hands in patients with chronic renal failure
|
|
|
- Sara Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
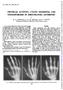
1 378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department of Radiology, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 R Sebben Correspondence to: D)r N P Hurst, Rheumatology Unit, Northern General Hospital, Ferry Road, Edinburgh leh5 2D1Q. Accepted for publication 21 July 1989 Premature development of erosive osteoarthritis of hands in patients with chronic renal failure I J S Duncan, N P Hurst, R Sebben, S C Milazzo, A Disney Abstract The prevalence ofgrade III or IV osteoarthritis was detennined in 210 patients with chronic renal failure, of whom 94 were receiving chronic haemodialysis and 116 had functioning renal transplants. The prevalence of grade III or IV osteoarthritis was three times greater in patients under 65 than in a control population, and all but two affected patients also had erosion of subchondral bone in at least one affected joint. The excess of osteoarthritis was apparent in both the transplant recipients and those receiving haemodialysis. Over the age of 65 there was no significant difference in prevalence. Metabolic bone disease, including osteopenia, might contribute to the development of erosive osteoarthritis in chronic renal failure. We recently reported two cases, one a patient receiving chronic haemodialysis and the other a I renal transplant recipient, who had developed severe progressive erosive osteoarthritis (OA) of the hands before the age of 35.' Previous studies of patients receiving chronic haemodialysis have noted degenerative changes in the small joints of hands but have not established whether this is in some way related to chronic renal failure or is simply related to age'9 There have been no comparable studies of renal transplant recipients. We have therefore conducted a survey of patients receiving chronic haemodialysis and renal transplant recipients at the Queen Elizabeth Hospital to establish the prevalence, age distribution, and clinical features of grade III and IV OA of the hands in patients with chronic renal disease. Patients and methods Ninety four (55 male, 39 female) of a possible 118 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis were surveyed between May 1986 and January 1987; this group has been described elsewhere.2 Of a possible 188 renal transplant recipients, 116 (74 male, 42 female) seen consecutively at the renal outpatient clinic between April and June 1988 were also studied. Patients who received renal allografts between the time of the survey of dialysis and transplant recipients were included only in the group receiving chronic haemodialysis. Five transplant recipients declined to participate. All patients underwent anteroposterior radiographs of hands and were questioned about the presence of pain and stiffness in the fingers. Radiographs were screened by RS for the presence of OA. Abnormal radiographs were reviewed in a blinded fashion by IJSD and NPH and graded 0 to IV for OA according to the method of Lawrence and Kellgren' ; those patients with radiological grade III or IV OA in at least one joint were selected for further study. Grade III OA comprises moderate joint space narrowing and definite osteophytes, whereas grade IV comprises complete loss of joint space with florid osteophytes and subchrondral sclerosis. Figure 1: Radiographs ofthe distal interphalangeal joint of the left middlefinger ofa femak transplant recipient (17years' duration; no haemodialysis) at age 29 (a) and 37 (b), showing progressive loss ofarticular cartilage, erosion ofsubchondral bone, and osteophytosis. Similar radiological changes in different stages ofevolution were present in other distal interphalangealjoints. Severalfingers in both hands were affected by Heberden's nodes, and a cystic node had occurredwithoutinflammationoverthedistalinterphalangeal joint of the left little finger at age 36. All distal interphalangealjoints were stiffand restricted.
2 Erosive osteoarthritis of hands 379 Prevalence ofgrade III and IV osteoarthritis in hands ofpatients with chronic renal disease. Number (%) ofpatients is given Age (years) Controls 1 (0-3) 1 (0 3) 3 (0 7) 14 (3) 34 (10-5) 115 (29-7) All renal patients 0 (0) 1 (3 5) 3 (5-9) 3 (6 3) 11 (19 3) 3 (15-8) Patients receiving CHD* 0 (0) 1 (10) 1 (5-6) 1 (5-6) 8 (25-8) 2 (13-3) Transplant recipients 0(0) 0(0) 2 (6-1) 2 (67) 3 (11-5) 1(25) $CHD=chronic haemodialysis. Those patients with the additional feature of erosion of subchondral bone were designated as having erosive OA. Control data were obtained from the Leigh and Wensleydale survey." The prevalences of grade III or IV OA in the distal interphalangeal joints in that study were used as our control values. Statistical analyses were performed with Figure 2: Radiographs offingers of the right hand ofa female transplant recipient (15 years' duration; one vear haemodialysis) at age 53 (a) and 58 (b). Note progression ofarthritis, resulting in severe loss ofsubchondral bone, osteophytosis, and deformity in the distal interphalangeal joint ofthe little finger, and loss ofarticular cartilage, subchondral sclerosis, osteophvtosis, and deformity in the interphalangeal joint ofthe middle finger. Less severe osteoarthritis is present in other distal interphalangealjoints. the x2 test (with Yates's correction for small numbers). Results The prevalence of grade III or IV OA amongst the renal patients (chronic haemodialysis and transplant recipients combined) aged years (9-4%) was significantly higher than in the normal population (3%) (p<0-001). Over the age of 65, however, the number of renal patients available for study was small (19 total), and in this group there was no significant difference in prevalence of OA compared with controls. The sex ratios (female to male) in the transplant recipients, those receiving chronic haemodialysis, and controls were 2-9, 1-64, and 1-86 respectively. Analysis of prevalence by decennial cohorts (24-34; 35-44; 45-54; 55-64; >65 years) showed that compared with the control data there was an excess of grade III or IV OA among patients with renal disease in each cohort up to the age of 65. This excess was apparent in both the patients receiving chronic haemodialysis >25 years and the transplant recipients >35 years (table). The differences between the renal patients and control data reached significance in the age cohorts (p<005) and (p<0-05). Of the 21 patients with grade III or IV OA, all had distal interphalangeal joint involvement, and in addition five and nine respectively had proximal interphalangeal joint and first carpometacarpal joint involvement. All but two of the 21 patients also had erosion of subchondral bone in at least one of the affected joints. In most patients the joints were affected in an asymmetrical fashion with articular abnormalities ranging from normal in some joints to severe destructive changes in others. Review of earlier hand radiographs showed that minor osteoarthritic changes often progressed rapidly to destructive erosive OA (figs 1-3), a phenomenon which we had observed previously in our index cases.' No patients had degenerative changes isolated to the proximal interphalangeal or first carpometacarpal joints. In 17 of these 21 patients Heberden's nodes were clinically apparent, and three of the five with proximal interphalangeal joint involvement had Bouchard's nodes. None of the patients gave a definite history of an inflammatory episode involving affected joints, but 14 of the 21 affected had joint pain or stiffness with mild to moderate loss of function. Several patients had marked vascular calcification, but significant periarticular soft tissue calcification was present in only one patient with OA.
3 380 Duncan, Hurst, Sebben, Milazzo, Disney -1 _ Series I Figure 3: Radiographs offingers ofthe right hand (a), left hand (b), and right thumb (c) at ages 59 (series I) and 63 (series II, facing page) ofa patient receiving chronic haemodialysis (five years' haemodialysis; no transplant). Note the progression of arthritts tn the thumb, resulting in severe resorption ofsubchondral bone and deformity. Progressive arthritic changes have occurred in various interphalangealjoints offingers from age 59 to 63, with loss ofarticular cartilage, subchondral sclerosis, osteophytosis, and, eventually, resorption ofsubchondral bone. Note that changes are in different stages ofevolution in different fingers. Discussion In this study our aim was to determine whether there is an increase in prevalence of grade III or IV OA of hands in chronic renal failure and whether the condition is accelerated and occurs at an earlier age. Our data suggest that although there is no overall increase in prevalence of grade III or IV OA, it does occur at an earlier age in patients with chronic renal failure and shows a marked propensity to progress to erosion of subchondral bone. Furthermore this phenomenon is apparent both in patients receiving chronic haemodialysis and in transplant recipients. The radiological appearances are indistinguishable from those associated with so called 'erosive OA', but our patients did not report inflammatory symptoms or signs in affected joints. One transplant recipient who developed a typical cystic Heberden's node had no associated inflammation. The usual inflammatory changes might have been suppressed by her corticosteroid treatment. An important question is whether our use of the Leigh and Wensleydale study for our control data is valid. The radiographic criteria used were the same, but the population from which that sample was taken may not be comparable with our regional referral population for which no equivalent data are available. A recent survey from Holland found a prevalence of grade III or IV OA in distal interphalangeal joints of hands of 3-8% in men and 5-9% in women aged years.'2 In the Leigh and Wensleydale survey the prevalences were in fact slightly higher-4-7% of men and 7.4% of women. Higher prevalences of OA have been
4 Erosive osteoarthritis ofhands 381 noted in Pima and Blackfeet Indians and in one Japanese group.13 Most patients in our study were of Northern European descent, however, and it is unlikely that our referral population had a substantially different prevalence of OA from the United Kingdom or Dutch populations. Interpretation of radiological changes in the finger joints of patients with chronic renal failure has been controversial.' Sundaram et al described erosive changes affecting the distal interphalangeal or metacarpophalangeal joints in 24 of 80 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis.3 In some patients these were associated with degenerative changes resembling erosive OA, but exact numbers or ages of patients were not listed. Rubin et al in a study of 59 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis showed a similar prevalence of small joint erosions and noted 'coincidental' OA in small joints of the hands or knees in 24% of their patients.4 Naidich et al reported a radiological survey of 81 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis and identified 32 with severe 'erosive osteoarthropathy' affecting equally distal interphalangeal, proximal interphalangeal, and first carpometacarpal joints.5 Affected joints were grossly Series! narrowed with the gull's wing appearance and lateral subluxation typical of erosive OA."4 Surprisingly, Naidich concluded that the changes were not typical of OA because of the presence of osteopenia, cystic change, and sometimes soft tissue calcification. Goldstein et al7 also described 11 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis who had a chronic hand arthropathy with similar radiographic features but noted an absence of 'spurring'-that is, osteophytes, and thus also concluded that the condition is distinct from OA. In our study we specifically identified those patients with radiological grade III or IV OA, who by definition have prominent osteophytes, and our data confirm that there is an association between chronic renal failure and premature onset of severe OA. In addition, almost all our patients showed evidence of progression to erosion of subchondral bone typical of erosive OA. Most authors have not commented on whether the above radiological changes result in functional loss, and only two reports suggest that significant symptoms or deformity may develop.4 7 We have found OA in the hands to be a significant source of symptoms and functional loss in patients with chronic renal failure.
5 382 Duncan, Hurst, Sebben, Milazzo, Disney A similar conclusion was drawn in a recent survey of dialysis related arthropathy undertaken in this hospital, which found that OA is a common cause of small joint stiffness and pain.2 Our study also extends this finding to transplant recipients. The pathogenesis of articular damage in chronic renal failure remains speculative.' The concept suggested by Bywaters et al that erosions may result from collapse of softened subchondral bone at sites of mechanical pressure may be important in patients with chronic renal failure. 5 Sundaram et al also concluded that this was a likely mechanism of articular damage in patients receiving chronic haemodialysis.3 The progression from minor osteoarthritic changes to marked bone erosion observed in our patients is consistent with Bywater's hypothesis. Thus metabolic bone disease, including osteopenia,'6 which is multifactorial and ubiquitous in chronic renal failure, might contribute to the development of erosive OA in patients receiving chronic haemodialysis and in transplant recipients. We conclude that chronic renal failure is a risk factor for the premature development of grade III or IV OA and that this risk remains even after successful renal transplantation. Furthermore, these patients also develop progressive erosion of subchondral bone typical of erosive OA. Metabolic factors associated with chronic renal failure are presumed to be responsible. Our findings may be relevant to the understanding of the pathogenesis of nodal and erosive OA in the normal aging population. I Duncan I J S, Hurst N P, Disney A, Sebben R, Milazzo S C. Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 1989; 48: Hurst N P, van den Berg R, Disney A, et al. Dialysis related arthropathy: a survey of 95 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis with special reference to 1P2 microglobulin related amyloidosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1989; 48: Sundaram M, Wolverson M K, Heiberg E, Grider R D. Erosive azotaemic osteodystrophy. AjR 1981; 136: Rubin L A, Fam A G, Rubenstein J, Campbell J, Saiphoo C. Erosive azotaemic arthropathy. Arthritis Rheum 1984; 27: Naidich J B, Karmel M I, Mossey R T, Bluestone P A, Stein H L. Osteoarthropathy of the hand and wrist in patients undergoing longterm haemodialysis. Radiology 1987; 164: Resnick D L. Erosive arthritis of the hand and wrist in hyperparathyroidism. Radiology 1974; 110: Goldstein S, Winston E, Chung T J, Shreekant C, Pariser K. Chronic arthropathy in long-term haemodialysis. Am 7 Med 1985; 78: Brown E A, Arnold I R, Gower P E. Dialysis arthropathy: complication of long term treatment with haemodialysis. Br MedJ 1986; 292: Hamilton S, Knickerbocker W J. Peri-articular erosions in the hands and wrists in haemodialysis patients. Clin Radiol 1982, 33: Lawrence J S, Kellgren J H. Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957; 16: Lawrence J S, Bremner J M, Bier F. Osteoarthrosis prevalence in the population and relationship between symptoms and x-ray changes. Ann Rheum Dis 1966; 25: van Saase J L C M, Vandenbroucke J P, Romunde L K J van, Valkenburg H A. Osteoarthritis and obesity in the general population. A relationship calling for an explanation. 7 Rheumatol 1988; 15: van Saase J L C M, van Romunde L K J, Cats A, Vandenbroucke J P, Valkenburg H A. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Zoetermeer survey. Comparison of radiological osteoarthritis in a Dutch population with that in 10 other populations. Ann Rheum Dis 1989; 48: Ehrlich G E. Erosive inflammatory and primary generalized osteoarthritis. In: Moskowitz R W, Howell D S, Goldberg V M, Mankin H J, eds. Osteoarthritis-diagnosis and management. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1984: Bywaters E G L, Dixon A St J, Scott J T. Joint lesions of hyperparathyroidism. Ann Rheum Dis 1963; 22: Smythe H A. Osteoarthritis, insulin, and hone density. I Rheumatol 1987; 14 (suppl): Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 June Downloaded from on 13 January 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Radiologic features of a pyrophosphate-like arthropathy associated with long-term dialysis
 Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16:437-441 Skeletal Radiology Radiologic features of a pyrophosphate-like arthropathy associated with long-term dialysis Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Kathleen Menerey, M.D. 2, William
Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16:437-441 Skeletal Radiology Radiologic features of a pyrophosphate-like arthropathy associated with long-term dialysis Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Kathleen Menerey, M.D. 2, William
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
Osteoarthritis. RA Hughes
 Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
Osteoarthritis RA Hughes Osteoarthritis (OA) OA is the most common form of arthritis and the most common joint disease Most of the people who have OA are older than age 45, and women are more commonly
An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Radiographic patterns and associations of
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
Study of 500 patients with limb joint osteoarthritis. symptomatic joint sites. I. Analysis by age, sex, and distribution of SCIENTIFIC PAPERS
 8 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 8-13 SCIENTIFIC PAPERS Rheumatology Unit, Bristol Royal Inirmar, Bristol BS2 8HW J Cushnaghan P Dieppe Correspondence to: Dr J Cnaghan. Accepted for publication
8 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 8-13 SCIENTIFIC PAPERS Rheumatology Unit, Bristol Royal Inirmar, Bristol BS2 8HW J Cushnaghan P Dieppe Correspondence to: Dr J Cnaghan. Accepted for publication
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
Clinical and radiological survey of the
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (976), 5, 49 Clinical and radiological survey of the incidence of osteoarthrosis among obese patients RICHARD H. GOLDIN, LAWRENCE McADAM, JAMES S. LOUIE, RICHARD GOLD, AND RODNEY BLUESTONE
Ann. rheum. Dis. (976), 5, 49 Clinical and radiological survey of the incidence of osteoarthrosis among obese patients RICHARD H. GOLDIN, LAWRENCE McADAM, JAMES S. LOUIE, RICHARD GOLD, AND RODNEY BLUESTONE
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
HEMOCHROMATOSIS HIP ARTHROPATHY IN GENETIC. Radiographic and Histologic Features
 357 HIP ARTHROPATHY IN GENETIC HEMOCHROMATOSIS Radiographic and Histologic Features J. S. AXFORD, A. BOMFORD, P. REVELL, 1. WATT, R. WILLIAMS, and E. B. D. HAMILTON Genetic hemochromatosis, a disorder
357 HIP ARTHROPATHY IN GENETIC HEMOCHROMATOSIS Radiographic and Histologic Features J. S. AXFORD, A. BOMFORD, P. REVELL, 1. WATT, R. WILLIAMS, and E. B. D. HAMILTON Genetic hemochromatosis, a disorder
Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 485-491 Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome scanning, bone scanning, and radiography M M O'SULLIVAN,' N POWELL,- A P FRENCH, K E WILLIAMS,4
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 485-491 Inflammatory joint disease: a comparison of liposome scanning, bone scanning, and radiography M M O'SULLIVAN,' N POWELL,- A P FRENCH, K E WILLIAMS,4
Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 311-318 Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease Pathogenesis and roentgen appearance D. RESNICK AND G. NIWAYAMA
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 311-318 Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease Pathogenesis and roentgen appearance D. RESNICK AND G. NIWAYAMA
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis
 AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis (General) = inflamed joint - NOT a single disease: covers >100 types - Involves disability + decreased quality of life o Can also occur in young people (not just the
AOS 3: Rheumatoid Arthritis Arthritis (General) = inflamed joint - NOT a single disease: covers >100 types - Involves disability + decreased quality of life o Can also occur in young people (not just the
'Dialysis related arthropathy': a survey of 95 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis with special reference
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 409-420 'Dialysis related arthropathy': a survey of 95 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis with special reference to 132 microglobulin related amyloidosis
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 409-420 'Dialysis related arthropathy': a survey of 95 patients receiving chronic haemodialysis with special reference to 132 microglobulin related amyloidosis
Radiographic patterns and associations of osteoarthritis of the knee in patients referred to hospital
 520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
High Impact Rheumatology
 High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS
 INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the Framingham Study
 Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Fast Facts. Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis. Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan MB BS PhD FRACP FRCP Professor of Musculoskeletal Medicine University of
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan MB BS PhD FRACP FRCP Professor of Musculoskeletal Medicine University of
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
predicts radiographic change
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Bones? Did someone say bones? 12/31/2012. W.R Reinus, MD MBA FACR
 William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
NEW RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING SCALES FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HAND
 1584 NEW RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING SCALES FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HAND Reliability for Determining Prevalence and Progression DOUGLAS A. KALLMAN, FREDRICK M. WIGLEY, WILLIAM W. SCOTT, JR.. MARC C. HOCHBERG,
1584 NEW RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING SCALES FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HAND Reliability for Determining Prevalence and Progression DOUGLAS A. KALLMAN, FREDRICK M. WIGLEY, WILLIAM W. SCOTT, JR.. MARC C. HOCHBERG,
BRIEF REPORT. KENNETH D. BRANDT, ROSE S. FIFE, ETHAN M. BRAUNSTEIN, and BARRY KATZ. From the Department of Medicine, the Department of
 1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
Artropathies: what can be seen in hands?
 Artropathies: what can be seen in hands? Poster No.: C-2452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Torres Rodrigues, J. C. Ruivo Rodrigues, C. Albuquerque, D. Silva; Viseu/PT Keywords:
Artropathies: what can be seen in hands? Poster No.: C-2452 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. M. Torres Rodrigues, J. C. Ruivo Rodrigues, C. Albuquerque, D. Silva; Viseu/PT Keywords:
developed in both knees, anikles, radiocarpal joints,
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 1021-1026 Case report Relapsing polychondritis arthritis mimicking rheumatoid P SCHLAPBACH,1 N J GERBER,1 P RAMSER,2 AND F M VAN'T HOOFT2 From the 'Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1988; 47, 1021-1026 Case report Relapsing polychondritis arthritis mimicking rheumatoid P SCHLAPBACH,1 N J GERBER,1 P RAMSER,2 AND F M VAN'T HOOFT2 From the 'Department
population with that in 10 other populations
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 271-28 Scientific papers Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Zoetermeer survey. Comparison of radiological osteoarthritis in a Dutch population with that in 1 other
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 271-28 Scientific papers Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Zoetermeer survey. Comparison of radiological osteoarthritis in a Dutch population with that in 1 other
Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying Radiographic Features of Osteoarthritis
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 4, April 2012, pp 533 538 DOI 10.1002/acr.21586 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 4, April 2012, pp 533 538 DOI 10.1002/acr.21586 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying
Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views
 Original Article Page 1 of 8 Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views Hwee-Yee Christian Heng, Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak, Amit Kanta
Original Article Page 1 of 8 Radiographic grading of the patellofemoral joint is more accurate in skyline compared to lateral views Hwee-Yee Christian Heng, Hamid Rahmatullah Bin Abd Razak, Amit Kanta
Pain in Osteoarthritis
 Pain in Osteoarthritis By Edward L. Treadwell, MD Professor of Medicine- Rheumatology/Immunology Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University School of Medicine Greenville, NC 27834 E-mail: treadwelle@ecu.edu
Pain in Osteoarthritis By Edward L. Treadwell, MD Professor of Medicine- Rheumatology/Immunology Brody School of Medicine at East Carolina University School of Medicine Greenville, NC 27834 E-mail: treadwelle@ecu.edu
Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: Relation to a Diagnosis of Knee Osteoarthritis
 International Journal of Chinese Medicine 2017; 1(3): 102-107 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcm doi: 10.11648/j.ijcm.20170103.15 Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis
International Journal of Chinese Medicine 2017; 1(3): 102-107 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcm doi: 10.11648/j.ijcm.20170103.15 Significant Clinical Symptoms and Signs in Knee Osteoarthritis
Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology
 Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology Poster No.: C-1599 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Pissarra, R. R. Domingues Madaleno,
Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology Poster No.: C-1599 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Pissarra, R. R. Domingues Madaleno,
The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 327-331 The knees and ankles in sport and veteran military parachutists C. F. MURRAY-LESLIE, D. J. LINTOTT, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Relation between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A study of 40 patients
 2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
Erosive osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis and pseudogout; a casual association?
 DOI 10.1007/s10067-015-2927-9 CASE BASED REVIEW Erosive osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis and pseudogout; a casual association? Ariela Hoxha 1 & Amelia Ruffatti 1 & Enrico Alberioli 2 & Mariagrazia Lorenzin
DOI 10.1007/s10067-015-2927-9 CASE BASED REVIEW Erosive osteoarthritis, psoriatic arthritis and pseudogout; a casual association? Ariela Hoxha 1 & Amelia Ruffatti 1 & Enrico Alberioli 2 & Mariagrazia Lorenzin
For patients with musculoskeletal pain, imaging can aid in making or confirming
 Clinical basics Rheumatology: 3. Getting the most out of radiology Review Synthèse Graham Reid, * John M. Esdaile The case A 72-year-old man has been seeing the same physician for 2 decades, and his only
Clinical basics Rheumatology: 3. Getting the most out of radiology Review Synthèse Graham Reid, * John M. Esdaile The case A 72-year-old man has been seeing the same physician for 2 decades, and his only
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
ARTHRITIS. What Is Arthritis?
 There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
There are many types of arthritic processes that can cause joint changes, pain and loss of motion and strength in the hands. Many excellent and detailed resources are available and will be listed under
Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis?
 International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2014; 17: 299 303 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis? Ozlem CEMEROGLU, 1 Halil
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 2014; 17: 299 303 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hand and heart, hand in hand: is radiological hand osteoarthritis associated with atherosclerosis? Ozlem CEMEROGLU, 1 Halil
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review
 Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Journal of the OsteoArthritis Research Society International
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $33-$37 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi:10.1053/joca.2000.0334, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on It Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $33-$37 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi:10.1053/joca.2000.0334, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on It Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement
 \>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
\>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Journal of the OsteoArthritis Research Society International
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $64-$69 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi: 10.1053/joca. 1999.0340, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on D IF --JI~=L
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, Supplement A, $64-$69 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi: 10.1053/joca. 1999.0340, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on D IF --JI~=L
Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional Study
 Arthritis Volume 2012, Article ID 984060, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/984060 Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional
Arthritis Volume 2012, Article ID 984060, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/984060 Clinical Study Relationships between Pain, Function and Radiographic Findings in Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Cross-Sectional
End-Stage Hemophilic Arthropathy: The Journey to Joint Replacement
 Slide no 1 End-Stage Hemophilic Arthropathy: The Journey to Joint Replacement Husam Darwish, MD, FRCSC Asst. Professor and Consultant Department of Orthopaedic Surgery King Abdulaziz University Jeddah,
Slide no 1 End-Stage Hemophilic Arthropathy: The Journey to Joint Replacement Husam Darwish, MD, FRCSC Asst. Professor and Consultant Department of Orthopaedic Surgery King Abdulaziz University Jeddah,
Analysis of Osteoarthritis in Knee X-Ray Image
 Analysis of Osteoarthritis in Knee X-Ray Image 1 Shashikala R, 2 Divya.M.Shetty, 3 Anupa, 4 Deepikaraj Ballal, 5 Rakshitha 1 Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 Student (BE) Department of Electronics & Communication
Analysis of Osteoarthritis in Knee X-Ray Image 1 Shashikala R, 2 Divya.M.Shetty, 3 Anupa, 4 Deepikaraj Ballal, 5 Rakshitha 1 Assistant Professor, 2,3,4,5 Student (BE) Department of Electronics & Communication
ARTHRITIS RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC SKELETAL HYPEROSTOSTS
 ARTHRITIS 82 RHEUMATISM OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCiA I ION SECTION OF THE ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION 1 RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC
ARTHRITIS 82 RHEUMATISM OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCiA I ION SECTION OF THE ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION 1 RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC
Inflammatory rheumatic diseases
 Learning objectives Inflammatory rheumatic diseases Bruce Kidd Barts & The London, Queen Mary, University of London To understand: 1. prevalence and range of the rheumatological s 2. clinical features
Learning objectives Inflammatory rheumatic diseases Bruce Kidd Barts & The London, Queen Mary, University of London To understand: 1. prevalence and range of the rheumatological s 2. clinical features
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 117-121 117 CASE REPORT Monostotic Paget s Disease: A Case Report CHI-CHEN HOU 1 CHI WEI LO 2 JINN-MING CHANG 1 CHING-CHERNG TZENG 3 Department of Diagnostic Radiology 1, Orthopedics
Chopstick Arthropathy
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2004, pp 1495 1500 DOI 10.1002/art.20145 2004, American College of Rheumatology Chopstick Arthropathy The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study David J. Hunter, 1 Yuqing
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 50, No. 5, May 2004, pp 1495 1500 DOI 10.1002/art.20145 2004, American College of Rheumatology Chopstick Arthropathy The Beijing Osteoarthritis Study David J. Hunter, 1 Yuqing
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
HERITABILITIES OF RADIOLOGIC OSTEOARTHRITIS IN PERIPHERAL JOINTS AND OF DISC DEGENERATION OF THE SPINE
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 42, No. 8, August 1999, pp 1729 1735 1999, American College of Rheumatology 1729 HERITABILITIES OF RADIOLOGIC OSTEOARTHRITIS IN PERIPHERAL JOINTS AND OF DISC DEGENERATION OF
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 42, No. 8, August 1999, pp 1729 1735 1999, American College of Rheumatology 1729 HERITABILITIES OF RADIOLOGIC OSTEOARTHRITIS IN PERIPHERAL JOINTS AND OF DISC DEGENERATION OF
Arthritis & Rheumatism
 ~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: 07/26/17 Page 1 of 9
 Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Wrist cysts and fistulae
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 388 Wrist cysts and fistulae An arthrographic study of the rheumatoid wrist* J. M. I. IVESON, A. G. S. HILL, AND V. WRIGHT From the Department of Rheumatology, General Infirmary
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 388 Wrist cysts and fistulae An arthrographic study of the rheumatoid wrist* J. M. I. IVESON, A. G. S. HILL, AND V. WRIGHT From the Department of Rheumatology, General Infirmary
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
Quantitative radiography of osteoarthritis
 268 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 268-275 REVIEW Division ofanatomy and Cell Biology, United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy's and St Thomas's Hospitals, London, United Kingdom J C Buckland-Wright
268 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 268-275 REVIEW Division ofanatomy and Cell Biology, United Medical and Dental Schools of Guy's and St Thomas's Hospitals, London, United Kingdom J C Buckland-Wright
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis
 the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
Computed tomography for the detection of thumb base osteoarthritis, comparison with digital radiography.
 Computed tomography for the detection of thumb base osteoarthritis, comparison with digital radiography. Poster No.: C-1981 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. S. Saltzherr, J. W. van
Computed tomography for the detection of thumb base osteoarthritis, comparison with digital radiography. Poster No.: C-1981 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. S. Saltzherr, J. W. van
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs
 Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping
 Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Medial Knee Osteoarthritis Precedes Medial Meniscal Posterior Root Tear with an Event of Painful Popping Dhong Won Lee, M.D, Ji Nam Kim, M.D., Jin Goo Kim, M.D., Ph.D. KonKuk University Medical Center
Mr. OA: Case Presentation
 CLINICAL CASES Case 1: Mr. OA OA Mr. OA: Case Presentation 62-year-old lawyer Mild left knee pain for 3 month, but became worse 1 week ago No swelling 1 week earlier: 2-hour walk in the countryside 2 days
CLINICAL CASES Case 1: Mr. OA OA Mr. OA: Case Presentation 62-year-old lawyer Mild left knee pain for 3 month, but became worse 1 week ago No swelling 1 week earlier: 2-hour walk in the countryside 2 days
3 脊椎変形の相互関係とリスク分析の今後の方向
 Reprint request: DEGENERATIVE SPINE AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN ELDERLY PEOPLE Toshitaka NAKAMURA Department of Orthopedics, University of Occupational and Environmental Health School of Medicine Vertebral osteophytes,
Reprint request: DEGENERATIVE SPINE AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN ELDERLY PEOPLE Toshitaka NAKAMURA Department of Orthopedics, University of Occupational and Environmental Health School of Medicine Vertebral osteophytes,
The distribution of distal femoral osteophytes in a human skeletal population
 EXTENDED REPORT The distribution of distal femoral osteophytes in a human skeletal population Lee Shepstone, Juliet Rogers, John Kirwan, Bernard Silverman School of Health Policy and Practice, University
EXTENDED REPORT The distribution of distal femoral osteophytes in a human skeletal population Lee Shepstone, Juliet Rogers, John Kirwan, Bernard Silverman School of Health Policy and Practice, University
Ultrasound in Rheumatology
 Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Arthritis Research UK Primary Care Centre Winner of a Queen s Anniversary Prize For Higher and Further Education 2009 Ultrasound in Rheumatology Alison Hall Consultant MSK Sonographer/Research Fellow Primary
Physical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 1. Dec
 Physical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 1. Dec. 2015. Evaluation of patients with musculoskeletal complaints Anatomic localization
Physical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 1. Dec. 2015. Evaluation of patients with musculoskeletal complaints Anatomic localization
Bone mineral density and bone turnover in spinal
 Annals ofthe Rheumatc Diseases 1995; 54: 867-871 867 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Human Metabolism and Clinical Biochemistry, University of Sheffield, Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Annals ofthe Rheumatc Diseases 1995; 54: 867-871 867 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Human Metabolism and Clinical Biochemistry, University of Sheffield, Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, United Kingdom
Haemophilia. Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View. Epidemiology of Haemophilic joint disease
 Haemophilia Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View Dr. Alexander Chan Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Prince of Wales Hospital Deficiency of clotting factor VIII, and
Haemophilia Management of Haemophiliac Arthropathy Orthopaedic Point of View Dr. Alexander Chan Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology Prince of Wales Hospital Deficiency of clotting factor VIII, and
RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY FOLLOWING MINOR JOINT TRAUMA IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEUROPATHY
 ~ 412 - - - _... - - BRIEF REPORT RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY FOLLOWING MINOR JOINT TRAUMA IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEUROPATHY SALLY D. SLOWMAN-KOVACS, EI'HAN M. BKAUNSTEIN, and KENNETH D.
~ 412 - - - _... - - BRIEF REPORT RAPIDLY PROGRESSIVE CHARCOT ARTHROPATHY FOLLOWING MINOR JOINT TRAUMA IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEUROPATHY SALLY D. SLOWMAN-KOVACS, EI'HAN M. BKAUNSTEIN, and KENNETH D.
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31,112 Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand K. M. BACKHOUSE From the Royal College ofsurgeons ofengland, the Chielsea and Kensington Rheumatology Unit, and the Royal London
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31,112 Extensor expansion of the rheumatoid hand K. M. BACKHOUSE From the Royal College ofsurgeons ofengland, the Chielsea and Kensington Rheumatology Unit, and the Royal London
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2. Inflammatory Diseases. Definition. Imaging Signs
 Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
Rheumatoid Arthritis 2 Definition " Epidemiology Affects 2% of the population Peak incidence (diagnosis) in 4th and 5th decades Women affected 3 4 times more often than men Increased familial incidence
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
Presenter Disclosure Information
 4:15 5:45 pm Diagnostic Challenges of Rheumatologic Disease SPEAKER Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Peng Thim Fan,
4:15 5:45 pm Diagnostic Challenges of Rheumatologic Disease SPEAKER Peng Thim Fan, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Peng Thim Fan,
