A nkylosing spondylitis (AS), the prototype of the
|
|
|
- Valerie Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXTENDED REPORT Staging of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a preliminary proposal J Braun, D van der Heijde, M Dougados, P Emery, M A Khan, J Sieper, Sj van der Linden... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Professor J Braun, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Landgrafenstr. 15, Herne, and UKBF, Free University, Berlin, Germany; j.braun@ rheumazentrum-ruhrgebiet.de... Ann Rheum Dis 2002;61(Suppl III):iii19 iii23 Patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) are characterised by a wide range of clinical presentations, radiographic profiles, and outcomes, which are not well differentiated by current diagnostic and classification systems for the disorder. Inadequacies in these systems may limit clinicians ability to manage their patients with AS appropriately and act as an obstacle to reasonable comparison of therapeutic trial results. A standardised staging system for AS is therefore proposed that would provide a more detailed categorisation of patients based on assessment of structural damage, peripheral joint and organ involvement, presence of concomitant diseases, and the severity and extent of disease activity and functional impairment. The proposed system needs to be evaluated closely and amended as needed to assure its usefulness in clinical and research settings. A nkylosing spondylitis (AS), the prototype of the spondyloarthropathies (SpAs), is one of the most common inflammatory rheumatic diseases. 1 Like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), AS is associated with significant disability 2 and increased socioeconomic costs. 34 However, compared with the treatment available for RA, therapeutic options for AS are limited. Only non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs and physiotherapy are currently accepted treatments for reducing the signs and symptoms of AS based on clinical research. 5 No available agents have demonstrated a disease modifying effect in AS, although anti-tumour necrosis factor α therapy holds promise in this regard. An increasing number of treatment trials in AS are being conducted, heralding the potential availability of more effective treatments in the future. To allow comparison of findings between trials of different agents, a better classification system of patients with AS is needed. Because AS is a chronic disease with a wide variety of clinical presentations and outcomes, the development of a staging system that categorises patients accordingly seems mandatory. This paper will review existing assessment tools used in AS and propose improvements that will help satisfy emerging needs. DIAGNOSTIC AND CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA The difference between diagnostic and classification criteria has been the subject of considerable debate in recent years. Basic epidemiological research indicates that diagnostic criteria should be very sensitive, particularly at an early stage of disease, whereas classification criteria need to be very specific. However, given the high prevalence of back pain and much lower relative prevalence of AS in the population, diagnostic criteria with a high specificity would be very desirable. High specificity in clinical practice is increasingly important because the diagnosis of a patient is more critical in light of financial and legal issues such as disability, pensions, insurance, and reimbursement. Thus, with the existence of diagnosis related groups and expensive, but very effective, new biological treatments, the need for specific criteria in clinical practice is particularly great. Throughout the past decade, in clinical studies and especially daily practice, the diagnosis of AS has often been made based on the 1984 modified New York criteria. 6 These criteria have established radiographic evidence of sacroiliitis iii19 as the most important factor for the diagnosis of AS. In practice, the cut off of grade II radiographic assessments of sacroiliitis has proved difficult. 7 However, this criterion has been used successfully because the vast majority of patients with AS do have sacroiliitis, 8 indicating a high sensitivity in established disease. As a result, the modified New York diagnostic criteria, as published in 1984, are currently used as classification criteria and diagnostic criteria. The ESSG criteria have a >80% sensitivity to recognise patients with an established disease belonging to the spectrum of SpA. 16 Thus, it needs to be emphasised that all available criteria lack sensitivity in early disease, making their use unacceptable for such patients. Therefore, many clinicians are attempting to diagnose sacroiliitis with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) early in the disease course of AS. Significant progress has also been made in standardising the measurement of clinical disease activity and functional ability in AS. The Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) 9 and the Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI) 10 are easy to use, reliable, sensitive tools that have become frequently used to define disease status. 11 A real step forward was the definition of core sets of end points by the Ankylosing Spondylitis Assessment (ASAS) Working Group for use in different research settings and in clinical practice. DEFINING THE SPECTRUM OF DISEASE It is important to recognise AS as merely a single disorder, albeit a dominant one, in the broader spectrum of the SpAs. 14 In 1991, milestone classification criteria were proposed by the European Spondylarthropathy Study Group (ESSG) that defined AS and the other disorders categorised as SpA,... Abbreviations: AS, ankylosing spondylitis; ASAS, Ankylosing Spondylitis Assessment (Working Group); BASDAI, Bath AS Disease Activity Index; BASFI, Bath AS Functional Index; CRP, C reactive protein; DC-ART, disease controlling anti rheumatic treatment; DISH, diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis; ESSG, European Spondylarthropathy Study Group; HAQ, Health Assessment Questionnaire; IBD, inflammatory bowel disease; J, joint; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NSAID, non-steroidal antirheumatic drug; O, organ; Ps, psoriasis; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; ReA, reactive arthritis; SAPHO, synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis; SpA, spondyloarthropathy; TNF, tumour necrosis factor; uspa, undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy
2 iii20 including psoriatic arthritis, reactive arthritis (ReA), inflammatory bowel disease-related arthritis (IBD-A), and undifferentiated spondyloarthropathy (uspa). 15 The ESSG criteria pose a problem for the clinical rheumatologist, in that patients with only peripheral joint or entheseal inflammation are classified as having SpA (that is, spondyloarthropathy ), which may suggest both inflammatory and non-inflammatory involvement of spinal structures. A proposed solution to this terminological problem is the use of spondyloarthritides to define the entire spectrum of these partially human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-B27 related rheumatic diseases similar to the use of connective tissue diseases for partly antinuclear autoantibody related rheumatic diseases, such as lupus and scleroderma. Although several arguments favour the term spondyloarthropathy, 17 we suggest that spondyloarthritis be used instead to emphasise the inflammatory nature of these disorders, which are defined by their involvement of spinal and peripheral structures of the musculoskeletal system and provide a common solution. In addition, the clinical rheumatologist may find it difficult to diagnose AS in patients who demonstrate only the distinct radiographic degree of grade II sacroiliac changes bilaterally as defined by the New York criteria. The difficulty may stem, at least in part, from the significant inter- and intraobserver variability associated with the interpretation of radiographs, 18 a major problem in the diagnosis of AS, but not SpA. Differentiation between possible early and abortive cases is often incomplete when only conventional radiography (roentgenography) is used. MRI provides better visualisation of sacroiliitis in the early stages but is not yet widely available or sufficiently standardised to be generally used. Because spondylitis is itself part of the term AS (that is, ankylosing spondylitis), it would seem to define inflammatory involvement of the vertebral column as a condition sine qua non for a diagnosis of AS. As a result, many rheumatologists diagnose AS only in patients with clear cut clinical or radiographic evidence of spinal involvement. This may imply the presence of syndesmophytes, calcification of spinal ligaments, or other radiographic signs of spondylitis, spondylodiscitis or arthritis of the zygapophysial joints. 21 However, as previously mentioned, spondylitis without sacroiliitis is rare and often a late phenomenon, and no data or consensus exist about the quantity or size of syndesmophytes required to establish a diagnosis of AS. Moreover, the differentiation from diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) can sometimes be a serious problem. An HLA-B27 positive patient with a radiological image of DISH can sometimes be a challenge. 22 In such cases, the presence or absence of other signs of SpA (other than diminished spinal mobility and impaired chest expansion) or radiographic signs of sacroiliac and zygapophysial joint involvement can be helpful but may sometimes require computed tomography for conclusive assessment A history of inflammatory back pain is usually absent in young patients with DISH. The diagnostic role of MRI in detecting spinal inflammation at an early stage is not sufficiently well established to recommend its routine use at present. RATIONALE FOR AS STAGING SYSTEM AS encompasses a broad spectrum of clinical presentations, disease courses, and outcomes, with differing pain, function, quality of life, and radiographic damage. The disease in some patients does not progress beyond sacroiliitis; other patients have rapidly progressing disease and experience complete ankylosis at a young age. In addition to the varying rates of progression and severity of spinal disease, AS can also affect peripheral joints, entheses, anterior uvea, and other structures, such as the aortic valve, the aorta, and the lung. Because differences in disease severity, extent, or outcome are not captured when using the New York criteria, the diagnosis of AS Braun, van der Heijde, Dougados, et al currently does not distinguish between patients with very different disease manifestations and courses. The classification of AS shows no more than that the patient has at least grade II radiographic sacroiliitis. For a clinical diagnosis of AS, it seems at present best to ask for definite radiographic sacroiliitis as the main differentiation factor towards uspa and non-spa rheumatic diseases and syndromes and then use different stages to describe the current status of disease as follows. In clinical practice, the lack of a standard staging system for AS impedes the precise characterisation of individual patients. In clinical studies, patients in varying stages of AS are not differentiated, and potential differences in their responses therefore cannot be evaluated. Moreover, findings across studies cannot be reasonably compared without sufficient information about patients disease status. The latter is particularly important in view of the extreme differences in disease duration among patients with AS enrolled in previously conducted therapeutic trials (5 20 years) for example, trials of sulfasalazine in AS This paper proposes a standardised staging system for AS that would allow more specific categorisation of patients included in future studies, recognising differences in structural damage, disease severity and extent, and outcome. Different degrees of spinal changes have been shown significantly to affect radiological scoring by using methods published to date Furthermore, a core set of end points for clinical trials in AS has been published by the ASAS expert group, 12 which also recently proposed criteria for short term clinical improvement. 31 DOMAINS IN RHEUMATIC DISEASE STAGING In rheumatology, staging is typically used to describe the patient s status in reference to the disease process and damage. To date, staging in rheumatology has relied on the classical Steinbrocker therapeutic criteria established in 1949 for RA 32 and, less directly, the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) 33 and SpA adjusted HAQ. The latter adds five items to the original HAQ in recognition of the functional importance of neck rotation. 34 To describe the stage of a rheumatic disease in general, we suggest that four different, although related, domains be delineated to cover different aspects of the disease and its consequences: Disease activity The biological inflammatory processes that may transiently or permanently influence structure and function. Damage The partly reversible or irreversible structural and/or functional changes caused by the disease in musculoskeletal or organ systems. Although functional changes are usually reversible, structural changes are generally irreversible. Health status A person s situation (impairments, limitations, and handicaps) on a variety of health dimensions or domains, independent of disease and diagnosis, which is influenced by changes in structure and function. Appreciation of health status An estimation of health status as valued by an individual or by a society, which is usually expressed as utilities or satisfaction. DEFINING THE STATE OF DISEASE IN ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS To put our proposal in a broad context covering practical and scientific aspects of the disease, we start by describing the different levels of information which are required to define the state of disease. When describing a patient with SpA in daily practice or for precise inclusion criteria in clinical research studies, the following basic definitions need to be clarified:
3 Staging of patients with ankylosing spondylitis 1 Definite disease diagnosis, classification 2 Disease activity (signs, symptoms, imaging) 3 Disease severity (stage, burden of disease) 4 Potentially severe prognosis, prognostic factors 5 Refractory to treatment, treatment options, evidence based medicine. Diagnosis, classification Available classification criteria are either the modified 1984 New York criteria (which require the presence of radiological sacroiliitis) or the ESSG (European Spondylarthropathy Study Group) set of criteria. There are no definite criteria for presence or proof of axial disease. These might possibly include: Spinal pain Reduced spinal mobility Imaging (MRI, x ray examination) Disease activity Mainly clinical and laboratory variables evaluating the inflammatory process of the disease but, possibly, imaging tools may also be used. In clinical research studies definitions of a particular value of the BASDAI (for example, at least 30 or 40) or a specific value of nocturnal pain and/or duration of morning stiffness and/or a certain level of C reactive protein (CRP) may be used. In fact, such a definition (which summarises the main inclusion criteria for a specific trial) depends on the objective of the therapeutic trial and on the nature of the treatment (differing when evaluating a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) from when evaluating a potential disease controlling antirheumatic treatment). In daily practice, one might consider an important measure to be the level of NSAID intake required in order to maintain the patient s disease at an acceptable level (low disease activity). Severity of disease This measure usually refers to the level of functional disability and to structural damage. There is no consensus about this definition. Here the staging parameters proposed in this article (see below) become relevant. Especially important parameters leading to significant functional disability are: Widespread ankylosis, bamboo spine Intervertebral ossification bridges (zygapophysial joints, entheses, ligaments) Hip joint involvement Bad prognosis of disease This definition is probably one of the most important to consider because of the interest of potentially costly, aggressive but also effective treatments, such as drug treatment (for example, anti-tnfα) or non-drug treatment (for example, admission to hospital in a department of rehabilitation). There is no specific recommendation. However, it seems that an early rapid structural progression and constantly raised CRP levels can be considered important to take into account for this definition. Unresponsiveness to previous treatment This definition is important when considering the initiation of potentially active disease controlling antirheumatic treatment (DC-ART) such as anti-tumour necrosis factor α (anti-tnfα) therapies in patients already taking NSAIDs. There is no consensus on this definition yet. However, the following characteristics can be taken into account: Use of a conventional DC-ART (sulfasalazine) Number of NSAIDs tested iii21 Use of an optimal dose for each NSAID Duration of NSAID intake. Other points of interest in this regard are relevant comorbidity factors which possibly affect NSAID intake for example, in cases of renal insufficiency. AS STAGING SYSTEM Radiographic grading Staging should be basically unidirectional, such that a patient in a more advanced stage of disease cannot improve and be classified into a lower stage over time. Therefore, we propose to use radiographic bony changes of the sacroiliac joints and spine as the main parameter to differentiate between the stages of AS, as has been previously suggested by the German rheumatologists Ott 35 and Schilling. 36 Expanding on their work, which has not been published in English, we recommend the following radiographic grading system for AS diagnosed on the basis of the 1984 Modified New York criteria: x Stage I Grade II or higher bilateral radiographic sacroiliitis x Stage II Minor radiographic evidence of spinal involvement in <1 spinal segment (<3 vertebrae which equals <15% of the spine) x Stage III Moderate radiographic evidence of spinal involvement in <2 spinal segments (4 12 vertebrae which equals 15 <50% of the spine) x Stage IV Radiographic evidence of spinal involvement in >2 spinal segments (13 19 vertebrae which equals 50 <80% of the spine) x Stage V Widespread (>80%) fusion of the spine (>20 vertebrae) Radiographic spinal involvement suggests evidence of spondylitis, spondylodiscitis, square vertebrae, syndesmophytes, ligament ossification, ankylosis, or arthritis of zygapophysial joints. Because zygapophysial joints are known to be difficult to assess and are often affected in patients with degenerative spinal disease, the involvement of these joints needs to be evaluated carefully. The basis for grading stages II to IV is involvement of one or more spinal segments, with stage V indicating widespread ankylosis (bamboo spine). One spinal segment indicates involvement of the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. Vertebral counts and percentages of vertebrae are included in brackets with the stage definitions to allow an individual approach to be taken with patients. This approach would allow a patient with minor involvement in two or three spinal segments to be graded at a lower stage. For example, a patient with involvement of the lumbar and thoracic spine affecting eight vertebrae would be graded at stage III, whereas a patient with involvement of the lumbar and thoracic spine affecting 20 vertebrae would be graded at stage V. As a general rule, spinal involvement should be obvious. Clear cut disease at one site (Anderson or Romanus lesion) or minor changes at two or more sites should be present in any stage of spinal involvement. For example, one very small syndesmophyte seems insufficient to clearly indicate spinal disease in AS. The clinician currently is responsible for the final judgment in individual cases, but digitalised programs may be available in the future to make such assessments. Nevertheless, using this staging system as a framework, for the first time clinicians will be able to clearly differentiate patients by degree of spinal involvement. Peripheral joint and organ involvement To classify patients with AS further, additional information about the involvement of other joints or organs may be provided. Past or present clinical evidence of the following may be included in the staging system:
4 iii22 Joints (J+) Peripheral joints (pj+) Root joints (rj+) Enthesitis, dactylitis (e+d+) Anterior uveitis (au+) Other organs (oo+) Root joints are defined as sternoclavicular joints, acromioclavicular joints, shoulders, and hips. Peripheral arthritis has been shown to influence outcome significantly. As many as 10 20% of patients with AS have hip involvement, with many requiring joint replacement surgery 36 ; clinical status after surgical intervention may also become relevant. Anterior uveitis is relatively common 38 and may be a severe problem, 39 and other organ involvement, albeit rare, may also be a concern, as in the case of aortic valve disease and renal amyloidosis. 38 The involvement of non-axial joints and other organ systems has variable onset among patients with AS, and the timing of onset can be difficult to classify. Therefore, we prefer not to distinguish between previous, recent, or current onset of involvement, but rather to record the involvement regardless of the time of onset. Concomitant disease In about 85% of patients, AS develops without other preceding or accompanying diseases (that is, primary AS). 40 However, in the remainder, AS may be triggered by, or occur concomitantly with, other disorders, such as psoriasis (Ps), ReA (including Reiter s syndrome), IBD, and the synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome. The proposed staging system would also include information about the presence of such disorders for example, AS + Ps, ReA, IBD, SAPHO. Clinical activity/function We also propose to indicate the current clinical activity and the functional status of patients with inflammatory spinal pain in their staging index by adding their respective BASDAI and BASFI scores. To specify whether spinal or peripheral symptoms predominate, an s or p may be included with the BASDAI score. The proposed staging system allows the possible differentiation of 20 stages based only on the radiographic grading from I to V and the specification of joint/organ involvement (that is, J+,O+; J+,O ; J,O+; J,O ). Inclusion of additional components exponentially increases the number of possible stages. For example, the staging notation for a patient with active AS, including a full complement of indices, might be: stage III; J+, Ps; BASDI 4.7s; BASFI 3.5. Only positive involvement is noted. When used in combination with the AS core set of end points, such a detailed staging system would provide a thorough description of structural damage, disease activity, and function. SUMMARY Currently available diagnostic and classification criteria are inadequate in differentiating patients with AS, who demonstrate a wide spectrum of clinical presentations, radiographic profiles, and outcomes. To improve care for individual patients in clinical practice and interpretation of clinical study results, we propose an AS staging system based on grading of radiographic data and assessment of peripheral joint and organ involvement, concomitant diseases, and the severity and extent of clinical activity and functional deficits. Clearly, the proposal should be evaluated to determine its feasibility and potential benefits in different settings. Discussion and refinement of the proposed system will hopefully lead to much needed improvements in the classification and treatment of patients with AS. Braun, van der Heijde, Dougados, et al... Authors affiliations J Braun, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Germany and Department of Gastroenterology and Rheumatology, Free University, Berlin, Germany J Sieper, Department of Gastroenterology and Rheumatology, Free University, Berlin, Germany D van der Heijde, Sj van der Linden, Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Rheumatology, University Hospital Maastricht, Maastricht, The Netherlands M Dougados, Department of Rheumatology, René Descartes University, Hôpital Cochin, Paris, France P Emery, University of Cleveland, Cleveland, Ohio, USA M Khan, School of Medicine, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, USA REFERENCES 1 Braun J, Bollow M, Remlinger G, Eggens U, Rudwaleit M, Distler A, et al. Prevalence of spondylarthropathies in HLA-B27-positive and negative blood donors. Arthritis Rheum 1998;41: Zink A, Listing J, Klindworth C, Zeidler H, German Collaborative Arthritis Centres. The national database of the German Collaborative Arthritis Centres: I. Structure, aims, and patients. Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60: Zink A, Braun J, Listing J, Wollenhaupt J. Disability and handicap in rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis results from the German rheumatological database. German Collaborative Arthritis Centres. J Rheumatol 2000;27: Boonen A, Chorus A, Miedema H, van der Heijde D, van der Tempel H, van der Linden S. Employment, work disability, and work days lost in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a cross sectional study of Dutch patients. Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60: Amor B, Dougados M, Khan MA. Management of refractory ankylosing spondylitis and related spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1995;21: Van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 1984;27: Braun J, Sieper J, Bollow M. Imaging of sacroiliitis. Clin Rheumatol 2000;19: Khan MA, van der Linden SM, Kushner I, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Spondylitic disease without radiologic evidence of sacroiliitis in relatives of HLA-B27 positive ankylosing spondylitis patients. Arthritis Rheum 1985;28: Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy LG, Whitelock HC, Gaisford P, Calin A. A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol 1994;21: Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy LG, O Hea J, Mallorie P, et al. A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol 1994;21: Brandt J, Haibel H, Cornely D, Golder W, Gonzalez J, Reddig J, et al. Successful treatment of active ankylosing spondylitis with the anti-tumor necrosis factor α monoclonal antibody infliximab. Arthritis Rheum 2000;43: van der Heijde D, Bellamy N, Calin A, Dougados M, Khan MA, van der Linden S. Preliminary core sets for endpoints in ankylosing spondylitis. Assessments in Ankylosing Spondylitis Work Group. J Rheumatol 1997;24: van der Heijde D, Calin A, Dougados M, Khan MA, van der Linden S, Bellamy N. Selection of instruments in the core set for DC-ART, SMARD, physical therapy, and clinical record keeping in ankylosing spondylitis. Progress report of the ASAS Working Group. Assessments in Ankylosing Spondylitis. J Rheumatol 1999;26: Francois RJ, Eulderink F, Bywaters EG. Commented glossary for rheumatic spinal diseases, based on pathology. Ann Rheum Dis 1995;54: Dougados M, van der Linden S, Juhlin R, Huitfeldt B, Amor B, Calin A, et al. The European Spondylarthropathy Study Group preliminary criteria for the classification of spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum 1991;34: Brandt J, Bollow M, Häberle J, Rudwaleit M, Eggens U, Distler A, et al. Studying patients with inflammatory back pain and arthritis of the lower limbs clinically and by magnetic resonance imaging: many, but not all patients with sacroiliitis have spondyloarthropathy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 1999;38: Braun J, Sieper J. Commented glossary for rheumatic spinal diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 1996;55:76; discussion Hollingsworth PN, Cheah PS, Dawkins RL, Owen ET, Calin A, Wood PH. Observer variation in grading sacroiliac radiographs in HLA-B27 positive individuals. J Rheumatol 1983;10: Braun J, Bollow M, Eggens U, Konig H, Distler A, Sieper J. Use of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with fast imaging in the detection of early and advanced sacroiliitis in spondylarthropathy patients. Arthritis Rheum 1994;37: Braun J, Bollow M, Sieper J. Radiologic diagnosis and pathology of the spondyloarthropathies. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 1998;24: de Vlam K, Mielants H, Veys EM. Involvement of the zygapophyseal joint in ankylosing spondylitis: relation to the bridging syndesmophyte. J Rheumatol 1999;26:
5 Staging of patients with ankylosing spondylitis 22 Rahman P, Alderdice C, Curtis B, Battcock S, Pike E. Spinal hyperostosis a rare skeletal manifestation of psoriasis vulgaris. J Rheumatol 2000;27: Yagan R, Khan MA. Confusion of roentgenographic differential diagnosis of ankylosing hyperostosis (Forestier s disease) and ankylosing spondylitis. Spine: State of the Art Reviews 1990;4: Yagan R, Khan MA. Confusion of roentgenographic differential diagnosis between ankylosing hyperostosis (Forestier s disease) and ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 1983;2: Nissila M, Lehtinen K, Leirisalo-Repo M, Luukkainen R, Mutru O, Yli-Kerttula U. Sulfasalazine in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. A twenty-six-week, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arthritis Rheum 1988;31: Dougados M, van der Linden S, Leirisalo-Repo M, Huitfeldt B, Juhlin R, Veys E, et al. Sulfasalazine in the treatment of spondylarthropathy. A randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 1995;38: Clegg DO, Reda DJ, Weisman MH, Blackburn WD, Cush JJ, Cannon GW, et al. Comparison of sulfasalazine and placebo in the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis. A Department of Veterans Affairs Cooperative Study. Arthritis Rheum 1996;39: Averns HL, Oxtoby J, Taylor HG, Jones PW, Dziedzic K, Dawes PT. Radiological outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: use of the Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (SASSS). Br J Rheumatol 1996;35: Mackay K, Mack C, Brophy S, Calin A. The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index (BASRI). A new, validated approach to disease assessment. Arthritis Rheum 1998;41: Spoorenberg A, de Vlam K, van der Heijde D, de Klerk E, Dougados M, Mielants H, et al. Radiological scoring methods in ankylosing spondylitis: reliability and sensitivity to change over one year. J Rheumatol 1999;26: iii23 31 Anderson JJ, Baron G, van der Heijde D, Felson DT, Dougados M. Ankylosing Spondylitis Assessment Group preliminary definition of short-term improvement in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 2001;44: Steinbrocker O, Traeger CH, Batterman RC. Therapeutic criteria in rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA 1949;140: Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA Jr, Wallston KA, Hummon NP. Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily living using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum 1983;26: Daltroy LH, Larson MG, Roberts NW, Liang MH. A modification of the Health Assessment Questionnaire for the spondyloarthropathies. J Rheumatol 1990;17: Ott VR. Klinik und Therapie der ankylosierenden Spondylitis (Morbus-Strümpell-Marie-Bechterew). In: Brügel H, ed. Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der rheumatischen Erkrankungen und der degenerativen Gelenkerkrankungen. Stuttgart: Schattauer, 1972: Schilling F. Spondylitis ankylopoetica. Die sogenannte Bechterewsche Krankheit und ihre Differentialdiagnose (einschliesslich Spondylitis hyperostotica, Spondylitis psoriatica und chronischem Reitersyndrom). In: Diethelm L, ed. Handbuch der medizinischen Radiologie.Band VI/2. Röntgendiagnostik der Wirbelsäule. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer, 1981: Guillemin F, Briancon S, Pourel J, Gaucher A. Long-term disability and prolonged sick leaves as outcome measurements in ankylosing spondylitis. Possible predictive factors. Arthritis Rheum 1990;33: Gran JT, Skomsvoll JF. The outcome of ankylosing spondylitis: a study of 100 patients. Br J Rheumatol 1997;36: Linssen A, Meenken C. Outcomes of HLA-B27-positive and HLA-B27-negative acute anterior uveitis. Am J Ophthalmol 1995;120: Edmunds L, Elswood J, Kennedy LG, Calin A. Primary ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic and enteropathic spondyloarthropathy: a controlled analysis. J Rheumatol 1991;18: Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard.61.suppl_3.iii19 on 1 November Downloaded from on 12 September 2018 by guest. Protected by copyright.
T he spondyloarthritides (SpA) comprise five subtypes:
 1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
1305 EXTENDED REPORT Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine and the sacroiliac joints in ankylosing spondylitis and undifferentiated spondyloarthritis during treatment with etanercept M Rudwaleit*, X
A nkylosing spondylitis (AS) is a common chronic
 1046 EXTENDED REPORT Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems
1046 EXTENDED REPORT Analysing chronic spinal changes in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic comparison of conventional x rays with magnetic resonance imaging using established and new scoring systems
A mong the inflammatory rheumatic diseases
 659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
659 REVIEW Early referral recommendations for ankylosing spondylitis (including pre-radiographic and radiographic forms) in primary care J Sieper, M Rudwaleit... An earlier diagnosis of ankylosing spondylitis
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP)
 European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
European Medicines Agency Pre-Authorisation Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 23 April 2009 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/4891/03 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON CLINICAL
2004 Health Press Ltd.
 ... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
... Ankylosing spondylitis Maxime Dougados MD Professor of Rheumatology Hôpital Cochin René Descartes University Paris, France Désirée van der Heijde MD PhD Professor of Rheumatology University Hospital
Chapter 2. Overview of ankylosing spondylitis
 Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
Chapter 2 Overview of ankylosing spondylitis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises AS, reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis associated with
What is Axial Spondyloarthritis?
 Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
Physiotherapist Module 2 What is Axial Spondyloarthritis? How does it apply to physiotherapists? Claire Harris, Senior Physiotherapist, London North West Healthcare NHS Trust Susan Gurden, Advanced Physiotherapy
5/4/2018. Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis. Learning Objectives. Outcome Measures Clinical Outcome Assessments
 Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis Marina N Magrey MD Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives What are outcome measures
Outcome Measures in Spondyloarthritis Marina N Magrey MD Associate Professor Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine at MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives What are outcome measures
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/43590 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Machado, Pedro Title: Health and imaging outcomes in axial spondyloarthritis Issue
Axial Spondyloarthritis. Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital
 Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
Axial Spondyloarthritis Doug White, Rheumatologist Waikato Hospital Disclosures Presentations / Consulting Abbott Laboratories AbbVie MSD Novartis Roche Clinical Trials Abbott Laboratories AbbVie Actelion
T he emergence of new treatment options in ankylosing
 iii24 EXTENDED REPORT Treatment trials in ankylosing spondylitis: current and future considerations D van der Heijde, J Braun, D McGonagle, J Siegel... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
iii24 EXTENDED REPORT Treatment trials in ankylosing spondylitis: current and future considerations D van der Heijde, J Braun, D McGonagle, J Siegel... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Key words Ankylosing spondylitis, radiographic scoring methods, intra- and interobserver reliability, BASRI, msasss.
 Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score F. Salaffi 1, M.
Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score F. Salaffi 1, M.
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation
 Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
Do HLA-B27 positive patients differ from HLA-B27 negative patients in clinical presentation and imaging? Results from the DESIR cohort of patients with recent onset axial spondyloarthritis Ho Yin Chung
SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro?
 Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
Rheumatology Department of Lucania, S. Carlo Hospital of Potenza and Madonna delle Grazie Hospital of Matera SpA non-radiografica: fase precoce di spondilite anchilosante o altro? Ignazio Olivieri Disclosures
I n 1995, the ASsessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis
 127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
127 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of enthesitis in ankylosing spondylitis L Heuft-Dorenbosch, A Spoorenberg, A van Tubergen, R Landewé, H van der Tempel, H Mielants, M Dougados, D van der Heijde... See end
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.044206 Combining information obtained from MRI and conventional radiographs in order to detect sacroiliitis in patients with recent-onset
The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.27, No. 3, September 2005 The Relationship Between Clinical Activity And Function In Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients Jane Kawar, MD* Hisham Al-Sayegh, MD* Objective: To assess
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Ho Yin Chung & Chak Sing Lau & Ka Pik Wu & Woon Sing Wong & Mo Yin MOK
 Clin Rheumatol (2011) 30:947 953 DOI 10.1007/s10067-011-1693-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of performance of the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society, the European Spondyloarthropathy
Clin Rheumatol (2011) 30:947 953 DOI 10.1007/s10067-011-1693-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of performance of the Assessment of Spondyloarthritis International Society, the European Spondyloarthropathy
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE. Proposed Health Technology Appraisal
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Proposed Health Technology Appraisal Secukinumab for treating ankylosing spondylitis after inadequate response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With Magnetic Resonance Imaging Determined Early Sacroiliitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 4, April 2009, pp 946 954 DOI 10.1002/art.24408 2009, American College of Rheumatology Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 60, No. 4, April 2009, pp 946 954 DOI 10.1002/art.24408 2009, American College of Rheumatology Clinical and Imaging Efficacy of Infliximab in HLA B27 Positive Patients With
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies
 Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
Performance of the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) in patients under biological therapies 1. Introduction The Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) is a new instrument
Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Antunes da Cunha Oliveira
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Ankylosing spondylitis: Assessment and analysis of long-term outcome Ramiro, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Antunes da Cunha Oliveira
Assessment of disability with the World Health Organisation Disability Assessment Schedule II in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 140 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of disability with the World Health Organisation Disability Assessment Schedule II in patients with ankylosing spondylitis A van Tubergen, R Landewé, L Heuft-Dorenbosch,
140 EXTENDED REPORT Assessment of disability with the World Health Organisation Disability Assessment Schedule II in patients with ankylosing spondylitis A van Tubergen, R Landewé, L Heuft-Dorenbosch,
ABSTRACT Objective: To validate and refine two sets of candidate criteria for the classification/diagnosis of axial spondyloarthritis
 1 Rheumatology, Med Klinik I, Charité, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany; 2 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; 3 Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, The Netherlands;
1 Rheumatology, Med Klinik I, Charité, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Berlin, Germany; 2 Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden, The Netherlands; 3 Maastricht University Medical Center, Maastricht, The Netherlands;
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Spondyloarthritis: Characteristic Parameters Used for Diagnosis I Symptoms Inflammatory back pain Imaging Lab ESR/CRP Patient s history Good response to NSAIDs Spondyloarthritis-Characteristic
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
BRIEF REPORT. Denis Poddubnyy, 1 Hildrun Haibel, 1 J urgen Braun, 2 Martin Rudwaleit, 3 and Joachim Sieper 1
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 9, September 2015, pp 2369 2375 DOI 10.1002/art.39225 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Clinical Course Over Two Years in Patients With Early
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 67, No. 9, September 2015, pp 2369 2375 DOI 10.1002/art.39225 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology BRIEF REPORT Clinical Course Over Two Years in Patients With Early
adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott)
 adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott) 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
adalimumab, 40mg/0.8mL, solution for injection (Humira ) SMC No. (858/13) AbbVie Ltd (previously part of Abbott) 08 March 2013 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Peak onset between 20 and 30 years Form of spondyloarthritis (cause inflammation around site of ligament insertion into bone) and association with HLA-B27 Prevalence as high
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G)
 British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:66-71 THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G) S. D. JONES, A. STEINER,* S. L. GARRETT and A. CALIN Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases,
British Journal of Rheumatology 1996;35:66-71 THE BATH ANKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS PATIENT GLOBAL SCORE (BAS-G) S. D. JONES, A. STEINER,* S. L. GARRETT and A. CALIN Royal National Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases,
Assessment of fatigue in the management of patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 Rheumatology Advance Access published September 16, 2003 Rheumatology 2003; 1 of 6 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg421, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Assessment of fatigue in the management
Rheumatology Advance Access published September 16, 2003 Rheumatology 2003; 1 of 6 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keg421, available online at www.rheumatology.oupjournals.org Assessment of fatigue in the management
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line
 Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line August 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
Certolizumab pegol (Cimzia) for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis second or third line August 2011 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Curr Opin Rheumatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 January 20.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2010 September ; 22(5): 603 607. doi:10.1097/bor.0b013e32833c7255. Early axial spondyloarthritis Robert A Colbert
Guideline on the Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products for the Treatment of Axial Spondyloarthritis
 12 October 2017 EMA/CPMP/EWP/4891/03 Rev.1 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Guideline on the Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products for the Treatment of Axial Draft agreed by
12 October 2017 EMA/CPMP/EWP/4891/03 Rev.1 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Guideline on the Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products for the Treatment of Axial Draft agreed by
Chapter 2 Criteria and Disease Activity Measures in Axial Spondyloarthropathies
 Chapter 2 Criteria and Disease Activity Measures in Axial Spondyloarthropathies Jose Aliling 1 and Lawrence H Brent 1* Einstein Medical Center, USA * Corresponding Author: Lawrence H Brent, Einstein Medical
Chapter 2 Criteria and Disease Activity Measures in Axial Spondyloarthropathies Jose Aliling 1 and Lawrence H Brent 1* Einstein Medical Center, USA * Corresponding Author: Lawrence H Brent, Einstein Medical
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies. Dr. M Jokar
 Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Sronegative Spondyloarthropathies Dr. M Jokar 1 Definition The spondyloarthropathies are a group of disorders that share certain clinical features and an association with the HLA-B27 allele 2 Spondyloarthropathies
Clinical Tools to Assess and Monitor Spondyloarthritis
 Curr Rheumatol Rep (2015) 17: 47 DOI 10.1007/s11926-015-0522-3 SPONDYLOARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Clinical Tools to Assess and Monitor Spondyloarthritis Robert Landewé 1,2 & Astrid van Tubergen
Curr Rheumatol Rep (2015) 17: 47 DOI 10.1007/s11926-015-0522-3 SPONDYLOARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Clinical Tools to Assess and Monitor Spondyloarthritis Robert Landewé 1,2 & Astrid van Tubergen
Introduction. Natural Progression of AS. Sacroiliac Joint. Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Clinical Features and Assessment of Ankylosing Spondylitis Dr. YIM, Cheuk Wan Specialist in Rheumatology United Christian Hospital Introduction Ankylo=fusion Spondylitis=inflammation of spine Affect 0.1-0.5%
Spondylarthropathies. Outline. Introduction. Spondylarthropathy other than AS. Mimickers of spondylarthropathy. Conclusions.
 Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Spondylarthropathies Filip M. Vanhoenacker Johan Van Goethem General Hospital St-Maarten Duffel-Mechelen Universities of Antwerp and Ghent Outline Introduction Spondylarthropathy other than AS Mimickers
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis
 Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Imaging of axial spondyloarthritis including ankylosing spondylitis ACR 2012 Prof. Dr. med. J. Braun Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne Ruhr-Universität Bochum Germany Modified New York Criteria 1984 for
Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice
 Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 7, Issue 1, JanuaryMarch 2014, pp.7883 Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice Popescu C* **, Trandafir M*, Bădică AM*, Morar F*, Predeţeanu
Journal of Medicine and Life Vol. 7, Issue 1, JanuaryMarch 2014, pp.7883 Ankylosing spondylitis functional and activity indices in clinical practice Popescu C* **, Trandafir M*, Bădică AM*, Morar F*, Predeţeanu
Scottish Medicines Consortium
 Scottish Medicines Consortium etanercept 25mg vial of powder for subcutaneous injection (Enbrel ) (No. 212/05) Wyeth New indication: severe active ankylosing spondylitis inadequately controlled by conventional
Scottish Medicines Consortium etanercept 25mg vial of powder for subcutaneous injection (Enbrel ) (No. 212/05) Wyeth New indication: severe active ankylosing spondylitis inadequately controlled by conventional
Hierarchy of Impairment of Spinal Mobility Measures in Ankylosing Spondylitis: Twelve-Year Data
 Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 67, No. 11, November 2015, pp 1571 1577 DOI 10.1002/acr.22614 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hierarchy of Impairment of Spinal Mobility Measures
Arthritis Care & Research Vol. 67, No. 11, November 2015, pp 1571 1577 DOI 10.1002/acr.22614 VC 2015, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hierarchy of Impairment of Spinal Mobility Measures
Do extra-articular manifestations influence outcome in ankylosing spondylitis? 12-year results from OASIS
 Do extra-articular manifestations influence outcome in ankylosing spondylitis? 12-year results from OASIS I. Essers 1, S. Ramiro 2, C. Stolwijk 1, M. Blaauw 1, R. Landewé 3, D. van der Heijde 2, F. Van
Do extra-articular manifestations influence outcome in ankylosing spondylitis? 12-year results from OASIS I. Essers 1, S. Ramiro 2, C. Stolwijk 1, M. Blaauw 1, R. Landewé 3, D. van der Heijde 2, F. Van
Rheumatology. Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications. Definition of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Spondyloarthropathies
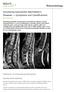 Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
Rheumatology Ankylosing Spondylitis (Bechterew s Disease) Symptoms and Classifications See online here Ankylosing spondylitis, formerly known as Bechterew s disease or Marie- Strümpell disease, is a type
SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION
 European Medicines Agency London, 20 September 2007 Product name: Remicade Procedure number: EMEA/H/C/240/II/95 SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION 7 Westferry Circus, Canary Wharf, London, E14 4HB, UK Tel. (44-20)
European Medicines Agency London, 20 September 2007 Product name: Remicade Procedure number: EMEA/H/C/240/II/95 SCIENTIFIC DISCUSSION 7 Westferry Circus, Canary Wharf, London, E14 4HB, UK Tel. (44-20)
Quality indicators, guidelines and outcome measures in ankylosing spondylitis
 Quality indicators, guidelines and outcome measures in ankylosing spondylitis J. Zochling, J. Braun Jane Zochling, MBBS, MMed (ClinEpi), PhD, Research Fellow, Menzies Research Institute, Hobart, Australia;
Quality indicators, guidelines and outcome measures in ankylosing spondylitis J. Zochling, J. Braun Jane Zochling, MBBS, MMed (ClinEpi), PhD, Research Fellow, Menzies Research Institute, Hobart, Australia;
Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Juvenile Spondyloarthritis / Enthesitis Related Arthritis (SpA-ERA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS JUVENILE SPONDYLOARTHRITIS/ENTHESITIS- RELATED ARTHRITIS (SpA-ERA)
Overview of axial spondyloarthritis
 Chapter 2 Overview of axial spondyloarthritis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises ankylosing spondylitis (AS), reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis
Chapter 2 Overview of axial spondyloarthritis The concept and classification of spondyloarthritis The term spondyloarthritis (SpA) comprises ankylosing spondylitis (AS), reactive arthritis, arthritis/spondylitis
37 year old male with several year history of back pain
 37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
37 year old male with several year history of back pain Inflammatory Low Back Pain Clues onset before the age of 40 years insidious onset, chronic (>3 months) pain morning stiffness for longer than 30
Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona
 University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen Clinical and spinal radiographic outcome in axial spondyloarthritis Maas, Fiona IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis
 C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
C. Imaging the spine in arthritis Poster No.: A-173 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Musculoskeletal - Without Subtopic Authors: A. G. Jurik; Århus C/DK Keywords: arthritis, spondyloarthritis,
ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING
 ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING July 23, 2013 sbla 125057/323: adalimumab for the treatment of Active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in adults with objective signs of inflammation by elevated
ARTHRITIS ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING July 23, 2013 sbla 125057/323: adalimumab for the treatment of Active non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis in adults with objective signs of inflammation by elevated
LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS
 ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
ARD Online First, published on March 18, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2004.027086 LUMBOSACRAL RADIOGRAPHIC SIGNS IN PATIENTS WITH PREVIOUS ENTERO- OR UROARTHRITIS (extended report) Antti Mannoja, Johanna Pekkola,
Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis
 DOI 10.1007/s11926-012-0274-2 SERONEGATIVE ARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis Salih Ozgocmen & Muhammad Asim Khan
DOI 10.1007/s11926-012-0274-2 SERONEGATIVE ARTHRITIS (MA KHAN, SECTION EDITOR) Current Concept of Spondyloarthritis: Special Emphasis on Early Referral and Diagnosis Salih Ozgocmen & Muhammad Asim Khan
Dr Tracey Kain. Associate Professor Ed Gane
 Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Associate Professor Ed Gane New Zealand Liver Transplant Unit Auckland Dr Tracey Kain Consultant Rheumatologist Grace Orthopaedic Centre Tauranga Hospital Tauranga 7:00-7:55 Abbvie Breakfast Session 1.
Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients
 Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients E. Koumakis, L. Gossec, M. Elhai, V. Burki, A. Durnez, I. Fabreguet, M. Meyer, J. Payet, F. Roure, S. Paternotte, M. Dougados
Heel pain in spondyloarthritis: results of a cross-sectional study of 275 patients E. Koumakis, L. Gossec, M. Elhai, V. Burki, A. Durnez, I. Fabreguet, M. Meyer, J. Payet, F. Roure, S. Paternotte, M. Dougados
Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography
 Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
Clin Rheumatol (2010) 29:1433 1438 DOI 10.1007/s10067-010-1480-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Discovertebral (Andersson) lesions in severe ankylosing spondylitis: a study using MRI and conventional radiography Mirjam
The effect of two golimumab doses on radiographic progression in ankylosing spondylitis: results through 4 years of the GO-RAISE trial
 Handling editor Tore K Kvien 1 Department of Rheumatology, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical School, Berlin, Germany 3 Division of Arthritis & Rheumatic
Handling editor Tore K Kvien 1 Department of Rheumatology, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet, Herne, Germany 2 Department of Radiology, Charité Medical School, Berlin, Germany 3 Division of Arthritis & Rheumatic
Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis
 REVIEW Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Xenofon Baraliakos, Robert Landewé & Juergen Braun Author for correspondence Ruhr-University, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne, Bochum, Germany
REVIEW Magnetic resonance imaging in ankylosing spondylitis Xenofon Baraliakos, Robert Landewé & Juergen Braun Author for correspondence Ruhr-University, Rheumazentrum Ruhrgebiet Herne, Bochum, Germany
C hronic low back pain (LBP) is a common problem in
 535 EXTENDED REPORT How to diagnose axial spondyloarthritis early M Rudwaleit, D van der Heijde, M A Khan, J Braun, J Sieper... Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63:535 543. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.011247 See end of article
535 EXTENDED REPORT How to diagnose axial spondyloarthritis early M Rudwaleit, D van der Heijde, M A Khan, J Braun, J Sieper... Ann Rheum Dis 2004;63:535 543. doi: 10.1136/ard.2003.011247 See end of article
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care
 Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Identification of Psoriatic Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Early Detection to Facilitate Appropriate Care Joy Schechtman D.O. Professor Midwestern University 64C-1876207 Disclosures None 3 64C-1876207
Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 19, No. 3, June, 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.3.132 Original Article Gender Differences in Clinical Features and Anti-TNF Agent Use in Korean Ankylosing
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
 Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Undifferentiated SpA Juvenile SpA Ankylosing Spondylitis Psoriatic Arthritis Arthritis associated with Ulcerative Colitis/ Crohn s Disease Reactive Arthritis Acute anterior
Concept of Spondyloarthritis (SpA) Undifferentiated SpA Juvenile SpA Ankylosing Spondylitis Psoriatic Arthritis Arthritis associated with Ulcerative Colitis/ Crohn s Disease Reactive Arthritis Acute anterior
Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance
 Ghosh and Ruderman Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:286 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1493-8 REVIEW Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance Nilasha Ghosh and Eric M.
Ghosh and Ruderman Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:286 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1493-8 REVIEW Nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis: clinical and therapeutic relevance Nilasha Ghosh and Eric M.
Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs Reduce Radiographic Progression in Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 6, June 2005, pp 1756 1765 DOI 10.1002/art.21054 2005, American College of Rheumatology Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs Reduce Radiographic Progression in Patients
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 6, June 2005, pp 1756 1765 DOI 10.1002/art.21054 2005, American College of Rheumatology Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory Drugs Reduce Radiographic Progression in Patients
Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 6, June 2016, pp 1415 1421 DOI 10.1002/art.39542 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 6, June 2016, pp 1415 1421 DOI 10.1002/art.39542 VC 2016, American College of Rheumatology Progression of Nonradiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis to Ankylosing Spondylitis
2016 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis. Online supplementary material
 2016 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis Online supplementary material 1. Introduction A systematic literature review (SLR) was performed to inform the
2016 update of the ASAS/EULAR recommendations for the management of axial spondyloarthritis Online supplementary material 1. Introduction A systematic literature review (SLR) was performed to inform the
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies
 Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Axial Spondyloarthritis: Issues & Controversies Atul Deodhar, MD Professor of Medicine Oregon Health & Science University Portland, OR WRA 2018 Annual Meeting, Leavenworth, WA. 16 th September, 2018 Disclosures:
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29572 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Berg, Rosaline van den Title: Spondyloarthritis : recognition, imaging, treatment
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies
 A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Spondyloarthropathies 763 Larkfield Road 2nd Floor Commack, NY 11725 Phone: (631) 462-2225 Fax: (631) 462-2240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2010;49:426 432 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kep427 Advance Access publication 11 January 2010 Review The evidence for whole-spine MRI in the assessment of axial spondyloarthropathy
Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis
 Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
Eur Radiol (2014) 24:866 871 DOI 10.1007/s00330-013-3074-9 MUSCULOSKELETAL Diagnostic value of pelvic enthesitis on MRI of the sacroiliac joints in spondyloarthritis L. Jans & C. van Langenhove & L. Van
I J Sørensen,15 R Valle-Oñate,16 U Weber,17 J Wei,18 J Sieper,1,19
 See Editorial, pg 1 Additional data (supplementary table) are published online only. To view these fi les please visit the journal online (http://ard.bmj. com). 1 Department of Medicine, Charité University
See Editorial, pg 1 Additional data (supplementary table) are published online only. To view these fi les please visit the journal online (http://ard.bmj. com). 1 Department of Medicine, Charité University
Mikhail Protopopov 1, Joachim Sieper 1, Hildrun Haibel 1, Joachim Listing 2, Martin Rudwaleit 1,3 and Denis Poddubnyy 1,2*
 Protopopov et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:240 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1453-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relevance of structural damage in the sacroiliac joints for the functional status
Protopopov et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2017) 19:240 DOI 10.1186/s13075-017-1453-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relevance of structural damage in the sacroiliac joints for the functional status
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases
 Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
Gender differences in effectiveness of treatment in rheumatic diseases Irene van der Horst-Bruinsma Associate Professor Rheumatology Center of Excellence of Axial Spondyloarthritis ARC/VU University Medical
MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with Moderate to Severe Ankylosing Spondylitis
 MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
MRI of Sacroiliac Joints in Patients with nkylosing Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research M E D E N T U R I L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1420 1426 0361 803X/06/1876 1420 merican Roentgen
Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics
 Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
Philippine Journal of Internal Medicine Original Paper Disease Characteristics of Filipino Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients in Metro Manila Rheumatology Clinics Ma. Lucila Dianongco, M.D.*; Marc Gregory
The Challenge of Diagnosis and Classification in Early Ankylosing Spondylitis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 4, April 2005, pp 1000 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.20990 2005, American College of Rheumatology COMMENTARY The Challenge of Diagnosis and Classification in Early Ankylosing
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 52, No. 4, April 2005, pp 1000 1008 DOI 10.1002/art.20990 2005, American College of Rheumatology COMMENTARY The Challenge of Diagnosis and Classification in Early Ankylosing
8/29/2012. Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. 1. Classification-ILAR. 1. Classification-clinical diagnosis. 1. JIA classification
 Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Outline Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 1. Classification and symptoms (ILAR-International league of Associations for Rheumatology) 2. Imaging J. Herman Kan, M.D. Section chief, musculoskeletal imaging Edward
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary?
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Inflammatory Lesions in the Spine in Ankylosing Spondylitis Clinical Trials: Is Paramagnetic Contrast Medium Necessary? KAY-GEERT A. HERMANN, ROBERT B.M. LANDEWÉ, JÜRGEN BRAUN,
Are gender-specific approaches needed in diagnosing early axial spondyloarthritis? Data from the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early cohort
 Ortolan et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:218 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1705-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Are gender-specific approaches needed in diagnosing early axial spondyloarthritis? Data
Ortolan et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:218 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1705-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Are gender-specific approaches needed in diagnosing early axial spondyloarthritis? Data
Frequency of low bone mineral density in spondyloarthropathy presenting at a tertiary care hospital
 973 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of low bone mineral density in spondyloarthropathy presenting at a tertiary care hospital Lubna Nazir, Shafique Rehman, Amir Riaz, Mohammad Saeed, Tahira Perveen Abstract
973 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of low bone mineral density in spondyloarthropathy presenting at a tertiary care hospital Lubna Nazir, Shafique Rehman, Amir Riaz, Mohammad Saeed, Tahira Perveen Abstract
Evaluation of multiple referral strategies for axial spondyloarthritis in the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort
 To cite: Abawi O, van den Berg R, van der Heijde D, et al. Evaluation of multiple referral strategies for axial spondyloarthritis in the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort. RMD Open 2017;3:e000389.
To cite: Abawi O, van den Berg R, van der Heijde D, et al. Evaluation of multiple referral strategies for axial spondyloarthritis in the SPondyloArthritis Caught Early (SPACE) cohort. RMD Open 2017;3:e000389.
Primary Results Citation 2
 Table S1. Adalimumab clinical trials 1 ClinicalTrials.gov Rheumatoid Arthritis 3 NCT00195663 Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical
Table S1. Adalimumab clinical trials 1 ClinicalTrials.gov Rheumatoid Arthritis 3 NCT00195663 Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical
Low bone mineral density predicts the formation of new syndesmophytes in patients with axial spondyloarthritis
 Kim et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:231 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1731-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Low bone mineral density predicts the formation of new syndesmophytes in patients
Kim et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2018) 20:231 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1731-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Low bone mineral density predicts the formation of new syndesmophytes in patients
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Review article. early diagnosis? HLA-B27 and spondyloarthropathy: value for. Why subjects carrying HLA-B27 are prone. Jan Tore Gran, Gunnar Husby
 _JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
_JMed Genet 1995;32:497-501 Review article 497 Department of Rheumatology, Aust Agder Central Hospital, 4800 Arendal, Norway J T Gran *Oslo Sanitetsforening Rheumatism Hospital, Oslo, Norway G Husby Correspondence
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R
 The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
The Complex/Challenging Spine Patient Steve Wisniewski, M.D. Department of PM&R 2011 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2011 MFMER slide-2 Learning Objectives Review indications for obtaining imaging studies
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor
 Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Golimumab: a novel anti-tumor necrosis factor Rossini M, De Vita S, Ferri C, et al. Biol Ther. 2013. This slide deck represents the opinions of the authors, and not necessarily the opinions of the publisher
Jane T Osterhaus 1* and Oana Purcaru 2
 Osterhaus and Purcaru Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R164 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Discriminant validity, responsiveness and reliability of the arthritis-specific Work Productivity Survey assessing
Osterhaus and Purcaru Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:R164 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Discriminant validity, responsiveness and reliability of the arthritis-specific Work Productivity Survey assessing
M Bollow, T Fischer, H Reiβhauer, M Backhaus, J Sieper, B Hamm, J Braun
 Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:135 140 135 Radiology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany M Bollow T Fischer B Hamm Pathology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University H Reiβhauer Rheumatology and
Ann Rheum Dis 2000;59:135 140 135 Radiology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany M Bollow T Fischer B Hamm Pathology, Klinikum Charité, Humboldt University H Reiβhauer Rheumatology and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION
 Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
Arthritis & Rheumatism (Arthritis Care & Research) Vol. 53, No. 5, October 15, 2005, pp 703 709 DOI 10.1002/art.21445 2005, American College of Rheumatology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Spondyloarthritis Research
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis, translation, questionnaires, BASFI, health status.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Brazilian-Portuguese version of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) Karla Garcez Cusmanich 1, Sérgio Candido Kowalski
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of the Brazilian-Portuguese version of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) Karla Garcez Cusmanich 1, Sérgio Candido Kowalski
Employment, work disability, and work days lost in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a cross sectional study of Dutch patients
 Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60:353 358 353 Employment, work disability, and work days lost in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a cross sectional study of Dutch patients A Boonen, A Chorus, H Miedema, D van
Ann Rheum Dis 2001;60:353 358 353 Employment, work disability, and work days lost in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a cross sectional study of Dutch patients A Boonen, A Chorus, H Miedema, D van
The Journal of Rheumatology Volume 38, no. 8
 The Journal of Rheumatology Volume 38, no. 8 Serum MMP-3 Level as a Biomarker for Monitoring and Predicting Response to Etanercept Treatment in Ankylosing Spondylitis SUZANNE ARENDS, EVELINE van der VEER,
The Journal of Rheumatology Volume 38, no. 8 Serum MMP-3 Level as a Biomarker for Monitoring and Predicting Response to Etanercept Treatment in Ankylosing Spondylitis SUZANNE ARENDS, EVELINE van der VEER,
