MR Imaging of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine. Acknowledgements 3/3/2016 MRI
|
|
|
- Lambert Paul
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MR Imaging of the Degenerative Lumbar Spine Gina A. Ciavarra Assistant Professor of Radiology NYU-Langone Medical Center 4/1/2016 Acknowledgements Thank you to Leon Rybak, M.D. and Michael Mechlin, M.D., Department of Radiology, NYU-Langone Medical Center MRI Pros Exquisite bone and soft tissue detail (including disks, ligaments, nerves) Very sensitive for subtle and early abnormalities (e.g. occult fracture, early stress injury, tumor, infection) IV gadolinium assists in evaluating soft tissue and osseous pathology Multiplanar Can directly evaluate disk and ligament pathology Cons Expensive, not readily available Sensitive but sometimes not specific Operator and equipment dependent Time consuming (not for acute trauma or large body parts) Important contraindications (PPM, neurostimulators, cochlear implants, CLAUSTROPHOBIA) Degraded by minimal patient motion, susceptible to artifact (gas, metal newer metal-reducing protocols), gadolinium cannot be used as widely as previously thought (NSF, allergies) 1
2 T1 = TR*, TE* T2 = TR, TE PD = TR, TE TR Low 1000 High 2000 TE High 60 Low 30 MRI Fundamentals TR TE T1 T2 TR = Time to repetition TE = Time to excitation PD T1 = Anatomic weighting Fat is bright T2 = Pathology weighting Water is bright PD = combination MRI Fundamentals MRI Basic Planes Axial 2
3 MRI Basic Planes Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Basic Protocols Lumbar spine Sagittal and axial T1 Marrow evaluation Neural foramina Fat around nerve roots Ligamentum flavum Facets Sagittal and axial T2 Myelographic effect - thecal sac Central nerve roots Marrow edema Magnetic Resonance Imaging Basic Protocols Lumbar spine Sagittal and axial T1 Marrow evaluation Neural foramina Fat around nerve roots Ligamentum flavum Facets Sagittal and axial T2 Myelographic effect - thecal sac Central nerve roots Marrow edema 3
4 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Basic Protocols Lumbar spine Sagittal and axial T1 Marrow evaluation Neural foramina Fat around nerve roots Ligamentum flavum Facets Sagittal and axial T2 Myelographic effect - thecal sac Central nerve roots Marrow edema Magnetic Resonance Imaging Basic Protocols Lumbar spine Sagittal and axial T1 Marrow evaluation Neural foramina Fat around nerve roots Ligamentum flavum Facets Sagittal and axial T2 Myelographic effect - thecal sac Central nerve roots Marrow edema Magnetic Resonance Imaging Special Considerations Axial Images Stacked Angled to disc spaces Continuous Pick up small discs and fragments Fat Saturation Accentuate fluid signal Particularly useful for compression fractures, trauma & demyelinating disease Coronal Images 4
5 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Special Considerations Axial Images Stacked Angled to disc spaces Continuous Pick up small discs and fragments Fat Saturation Accentuate fluid signal Particularly useful for compression fractures, trauma & demyelinating disease Coronal Images Magnetic Resonance Imaging Special Considerations Axial Images Stacked Angled to disc spaces Continuous Pick up small discs and fragments Fat Saturation Accentuate fluid signal Particularly useful for compression fractures, trauma & demyelinating disease Coronal Images 5
6 Normal Disc Anatomy Nucleus Pulposus: composed centrally of collagen and hydrophilic proteoglycans Annulus fibrosis: collagenous ring that maintains the NP within the confines of the edges of the adjacent vertebral bodies. Peripheral fibers (Sharpey s) attach to adjacent endplates and anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments. Fissures/tears in the AF allow escape of the NP. Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Amphiarthodial (symphyseal) joint Nucleus Water + Proteoglycans T1 <vertebral body T2 >vertebral body Annulus Concentric lamellae Inner fibers Type II collagen (cartilage) Signal = nucleus Outer fibers Type I collagen (ligaments) Low signal Sharpey s fibers Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Amphiarthodial (symphyseal) joint Nucleus Water + Proteoglycans T1 <vertebral body T2 >vertebral body Annulus Concentric lamellae Inner fibers Type II collagen (cartilage) Signal = nucleus Outer fibers Type I collagen (ligaments) Low signal Sharpey s fibers 6
7 Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Amphiarthodial (symphyseal) joint Nucleus Water + Proteoglycans T1 <vertebral body T2 >vertebral body Annulus Concentric lamellae Inner fibers Type II collagen (cartilage) Signal = nucleus Outer fibers Type I collagen (ligaments) Low signal Sharpey s fibers Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Posterior contour Concave above L4/5 Flat at L4/5 Convex L5/S1 Vertebra Venous plexus Basivertebral vein Facet Joints True synovial or diarthrodial joint Normal orientation Articular surfaces lined by hyaline cartilage (high signal T2) Innervated by medial branch of dorsal ramus L3/4 Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Posterior contour Concave above L4/5 Flat at L4/5 Convex L5/S1 Vertebra Venous plexus Basivertebral vein Facet Joints True synovial or diarthrodial joint Normal orientation Articular surfaces lined by hyaline cartilage (high signal T2) Innervated by medial branch of dorsal ramus L4/5 7
8 Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Posterior contour Concave above L4/5 Flat at L4/5 Convex L5/S1 Vertebra Venous plexus Basivertebral vein Facet Joints True synovial or diarthrodial joint Normal orientation Articular surfaces lined by hyaline cartilage (high signal T2) Innervated by medial branch of dorsal ramus L5/S1 Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Posterior contour Concave above L4/5 Flat at L4/5 Convex L5/S1 Vertebra Venous plexus Basivertebral vein Facet Joints True synovial or diarthrodial joint Normal orientation Articular surfaces lined by hyaline cartilage (high signal T2) Innervated by medial branch of dorsal ramus Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Posterior contour Concave above L4/5 Flat at L4/5 Convex L5/S1 Vertebra Venous plexus Basivertebral vein Facet Joints True synovial or diarthrodial joint Normal orientation Articular surfaces lined by hyaline cartilage (high signal T2) Innervated by medial branch of dorsal ramus 8
9 Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Posterior contour Concave above L4/5 Flat at L4/5 Convex L5/S1 Vertebra Venous plexus Basivertebral vein Facet Joints True synovial or diarthrodial joint Normal orientation Articular surfaces lined by hyaline cartilage (high signal T2) Innervated by medial branch of dorsal ramus Normal MRI Anatomy Discs Posterior contour Concave above L4/5 Flat at L4/5 Convex L5/S1 Vertebra Venous plexus Basivertebral vein Facet Joints True synovial or diarthrodial joint Normal orientation Articular surfaces lined by hyaline cartilage (high signal T2) Innervated by medial branch of dorsal ramus L5/S1 L3/4 L4/5 Fenton, Douglas S.; Czervionke, Leo F. "Image Guided Spine Intervention", Harcourt Publishers, Ltd., December Water and proteoglycans replaced by collagen Earliest sign = fibrous intranuclear cleft Disc dessication Loss of disc height Bulging annulus Vacuum disc Nitrogen from extracellular fluid in cracks and fissures If supine, may accumulate fluid with T2 signal The Aging Disc 9
10 Water and proteoglycans replaced by collagen Earliest sign = fibrous intranuclear cleft Disc dessication Loss of disc height Bulging annulus Vacuum disc Nitrogen from extracellular fluid in cracks and fissures If supine, may accumulate fluid with T2 signal The Aging Disc Water and proteoglycans replaced by collagen Earliest sign = fibrous intranuclear cleft Disc dessication Loss of disc height Bulging annulus Vacuum disc Nitrogen from extracellular fluid in cracks and fissures If supine, may accumulate fluid with T2 signal The Aging Disc 10
11 Role of Imaging Location and type of disk (or other) pathology Compression of Nerves Location assist in surgical planning Mechanism of compression Disc, osteophyte, ligament or other Instability/Listhesis Dynamic Isthmic or degenerative Discogenic disease Disc degeneration and associated changes Terminology Spondylosis: generic term for degenerative disk disease with ostephytes Annular fissure: disruption of fibers of outer portion of disk (preferred over tear) High intensity zone: increased T2 signal in outer annulus, may or may not reflect a tear, although HIZ and annular tear often used interchangeably 11
12 Terminology, continued Multidisciplinary joint task force North American Spine Society (NASS) American Society of Spine Radiology (ASSR) American Society of Neuroradiology (ASNR) Document published in 2001 in Spine, and on the ASSR and ASNR websites attempting to standardize nomenclature for description of disk pathology. Updated in 2014 (Lumbar disc nomenclature: Version 2.0. Spine Volume 39, Number 24, pp E1448-E1465) Accepted definitions Annular tear Disc bulge symmetric asymmetric Disc herniation disc protrusion disc extrusion disc sequestration Disc Bulge Generalized displacement of disc material in the axial plane beyond the limits of the intervertebral disc space which is defined as greater than 25% (90 degrees) of the periphery of the disc Not considered a form of herniation Can be symmetric (circumferential) or asymmetric (still has to be greater than 25%) 12
13 Disc Herniation Defined as a localized displacement of disc material beyond the limits of the intervertebral disc space Localized displacement in the axial plane can be focal (less than 25% of the disc circumference or 90 degrees) Description of a disc herniation Morphology protrusion or extrusion Continuity/Containment/Relationship to the posterior longitudinal ligament Location axial and sagittal plane Volume Composition Disc herniations classified on the basis of the shape of the displaced material Protrusion is present if the greatest distance between the edges of the disc material beyond the disc space is less than the distance between the edges of the base Extrusion is present when, in at least one plane, any one distance between the edges of the disc material beyond the disc space is greater than the distance between the edges of the base 13
14 Location of disc herniation in axial plane Central Right (or left) paracentral if extends laterally Right (or left) subarticular lateral recess Right (or left) foraminal Right or left extraforaminal far lateral Anterior Location of Herniation Extraforaminal Foraminal Subarticular Central Location of disc herniation in the sagittal plane Disc level Infra-pedicular level usually from disc level below and extruded superiorly Supra-pedicular level usually from the disc level above and extruded inferiorly 14
15 Schmorl s node Also known as intervertebral osteochondrosis Herniated disc in the cranio-caudal (vertical) direction through a weak region in the vertebral body endplate referred to as an intravertebral herniation Canal compromise axial images Less than 1/3 = mild Between 1/3 and 2/3 = moderate Greater than 2/3 = severe Use similar grading scheme for describing neural foraminal stenosis Annular fissures May be symptomatic Radial and concentric High intensity zone (HIZ) Not all fissures radiographically apparent Disc Contour nclature/ 15
16 Annular fissures May be symptomatic Radial and concentric High intensity zone (HIZ) Not all fissures radiographically apparent Disc Contour Annular fissures May be symptomatic Radial and concentric High intensity zone (HIZ) Not all fissures radiographically apparent Disc Contour Disc bulge Concentric >25% ( ) <3mm beyond margins Clinical Up to 39% of adults have asymptomatic bulge Disc Contour nclature/ 16
17 Disc bulge Concentric >25% ( ) <3mm beyond margins Clinical Up to 39% of adults have asymptomatic bulge Disc Contour Disc herniation Type Protrusion Extrusion Degree Focal <25% or 90 (greater than 25% now considered bulge) Disc Contour Disc herniation Type Protrusion Extrusion Degree Focal <25% or 90 (greater than 25% now considered bulge) Disc Contour
18 Disc herniation Type Protrusion Extrusion Degree Focal <25% or 90 (greater than 25% now considered bulge) Disc Contour Disc herniation Type Protrusion Extrusion Degree Focal <25% or 90 (greater than 25% now considered bulge) Disc Contour Protrusion Wider at base than apex Some of outer annular fibers intact contained disc May be asymptomatic Disc Contour 18
19 Extrusion Wider at apex than base Disruption of outer annular fibers Migration in continuity with parent disc May have surrounding inflammatory reaction Pain mechanically and chemically Rarely asymptomatic Disc Contour Sequestered disc No attachment to parent disc May see low signal line between parent disc and fragment Can migrate Usually within 5 mm Epidural location Anterior>>Posterior Rarely intradural Disc Contour 19
20 Disc Contour Location Level 90% at L4/5 or L5/S1 Short axis Central Right and left lateral Subarticular zone Foraminal zone (L3/4 and L4/5) Extraforaminal zone (far lateral) Long axis Suprapedicular Pedicular Infrapedicular Disc level Wiltse LL, Berger PE, McCulloch JA: A system for reporting the size and location of lesions in the spine Spine 22: ,1997 Location Level 90% at L4/5 or L5/S1 Short axis Central Right and left lateral Subarticular zone Foraminal zone (L3/4 and L4/5) Extraforaminal zone (far lateral) Long axis Suprapedicular Pedicular Infrapedicular Disc level Disc Contour 20
21 Location Level 90% at L4/5 or L5/S1 Short axis Central Right and left lateral Subarticular zone Foraminal zone (L3/4 and L4/5) Extraforaminal zone (far lateral) Long axis Suprapedicular Pedicular Infrapedicular Disc level Disc Contour Location Level 90% at L4/5 or L5/S1 Short axis Central Right and left lateral Subarticular zone Foraminal zone (L3/4 and L4/5) Extraforaminal zone (far lateral) Long axis Suprapedicular Pedicular Infrapedicular Disc level Disc Contour Location Level 90% at L4/5 or L5/S1 Short axis Central Right and left lateral Subarticular zone Foraminal zone (L3/4 and L4/5) Extraforaminal zone (far lateral) Long axis Suprapedicular Pedicular Infrapedicular Disc level Disc Contour 21
22 Disc Contour Location Level 90% at L4/5 or L5/S1 Short axis Central Right and left lateral Subarticular zone Foraminal zone (L3/4 and L4/5) Extraforaminal zone (far lateral) Long axis Suprapedicular Pedicular Infrapedicular Disc level Wiltse LL, Berger PE, McCulloch JA: A system for reporting the size and location of lesions in the spine Spine 22: ,1997 Location Level 90% at L4/5 or L5/S1 Short axis Central Right and left lateral Subarticular zone Foraminal zone (L3/4 and L4/5) Extraforaminal zone (far lateral) Long axis Suprapedicular Pedicular Infrapedicular Disc level Disc Contour Wiltse LL, Berger PE, McCulloch JA: A system for reporting the size and location of lesions in the spine Spine 22: ,1997 Confounders Epidural hematoma Lenticular Complex signal High signal discs on T2 May be more apparent on T1 Disc Contour
23 Confounders Epidural hematoma Lenticular Complex signal High signal discs on T2 May be more apparent on T1 Disc Contour Confounders Epidural hematoma Lenticular Complex signal High signal discs on T2 May be more apparent on T1 Disc Contour
24 Osteophytes Spondylosis deformans Traction at Sharpey s fibers Endplates Osteophytes Spondylosis deformans Traction at Sharpey s fibers Endplates 24
25 Modic 1 T1, T2 Edematous change Granulation tissue Modic 2 T1, T2 Fatty change Modic 3 T1, T2 Sclerotic change Endplates Modic 1 T1, T2 Edematous change Granulation tissue Modic 2 T1, T2 Fatty change Modic 3 T1, T2 Sclerotic change Endplates Modic 1 T1, T2 Edematous change Granulation tissue Modic 2 T1, T2 Fatty change Modic 3 T1, T2 Sclerotic change Endplates 25
26 Schmorl s node Herniation of disc material through endplate May occur if bone weak Osteoporosis, tumor, metabolic dz May be acute/traumatic Most asymptomatic Painful Surrounding inflammation T2, enhancement If chronic Fatty or sclerotic change Endplates Schmorl s node Herniation of disc material through endplate May occur if bone weak Osteoporosis, tumor, metabolic dz May be acute/traumatic Most asymptomatic Painful Surrounding inflammation T2, enhancement If chronic Fatty or sclerotic change Endplates Schmorl s node Herniation of disc material through endplate May occur if bone weak Osteoporosis, tumor, metabolic dz May be acute/traumatic Most asymptomatic Painful Surrounding inflammation T2, enhancement If chronic Fatty or sclerotic change Endplates 26
27 + malig Schmorl s, inferior, halo True synovial joint Cartilage wear Subchondral sclerosis Osteophytes (mushroom) Marrow changes in adjacent pedicles Cysts 90% in lumbar 70-80% at L4/5 Small veins may mimic Facet Joints True synovial joint Cartilage wear Subchondral sclerosis Osteophytes (mushroom) Marrow changes in adjacent pedicles Cysts 90% in lumbar 70-80% at L4/5 Small veins may mimic Facet Joints 27
28 True synovial joint Cartilage wear Subchondral sclerosis Osteophytes (mushroom) Marrow changes in adjacent pedicles Cysts 90% in lumbar 70-80% at L4/5 Small veins may mimic Facet Joints True synovial joint Cartilage wear Subchondral sclerosis Osteophytes (mushroom) Marrow changes in adjacent pedicles Cysts 90% in lumbar 70-80% at L4/5 Small veins may mimic Facet Joints True synovial joint Cartilage wear Subchondral sclerosis Osteophytes (mushroom) Marrow changes in adjacent pedicles Cysts 90% in lumbar 70-80% at L4/5 Small veins may mimic Facet Joints 28
29 True synovial joint Cartilage wear Subchondral sclerosis Osteophytes (mushroom) Marrow changes in adjacent pedicles Cysts 90% in lumbar 70-80% at L4/5 Small veins may mimic Facet Joints Pain Mechanical compression of nerve Osteophytes Buckling of lig flavum Pain from facets Medial branch Worse with extension LS -buttock, thighs and hips not below knees Facet Joints 29
30 Baastrup Disease Hyperlordosis or loss of height with apposition of spinous processes and damage to interspinous ligaments Eburnation with osteophytes Form bursa or synovial joints Spinous Processes Jinkins, JR Acquired Degenerative Changes of the Intervertebral Segments at and Suprajacent to the Lumbosacral Junction in Imaging of Low Back Pain, Rad Clin of North Am, 39:1;73-99, 2001 Baastrup Disease Hyperlordosis or loss of height with apposition of spinous processes and damage to interspinous ligaments Eburnation with osteophytes Form bursa or synovial joints Spinous Processes Baastrup Disease Hyperlordosis or loss of height with apposition of spinous processes and damage to interspinous ligaments Eburnation with osteophytes Form bursa or synovial joints Spinous Processes 30
31 Baastrup Disease Hyperlordosis or loss of height with apposition of spinous processes and damage to interspinous ligaments Eburnation with osteophytes Form bursa or synovial joints Spinous Processes Jinkins, JR Acquired Degenerative Changes of the Intervertebral Segments at and Suprajacent to the Lumbosacral Junction in Imaging of Low Back Pain, Rad Clin of North Am, 39:1;73-99, 2001 Baastrup Disease Hyperlordosis or loss of height with apposition of spinous processes and damage to interspinous ligaments Eburnation with osteophytes Form bursa or synovial joints Spinous Processes Pathology-Physiologic 31
32 Stenosis - Central Canal Acquired Congenital (Developmental) Rarely symptomatic unless acquired component Symptoms Back pain neurogenic claudication relieved by sitting or flexion Stenosis - Central Canal Acquired Congenital (Developmental) Rarely symptomatic unless acquired component Symptoms Back pain neurogenic claudication relieved by sitting or flexion Stenosis - Central Canal Acquired Congenital (Developmental) Rarely symptomatic unless acquired component Symptoms Back pain neurogenic claudication relieved by sitting or flexion 32
33 Stenosis - Central Canal Acquired Congenital (Developmental) Rarely symptomatic unless acquired component Symptoms Back pain neurogenic claudication relieved by sitting or flexion Stenosis - Central Canal Disc anteriorly Facets/Lig flavum posteriorly Other factors Epidural lipomatosis Post-surgical scar OPLL Degenerative listhesis Stenosis - Central Canal Shape Normal = round or nearly round Stenosis = trephoil Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 AP diameter <12mm relative <10mm absolute Wiltse LL, Berger PE, McCulloch JA: A system for reporting the size and location of lesions in the spine Spine 22: ,
34 Stenosis - Central Canal Shape Normal = round or nearly round Stenosis = trephoil Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 AP diameter <12mm relative <10mm absolute Wiltse LL, Berger PE, McCulloch JA: A system for reporting the size and location of lesions in the spine Spine 22: ,1997 Stenosis - Central Canal Shape Normal = round or nearly round Stenosis = trephoil Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 AP diameter <12mm relative <10mm absolute Stenosis - Central Canal Shape Normal = round or nearly round Stenosis = trephoil Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 AP diameter <12mm relative <10mm absolute 34
35 Stenosis - Central Canal Shape Normal = round or nearly round Stenosis = trephoil Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 AP diameter <12mm relative <10mm absolute Wiltse LL, Berger PE, McCulloch JA: A system for reporting the size and location of lesions in the spine Spine 22: ,1997 Stenosis - Central Canal Shape Normal = round or nearly round Stenosis = trephoil Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 AP diameter <12mm relative <10mm absolute Stenosis - Neural Foramen Radicular pain Disc anteroinferiorly Facet/lig flavum posterosuperiorly Jinkins, JR Acquired Degenerative Changes of the Intervertebral Segments at and Suprajacent to the Lumbosacral Junction in Imaging of Low Back Pain, Rad Clin of North Am, 39:1;73-99,
36 Stenosis - Neural Foramen Shape Normal = vertical oval Stenosis = keyhole, lobulated, figure of 8, horizontal Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 Disc in inferior foramen not without consequence CT may help differentiate disc from bone Stenosis - Neural Foramen Shape Normal = vertical oval Stenosis = keyhole, lobulated, figure of 8, horizontal Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 Disc in inferior foramen not without consequence CT may help differentiate disc from bone Stenosis - Neural Foramen Shape Normal = vertical oval Stenosis = keyhole, lobulated, figure of 8, horizontal Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 Disc in inferior foramen not without consequence CT may help differentiate disc from bone 36
37 Stenosis - Neural Foramen Shape Normal = vertical oval Stenosis = keyhole, lobulated, figure of 8, horizontal Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 Disc in inferior foramen not without consequence CT may help differentiate disc from bone Stenosis - Neural Foramen Shape Normal = vertical oval Stenosis = keyhole, lobulated, figure of 8, horizontal Relative size Mild <1/3 Moderate 1/3 2/3 Severe >2/3 Disc in inferior foramen not without consequence CT may help differentiate disc from bone 37
38 Instability - Dynamic Plain radiographs Flexion/extension Dynamic assessment Sagittal-plane translation of 3 mm Sagittal-plane rotation of 9 MRI Joint effusions Edematous endplate changes Flexion Extension Instability - Dynamic Plain radiographs Flexion/extension Dynamic assessment Listhesis of Change in angle of MRI Joint effusions Edematous endplate changes Fluid in disk (sometimes can mimic infection) 38
39 Instability Spondylolisthesis - Isthmic Pars defect (non-union) Chronic repetitive microtrauma L5/S1 most common with pars defects at L5(82%) 10-15% unilateral Buildup of osseous, cartilaginous or fibrous material at defects with mass effect 80% asymptomatic Pain on hyperextension Hamstring tightness Instability Spondylolisthesis - Isthmic Pars defect (non-union) Chronic repetitive microtrauma L5/S1 most common with pars defects at L5(82%) 10-15% unilateral Buildup of osseous, cartilaginous or fibrous material at defects with mass effect 80% asymptomatic Pain on hyperextension Hamstring tightness 39
40 Instability Spondylolisthesis - Isthmic Imaging Canal widened Horizontally oriented neural foramina Marrow changes in pedicles and articular processes 40
41 Instability Spondylolisthesis - Isthmic Imaging Canal widened Horizontally oriented neural foramina Marrow changes in pedicles and articular processes Instability Spondylolisthesis-Degenerative Degeneration of disc and facets with instability L4/5 most common Present clinically and managed similarly to central stenosis Imaging Central canal stenosis Intact pars Horizontally oriented neural foramina Jinkins, JR Acquired Degenerative Changes of the Intervertebral Segments at and Suprajacent to the Lumbosacral Junction in Imaging of Low Back Pain, Rad Clin of North Am, 39:1;73-99, 2001 Instability Spondylolisthesis-Degenerative Degeneration of disc and facets with instability L4/5 most common Present clinically and managed similarly to central stenosis Imaging Central canal stenosis Intact pars Horizontally oriented neural foramina 41
42 Instability Spondylolisthesis-Degenerative Degeneration of disc and facets with instability L4/5 most common Present clinically and managed similarly to central stenosis Imaging Central canal stenosis Intact pars Horizontally oriented neural foramina Instability Spondylolisthesis-Degenerative Degeneration of disc and facets with instability L4/5 most common Present clinically and managed similarly to central stenosis Imaging Central canal stenosis Intact pars Horizontally oriented neural foramina Internal Disc Derangement Disruption of annulus Can have pain from contained annular tear Over time loss of disc height overlap of facets and ligament laxity instability pain 42
43 Internal Disc Derangement Plain films Instability MRI Disc dessication or bulge Radial tears High Intensity Zone (HIZ) Discography Can identify radial tears within central annulus Reproduce pain Internal Disc Derangement Plain films Instability MRI Disc dessication or bulge Radial tears High Intensity Zone (HIZ) Discography Can identify radial tears within central annulus Reproduce pain Internal Disc Derangement Plain films Instability MRI Disc dessication or bulge Radial tears High Intensity Zone (HIZ) Discography Can identify radial tears within central annulus Reproduce pain 43
44 Internal Disc Derangement Plain films Instability MRI Disc dessication or bulge Radial tears High Intensity Zone (HIZ) Discography Can identify radial tears within central annulus Reproduce pain 44
45 Imaging Special Situations The Post-Operative Spine Gadolinium Scar tissue enhances uniformly vs recurrent disk which peripherally enhances or does not enhanc Fast Spin Echo Reduce metal artifact Titanium< Stainless steel CT +/- myelography Pseudarthrosis Hardware malposition Imaging Special Situations The Post-Operative Spine Gadolinium Scar tissue enhances uniformly vs recurrent disk which peripherally enhances or does not enhanc Fast Spin Echo Reduce metal artifact Titanium< Stainless steel CT +/- myelography Pseudarthrosis Hardware malposition Imaging Special Situations The Post-Operative Spine Gadolinium Scar tissue enhances uniformly vs recurrent disk which peripherally enhances or does not enhanc Fast Spin Echo Reduce metal artifact Titanium< Stainless steel CT +/- myelography Pseudarthrosis Hardware malposition 45
46 Imaging Special Situations The Post-Operative Spine Gadolinium Scar tissue enhances uniformly vs recurrent disk which peripherally enhances or does not enhanc Fast Spin Echo Reduce metal artifact Titanium< Stainless steel CT +/- myelography Pseudarthrosis Hardware malposition EXTENSIVE HARDWARE ARTIFACT, MR >> CT 46
47 CT MYELOGRAM IN PATIENT WITH HARDWARE THANK YOU References Ross JS, Brant-Zawadzki M, Moore KR, et al. Diagnostic Imaging: Spine. Amirsys: Modic MT and Ross JS. Lumbar Degenerative Disk Disease. Radiology: Volume 245: Number 1- October Leone A, Guglielmi, Cassar-Pullicino VN, et al. Lumbar Intervertebral Instability: A Review. Radiology: Volume 245: Number 1-October Fardon DF, Williams AL, Dohring EJ, et al. Lumbar disc nomenclature: Version 2.0. Spine: Volume 39: Number 24, pp E1448-E
8/4/2012. Causes and Cures. Nucleus pulposus. Annulus fibrosis. Vertebral end plate % water. Deforms under pressure
 Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Causes and Cures Intervertebral discs Facet (zygopophyseal) joints Inter body joints Spinal nerve roots Nerve compression Pathological conditions Video Causes of back pain Nucleus pulposus Annulus fibrosis
Degenerative Disc Disease. Nafi Aygun, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology
 Degenerative Disc Disease Nafi Aygun, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Big Problem Great majority of adults suffer from at least one episode of acute low back pain during life time Disc degeneration
Degenerative Disc Disease Nafi Aygun, MD. Associate Professor of Radiology Big Problem Great majority of adults suffer from at least one episode of acute low back pain during life time Disc degeneration
Imaging the Degenerative Diseases of the Lumbar Spine
 221 Imaging the Degenerative Diseases of the Lumbar Spine David Malfair, MD a, Douglas P. Beall, MD b,c, * MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 15 (2007) 221 238 - Degenerative
221 Imaging the Degenerative Diseases of the Lumbar Spine David Malfair, MD a, Douglas P. Beall, MD b,c, * MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING CLINICS Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 15 (2007) 221 238 - Degenerative
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist. Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation
 Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Degenerative Disease of the Spine
 Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Degenerative Disease of the Spine Introduction: I. Anatomy Talk Overview II. Overview of Disease Processes: A. Spondylosis B. Intervertebral Disc Disease III. Diagnosis IV. Therapy Introduction: Myelopathy
Lumbar Disc Nomenclature: Version 2.0
 Lumbar Disc Nomenclature: Version 2.0 Recommendations of the Combined Task Forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology, and the American Society of Neuroradiology
Lumbar Disc Nomenclature: Version 2.0 Recommendations of the Combined Task Forces of the North American Spine Society, the American Society of Spine Radiology, and the American Society of Neuroradiology
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
3D imaging reformation was obtained. The 3D color imaging reformation was reviewed in a different high resolution setting.
 POST OPERATIVE SPINE WITH CONTRAST CLINICAL INDICATION: Low back pain, Patient is post operative status for L4/5 diskectomy TECHNIQUE: MRI of the lumbosacral spine was performed with multiplanar imaging
POST OPERATIVE SPINE WITH CONTRAST CLINICAL INDICATION: Low back pain, Patient is post operative status for L4/5 diskectomy TECHNIQUE: MRI of the lumbosacral spine was performed with multiplanar imaging
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
Spinal Imaging. ssregypt.com. Mamdouh Mahfouz MD
 Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002
 Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002 MICHAEL D. MARTIN, M.D., CHRISTOPHER M. BOXELL, M.D., F.A.C.S., AND DAVID G. MALONE, M.D. FROM
Pathophysiology of lumbar disc degeneration: a review of the literature Neurosurg Focus 13 (2): August, 2002 MICHAEL D. MARTIN, M.D., CHRISTOPHER M. BOXELL, M.D., F.A.C.S., AND DAVID G. MALONE, M.D. FROM
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
 CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: A 66 years old male patient presented clinically with non specific lumbar spine pain. RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS:
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: A 66 years old male patient presented clinically with non specific lumbar spine pain. RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS:
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Anatomy & Physiology II. Trunk
 Anatomy & Physiology II Trunk Bones and Landmarks of the Vertebral column 24 vertebrae Sacrum - consists of 5 vertebrae that fuse into one bone Median sacral crest Sacral hiatus 4 sacral foramina Coccyx
Anatomy & Physiology II Trunk Bones and Landmarks of the Vertebral column 24 vertebrae Sacrum - consists of 5 vertebrae that fuse into one bone Median sacral crest Sacral hiatus 4 sacral foramina Coccyx
Lumbar spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 08
 What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
What is lumbar spinal canal stenosis? This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, and of the lateral recesses (recesssus laterales) and exit openings (foramina intervertebralia) for the
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Imaging the Intervertebral Disk Age-Related Changes, Herniations, and Radicular Pain
 Imaging the Intervertebral Disk Age-Related Changes, Herniations, and Radicular Pain Filippo Del Grande, MD, MBA, MHEM a, *, Timothy P. Maus, MD b, John A. Carrino, MD, MPH c KEYWORDS Intervertebral disk
Imaging the Intervertebral Disk Age-Related Changes, Herniations, and Radicular Pain Filippo Del Grande, MD, MBA, MHEM a, *, Timothy P. Maus, MD b, John A. Carrino, MD, MPH c KEYWORDS Intervertebral disk
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN. Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms.
 THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN Average adult length: In male: about 70 cms. In female: about 65 cms. 1 Vertebral Column (Regions and Curvatures) Curvatures of the vertebral column: A. Primary curvature: C-shaped;
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at (sent 5/9/17) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete
 Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Review the pathophysiology of the
Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Review the pathophysiology of the
Cox Technic Case Report #124 published at ( sent October 2013 ) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #124 published at www.coxtechnic.com ( sent October 2013 ) 1 5 th Lumbar Disc Herniation with Spondylolisthesis Treated with Cox Technic Flexion Distraction by Travis Cross BS,
Cox Technic Case Report #124 published at www.coxtechnic.com ( sent October 2013 ) 1 5 th Lumbar Disc Herniation with Spondylolisthesis Treated with Cox Technic Flexion Distraction by Travis Cross BS,
ABCs of the degenerative spine
 Insights into Imaging (2018) 9:253 274 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-017-0584-z PICTORIAL REVIEW ABCs of the degenerative spine Sergiy V. Kushchayev 1 & Tetiana Glushko 1 & Mohamed Jarraya 1 & Karl H.
Insights into Imaging (2018) 9:253 274 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13244-017-0584-z PICTORIAL REVIEW ABCs of the degenerative spine Sergiy V. Kushchayev 1 & Tetiana Glushko 1 & Mohamed Jarraya 1 & Karl H.
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics. Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6. Typical Cervical Vertebra Anterior 10/5/2017
 Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
Cervical Spine Anatomy and Biomechanics Typical Cervical Vertebra C3 6 Small, relatively broad body Bifid SpinousProcess Long and narrow laminae Spinal Canal: large, triangular; remarkably consistent dimensions
MD Bones & Joints of the Back. A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience
 MD 2017 Bones & Joints of the Back A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
MD 2017 Bones & Joints of the Back A/Prof Chris Briggs Department of Anatomy & Neuroscience WARNING This material has been provided to you pursuant to section 49 of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act) for
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
Imaging of degenerative lumbar intervertebral discs; linking anatomy, pathology and imaging
 Imaging of degenerative lumbar intervertebral discs; linking anatomy, pathology and imaging Ashok Adams, 1 Oran Roche, 2 Asif Mazumder, 3 Indran Davagnanam, 4 Kshitij Mankad 5 1 The Royal London Hospital,
Imaging of degenerative lumbar intervertebral discs; linking anatomy, pathology and imaging Ashok Adams, 1 Oran Roche, 2 Asif Mazumder, 3 Indran Davagnanam, 4 Kshitij Mankad 5 1 The Royal London Hospital,
Spinal canal stenosis Degenerative diseases F 06
 What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
What is spinal canal stenosis? The condition known as spinal canal stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) of the spinal canal that in most cases develops due to the degenerative (wear-induced) deformation
MRI Evaluation of Disc Lesions Causing Lumbar Canal Stenosis and Backache Y Aditya 1 *, Janardhan Reddy K 2 and MV Ramanappa 3
 Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 3, November, 2014, pp- 242-247 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00022.3 Original Research MRI Evaluation of Disc Lesions Causing Lumbar Canal Stenosis
Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 3, November, 2014, pp- 242-247 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00022.3 Original Research MRI Evaluation of Disc Lesions Causing Lumbar Canal Stenosis
Western Orthopedics, PC Denver, CO Presbyterian/St. Luke s Medical Center
 Tim Birney, MD Western Orthopedics, PC Denver, CO Presbyterian/St. Luke s Medical Center Treating Neck & Low Back Pain The Fundamentals, and What s Old And What s New? Normal Anatomy Dual function of the
Tim Birney, MD Western Orthopedics, PC Denver, CO Presbyterian/St. Luke s Medical Center Treating Neck & Low Back Pain The Fundamentals, and What s Old And What s New? Normal Anatomy Dual function of the
Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04
 Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04 How is a herniated cervical intervertebral disc treated? Conservative treatment is generally sufficient for mild symptoms not complicated
Cervical intervertebral disc disease Degenerative diseases F 04 How is a herniated cervical intervertebral disc treated? Conservative treatment is generally sufficient for mild symptoms not complicated
The Biomechanics of the Human Spine. Basic Biomechanics, 6 th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
 Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment
 Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Artificial intervertebral disc
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Artificial intervertebral disc Vikas Ghai Medical University of Ohio Follow this and additional works
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Artificial intervertebral disc Vikas Ghai Medical University of Ohio Follow this and additional works
2/5/2019. Facet Joint Pain. Biomechanics
 Facet Arthropathy as a Pain Source Evaluation and Management Shelby Spine Jan 31 st Feb 2 nd, 2019 Kushagra Verma MD, MS Adult and Pediatric Scoliosis And Spine Deformity Beach Orthopaedics Specialty Institute
Facet Arthropathy as a Pain Source Evaluation and Management Shelby Spine Jan 31 st Feb 2 nd, 2019 Kushagra Verma MD, MS Adult and Pediatric Scoliosis And Spine Deformity Beach Orthopaedics Specialty Institute
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study.
 ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study. A multi-center, prospective, randomized clinical trial. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Indications, Contraindications
MRI of LEFT KNEE. There is a fluid collection seen anterior to and inferior to the superiorly displaced patella.
 MRI of LEFT KNEE Protocol: Multiplanar MRI of the left knee joint performed in the sagittal, coronal and transverse planes using T1 weighted spin echo, T2 and proton-density weighted fast spin echo, fatsaturated
MRI of LEFT KNEE Protocol: Multiplanar MRI of the left knee joint performed in the sagittal, coronal and transverse planes using T1 weighted spin echo, T2 and proton-density weighted fast spin echo, fatsaturated
Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica
 87 (98) Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica Shobeiri E, Khalatbari M R, Taheri M S, Tofighirad N, Moharamzad Y ABSTRACT Introduction:
87 (98) Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of patients with low back pain and those with sciatica Shobeiri E, Khalatbari M R, Taheri M S, Tofighirad N, Moharamzad Y ABSTRACT Introduction:
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma. Introduction. Anatomic Considerations 7/23/2018
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
ProDisc-L Total Disc Replacement. IDE Clinical Study
 Total Disc Replacement IDE Clinical Study Study Design TDR vs. circumferential fusion: Multi-center, prospective, randomized trial 17 centers, 292 patients 162 patients 80 fusion patients 50 non-randomized
Total Disc Replacement IDE Clinical Study Study Design TDR vs. circumferential fusion: Multi-center, prospective, randomized trial 17 centers, 292 patients 162 patients 80 fusion patients 50 non-randomized
RETROLISTHESIS. Retrolisthesis. is found mainly in the cervical spine and lumbar region but can also be often seen in the thoracic spine
 RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
RETROLISTHESIS A retrolisthesis is a posterior displacement of one vertebral body with respect to adjacent vertebrae Typically a vertebra is to be in retrolisthesis position when it translates backward
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine. Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation
 Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
Functional Anatomy and Exam of the Lumbar Spine Thomas Hunkele MPT, ATC, NASM-PES,CES Coordinator of Rehabilitation Disclosure Anatomical Review Quick Review of Bony and Ligamentous structures Discal anatomy
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
CERVICAL SPINE: Radiographs and MRI Cases
 www.jprad.com Radiology reports with recommendations & clinical information - $30 per region, x-ray - $50 per MRI - Medpay Monthly Newsletter 700 East Redlands Blvd, Redlands CA 92373 909.353.9348 jpedley299@yahoo.com
www.jprad.com Radiology reports with recommendations & clinical information - $30 per region, x-ray - $50 per MRI - Medpay Monthly Newsletter 700 East Redlands Blvd, Redlands CA 92373 909.353.9348 jpedley299@yahoo.com
University of Jordan. Professor Freih Abuhassan -
 Freih Odeh Abu Hassan F.R.C.S.(Eng.), F.R.C.S.(Tr.& Orth.). Professor of Orthopedics University of Jordan 1 A. Sacroiliitis History Trauma is very common Repetitive LS motion--lumbar rotation or axial
Freih Odeh Abu Hassan F.R.C.S.(Eng.), F.R.C.S.(Tr.& Orth.). Professor of Orthopedics University of Jordan 1 A. Sacroiliitis History Trauma is very common Repetitive LS motion--lumbar rotation or axial
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE
 MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain
 Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
The Lumbar MRI in Clinical Practice
 The Lumbar MRI in Clinical Practice Lecture Notebook William E. Morgan, DC The Lumbar MRI in Clinical Practice A Survey of Lumbar MRI for Musculoskeletal Clinicians William E. Morgan Disclaimer and Copyright
The Lumbar MRI in Clinical Practice Lecture Notebook William E. Morgan, DC The Lumbar MRI in Clinical Practice A Survey of Lumbar MRI for Musculoskeletal Clinicians William E. Morgan Disclaimer and Copyright
Francine M. Pulver, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Ohio State University Medical Center
 Oh My Aching Back! Francine M. Pulver, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Ohio State University Medical Center Epidemiology 90% of episodes of LBP resolves
Oh My Aching Back! Francine M. Pulver, MD, Clinical Assistant Professor Department of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Ohio State University Medical Center Epidemiology 90% of episodes of LBP resolves
SpineFAQs. Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
 SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache
 Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
by Joseph E. Muscolino figure illustrations by Giovanni Rimasti photographs by Yanik Chauvin
 Expert Content by Joseph E. Muscolino figure illustrations by Giovanni Rimasti photographs by Yanik Chauvin whenever two differing treatment approaches exist, usually both are valid. To Flex or Extend?
Expert Content by Joseph E. Muscolino figure illustrations by Giovanni Rimasti photographs by Yanik Chauvin whenever two differing treatment approaches exist, usually both are valid. To Flex or Extend?
Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy
 Original Article Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27541:2282 Radiology Section Mallikarjun MD, Chetan
Original Article Evaluation of Degenerative Lumbosacral Diseases and Common Location of Disc Herniations causing Radiculopathy DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/27541:2282 Radiology Section Mallikarjun MD, Chetan
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Current Spine Procedures
 SPINE BOOT CAMP: WHAT YOU DON T KNOW MAY COST YOU! David Abraham, M.D. The Reading Neck and Spine Center Reading, PA Current Spine Procedures Epidural/Transforaminal Injections Lumbar Procedures Laminectomy
SPINE BOOT CAMP: WHAT YOU DON T KNOW MAY COST YOU! David Abraham, M.D. The Reading Neck and Spine Center Reading, PA Current Spine Procedures Epidural/Transforaminal Injections Lumbar Procedures Laminectomy
Disclosures 5/27/2016. Narrowing of the spinal canal or neuroforamina causing a symptomatic compression of the neural element.
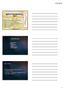 Radiculopathy Saggital MRI view Contained disc extrusion uplifting PLL from bone Terrence Julien, MD, FACS, (blue FAANS arrows) Associate Professor of Neurosurgery System Director, Surgical Neuro-Oncology
Radiculopathy Saggital MRI view Contained disc extrusion uplifting PLL from bone Terrence Julien, MD, FACS, (blue FAANS arrows) Associate Professor of Neurosurgery System Director, Surgical Neuro-Oncology
Outline. Introduction / Epidemiology. Anatomy / Pain generators. Diagnosis. Treatment. Most Important lecture!!
 Acute Low Back Pain Outline Introduction / Epidemiology. Most Important lecture!! Anatomy / Pain generators Diagnosis Treatment Course Objectives Know the RED FLAGS in history taking. Know the Pain Generators
Acute Low Back Pain Outline Introduction / Epidemiology. Most Important lecture!! Anatomy / Pain generators Diagnosis Treatment Course Objectives Know the RED FLAGS in history taking. Know the Pain Generators
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE. Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV. Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY
 MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
MRI KNEE WHAT TO SEE Dr. SHEKHAR SRIVASTAV Sr.Consultant KNEE & SHOULDER ARTHROSCOPY MRI KNEE - WHAT TO SEE MRI is the most accurate and frequently used diagnostic tool for evaluation of internal derangement
The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1803.004 The Relationship amongst Intervertebral Disc Vertical Diameter, Lateral Foramen Diameter and Nerve Root Impingement in Lumbar Vertebra Yusof MI, MMed Orth, Hassan
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Peggers Super Summaries: The Aging Spine
 Aging Spine: AGING PROCESS Osteopenia 10% of 50 year old males and 25% of 50 year females Disc dehydration Facet degeneration Soft tissue hypertrophy 2 0 deformity Leg pain worse than back pain from nerve
Aging Spine: AGING PROCESS Osteopenia 10% of 50 year old males and 25% of 50 year females Disc dehydration Facet degeneration Soft tissue hypertrophy 2 0 deformity Leg pain worse than back pain from nerve
Orthopadic cors. Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis)
 Orthopadic cors Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis) Cervical spondylitis. Definition : - a painful condition of the cervical spine resulting from the
Orthopadic cors Topic : -Cervical spondylitis. -Development disorders(spondylolysis and Spodylolsithesis) Cervical spondylitis. Definition : - a painful condition of the cervical spine resulting from the
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Spinal Terminology Basics
 Spinal Terminology Basics Anterior The front portion of the body. It is often used to indicate the position of one structure relative to another. Annulus Fibrosus The outer, fibrous, ring like portion
Spinal Terminology Basics Anterior The front portion of the body. It is often used to indicate the position of one structure relative to another. Annulus Fibrosus The outer, fibrous, ring like portion
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Technique Guide. StenoFix. Interspinous distraction after surgical decompression.
 Technique Guide StenoFix. Interspinous distraction after surgical decompression. Table of Contents Introduction StenoFix 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning
Technique Guide StenoFix. Interspinous distraction after surgical decompression. Table of Contents Introduction StenoFix 2 Indications and Contraindications 4 Surgical Technique Preoperative Planning
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
European Journal of Radiology 50 (2004) J. Randy Jinkins a,b,
 European Journal of Radiology 50 (2004) 134 158 Acquired degenerative changes of the intervertebral segments at and suprajacent to the lumbosacral junction A radioanatomic analysis of the nondiscal structures
European Journal of Radiology 50 (2004) 134 158 Acquired degenerative changes of the intervertebral segments at and suprajacent to the lumbosacral junction A radioanatomic analysis of the nondiscal structures
Non-Operative Management of Low Back Pain in the Elderly
 www.4-no-pain.com Non-Operative Management of Low Back Pain in the Elderly Brian Kahan, D.O., FAAPMR Low Back Pain Outline Etiologies Initial Assessment Physical examination and Diagnostic work-up Clinical
www.4-no-pain.com Non-Operative Management of Low Back Pain in the Elderly Brian Kahan, D.O., FAAPMR Low Back Pain Outline Etiologies Initial Assessment Physical examination and Diagnostic work-up Clinical
Skeletal System. Axial Division
 Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know
 The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know Poster No.: C-1018 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit D. Shah 1, C. J. Burke 1, A. C. andi 2, R. Houghton
The imaging features of spondylolisthesis : what the clinician needs to know Poster No.: C-1018 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit D. Shah 1, C. J. Burke 1, A. C. andi 2, R. Houghton
The vault bones Frontal Parietals Occiput Temporals Sphenoid Ethmoid
 The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
The Vertebral Column Head, Neck and Spine Bones of the head Some consider the bones of the head in terms of the vault bones and the facial bones hanging off the front of them The vault bones Frontal Parietals
Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Description
 Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
human anatomy 2015 lecture four Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
The Vertebral Column the vertebral columnis central pillar of the body.it serve to protect the spinal cord and support the weight of the head trunk, which it transmits to the hip bones & the lower limbs.
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
Initiation and Progression of Lumbar Disc Degeneration under Cyclic Loading: A Finite Element Study
 Initiation and Progression of Lumbar Disc Degeneration under Cyclic Loading: A Finite Element Study By Muhammad Qasim BSc. Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan,
Initiation and Progression of Lumbar Disc Degeneration under Cyclic Loading: A Finite Element Study By Muhammad Qasim BSc. Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan,
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending
 A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending William Anderst, Mara Palmer, Joon Lee, William Donaldson, James
A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending William Anderst, Mara Palmer, Joon Lee, William Donaldson, James
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE
 CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
CERVICAL SPONDYLOSIS & CERVICAL DISC DISEASE Cervical spondylosis l Cervical osteophytosis l Most common progressive disease in the aging cervical spine l Seen in 95% of the people by 65 years Pathophysiology
Dr JC Carter PO Box 3548 Danville, CA (925)
 Dr JC Carter PO Box 3548 Danville, CA 94526 (925)736-8906 jcarter@lifewest.edu Terminology Disc/Body Uncovertebral joints Facet joints Degenerative Disc Disease/DDD End-plate Disc Spondylosis Osteophytes/spondylophytes
Dr JC Carter PO Box 3548 Danville, CA 94526 (925)736-8906 jcarter@lifewest.edu Terminology Disc/Body Uncovertebral joints Facet joints Degenerative Disc Disease/DDD End-plate Disc Spondylosis Osteophytes/spondylophytes
NEURORADIOLOGY. Part III. Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part III Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders inflammatory processes
NEURORADIOLOGY Part III Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders inflammatory processes
Contact Fusion Cage. Surgical Technique
 Contact Fusion Cage Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction by a surgeon experienced
Contact Fusion Cage Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction by a surgeon experienced
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
Typical MRI Findings in Sports Medicine Evaluation for Degenerative Disc Disease
 Typical MRI Findings in Sports Medicine Evaluation for Degenerative Disc Disease Sports medicine patients are a subgroup who may be prone to low back pain. CT evaluation, while accurate, exposes patients
Typical MRI Findings in Sports Medicine Evaluation for Degenerative Disc Disease Sports medicine patients are a subgroup who may be prone to low back pain. CT evaluation, while accurate, exposes patients
