Psoriatic Spondylitis: A Clinical and Radiological Description of the Spine in Psoriatic Arthritis
|
|
|
- Rodney Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series XLVI, No. 8, pp. -5, October 977 Psoriatic Spondylitis: A Clinical and Radiological Description of the Spine in Psoriatic Arthritis J. R. LAMBERT AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit, University Department of Medicine, General Infirmary, Leeds; and The Royal Bath Hospital, Harrogate Accepted 8 April 977 SUMMARY In a review of patients with psoriatic, spondylitis was noted in per cent. Sacro-iliitis was observed in per cent and was present either when axial disease was predominant (seven patients) or in association with peripheral poly (5 patients). The groups differed in that most of those with axial disease were males who had developed psoriasis later in life. In those with disease of the axial skeleton, nail dystrophy was less common, and iritis, chronic back pain and restriction of spinal mobility were more common. They had higher values of E.S.R. In both there was a high incidence of the histocompatibility antigen B7. The axial group resembled idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis and the New York criteria were fulfilled by 8 per cent compared with 7 per cent of those who had peripheral as well. This latter group was frequently without symptoms or signs of spondylitis. Syndesmophytes are accepted as a radiological manifestation of spondylitis. They were noted in 5 per cent of patients and in per cent of these the sacroiliac joints were normal radiologically. Anterior syndesmophytes alone were found only in the cervical spine and were more common in patients without sacro-iliitis. Lateral syadesmophytes were most commonly found in the lumbar and lower dorsal vertebrae and were slightly less common in patients without sacro-iliitis. Patients with syndesmophytes and normal sacro-iliac joints had a small male preponderance. They were no more likely to have symptoms or signs of spinal disease than those with normal spine radiographs. Downloaded from by guest on May, INTRODUCTION The association of psoriasis and ankylosing spondylitis was first recorded nearly fifty years ago (Zellner, 98) and a number of case reports have followed (Bauer and Vogl, 9; Sharp and Purser, 9; Bunim, 9; Strohfeldt, 97). Boijens (99) classified 'psoriasis arthropathica' in eight types, one being associated with spondylitis though this he considered rare. This opinion was supported by several authors (Vilanova and Pinol, 95; Sherman, 95; Lassus, Mustakallio, and
2 J. R. Lambert and V. Wright Laine, 9). However, other reports contradict this (Dawson and Tyson, 98; Epstein, 99; Avila, Pugh, Slocumb, and Winkehnann, 9; Bardnagni and Carhsimo, 97) and some have demonstrated a high prevalence (Reiter and Norholm-Pedersem, 95; Sterne and Schneider, 95; Graber-Duvernay, 957; Wright, 957; Coste, Francon, Touraine, and Loyau, 958; Reed, 9; Baker, Golding, and Thompson, 9; Peterson and Silbiger, 97; Polotski, 97; Schilling and Schacherl, 97). Harvie, Lester, and Little (97) found that in patients admitted to hospital for treatment of severe psoriasis, sacro-iliitis was particularly common. The occurrence of psoriasis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis has been recorded from between two and per cent (Aalvik, 9; Clemmesen and Arns, 95; Fletcher and Rose, 955; Lefkovits and Thomas, 958;Smythe, 9). Whilst the diagnostic criteria for spondylitis and for psoriatic were not standardized in these studies their association seemed likely and Fletcher and Rose (955) proposed the term 'psoriasis spondylitica'. Wright (9) found that radiological sacro-iliitis was more common in patients with psoriatic compared with patients with rheumatoid. Dixon and Lience (9) found a higher prevalence than in a group of controls. However, Kaplan, Plotz, Nathanson, and Frank (9) found that apophyseal joint narrowing and sclerosis and anterior ligamentous calcification in the cervical spine were common in patients with psoriasis whether or not they had peripheral. The changes were indistinguishable from those of 'rheumatoid (ankylosing) spondylitis', but the lumbar spine and sacro-iliac joints were not affected. Unusual, non-marginal syndesmophytes were reported in four patients with psoriatic by Bywaters and Dixon (95). Coste and Solnica (9) reporting spondylitis in one third of patients, frequently with peripheral, noted changes in patients without symptoms and that para-vertebral ossification occurred without sacro-iliitis in some patients. Syndesmophytes and sacro-iliitis were noted in. the majority of patients with psoriatic investigated by Jajic (98). He thought the changes were distinct from those of ankylosing spondylitis. These were investigated by McEwen, Di Tata, Lingg, Porini, Good, and Rankin (97) who listed the clinical and radiological differences and similarities between the spondylitis of psoriatic or Reiter's disease and that found in ankylosing spondylitis or with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Langeland and Roaas (97) suggested that spondylitis was associated with pustular psoriasis and that solid fusion of thoracic vertebrae, preceded by destruction of adjacent vertebral bodies, was a characteristic feature. A high prevalence of sacro-iliitis and coarse asymmetrical syndesmophytes distinguishable from idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis was reported by Killebrew, Gold, and Sholkoff (97). Sundaram and Patton (975) felt that non-marginal syndesmophytes may be the sole or major radiological abnormality of psoriatic, occurring commonly with normal sacro-iliac joints and without typical changes in the hands. On the other hand Moll (97) who drew on the literature and his personal experience felt that psoriatic spondylitis was probably a specific entity as an alternative expression of psoriatic, but that in most cases Downloaded from by guest on May,
3 Psoriatic Spondylitis there were no clinical or radiological differences from idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis. It seemed probable that psoriatic spondylitis was an entity, though the prevalence and characteristics (particularly the significance of syndesmophytes) were uncertain. We therefore reviewed patients with psoriatic with particular emphasis on clinical and radiological examination of the spine in all patients, whether or not they had symptoms. The findings were compared with those in idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis. MATERIALS AND METHODS One hundred and thirty patients (57 men and 7 women) were studied and all fulfilled the criteria of Moll and Wright (97) for psoriatic. A full history was taken and examination performed with special attention to spinal pain and mobility. Subjective assessment was made of neck movement in three planes. Circumferential chest expansion was assessed in 8 patients by the method described by Moll and Wright (97). Lumbar spinal movement was measured in three planes as detailed by Moll and Wright (97) and compared with their range of normal values. Measurements were available in 8 patients, a subjective assessment of the range of movement only having been made for the remainder. Anteroposterior radiographs of the sacro-iliac joints were available for patients, further views being taken in doubtful cases. Radiographs of the cervical spine were available for 78 patients, of the dorsal spine for 58 patients, of the lumbar spine for 8 patients and of the symphysis pubis for 57 patients. Fifty-one had radiographs of the complete spine and sacro-iliac joints. Radiographs of the peripheral joints were available for 9 patients. Seventy-eight had films of both hands and feet, of hands only and three offset only. Ankylosing spondylitis was diagnosed and graded by the New York criteria (Bennett and Wood, 98), except that assessment of joint space was not included (Macrae, Haslock, and Wright, 97). The peripheral was graded subjectively as: nil; mild (only a few joints affected with no loss of function); moderate (a few joints affected with deformity and/or loss of function, or many joints affected with only slight impairment of function); and severe (marked deformity and disability including mutilans). The values of erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), haemoglobin and white blood cell count were available for all patients. Rheumatoid factor was screened in all patients by the latex fixation test and where this was positive the sheep cell agglutination titre was performed. Histocompatibility (HLA) antigen typing was performed on 8 patients and tests for anti-nuclear factor were available on 9 patients. Downloaded from by guest on May, RESULTS Radiological Features Sacro-iliitis was noted in men and women ( per cent). Table shows that changes were unilateral in five cases and bilaterally asymmetrical in five. Advanced ankylosis was found in seven patients. Sacro-iliitis was present as either a predominantly spinal disease, a form we have termed axial, or with a generalized
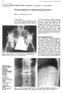
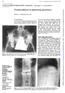
4 J. R. Lambert and V. Wright Fio.. Anterior syndesmophytes of dorsal spine. Downloaded from by guest on May, Fio.. Anterior syndesmophytes of cervical spine.
5 Psoriatic Spondylitis 5 TABLE. Radiological characteristics of sacro-iliitis in the varieties of spondylitis Patients with Patients with All patients sacro-iliitifl sacro-iliitis Patientfl with with and axial and peripheral syndesmophytes sacro-iliitis disease and sacro-iliitis Bilateral symmetrical sacro-iliitis 9 7 Asymmetrical sacroiliitis 5 Unilateral sacroiliitis 5 which we have termed the peripheral form. Sacro-iliitis was more likely to be unilateral in the peripheral variety. Syndesmophytes are not always distinguished easily from osteophytes or senile ankylosing hyperostosis. The problems of identification have been discussed by Riley, Ansell, and Bywaters (97), whose recommendations we followed. Syndesmophytes were found in men and women (5 per cent). Anterior syndesmophytes (Figs. and ) were found alone only in the cervical spine (eight patients), while the commonest lateral sites were the lumbar and lower thoracic regions. Marginal syndesmophytes (Fig. ) were noted in the dorsal spines of and the lumbar spines of patients. They were more common than non-marginal syndesmophytes (Fig. ) which were found in four dorsal and five lumbar spines. Non-marginal syndesmophytes were more often unilateral (four of seven cases) than were marginal syndesmophytes (five of 8 cases) though the difference was not of statistical significance. Twelve patients had. both sacro-iliitis and syndesmophytes though in 8 patients with normal sacro-iliac joints syndesmophytes were present. Table shows that there were no differences in the radiological characteristics of sacro-iliitis in those with or without syndesmophytes. The radiological features of syndesmophytes are related to sacro-iliitis in Table. Patients with normal sacro-iliac joints had a higher prevalence of only anterior syndesmophytes. Patients with peripheral were more likely to have small numbers of unilateral or asymmetrical syndesmophytes. Narrowing, erosion or sclerosis of the apophyseal joints were noted in sets of films of the cervical spine ( per cent), four of the dorsal spine (seven per cent) and five of the lumbar spine (seven per cent). Of those with cervical lesions six patients had sacro-iliitis and syndesmophytes, one patient sacro-iliitis alone, six patients syndesmophytes alone (two of these being confined to the cervical spine) and patients ( per cent) had neither. Thus patients had abnormality of the neck alone. Vertebral body squaring or erosions were seen in only patients. The cervical spine was affected infive (six per cent), the dorsal spine infive (nine per cent) and the lumbar spine in seven (ten per cent). Seven patients had sacro-iliitis, seven had syndesmophytes and two had neither. Interspinous ligamentous ossification was present in seven patients. The cervical Downloaded from by guest on May,
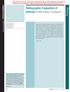
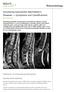
6 J. R. Lambert and V. Wright FIG.. Marginal symdesmophytes dorsal spine. Downloaded from by guest on May, Fio.. Non-marginal eyndesmophytes.
7 Psoriatic Spondylitis 7 TABLE. Radiological features of syndesmophytes in patients with and without sacro-iliitis All patients with psoriatic All patients with saoro-iliitis Patients with SAcro-iliitis and axial disease Patient* with sacro-iliitis and peripheral Patients with normal sacroiliac joints radiographically No. with syndesmophytes No. with anterior gyndes No. with lateral syndea No. with anterior and lateral syndes No. with unilateral syndes No. with asymmetrical syndes No. with symmetrical syndea No. with marginal syndea No. with non-marginal ayndee No. with both No. with single syndea No. with syndes No. with or more fyndes t 7 8 ot 7 S * e 7 t p < -8 compared with patients with normal saoro-iliac joints. * p < - compared with patients with sacro-iliitis and axial disease. spine was affected in four, the dorsal in three and lumbar in two. One patient did not have sacro-iliitis and one other did not have syndesmophytes. The bamboo spine appearance, typical of ankylosing spondylitis, was seen in only three patients. The symphysis pubis was abnormal in only five cases (nine per cent); one man with sacro-iliitis and syndesmophytes and three men and one woman with syndesmophytes. Intervertebral disc space narrowing was noted in the cervical spines of patients and the lumbar spines of six patients. Of these,five had sacro-iliitis and a further nine syndesmophytes. Osteophytes were seen in 5 patients. They were found in the cervical spine in cases, the dorsal spine in 8 and the lumbar spine in 7 cases. Erosion of the sternomanubrial joint was present in one female, who also had cervical syndesmophytes. Erosive changes of the extremities were present in 5 patients (8 per cent) and these affected the distal interphalangeal joints in 8 cases ( per cent). Two patients had an mutilans. Radiographs of hands and feet were available for 7 patients with syndesmophytes and normal sacro-iliac joints, and in three there was no suggestion of inflammatory at these sites. Erosive changes were present in patients (55 per cent) and affected the distal interphalangeal joints in nine (5 per cent). Nine patients with syndesmophytes and sacro-iliitis had radiographs of the hands and feet. There was no clinical suggestion of peripheral in the four for whom films were not available. Erosions were noted in four Downloaded from by guest on May,
8 to t I TABLE. Clinical features related to spondylitis No. of males No. of females Ratio males: females Mean age at review (yrs) Mean age of onset of (yrs) Mean duration of (yrs) Mean age of onset of psoriasis (yrs) Mean duration of psoriasis (yrs) % with nail involvement Mean age at onset of nail ohanges (yrs) Prevalence of iritis % All patients All patients Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with normal spines with with sacro-iliitis sacro-iliitis syndesmophytes syndesmophytes psoriatio sacro-iliitis and axial and normal dia sacro-iliao joints : : : and peripheral 9-7: : Downloaded from by guest on May, and sacro-iliitis Clinical and Clinical radiological: and/or complete set radiological 8 : of films t 8 -: t 57 -: patients: saoro-iliac joints and some areas of spine examined by X-ray "I f 5 patients: sacro-iliac joints and whole spine examined by X-ray V Tables -7. J patients: clinical and/or radiological examination of spine J
9 Psoriatic Spondylitis 9 patients ( per cent), and this affected the distal interphalangeal joints in three ( per cent). One patient had mutilans. There is therefore no significant difference in prevalence of erosive changes related to the presence of or variety of spondylitis, though distal interphalangeal joint erosions were more frequently associated with syndesmophytes. CLINICAL FEATURES Table summarizes the clinical features and relates these to the variety of spondylitis. Females were slightly more common accounting for 5 per cent. The onset of psoriasis tended to antedate the. The prevalence of nail changes and their temporal relationship to the onset of is in keeping with that found by previous authors (Wright, 959; Baker, et ai., 9). The prevalence of iritis is the same as that in rheumatoid (Hart, 95). Patients with sacro-iliitis were older than those without spondylitis (p < -5). The sex distribution was equal and was not influenced by the presence of spondylitis. However, the group of patients in whom sacro-iliitis was present without peripheral differed from those with both sacro-iliitis and peripheral in that most were male, nail changes were less common and the psoriasis of shorter duration. These differences were significant (p < -5). The group with sacro-iliitis and axial disease differed markedly from that in which radiological sacro-iliitis was absent. Males were much more common (p < -5). Nail dystrophy was less common (p < -) and iritis was more often noted but this difference was not significant. Those with sacro-iliitis and peripheral differed from those with neither. They were older (p < -5), and the duration of psoriasis (p < -5) and (p < -) were both longer. Patients with syndesmophytes and normal sacro-iliac joints differed from those with normal radiographs, and were older at review (p < -5). Though the duration of and of psoriasis was longer, and males were dominant, these differences were not significant. There were no significant differences between the group with sacro-iliitis and that with syndesmophytes and normal sacro-iliac joints. These patients resembled the group with sacro-iliitis and peripheral. They differed from patients with sacro-iliitis without peripheral in having a greater prevalence of nail dystrophy, and an earlier onset and longer duration of psoriasis (p < -5). There were no differences between patients with both syndesmophytes and sacro-iliitis, and those with syndesmophytes and normal sacro-iliac joints. Table relates back pain and restriction of spinal movement to the varieties of spondylitis. Chest expansion was reduced in six men and six women, though two of the female patients had significant chronic obstructive airways disease. Restriction of neck movement was the most common abnormality, and nearly half the patients had persistent back pain. The prevalence of chronic back pain was higher in those with sacro-iliitis (p < -5) but this was predominantly in those with axial disease. The prevalence was no higher in those with syndesmophytes alone. Restriction of spinal mobility Downloaded from by guest on May,
10 to t I TABLE. Clinical features related to spondylitis No. of males No. of females Ratio males: females Mean age at review (yrs) Mean age of onset of (yrs) Mean duration of (yrs) Mean age of onset of psoriasis (yrs) Mean duration of psoriasis (yrs) % with nail involvement Mean age at onset of nail ohanges (yrs) Prevalence of iritis % All patients All patients Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with normal spines with with sacro-iliitis sacro-iliitis syndesmophytes syndesmophytes psoriatio sacro-iliitis and axial and normal dia sacro-iliao joints : : : and peripheral 9-7: : Downloaded from by guest on May, and sacro-iliitis Clinical and Clinical radiological: and/or complete set radiological 8 : of films t 8 -: t 57 -: patients: saoro-iliac joints and some areas of spine examined by X-ray "I f 5 patients: sacro-iliac joints and whole spine examined by X-ray V Tables -7. J patients: clinical and/or radiological examination of spine J
11 All All Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with normal spines patients patients sacro-iliitis sacro-iliitis syndesmophytes syndesmophytes with with and axial and and normal and sacro-iliitis Clinical and Clinical psoriatic saoro-iliitia disease peripheral sacro-iliao radiological: and/or joints complete set radiological of films to I a I TABLE. Corretation of clinical findings to varieties of radiological spondylitis Downloaded from by guest on May, Back pain-5 ft % I Chest expansion ][Vr % Neck movement i(ft 8% I Lumbar movement -j [VT 9% tf 7% ft 5% ft % ft % } % 7% $ 8% 7% T*r % ft ft 5% ft 5% T^ % ft 5% ft 8% ft 75% ft % ft 8% A 5% ft 7% TV n% ft % TV5% H % A 7% H 5% TV %
12 All All Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with normal spines patients patients sacro-iliitis sacro-iliitis syndesmophytes syndesmophytes with with and axial and and normal and sacro-iliitis Clinical and Clinical psoriatic saoro-iliitia disease peripheral sacro-iliao radiological: and/or joints complete set radiological of films to I a I TABLE. Corretation of clinical findings to varieties of radiological spondylitis Downloaded from by guest on May, Back pain-5 ft % I Chest expansion ][Vr % Neck movement i(ft 8% I Lumbar movement -j [VT 9% tf 7% ft 5% ft % ft % } % 7% $ 8% 7% T*r % ft ft 5% ft 5% T^ % ft 5% ft 8% ft 75% ft % ft 8% A 5% ft 7% TV n% ft % TV5% H % A 7% H 5% TV %
13 TABLE 5. Blood tests related to radiological type of spondylitis All All Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with normal spines patients patients sacro-iliitis sacro-iliitis syndesmophytes syndesmophytes - with with and axial and and normal and sacro-iliitis Clinical and Clinical psoriatic sacro-iliitis disease peripheral sacro-iliac joints Downloaded from by guest on May, radiological: complete set of films and/or radiological Rh. Factor HLAB7 ANF E.S.R. < H -rh % r -5% % % 8% % H 7% 5 % 5% % 8% 9% 7% % 9% 9% 9% % 9 8% 9% 5% % I 78% Hb -5% 9% 9% 7% % % % 7% W.C.C. > 5 % 5% 7% % 5% % % % % % 9% 5% 7% % 8 5 8% % 8% % 9% 9% 8 8 9% % % 7% % %
14 J. R. Lambert and V. Wright was associated with the axial form of disease with sacro-iliitis, though restricted neck movement was also found in those with both peripheral disease and sacroiliitis. Patients with syndesmophytes showed no greater tendency to restricted movement compared with those with normal films. The New York criteria (Bennett and Wood, 98) for ankylosing spondylitis was fulfilled by patients, six with axial sacro-iliitis and four with peripheral sacroiliitis. Blood tests These are tabulated and related to the form of spondylitis in Table 5. Tests for rheumatoid factor were negative in all cases though two females had had low titres (: and :8) at the onset of. HLA-B7 was present in patients ( per cent), significantly more than in controls (7 per cent, p < -5). The prevalence of positive tests for anti-nuclear factor is that expected in the general population. Only two patients had significant anaemia (haemoglobin less than llg d I" in males or G d I" in females). Both of these had sacro-iliitis and syndesmophytes and predominantly axial disease. The prevalence of HLA-B7 was raised in patients with sacro-iliitis and either peripheral or axial disease. Table relates the presence and severity of peripheral to spinal disease. Patients with sacro-iliitis and axial disease had by definition a milder peripheral disease, though there were no other differences. The severity of psoriasis is related to spinal disease in Table 7. There are no significant differences between the various groups. The prevalence of iritis was high only in patients with sacro-iliitis and predominantly axial disease and less so in those with both sacro-iliitis and syndesmophytes (Table ). No patient had an abnormal heart. Downloaded from by guest on May, DISCUSSION The high prevalence of sacro-iliitis at about per cent is similar to that reported by TTill (9) and Baker, Golding, and Thompson (9), though higher than reported by Dawson and Tyson (98), Avila et al. (9), Bardnagni et al. (97). The significance of syndesmophytes in psoriatic is uncertain; they may represent inflammatory or degenerative spinal disease. Though we ignored doubtful cases the presence of syndesmophytes, unlike that of sacro-iliitis, was not related to back pain or restricted spinal mobility. Syndesmophytes are not included in the diagnostic criteria of ankylosing spondylitis (Kellgren, 9; Bennett and Wood, 98), but are generally accepted as a manifestation of spondylitis (Collins, 99; Romanus and Ydens, 955; McEwen et al, 97). The pathogenesis of syndesmophytes in psoriatic spondylitis is unknown. It has been suggested that the calcification may result from an inflammatory process in paravertebral connective tissues or be a form of periosteal reaction secondary to traction on bone (Bywaters and Dixon, 955), or there may be an enthesopathy as described in ankylosing spondylitis (Ball, 97) but with a different distribution.
15 (%) (9%) (9%) 55 (%) (%) (%) to w TABLE. Severity of peripheral related to radiological changes Peripheral Arthritia Nil Mild Moderate Severe All patients with psoriatio (5%) 57 (%) 9 (8%) 8 (%) All patients with sacro-iliitis (8%) (5%) 5 (%) (%) Patients w: sacro-iliitis and axial disease (%) (57%) Patients with Patients with Patients with Patients with normal spines sacro-iliitis syndesmophytes syndesmophytes and and normal and sacro-iliitis Clinical and Clinical peripheral sacro-iliao joints radiological: and/or complete radiological set of films (7%) (%) (%) (%) 8 (%) 7 (9%) (7%) Downloaded from by guest on May, (5%) 5 (%) (7%) (7%) (5%) 7 (%) (8%) (%) (%) 9 (%) 7 (%) (%) a s- TABLE 7. Severity of psoriasis related to radiological changes All patients with psoriatio All patients with sacro-iliitis Patients with sacro-iliitis and axial disease Patients with sacro-iliitis and peripheral Patients with Patients with Patients with normal spines syndesmophytes syndesmophytes ^ and normal and sacro-iliitis Clinical and Clinical sacro-iliao joints radiological: complete set of films and/or radiologioal Mild Moderate Severe 8 (%) 9 (%) 9 (7%) 8 (8%) (9%) (9%) (8%) (%) (8%) (7%) (%) 9 (5%) 7 (9%) (%) 9 (75%) (7%) (8%)
16 J. B. Lambert and V. Wright That syndesmophytes are not degenerative in origin is suggested by their occurrence in a group younger than the group with normal spines. Their association with HLA-B7 is further evidence of the aetiological similarity to ankylosing spondylitis. It seems, therefore, that in their presence a presumption of spondylitis is reasonable even in the absence of sacro-iliitis. Those patients with sacro-iliitis fall readily into two groups; those in whom spinal was the major disability and those in whom there was a significant peripheral. The two groups differ clinically and radiologically. Those with mainly spinal resembled idiopathic ankylosing spondylitis, with a male dominance, high prevalence of iritis, a lower prevalence of nail dystrophy, and shorter duration of psoriasis. It is of interest that HLA-B7 was found in a similar proportion of both groups, while clinical symptoms and signs of spondylitis were more common in the axial group, in which disease activity as indicated by the E.S.R. was low. It is likely that the axial group represent the chance association of psoriasis and ankylosing spondylitis, the prevalence being about 7 per cent. Psoriatic spondylitis is characterized radiologically by sacro-iliitis and by syndesmophytes. This differs from ankylosing spondylitis clinically and radiologically. There was no sex difference and the mean age of onset of was higher. Spondylitis usually caused no symptoms and no signs of restricted spinal mobility. Peripheral was more extensive and a more important aspect of the disease than in ankylosing spondylitis. Extra-articular manifestations were not encountered. Sacro-iliitis was more frequently unilateral or asymmetrical and syndesmophytes which occurred in small numbers, were unilateral or asymmetrical and were more often non-marginal. HLA-B7 was associated with sacro-iliitis and was present more often than normal in those with only syndesmophytes. REFERENCES AALVTK, T., 9. Nord. med. 5, 7. AVTLA, R., PTJGH, D. G., SLOCUMB, C. H. and WLNXELMANN, R. K., 9. Radiology, 75, 9. BAKER, H., GOLDING, D. N., and THOMPSON, M., 9. Ann. intern. Med. 58, Brit. J. Derm. 7, 59. BALL, J., 97. Ann. rheum. Dis.,. BABDNAGNI, O., and CXSLISIMO, O. A., 97. Policlinico, Sez. prat. 7,. BAUER, J., and VOGL, A. 9. Klin. Wschr., 7. BENNETT, P. H., and WOOD, P. N. H. (editors) 98. "Population studies of the rheumatic diseases", Proc. rd Int. Symp., New York, 9. Int. Congr. p. 5. Ser. No. 8. Amsterdam, Excerpta Medica Foundation. BOIJENS, F. VAN DEB, 99. "La rheumatism psoriatique". Paris, de Francois. BOTJIM, J. J., 9. Ann. intern. Med. 57, 8. BYWAXEBS, E. G. L., and DIXON, A. St. J., 95. Ann. rheum. Dis.,. CLEMMESEN, S., and ABNSO, E., 95. "Rheumatic Diseases": based on the Proceedings of the 7th Int. Congr. on Rh. Dis. p. 5, Philadelphia, Saunders. COLLINS, D. H., 99. "The pathology of articular and spinal diseases". st Edition, London, Arnold. COSTE, F., FBANCON, J., TOUBAINE, R., and LOYATJ, G., 958. Rev. Rhum. 5, 75. and SOLNICA, J., 9. Rev.franc, fitud. din. biol., 578. DAWSON, M. H., and TYSON, T. L., 98. Trans. Ass. Amer. Phycns. 5,. DIXON, A. ST. J., and LIENOE, E., 9. Ann. rheum. Dis., 7. EPSTEIN, E., 99. Arch. Derm. Syph. (Chic.), 57. FLETCHEB, E., and Rose, F. C, 955. Lancet, i, 95. Downloaded from by guest on May,
17 Psoriatic Spondylitis 5 GRABER-DUVERNAY, J., 957. Rev. Rhum., 88. HART, F. D., 95. Trans. ophfral. Soc., U.K. 7, 7. HABVTE, J. N., LESTER, R. S. and LITTLE, A. H., 97. Amer. J. Roentgenol. 7, 79. HILL, A. G. S., 9. Ann. rheum. Dis., 57. JAJIC, I., 98. Ann. rheum. Dis. 7,. KAPLAN, D., PLOTZ, C. M., NATHANSON, L. and FRANK, L., 9. Ann. rheum. Dis., 5. KELLGBEN, J. H., 9. Bull, rheum. Dis., 9. KTLLEBREW, K., GOLD, R. H., and SHOLKOFF, S. D., 97. Radiology, 8, 9. LANQKT.AND, N., and ROAAS, A. 97. Ada orthop. Scand., 9. LABSTJS, A., MUSTAKALLIO, K. K., and LADTE, V., 9. Ada Rheum. Scand.,. LAWBENOB, J. S., 97. Brit. J. vener. Dis. 5,. LEFKOVITS, A. M., and THOMAS, J. R., 958. Ann. intern. Med. 9, 89. MACBAE, I. F. F HASLOCK, D. I., and WRIGHT, V., 97. Ann. rheum. Die., 58. MOEWEN, C, Di TATA, D., LINGG, C, PORENI, A., GOOD,A., and RANKIN, R. F 97. Arth. and Rheum., 9. MOLL, J. M. H., 97. Proc. roy. Soc. Med. 7,. HASLOCK, I., MACRAE, I. F., and WRIGHT, V. 97. Medicine (Baltimore), 5,. and WRIGHT, V., 97. Ann. rheum. Dis., Ann. rheum. Dis.,. 97. Sem. Arth. and Rheum., 5. PETERSON, C. C. JR., and SLLBIGER, M. L. 97. Amer. J. Roentgenol., 8. POLOTSKI, I. I., 97. Vestn. Derm. Vener., 7. REED, W. B., 9. Ada Derm.-venereol. (Stockh.), 9. REITEB, H. F. H., and NORHOLM-PEDERSON, A., 95. Ada Derm.-venereol. (Stockh.), 7. RILEY, M. J., ANSELL, B. M., and BYWATERS, E. G. L., 97. Ann. rheum. Dis., 8. ROMASTUS, R., and YDENS, S., 955. Pelvo-Spondylitis Ossificans, st Edition, Pp. 8-9, Copenhagen, Munksgaard. SCHILLING, F., and SCHACHERL, M., 97. Z. Rheumaforsch., 5. SOHLOSSTEIN, L., TERSAEE, P. I., BLUESTONE, R., and PEARSON, C. M., 97. NewEngl.J. Med. 88, 7. SEZE, S. DE LACAPERE, J. P., and AMOTJDRUZ, J. 95. Rev. Rhum., 9, 7. SHARP, J., and PURSER, D. W., 9. Ann rheum. Dis., 7. SHERMAN, M. S., 95. J. BoneJt. Surg. A, 8. SKYTHE.H. A., 9. Cited by REED, W. B., BECKER, S. W., ROHDE, R. andheiskell, C. L., Arch. Derm. 8, 5. STEBNE, E. H., and SCHNEIDER, B., 95. Ann. intern. Med. 8, 5. STROHFELD*. P., 97. Therapiewoche,,. STODARAM, M., and PATTON, J. T., 975. Brit. J. Radiol. 8, 8. VrLANOVA, X., and PINOL, J., 95. Rheumatism, 7, 97. WEIGHT, V., 957. Brit. J. Radiol., Arch. Derm. 8, Ann. rheum. Dis.,. ZELLNER, E., 98. Munch, med. Wschr. 75, 9. Downloaded from by guest on May,
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Radiological and Familial Aspects
 46 Proc. roy. Soc. Med. Volume 67 January 1974 2 shows shrunken fibrotic upper lobes with a mycetoma in the right apical cavity (Figs 1 and 2). He has strongly positive precipitating antibodies to Aspergillusfumigatus.
46 Proc. roy. Soc. Med. Volume 67 January 1974 2 shows shrunken fibrotic upper lobes with a mycetoma in the right apical cavity (Figs 1 and 2). He has strongly positive precipitating antibodies to Aspergillusfumigatus.
Case reports CASE 1. A 67-year-old white man had back pain since the age. our clinic several years later with progressive symptoms.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 574-578 Late-onset peripheral joint disease in ankylosing spondylitis MARC D. COHEN AND WILLIAM W. GINSBURG From the Division ofrheumatology and Internal Medicine,
Relation between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A study of 40 patients
 2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
2018; 2(4): 43-47 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 43-47 Received: 19-08-2018 Accepted: 23-09-2018 Dr. Hardik Sethi Orthopaedics, Govt.
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review
 Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
Seronegative spondyloarthropathies : A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0008 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1
ARTHRITIS* x rays of the cervical spine from patients with. with similar films from a control population.
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 50. CERVICAL SPINE IN PSORIASIS AND IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS* BY DAVID KAPLAN, CHARLES M. PLOTZ, LOUIS NATHANSON, AND LAWRENCE FRANK From the Downstate Medical Center, State
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1964), 23, 50. CERVICAL SPINE IN PSORIASIS AND IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS* BY DAVID KAPLAN, CHARLES M. PLOTZ, LOUIS NATHANSON, AND LAWRENCE FRANK From the Downstate Medical Center, State
Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 220 Patients
 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 62, No. 238, pp. 12-141, February 198 Psoriatic Arthritis (PSA) - An Analysis of 22 Patients D. D. GLADMAN, R. SHUCKETT, M. L. RUSSELL, J. C. THORNE, and R. K.
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Abstract Objective In 1971 McEwen and colleagues suggested that the radiological changes of classic ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and the
 Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
Ann Rheum Dis 1998;57:135 140 135 EXTENDED REPORTS Do the radiological changes of classic ankylosing diver from the changes found in the associated with inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and reactive?
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 741-745 Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27 ADRIAN B. BECKINGSALE, JONATHAN DAVIES, JONATHAN M. GIBSON, AND A. RALPH ROSENTHAL
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 741-745 Acute anterior uveitis, ankylosing spondylitis, back pain, and HLA-B27 ADRIAN B. BECKINGSALE, JONATHAN DAVIES, JONATHAN M. GIBSON, AND A. RALPH ROSENTHAL
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
in the 77 adults suffering from rheumatoid arthritis ranged from 22 to 79 years (mean 52) and in the 23 with juvenile
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
Ann. rheum. Dis. (972), 3, 364 Cervical spine involvement in patients with chronic undergoing orthopaedic surgery E. ORNILLA, B. M. ANSELL, AND A. J. SWANNELL MRC Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1963, 38, 492. ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS BY PHILIP JACOBS From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital, Birmingham (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 28, 1963) Ankylosing
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1963, 38, 492. ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS IN CHILDREN AND ADOLESCENTS BY PHILIP JACOBS From the Royal Orthopaedic Hospital, Birmingham (RECEIVED FOR PUBLICATION FEBRUARY 28, 1963) Ankylosing
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Elective Student P. H.
 Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Radiologic-Pathologic Correlations of the Vertebral Column Component of Ankylosing Spondylitis 2009 2 Elective Student P. H. Case 63 year old man Chief complaint Tingling sensation of left leg Gait disturbance
Ankylosing Spondylitis*
 Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
Ankylosing Spondylitis* JOHN BAUM, M.D. Professor of Medicine, Pediatrics, and Preventive Medicine and Community Health, University of Rochester School of Medicine, Rochester, New York Within the last
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Spondylarthropathies
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Spondylarthropathies Spondylarthropathies Undifferentiated Ankylosis spondylitis Psoriatic arthritis Enteropathic arthritis Reactive arthritis (and Reiter syndrome) Spondylarthropathies
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 12 Radiological manifestations of Reiter's syndrome WILLIAM MARTEL From the University of Michigan Hospital, Michigan, USA Reiter's syndrome (RS) presents with
arthritis: a clinical, radiological and immunogenetic study
 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 73-77 2nd Divisione di Medicina (Unita Reumatologica), USL N9, Reggio Emilia, Italy C Salvarani P Macchioni F Rossi N Capozzoli R Baricchi I Portioli 2 Dipartimento
Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 73-77 2nd Divisione di Medicina (Unita Reumatologica), USL N9, Reggio Emilia, Italy C Salvarani P Macchioni F Rossi N Capozzoli R Baricchi I Portioli 2 Dipartimento
Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1982, 41, 237-241 Spondylitis erosiva: report on 9 patients I. JAJIC, Z. FURST, AND B. VUKSIC From the Ward for Rheumatic Diseases of the Orthopaedic Hospital, the Medical
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS
 ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLOSIS Page 1 1. General Information Medical Services One of the group of conditions known as the Spondyloarthropathies. Ankylosing spondylitisis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
Annals of the Rheumatic Disease, 1981, 4G, 547-553 Clinical features of 53 cases with pustulotic arthroosteitis H. SONOZAKI1, H. MITSUI2, Y. MIYANAGA2, K. OKITSU2, M. IGARASHI2, Y. HAYASHI2, M. MATSUURA3,
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA)
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies (SpA) Objectives: Introduction SpA disease information Pathogenesis Clinical features Team Members: Ameera Niazi - Lulwah AlShiha - Qaiss Almuhaideb - Abdullah Hashem
Vertebral sclerosis in adults
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 18-22 Vertebral sclerosis in adults A. S. RUSSELL,' J. S. PERCY,1 AND B. C. LENTLE2 'From the Rheumatic Disease Unit, Department of Medicine, University of Alberta,
ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS*
 k Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1959), 35, 71. It would seem appropriate to begin this paper by reflecting for a moment on the lady to whom, perhaps, venereologists owe everything, for is it not at least possible
k Brit. J. vener. Dis. (1959), 35, 71. It would seem appropriate to begin this paper by reflecting for a moment on the lady to whom, perhaps, venereologists owe everything, for is it not at least possible
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Arthritis and Crohn's disease
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 479 Arthritis and Crohn's disease A family study IAN HASLOCK* From the Rheumatism Research Unit, Department ofmedicine, University ofleeds, and the General Infirmary at Leeds
Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1979), 38, Supplement p. 79 Pauciarticular juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and immunogenetic aspects CHESTER W. FINK, AND PETER STASTNY From the University of Texas Southwestern
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis: Atlantoaxial Ankylosis and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 24, No. 1, February, 2017 https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2017.24.1.21 Original Article Manifestations of Cervical Spine Involvement in Longstanding Ankylosing Spondylitis:
HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 504-509 HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis J. C. WOODROW, AND C. J. EASTMOND From the Department of Medicine, Liverpool University SUMMARY One
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 504-509 HLA B27 and the genetics of ankylosing spondylitis J. C. WOODROW, AND C. J. EASTMOND From the Department of Medicine, Liverpool University SUMMARY One
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
ligament as a cause of cervical myelopathy
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 263-268 Ossification in the region of the posterior longitudinal ligament as a cause of cervical myelopathy L. BAKAY, H. L. CARES, AND R. J. SMITH From the Division
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1970, 33, 263-268 Ossification in the region of the posterior longitudinal ligament as a cause of cervical myelopathy L. BAKAY, H. L. CARES, AND R. J. SMITH From the Division
CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 125 1 CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS JOSE A. MALDONADO-COCCO, OSVALDO GARCIA-MORTEO, ALBERT0 J. SPINDLER, OSVALDO HUBSCHER. and SUSANA GAGLIARDI Forty-seven of 100 consecutive juvenile
125 1 CARPAL ANKYLOSIS IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS JOSE A. MALDONADO-COCCO, OSVALDO GARCIA-MORTEO, ALBERT0 J. SPINDLER, OSVALDO HUBSCHER. and SUSANA GAGLIARDI Forty-seven of 100 consecutive juvenile
THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT
 THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT J.M.H. MOLL Emeritus Consultant Rheumatologist, Sheffield, UK SUMMARY In the 1960s, Professor Verna Wright became increasingly interested
THE LEEDS IDEA : AN HISTORICAL ACCOUNT OF THE SPONDARTHRITIS CONCEPT J.M.H. MOLL Emeritus Consultant Rheumatologist, Sheffield, UK SUMMARY In the 1960s, Professor Verna Wright became increasingly interested
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
development of erosive osteoarthritis?
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1989; 48, 183-187 Scientific papers Is chronic renal failure a risk factor for the development of erosive osteoarthritis? I J S DUNCAN,' N P HURST,' A DISNEY,2 R SEBBEN,3
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF CALCIFICATION OF
 CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF CALCIFICATION OF THE MITRAL REGION BY EINO LINKO AND ERKKI SYSIMETSA From the Medical Clinic and the Cardio-Respiratory Research Unit, University of Turku, Finland
CLINICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF CALCIFICATION OF THE MITRAL REGION BY EINO LINKO AND ERKKI SYSIMETSA From the Medical Clinic and the Cardio-Respiratory Research Unit, University of Turku, Finland
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach
 Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Articular disease of the hand - the target joint approach Poster No.: C-1817 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. R. Domingues Madaleno 1, A. P. Pissarra 1, I. Abreu 2, A. Canelas 1,
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS
 EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS ACTIVITY 1: EARLY COLLABORATION IN THE TREATMENT OF PSA Key Slides COMMON COMORBIDITIES OF PSORIATIC DISEASE
EXAMINING THE CRUCIAL COALITION BETWEEN DERMATOLOGY AND RHEUMATOLOGY IN PSORIATIC ARTHRITIS ACTIVITY 1: EARLY COLLABORATION IN THE TREATMENT OF PSA Key Slides COMMON COMORBIDITIES OF PSORIATIC DISEASE
Skeletal Radiology. Productive osseous changes about the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis. Robert M. Cantor, M.D., and Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D.
 Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16: 397-402 Skeletal Radiology Productive osseous changes about the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis Robert M. Cantor, M.D., and Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. Department of Radiology, University
Skeletal Radiol (1987) 16: 397-402 Skeletal Radiology Productive osseous changes about the wrist in rheumatoid arthritis Robert M. Cantor, M.D., and Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. Department of Radiology, University
Radiography is typically the first imaging study in evaluation for arthritis. On radiographs, one critical assessment is differentiating inflammatory
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatoid Arthritis. RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling. Rheumatic Diseases
 RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
RCS 6080 Medical and Psychosocial Aspects of Rehabilitation Counseling Rheumatic Diseases The prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in most Caucasian populations approaches 1% among adults 18 and over and
Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 524-531 Rheumatoid involvement of the lumbar spine H. SIMS-WILLIAMS,' M. I. V. JAYSON,1 AND H. BADDELEY2 From the Department of Medicine, University ofbristol,
SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro?
 Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Histocompatibility antigens in inflammatory
 Gut, 1976, 17, 906-910 Histocompatibility antigens in inflammatory bowel diseaset Their clinical significance and their association with arthropathy with special reference to HLA-B27 (W27) ELIAS G. MALLAS,
Gut, 1976, 17, 906-910 Histocompatibility antigens in inflammatory bowel diseaset Their clinical significance and their association with arthropathy with special reference to HLA-B27 (W27) ELIAS G. MALLAS,
강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예
 대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
대한내과학회지 : 제 84 권제 6 호 2013 Http://Dx.Doi.Org/10.3904/Kjm.2013.84.6.873 강직성척추염환자에서대동맥박리를동반한마르팡증후군 1 예 을지대학교의과대학내과학교실 류지원 박지영 송은주 허진욱 A Case of Aortic Dissection with Marfan Syndrome and Ankylosing Spondylitis
Jurnal Medical Aradean (Arad Medical Journal) Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 2015, pp Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.
 Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 15, pp. 4-45 15 Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.ro) DEMOGRAPHIC AND CLINICAL PARAMETERS EVALUATION FOR PATIRNTS WITH PSORIATIC VERSUS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Camelia Ciacli
Vol. XVIII, issue 1, 15, pp. 4-45 15 Vasile Goldis University Press (www.jmedar.ro) DEMOGRAPHIC AND CLINICAL PARAMETERS EVALUATION FOR PATIRNTS WITH PSORIATIC VERSUS RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Camelia Ciacli
Bones? Did someone say bones? 12/31/2012. W.R Reinus, MD MBA FACR
 William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
William R. Reinus, MD MBA FACR Temple University Medical Center Aug 2012 (55) 1 Bones? Did someone say bones? 2 ABC S OF ARTHRITIS Arthritis: By definition, any disease that is jointcentered: Both sides
The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis
 SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
SPINE The Andersson lesion in ankylosing spondylitis DISTINGUISHING BETWEEN THE INFLAMMATORY AND TRAUMATIC SUBTYPES Y.-S. Park, J.-H. Kim, J.-A. Ryu, T.-H. Kim From Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College
Rib erosions in rheumatoid arthritis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 16 Rib erosions in rheumatoid arthritis I. F. ANDERSON, A. B. CORRIGAN, AND G. D. CHAMPION North Shore Hospital, St. Leonards, New South Wales 2065, Australia Defects in the
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 16 Rib erosions in rheumatoid arthritis I. F. ANDERSON, A. B. CORRIGAN, AND G. D. CHAMPION North Shore Hospital, St. Leonards, New South Wales 2065, Australia Defects in the
9 Lecture. Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม
 9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
9 Lecture Spondyloarthropathy แพทย หญ งน นทนา กส ตานนท คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยเช ยงใหม Spondyloarthritis: SpA Nuntana Kasitanon Division of Rheumatology Department of Medicine Spondyloarthritis: SpA
RADIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE IN
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 333 RADIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS BY K. A. E. MEIJERS*, S. F. C. HEERMA VAN VOSSt, AND R. J. FRANCOIS+ From the Departments of Rheumatology*
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 333 RADIOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE CERVICAL SPINE IN ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS BY K. A. E. MEIJERS*, S. F. C. HEERMA VAN VOSSt, AND R. J. FRANCOIS+ From the Departments of Rheumatology*
Review article. early diagnosis? HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for. Why subjects carrying HLA-B27 are prone. Jan Tore Gran, Gunnar Husby
 _JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
_JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
Diagnosis of "Rheumatoid Variants"
 Refer to: Reynolds MD, Rankin TJ: Diagnosis of "rheumatoid variants"-ankylosing spondylitis, the arthritides of gastrointestinal diseases and psoriasis, and Reiter's syndrome. West J Med 120:441-447, Jun
Refer to: Reynolds MD, Rankin TJ: Diagnosis of "rheumatoid variants"-ankylosing spondylitis, the arthritides of gastrointestinal diseases and psoriasis, and Reiter's syndrome. West J Med 120:441-447, Jun
Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 J. med. Genet. (1967). 4, 239. Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis ALAN E. H. EMERY and JOHN S. LAWRENCE From the Manchester University Department of Medical Genetics, The Royal Infirmary, Manchester 13,
J. med. Genet. (1967). 4, 239. Genetics of Ankylosing Spondylitis ALAN E. H. EMERY and JOHN S. LAWRENCE From the Manchester University Department of Medical Genetics, The Royal Infirmary, Manchester 13,
Vertical subluxation of the axis
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 359 Vertical subluxation of the axis in rheumatoid arthritis D. R. SWINSON,* E. B. D. HAMILTON,* J. A. MATHEWSt, AND D. A. H. YATESt From the *Department ofphysical Medicine
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1972), 31, 359 Vertical subluxation of the axis in rheumatoid arthritis D. R. SWINSON,* E. B. D. HAMILTON,* J. A. MATHEWSt, AND D. A. H. YATESt From the *Department ofphysical Medicine
Bone mineral density and vertebral compression fracture rates in ankylosing spondylitis
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 117-121 117 Rheumatology, Whipps Cross Hospital, Leytonstone, London, United S Donnelly D V Doyle A Denton I Rolfe Human Metabolism, University of Sheffield Medical
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 117-121 117 Rheumatology, Whipps Cross Hospital, Leytonstone, London, United S Donnelly D V Doyle A Denton I Rolfe Human Metabolism, University of Sheffield Medical
A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis
 CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
CASE REPORT Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:614-618 A rare cause of dysphagia: compression of the esophagus by an anterior cervical osteophyte due to ankylosing spondylitis İlknur Albayrak 1, Sinan Bağcacı
subluxation: a radiographic comparison
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1980, 39, 485-489 Cervical collars in rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation: a radiographic comparison BO ALTHOFF AND IAN F. GOLDIE From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1980, 39, 485-489 Cervical collars in rheumatoid atlanto-axial subluxation: a radiographic comparison BO ALTHOFF AND IAN F. GOLDIE From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery
Rheumatology. Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications. Definition of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Spondyloarthropathies
 Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
asked to report to the out-patient clinic, those who
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 219 ULCERATIVE COLITIS WITH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS* MALCOLM I. Although ankylosing spondylitis and ulcerative colitis are uncommon diseases, there appears to be an association
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1968), 27, 219 ULCERATIVE COLITIS WITH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS* MALCOLM I. Although ankylosing spondylitis and ulcerative colitis are uncommon diseases, there appears to be an association
SPONTANEOUS dislocation of the atlas on the axis has been known
 CLEVELAND CLINIC QUARTERLY Copyright 1970 by The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Volume 37,Jaunary 1970 Printed in U.S.A. Spontaneous subluxation of the first and second cervical vertebrae, in rheumatoid arthritis,
CLEVELAND CLINIC QUARTERLY Copyright 1970 by The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Volume 37,Jaunary 1970 Printed in U.S.A. Spontaneous subluxation of the first and second cervical vertebrae, in rheumatoid arthritis,
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions
 Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Evaluation of MRI diffusion in spondylarthropathy axial skeleton lesions Poster No.: C-2353 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Dallaudiere, R. Dautry, A. Felter, J. LINCOT, P. Koch,
Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 984; 43, 3-37 Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine R. C. HILTON AND J. BALL From the Department of Rheumatology, Hope Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY The frequency,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 984; 43, 3-37 Vertebral rim lesions in the dorsolumbar spine R. C. HILTON AND J. BALL From the Department of Rheumatology, Hope Hospital, Manchester SUMMARY The frequency,
INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE BIOPSY DURING HAND SURGERY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE BIOPSY DURING HAND SURGERY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS By M. RILEY, M.B., M.R.C.P. and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S R.C.S. (Ed.) M.R.C. Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross
INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE BIOPSY DURING HAND SURGERY FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS By M. RILEY, M.B., M.R.C.P. and STEWART H. HARRISON, F.R.C.S., L.D.S R.C.S. (Ed.) M.R.C. Rheumatism Research Unit, Canadian Red Cross
Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation
 ~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
~~ arthritis arid rheumatism Official Journal of the American Rheumatism Association Section of the Arthritis Foundation EVALUATION OF DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA FOR ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS A Proposal for Modification
Axial Spondyloarthritis. Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital
 Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Remicade (Infliximab)
 Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Remicade (Infliximab) Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.04.016 11/18/2003 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 07/26/2013 Section: Prescription Drugs Place(s)
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology
 Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1984, 43, 769-773 Bone and joint symptoms in Paget's disease J. WINFIELD AND T. C. B. STAMP From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, 234 Great Portland Street, London
PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF AGE OF ONSET IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
