Naviculo-Medial Cuneiform Coalition:
|
|
|
- Joella Sutton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Naviculo-Medial Cuneiform Coalition: Radiological Features 1 Yun Sun Choi, M.D., Sung Moon Kim, M.D. 2, Kyung Tae Lee, M.D. 3, Ki Won Young, M.D. 3, Sang Jin Bae, M.D. 2, Joong Mo Ahn, M.D. 4, Myung Jin Shin, M.D. 2 Purpose: To define the radiological features of the naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition. Materials and Methods: This study examined 35 feet from 25 patients (mean age 26 years) with a naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition. The images were analyzed retrospectively with regard to irregular articular surface, subchondral sclerosis, subchondral cyst, beak-like spur, the change in joint space, bony fusion seen on plain radiographs (n=35) and CT (n=14), and the histological type of coalition on MRI (n=3). The extent of joint involvement was also evaluated. Results: Of the 35 feet, plain radiographs and/or CT showed an irregular articular surface in 34 (97.1%), subchondral sclerosis in 30 (85.7%), a subchondral cyst in 29 (82.9%), a beak-like spur in 23 (65.7%), a narrowing of the joint space in 24 (68.6%) and no bony fusions (0%). The T1-weighted images revealed low signal intensity, and the T2-weighted fast spin-echo and gradient images revealed high signal intensity in the three feet with a cartilaginous coalition. The coalition involved the plantar part of the joint in all 35 feet. Conclusion: The characteristic radiological features of a naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition include an irregular articular surface with possible secondary degenerative changes in the plantar margin of the joint, non-osseous type. Index words : Foot, abnormalities Foot, radiography Foot, CT Foot, MR A tarsal coalition is an abnormal fusion of fibrous (syndesmosis), cartilaginous (synchondrosis), or osseous 1 Department of Radiology, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine 2 Department of Radiology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine 3 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Eulji Hospital, Eulji University School of Medicine 4 Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University This article was supported by 2002 Eulji research grant (EJRG E25). Received June 14, 2005 ; Accepted August 3, 2005 Address reprint requests to : Yun Sun Choi, M.D., Department of Radiology, Eulji Hospital, 280-1, Hagye 1-dong, Nowon-gu, Seoul , Korea. Tel Fax cys0128@eulji.or.kr 381 (synostosis) tissues between the tarsal bones in the hind and midfoot. This union can be either congenital or acquired (14). The most commonly reported tarsal coalitions are the calcaneonavicular and talocalcaneal. Other coalitions including the talonavicular, calcaneocuboid, and cubonavicular have also been reported, but with much lower frequency (13). In addition, there have been few cases of a naviculocuneiform coalition between the navicular and one or more of the cuneiform bones (512). Miki et al first reported an isolated naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition in 1979, which was then believed to be an extremely rare condition (7). However, in 1996, Kumai et al reported an isolated nav-
2 iculo-medial cuneiform coalition in 60 feet from 40 patients, which showed that its incidence was much greater than previously reported (13). Nevertheless, to our knowledge, the radiological findings of a naviculomedial cuneiform coalition have not been reported in radiology literature. A lack of knowledge and understanding of the radiological findings of this condition may result in it being overlooked in many patients. The aim of this study was to define the plain radiographic, computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance (MR) imaging findings of a naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition. Materials and Methods Clinical data Thirty-five feet from 25 patients (10 bilateral, 10 male, 15 female; mean age 26 years; range years) with a naviculo-cuneiform coalition, which was clinically and radiographically confirmed between March 1997 and September 2003, were included. The cases were collected from three centers and were identified by reviewing various orthopedic databases. In all cases, experienced orthopedic foot surgeons performed the physical examinations. There was no history of inflammatory arthritis nor was there any swelling at the medial midfoot area in any of the cases examined. Twenty-two of the 35 feet (62.9%) were symptomatic (mean age 24 years; range 1043 years) and 13 (37.1%) reported no pain (mean age 28 years; range 1442 years). The most common symptom was pain on the plantar side of the midfoot. The pain was aggravated by standing or walking for lengthy periods of time and by physical activity such as soccer or judo in 11 out of 22 feet. The 22 symptomatic feet received non-steroid anti-inflammatory medication for 6 months and four of them were given additional arch supports. The symptoms were relieved by conservative treatment in 19 out of 22 feet, while the other three had persistent pain and received a fusion of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint after resecting the coalition. The 13 asymptomatic feet were found incidentally on plain radiographs performed during an evaluation of a calcaneal or navicular fracture (n=5), osteoarthritis of the first metatarsophalangeal joint (n=4), hallux valgus (n=3) and an instability of the intertarsal joints (n=1). Radiological assessment The radiological methods used in this study were plain radiographs (n=35), CT (n=14), and MR imaging (n=3). The plain radiographs of the foot were anteroposterior, lateral and oblique. CT was performed using either spiral CT or a 16 channel multi-detector CT machine. The CT images were as follows: an axial or reconstructed axial parallel to the naviculo-cuneiform joint, a reconstructed sagittal and a coronal perpendicular to the naviculo-cuneiform joint with a slice thickness ranging from 1.25 to 1.5 mm. MR imaging was performed using various 1.5-T systems. T1-weighted spin-echo (TR/TE, /1220 msec), T2-weighted fast spin-echo (TR/TE, /96 msec) and gradient echo (608/18 msec, flip angle; 20 degree) images were obtained. The field of view ranged from 12 to 18 cm, slice thickness ranged from 3 to 4 mm with a 00.8 mm inter-slice gap, and the matrix was 256 by 256. All of the imaging methods were reviewed retrospectively by a reviewer with no knowledge of the patients clinical information. In all cases the findings were obtained by consensus of two musculoskeletal radiologists. The images were analyzed with regard to irregular articular surface, subchondral sclerosis, subchondral cyst, beak-like spur, change of the joint space (narrow or wide), bony fusion and the extent of joint involvement on plain radiographs and/ or CT. The extent of joint involvement was evaluated on the lateral plain radiograph and/ or the reconstructed Table 1. Plain Radiographic and/ or CT Findings of the Naviculo-Medial Cuneiform Coalition Symptomatic feet (n=22) Asymptomatic feet (n=13) Total (n=35) Cortical irregularity 22 (100%) 12 (92.3%) 34 (97.1%) Subchondral sclerosis 18 (81.8%) 12 (92.3%) 30 (85.7%) Subchondral cyst 19 (86.4%) 10 (76.9%) 29 (82.9%) Beak-like spur 15 (68.2%) 08 (66.7%) 23 (65.7%) Change of joint space 16 (72.7%) 09 (69.2%) 25 (71.4%) Narrowing 15 (68.2%) 09 (69.2%) 24 (68.6%) Widening 01 (4.5%) 1 (2.9%) Intraarticular loose body 02 (9.1%) 01 (7.7%) 3 (8.6%) Dorsal spur at navicular 00 (0%) 01 (7.7%) 1 (2.9%) Bony fusion 00 (0%) 00 (0%) 0 (0%)0. 382
3 sagittal CT images. Irregular articular surfaces were defined as irregular deformities of the opposing surfaces of the abnormal articulation; subchondral sclerosis was defined as an increased density of the subchondral bone; subchondral cysts were defined as subchondral lucences with a cavity; and beak-like spurs were defined as bony excrescences at the articular margin. MR imaging was also used to analyze the signal intensity on the articular side of the lesion which suggests the histologic type of coalition. Associated abnormalities such as a peroneal spastic foot or a flat foot, a talar neck deformity, osteonecrosis of the navicular bone were also evaluated by reviewing the clinical data and examining the radiological results. Results Plain radiographs (n=35) and/ or CT (n=14) showed an irregular articular surface in 34 out of 35 feet (97.1%), subchondral sclerosis in 30 feet (85.7%), a subchondral cyst in 29 feet (82.9%), a change in the joint space in 25 feet (narrowing; n=24, widening; n=1) (71.4%), and a beak-like spur at the medial articular margin of the medial cuneiform and navicular bone in 23 feet (65.7%) (Fig. 13). No bony fusions were found in any of the 35 feet. Plain radiographs and/or CT also showed an intraarticular loose body in three feet. Two of them had a navicular fracture and one foot had a dorsal spur on the navicular bone. Table 1 shows the radiological findings in the symptomatic and asymptomatic feet. The plantar part of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint was involved in all 35 feet (100%), and the dorsal half of the joint was involved in one. MR showed a low signal intensity on T1-weighted, a high signal intensity on T2- weighted fast spin-echo and a high signal intensity lesion on gradient (T2*) image with an irregular articular surface in the plantar margin of the joint, suggesting a partial cartilaginous coalition in all three symptomatic feet that had been examined by MRI. One of those was confirmed during surgery as being a cartilaginous union (Fig. 3). There were no associated abnormalities such as a peroneal spastic foot or a flat foot, a talar neck deformity, or osteonecrosis of the navicular bone in the tarsal bones and joints. Fig year-old female judo player with a painful naviculomedial cuneiform coalition in her right foot. Anteroposterior radiograph shows an irregular articular surface of the naviculocuneiform joint (arrows). The joint space appears to be maintained. 383 Discussion The tarsal coalition has been reported in Western countries as being predominantly calcaneonavicular and talocalcaneal coalitions. There were only 10 cases of isolated naviculo-medial cuneiform coalitions reported before Kumai et al reported 60 cases. The reported cases were Japanese, Hispanics and people from African decent (713). Kumai et al classified the morphology of this coalition into three patterns, an irregular type, a cystic type and a combined type using CT with clinical analysis (13). Sato et al described this coalition as being an irregular osteolytic and peripheral sclerotic change in the joint surface and an osseous fusion of the joint (11). Green et al reported an irregularity between the navicular bone and the medial cuneiform bone, as well as an erosive change and a bony coalition (synostosis) (12). In this study, plain radiographic and CT findings of most cases revealed an irregular articular surface, subchondral sclerosis and a subchondral cyst. Narrowing of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint space and a beaklike spur at the medial margin of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint was also seen in several cases. Histopathological analysis was performed in three cases and these findings indicated fibrocartilaginous coali-
4 Yun Sun Choi, et al : Naviculo-Medial Cuneiform Coalition tions. None of the cases showed an osseous coalition. Miki et al reported that most naviculo-cuneiform coalitions consist histologically of fibrous connective tissue containing islands of scattered chondroid tissue (8). Subchondral sclerosis, subchondral cysts, beak-like spurs and a marked narrowing of the joint space, were believed to be a reactive bone change in fibrocartilaginous naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition. Intra-articular loose bodies were seen in three cases, and were considered to be osteocartilaginous fragments. It is believed that in the isolated naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition, a fibrocartilaginous coalition may cause microfractures and remodeling on the borders between the underlying bone and the coalition, which can then lead to secondary degenerative changes. These changes may resemble osteoarthritis. In all cases, the plantar site of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint had continuous fibrocartilaginous tissue, and the dorsal site was a normal joint surface with the exception of one case. These changes are believed to be characteristic of this condition because they are A rarely observed in other types of coalitions. Many cases of naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition have either been overlooked or diagnosed as osteoarthritis, bony cysts or inflammatory synovitis (6, 13). In osteoarthritis, the dorsal portion of the joint is obliterated with large dorsal spurs and the articular surface is not irregular, which is different from those observed in a naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition. Subchondral sclerosis and beaklike spurs are usually not detected in inflammatory synovitis such as in a rheumatological process. An association between a naviculocuneiform coalition and Kohler s disease of the tarsal navicular bone has been suggested, but this association was not seen in this study (6). There was no evidence of a peroneal spastic foot, which has been observed in other tarsal coalitions. In this study, 22 out of 35 feet (62.9%) were symptomatic. Sato et al reported that the pain was the result of a weakness in the cartilagenous bridges relative to the weight-bearing force over the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint (11). Naviculo-medial cuneiform coalitions may also be discovered incidentally in asymptomatic feet (12, 13). B Fig year-old woman with a painful naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition in both feet. A, Both anteroposterior radiographs (R: right, L: left) show an irregular articular surface, subchondral cysts (small white arrows) and subchondral sclerosis (large black arrows) with a narrowing of the joint space. There are beak-like spurs at the medial margin of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joints of both feet. B. The lateral view and the reconstructed sagittal CT scan of the left foot with a slice thickness of 1.5 mm (right upper corner), the plantar portion of the joint space is narrow and incompletely fused (arrows). C. The axial CT scan (R: right, L: left) with a slice thickness of 1.5 mm confirms the presence of a bilateral coalition with secondary degenerative changes (arrows). C 384
5 J Korean Radiol Soc 2005;53: B A C E D Fig year-old boy with a surgically confirmed naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition in his right foot. A, B. Anteroposterior (A) and lateral (B) radiographs show a cortical irregularity (large arrows) and a subchondral cyst (small arrow) with reactive sclerosis on the medioplantar side of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint. C. Sagittal T1-weighted spin echo image (TR/TE, 500/12) shows a low signal-intensity fusion on the plantar side of the naviculo-medial cuneiform joint (arrows). D, E. Sagittal T2-weighted (D) fast spin-echo (TR/TE, 3000/96) and axial T2* (E) (TR/TE, 608/18, flip angle 20 degree) images show high signal intensity of this lesion with an irregular articular surface (arrows). This was confirmed at surgery as being a cartilaginous coalition. 385
6 In this study, 13 of the 35 feet (37.1%) were discovered incidentally on plain radiographs. In Kumai s report, 15 of 60 cases (25%) were asymptomatic (13), which raises the question as to the overall incidence of this type of coalition. It is possible that more cases exist, but they have gone undetected because of their asymptomatic nature. Symptoms may not appear in the early stages because the naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition occurs in a joint with a small range of motion (14). A radiological diagnosis of this entity can be made using plain radiographs. CT confirmed the presence of a coalition along with its precise extent, and MR imaging helped determine the histological type of the naviculomedial cuneiform coalition. In conclusion, the characteristic radiological features of the naviculo-medial cuneiform coalition include an irregular articular surface with possible secondary degenerative changes in the plantar margin of the joint, nonosseous type. References 1. Varner KE, Michelson JD. Tarsal coalition in adults. Foot Ankle Int 2000;21: Newman JS, Newberg AH. Congenital tarsal coalition: multimodality evaluation with emphasis on CT and MR imaging. Radiographics 2000;20: Stormont DM, Peterson HA. The relative incidence of tarsal coalition. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1983;181: Leonard MA. The inheritance of tarsal coalition and its relationship to spastic flatfoot. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1974;56-B: Lusby HL. Naviculo-cuneiform synostosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1959;41-B: Gregersen HN. Naviculocuneiform coalition J Bone Joint Surg Am 1977;59-A: Miki T, Oka M, Shima M and Tanaka S. Naviculocuneiform coalition: a case report. J Foot Surg 1979;18: Miki T, Yamamuro T, Iida H, Ohta S and Oka M. Naviculocuneiform coalition. A report of two cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1985;196: Hynes RA, Romash MM. Bilateral symmetrical synchondrosis of navicular first cuneiform joint presenting as a lytic lesion. Foot Ankle 1987;8: Wiles S, Palladino SJ and Stavosky JW. Naviculocuneiform coalition J Am Podiatr Assoc 1988;78: Sato K, Sugiura S. Naviculo-cuneiform coalition-report of three cases. Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi 1990;64: Green MR, Yanklowitz B. Asymptomatic naviculocuneiform synostosis with a ganglion cyst. J Foot Surg 1992;31: Kumai T, Tanaka Y, Takakura Y and Tamai S. Isolated first naviculocuneiform joint coalition. Foot Ankle Int 1996;17: Jack EA. Naviculo-cuneiform fusion in the treatment of flat foot. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1953 ;35-B:
Case. 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms. Your diagnosis?
 Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
A Pictorial Review of Congenital Tarsal Coalition
 A Pictorial Review of Congenital Tarsal Coalition Poster No.: C-2305 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Jethwa, M. Tapp; Torquay/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal
A Pictorial Review of Congenital Tarsal Coalition Poster No.: C-2305 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Jethwa, M. Tapp; Torquay/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal joint, Musculoskeletal
Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain
 May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
Section 4: Tarsal Coalitions
 Case H (Figure 2): PedCat CBCT transverse plane reconstruction of right Lisfranc midfoot dislocation compared to normal left foot. Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: The weight bearing CBCT study
Case H (Figure 2): PedCat CBCT transverse plane reconstruction of right Lisfranc midfoot dislocation compared to normal left foot. Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: The weight bearing CBCT study
Tarsal Coalition On MR
 Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
pedcat Clinical Case Studies
 pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
pedcat Clinical Case Studies C u r v e B e a m 1 7 5 T i t u s A v e, S u i t e 3 0 0 W a r r i n g t o n, P A 1 8 9 7 6 267-4 8 3-8081 w w w. c u r v e b e a m. c o m PedCAT: Clinical Evidence of diagnostic
Case Report The Rare Cuboid-Navicular Coalition Presenting as Chronic Foot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2015, Article ID 625285, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/625285 Case Report The Rare Cuboid-Navicular Coalition Presenting as Chronic Foot Pain Omer Awan 1,2,3 and
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2015, Article ID 625285, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/625285 Case Report The Rare Cuboid-Navicular Coalition Presenting as Chronic Foot Pain Omer Awan 1,2,3 and
Imaging oftarsal Coalition
 Imaging oftarsal Coalition Julia Crim, MD KEYWORDS C-sign Talar beak Subtalar coalition Calcaneonavicular coalition A coalition is a congenital bony, cartilaginous, or fibrous connection (called a bar)
Imaging oftarsal Coalition Julia Crim, MD KEYWORDS C-sign Talar beak Subtalar coalition Calcaneonavicular coalition A coalition is a congenital bony, cartilaginous, or fibrous connection (called a bar)
Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations
 Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations Case Study F: Lisfranc s Midfoot Dislocation Clinical History: J.K. a 28 year old female presents complaining of a painful right foot. She sustained an acute
Section 3: Foot Subluxations and Dislocations Case Study F: Lisfranc s Midfoot Dislocation Clinical History: J.K. a 28 year old female presents complaining of a painful right foot. She sustained an acute
Case Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case.
 Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Case 12910 Carpal coalition: 4 cases of a rare bony coalition between the capitate and trapezoid bone, with MRI findings in a symptomatic case. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 K. De Cuyper 1 M. Vansevenant 1, 2 K. Verstraete
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
CUBOID-NAVICULAR COALITION A RARE FINDING
 Case Report CR_018_2016 renanrochadanobrega@gmail.com CUBOID-NAVICULAR COALITION A RARE FINDING Nóbrega RR; Duarte ML; Prado JLMA; Scoppetta LCD SÃO PAULO - BRASIL The authors declare that they have no
Case Report CR_018_2016 renanrochadanobrega@gmail.com CUBOID-NAVICULAR COALITION A RARE FINDING Nóbrega RR; Duarte ML; Prado JLMA; Scoppetta LCD SÃO PAULO - BRASIL The authors declare that they have no
Section 6: Preoperative Planning
 Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
Clinical Relevance of the PedCat Study: In many ways the PedCat study confirmed radiographic findings. With the measuring tools embedded in the DICOM viewing software it was possible to gauge the thickness
RESECTION FOR SYMPTOMATIC TALOCALCANEAL COALITION
 RESECTION FOR SYMPTOMATIC TALOCALCANEAL COALITION P. H. WILDE, I. P. TORODE, D. R. DICKENS, W. G. COLE From the Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia Over a nine-year period, 2 feet with persistently
RESECTION FOR SYMPTOMATIC TALOCALCANEAL COALITION P. H. WILDE, I. P. TORODE, D. R. DICKENS, W. G. COLE From the Royal Children s Hospital, Melbourne, Australia Over a nine-year period, 2 feet with persistently
A radiological classification system for talocalcaneal coalition based on a multi-planar imaging study using CT and MRI
 Insights Imaging (2013) 4:563 567 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0267-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A radiological classification system for talocalcaneal coalition based on a multi-planar imaging study using CT and MRI
Insights Imaging (2013) 4:563 567 DOI 10.1007/s13244-013-0267-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A radiological classification system for talocalcaneal coalition based on a multi-planar imaging study using CT and MRI
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/29/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 105 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
A Different Type of Talocalcaneal Coalition With Os Sustentaculum: The Continued Necessity of Revision of Classification
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yun et al. Talocalcaneal Coalition With Os Sustentaculum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Seong Jong Yun 1,2 Wook Jin 2 Gou Young Kim 3 Jae Hoon Lee 4
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Yun et al. Talocalcaneal Coalition With Os Sustentaculum Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Seong Jong Yun 1,2 Wook Jin 2 Gou Young Kim 3 Jae Hoon Lee 4
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Cuboid navicular tarsal coalition: Presentation and evaluation with emphasis on magnetic resonance imaging appearance
 Cuboid navicular tarsal coalition: Presentation and evaluation with emphasis on magnetic resonance imaging appearance by Angela Chang BS 1, Carly A. Lockard MS 1, Márcio B. Ferrari MD 1, Thomas O. Clanton
Cuboid navicular tarsal coalition: Presentation and evaluation with emphasis on magnetic resonance imaging appearance by Angela Chang BS 1, Carly A. Lockard MS 1, Márcio B. Ferrari MD 1, Thomas O. Clanton
Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging Studies
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 130979, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/130979 Case Report Bipartite Medial Cuneiform: Case Report and Retrospective Review of 1000 Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging
Painful middle facet talocalcaneal coalition (TCC) is often. Klaus J. Kernbach, DPM, 1 and Neal M. Blitz, DPM, FACFAS 2
 The Presence of Calcaneal Fibular Remodeling Associated With Middle Facet Talocalcaneal Coalition: A Retrospective CT Review of 35 Feet. Investigations Involving Middle Facet Coalitions Part II Klaus J.
The Presence of Calcaneal Fibular Remodeling Associated With Middle Facet Talocalcaneal Coalition: A Retrospective CT Review of 35 Feet. Investigations Involving Middle Facet Coalitions Part II Klaus J.
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month a
 Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
A dissection and computer tomograph study of tarsal coalitions in 100 cadaver feet
 ELSEVIER Journal of Orthopaedic Research 21 (2003) 352-358 Journal of Orthopaedic Research www.elsevier.com/locate/ort hres A dissection and computer tomograph study of tarsal coalitions in 100 cadaver
ELSEVIER Journal of Orthopaedic Research 21 (2003) 352-358 Journal of Orthopaedic Research www.elsevier.com/locate/ort hres A dissection and computer tomograph study of tarsal coalitions in 100 cadaver
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot. Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine
 MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
MRI of Pediatric Ankle and Foot Mahesh Thapa, MD Associate Professor Seattle Children s University of Washington School of Medicine Disclosures Under contract with Lippincott Williams and Wilkins (LWW)
Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic
 Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
Original Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2014;71(5):258-264 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2014.71.5.258 Relationships between Rotator Cuff Tear Types and Radiographic Abnormalities
MR Imaging Findings of Painful Type II Accessory Navicular Bone: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Studies
 MR Imaging Findings of Painful Type II Accessory Navicular Bone: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Studies Yun Sun Choi, MD 1 Kyung Tai Lee, MD 2 Heung Sik Kang, MD 3 Eun Kyung Kim, MD 4 Index terms:
MR Imaging Findings of Painful Type II Accessory Navicular Bone: Correlation with Surgical and Pathologic Studies Yun Sun Choi, MD 1 Kyung Tai Lee, MD 2 Heung Sik Kang, MD 3 Eun Kyung Kim, MD 4 Index terms:
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1
 CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
CT Findings of Traumatic Posterior Hip Dislocation after Reduction 1 Sung Kyoung Moon, M.D., Ji Seon Park, M.D., Wook Jin, M.D. 2, Kyung Nam Ryu, M.D. Purpose: To evaluate the CT images of reduced hips
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Imaging of posterior ankle pain : Main etiologies and differential diagnosis
 Imaging of posterior ankle pain : Main etiologies and differential diagnosis Poster No.: C-2399 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Frikha, M. MECHRI, S. boukriba, H. RIAHI, M. CHELLI
Imaging of posterior ankle pain : Main etiologies and differential diagnosis Poster No.: C-2399 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Frikha, M. MECHRI, S. boukriba, H. RIAHI, M. CHELLI
Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis
 35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
35 J. Tokyo Med. Univ., 71 1 35 0 Facet orientation in patients with lumbar degenerative spondylolisthesis Wuqikun ALIMASI, Kenji ENDO, Hidekazu SUZUKI, Yasunobu SAWAJI, Hirosuke NISHIMURA, Hidetoshi TANAKA,
1 Relationship between degenerative change in the sesamoid-metatarsal joint and 2 displacement of the sesamoids in patients with hallux valgus 3 4
 1 Relationship between degenerative change in the sesamoid-metatarsal joint and 2 displacement of the sesamoids in patients with hallux valgus 3 4 Abstract 5 Background: To treat a patient with hallux
1 Relationship between degenerative change in the sesamoid-metatarsal joint and 2 displacement of the sesamoids in patients with hallux valgus 3 4 Abstract 5 Background: To treat a patient with hallux
Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial Subluxation
 Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:96-100 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.1.96 Congenital Anomaly of the Atlas Misdiagnosed as Posterior Arch Fracture of the Atlas and Atlantoaxial
Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
Ossicles associated with chronic pain around the malleoli of the ankle
 Ossicles associated with chronic pain around the malleoli of the ankle S. H. Han, W. J. Choi, S. Kim, S.-J. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea We undertook a
Ossicles associated with chronic pain around the malleoli of the ankle S. H. Han, W. J. Choi, S. Kim, S.-J. Kim, J. W. Lee From Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea We undertook a
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot. Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada.
 Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
It's normal, but it hurts! Painful sesamoid and accessory bone syndromes of the foot.
 It's normal, but it hurts! Painful sesamoid and accessory bone syndromes of the foot. Poster No.: P-0120 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. C. Vieira, A. Vieira, R. Cunha; Porto/PT
It's normal, but it hurts! Painful sesamoid and accessory bone syndromes of the foot. Poster No.: P-0120 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. C. Vieira, A. Vieira, R. Cunha; Porto/PT
The Spring Ligament, PTT Tear, and Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity On MRI
 The Spring Ligament, PTT Tear, and Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity On MRI (Part 2) By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in: The posterior tibial tendon is the primary stabilizer
The Spring Ligament, PTT Tear, and Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity On MRI (Part 2) By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in: The posterior tibial tendon is the primary stabilizer
Foot & Ankle Disorders
 Foot & Ankle Disorders Hillingdon PGMC 6-7-2013 Htwe Zaw FRCS (Tr&Orth) Consultant Foot & Ankle and Trauma Surgeon Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Anatomy: hindfoot-midfoot coupling
Foot & Ankle Disorders Hillingdon PGMC 6-7-2013 Htwe Zaw FRCS (Tr&Orth) Consultant Foot & Ankle and Trauma Surgeon Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Anatomy: hindfoot-midfoot coupling
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module
 1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
Accessory Ossicles of the Foot and Ankle
 Accessory Ossicles of the Foot and Ankle Poster No.: C-0978 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: U. Kesimal, M. OYNAK, C. Cevikol; Antalya/TR Keywords: Anatomy, Musculoskeletal bone, Musculoskeletal
Accessory Ossicles of the Foot and Ankle Poster No.: C-0978 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: U. Kesimal, M. OYNAK, C. Cevikol; Antalya/TR Keywords: Anatomy, Musculoskeletal bone, Musculoskeletal
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery
 Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Outcomes in Ankle Arthritis Patients Based on Treating with and without Total Ankle Replacement Surgery Chayanin Angthong MD* * Division of Foot and Ankle
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, cont
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Two Consecutive Levels of Unilateral Cervical Spondylolysis on Opposite Sides 두개의연속된척추에서반대쪽편측에발생한경추척추분리증
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.3.181 Two Consecutive Levels of Unilateral Cervical Spondylolysis on Opposite Sides 두개의연속된척추에서반대쪽편측에발생한경추척추분리증 Kyeong
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.3.181 Two Consecutive Levels of Unilateral Cervical Spondylolysis on Opposite Sides 두개의연속된척추에서반대쪽편측에발생한경추척추분리증 Kyeong
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia
 220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
220 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 220 225 How to avoid complications of distraction osteogenesis for first brachymetatarsia Keun-Bae Lee, Hyun-Kee Yang, Jae-Yoon Chung, Eun-Sun Moon, and Sung-Taek Jung
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Duration of Follow-up (mo)
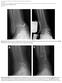 Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
Page 1 of 7 Fig. E-1 Fig. E-2 Fig. E-1 Medial ankle arthritis with medial translation of the talus and mortise widening. Note the shape of the medial malleolus (white arrow). Fig. E-2 Measurement of mortise
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
What a Pain! Radiology Evaluation of Leg Complaints and Limping. I have nothing to disclose. Leg Complaints. Leg Complaints
 What a Pain! Radiology Evaluation of Leg Complaints and Limping I have nothing to disclose Maria-Gisela Mercado-Deane, MD FAAP Christus Santa Rosa Children Hospital San Antonio, TX Age groups Infant and
What a Pain! Radiology Evaluation of Leg Complaints and Limping I have nothing to disclose Maria-Gisela Mercado-Deane, MD FAAP Christus Santa Rosa Children Hospital San Antonio, TX Age groups Infant and
pathologic feature of early ankle arthritis.
 Joint space widening may be a paradoxical pathologic Ji-Beom Kim, MD Young Yi, MD Woo-Chun, Lee Seoul Foot & Ankle Center, Dubalo Orthopaedic Clinic. Disclosure NO CONFLICT TO DISCLOSURE Joint space widening
Joint space widening may be a paradoxical pathologic Ji-Beom Kim, MD Young Yi, MD Woo-Chun, Lee Seoul Foot & Ankle Center, Dubalo Orthopaedic Clinic. Disclosure NO CONFLICT TO DISCLOSURE Joint space widening
30 Freiberg's Disease
 30 Freiberg's Disease T.W.D. SMITH D.N. KREIBICH Infraction of the second metatarsal bone was first described by Cincinnati surgeon Albert Freiberg in 1914. 1 In much of the English-speaking world the
30 Freiberg's Disease T.W.D. SMITH D.N. KREIBICH Infraction of the second metatarsal bone was first described by Cincinnati surgeon Albert Freiberg in 1914. 1 In much of the English-speaking world the
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Radiologic Imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 Radiologic Imaging X-ray has always been the golden rule in diagnosing and treating podiatric patients. Unfortunately, for some patients the diagnosis is not as evident. That is when we need to utilize
Radiologic Imaging X-ray has always been the golden rule in diagnosing and treating podiatric patients. Unfortunately, for some patients the diagnosis is not as evident. That is when we need to utilize
Stress Fracture of the Capitate
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:135-139 Stress Fracture of the Capitate Hyung Joon Cho 1, Ki Taek Hong 2, Chang Ho Kang 1, Kyung-Sik Ahn 1, Yura Kim 2, Sung Tae Hwang 1 1 Department of Radiology,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:135-139 Stress Fracture of the Capitate Hyung Joon Cho 1, Ki Taek Hong 2, Chang Ho Kang 1, Kyung-Sik Ahn 1, Yura Kim 2, Sung Tae Hwang 1 1 Department of Radiology,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
FREIBERG S INFRACTION TREATMENT WITH METATARSAL NECK DORSAL CLOSING WEDGE OSTEOTOMY: REPORT OF TWO CASES
 FREIBERG S INFRACTION TREATMENT WITH METATARSAL NECK DORSAL CLOSING WEDGE OSTEOTOMY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Sung-Yen Lin, 1 Yuh-Min Cheng, 1,2 and Peng-Ju Huang 1,2 1 Department of Orthopedics, Kaohsiung
FREIBERG S INFRACTION TREATMENT WITH METATARSAL NECK DORSAL CLOSING WEDGE OSTEOTOMY: REPORT OF TWO CASES Sung-Yen Lin, 1 Yuh-Min Cheng, 1,2 and Peng-Ju Huang 1,2 1 Department of Orthopedics, Kaohsiung
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls
 MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
MRI of the sacroiliac joints: what to report and its pitfalls Poster No.: C-1920 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Goncalves, A. Y. Aihara, C. Longo, H. Guidorizzi, P. Aguiar, 1
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot. Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University
 Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Metatarsus Adductus Skewfoot Hallux Valgus Hallux Valgus
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Metatarsus Adductus Skewfoot Hallux Valgus Hallux Valgus
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation
 Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Case Report Sonographic Findings of Adductor Insertion Avulsion Syndrome With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlation Jennifer S. Weaver, MD, Jon A. Jacobson, MD, David A. Jamadar, MBBS, Curtis W. Hayes,
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Complexities surrounding Lisfranc injuries
 Complexities surrounding Lisfranc injuries Lisfranc injuries are commonly associated with sporting injuries and are easily diagnosed with severe midfoot pain, swelling, deformity and inability to bear
Complexities surrounding Lisfranc injuries Lisfranc injuries are commonly associated with sporting injuries and are easily diagnosed with severe midfoot pain, swelling, deformity and inability to bear
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of Anterior Chest Wall Joint and Bone Disorders
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Spiral Ct with Three-Dimensional and Multiplanar Reconstruction in the Diagnosis of
Unilateral osteonecrosis. imaging findings
 Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
Skeletal Radiol (2001) 30:643 647 DOI 10.1007/s002560100423 CASE REPORT F. Abascal L. Cerezal F. del Piñal R. García-Valtuille A. García-Valtuille A. Canga J. Torcida Unilateral osteonecrosis in a patient
Current Concepts Review: Tarsal Coalition
 FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2006 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Current Concepts Review: Tarsal Coalition Frederick Lemley, M.D. 1 ; Gregory Berlet, M.D. 2 ; Keith Hill,
FOOT &ANKLE INTERNATIONAL Copyright 2006 by the American Orthopaedic Foot & Ankle Society, Inc. Current Concepts Review: Tarsal Coalition Frederick Lemley, M.D. 1 ; Gregory Berlet, M.D. 2 ; Keith Hill,
Clinical results of modified Mitchell s osteotomy for hallux valgus augmented with oblique lesser metatarsal osteotomy
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):245-252 Clinical results of modified Mitchell s osteotomy for hallux valgus augmented with oblique lesser metatarsal osteotomy K Yamamoto, A Imakiire, Y Katori,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005:13(3):245-252 Clinical results of modified Mitchell s osteotomy for hallux valgus augmented with oblique lesser metatarsal osteotomy K Yamamoto, A Imakiire, Y Katori,
Resection of calcaneonavicular bar with interposition of extensor digitorum brevis. A questionnaire review
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 83-87 ORIGINAL STUDY Resection of calcaneonavicular bar with interposition of extensor digitorum brevis. A questionnaire review Debbie VAn REntERgHEM, Koen DE RiDDER From
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 83-87 ORIGINAL STUDY Resection of calcaneonavicular bar with interposition of extensor digitorum brevis. A questionnaire review Debbie VAn REntERgHEM, Koen DE RiDDER From
Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment
 119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
119 Pictorial Essay H............ - Hallux Valgus Deformity: Preoperative Radiologic Assessment David Karasick1 and Keith L. Wapner An estimated 40% of the American adult population experiences foot problems,
Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Characterizing scaphoid nonunion deformity using 2-D and 3-D imaging techniques ten Berg, P.W.L. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): ten Berg,
The Relationship between Medial Longitudinal Arch and Peroneal Tubercle
 The Relationship between Medial Longitudinal Arch and Peroneal Tubercle -Anatomical Study- Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Kangwon National University Hospital Chuncheon, Republic of Korea Chang Hyun
The Relationship between Medial Longitudinal Arch and Peroneal Tubercle -Anatomical Study- Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Kangwon National University Hospital Chuncheon, Republic of Korea Chang Hyun
Change of Alignment by Calcaneocuboid Distraction Arthrodesis for Acquired Flatfoot
 Change of Alignment by Calcaneocuboid Distraction Arthrodesis for Acquired Flatfoot Akira Taniguchi, Yasuhito Tanaka, Kunihiko Kadono, Kiyonori Tomiwa, So Kameda, Hiroaki Kurokawa, Takenori Matsuda, Tsukasa
Change of Alignment by Calcaneocuboid Distraction Arthrodesis for Acquired Flatfoot Akira Taniguchi, Yasuhito Tanaka, Kunihiko Kadono, Kiyonori Tomiwa, So Kameda, Hiroaki Kurokawa, Takenori Matsuda, Tsukasa
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings
 Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction
 The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, South Korea
The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, South Korea
Mid-Term Results of Triple Osteotomy in Hallux Valgus with Highly Increased Distal Metatarsal Articular Angle
 AOFAS Annual Meeting 2012 The Korean Foot & Ankle Society Mid-Term Results of Triple Osteotomy in Hallux Valgus with Highly Increased Distal Metatarsal Articular Angle Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Ki Won Young,
AOFAS Annual Meeting 2012 The Korean Foot & Ankle Society Mid-Term Results of Triple Osteotomy in Hallux Valgus with Highly Increased Distal Metatarsal Articular Angle Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Ki Won Young,
Marut Arunakul, M.D. Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. Jessica Goetz, PhD. John Femino, M.D. Annunziato Amendola, M.D. University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics
 Marut Arunakul, M.D. Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. Jessica Goetz, PhD. John Femino, M.D. Annunziato Amendola, M.D. University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Tripod Index Part 1: New radiographic parameter assessing
Marut Arunakul, M.D. Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. Jessica Goetz, PhD. John Femino, M.D. Annunziato Amendola, M.D. University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Tripod Index Part 1: New radiographic parameter assessing
Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis
 Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis Dong Dong Wan, MD; Dong woo Shim, MD; Yoo Jung Park, MD; Yeokgu Hwang, MD; Jin Woo Lee, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic
Short Term Clinical and Radiographic Results of the Salto Mobile Version Ankle Prosthesis Dong Dong Wan, MD; Dong woo Shim, MD; Yoo Jung Park, MD; Yeokgu Hwang, MD; Jin Woo Lee, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic
ABC of Emergency Radiology
 l ja ) $% _2) < j> ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~foot ABC of Emergency Radiology THE FOOT D A Nicholson, D O'Keeffe, P A Driscoll Accurate clinical assessment of injuries to the foot will avoid unnecessary exposure
l ja ) $% _2) < j> ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~foot ABC of Emergency Radiology THE FOOT D A Nicholson, D O'Keeffe, P A Driscoll Accurate clinical assessment of injuries to the foot will avoid unnecessary exposure
Osseous variants generating symptoms in ankle and foot
 Osseous variants generating symptoms in ankle and foot Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Daineffe, B. G. H. G. Pilet, S. Van de Perre, E. De Smet, 1 2 1 3 5 1
Osseous variants generating symptoms in ankle and foot Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Daineffe, B. G. H. G. Pilet, S. Van de Perre, E. De Smet, 1 2 1 3 5 1
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
분당제생병원재활의학과이태임 COMMON PAINFUL CONDITIONS OF PEDIATRIC FOOT
 분당제생병원재활의학과이태임 COMMON PAINFUL CONDITIONS OF PEDIATRIC FOOT CASE M/12 CC Insidous onset of heel pain 축구를좋아해서많이했다. 걷거나뛰면더아프다. PE pes planus heelcord tightness Tenderness over the posterior calcaneus Sqeeze
분당제생병원재활의학과이태임 COMMON PAINFUL CONDITIONS OF PEDIATRIC FOOT CASE M/12 CC Insidous onset of heel pain 축구를좋아해서많이했다. 걷거나뛰면더아프다. PE pes planus heelcord tightness Tenderness over the posterior calcaneus Sqeeze
AUGMENT. Bone Graft. Tibiotalar Fusion. rhpdgf-bb/β-tcp THE FIRST AND ONLY PROVEN ALTERNATIVE TO AUTOGRAFT IN ANKLE AND HINDFOOT ARTHRODESIS
 rhpdgf-bb/β-tcp AUGMENT Bone Graft THE FIRST AND ONLY PROVEN ALTERNATIVE TO AUTOGRAFT IN ANKLE AND HINDFOOT ARTHRODESIS CASE REPORT Tibiotalar Fusion as presented by Mark Glazebrook, MD Assoc Professor
rhpdgf-bb/β-tcp AUGMENT Bone Graft THE FIRST AND ONLY PROVEN ALTERNATIVE TO AUTOGRAFT IN ANKLE AND HINDFOOT ARTHRODESIS CASE REPORT Tibiotalar Fusion as presented by Mark Glazebrook, MD Assoc Professor
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 11/24/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 100 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Intraosseous hemangioma is an uncommon benign
 Case Report 71 An Intraosseous Capillary Hemagioma Of The Foot In A Child Kah-Wai Ngan, MD; Hui-Ling Hsu 1, MD; Shir-Hwa Ueng, MD An 8-year-old boy presented with an osteolytic lesion at the fourth metatarsal
Case Report 71 An Intraosseous Capillary Hemagioma Of The Foot In A Child Kah-Wai Ngan, MD; Hui-Ling Hsu 1, MD; Shir-Hwa Ueng, MD An 8-year-old boy presented with an osteolytic lesion at the fourth metatarsal
Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography?
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 230-238 ORIGINAL STUDY Fracture risk in unicameral bone cyst. Is magnetic resonance imaging a better predictor than plain radiography? Nathalie PiREAU, Antoine DE GHELDERE,
The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate
 The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate PROCEDURE GUIDE www.flowerortho.com The Flower Foot & Ankle Application NC FUSION PLATE 2-HOLE COMPRESSION PLATE TMT FUSION PLATE LAPIDUS FUSION PLATE COMPRESSION
The Flower Medial Column Fusion Plate PROCEDURE GUIDE www.flowerortho.com The Flower Foot & Ankle Application NC FUSION PLATE 2-HOLE COMPRESSION PLATE TMT FUSION PLATE LAPIDUS FUSION PLATE COMPRESSION
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
GENERAL STUDY OF BONY SYNOSTOSIS IN HUMAN SKELETON
 GENERAL STUDY OF BONY SYNOSTOSIS IN HUMAN SKELETON Dhapate S.S. and *Chavan S.B. Department of Anatomy, SRTR Government Medical College, Ambajogai/MUHS Nashik Maharashtra, India *Author of Correspondence
GENERAL STUDY OF BONY SYNOSTOSIS IN HUMAN SKELETON Dhapate S.S. and *Chavan S.B. Department of Anatomy, SRTR Government Medical College, Ambajogai/MUHS Nashik Maharashtra, India *Author of Correspondence
Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Ki Won Young, M.D.*, Young Uk Park, M.D. +, Hyuk Jegal, M.D., Jin Su Kim, M.D.*
 Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Ki Won Young, M.D.*, Young Uk Park, M.D. +, Hyuk Jegal, M.D., Jin Su Kim, M.D.* KT Lee s Foot and Ankle Hospital, Seoul, Korea Foot and Ankle Clinic, Eulji Medical Center, Seoul, Korea*
Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Ki Won Young, M.D.*, Young Uk Park, M.D. +, Hyuk Jegal, M.D., Jin Su Kim, M.D.* KT Lee s Foot and Ankle Hospital, Seoul, Korea Foot and Ankle Clinic, Eulji Medical Center, Seoul, Korea*
The Cause of Pain in Symptomatic Accessory Navicular Syndrome : comparison between Athletes and Non-Athletes
 The Cause of Pain in Symptomatic Accessory Navicular Syndrome : comparison between Athletes and Non-Athletes Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Young Uk Park, M.D. *, Hyuk Jegal, M.D., Young Tae Rho, M.D. KT Lee s Orthopedic
The Cause of Pain in Symptomatic Accessory Navicular Syndrome : comparison between Athletes and Non-Athletes Kyung Tai Lee, M.D., Young Uk Park, M.D. *, Hyuk Jegal, M.D., Young Tae Rho, M.D. KT Lee s Orthopedic
