by Regional Abnormalities
|
|
|
- Lorin Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Edema of the Extremities Caused Primarily by Regional Abnormalities By JOHN F. FAIRBAIRN II, M.D. WT HEN edema of the lower extremities " cannot be ascribed to systemic disease, the cause may be due to abnormalities in the lower extremity. The factors that tend to promote localized edema and the regional disease processes that cause edema are noted in table 1. The upper extremity also may uncommonly be involved in most of these conditions. However, in this report reference will be made only to edema in the lower extremity.' A summary of the distinguishing features of some common types of regional edema can be found in table 2. Physiologic Edema Gravitational (Orthostatic) Edema Gravitational or dependency edema is a common cause of swelling of the lower extremities. It is a type of physiologic edema related to dependent and inactive lower extremities. Prolonged standing or sitting will easily produce it, and it is frequenitly noted in persons traveling long distances in trains or automobiles and in elderly persons who become physically inactive. Paraplegics or others confined to wheelchairs will note such swelling of their legs. Patients with occlusive arterial disease who have severe neuropathy often experience edema that is related, in part, to dependency and inactivity of the painful extremity; some of the edema may be related to anoxia and maliutrition of the capillaries. These patients may find relief of pain by hanging the legs over the edge of the bed for long periods. Edema may be enhanced by excess intake of salt and seems to be aggravated by an increase in environmental temperature. At times the edema may be marked, and the cause will be of great concern to the patient. Edema due to dependency is soft and pit- From the Section of Medicine, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota. 981 ting, causes no changes in the skin, and usually disappears quickly when the patient becomes active or lies down. Occasionally a salt-restricted diet may be needed and diuretic therapy with thiazide drugs may be indicated. Other Types of Physiologic Edema Some patients may experience physiologic edema and yet their lower extremities are not unusually dependent or illactive during the time edema is noted. Included in this group are patients who experience premenstrual edema and the edema related to pregnancy. In both instances evidence of retention of sodium chloride and water exists, which may be caused by the evident changes in concentration of various hormones in the blood and urine.2 During pregnancy, the uterine pressure exerted on the large veins of the pelvis and on the lymphatic drainage may promote edema of the lower extremity. A restricted intake of sodium chloride with or without the use of the thiazide diuretics is usually effective therapy. Lymphedema Lymphedema, an uncommon condition in the general population, accounts for a considerable percentage of patients who have edema of local origin. ljymphedema results when channels and valves of the lymphatic system are incompetent owing to developmental or acquired processes. Congenital forms of the disease are the extremely rare familial type, known as Milroy's disease, and the more common simple, nonfamilial type, both of which appear at birth or in infancy. A type of lymphedema that probably owes its inception to an inherited inadequacy of lymphatic development is called "lymphedema praecox." Although the appearance of this form is delayed usually until adolescence or early adulthood, the abnormalities in the lymphatic
2 FAIRBAIRN 982 Table 1 Classification of Edema, of the Lower Extremity Based on Cause or Upper Physiologic edema Gravitational edema Other types Lymphedema Lipedema Edema of thrombophlebitis Edema of chronic venous insufficiency Drug-induced edema Edema of other causes Pretibial myxedema Edema of livedo reticularis Edema following compression of popliteal vein Angioneurotic edema Edema associated with plantar neuroma and tenosynovitis structures of the lower extremities appear to be similar to those in the congenital varieties. These similarities are more qualitative than quantitative. Some additional unknown factor seems to precipitate the appearance of lymphedema praecox during the teens or early adulthood. Secondary lymphedema results when the lymphatic channels, apparently normal in structure, are obstructed by lymnphangitis, invasion by a malignant lesion, or by other inflammatory or obstructive processes. The lymphedema that often follows axillary or groin dissection for malignant processes and that which follows trichophytic infection are examples of secondary lymphedema. The cause of lymphedema of the extremities usually cannot be determined by clinical examination alone. Lymphangiography may help, but the historieal background against which the disease develops is of utmost importance in differentiating the primary or congenital from secondary formes. There are two lymphatic systems in the leg,3 the deep and the superficial, divided by the deep muscular fascia. The superficial system is principally involved in primary and secondary lymphedema. At first, lymphedema may be indistinguishable from any other soft pitting edema that will disappear on elevation of the leg. This is true when the lymphedema first involves the foot, ankle, and lower part of the leg (fig. 1). If, however, the edema is painless, first appears in the thigh, and progresses distally, this type of onset would be pathognomonie of obstructive or secondary lymphedema. Lymphedema of this type is almost always secondary to malignant invasion of lymph nodes of the pelvis or groin. As the edema persists, secondary changes occur in the skin and the subcutaneous tissues that allow differentiation from most other types of edema. The skin overlying the edematous portion becomes thickened, the skin surrounding the hair follicles is elevated due to hypertrophy leaving the hair follicle depressed (socalled pig skin appearance), and the entire linib may become chronically enlarged and distorted due to hypertrophy of the subeutatieous tissues. The appearance of lymphedema may be the initial clue to obscure malignant lesions, often pelvic or retroperitoneal, or a nmanifestation of a rare disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis. When secondary to inflammation, lymphedema mlay follow only a single episode of lymphangitis or may not appear until multiple inflammatory episodes have occurred. Figure 1 Lymphedema. Note unilateral swelling of entire left leg incltuding the foot.
3 SYMPOSIUM-PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISORDERS 983 Table 2 Distinguishing Features of Some Common Types of Regional Edema 1. Thickening of skin 2. Ulceration associated 3. Pigmentation of skin of edematous leg Gravitational edema (orthostatic) None, except rarely in severe edema of long duration 4. Bilateral edema Always 5. Soft, pitting edema 6. Involvement of foot as well as of more proximal areas 7. Local factors other than retention of fluid in the enlargement None Lymphedema Very marked Rare* Often Occurs only when lymphedema is of short duration Hypertrophy of tissues *Rarely a lymphangiosarcomatous ulceration may be Treves syndrome). Treatment of lymphedema,4 regardless of cause, consists of (1) the elevation of the extremities for several days with the patient at complete rest in bed to eliminate fluid from the extremity; (2) the use of thiazide diureties such as chlorothiazide (Diuril) in doses of 500 mg. twice a day to help mobilize fluid quickly while the patient is bedfast prior to the use of an elastic support; the drug may be administered also after elastic support has been applied; (3) the use of elastic support when the patient is ambulatory to prevent reaccumulation of edema; (4) prophylaxis to prevent lymphangitis, which is common in the lymphedematous limb; and (5) measures to attack the cause of the lymphatic obstruction if due to malignant disease. Surgical treatment of lymphedema consists of various procedures to excise large blocks of subcutaneous tissue. This treatment results in a persistently deformed but smaller limb and is reserved Lipedema Always Occurs usually in minimal amounts Deposition of subeutaneous fat Chronic venous insufficiency May occur if regional lymphedema is additionally present Common Occasionally None seen, especially in postmastectomy lymphedema (Stuartfor massively enlarged limbs. Postoperatively the patient must still follow the previously outlined medical treatment program. The treatment program should be initiated as early in the course of the disease as possible. Delaying treatment or instituting treatment after massive hypertrophy occurs is not desirable. Early use of adequate elastic support, diuretic therapy with thiazide drugs, and prevention of lymphangitis are strongly recommended. Only these measures will prevent later deformity and disability. Lipedema Lipedema,5 a strange malady primarily affecting women, is a painless, symmetrical, and bilateral deposition of fat in the lower extremities (fig. 2). It is the source of great emotional problems for some. Lipedema is often unassociated with fluid accumulation, but with enlargement of the legs, the patient is certain that the swelling is due primarily to retention
4 984 FAIRBAIRN Figure 2 Lipedema. Note symmetrical bilateral swelling of legs and a(nkles writhout involvement of the foot. of fluid. In some instanees, associated edema is present to some degree. This disorder is often accompanied by lipodystrophy (excess deposition of fat about the thighs, hips, and buttocks). While the upper extremities may rarely be involved, greater disability occurs in the legs. The feet are always spared from fatty deposition, which is one of the distinguishing features of lipedema. There is often a family history of enlarged extremities in female siblings or other female relatives. The patient may have had either slightly enlarged legs for years or perfectly normal legs until such time as a gain in weight is noticeable. Then fatty enlargement of the legs may accompany general body obesity. Later reduction in weight will not appreciably reduce the volume of the subcutaneous fat in the legs. Because the fatty deposition is gradual and often confined to the legs, not all patients with lipedema will note its appearance at a time of general obesity. Although the cosmetic disfigurement is usually the primary complaint, some patients will mention an associated edema due to retention of fluid, whereas others will complain of discomfort in the swollen legs, varying from mild hypersensitivity of the skin of the dependent limb to rather marked aching distress. Inspection of the legs will reveal the fatty nature of the swelling, its bilateral and symmetrical nature, and the absence of fatty deposits in the feet. If pitting edema is present, the fluid accumulation is usually not severe. The skin is not thickened or changed as in lymphedema and there are no pigmentary changes, dermatitis, or ulceration as found in chronic venous insufficiency. Palpation of the leg often reveals hypersensitivity to pressure. Unfortunately, not much effective therapy is available. If edema fluid is present, a diet restricted in sodium chloride and the use of thiazide diuretics may be employed but these measures are often ineffective. Elastic support is usually not tolerated by these patients because of the hypersensitivity of the skin, but it may be tried. Although obese patients should be urged to reduce, it is generally ineffective in reducing the size of the lower extremities. Frank symnpathetic discussion about the nature of the process and treatment should be given to the patient. The patient should be urged to accept the presence of lipedema and to keep weight normal, since a gain may result in further fatty deposition in the legs. Edema of Thrombophlebitis See the section on "Venous Thrombo-embolism." Edema of Chronic Venous Insufficiency Impaired venous return, whether due to valvular insufficiency of the deep, the communicating, or the superficial veins may result in chronic venous insufficiency. This condition is characterized primarily and initially by edema but often is accompanied later by secondary changes in the skin such as pigmentation, dermatitis, or ulceration. Chronic venous insufficiency rarely, if ever, occurs unless the valves in these veins are abnormal. The valves may be congenitally ab*article by Spittell in this symposium. Circulation, Volume XX VII, May 1963
5 SYMPOSIUM-PERIPHERALI VASCULAR DISORDERS 985 sent, present but congenitally abnormal, or incompetent as the result of previous throinbophlebitis. Except in the case of primary varicose veins with congenitally weak walls and valves, the most common cause of incompetent valves is thrombophlebitis. When pressure in a segment of the venous tree is greatly elevated for a short time or moderately elevated for a long time, even normal valves may become incompetent, resulting in chronic venous insufficiency. This type of valvular incompetence may occur in patients with arteriovenous fistula. Whenever a patient has chronic venous insufficiency, the possibility of an arteriovenous fistula should be considered. Although thrombophlebitis may not result in any venous insufficiency, whenever insufficient venous circulation does occur after thrombophlebitis, it usually follows the more severe forms, such as iliofemoral thrombophlebitis, other sites of deep venous thrombosis, or extensive and recurrent superficial thrombosis. The effect of incompetent valves in the proximal veins is to increase the venous pressure distally and to decrease venous blood flow.6 Normally, the venous pressure at the ankle level is highest when the person is standing, falls rapidly on walking, and is lowest in recumbency. These facts are due to the pumping action of the muscles in the presence of normal valvular action. With incompetent valves, the venous pressure at the ankle remains elevated during walking. This rather persistent and abnormally high venous pressure permits transudation of fluid through the distended capillaries, resulting in edema. Edema may also be enhanced by malnutrition of the smaller veins and capillaries as the result of stagnation of blood and relative anoxia. In areas of dermatitis and ulceration degenerative changes in the walls of arterioles and venules in the skin have been noted in cases of chronic venous insufficiency. The secondary changes in the skin such as dermatitis, pigmentation, fibrosis, and ulceration ordinarily do not occur until edema has been chronic for months or years. The edema that accompanies chronic venous Circulation, Volume XXVII, May 1961 insufficiency is initially soft and pitting. In addition, because of venous stasis and engorgement, there may often be distinguishing features such as increased warmth, slightly distended veins, and a cyanotic hue in the involved extremity. Later, varicose veins may be noted, and the cutaneous signs of venous insufficiency often appear. The edema of chronic venous insufficiency can usually be mobilized by elevation of the patient's leg and complete rest in bed for several days. This is in contradistinction to chronic lymphedema in which tissue hypertrophy usually prevents return of the leg to normal size. Early in their courses, lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency are quite similar, making it difficult to distinguish them, but the cutaneous signs mentioned previously are clues that venous and not lymphatic insufficiency is present. Some patients with the postphlebitic syndrome or other types of chronic venous insufficiency have chronic indurative cellulitis which may be associated with periodic lymphangitis and subsequent lymphatic obstruction, leading to localized or regional lymphedema. Indurative cellulitis is probably due to a lowgrade inflammatory process in the subcutaneous tissues of some patients with long-standing chronic venous insufficiency, which develops into firm, brawny irregular induration. This induration, with signs of inflammation, often is painful and usually is located on the arteriomedial aspect of the leg above the malleolus. The treatment of chronic venous insufficiency is prophylactic and symptomatic. Prophylaxis Thrombophlebitis involving a long segment of vein, whether deep or superficial, will result in some degree of valvular incompetence. When many valves are involved because the venous thrombosis is extensive, the degree of chronic venous insufficiency is increased. By prompt and effective anticoagulant therapy, further extension of the thrombophlebitis may be halted, preventing a major type of chronic venous insufficiency. All patients who have iliofemoral thrombo-
6 986 phlebitis and a large number who have thrombophlebitis in the calf will manifest some degree of venous insufficiency when they become ambulatory. If mild venous insufficiency with edema is untreated, it often becomes more severe and cutaneous changes will appear. As part of prophylaxis, therefore, adequate elastic support, applied to the extremity as soon as the patient is ambulatory, after an episode of deep thrombophlebitis, is necessary. The patient should be instructed in the proper application of the elastic bandage, and should wear the bandage throughout the entire day. Elastic support should be used for at least 2 to 3 months or perhaps longer after the acute episode of thrombophlebitis, and in some instances, indefinitely. The use of elastic support can be stopped only when all edema is absent after removal of the bandages. Symptomatic Measures If, when first examined, the patient has chronic venous iiisufficiency, the following procedures are effective: (1) enlistment of the patient's cooperation in the program of elastic support; (2) elevation of leg with the patient at complete rest in bed until all edema subsides; (3) use of a protective sponge-rubber pad over areas of dermatitis and previous ulceration; (4) use of proper elastic support; (5) treatment of uleerations either by medical or surgical meanis; and (6) operation on veins when superficial incompetence may be the cause of the edema, dermatitis, or ulceration. DruglInduced Edema Edema of the lower extremities may be Table 3 Drugs that May Cause Edema of Lower Extremities Horrmones Corticosteroids and adrenocorticotropins Estrogen Progesterone Testosterone Antihypertensive Drugs Guanethidine sulfate (Ismelin) Hydralazine hydrochloride (Apresoline hydrochloride) Rauwolfia preparations 9FAIRBAIRN caused by ingestion of certaini drugs, a list of which can be found in table 3. Nothing can differentiate the drug-induced type of edema from gravitational or physiologic edema except the history of use of the drug during the time edema occurs. In some instances, such as with hydralazine hydrochloride, the edema may appear abruptly and mnay be extensive enough to involve the leg as well as the foot. In most situations drug-induced edema is of mild-to-moderate severity and subsides promptly on withdrawal of the offending medicament. Edema of Other Causes Pretibial Myxedema An unusual type of local edema, termed "localized " or " pretibial " myxedema may occur only in the pretibial region or on the dorsum of the foot.7 However, the terminology is not adequate, since the condition bears no relationship to the presenee or absence of generalized myxedema; instead, it is only seen in patients with exophthalmic goiter. It is usually a self-limiting process that disappears over the course of years. Treatment should be directed toward the exophthalmic goiter. Edema of Livedo Reticularis Some patients, almost always females, will note cyclic and recurrent edema in association with livedo reticularis.5 Ulcerations are frequently associated and niay occur simultaneously with the edema. Some patients seem to note edema primarily in the summer months while in others the edema occurs during the winter months. Although the mechanism is obscure, edema may be benefited by elastic support. Ed,ema Following Compression of Popliteal Vein This type is singled out from edema due to chronic venous insufficiency for two reasons: (1) to emphasize its causes and (2) because venous insufficiency is not necessarily a result. A Baker's cyst or a popliteal aneurysm may enlarge enough to compress the popliteal vein, causing edema and other signs of increased venous pressure in distal areas. If thrombosis of the vein has not occurred,
7 SYMPOSIUM PERIPHERAL VASCULAR DISORDERS 987 surgical correction of the mass should return venous circulation to normal. Angioneurotic Edema Angioneurotic edema rarely would be found in the lower extremities. However, its sudden onset, usual unilateral location, and episodic nature tend to exclude almost all other causes of local edema. In addition, angioneurotic edema, when severe, will often simultaneously involve other parts of the body. Edema Associated with Plantar Neuroma or Tenosynovitis In an occasional case, edema, usually localized to the area involved, is associated with plantar neuroma and tenosynovitis. In patients with plantar neuroma, the edema may involve the dorsum of the foot. Tenosynovitis may be extensive enough to cause edema. Both conditions are painful, localized, and usually are readily differentiated from other causes of local edema. A Note on the Proper Type of Elastic Support and Its Use Although elastic support is designed to prevent the reaccumulation of edema fluid, it will never promote removal of fluid already present. Therefore, before any elastic support is applied, the extremity should be freed of edema by complete rest in bed accompanied by elevation of the extremities. If the rest in bed is only partial, the edema will usually reaccumulate within a few minutes after the patient is ambulant. If the edema is chronic, as in lymphedema and chronic venous insufficiency, elevation of the feet well above cardiac level is necessary. With the patient resting in bed, diuretic therapy with one of the thiazide drugs is helpful in mobilizing the fluid, especially that due to lymphatic obstruction. A dose of the thiazide diuretics comparable to 500 mg. of chlorothiazide twice a day can be used. When the limb is reduced to normal size, or in the case of lymphedema when the limb reaches a stationary although not normal size, elastic support should be applied to the leg prior to ambulation. Elastic bandages and stockings vary great- Circulation, Vonume XXVII, May 196S ly in strength and ability to control edema. In general, the more marked the edema is, the heavier the elastic support required. For the patient with minimal venous insufficiency an elastic stocking or one elastic bandage may be sufficient. For patients with more marked venous insufficiency or lymphedema, two heavy elastic bandages or a strong elastic stocking will be needed. A strong elastic stocking (Jobst* type) can be prescribed when the extremity is free from edema. This type of stocking fits the measurements of the patient's edema-free extremity. Knee-length, full-length, and leotard types are available in three different strengths (heavy, medium, and light). Occasionally, a pure rubber bandaget is needed to control marked lymphedema. When, used, bandages are applied as follows: Two turns are made around the foot and ankle so that the toes and a small portion of the heel are left exposed. The bandaging is continued up the leg in a spiral manner ending below the knee. When a second bandage is used, the first bandage is terminated about midway between the ankle and the knee, and the second bandage is started from that point, overlapping the first bandage with several spiral turns and terminating below the knee. Bandaging above the knee is not necessary and cannot be carried out successfully. After applying the bandage several times with supervision, the patient can do it without further help. Repeated experience will teach him when the bandage has been applied with the correct pressure on the leg. If edema is present at the end of the day, either the bandage is inherently unsatisfactory or it has been applied too loosely. If applied too tightly, the bandage is likely to cause much discomfort. The patient soon learns the amount of overlapping necessary for each turn so that the bandage terminates just below the knee and he learns how to make the figure-of-eight turn about the foot and ankle in order to leave exposed only a *Jobst Co., Toledo, Ohio. t ' Rochester Bandage, Davol Rubber Co., Providence, Rhode Island.
8 988 small portion of the heel and the toes. If mnueh perspiration occurs, the bandages should be removed, talcum powder applied to the leg, and the bandages reapplied. Since edema may begin to accumulate within 10 miinutes after arising, the patient should apply the bandages before getting out of bed in the morning. The patient should wear the bandages throughout the day until he retires. The bandages may be removed once or twice during the day but should be reapplied immediately. This removal allows the patient to massage the skin and reapply the bandages to ensure that pressure produced by the edges of the bandages is not continuously applied to one area for more than 6 hours at a time. The prolonged use of elastic support of any kind is burdensome and cosmetically unattractive. In order to prevent chronic edema, the patient must be encouraged to wear the elastic support for as long as edema persists. Frequent discussions are necessary so that the patient understands the need for continued elastic support. References 8FAIRBAIRN 1. FAIRBAIRN, J. F., II: Diagnosis and treatment of local edema of lower extremities. Minnesota Med. 41: 256, MOYER, J. H., AND FUCHS, AM. (ED): Edema, Mechanisms and Management: A Hahnemann Symposium on Salt and Water Retention. Philadelphia, W. B. Saunders Company, YOFFEY, J. M., AND COLTRTICE, F. C.: Lymphatics, Lymph and Lymphoid Tissue. Ed. 2. London, E. Arnold and Company, 1956, 510 pp. 4. ALLEN, E. V., BARKER, N. W., AND HINES, E. A., JR.: Peripheral Vascular Diseases. Ed. 3, Philadelphia, W. B. Saunders Company, 1962, pp. 23; 690; 745; ALLEN, E. V., AND HINES, E. A., JR.: Lipedema of the legs: A syndrome characterized by fat legs and orthostatic edema. Proc. Staff Meet., Mayo Clin. 15: 184, POLLACK, A. A., TAYLOR, B. E., MYERS, T. T., AND WOOD, E. H.: The effect of exercise and body position on the venous pressure at the ankle in patients having venous valvular defects. J. Clin. Invest. 28: 559, GIMLETTE, T. M. D.: Pretibial myxoedema. Brit. M. J. 2: 348, FELDAKER, M., HINES, E. A., JR., AND KIERLAND, R. R.: Livedo reticularis with summer ulcerations. Arch. Dermat. 72: 31, 1955.
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers. Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities. Evidence of healed ulcers. Dermatitis. Normal ABI.
 Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Peripheral Vascular Examination. Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment
 Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
Peripheral Vascular Examination Dr. Gary Mumaugh Western Physical Assessment Competencies 1. Inspection of upper extremity for: size symmetry swelling venous pattern color Texture nail beds Competencies
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS
 VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
VASCULAR DISEASE: THREE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW JAMES A.M. SMITH, D.O. KANSAS VASCULAR MEDICINE, P.A. WICHITA, KANSAS KANSAS ASSOCIATION OF OSTEOPATHIC MEDICINE ANNUAL CME CONVENTION APRIL 13, 2018 THREE
Occasional pain or other discomfort (ie, not restricting regular daily activity)
 Revised Venous Clinical Severity Score Pain : 0 Mild: 1 or other discomfort (ie, aching, heaviness, fatigue, soreness, burning) Occasional pain or other discomfort (ie, not restricting regular daily activity)
Revised Venous Clinical Severity Score Pain : 0 Mild: 1 or other discomfort (ie, aching, heaviness, fatigue, soreness, burning) Occasional pain or other discomfort (ie, not restricting regular daily activity)
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL Policy Number: MP.015.MH Last Review Date: 11/08/2018 Effective Date: 02/01/2019
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar CareFirst PPO MedStar Health considers Compression Garments and
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar CareFirst PPO MedStar Health considers Compression Garments and
RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION. Professor M Baguneid MB ChB MD FRCS
 RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION This minimally invasive treatment involves closing the faulty veins using a keyhole approach thereby avoiding the larger cuts and avoiding stripping of the veins. Professor M Baguneid
RADIOFREQUENCY ABLATION This minimally invasive treatment involves closing the faulty veins using a keyhole approach thereby avoiding the larger cuts and avoiding stripping of the veins. Professor M Baguneid
How varicose veins occur
 Varicose veins are a very common problem, generally appearing as twisting, bulging rope-like cords on the legs, anywhere from groin to ankle. Spider veins are smaller, flatter, red or purple veins closer
Varicose veins are a very common problem, generally appearing as twisting, bulging rope-like cords on the legs, anywhere from groin to ankle. Spider veins are smaller, flatter, red or purple veins closer
Bumex vs lasix in hypoalbuminemia
 Bumex vs lasix in hypoalbuminemia What other foods in the diet cause edema?. The veins in the legs are responsible for transporting blood up to the veins of the torso, where it is then returned to the
Bumex vs lasix in hypoalbuminemia What other foods in the diet cause edema?. The veins in the legs are responsible for transporting blood up to the veins of the torso, where it is then returned to the
Varicose Vein Information Sheet
 Neil Goldstein, MD Joseph Hewett, MD Board- Certified Physicians in Interventional, Diagnostic, and Vascular Radiology, Surgery, Vascular Surgery and Phlebology Varicose Vein Information Sheet PREVALENCE
Neil Goldstein, MD Joseph Hewett, MD Board- Certified Physicians in Interventional, Diagnostic, and Vascular Radiology, Surgery, Vascular Surgery and Phlebology Varicose Vein Information Sheet PREVALENCE
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge
 Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Reducing the risk of venous thrombo-embolism (VTE) in hospital and after discharge What is a venous thromboembolism (VTE)? This is a medical term that describes a blood clot that develops in a deep vein
Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond
 Disclosure of Conflict of Interest Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond Shawn Amyot, MD, CCFP Fellow of the Canadian Society of Phlebology Ottawa Vein Centre I do not have relevant financial
Disclosure of Conflict of Interest Chronic Venous Insufficiency Compression and Beyond Shawn Amyot, MD, CCFP Fellow of the Canadian Society of Phlebology Ottawa Vein Centre I do not have relevant financial
Latmedical, LLC is the exclusive Caribbean distributor
 No-Varix Graduated Compression Hosiery is manufactured by TEXPON S.A., the only Latin- American company certified with the norm ISO 9001:00 with scope of manufacture of graduate compression hosiery for
No-Varix Graduated Compression Hosiery is manufactured by TEXPON S.A., the only Latin- American company certified with the norm ISO 9001:00 with scope of manufacture of graduate compression hosiery for
MP.015.MH Compression Stockings and Garments
 MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.015.MH Compression Stockings and Garments This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar
MedStar Health, Inc. POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL MP.015.MH Compression Stockings and Garments This policy applies to the following lines of business: MedStar Employee (Select) MedStar MA DSNP CSNP MedStar
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: 01/23/2019
 Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY
 PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY CONTENTS 1.0. PRESSURE THERAPY 1.1. The physiological effects of pressure therapy 1.2. When pressure therapy is indicated 2.0.
PRESOR-03 STUDY ON THE EFFECTIVENESS OF USING THE SORISA PRESSURE THERAPY CONTENTS 1.0. PRESSURE THERAPY 1.1. The physiological effects of pressure therapy 1.2. When pressure therapy is indicated 2.0.
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure
 When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
When is Limb Edema Not Heart Failure An Approach to the Swollen Leg Greg Harding M.D. Vascular Surgeon Faculty/Presenter Disclosure Faculty: Greg Harding M.D. Relationships with commercial interests: None
Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in joint replacement surgery
 Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in joint replacement surgery Even though joint replacement surgery is an effective procedure and in expert hands yields a low complication rate, deep venous
Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in joint replacement surgery Even though joint replacement surgery is an effective procedure and in expert hands yields a low complication rate, deep venous
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
Deep Vein Thrombosis Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in a vein. This condition can affect men and women of any age and race. DVT is a potentially serious condition. If not treated,
The Peripheral Vascular System
 The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
The Peripheral Vascular System Anatomy and Physiology Arteries Arteries contain 3 concentric layers of tissue: - the intima - the media - the adventitia The intima The endothelium of the intima has metabolic
THE MANAGEMENT OF THE SWOLLEN ARM IN CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST
 THE MANAGEMENT OF THE SWOLLEN ARM IN CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST NORMAN TREVES, M.D. The terms "brawny arm" and "lymphedema" have been given to the swollen arm which may complicate the inoperable, recurrent,
THE MANAGEMENT OF THE SWOLLEN ARM IN CARCINOMA OF THE BREAST NORMAN TREVES, M.D. The terms "brawny arm" and "lymphedema" have been given to the swollen arm which may complicate the inoperable, recurrent,
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE
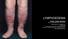 LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome
 Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Management of Post-Thrombotic Syndrome Thanainit Chotanaphuti Phramongkutklao College of Medicine Bangkok, Thailand President of CAOS Asia President of Thai Hip & Knee Society President of ASEAN Arthroplasty
Varicose Veins. These are abnormal veins in the legs that appear as unsightly or cause other problems.
 Varicose Veins What are varicose veins? These are abnormal veins in the legs that appear as unsightly or cause other problems. They develop due to abnormal valve function that allows the blood to travel
Varicose Veins What are varicose veins? These are abnormal veins in the legs that appear as unsightly or cause other problems. They develop due to abnormal valve function that allows the blood to travel
Lipedema COMMON CLINICAL ENTITY RARELY DIAGNOSED FVS 2018
 1 Lipedema COMMON CLINICAL ENTITY RARELY DIAGNOSED FVS 2018 No disclosures 2 Lipedema 3 Bilateral symmetrical fat deposition from hips to ankles Trunk is spared, chest small Not obesity, note waist/hip
1 Lipedema COMMON CLINICAL ENTITY RARELY DIAGNOSED FVS 2018 No disclosures 2 Lipedema 3 Bilateral symmetrical fat deposition from hips to ankles Trunk is spared, chest small Not obesity, note waist/hip
Venous drainage of the lower limb
 Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
Venous drainage of the lower limb INTRODUCTION It is of immense clinical and surgical importance. The venous blood against gravity. FACTORS HELPING THE VENOUS DRAINAGE OF THE LOWER LIMB The contraction
Improving customer care in compression hosiery
 Improving customer care in compression hosiery Introduction Within the modern NHS, the Pharmacy Team provides the front line service that most patients have contact with. Compression hosiery has a key
Improving customer care in compression hosiery Introduction Within the modern NHS, the Pharmacy Team provides the front line service that most patients have contact with. Compression hosiery has a key
THE popliteal artery is the second most common site of aneurysm. The
 POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
POPLITEAL ANEURYSM Treatment by Vein Graft: Case Report A. W. HUMPHRIES, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery F. A. LeFEVRE, M.D. and V. G. dewolfe, M.D. Department of Cardiovascular Disease THE popliteal
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA. John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA
 When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
How to prevent blood clots whilst in hospital and after your return home
 How to prevent blood clots whilst in hospital and after your return home Patient information WHAT What IS is DEEP deep VEIN vein THROMBOSIS? thrombosis? Deep Vein Thrombosis DVT is a blood clot within
How to prevent blood clots whilst in hospital and after your return home Patient information WHAT What IS is DEEP deep VEIN vein THROMBOSIS? thrombosis? Deep Vein Thrombosis DVT is a blood clot within
Dr Paul Thibault. Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology
 Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology Prescribing Effective Compression and PTS Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist, Newcastle,
Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist & Assistant Editor Phlebology (International Journal) Australasian College of Phlebology Prescribing Effective Compression and PTS Dr Paul Thibault Phlebologist, Newcastle,
Priorities Forum Statement
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 9 Subject Varicose Vein Surgery Date of decision September 2014 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review September 2018 Relevant OPCS codes: L841-46, L848-49, L851-53,
Priorities Forum Statement Number 9 Subject Varicose Vein Surgery Date of decision September 2014 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review September 2018 Relevant OPCS codes: L841-46, L848-49, L851-53,
Healthy Legs For Life! Prevention is better then cure
 Healthy Legs For Life! Prevention is better then cure Ellie Lindsay Independent Specialist Practitioner Associate Lecturer, CRICP, London Visiting Fellow, Queensland University of Technology Occurrence
Healthy Legs For Life! Prevention is better then cure Ellie Lindsay Independent Specialist Practitioner Associate Lecturer, CRICP, London Visiting Fellow, Queensland University of Technology Occurrence
EIDO Healthcare Ltd. Patient details (Place sticky label here) Patient information and consent Day Case - Varicose Veins Surgery Ref: INFOrm4U DC09
 Patient information and consent Day Case - Varicose Veins Surgery Ref: INFOrm4U DC09 What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins in the leg. They are very common and affect up
Patient information and consent Day Case - Varicose Veins Surgery Ref: INFOrm4U DC09 What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins in the leg. They are very common and affect up
DISORDERS OF VENOUS SYSTEM
 DISORDERS OF VENOUS SYSTEM Varicose Veins Any dilated, elongated and tortuous vein irrespective of size Varicose veins are common in the superficial veins of the leg which are subject to high pressure
DISORDERS OF VENOUS SYSTEM Varicose Veins Any dilated, elongated and tortuous vein irrespective of size Varicose veins are common in the superficial veins of the leg which are subject to high pressure
Definitions and criteria
 Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Several disciplines are involved in the management of diabetic foot disease and having a common vocabulary is essential for clear communication. Thus, based on a review of the literature, the IWGDF has
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments. Medical Provider:
 Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
Listing Form: Heart or Cardiovascular Impairments Medical Provider: Printed Name Signature Patient Name: Patient DOB: Patient SS#: Date: Dear Provider: Please indicate whether your patient s condition
When Varicose Veins a Circulatory Problem and how to screen. By Ariel D. Soffer, MD, FACC NCVH MIAMI, 2015
 When Varicose Veins a Circulatory Problem and how to screen. By Ariel D. Soffer, MD, FACC NCVH MIAMI, 2015 Bio-Ariel Soffer, MD, FACC Fellow of the American College of Cardiology since 1998 with post-graduate
When Varicose Veins a Circulatory Problem and how to screen. By Ariel D. Soffer, MD, FACC NCVH MIAMI, 2015 Bio-Ariel Soffer, MD, FACC Fellow of the American College of Cardiology since 1998 with post-graduate
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION. Vol. 11: Peripheral Vascular System
 BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 11: Peripheral Vascular System Hello, Mrs. Roth, welcome to our clinic. Thank you. Your learning objectives for mastering the examination of the Peripheral
BATES VISUAL GUIDE TO PHYSICAL EXAMINATION Vol. 11: Peripheral Vascular System Hello, Mrs. Roth, welcome to our clinic. Thank you. Your learning objectives for mastering the examination of the Peripheral
Additional Information S-55
 Additional Information S-55 Network providers are encouraged, but not required to participate in the on-line American Venous Forum Registry (AVR) - The First National Registry for the Treatment of Varicose
Additional Information S-55 Network providers are encouraged, but not required to participate in the on-line American Venous Forum Registry (AVR) - The First National Registry for the Treatment of Varicose
Interactive Learning Session
 Chronic Venous Disease - Part I Interactive Learning Session 2011 Ali Sabbour Prof of Vascular Surgery http://mic.shams.edu.eg/moodle6 Login as a guest Surgery 2 Ali Sabbour - Chronic Venous Disease Intended
Chronic Venous Disease - Part I Interactive Learning Session 2011 Ali Sabbour Prof of Vascular Surgery http://mic.shams.edu.eg/moodle6 Login as a guest Surgery 2 Ali Sabbour - Chronic Venous Disease Intended
Reality TV Managing patients in the real world. Wounds UK Harrogate 2009
 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Wounds UK Harrogate 2009 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Brenda M King Nurse Consultant Tissue Viability Sheffield PCT Harrogate 2009 Familiar
Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Wounds UK Harrogate 2009 Reality TV Managing patients in the real world Brenda M King Nurse Consultant Tissue Viability Sheffield PCT Harrogate 2009 Familiar
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND COMPRESSION GARMENTS. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Equipment/ Supplies
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including
End Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Lymphedema. Original Policy Date
 MP 2.02.12 End Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Lymphedema Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date
MP 2.02.12 End Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Lymphedema Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date
PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION DEVICES IN THE HOME SETTING
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Medicine Policy Number: II-60 Effective Date: 05/19/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Medicine Policy Number: II-60 Effective Date: 05/19/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
High Level Overview: Venous Anatomy of Lower Extremities. Anatomy of a Vein 5/11/2015. Barbara Deusterman, RN
 High Level Overview: Venous Anatomy of Lower Extremities Barbara Deusterman, RN What does this anatomy lecture have to do with visually guided sclerotherapy (VGS)? May 11, 2015 2 Anatomy of a Vein Almeida,
High Level Overview: Venous Anatomy of Lower Extremities Barbara Deusterman, RN What does this anatomy lecture have to do with visually guided sclerotherapy (VGS)? May 11, 2015 2 Anatomy of a Vein Almeida,
lipodermatosclerosis standards of medical practitioners and the quality of patient care related to the treatment of venous disorders.
 Chattanooga s premiere VEIN CENTER Update on Venous Insufficiency, Varicose and Spider Veins 2016 Vincent W. Gardner, MD, FACS, RPVI Fellow, American College of Surgeons Board Certified, American Board
Chattanooga s premiere VEIN CENTER Update on Venous Insufficiency, Varicose and Spider Veins 2016 Vincent W. Gardner, MD, FACS, RPVI Fellow, American College of Surgeons Board Certified, American Board
UNDERSTANDING VEIN PROBLEMS
 UNDERSTANDING VEIN PROBLEMS Varicose Veins, Chronic Venous Insufficiency, and DVT Do You Have a Vein Problem? Have you noticed pain or swelling in your legs? Do your symptoms worsen when you re sitting
UNDERSTANDING VEIN PROBLEMS Varicose Veins, Chronic Venous Insufficiency, and DVT Do You Have a Vein Problem? Have you noticed pain or swelling in your legs? Do your symptoms worsen when you re sitting
Address: Left Leg. other: Nails: thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal thick yellow brittle fungus abnormal
 South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
South West Regional Wound Care Toolkit: Interdisciplinary Lower Leg Assessment Form Instructions for use: Competent/ Proficient/ Expert level HCP to complete if lower leg ulcer present or risk of ulcer
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING II VNRS B85 ASSESSING CLIENTS WITH PERIPHERAL VASCULAR AND LYMPHATIC DISORDERS
 MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING II VNRS B85 ASSESSING CLIENTS WITH PERIPHERAL VASCULAR AND INTRODUCTION: Clients with disorders of the peripheral vascular and lymphatic system experience a wide variety of circulatory
MEDICAL SURGICAL NURSING II VNRS B85 ASSESSING CLIENTS WITH PERIPHERAL VASCULAR AND INTRODUCTION: Clients with disorders of the peripheral vascular and lymphatic system experience a wide variety of circulatory
Reducing the Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) whilst in hospital and following your discharge home
 Reducing the Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) whilst in hospital and following your discharge home 1 Part of: South Tyneside and Sunderland Healthcare Group Introduction This leaflet explains what Deep
Reducing the Risk of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) whilst in hospital and following your discharge home 1 Part of: South Tyneside and Sunderland Healthcare Group Introduction This leaflet explains what Deep
Patient Information. Venous Insufficiency and Varicose Veins
 Patient Information Venous Insufficiency and Varicose Veins What is a Varicose Vein? Gitter Vein Institute-revised 3/8/2016 2 Frequently Asked Questions What is the difference between varicose and spider
Patient Information Venous Insufficiency and Varicose Veins What is a Varicose Vein? Gitter Vein Institute-revised 3/8/2016 2 Frequently Asked Questions What is the difference between varicose and spider
VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT
 VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT Lucy Stopher, A/CNS Vascular Surgery ...it is best to think of a wound not as a disease, but rather as a manifestation of disease. Joe McCulloch In order
VASCULAR WOUNDS PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND MANAGEMENT Lucy Stopher, A/CNS Vascular Surgery ...it is best to think of a wound not as a disease, but rather as a manifestation of disease. Joe McCulloch In order
Person s Name: ID Number: Date:
 South West Regional Wound Care Program Person s Name: ID Number: Interdisciplinary Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Assessment Form MEDICAL HISTORY: Question Year diabetes diagnosed: Characteristics of onset
South West Regional Wound Care Program Person s Name: ID Number: Interdisciplinary Diabetic/Neuropathic Foot Assessment Form MEDICAL HISTORY: Question Year diabetes diagnosed: Characteristics of onset
A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management.
 A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management. Poster No.: C-1030 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. J. Ley, E.
A review of lymphoscintigraphy - what constitutes a positive result and how this affects the patients management. Poster No.: C-1030 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. J. Ley, E.
ARIZONA VEIN & VASCULAR CENTER
 ARIZONA VEIN & VASCULAR CENTER New Year, New You January-March 2015 Highlighted Articles: What is this painful bump on the back of my heel? By: Dr. Ronald D. Holgado What is Lymphedema? By: Dr. Baljeet
ARIZONA VEIN & VASCULAR CENTER New Year, New You January-March 2015 Highlighted Articles: What is this painful bump on the back of my heel? By: Dr. Ronald D. Holgado What is Lymphedema? By: Dr. Baljeet
The Lymphatic System. Oedema (Edema) Lymphoedema (Lymphedema)
 The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
The Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is similar to the blood system and has just as many vessels - but they contain lymph, which is clear and so cannot be seen (unless a suitable dye is injected).
Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT)
 Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT) Day Surgery Unit Patient information leaflet What is Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT)? Endovenous laser therapy is a treatment for varicose veins which seals the vein
Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT) Day Surgery Unit Patient information leaflet What is Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT)? Endovenous laser therapy is a treatment for varicose veins which seals the vein
Venous thrombosis is common and often occurs spontaneously, but it also frequently accompanies medical and surgical conditions, both in the community
 Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Venous Thrombosis Venous Thrombosis It occurs mainly in the deep veins of the leg (deep vein thrombosis, DVT), from which parts of the clot frequently embolize to the lungs (pulmonary embolism, PE). Fewer
Sores That Will Not Heal
 Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Sores That Will Not Heal Introduction Some sores have trouble healing on their own. Sores that will not heal are a common problem. Open sores that will not heal are also known as wounds or skin ulcers.
Varicose Vein Cyanoacrylate Glue treatment
 The South West s premier independent healthcare and cosmetic clinic Varicose Vein Cyanoacrylate Glue treatment Varicose veins are a sign of underlying venous insufficiency and affect 20 30% of adults.
The South West s premier independent healthcare and cosmetic clinic Varicose Vein Cyanoacrylate Glue treatment Varicose veins are a sign of underlying venous insufficiency and affect 20 30% of adults.
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome(PTS) Conservative Treatment Options
 Post-Thrombotic Syndrome(PTS) Conservative Treatment Options Dr. S. Kundu Scarborough Hospital-General Division Scarborough Vascular Group Toronto Endovascular Centre The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough
Post-Thrombotic Syndrome(PTS) Conservative Treatment Options Dr. S. Kundu Scarborough Hospital-General Division Scarborough Vascular Group Toronto Endovascular Centre The Vein Institute of Toronto Scarborough
Varicose veins. Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute
 Varicose veins Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute You have been diagnosed as having varicose veins. This leaflet explains more about varicose veins and answers some of the most frequently
Varicose veins Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute You have been diagnosed as having varicose veins. This leaflet explains more about varicose veins and answers some of the most frequently
OHTAC Recommendation. Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins. Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009
 OHTAC Recommendation Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009 April 2010 Issue Background The Ontario Health Technology
OHTAC Recommendation Endovascular Laser Treatment for Varicose Veins Presented to the Ontario Health Technology Advisory Committee in November 2009 April 2010 Issue Background The Ontario Health Technology
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions
 Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Total Hip Replacement Rehabilitation: Progression and Restrictions The success of total hip replacement (THR) is a result of predictable pain relief, improvements in quality of life, and restoration of
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information
 Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Guideline Quick View: Venous Thromboembolism
 Guideline Quick View: Venous Thromboembolism The AORN Guideline Quick View is a key component of Guideline Essentials, a suite of online implementation tools designed to help the perioperative team translate
Guideline Quick View: Venous Thromboembolism The AORN Guideline Quick View is a key component of Guideline Essentials, a suite of online implementation tools designed to help the perioperative team translate
End-Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Lymphedema
 End-Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
End-Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Appendix D: Leg Ulcer Assessment Form
 Nursing Best Practice Guideline Appendix D: Ulcer Assessment Form Person Completing Assessment: Date: Client Name: Caf # CM# VON ID #: District CCAC ID # Address Telephone Home: Work: Date of Birth Y/M/D:
Nursing Best Practice Guideline Appendix D: Ulcer Assessment Form Person Completing Assessment: Date: Client Name: Caf # CM# VON ID #: District CCAC ID # Address Telephone Home: Work: Date of Birth Y/M/D:
The Venous System. Discussion paper prepared for. The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal. October Prepared by:
 Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal October 2004 Prepared by: Robert Maggisano MD, FRCS(C), FACS, GKHS Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Chief of
Discussion paper prepared for The Workplace Safety and Insurance Appeals Tribunal October 2004 Prepared by: Robert Maggisano MD, FRCS(C), FACS, GKHS Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Chief of
Varicose Veins: A guide for patients
 Varicose Veins: A guide for patients Varicose Veins: A guide for patients What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are swollen, twisted and unsightly veins (usually on the legs) that look lumpy and bluish
Varicose Veins: A guide for patients Varicose Veins: A guide for patients What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are swollen, twisted and unsightly veins (usually on the legs) that look lumpy and bluish
Leg ulcer assessment and management
 Leg ulceration The views expressed in this presentation are solely those of the presenter and do not necessarily represent the views of Smith & Nephew. Smith & Nephew does not guarantee the accuracy or
Leg ulceration The views expressed in this presentation are solely those of the presenter and do not necessarily represent the views of Smith & Nephew. Smith & Nephew does not guarantee the accuracy or
Chief complaint. A mass at right chest
 Chief complaint A mass at right chest Present illness This 1-year-5-month-old girl had a mass at right side chest since one month ago. flat and not tender at first In the recent 2 days, the mass enlarged
Chief complaint A mass at right chest Present illness This 1-year-5-month-old girl had a mass at right side chest since one month ago. flat and not tender at first In the recent 2 days, the mass enlarged
Lymphoedema Network Northern Ireland. Advice for patients at risk of developing lymphoedema
 Lymphoedema Network Northern Ireland Advice for patients at risk of developing lymphoedema Conditions related to increased risk of developing lymphoedema: High risk referral criteria Do you have any of
Lymphoedema Network Northern Ireland Advice for patients at risk of developing lymphoedema Conditions related to increased risk of developing lymphoedema: High risk referral criteria Do you have any of
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND COMPRESSION GARMENTS. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Equipment/ Supplies
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 8 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
Clinical Examination of VASCULAR PATIENTS. Stephanie Hirst & Alexander Sunde
 Clinical Examination of VASCULAR PATIENTS Stephanie Hirst & Alexander Sunde Goals of Medical History To record the patient s symptoms at time of presentation. To organize the events which have lead to
Clinical Examination of VASCULAR PATIENTS Stephanie Hirst & Alexander Sunde Goals of Medical History To record the patient s symptoms at time of presentation. To organize the events which have lead to
Wound Classification. Overview
 Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
Overview Jeffrey A. Niezgoda, MD FACHM, MAPWCA, CHWS Review of Initial Wound Care Consultation Rational for Classification Wound Appearance Wound Etiology Management Algorithms Initial Wound Care Consult
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND COMPRESSION GARMENTS. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Equipment/ Supplies
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Documentation Tips Job Aid
 Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
Determining Wound Diagnosis and Job Aid 1 Coding Is this a traumatic injury from an accident? 800 Codes - Injury Section of the Coding Manual Code by specific site of injury. Only use for accidents or
This information is intended as a general guide only. Please ask if you have any questions relating to this information.
 Foam Sclerotherapy (Varicose vein injections) Vascular Surgery This information is intended as a general guide only. Please ask if you have any questions relating to this information. Varicose Veins Veins
Foam Sclerotherapy (Varicose vein injections) Vascular Surgery This information is intended as a general guide only. Please ask if you have any questions relating to this information. Varicose Veins Veins
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth
 Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Spider & Varicose Veins It s more common than you think
 Spider & Varicose Veins It s more common than you think Spider veins are small blue or red veins shaped like tree branches that often appear later in life on the calves and ankles. Varicose veins are veins
Spider & Varicose Veins It s more common than you think Spider veins are small blue or red veins shaped like tree branches that often appear later in life on the calves and ankles. Varicose veins are veins
Alberta Health. Alberta Aids to Daily Living Compression Stockings and Lymphedema Sleeves Ready Made Benefits Policy & Procedures Manual
 Alberta Health Alberta Aids to Daily Living Compression Stockings and Lymphedema Sleeves Ready Made Benefits Policy & Procedures Manual March 7, 2016 Revision History Description Date N-03, N 05 and N-07:
Alberta Health Alberta Aids to Daily Living Compression Stockings and Lymphedema Sleeves Ready Made Benefits Policy & Procedures Manual March 7, 2016 Revision History Description Date N-03, N 05 and N-07:
Company Introduction
 Company Introduction We are the leading company of various pneumatic medical systems since 1986. We are exporting our products to 60 countries. We provide the products with high quality and competitive
Company Introduction We are the leading company of various pneumatic medical systems since 1986. We are exporting our products to 60 countries. We provide the products with high quality and competitive
V11 Endovenous Ablation
 For the personal patients of Bruce Braithwaite V11 Endovenous Ablation What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins in the leg. They are common, affecting up to 3 in 10 people.
For the personal patients of Bruce Braithwaite V11 Endovenous Ablation What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are enlarged and twisted veins in the leg. They are common, affecting up to 3 in 10 people.
Ligation with Stripping
 Ligation with Stripping Understanding Problem Leg Veins Do your legs feel tired and achy at the end of the day? Have you stopped wearing shorts because you don t like the way your legs look? Vein problems
Ligation with Stripping Understanding Problem Leg Veins Do your legs feel tired and achy at the end of the day? Have you stopped wearing shorts because you don t like the way your legs look? Vein problems
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital
 Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
Steven Hadesman, MD Chief Medical Officer, MeridianRx Internal Medicine Physician, St. John Hospital Deep Venous Thrombosis Varicose Veins Venous insufficiency Phlebitis Lymphedema Elephantiasis nostras
Velcro Compression Devices
 Velcro Compression Devices Joseph A. Caprini, MD, MS, FACS, RVT, FACCWS Louis W. Biegler Chair of Surgery NorthShore University HealthSystem, Evanston, IL Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Chicago
Velcro Compression Devices Joseph A. Caprini, MD, MS, FACS, RVT, FACCWS Louis W. Biegler Chair of Surgery NorthShore University HealthSystem, Evanston, IL Clinical Professor of Surgery University of Chicago
Determine the patients relative risk of thrombosis. Be confident that you have had a meaningful discussion with the patient.
 Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
Patient Assessment :Venous History, Examination and Introduction to Doppler and PPG Dr Louis Loizou The 11 th Annual Scientific Meeting and Workshops of the Australasian College of Phlebology Tuesday 18
Varicose Vein Surgery. Varicose Vein Surgery
 What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are veins under the skin of the legs which have become widened, bulging and twisted. They are very common and do not cause medical problems in most people. Normally
What Are Varicose Veins? Varicose veins are veins under the skin of the legs which have become widened, bulging and twisted. They are very common and do not cause medical problems in most people. Normally
Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema. Sue Lawrance
 Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema Sue Lawrance Abstract Lymphoedema and chronic lower limb oedema are conventionally treated with multi-layer bandaging,
Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema Sue Lawrance Abstract Lymphoedema and chronic lower limb oedema are conventionally treated with multi-layer bandaging,
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Questionnaire for Lipedema Patients
 Questionnaire for Lipedema Patients Name Date of diagnosis Date Name of physician making diagnosis Do you also have lymphedema? What areas of the body are affected? Outside of thighs Inner thighs Knees
Questionnaire for Lipedema Patients Name Date of diagnosis Date Name of physician making diagnosis Do you also have lymphedema? What areas of the body are affected? Outside of thighs Inner thighs Knees
CASE STUDY. Potential conflict of interest:
 CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
Veins that are firm to
 Intravenous cannulation is a technique in which a cannula is placed inside a vein to provide venous access. Venous access allows sampling of blood as well as administration of fluids, medications, parenteral
Intravenous cannulation is a technique in which a cannula is placed inside a vein to provide venous access. Venous access allows sampling of blood as well as administration of fluids, medications, parenteral
Case report. Your Diagnosis?
 Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Case report 18 year Male Panel beater referred with a tibial shin syndrome with pain of 6 months. Pain over the anterolateral aspect of leg, bilateral and is precipitated walking 10 minutes. Your Diagnosis?
Autosana. Compression bandages for phlebology, lymphology and orthopaedic use
 Autosana Compression bandages for phlebology, lymphology and orthopaedic use Autosana Foam, long-stretch compression bandage VERSATILE HIGH NUMBER OF OPEN PORES KIND TO THE SKIN Overview Composition High-grade,
Autosana Compression bandages for phlebology, lymphology and orthopaedic use Autosana Foam, long-stretch compression bandage VERSATILE HIGH NUMBER OF OPEN PORES KIND TO THE SKIN Overview Composition High-grade,
Hip Pain. Anatomy of the hip
 Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
Hip Pain Anatomy of the hip The hip is a ball and socket joint, the ball is on the head of femur (the top of the thigh bone) and the socket (acetabulum) is a part of the pelvis. It s surrounded by tendons
VeinOPlus Vascular Peripheral Vascular & Wound Therapy Device
 VeinOPlus Vascular Peripheral Vascular & Wound Therapy Device Calf Muscle Pump Dysfunction Therapy Increases blood flow, accelerates wound healing, and improves CVD and PAD symptoms Tomorrow s Technology
VeinOPlus Vascular Peripheral Vascular & Wound Therapy Device Calf Muscle Pump Dysfunction Therapy Increases blood flow, accelerates wound healing, and improves CVD and PAD symptoms Tomorrow s Technology
