following central cervical corpectomy: magnetic
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending
 A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending William Anderst, Mara Palmer, Joon Lee, William Donaldson, James
A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending William Anderst, Mara Palmer, Joon Lee, William Donaldson, James
Imaging of Articular Cartilage
 Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
To review the mechanisms, characteristics and diagnostic roles of fatsuppressed water bright magnetic resonance images such as short tau
 Differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic vertebral and paravertebral disorders with increased signal intensity on short tau inversion recovery (STIR) or fat-suppressed T2weighted images Poster No.: C-1375
Differential diagnosis of non-neoplastic vertebral and paravertebral disorders with increased signal intensity on short tau inversion recovery (STIR) or fat-suppressed T2weighted images Poster No.: C-1375
MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Moderate to Severe Ankylosing Spondylitis
 MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
3 脊椎変形の相互関係とリスク分析の今後の方向
 Reprint request: DEGENERATIVE SPINE AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN ELDERLY PEOPLE Toshitaka NAKAMURA Department of Orthopedics, University of Occupational and Environmental Health School of Medicine Vertebral osteophytes,
Reprint request: DEGENERATIVE SPINE AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN ELDERLY PEOPLE Toshitaka NAKAMURA Department of Orthopedics, University of Occupational and Environmental Health School of Medicine Vertebral osteophytes,
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
Spinal Imaging. ssregypt.com. Mamdouh Mahfouz MD
 Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis
 What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis Poster No.: C-2383 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Gutierrez, V. Familiar
What rheumathologist expect from radiologist in spinal MRI studies: Imaging findings in Spondiloarthritis Poster No.: C-2383 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Gutierrez, V. Familiar
Degenerative Disc Disease. Nafi Aygun, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology
 Degenerative Disc Disease Nafi Aygun, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Big Problem Great majority of adults suffer from at least one episode of acute low back pain during life time Disc degeneration
Degenerative Disc Disease Nafi Aygun, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Big Problem Great majority of adults suffer from at least one episode of acute low back pain during life time Disc degeneration
Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy
 Original Article Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27541:2282 Radiology Section Mallikarjun MD, Chetan
Original Article Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27541:2282 Radiology Section Mallikarjun MD, Chetan
IMAGISTICÃ. Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of spinal injury
 IMGISTICÃ Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of spinal injury NICOLE OLOG, M.D., IRINEL ONCE, M.D. Radiology & Imaging Department, ucharest Emergency Clinical Hospital uthor for correspondence: NICOLE
IMGISTICÃ Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of spinal injury NICOLE OLOG, M.D., IRINEL ONCE, M.D. Radiology & Imaging Department, ucharest Emergency Clinical Hospital uthor for correspondence: NICOLE
