Radiographic patterns and associations of
|
|
|
- Mildred Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom S Dawson B Preston Department of Orthopaedics, University Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom G Milligan Correspondence to: Dr J M Ledingham, Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 IPB, United Kingdom. Accepted for publication 15 May 1992 Radiographic patterns and associations of osteoarthritis of the hip Joanna Ledingham, Stewart Dawson, Bryan Preston, George Milligan, Michael Doherty Abstract A number of patterns of osteoarthritis of the hip are described, though studies are conflicting with respect to the frequency of such patterns and their associations. Two hundred and eleven patients (133 women, 78 men; mean age 66 years, range 29-86) referred to hospital with osteoarthritis of the hip were studied. Involvement was unilateral in 108 (51%) and bilateral in 89 (42%); 14 (7%) had undergone arthroplasty and were presenting with osteoarthritis in their second hip (total 300 osteoarthritic hips). Sixty one per cent of hips had severe, 28% moderate, and 11% mild changes (Keligren grade). Superior pole migration occurred in 82% (46% superolateral, 25% intermediate, 11% superomedial), medial/axial migration occurred in only 8%, and in 10% the pattern was indeterminate. In bilateral osteoarthritis of the hip the pattern was generaily symmetrical. Superomedial and medial/axial patterns were proportionately more common in women, whereas superlateral osteoarthritis predominated in men. No association was found between multiple clinical nodes, radiographic polyarticular interphalangeal or first carpometacarpal osteoarthritis and any migration pattern. Any interphalangeal osteoarthritis was negatively associated with medial migration. Only 40% of hips could be categorised as hypertrophic or atrophic; chondrocalcinosis at any site was associated with atrophic osteoarthritis; no associations were seen with Forestier's disease. This large survey confirms the association between chondrocalcinosis and atrophic osteoarthritis of the hip. Importantly it suggests that gender, rather than associated osteoarthritis at other sites, is a major determinant of the pattern of osteoarthritis of the hip. (Ann Rheum Dis 1992; 51: ) The definition, description, and classification of osteoarthritis remain problematic. Although osteoarthritis of the hip is usually characterised predominantly in terms of radiographic appearance, differing aspects have been emphasised. For example, the severity of osteoarthritis can be estimated using a global method such as that described by Kellgren and Lawrence,' or by assessing separate features (e.g. osteophyte, narrowing) to give a summated or individual character score.2 Subclassification has been attempted mainly according to the pattern of migration of the femoral head within the acetabulum, 7 or by the pattern of bone response to cartilage loss.7 The significance of these described patterns remains unclear,"'8 but associations with factors outside the hip have been described. For example, in some reports Heberden's nodes are associated with medial migration at the hip,8 9 and as medial and axial migration patterns typically occur in inflammatory arthropathies this has been taken as evidence to support an inflammatory aetiology for this generalised 'subset'. Similarly the presence of chondrocalcinosis at other joints has been associated with atrophic bone response and poor outcome at the hip,1921 though mechanisms to explain this have not been proposed. As a result of the marked heterogeneity of osteoarthritis differences in radiographic patterns at the hip could be useful in elucidating differences in aetiology and prognosis. This study was therefore undertaken to evaluate more fully the various radiographic patterns of osteoarthritis of the hip that have been described, namely the patterns of migration of the femoral head, patterns of bone response, and individual radiographic features of osteoarthritis of the hip, and to assess their associations with factors such as the presence of Heberden's nodes, interphalangeal osteoarthritis, multiple large joint osteoarthritis at other sites, and chondrocalcinosis. The relations of these factors to progression of osteoarthritis of the hip are addressed in a separate study. Patients and methods Over a two year period consecutive patients attending one rheumatology and three orthopaedic clinics (all general) with symptomatic osteoarthritis of the hip were recruited into the study. The diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the hip was defined as the presence of radiographic change (joint space narrowing and osteophyte, with or without cyst formation, sclerosis, or attrition) together with pain or clinical abnormalities, or both, at that site. Alternative arthropathies were excluded by clinical examination, blood tests (including erythrocyte sedimentation rate, serum calcium concentrations, rheumatoid factor (latex and Rose- Waaler tests (titre < 1/64)), and absence of sacroiliitis, isolated osteonecrosis, and marginal erosions on radiographic screening. Aspiration of other affected joints (predominantly the knee) was undertaken to exclude gout and to confirm associated calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition (compensated polarised light microscopy).
2 1112 Each patient underwent a full rheumatological history and examination with particular emphasis on the presence of activity, rest and night pain, duration of symptoms and past history of previous major trauma or surgery to the hips. On examination, clinical abnormalities consistent with osteoarthritis were noted for non-axial joints. Nodal change was defined clinically as the presence of typical superolateral Heberden's or Bouchard's nodes, or both, affecting at least three rays of each hand. In each patient plain radiographs were taken of the pelvis (supine anteroposterior), hands (to include wrists), shoulders, knees (standing anteroposterior plus 200 flexion lateral views), lumbar spine (anteroposterior and lateral), and thoracic spine (anteroposterior), together with any other clinically affected joint. Films were examined and scored by two observers during an initial training period. Subsequently one observer scored all hip films (observer 1) and the other all other films (observer 2). Both observers independently and blindly rescored 50 complete sets of radiographs selected at random. For the hips intra- (observer 1) and interobserver variability was determined by comparing these repeat gradings with the original assessment. Likewise for the other joint sites intra- (observer 2) and interobserver variability was also determined. The Kellgren and Lawrence grading system' was used to assess radiographic severity of osteoarthritis at the hips and other joints. Osteoarthritis was recorded as present in any joint scored as Kellgren grade 2 or more, and multiple large joint osteoarthritis was defined as at least one other large joint (knee, shoulder) affected in addition to the hip. Polyarticular interphalangeal osteoarthritis was defined by involvement (Kellgren score 2 or more) in at least three rays of both hands. Chondrocalcinosis and Forestier's disease (spinal hyperostosis with bridging new bone across four contiguous vertebrae3) were recorded if present. The pattern of migration of the femoral head within the acetabulum was classified into superolateral, superomedial, superior intermediate, medial or axial patterns according to Table I Patient characteristics: radiographic osteoarthritis was defined as Kellgren grades 2-4 Patient characteristic Men Women Odds ratios for women v men (95% confidence intervals) Median (range) age (years) Median (range) symptom duration (years) Mean (range) ponderal index 65 (29-84) 5 5 (1-36) 27-1 ( ) -.1 No (%) with osteoarthritis of the hip Unilateral 39 (50) Bilateral 37 (47) Previous THR 2 (3) No (%) with isolated osteoarthritis of the hip 29 (37) No (%) with no radiographic osteoarthritis of the hand 35 (45) No (%) with radiographic osteoarthritis at other sites Polyarticular interphalangeal joints 6 (8) Any interphalangeal joint 30 (38) First carpometacarpal joint 18 (23) Knee joint 18 (23) Glenohumeral joints 4 (5) No (%) with nodal changes 6 (8) No (%) with chondrocalcinosis Hip 2 (3) Other sites 7 (9) No (%) with Forestier disease 9 (12) 68 (42-86) 7 (1-50) 26-5 ( ) 69 (52) 52 (39) 12 (9) 24 (18) 36 (27) 24 (18) 80 (60) 53 (40) 50 (38) 17 (13) 21 (16) 0 (0) 14(11) 4 (3) 1-08 (1-64 to 1 91) 0-71 (0-40 to 0-80) 3-77(11 to 15-8) 0-37 (0-20 to 0 69) 0-46(026 to 082) 2-60 (6-38 to 10-6) 2-42 (1-37 to 4-26) 2-21 (1-18 to 4-13) 2-01 (1-07 to 377) 1-03 (3 55 to 3-76) 2 25 (1-13 to 5-72) 1 19 (2 16 to 3 07) 0-24 (0-08 to 0 74) Ledingham, Dawson, Preston, Milligan, Doherty the direction of movement of the femoral head.3 If migration could not be classified (due either to early osteoarthritis or severe attrition) the hip was categorised as indeterminate. The bone response at each hip was categorised as either atrophic or hypertrophic as described by Solomon7; an indeterminate category was used for hips demonstrating a mixed pattern of bone response. In addition, individual features of osteoarthritis were graded 0-3 using a modification of the method of Thomas et a12 at specific sites, namely narrowing (site of maximum narrowing only, maximum score 3), osteophyte (femoral neck, inferior and superior femoral head, medial and lateral acetabulum; maximum score 15), sclerosis (at site of maximum sclerosis; maximum score 3), cysts (acetabular roof, remainder of acetabulum, femoral head; maximum score 9), and attrition (femoral and acetabular components; maximum score 3). Statistical analysis was performed using the x2 (with Yates's correction) and Fisher's tests as appropriate. The x statistic was used to assess intra- and interobserver variability22; multiple exclusive categories were used without the use of 'weights'. Odds ratios were calculated with respect to the presence or absence of putative risk factors. Results PATIENT CHARACTERISATION Two hundred and eleven patients (133 women, 78 men; mean age 66 years, range 29-86) were recruited into the study (table 1). The mean age at onset of hip symptoms was 59 (range 16-84) years, giving a median symptom duration at the time of hospital referral of six (range ) years. Fifty one per cent had unilateral and 43% had bilateral hip osteoarthritis; 6% had received a previous hip replacement and were presenting with their second hip affected. A total of 300 osteoarthritic hips was therefore assessed. Sixty one per cent of hips had severe, 28% moderate, and 11% mild radiographic changes (corresponding to Kellgren grades 4, 3, and 2 respectively). Of the symptomatic hips 94% had definite radiographic osteoarthritis (Kellgren grade 2 or more (definite narrowing and other changes of osteoarthritis)) and 6% (all of whom had symptoms and definite radiographic osteoarthritis in the contralateral hip) had Kellgren grade 0 or 1. Sixteen per cent of hips showing definite radiographic osteoarthritis were asymptomatic; these included hips with marked attrition and similar severity of change as in the contralateral symptomatic hip. Twenty five per cent of patients had osteoarthritis confined to the hip; the remainder had either multiple large joint osteoarthritis (knees 32%, shoulders 10%) or hand osteoarthritis (66%) with nodal changes occurring in 14%. Women more commonly had nodal changes (table 1) and multiple joint involvement whereas men more commonly had isolated hip osteoarthritis (odds ratio 2-69; confidence interval 1*36 to 5*35). PATTERNS OF MIGRATION The patterns of migration of the femoral head within the acetabulum could be accurately
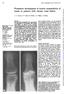
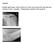
3 Radiographic patterns and associations ofosteoarthritis ofthe hip 1113 Table 2 Migration and bone response patterns. Results given as number (%) of patients Men Women Age (years) < Migration Superolateral 66 (58) 73 (39) 27 (19) 68 (49) 44 (32) Superior intermediate 28 (24) 48 (26) 7 (9) 27 (36) 42 (55) Superomedial 3 (3) 29 (16) 4 (12) 14 (44) 14 (44) Axial 1 (1) 4 (2) 0 (0) 3 (60) 2 (40) Medial 5 (4) 14 (8) 3 (16) 11 (58) 5 (26) Indeterminate 12 (10) 17 (9) 4 (14) 11 (38) 14 (48) Bone response Atrophic 20 (17) 37 (20) 6 (10) 22 (39) 29 (51) Hypertrophic 23 (20) 38 (20) 12 (19) 34 (56) 15 (25) Indeterminate 72 (63) 110 (60) 27 (15) 78 (43) 77 (42) categorised in 90% of affected hips (table 2, fig 1). Superior migration predominated, the superolateral pattern being the most common (46%; fig 2), followed by superior intermediate (25%), and superomedial (11%). The medial and axial patterns were infrequent, occurring in l only 6 and 2% of hips respectively (fig 3). Patients with bilateral hip osteoarthritis gener- ally showed symmetry in terms of the.pattern of Figure 2 Radiograph showing superolateralfemoral head femoral head migration (p<o001); the axial migration. pattern was only seen in those with bilateral osteoarthritis and, except for one patient, this was also true for the medial pattern. The exception (a 45 year old man who had undergone internal fixation of one femoral neck following a fracture at the age of 12) was >::._ superolateral migration in one hip with medial migration in the other (fig 4). PATTERNS OF BONE RESPONSE Bone response at the hip could be categorised as atrophic or hypertrophic in only 40% of patients. The atrophic response was seen in 199/%, hypertrophic in 21%. No significant sex or age associations were noted for either pattern, though there was an increased frequency of the atrophic pattern with age. 46~~ Fi'gure 3 Radiograph showing the medial pattern of femoral head migration. INDIVIDUAL RADIOGRAPHIC FEATURES,By6 defiition mild, moderate, and complete * ~~joint space narrowing was seen in hips graded as Kellgren grade 2, 3, and 4 respectively. Marked osteophyte formation (score >10O), cystic change (score >6), sclerosis (score >2), and attrition * ~~~(score > 1) were all seen exclusively in hips of -Kellgren grade 4. Complete absence of each of these radiographic features (in isolation or in combination), however, were seen in all of the * Kellgren categories. Of the 18 symptomatic hips with no osteoarthritis on the Kellgren grading system (i.e. grades 0 and 1), 12 had mild osteophytosis, eight had mild cystic change, and three had mild sclerosis using the method of Figre I Diagram showingfemoral head migration Thomas et al.' Again by definition none of these Patters in the 270 (90/) hips that could be categorised. hips had definite joint space narrowing.
4 114 Ledingham, Dawson, Preston, Milligan, Doherty Figure 4 Radiograph of the only patient showing discordance in migration pattern with superolateral migration in the left and medial migration in the right hip (the latter having received mechanical insult and surgical intervention at the age of 12 years). Table 3 ASSOCIATIONS x Values for observer variation Generalised nodal osteoarthritis Interphalangeal osteoarthritis Forestier disease Kellgren grade (hip) Migration pattern Bone response pattern Hip attrition Hip sclerosis Hip osteophyte Hip cyst Owing to the small numbers of hips showing medial or axial patterns of migration these two groups were merged for statistical analysis. Superomedial, medial, and axial patterns were proportionately more common in women (26% of women v 8% of men; p<0001) and the superolateral pattern was more common in men (58% of men v 39% of women; p<0.01). No association was found between the migration pattern and age, the presence of nodal change, polyarticular interphalangeal osteoarthritis, first carpometacarpal joint osteoarthritis, or chondrocalcinosis. Medial and axial migration patterns were seen less frequently in patients with interphalangeal osteoarthritis compared with those without (4% v 12-5%; p<0.05). Chondrocalcinosis, either at the hip or at other sites, was more commonly associated with an atrophic bone response (occurring in 19, 3, and 9% of atrophic, hypertrophic, and indeterminate hips respectively; p<001). There was no association between the type of bone response and the presence or absence offorestier's disease, nodal change, first carpometacarpal joint osteoarthritis, polyarticular or pauciarticular interphalangeal osteoarthritis. With regard to the individual radiographic features of osteoarthritis, bone attrition associated strongly with the atrophic bone response pattern and with reporting of night pain (p<0-001). No significant associations were found between bone attrition, subchondral cyst or osteophyte formation, and the presence of nodal change, polyarticular or pauciarticular interphalangeal osteoarthritis, first carpometacarpal joint osteoarthritis, chondrocalcinosis or Intra- 95% Interobserver Confidence observer variability interval vanrability to to to to to to to to to to % Confidence interval 0-01 to to to to to to to to to 0 63 Forestier's disease. A low total osteophyte score (<6) associated strongly with the atrophic bone response pattern whereas a high score (>9) associated with the hypertrophic pattern and was more commonly seen with superolateral migration. The most frequent site for osteophyte, regardless of the migration pattern, was the superior femoral head. Although mild degrees of femoral neck osteophyte were seen in all migration patterns, moderate to florid osteophyte only occurred with superior patterns, most commonly with the superolateral (68%) and least commonly with the superomedial (10%). Osteophyte most often developed on the superior femoral head, femoral neck and lateral acetabulum with superolateral migration, and on the superior and inferior femoral head and neck with supermedial migration. Hips with medial and axial migration most often developed osteophyte on the femoral head with little osteophyte arising from the acetabulum or the femoral neck. REPRODUCIBILITY Table 3 gives the x values for intra- and interobserver variability. Reproducibility was good for the pattern of femoral head migration, Kellgren grading of the hip, and to a lesser extent for the pattern of the bone response. Reproducibility was also good for assessment of osteoarthritis at joints other than the hip (range x 0-65 for metacarpophalangeal joint osteoarthritis to 0-95 for knee osteoarthritis). Assessment of Forestier's disease was less reliable, as were assessments of individual radiographic features of osteoarthritis at the hip such as sclerosis, cyst, and osteophyte formation. Discussion There is no agreed method for radiographically assessing the severity or type of osteoarthritis of the hip. Several systems were therefore utilised in this large cross sectional study. Although the grading scale devised by Kellgren and Lawrence' is probably the most widely used method to assess severity it is primarily intended for epidemiological studies, places disproportionate emphasis on joint space narrowing and osteophyte (taking little account of features such as attrition and cyst formation), and assumes that the individual features of osteoarthritis show a linked and consistent pattern of progression. By contrast the grading system designed by Thomas et al, initially for use at the knee,2 assesses each individual radiographic feature of osteoarthritis. Though more complex and time consuming this system may allow more sensitive estimation of the process of osteoarthritis. In addition to these methods relating to 'severity', the pattern of migration of the femoral head' and the pattern of bone response to cartilage loss7 have also been proposed as useful methods to categorise osteoarthritis of the hip. We found the assessment of femoral head migration patterns easy to use and reliable, with good intra- and interobserver agreement. By
5 Radiographic patterns and associations ofosteoarthritis ofthe hip contrast the pattern of bone response was more difficult to apply. Most hips did not fall into the specified categories of atrophic or hypertrophic, the high percentage of 'indeterminate' hips reflecting the common concurrence of atrophic and hypertrophic features in advanced osteoarthritis and difficulty in classifying hips with early or mild osteoarthritis. Good associations between the hypertrophic pattern and a high osteophyte score, and between the atrophic pattern and a low osteophyte score and presence of attrition, however, suggest that our assessments were consistent with the rationale proposed for division into these two extreme patterns.7 The grading of individual features using a modification of the system of Thomas et a12 was easy to use but time consuming and proved less reproducible than the global grading system of Kellgren and Lawrence.' The pattern of femoral head migration within the acetabulum has been assessed by a variety of investigators with some conflicting results regarding patterns and gender associations.' In most studies the superior pole migration patterns predominate with the superolateral pattern in general being unilateral.3 We also found superior patterns to predominate with superolateral osteoarthritis clearly associating with male gender and female patients showing a stronger tendency to more medial patterns. Differences from other studies with regard to gender associations may in part relate to patient selection and study size. Previous reports relate to smaller numbers of patients principally recruited from orthopaedic clinics. Our study included a broad spectrum of rheumatology and orthopaedic clinic referrals, and allowed examination of 300 osteoarthritic hips. Nevertheless, it was still limited to symptomatic hospital referred patients and it is feasible that different findings could result from a community based study. In accord with previous studies there was a low frequency of the medial and, in particular, the axial migration patterns.' Unlike previous reports, however, we found no association between these patterns and nodal change.8 9 This difference may again relate to the larger size of this study or to definition in that we arbitrarily defined 'nodal' change clinically as the presence of Heberden's or Bouchard's nodes, or both, in at least three rays of each hand, rather than the presence of just one or a few nodes. Alternatively it is possible that the previously reported association between nodes and medial/axial hip patterns is indirect, reflecting the increased occurrence of both in women. The demonstrated negative association between medial and axial patterns and the presence of radiographic interphalangeal osteoarthritis (either polyarticular, widespread, or pauciarticular, limited) must seriously question any positive association between hand and hip osteoarthritis. Nodes and interphalangeal osteoarthritis may form different associations and are probably best considered separately for study purposes. Such discrepancies highlight the problems of definition and consistency between studies of osteoarthritis. Symmetry of migration patterns in patients 1115 with bilateral hip osteoarthritis was striking and applied to all patterns. It has been suggested that medial and axial patterns, as they reportedly occur more commonly in both hips, are likely to result from a systematic disturbance whereas the superolateral pattern, reported to be more commonly unilateral, is likely to result from local mechanical factors (such as mild abnormalities of the contour of the femoral head or acetabulum23). This study was not designed specifically to assess aetiology and the relative importance of systemic and local factors in the development and subsequent pattern of osteoarthritis at the hip remains unclear. The lack of association between nodes or radiographic interphalangeal osteoarthritis with migration patterns that classically occur in inflammatory arthropathies (medial/axial, reflecting more widespread rather than focal cartilage damage) must question the concept of a distinct subgroup of osteoarthritis resulting from a generalised inflammatory process and characterised clinically by nodal change. Although surprisingly little is known of sex differences in human hip anatomy it is established that the CE angle,24 a measure of acetabular depth, is larger in women. This could be a more reasonable explanation for the predominance of lateral migration in men and medial migration in women. The possibility that mechanical factors, resulting from gender differences in anatomy, are principal determinants of migration patterns in osteoarthritis of the hip is further supported by the one example of discordance in migration patterns that we encountered: a man with superolateral ('male') migration in one hip, but medial ('female') migration in the hip that had undergone surgical realignment (fig 4). The distribution of osteophyte in the different migration patterns is also of interest with respect to mechanical determination. Hips with superolateral migration principally develop femoral neck 'buttressing' and osteophyte around the lateral joint margin, whereas hips with medial or axial migration develop osteophyte at the femoral head margins but little at the femoral neck or acetabulum. These findings support the concept that osteophyte formation is an active remodelling process that responds to altered biomechanical demands. The association between chondrocalcinosis and atrophic hip osteoarthritis supports previous reports associating knee chondrocalcinosis with rapidly progressive osteoarthritis of the hip. 19-2' This association, which remains unexplained, is particularly intriguing as calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition at other sites such as the knee has been associated with hypertrophic radiographic changes at the site of deposition.25 Whatever the explanation this finding is contrary to the hypothesis that calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition is a marker in subjects with osteoarthritis for a generalised (compared with local) tendency to a good bone response.25 No association was found between Forestier's disease and prominence of osteophyte or pattern of bone response. The principal conclusions of this large study of osteoarthritis of the hip are that patient gender and local mechanical factors are impor-
6 1116 Ledingham, Dawson, Preston, Milligan, Doherty tant determinants of the pattern of femoral head migration. Although other constitutional or systemic factors may affect the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis of the hip the reported association between particular patterns of osteoarthritis of the hip and either nodal change or interphalangeal osteoarthritis is questioned. J L is a Roussel (UK) Osteoarthritis Research Fellow. We are additionally grateful to Trent Regional Health Authority for financial support, and Professor A Wallace, Mr I W Forster, and Mr C J Howell for assistance in patient recruitment. I Kellgren J H, Lawrence J S. Radiological assessment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957; 16: Thomas R H, Resnick D, Alazraki N P, Daniel D, Greenfield R. Compartmental evaluation of osteoarthritis of the knee. Radiology 1975; 116: Resnick D, Niwayama G. Degenerative disease at extraspinal locations. In: Resnick D, Niwayama G, eds. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. Vol. 2. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1981: Resnick D. Patterns of migration of the femoral head in osteoarthritis of the hip. Roentgenographic-pathologic correlation and comparison with rheumatoid arthritis. AmJ Roentgenol 1975; 124: Gofton J P. Studies in osteoarthritis of the hip: part 1. Classification. Can Med AssocJf 1971; 104: Hayward I, Bjorkengren A G, Pathria M N, Zlatkin M B, Sartoris D J, Resnick D. Patterns of femoral head migration in osteoarthritis of the hip: a reappraisal with CT and pathologic correlation. Radiology 1988; 166: Solomon L. Patterns of osteoarthritis of the hip. Y Bone Joint Surg [Br] 1976; 58: Marks J S, Stewart I M, Hardinge K. Primary osteoarthritis of the hip and Heberden's nodes. Ann Rheum Dis 1979; 38: McGoldrick F, O'Brien T. Osteoarthritis of the hip and Heberden's nodes. Ann Rheum Dis 1989; 48: Meachim G, Whitehouse G H, Pedley R B, Nichol F E, Owen R. An investigation of radiological, clinical and pathological correlations in osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Radiol 1980; 31: Jeffery A K. Osteophytes and the osteoarthritic femoral head. J Bone Joint Surg [Brn 1975; 57: Resnick D. Osteophytes of the femoral head and neck. Arthritis Rheum 1983; 26: Solomon L. Geographical and anatomical patterns of osteoarthritis. BrJ_ Rheumatol 1984; 23: Goften J P. A classification of osteoarthritis of the hip and its relevance to pathogenesis. J Rheumatol 1983; 10 (suppl 9): Hermodsson I. Roentgen appearance of coxarthrosis. Relationship between the anatomy, pathologic changes, and roentgen appearance. Acta OrthopScand 1970; 41: Cameron H U, Macnab I. Observations on osteoarthritis of the hip joint. Clin Orthop Rel Res 1975; 108: Macys J R, Bullough P G, Wilson P D. Coxarthrosis: a study of the natural history based on ia correlation of clinical, radiographic, and pathologic findings. Semin Arthritis Rheum 1980; 10: Harrison M H M, Schajowicz F, Trueta J. Osteoarthritis of the hip: a study of the nature and evolution of the disease. 7 BoneJoint Surg[BrJ 1953; 35: Menkes C J, Decraemere W, Postel M, Forest M. Chondrocalcinosis and rapid destruction of the hip. J7 Rheumatol 1985; 12: Menkes C J, Simon F, Delrieu F, Forest M, Delbarre F. Destructive arthropathy in chondrocalcinosis articularis. Arthritis Rheum 1976; 19: Gerster J C, Vischer T L, Fallet G H. Destructive arthropathy in generalised osteoarthritis with articular chondrocalcinosis. J Rheumatol 1975; 2: Cohen J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Education& Psychological Measurement 1960; 20: Murray R 0. The aetiology of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. BrJ Radiol 1965; 38: Resnick D, Niwayama G. Anatomy of individual joints. In: Resnick D, Niwayama G, eds. Diagnosis of bone and joint disorders. Vol. 1. Philadelphia: Saunders, 1981: Doherty M, Dieppe P A. Clinical aspects of calcium pyrosphosphate dihydrate crystal deposition. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1988; 14: Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 October Downloaded from on 3 November 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Radiographic patterns and associations of osteoarthritis of the knee in patients referred to hospital
 520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
520 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1993; 52: 520-526 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG5 1PB, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Regan A Jones M Doherty Correspondence to: Dr J
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
hands in patients with chronic renal failure
 378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: 965-969 965 Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Types of osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
ARTHRITIS Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease is the most common joint disorder. It is a frequent part of aging and is an important cause of physical disability in persons older than 65 years
4 2 Osteoarthritis 1
 Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
Osteoarthritis 1 Osteoarthritis ( OA) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease and the most common of all rheumatological disorders. It particularly affects individuals over the age of 65 years. The prevalence
H ip osteoarthritis (OA) affects 7 25% of white people
 1028 EXTENDED REPORT Predictive factors of total hip replacement due to primary osteoarthritis: a prospective 2 year study of 505 patients L Gossec, F Tubach, G Baron, P Ravaud, I Logeart, M Dougados...
1028 EXTENDED REPORT Predictive factors of total hip replacement due to primary osteoarthritis: a prospective 2 year study of 505 patients L Gossec, F Tubach, G Baron, P Ravaud, I Logeart, M Dougados...
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Primary osteoarthritis of the elbow
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1989; 48: 743-747 Primary osteoarthritis of the elbow MICHAEL DOHERTY' AND BRYAN PRESTON2 From the 'Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital; and the 2Department of Radiology,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1989; 48: 743-747 Primary osteoarthritis of the elbow MICHAEL DOHERTY' AND BRYAN PRESTON2 From the 'Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital; and the 2Department of Radiology,
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Study of 500 patients with limb joint osteoarthritis. symptomatic joint sites. I. Analysis by age, sex, and distribution of SCIENTIFIC PAPERS
 8 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 8-13 SCIENTIFIC PAPERS Rheumatology Unit, Bristol Royal Inirmar, Bristol BS2 8HW J Cushnaghan P Dieppe Correspondence to: Dr J Cnaghan. Accepted for publication
8 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1991; 50: 8-13 SCIENTIFIC PAPERS Rheumatology Unit, Bristol Royal Inirmar, Bristol BS2 8HW J Cushnaghan P Dieppe Correspondence to: Dr J Cnaghan. Accepted for publication
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, Osteoarthritis Research Society /95/ $08.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
BRIEF REPORT. KENNETH D. BRANDT, ROSE S. FIFE, ETHAN M. BRAUNSTEIN, and BARRY KATZ. From the Department of Medicine, the Department of
 1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
1381 BRIEF REPORT RADIOGRAPHIC GRADING OF THE SEVERITY OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS: RELATION OF THE KELLGREN AND LAWRENCE GRADE TO A GRADE BASED ON JOINT SPACE NARROWING, AND CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE
HEMOCHROMATOSIS HIP ARTHROPATHY IN GENETIC. Radiographic and Histologic Features
 357 HIP ARTHROPATHY IN GENETIC HEMOCHROMATOSIS Radiographic and Histologic Features J. S. AXFORD, A. BOMFORD, P. REVELL, 1. WATT, R. WILLIAMS, and E. B. D. HAMILTON Genetic hemochromatosis, a disorder
357 HIP ARTHROPATHY IN GENETIC HEMOCHROMATOSIS Radiographic and Histologic Features J. S. AXFORD, A. BOMFORD, P. REVELL, 1. WATT, R. WILLIAMS, and E. B. D. HAMILTON Genetic hemochromatosis, a disorder
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
O steoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent form of
 319 EXTENDED REPORT Characterisation of size and direction of in knee osteoarthritis: a radiographic study Y Nagaosa, P Lanyon, M Doherty... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
319 EXTENDED REPORT Characterisation of size and direction of in knee osteoarthritis: a radiographic study Y Nagaosa, P Lanyon, M Doherty... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Papers. Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study. Abstract. Participants and methods.
 Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study Peter Lanyon, Kenneth Muir, Sally Doherty, Michael Doherty Abstract Objectives To study the influence of genetics on the
Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study Peter Lanyon, Kenneth Muir, Sally Doherty, Michael Doherty Abstract Objectives To study the influence of genetics on the
CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 125 1 CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS JOSE A. MALDONADO-COCCO, OSVALDO GARCIA-MORTEO, ALBERT0 J. SPINDLER, OSVALDO HUBSCHER. and SUSANA GAGLIARDI Forty-seven of 100 consecutive juvenile
125 1 CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS JOSE A. MALDONADO-COCCO, OSVALDO GARCIA-MORTEO, ALBERT0 J. SPINDLER, OSVALDO HUBSCHER. and SUSANA GAGLIARDI Forty-seven of 100 consecutive juvenile
Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement
 \>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
\>»*i*c*»üj^h«< %Χ»*1»#Ί*#Ι 1» Rheumatoid Pseudocyst (Geode) of the Femoral Neck Without Apparent Joint Involvement BERNARD F. MORREY, M.D., Department of Orthopedics Typically, rheumatoid cysts are associated
Prevalence of cartilage lesions in foot joints: a test of
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 515-519 Prevalence of cartilage lesions in foot joints: a test of the concept of limited and progressive lesions H R YOUNGMAN,' F COOPER,' AND PAUL BYERS2 From
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 515-519 Prevalence of cartilage lesions in foot joints: a test of the concept of limited and progressive lesions H R YOUNGMAN,' F COOPER,' AND PAUL BYERS2 From
predicts radiographic change
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1986; 45, 622-626 99mTc HMDP bone scanning in generalised nodal osteoarthritis. II. The four hour bone scan image predicts radiographic change C W HUTTON,' E R HIGGS,'
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS
 INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
INFLAMMATION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS BY PAUL DIEPPE SUMMARY Osteoarthritis is usually regarded as a non-inflammatory disease. However, several authors have stressed the importance of an inflammatory phase early
Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in the community: definitions and normal joint space
 Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
The New Science of Osteoarthritis
 The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
The New Science of Osteoarthritis What it means in managing our patients Terence W. Starz MD Clinical Professor of Medicine University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Osteoarthritis: Key Points Perspective:
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs
 Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 311-318 Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease Pathogenesis and roentgen appearance D. RESNICK AND G. NIWAYAMA
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 311-318 Carpal instability in rheumatoid arthritis and calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease Pathogenesis and roentgen appearance D. RESNICK AND G. NIWAYAMA
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA
 Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
Central Reading of Knee X-rays for Kellgren & Lawrence Grade and Individual Radiographic Features of Tibiofemoral Knee OA 1. Overview... 1 1.1 SAS dataset... 1 1.2 Contents of dataset... 1 1.3 Merging
Radiologic features of a pyrophosphate-like arthropathy associated with long-term dialysis
 Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16:437-441 Skeletal Radiology Radiologic features of a pyrophosphate-like arthropathy associated with long-term dialysis Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Kathleen Menerey, M.D. 2, William
Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16:437-441 Skeletal Radiology Radiologic features of a pyrophosphate-like arthropathy associated with long-term dialysis Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Kathleen Menerey, M.D. 2, William
Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology
 Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology Poster No.: C-1599 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Pissarra, R. R. Domingues Madaleno,
Arthritis due to deposition diseases: differential diagnosis in conventional radiology Poster No.: C-1599 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. P. Pissarra, R. R. Domingues Madaleno,
OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT
 375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
375 OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE TRAPEZIOSCAPHOID JOINT A. CAROLINE PATTERSON Isolated osteoarthritis (OA) of the trapezioscaphoid (TS) joint is little recognized. Nine cases that were examined clinically and
Gout. Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives. Crystal associated arthropathies. Clinical Stages of Gout 07/06/60
 Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
Crystal associated arthropathies Crystal deposition disease: Imaging perspectives Warapat Virayavanich, MD Ramathibodi hospital, Mahidol University Commonly seen arthropathy MSU (gout) CPPD HADD Uncommon
triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 46 Early abnormalities of pisiform and triquetrum in rheumatoid arthritis DONALD RESNICK From the Department of Radiology, Veterans Administration Hospital, San Diego, and
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS
 February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
February 2002 Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis PVNS Amy Gillis, Harvard Medical School Year III 47 year old female Our Patient Right hip pain since age 20 No history of trauma Diagnosed with DJD of R hip
Arthritis & Rheumatism
 ~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
~ Arthritis & Rheumatism Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN ARTHROSCOPIC EVIDENCE OF CARTILAGE DAMAGE AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVIDENCE OF JOINT SPACE NARROWING IN EARLY
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target?
 JT [2]2 Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target? Professor Jon Tobias Musculoskeletal Research Unit University of Bristol Slide 1 JT [2]2 I'd like to thank the organisers for inviting me to
JT [2]2 Bony Phenotype: Worthwhile as a Therapeutic Target? Professor Jon Tobias Musculoskeletal Research Unit University of Bristol Slide 1 JT [2]2 I'd like to thank the organisers for inviting me to
Case 61. Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative.
 Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
Case 61 Middle aged farmer with a history of trivial injury and since then pain and stiffness in the L shoulder. Inflammatory markers were negative. Diagnosis GLENOID DYSPLASIA DEFINITION The classic constellation
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
Leg Length Discrepancy in a Patient with Ipsilateral Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty
 texas orthopaedic journal CASE REPORT Leg Length Discrepancy in a Patient with Ipsilateral Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty Gaurav S. Sharma, BA; Ronald W. Lindsey, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
texas orthopaedic journal CASE REPORT Leg Length Discrepancy in a Patient with Ipsilateral Total Knee and Total Hip Arthroplasty Gaurav S. Sharma, BA; Ronald W. Lindsey, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Clinical and radiological survey of the
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (976), 5, 49 Clinical and radiological survey of the incidence of osteoarthrosis among obese patients RICHARD H. GOLDIN, LAWRENCE McADAM, JAMES S. LOUIE, RICHARD GOLD, AND RODNEY BLUESTONE
Ann. rheum. Dis. (976), 5, 49 Clinical and radiological survey of the incidence of osteoarthrosis among obese patients RICHARD H. GOLDIN, LAWRENCE McADAM, JAMES S. LOUIE, RICHARD GOLD, AND RODNEY BLUESTONE
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY
 BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Definition and Risk Factors Idiopathic vs. Secondary OA Clinical Features Diagnosis Radiologic Features ACR OA
BY Mrs. K.SHAILAJA., M. PHARM., LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACY PRACTICE, SRM COLLEGE OF PHARMACY Definition and Risk Factors Idiopathic vs. Secondary OA Clinical Features Diagnosis Radiologic Features ACR OA
Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the Framingham Study
 Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
Rheumatology 2003;42:343 348 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg110, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Symmetry and clustering of symptomatic hand osteoarthritis in elderly men and women: the
APLICATION TO EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR CLINICAL AFFAIRS (ESCCA)
 APLICATION TO EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR CLINICAL AFFAIRS (ESCCA) EULAR RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TERMINOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CALCIUM PYROPHOSPHATE CRYSTAL ASSOCIATED ARTHRITIS Convenors: Michael
APLICATION TO EULAR STANDING COMMITTEE FOR CLINICAL AFFAIRS (ESCCA) EULAR RECOMMENDATIONS FOR TERMINOLOGY, DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF CALCIUM PYROPHOSPHATE CRYSTAL ASSOCIATED ARTHRITIS Convenors: Michael
Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients
 Gout on CT: a symmetric arthropathy. Anthony J Doyle (corresponding author) Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients with gout using computed tomography (CT) and
Gout on CT: a symmetric arthropathy. Anthony J Doyle (corresponding author) Objectives: To assess the distribution of bone erosions in the feet of patients with gout using computed tomography (CT) and
Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty
 Rheumatology 2002;41:142 147 Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty J. F. Maillefert 1,4,A.Gueguen
Rheumatology 2002;41:142 147 Relevant change in radiological progression in patients with hip osteoarthritis. I. Determination using predictive validity for total hip arthroplasty J. F. Maillefert 1,4,A.Gueguen
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Bone formers: osteophyte and enthesophyte formation are positively associated
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1997;56:85 9 85 EXTENDED REPORTS Bone formers: osteophyte and enthesophyte formation are positively associated Juliet Rogers, Lee Shepstone, Paul Dieppe Rheumatology Unit,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1997;56:85 9 85 EXTENDED REPORTS Bone formers: osteophyte and enthesophyte formation are positively associated Juliet Rogers, Lee Shepstone, Paul Dieppe Rheumatology Unit,
in the 77 adults suffering from rheumatoid arthritis ranged from 22 to 79 years (mean 52) and in the 23 with juvenile
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
High Impact Rheumatology
 High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
High Impact Rheumatology Evaluation and Management of Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis: Case 1 A 65-year-old man comes to your office complaining of knee pain that began insidiously about a year ago. He has
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View
 Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout
 A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout Nausheen Khan, MB BS, FCRad (D) Irma van de Werke, MB ChB, FRCR Farzanah Ismail, MB ChB, FCRad (D) Department of Radiology, Kalafong Hospital,
A case of extensive synovial involvement by tophaceous gout Nausheen Khan, MB BS, FCRad (D) Irma van de Werke, MB ChB, FRCR Farzanah Ismail, MB ChB, FCRad (D) Department of Radiology, Kalafong Hospital,
Prevalence of generalised osteoarthritis in patients with advanced hip and knee osteoarthritis: The Ulm Osteoarthritis Study
 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:717 723 717 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Ulm, Ulm, Germany K P Günther S Sauerland I Zeissig S Kessler H P Scharf W Puhl Department of Epidemiology,
Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:717 723 717 EXTENDED REPORTS Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Ulm, Ulm, Germany K P Günther S Sauerland I Zeissig S Kessler H P Scharf W Puhl Department of Epidemiology,
Physical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 1. Dec
 Physical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 1. Dec. 2015. Evaluation of patients with musculoskeletal complaints Anatomic localization
Physical diagnosis of musculoskeletal system Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 1. Dec. 2015. Evaluation of patients with musculoskeletal complaints Anatomic localization
Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 366, pp. 39-45 0 1999 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Late Results of Total Shoulder Replacement in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jens 0. S@jbjerg,
Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 626 Giant granulomatous lesions of the femoral head and neck in rheumatoid arthritis C. L. COLTON AND A. J. DARBY London Local areas of subarticular bone erosion occurring
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research
 New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
Priorities Forum Statement GUIDANCE
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
Priorities Forum Statement Number 21 Subject Knee Arthroscopy including arthroscopic knee washouts Date of decision November 2016 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 Osteoarthritis of
ARTHRITIS RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC SKELETAL HYPEROSTOSTS
 ARTHRITIS 82 RHEUMATISM OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCiA I ION SECTION OF THE ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION 1 RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC
ARTHRITIS 82 RHEUMATISM OFFICIAL JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN RHEUMATISM ASSOCiA I ION SECTION OF THE ARTHRITIS FOUNDATION 1 RADIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES OF RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS IN PATIENTS WITH DIFFUSE IDIOPATHIC
F. Birrell 1,3, M. Lunt 1, G. Macfarlane 2 and A. Silman 1
 Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
For patients with musculoskeletal pain, imaging can aid in making or confirming
 Clinical basics Rheumatology: 3. Getting the most out of radiology Review Synthèse Graham Reid, * John M. Esdaile The case A 72-year-old man has been seeing the same physician for 2 decades, and his only
Clinical basics Rheumatology: 3. Getting the most out of radiology Review Synthèse Graham Reid, * John M. Esdaile The case A 72-year-old man has been seeing the same physician for 2 decades, and his only
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Hormone replacement therapy and patterns of osteoarthritis: baseline data from the Ulm Osteoarthritis Study
 Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:105 109 105 Department of Epidemiology, University of Ulm, Germany, Helmholtzstr 22, D-89081 Ulm, Germany A Erb H Brenner T Stürmer Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:105 109 105 Department of Epidemiology, University of Ulm, Germany, Helmholtzstr 22, D-89081 Ulm, Germany A Erb H Brenner T Stürmer Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of
Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying Radiographic Features of Osteoarthritis
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 4, April 2012, pp 533 538 DOI 10.1002/acr.21586 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 64, No. 4, April 2012, pp 533 538 DOI 10.1002/acr.21586 2012, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distribution of Finger Nodes and Their Association With Underlying
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions. Claudio Mella, MD
 Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
patients with rheumatoid arthritis
 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: -11 SCINTIFIC PAPRS Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands G J Kieft J L Bloem H M Kroon Department of Rheumatology,
Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: -11 SCINTIFIC PAPRS Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands G J Kieft J L Bloem H M Kroon Department of Rheumatology,
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis
 the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
the new accurate analysis and classification system of knee joint osteoarthritis i3a Soft- and Hardware Components created and assembled in Austria Due to the rapidly increasing fraction of aging people
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Pre-operative clinical and radiological
 Pre-operative clinical and radiological assessment of the patellofemoral joint in unicompartmental knee replacement and its influence on outcome D. J. Beard, H. Pandit, S. Ostlere, C. Jenkins, C. A. F.
Pre-operative clinical and radiological assessment of the patellofemoral joint in unicompartmental knee replacement and its influence on outcome D. J. Beard, H. Pandit, S. Ostlere, C. Jenkins, C. A. F.
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
Fast Facts. Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis. Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Health Press Ltd.
 Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan MB BS PhD FRACP FRCP Professor of Musculoskeletal Medicine University of
Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan and Leena Sharma Fast Facts Fast Facts: Osteoarthritis Philip G Conaghan MB BS PhD FRACP FRCP Professor of Musculoskeletal Medicine University of
RADIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF PROGRESSION
 1214 RADIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF PROGRESSION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS ROY D. ALTMAN, JAMES F. FRIES, DANIEL A. BLOCH, JOHN CARSTENS, T. DEREK COOKE, HARRY GENANT, PHILIP GOFTON, HARRY GROTH, DENNIS J. McSHANE,
1214 RADIOGRAPHIC ASSESSMENT OF PROGRESSION IN OSTEOARTHRITIS ROY D. ALTMAN, JAMES F. FRIES, DANIEL A. BLOCH, JOHN CARSTENS, T. DEREK COOKE, HARRY GENANT, PHILIP GOFTON, HARRY GROTH, DENNIS J. McSHANE,
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and Varus Knee Deformity Based on Two-Dimensional Assessment of Side-to-Side Differences
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2018;30(1):58-63 https://doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.17.007 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Relationship between Lateral Femoral Bowing and
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
subluxation: a radiographic comparison
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1980, 39, 485-489 Cervical collars in rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation: a radiographic comparison BO ALTHOFF AND IAN F. GOLDIE From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1980, 39, 485-489 Cervical collars in rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation: a radiographic comparison BO ALTHOFF AND IAN F. GOLDIE From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging
 Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
Salisbury Foundation Trust Radiology Department Referral Guidelines for Primary Care: Musculoskeletal Imaging These guidelines have been issued in conjunction with the Royal College of Radiology referral
T he goals of medical management of patients with
 1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
1061 EXTENDED REPORT Development of radiographic changes of osteoarthritis in the Chingford knee reflects progression of disease or non-standardised positioning of the joint rather than incident disease
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
