A QUANTITATIVE METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF INHIBITORS OF ACID GASTRIC SECRETION IN THE RAT
|
|
|
- Alberta Harvey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1958), 13, 118. A QUANTITATIVE METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF INHIBITORS OF ACID GASTRIC SECRETION IN THE RAT BY M. N. GHOSH* From the Department of Pharmacology, University College, London (RECEIVED SEPTEMBER 13, 1957) Assays of inhibitors of gastric secretion are described by a method of recording continuously acid gastric secretion in the rat. A number of doses of inhibitor comprising several assay blocks can be administered in one preparation and complete assays with known fiducial limits performed with only two rats. Assays were carried out with vasopressin against secretion induced by histamine, and with atropine, methanthelinium and atropine methylnitrate against secretion induced by methacholine. Methods for the quantitative assay of inhibitors of gastric secretion have been described for the rat and the dog. Visscher, Seay, Tazelaar, Veldkamp, and Vander Brook (1954) and Shea (1956) have described assay methods in the pylorus-ligated rat in which the reduction of spontaneous secretion due to an inhibitory drug is measured. Each rat receives only one dose of inhibitor, but by combining several experiments quantitative results can be obtained. In the pouch dog an essentially similar principle is used (Benjamin, Rosiere, and Grossman, 195). A submaximal secretion (Code, Hightower, and Hallenbeck, 1951) is induced by an intravenous infusion of histamine, and this is reduced by the inhibitory drug. Although in this assay the same animal can be used repeatedly, only one dose of inhibitor is administered in each test so that a number of experiments must be combined to give a quantitative result. The present method, which is based on the procedure for continuous recording of gastric secretion described in a previous paper (Ghosh and Schild, 1958), differs from the earlier methods in two main respects. (i) Several doses of inhibitor are administered in succession so that each experiment comprises one or more assay blocks. (ii) The inhibitory drug is given before the stimulant and is thus used to prevent rather than counteract the effect of the latter. In this respect the method resembles the " double histamine " test. The administration of several doses of inhibitor in the same preparation introduces certain complications * Present address: Department of Pharmacology, Calcutta School of Tropical Medicine, 2F Garcha Ist Lane, Calcutta 19. arising from persistence of the effect of the inhibitor, but it eliminates sources of error due to animal variation and renders the assay considerably more efficient than previous methods in terms of numbers of animals used. Two inhibitors were studied, vasopressin and atropine. Posterior pituitary hormones are known to inhibit gastric secretion (Dodds, Hills, Noble, and Williams, 1935; Gray, Culmer, Wells, and Wieczorowski, 1941; Wolf and Wolff, 1947) probably by their vasoconstrictor action (Cutting, Dodds, Noble, and Williams, 1937), and we have found vasopressin to be an effective inhibitor of histamine secretion in rats. The inhibitory effect of vasopressin is readily reversible so that in an assay there is relatively little interference from one dose to the next. The effects of atropine and related compounds, tested against methacholine stimulation, are less readily reversible and tend to be cumulative. This difficulty can be partly overcome by the use of a design in which the dose order is taken into account as recently shown by Rocha e Silva and Rothschild (1956): two atropine-like compounds, methanthelinium (Banthine) and atropine methylnitrate (Eumydrin) were assayed against atropine and it was possible to perform a statistically controlled assay with only two rats for each comparison. METHODS The method of Ghosh and Schild (1958) for the continuous recording of acid gastric secretion in the rat was used. Briefly, this method is based on perfusion of the stomach of the rat anaesthetized with
2 ASSAY OF INHIBITORS urethane with a dilute sodium hydroxide solution and graphical registration of the ph of the emerging fluid. All drugs were administered intravenously, usually by single injections, in a volume of.2 to.4 ml. Antagonists were usually injected immediately before the agonists. The following drugs were used: histamine acid phosphate (activity expressed in terms of base), vasopressin (Pitressin), atropine sulphate, atropine methylnitrate (Eumydrin), and methanthelinium (Banthine, Searle). RESULTS Effect of Vasopressin on Acid Secretion Induced by Histamine When an intravenous injection of vasopressin is administered together with or immediately before an intravenous injection of histamine, the normal secretory effect of histamine is inhibited. Fig. 1 shows (on the original circular chart) the V3+H i OF GASTRIC SECRETION 119 Three experiments with several doses of vasopressin in the same preparation were carried out. In one preparation three randomized blocks of four doses of vasopressin were administered and in the others two blocks of four doses. One of the assays with two blocks is shown in Fig. 3. A dose of 5 /Lg. histamine was combined with 14, 2, 42, and 6 mu. vasopressin and the experiment was treated as an assay of two solutions of vasopressin. Fig. 4 shows the regression lines for " standard " and " unknown." The activity ratio estimated from these results is 1.32 as against a true ratio of Analysis of variance of this experiment showed that: (i) the mean square for regression is significant at the 5% level though not at the 1% level; (ii) there is no evidence of deviation from parallelism; (iii) there is no significant difference between the two assay blocks. In the other two experiments similar results were obtained. The mean FIG. 1.-Effect of intravenous injections of 2,ug. histamine (H) and 2 mug. histamine with vasopressin (VIL= 12 mu., V2= 17 mu., Vs=34 mu., Vi=48 mu.), on ph of stomach perfusate. Original circular chart. Distance between horizontal lines= -5 ph units, between solid vertical lines= 1 hr. In this and subsequent figures the ordinate represents the ph of the stomach perfusate following intravenous injection of drugs in the rat under urethane at 3. effect of four doses of vasopressin injected together with histamine, each dose of inhibitor being followed by a dose of histamine alone. The inhibitory effect of vasopressin is graded according to dose. A graded effect could generally be obtained within a four-fold dose range. In Fig. 2a the responses from individual experiments are joined, and in Fig. 2b linear regression lines are fitted to each set of experimental points; with one exception, the effect increases with dose and the slopes of the regression lines are approximately parallel. Quantitative Assays with Vasopressin These assays were planned as assays with known concentrations of vasopressin. One or more blocks of four doses were administered in the same rat. At the beginning of each experiment, one or two control injections of histamine were given followed by combined injections of a constant dose of histamine with varying doses of vasopressin. 4. U Dose vasopressin (mu.) 1, , Dose vasopressin (mu.) FIG. 2.-Dose/effect curves for vasopressin. The ordinate represents reduction of secretory effect by histamine+vasopressin as compared with histamine alone. In the upper panel responses from individual experiments are joined. In the lower panel calculated regression lines were fitted. Numerals in circles correspond to regression lines.
3 12 M. N. GHOSH. 6 m 4. 4 FIo. 3.-T with a 6 mu A B C D C D A B square for regression was significant at P<.5 * *b * * * * * in one assay and at P<.1 in the other. There was no significant deviation from parallelism and no significant difference between successive assay 5 blocks. In another series a dose of histamine was interpolated between doses of vasopressin to allow for more complete recovery from inhibition. This series involved three rats, each of which received four doses of vasopressin, the 3 combined results being treated as a single assay. In the analysis of variance regression was highly I significant; there was no evidence of deviation Hr. from parallelism. Differences between assay rwo blocks of 4 doses of vasopressin injected together blocks were near-significant. Since each set of constant dose of histamine (5 pg.). A=2 mu.; B- four doses was administered to a different animal, J.;C= 14 mu.; D=42 mu. vasopressin. differences between assay blocks were to be expected. In conclusion, then, all the assays gave a satisfactory regression and no deviation from parallelism. The true and estimated activity ratios and the values for X in the four assays are _- A shown in Table I. The X value expresses the TABLE I TRUE'AND ESTIMATED ACTIVITIES AND A VALUES OF FOUR ASSAYS WITH HISTAMINE AND VASOPRESSIN -a C UI- E c L 2! i._ cn E I.6 _ 1.4 _ 1.2 r l--tb I..-o - I I 1.15 Log dose 1.62 FIG. 4.-Regression lines fitted to vasopressin assay of Fig. 3. Expt. No. e/ Activities True Estimated 194 (without recovery dose) ,,,,, " (with recovery dose) ) intrinsic precision of the experiment. All assays gave reasonable X values: the lowest value (highest precision) was obtained in the preparations which were allowed to recover between doses of inhibitor. Effect of Atropine-like Substances on Methacholine-stimulated Secretion Three experimental designs were employed to assay atropine-like substances against methacholine: 1. Continuous infusion of methacholine and inhibition by intermittent doses of atropine. When methacholine was administered by slow constant infusion in doses of 1 to 4 jtg./hr., it produced a continuous stimulation of acid secretion which could be counteracted by injections of atropine. Fig. 5 shows the effects of intravenous injections of doses of atropine ranging from.3 to.3,tg. in a preparation stimulated by constant infusion of methacholine. Although graded effects could be obtained in this way with atropine the responses were irregular, and after large doses A
4 ASSAY OF INHIBITORS OF GASTRIC SECRETION 121 I u METHACHOLINE 18pg/HOUR Hr. Fio. 5.-Inhibition of acid secretion by single intravenous doses of atropine superimposed on a slow intravenous infusion of methacholine. 3 was estimated as.47 jtg. Table II shows other estimates of this quantity with methacholine and carbachol used as a stimulant. The activity of homatropine tested in this way was about 2 times less than that of atropine. 3. Intermittent injections of methacholine and two atropine-like TABLE II DOSE OF ANTAGONIST REQUIRED TO REDUCE EFFECT OF AGONIST TO THAT OF HALF THE DOSE Stimulant Antagonist Antagonist Dose (pg.) Methacholine Atropine.76 Carbachol Methacholine Homatropine *5 substances. In these experiments constant doses of methacholine were combined with varying doses of atropine-like drugs. The experiments were carried out as assays in a Latin square design. In one assay, consisting of a comparison of methanthelinium and atropine by a 4 x 4 Latin square design, only two rats were used, each receiving two blocks of four doses. Within each block consecutive doses of antagonist were administered, but recovery doses of methacholine were interpolated between the blocks. The results of this assay are shown in Table III and one of the TABLE III RESULTS OF THE 2+2 ASSAY OF METHANTHELINIUM AND ATROPINE Dose Maximum Deflexion of ph in Total (pg.) Different Groups Atropine * Methanium Sum of groups the curve failed to return to the base line. Furthermore, continuous intravenous injection of methacholine produced considerable bronchial secretion, dyspnoea, and other toxic effects. 2. Intermittent injections of methacholine and atropine; dose-ratio assay. Single intravenous injections of methacholine produce a transient secretory response graded according to dose (Ghosh and Schild, 1958). Atropine reduces this response and the antagonism can be measured in terms of the dose of antagonist required to reduce the effect of a double dose of methacholine to that of a single dose. (This corresponds to a pa2 determination, except that the antagonist is measured as a dose instead of as a concentration.) An experiment of this kind is shown in Fig. 6. Methacholine (2.5 jug.) produced a deflexion of about 1 ph unit, whereas 5 ug. produced a larger deflexion. Atropine (.2 Mig.) caused a slight reduction of the effect of 5 jug. methacholine and.4 jug. a larger reduction. By graphical extrapolaltion, the dose of atropine which reduced the two experiments is illustrated in Fig. 7. The ratio effec t of methacholine to that of half the dose between large and small doses of inhibitor was three, and each time the larger dose pro- ATR. O4pg ATR.O2 pg duced a greater inhibition than the 2M M M \2M 2M M \2M smaller dose. The analysis of variance 7 of this assay (Table IV) gave highly significant F values for regression and Fie. 6 for difference between rats. The F value for dose order does not quite reach the 5% level, but it is sufficiently large to suggest that position in the block is impor- * tant. Fig. 8 shows that the regression lines for the two antagonists are parallel. Hr. The activity ratio for methanthelinium 6.-Inhibition of methacholine-induced secretion by simultaneous injection and atropine was 1.7 with 5% fiducial - nof,. raded -doses of Ga..w_ atroine. w-flimits of 8.2 and
5 122 This result is almost the opposite of that reported by Benjamin et al. (195), who estimated the activity ratio of methanthelinium and atropine against histamine secretion in the dog (Table VII). In view of this discrepancy the comparison was repeated, this time with one rat for each block and with doses of methacholine after each dose TABLE IV ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE OF THE RESULTS OF THE ASSAY OF METHANTHELINIUM AND ATROPINE Sum of Mean Source of Variation Squares d.f. Square F Between rats P<-1 Between groups P>-5 Dose order P>-5 Between " standard" and " unknown" Regression P<*1 Deviation from parallelism Error Total M. N. GHOSH of inhibitor. This assay gave an activity ratio of 1.7 (fiducial limits 4.4 to 29.1 at 5% level), thus confirming the previous results. The X values and fiducial limits in this and the previous assays are shown in Table V. The X value of the second methanthelinium assay was considerably larger than that of the first, suggesting that the more time-consuming method involving recovery doses had no special advantages in this instance. In another assay a comparison of atropine methylnitrate and atropine was carried out. This assay involved two rats, one of which TABLE V ESTIMATED ACTIVITY, FIDUCIAL LIMITS AND A VALUE OF THREE ATROPINE-LIKE DRUGS Fiducial Assay Activity Limits A Ratio (P=-95) Methanthelinium/atropine (without recovery dose). 2 rats Methatelnu/atropine (w~ith recovery dose). 4 rats Atropine methylnitrate/atropine (without recovery dose). 2 rats Fio. 7.-Part of Latin square assay of methanthelinium and atropine. The antagonists were injected together with a constant dose of methacholine (5 jpg.). M=methacholine 5 pug.; A=atropine 1 pg.+m; B=atropine 3 pg.+m; C=methanthelinium -3 pg. +M; D=methanthelinium -1 pg. +M. Each large horizontal division corresponds to -5 ph units. TABLE VI ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE OF THE RESULTS OF THE ASSAY OF ATROPINE METHYLNITRATE AND ATROPINE Sum of Mean Source of Variation Squares d.f. Square F Between groups P< -1 Dose order P>-5 Between " standard" and " unknown" -2-2 Regression P< -1 Deviation from parallelism P>-5 Error Total v~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. _gss... g~itt _ZZrZ 1 ti D.. VEg g! - ROW,~~~~~~~~~~~ '1St... v I.i Dose in fig FIo. 8.-Regression lines fitted to assay of Fig. 7. ATR Atropine; BAN= Methanthelmium FIG. 9.-Partofassay of atropine and atropine methylnitrate. Three blocks of 4 doses injected in the same rat. M-methacholine 1#g.; A=atropine mothylnitrate -3 pg.+m; B=atropine -3 pg.+m; C=atropine -9 pg.+m; D=atropine methylnitrate -1 Pg.+M.
6 ASSAY OF INHIBITORS OF GASTRIC SECRETION E e L. ar.8 C I Doses in jsg. FIG. 1.-Regression lines fitted to assay of Fig. 9. received one block and the other three blocks of four doses. The latter part of the assay is illustrated in Fig. 9. It shows a cumulative effect of successive doses of inhibitor which at first sight would seem to invalidate the result. Analysis of variance, however, shows that the result is nevertheless valid, since the F value for regression is highly significant and there is no significant deviation from parallelism (Fig. 1) (Table VI). The activity ratio of atropine methylnitrate and atropine was 3.1 with fiducial limits 2. and 4.8 at the 5% level. DISCUSSION The object of this work has been to devise statistically valid assays for inhibitors of gastric secretion making use of the continuous perfusion method described in an earlier paper (Ghosh and Schild, 1958). In this paper only inhibitors with a transient action are discussed. Assays of longlasting inhibitors of the urogastrone type will be discussed elsewhere (Ghosh, Gregory, and Schild, unpublished observations). TABLE VII ACTIVITY RATIOS FOR SECRETORY INHIBITORS Vasopressin is an example of a short-lasting inhibitor whose effect is probably due to vasoconstriction. A series of doses of vasopressin constituting one or more assay blocks can be given in the same preparation with relatively little interference from one dose to the next, although the more consistent results (lower X values) obtained by interpolating doses of histamine suggest that interference between successive doses of inhibitor is not completely eliminated. But lower X values have to be balanced against loss of time, and, in this sense, the method with the interpolated doses of histamine is less efficient. Atropine-like drugs produce more persistent effects than vasopressin, but it is nevertheless possible to administer repeated doses in one preparation and perform a satisfactory assay. Estimates of relative activity and fiducial limits could be obtained by the use of only two rats for a complete assay. In spite of interaction between successive doses the dose/response relation of the inhibitor is not obliterated; in each experiment the larger dose produced a significantly greater effect than the smaller. A Latin square design was adopted in order to equalize dose order and thus correct to some extent for persistence of effects. This design seemed justified, since in the analysis of variance the mean square for dose order considerably exceeds error; although the F ratio does not reach the 5% level of significance. In terms of number of animals required to achieve a given degree of accuracy the present assay method is much more efficient than the assay method in the pylorus-ligated rat. The efficiency of an assay can be expressed by n/x2 where n is the number of doses administered to one animal. In the present assays average values for n and X are 8 and.16. No X values have been published for the pylorusligation method, but a rough estimate on the basis of the published results of Visscher et al. (1954) gives a value of X =.85 with n = 1. The ratio of efficiencies of the two methods thus works out at 19. Inhibitor Administration Stimulant Preparation Activity RatioReenc Reference Methanthelinium/atropine Subcutaneous Histamine Gastric secretion (dog) 1/2 Benjamin et al. (195) Intravenous Spontaneous Gastric secretion (pylorus-ligated 1/1 Visscher et al. (1954) secretion rat) Methacholine Gastric secretion (rat stomach) 1 Present work Carbachol Salivary secretion (cat) 2-2 Johnson and Wood (1954) Atropine methyl iodide/atropine Intramuscular Spontaneous Gastric secretion (pylorus-ligated 1 Shea (1956) secretion rat) Atropine methylnitratelatropine Intravenous Methacholine Gastric secretion (rat) 3-1 Present work
7 124 M. N. GHOSH Such calculations have of course only limited validity, since different assay methods are not interchangeable and may give widely different results, especially when different stimulants are used. This is shown in Table VII, which gives the activity ratios for methanthelinium-atropine and methylatropine-atropine as secretory inhibitors when tested by different quantitative methods. REFERENCES Benjamin, F. B., Rosiere, C. E., and Grossman, M. I. (195). Gastroenterology, 15, 727. Code, C. F., Hightower, N. C., Jr., and Hallenbeck, G. A. (1951). Ibid., 19, 254. Cutting, W. C., Dodds, E. C., Noble, R. L., and Williams, P. C. (1937). Proc. roy. Soc., 123, 27. Dodds, E. C., Hills, G. M., Noble, R. L., and Williams, P. C. (1935). Lancet, 1, 199. Ghosh, M. N., and Schild, H.. (1958). Brit. J. Pharmacol., 13, 54. Gray, J. S., Culmer, C. U., Wells, J. A., and Wieczorowski, E. (1941). Amer. J. Physiol., 134, 623. Johnson, E. A., and Wood, D. R. (1954). Brit. J. Pharmacol., 9, 218. Rocha e Silva, M., and Rothschild, A. M. (1956). Ibid., 11, 252. Shea, S. M. (1956). Ibid., 11, 171. Visscher, F. E., Seay, P. H., Tazelaar, Jr., A. P., Veldkamp, W., and Vander Brook, M. J. (1954). J. Pharmacol., 11, 188. Wolf, S., and Wolff, H. G. (1947). Human Gastric Function, 2nd ed., p. 79. New York: Oxford University Press.
THE INHIBITORY EFFECT OF STILBOESTROL ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN CATS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 3S9. THE INHIBITORY EFFECT OF STILBOESTROL ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN CATS BY K. N. OJHA* AND D. R. WOOD From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 3S9. THE INHIBITORY EFFECT OF STILBOESTROL ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN CATS BY K. N. OJHA* AND D. R. WOOD From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, University of
QUANTITATIVE ASSAYS OF OXYTOCIC DRUGS ON THE HUMAN POSTPARTUM UTERUS
 Brit. J. Pharnacol. (1958), 13, 27. QUANTITATIVE ASSAYS OF OXYTOCIC DRUGS ON THE HUMAN POSTPARTUM UTERUS BY P. R. MYERSCOUGH AND H.. SCHILD From the Obstetric Unit, University College Hospital, and the
Brit. J. Pharnacol. (1958), 13, 27. QUANTITATIVE ASSAYS OF OXYTOCIC DRUGS ON THE HUMAN POSTPARTUM UTERUS BY P. R. MYERSCOUGH AND H.. SCHILD From the Obstetric Unit, University College Hospital, and the
described by Chang and Gaddum (1933). It consists in estimating the activity
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1947), 2, 251. THE USE OF DRUG ANTAGONISTS FOR THE IDENTIFICATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS BY H. 0. SCHILD From the Department of Pharmacology, University College, London (Received
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1947), 2, 251. THE USE OF DRUG ANTAGONISTS FOR THE IDENTIFICATION AND CLASSIFICATION OF DRUGS BY H. 0. SCHILD From the Department of Pharmacology, University College, London (Received
WELS~~~~ THE mode of action of acetyl choline upon the isolated ventricular strip
 THE ANTAGONISM OF ACETYL CHOLINE BY ATROPINE. BY A. J. CLARK. (From the Pharmacological Department, University College, London.) THE mode of action of acetyl choline upon the isolated ventricular strip
THE ANTAGONISM OF ACETYL CHOLINE BY ATROPINE. BY A. J. CLARK. (From the Pharmacological Department, University College, London.) THE mode of action of acetyl choline upon the isolated ventricular strip
might be due to a direct action on the thyroid, like that of the thiouracil
 288 J. Physiol. (1953) I20, 288-297 COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF THIOURACIL, THY- ROXINE AND CORTISONE ON THE THYROID FUNCTION OF RABBITS BY N. B. MYANT* From the Department of Clinical Research, University
288 J. Physiol. (1953) I20, 288-297 COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF THIOURACIL, THY- ROXINE AND CORTISONE ON THE THYROID FUNCTION OF RABBITS BY N. B. MYANT* From the Department of Clinical Research, University
RELEASE OF HISTAMINE INTO GASTRIC VENOUS BLOOD FOLLOWING INJURY BY ACETIC OR SALICYLIC ACID
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 52, No.3 Printed in U.S.A. RELEASE OF HISTAMINE INTO GASTRIC VENOUS BLOOD FOLLOWING INJURY BY ACETIC OR SALICYLIC ACID LEONARD R. JOHNSON
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 52, No.3 Printed in U.S.A. RELEASE OF HISTAMINE INTO GASTRIC VENOUS BLOOD FOLLOWING INJURY BY ACETIC OR SALICYLIC ACID LEONARD R. JOHNSON
ACTIVITY USING RATS A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC. subject and a variety of stimuli employed. In the examination of new compounds
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1946), 1, 255. A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC ACTIVITY USING RATS BY 0. L. DAVIES, J. RAVENT6S, AND A. L. WALPOLE From Imperial Chemical Industries, Ltd., Biological Laboratories,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1946), 1, 255. A METHOD FOR THE EVALUATION OF ANALGESIC ACTIVITY USING RATS BY 0. L. DAVIES, J. RAVENT6S, AND A. L. WALPOLE From Imperial Chemical Industries, Ltd., Biological Laboratories,
COMPARATIVE EFFECTS OF GASTRIN II AND HISTAMINE ON PEPSIN SECRETION IN MAN
 GASTROENTEROLOGY COpyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 52, No.5 Printed in U.S.A. COMPARATIVE EFFECTS OF GASTRIN II AND ISTAMINE ON PEPSIN SECRETION IN MAN G. M. MAKLOUF, M.B., PD., M.R.C.P.,
GASTROENTEROLOGY COpyright 1967 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 52, No.5 Printed in U.S.A. COMPARATIVE EFFECTS OF GASTRIN II AND ISTAMINE ON PEPSIN SECRETION IN MAN G. M. MAKLOUF, M.B., PD., M.R.C.P.,
PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF THE ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE OF
 Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Br. J. Pharmac. (198). 71, 35-4 PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY OF TH ANOCOCCYGUS MUSCL OF TH DOG A.R. DHPOUR, M.A. KHOYI, H. KOUTCHKI & M.R. ZARRINDAST Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 119-125. LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS BY N. ASSARSON AND N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden (Received October 8, 1963)
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 119-125. LEAKAGE OF TRANSMITTERS IN SALIVARY GLANDS BY N. ASSARSON AND N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden (Received October 8, 1963)
MECHANISM BY WHICH FAT IN THE UPPER SMALL INTESTINE INHIBITS GASTRIC ACID
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.3 Printea in U.S.A. MECHANISM BY WHICH FAT IN THE UPPER SMALL INTESTINE INHIBITS GASTRIC ACID H. T. DEBAS, M.D., B. S. BEDI, M.B.,
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.3 Printea in U.S.A. MECHANISM BY WHICH FAT IN THE UPPER SMALL INTESTINE INHIBITS GASTRIC ACID H. T. DEBAS, M.D., B. S. BEDI, M.B.,
ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN DOGS
 Gut, 960,, 345. THE EFFECT OF AN ADRENAL INHIBITOR (SU 4885) ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN DOGS BY J. W. McINTOSH, N. ANDERSON, H. L. DUTHIE, and A. P. M. FORREST From the University Department of Surgery, Western
Gut, 960,, 345. THE EFFECT OF AN ADRENAL INHIBITOR (SU 4885) ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN DOGS BY J. W. McINTOSH, N. ANDERSON, H. L. DUTHIE, and A. P. M. FORREST From the University Department of Surgery, Western
INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT
 Brit. J. Phawmacol. (1951), 6, 289. INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT BY From the Pharmacological Laboratory, University of St. Andrews, Medical School, Dundee (Received February 2, 1951)
Brit. J. Phawmacol. (1951), 6, 289. INSULIN AND THE SUPRARENAL GLAND OF THE RABBIT BY From the Pharmacological Laboratory, University of St. Andrews, Medical School, Dundee (Received February 2, 1951)
RESPONSE TO HISTAMINE OF THE BLOOD VESSELS OF THE HUMAN FOREARM
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1954), 9, 413. THE EFFECTS OF ANTIHISTAMINE SUBSTANCES ON THE RESPONSE TO HISTAMINE OF THE BLOOD VESSELS OF THE HUMAN FOREARM BY F. DUFF AND R. F. WHELAN From the Department of Physiology,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1954), 9, 413. THE EFFECTS OF ANTIHISTAMINE SUBSTANCES ON THE RESPONSE TO HISTAMINE OF THE BLOOD VESSELS OF THE HUMAN FOREARM BY F. DUFF AND R. F. WHELAN From the Department of Physiology,
vasopressin in an uncontrolled trial on patients with DI (Crawford, Kennedy & Hill, 1960), rats with
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1977), 59, 11-16 POTNTIATION OF TH RSPONS TO VASOPRSSIN (PITRSSIN) BY TRATMNT WITH A COMBINATION OF CHLORPROPAMID AND CHLOROTHIAZID IN BRATTLBORO RATS WITH HRDITARY HYPOTHALAMIC DIABTS
Br. J. Pharmac. (1977), 59, 11-16 POTNTIATION OF TH RSPONS TO VASOPRSSIN (PITRSSIN) BY TRATMNT WITH A COMBINATION OF CHLORPROPAMID AND CHLOROTHIAZID IN BRATTLBORO RATS WITH HRDITARY HYPOTHALAMIC DIABTS
The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal
 Gut, 1971, 12, 158-163 The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal and gallbladder contractions A. G. JOHNSON From the Department of Surgery, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The
Gut, 1971, 12, 158-163 The effect of metoclopramide on gastroduodenal and gallbladder contractions A. G. JOHNSON From the Department of Surgery, Charing Cross Hospital Medical School, London SUMMARY The
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES
 HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
liberated in the body is probably less than 1 part in a million. The
 547.435-292: 577.153 KINETICS OF CHOLINE ESTERASE. By A. J. CLARK, J. RAVENT6S, E. STEDMAN, and ELLEN STEDMAN. From the Departments of Pharmacology and Medical Chemistry, University of Edinburgh. (Received
547.435-292: 577.153 KINETICS OF CHOLINE ESTERASE. By A. J. CLARK, J. RAVENT6S, E. STEDMAN, and ELLEN STEDMAN. From the Departments of Pharmacology and Medical Chemistry, University of Edinburgh. (Received
ACETYLCHOLINE, HISTAMINE AND GASTRIN
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1977), 61, 279-284 THE EFFECT OF ATROPINE ON ACID SECRETION STIMULATED BY ACETYLCHOLINE, HISTAMINE AND GASTRIN IN THE ISOLATED WHOLE STOMACH OF THE RAT K.T. BUNCE, GILLIAN F. MARSH & M.E.
Br. J. Pharmac. (1977), 61, 279-284 THE EFFECT OF ATROPINE ON ACID SECRETION STIMULATED BY ACETYLCHOLINE, HISTAMINE AND GASTRIN IN THE ISOLATED WHOLE STOMACH OF THE RAT K.T. BUNCE, GILLIAN F. MARSH & M.E.
THE ACTION OF ANTISYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE URINARY EXCRETION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 380. THE ACTION OF ANTISYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE URINARY EXCRETION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE BY B. G. BENFEY, G. LEDOUX, AND M. SEGAL From the Department ofpharmacology,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 380. THE ACTION OF ANTISYMPATHOMIMETIC DRUGS ON THE URINARY EXCRETION OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE BY B. G. BENFEY, G. LEDOUX, AND M. SEGAL From the Department ofpharmacology,
SIMULTANEOUS MEASUREMENT OF THE PANCREATIC AND BILIARY RESPONSE TO CCK AND SECRETIN
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:403-407, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. SIMULTANEOUS MEASUREMENT OF THE PANCREATIC AND BILIARY RESPONSE TO CCK AND SECRETIN Primate
GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:403-407, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. SIMULTANEOUS MEASUREMENT OF THE PANCREATIC AND BILIARY RESPONSE TO CCK AND SECRETIN Primate
CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 505. CAROTID SINUS REFLEX AND CONTRACTION OF THE SPLEEN BY ROBERT L. DRIVER AND MARTHE VOGT From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Edinburgh (Received July 12,
EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
(Received 14 February 1951)
 510 J. Physiol. (I95I) II4, 5I0-54 PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF THE SWEAT RESPONSE TO ADRENALINE IN MAN BY T. M. CHALMERS jam C. A. KEELE From the Department of Pharmacology, Middlesex Hospital Medical
510 J. Physiol. (I95I) II4, 5I0-54 PHYSIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF THE SWEAT RESPONSE TO ADRENALINE IN MAN BY T. M. CHALMERS jam C. A. KEELE From the Department of Pharmacology, Middlesex Hospital Medical
Effect of acid infusion into various levels of the intestine on gastric and pancreatic secretion in the cat
 Gut, 1969, 10, 749-753 Effect of acid infusion into various levels of the intestine on gastric and pancreatic secretion in the cat S. J. KONTUREK, J. DUBIEL, AND B. GABRY9 From the Department of Medicine,
Gut, 1969, 10, 749-753 Effect of acid infusion into various levels of the intestine on gastric and pancreatic secretion in the cat S. J. KONTUREK, J. DUBIEL, AND B. GABRY9 From the Department of Medicine,
Gastrin derivatives investigated for secretory potency and for changes in gastric mucosal histamine formation
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 473-477. Gastrin derivatives investigated for secretory potency and for changes in gastric mucosal histamine formation ELSA ROSENGREN AND S. E. SVENSSON Institute of Physiology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 38, 473-477. Gastrin derivatives investigated for secretory potency and for changes in gastric mucosal histamine formation ELSA ROSENGREN AND S. E. SVENSSON Institute of Physiology,
SUPERSENSITIVITY OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND FOLLOWING EXCLUSION OF THE POSTGANGLIONIC PARASYMPATHETIC NEURONE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 356. SUPERSENSITIVITY OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND FOLLOWING EXCLUSION OF THE POSTGANGLIONIC PARASYMPATHETIC NEURONE BY N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1960), 15, 356. SUPERSENSITIVITY OF THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND FOLLOWING EXCLUSION OF THE POSTGANGLIONIC PARASYMPATHETIC NEURONE BY N. EMMELIN From the Institute of Physiology, University
Since, for many months after section of the right vagus in the neck,
 THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
THE INFLUENCE OF THE VAGUS ON THE ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Part II. The effect of cutting the vagus upon sugar tolerance. BY G. A. CLARK. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Sheffield University.) IN Part
SALICYLIC ACIDS AS METABOLIC STIMULANTS IN
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1958), 13, 419. THE RELATIVE POTENCIES OF SOME SUBSTITUTED SALICYLIC ACIDS AS METABOLIC STIMULANTS IN THE INTACT RAT BY MURIEL M. ANDREWS From the Clinical Chemotherapeutic Research
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1958), 13, 419. THE RELATIVE POTENCIES OF SOME SUBSTITUTED SALICYLIC ACIDS AS METABOLIC STIMULANTS IN THE INTACT RAT BY MURIEL M. ANDREWS From the Clinical Chemotherapeutic Research
DAVID J. COWLEY, M.D., CHARLES F. CODE, M.D., PH.D., AND RENE FIASSE, M.D.
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. GASTRC MUCOSAL BLOOD FLOW DURNG SECRETORY NHBTON BY GASTRN PENTAPEPTDE AND GASTRONE DAVD J. COWLEY, M.D., CHARLES
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. GASTRC MUCOSAL BLOOD FLOW DURNG SECRETORY NHBTON BY GASTRN PENTAPEPTDE AND GASTRONE DAVD J. COWLEY, M.D., CHARLES
GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which
 ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
ON THE ACTION OF PHLORHIZIN ON THE KIDNEY. By E. B. MAYRS. (From the Department of Pharmacology, Edinburgh.) GLUCOSE is the most important diffusible substance in the blood which is completely held back
blood-vessels of the isolated perfused lungs of the rat. Both Hirakawa
 547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
547.435-292: 547.781.5: 577.174.5: 612.215 THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE, ACETYLCHOLINE, AND HIS- TAMINE ON THE LUNGS OF THE RAT. By P. FoGGIE. From the Physiology Department, University of Edinburgh. (Received
EFFECT OF THYROID HORMONES ON HISTAMINE FORMATION IN THE RAT
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 17, 479-487. EFFECT OF THYROID HORMONES ON HISTAMINE FORMATION IN THE RAT BY T. BJURO, H. WESTLING AND H. WETTERQVIST From the Department of Clinical Physiology, University
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 17, 479-487. EFFECT OF THYROID HORMONES ON HISTAMINE FORMATION IN THE RAT BY T. BJURO, H. WESTLING AND H. WETTERQVIST From the Department of Clinical Physiology, University
THE EFFECTS OF ION CHANGES ON THE CONTRACTION OF THE RAT UTERUS STIMULATED BY OXYTOCIN
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 16, 45-49. THE EFFECTS OF ION CHANGES ON THE CONTRACTION OF THE RAT UTERUS STIMULATED BY OXYTOCIN BY P. J. BENTLEY AND ELEANOR McEWEN From the Department of Physiology, The
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 16, 45-49. THE EFFECTS OF ION CHANGES ON THE CONTRACTION OF THE RAT UTERUS STIMULATED BY OXYTOCIN BY P. J. BENTLEY AND ELEANOR McEWEN From the Department of Physiology, The
THE ANTIDIURETIC RESPONSE TO AND EXCRETION OF PITUITARY (POSTERIOR LOBE) EXTRACT IN MAN, WITH REFERENCE TO THE ACTION OF NICOTINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1951), 6, 471. THE ANTIDIURETIC RESPONSE TO AND EXCRETION OF PITUITARY (POSTERIOR LOBE) EXTRACT IN MAN, WITH REFERENCE TO THE ACTION OF NICOTINE BY GEORGE P. BURN AND R. SINGH GREWAL
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1951), 6, 471. THE ANTIDIURETIC RESPONSE TO AND EXCRETION OF PITUITARY (POSTERIOR LOBE) EXTRACT IN MAN, WITH REFERENCE TO THE ACTION OF NICOTINE BY GEORGE P. BURN AND R. SINGH GREWAL
PEPSIN SECRETION DURING DAMAGE BY ETHANOL AND SALICYLIC ACID
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyriht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No. 3 Printed in U.S. A. PEPSIN SECRETION DURING DAMAGE BY ETHANOL AND SALICYLIC ACID LEONARD R. JOHNSON, PH.D. Department of Physiology
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyriht 1972 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 62. No. 3 Printed in U.S. A. PEPSIN SECRETION DURING DAMAGE BY ETHANOL AND SALICYLIC ACID LEONARD R. JOHNSON, PH.D. Department of Physiology
principles. laboratory [Stehle & Fraser, 1935] and contains 200 pressor units and (Received 20 November 1940)
![principles. laboratory [Stehle & Fraser, 1935] and contains 200 pressor units and (Received 20 November 1940) principles. laboratory [Stehle & Fraser, 1935] and contains 200 pressor units and (Received 20 November 1940)](/thumbs/92/110006249.jpg) .#Lil-RAFY 4 233 J. Physiol. (I94I) IOO, 233-238 4 V>6x2.492.8:577.I52 I THE RATIO BETWEEN ANTIDIURETIC AND PRESSOR ACTIVITIES OF POSTERIOR PITUITARY EXTRACT SUBJECTED TO MILD HYDROLYSIS BY A. M. FRASER
.#Lil-RAFY 4 233 J. Physiol. (I94I) IOO, 233-238 4 V>6x2.492.8:577.I52 I THE RATIO BETWEEN ANTIDIURETIC AND PRESSOR ACTIVITIES OF POSTERIOR PITUITARY EXTRACT SUBJECTED TO MILD HYDROLYSIS BY A. M. FRASER
THE EFFECT OF SOME OXIMES IN SARIN POISONING
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1958), 13, 399. THE EFFECT OF SOME OXIMES IN SARIN POISONING BY From the Chemical Defence Experimental Establishment, Porton Down (RECEIVED JUNE 14, 1958) The effects of monoisonitrosoacetone
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1958), 13, 399. THE EFFECT OF SOME OXIMES IN SARIN POISONING BY From the Chemical Defence Experimental Establishment, Porton Down (RECEIVED JUNE 14, 1958) The effects of monoisonitrosoacetone
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
SYNTHETIC OXYTOCIN AS AN ANTAGONIST OF EXPERIMENTAL CARDIAC ANOXIC CHANGES IN RABBITS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 17, 218-223. SYNTHETIC OXYTOCIN AS AN ANTAGONIST OF EXPERIMENTAL CARDIAC ANOXIC CHANGES IN RABBITS BY K. I. MELVILLE AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1961), 17, 218-223. SYNTHETIC OXYTOCIN AS AN ANTAGONIST OF EXPERIMENTAL CARDIAC ANOXIC CHANGES IN RABBITS BY K. I. MELVILLE AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology
 Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
EFFECT OF VAGOTOMY ON PANCREATIC SECRETION STIMULATED BY ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS SECRETIN
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright,. 1971 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 60, No. 3 P>-inted in U. S. A. EFFECT OF VAGOTOMY ON PANCREATIC SECRETION STIMULATED BY ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS SECRETIN HARRIS J.
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright,. 1971 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 60, No. 3 P>-inted in U. S. A. EFFECT OF VAGOTOMY ON PANCREATIC SECRETION STIMULATED BY ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS SECRETIN HARRIS J.
estimates were made of the normal rate of increase in plasma urea over periods in skin and in plasma, hypertonic sodium chloride solution was
 482 J. Physiol. (I95I) II5, 482-487 THE STTE OF BODY WTER IN THE CT BY M. GRCE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 5 July 1951) In the course of an investigation
482 J. Physiol. (I95I) II5, 482-487 THE STTE OF BODY WTER IN THE CT BY M. GRCE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 5 July 1951) In the course of an investigation
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
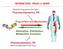 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
glands are reported to have no antidiuretic action) produce a principle gland of some lower vertebrates (teleost fishes, amphibians, reptiles), has
 246 J. Physiol. (I94I) 99, 246-256 577.I74.92:596 THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE PITUITARY ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE THROUGHOUT THE VERTEBRATE SERIES BY H. HELLER1 From the Department of Ph4rmacology, Oxford (Received
246 J. Physiol. (I94I) 99, 246-256 577.I74.92:596 THE DISTRIBUTION OF THE PITUITARY ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE THROUGHOUT THE VERTEBRATE SERIES BY H. HELLER1 From the Department of Ph4rmacology, Oxford (Received
DISTRIBUTION OF HAEMOGLOBIN LEVEL, PACKED CELL VOLUME, AND MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 81-87 DISTRIBUTION OF HAEMOGLOBIN LEVEL, PACKED CELL VOLUME, AND MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION IN WOMEN IN THE COMMUNITY The definition of anaemia in most
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 81-87 DISTRIBUTION OF HAEMOGLOBIN LEVEL, PACKED CELL VOLUME, AND MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION IN WOMEN IN THE COMMUNITY The definition of anaemia in most
Pharmacological analysis of muscarinic receptors coupled to oxyntic cell secretion in the mouse stomach
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1985), 86, 601-607 Pharmacological analysis of muscarinic receptors coupled to oxyntic cell secretion in the mouse stomach J.W. Black & N.P. Shankley The Rayne Institute, King's College
Br. J. Pharmac. (1985), 86, 601-607 Pharmacological analysis of muscarinic receptors coupled to oxyntic cell secretion in the mouse stomach J.W. Black & N.P. Shankley The Rayne Institute, King's College
THE REACTION OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS TO ANGIOTONIN, RENIN, AND OTHER PRESSOR AGENTS* BY RICHARD G. ABELL, ProD., ~
 Published Online: 1 March, 1942 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.75.3.305 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 18, 2018 THE REACTION OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS TO ANGIOTONIN, RENIN, AND OTHER
Published Online: 1 March, 1942 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.75.3.305 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on August 18, 2018 THE REACTION OF PERIPHERAL BLOOD VESSELS TO ANGIOTONIN, RENIN, AND OTHER
THE EFFECT OF SMOKING ON WATER DIURESIS IN MAN 1
 51 612.463.1:615.783.22 THE EFFECT OF SMOKING ON WATER DIURESIS IN MAN 1 By J. M. WALKER (From the Department of Pharmacology, Oxford) NICOTINE is the most widely used drug in this country and its effects
51 612.463.1:615.783.22 THE EFFECT OF SMOKING ON WATER DIURESIS IN MAN 1 By J. M. WALKER (From the Department of Pharmacology, Oxford) NICOTINE is the most widely used drug in this country and its effects
THE ACTION OF PROMETHAZINE (PHENERGAN) DUE TO HISTAMINE IN PROTECTING MICE AGAINST DEATH
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 510. THE ACTION OF PROMETHAZINE (PHENERGAN) IN PROTECTING MICE AGAINST DEATH DUE TO HISTAMINE BY B. N. HALPERN * AND D. R. WOODt From the Clinique Medicale Propedeutique
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1950), 5, 510. THE ACTION OF PROMETHAZINE (PHENERGAN) IN PROTECTING MICE AGAINST DEATH DUE TO HISTAMINE BY B. N. HALPERN * AND D. R. WOODt From the Clinique Medicale Propedeutique
pouches and in Heidenhain pouches the responses to 2-deoxy-D-glucose and to food were established, as were also the responses to gastrin pentapeptide
 J. Physiol. (197), 27, pp. 329-35 329 With 9 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain THE SECRETORY PATTERN OF THREE STOMACH PREPARATIONS IN THE RAT BY S. E. SVENSSON From the Institute of Physiology, University
J. Physiol. (197), 27, pp. 329-35 329 With 9 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain THE SECRETORY PATTERN OF THREE STOMACH PREPARATIONS IN THE RAT BY S. E. SVENSSON From the Institute of Physiology, University
gland, the tongue and the sweat glands of the cat. The submaxillary
 306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
306 547.435-292:6I2.8I7 THE LIBERATION OF ACETYLCHOLINE BY POTASSIUM. BY W. FELDBERG1 AND J. A. GUIMARAIS1,2. (From the National Institute for Medical Research, London, N.W. 3.) (Received November 22,
STIMULANT DRUGS THE COMPARISON OF RESPIRATORY. that amphetamine had a greater awakening effect upon mice than either picrotoxin
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1947), 2, 93. THE COMPARSON OF RESPRATORY STMULANT DRUGS BY From the Wellcome Physiological Research Laboratories, Beckenham, Kent (Received December 11, 1946) Drugs stimulating respiration
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1947), 2, 93. THE COMPARSON OF RESPRATORY STMULANT DRUGS BY From the Wellcome Physiological Research Laboratories, Beckenham, Kent (Received December 11, 1946) Drugs stimulating respiration
Smith, Miller and Grab er(4) state that the maintenance of an efficient
 THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE DIASTOLIC AND SYSTOLIC BLOOD-PRESSURES FOR THE MAINTENANCE OF THE CORONARY CIRCULATION. BY G. V. ANREP AND B. KING. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridge.) IT is generally
and of Kasr-el-Aini, Cairo, Egypt (Received 10 November 1952) METHODS
 419 J. Physiol. (I953) I20, 49-426 RELEASE OF HISTAMINE BY THE LIVER BY G. V. ANREP, G. S. BARSOUM AND M. TALAAT From the Physiological Laboratories, Medical Faculties of Alexandria and of Kasr-el-Aini,
419 J. Physiol. (I953) I20, 49-426 RELEASE OF HISTAMINE BY THE LIVER BY G. V. ANREP, G. S. BARSOUM AND M. TALAAT From the Physiological Laboratories, Medical Faculties of Alexandria and of Kasr-el-Aini,
(Received April 6, 1936)
 275 6I2.26 RESPIRATION AND FUNCTIONAL ACTIVITY BY W. DEUTSCH AND H. S. RAPER (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester) (Received April 6, 1936) IT has long been established that in
275 6I2.26 RESPIRATION AND FUNCTIONAL ACTIVITY BY W. DEUTSCH AND H. S. RAPER (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester) (Received April 6, 1936) IT has long been established that in
to food and histamine
 Gut, 97,, 53-57 Maximal acid response of Pavlov pouches to food and histamine A. MARVIN BROOKS AND MORTON I. GROSSMAN From the Veterans Administration Center and UCLA School of Medicine, Departments of
Gut, 97,, 53-57 Maximal acid response of Pavlov pouches to food and histamine A. MARVIN BROOKS AND MORTON I. GROSSMAN From the Veterans Administration Center and UCLA School of Medicine, Departments of
EFFECTS OF METIAMIDE AND PROPRANOLOL ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN ANESTHETIZED DOGS
 EFFECTS OF METIAMIDE AND PROPRANOLOL ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN ANESTHETIZED DOGS Susumu OKABE, Chen R. HUNG, Koji TAKEUCHI Yoshinobu TAKATA and Keijiro TAKAGI Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty
EFFECTS OF METIAMIDE AND PROPRANOLOL ON GASTRIC SECRETION IN ANESTHETIZED DOGS Susumu OKABE, Chen R. HUNG, Koji TAKEUCHI Yoshinobu TAKATA and Keijiro TAKAGI Department of Chemical Pharmacology, Faculty
ATROPINE AS AN ANTISIALOGOGUE, COMPARED WITH L-HYOSCYAMINE (BELLAFOLINE), SCOPOLAMINE BUTYLBROMIDE (BUSCOPAN) AND OXYPHENONIUM (ANTRENYL)
 Brit. J. Anaesth. (959), 3, 05 ATROPINE AS AN ANTISIALOGOGUE, COMPARED WITH LHYOSCYAMINE (BELLAFOLINE), SCOPOLAMINE BUTYLBROMIDE (BUSCOPAN) AND OXYPHENONIUM (ANTRENYL) BY H. DlAMANT The Ear, Nose and Throat
Brit. J. Anaesth. (959), 3, 05 ATROPINE AS AN ANTISIALOGOGUE, COMPARED WITH LHYOSCYAMINE (BELLAFOLINE), SCOPOLAMINE BUTYLBROMIDE (BUSCOPAN) AND OXYPHENONIUM (ANTRENYL) BY H. DlAMANT The Ear, Nose and Throat
A Memory Model for Decision Processes in Pigeons
 From M. L. Commons, R.J. Herrnstein, & A.R. Wagner (Eds.). 1983. Quantitative Analyses of Behavior: Discrimination Processes. Cambridge, MA: Ballinger (Vol. IV, Chapter 1, pages 3-19). A Memory Model for
From M. L. Commons, R.J. Herrnstein, & A.R. Wagner (Eds.). 1983. Quantitative Analyses of Behavior: Discrimination Processes. Cambridge, MA: Ballinger (Vol. IV, Chapter 1, pages 3-19). A Memory Model for
necessity for an investigation into possible different types of urine acidity. In
 456 J. Physiol. (I947) io6, 456-465 6I2.46i SOME FACTORS AFFECTING THE ACIDITY OF URINE IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 22 February 1947)
456 J. Physiol. (I947) io6, 456-465 6I2.46i SOME FACTORS AFFECTING THE ACIDITY OF URINE IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON From the Department of Physiology, University College, London (Received 22 February 1947)
Optimization of the GeneBLAzer H2 CRE-bla HEK 293T Cell Line
 GeneBLAzer Validation Packet Version No.: 1Sep Page 1 of 5 Optimization of the GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cell Line GeneBLAzer H HEK 93T DA Cells GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cells Catalog Numbers K17
GeneBLAzer Validation Packet Version No.: 1Sep Page 1 of 5 Optimization of the GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cell Line GeneBLAzer H HEK 93T DA Cells GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cells Catalog Numbers K17
capillaries, and a consequent increased transudation, without necessarily altering to any marked extent the total circulation of blood
 612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
612.463.4 THE CONTROL OF THE GLOMERULAR PRESSURE BY VASCULAR CHANGES WITHIN THE ISOLATED MAMMALIAN KIDNEY, DEMONSTRATED BY THE ACTIONS OF ADRENALINE. BY F. R. WINT0N (Beit Memorial Research Fellow). (Depaortment
Wick, Irish, Pauls & MacKay (1947) described a procedure consisting. Gray, Culmer, Wieczorowski & Adkison (1940) because of its similarity to
 J. Phy8iol. (1962), 162, pp. 163-172 163 With 4 txt-figuree Printed in Great Britain THE PREPARATION OF UROGASTRONE BY J. L. MONGAR AND V. M. ROSENOER From the Department of Pharmacology, Univer8ity College
J. Phy8iol. (1962), 162, pp. 163-172 163 With 4 txt-figuree Printed in Great Britain THE PREPARATION OF UROGASTRONE BY J. L. MONGAR AND V. M. ROSENOER From the Department of Pharmacology, Univer8ity College
possibility of a secretion of adrenaline from the suprarenal glands resulting
 355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
355 J Physiol. (I942) IOI, 355-36I 6i2.014.465:577 I74.5 THE EFFECT OF ANAESTHESIA ON THE ADRENALINE CONTENT OF THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS BY P. C. ELMES AND A. A. JEFFERSON From the Department of Pharmacology,
DRUG ANTAGONISM AND AUDIOGENIC SEIZURES IN MICE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 415. DRUG ANTAGONISM AND AUDIOGENIC SEIZURES IN MICE BY C. W. M. WILSON* From La Laboratoire de Physiologie Acoustique, Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique. Jouy-en-Josas,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959), 14, 415. DRUG ANTAGONISM AND AUDIOGENIC SEIZURES IN MICE BY C. W. M. WILSON* From La Laboratoire de Physiologie Acoustique, Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique. Jouy-en-Josas,
MUSCLE TO ANGIOTENSIN 11 AFTER NEPHRECTOMY
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1974), 51, 435439 SPECIFIC SUPERSENSITIVITY OF SMOOTH MUSCLE TO ANGIOTENSIN 11 AFTER NEPHRECTOMY P. MEYER, A. PAPADIMITRIOU & M. WORCEL Physiologie et Pharmacologie, Inserm U7, Hopital
Br. J. Pharmac. (1974), 51, 435439 SPECIFIC SUPERSENSITIVITY OF SMOOTH MUSCLE TO ANGIOTENSIN 11 AFTER NEPHRECTOMY P. MEYER, A. PAPADIMITRIOU & M. WORCEL Physiologie et Pharmacologie, Inserm U7, Hopital
G, radual shrinkage of ciliary processes
 Effect of parasympathomimetic and sympathomimetic drugs on secretion in vitro by the ciliary processes of the rabbit eye Lennart Berggren Secretion teas measured by determining differences in the area
Effect of parasympathomimetic and sympathomimetic drugs on secretion in vitro by the ciliary processes of the rabbit eye Lennart Berggren Secretion teas measured by determining differences in the area
(From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, Cambridge.)
 THE OXYGEN EXCHANGE OF THE SUPRARENAL GLAND. BY K. 0. NEUMAN. (From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, Cambridge.) THIS paper deals with the question of the amount of oxygen taken in by a unit weight of the
THE OXYGEN EXCHANGE OF THE SUPRARENAL GLAND. BY K. 0. NEUMAN. (From the Physiotogicat Laboratory, Cambridge.) THIS paper deals with the question of the amount of oxygen taken in by a unit weight of the
Mitchell (1963) and Szerb (1964) have found that there is an increased. of hyoscine with leptazol is described.
 J. Physiol. (1965), 181, pp. 317-323 317 With 3 text-figures Printed in Great Britain EFFECT OF YOSCINE ON TE OUTPUT OF ACETYLCOLINE INTO PERFUSED CEREBRAL VENTRICLES OF CATS BY R. L. POLAK* From the National
J. Physiol. (1965), 181, pp. 317-323 317 With 3 text-figures Printed in Great Britain EFFECT OF YOSCINE ON TE OUTPUT OF ACETYLCOLINE INTO PERFUSED CEREBRAL VENTRICLES OF CATS BY R. L. POLAK* From the National
UROPEPSIN EXCRETION BY MAN. II. UROPEPSIN EXCRETION
 UROPEPSIN EXCRETION BY MAN. II. UROPEPSIN EXCRETION BY HEALTHY MEN"12 By ROBERT H. BROH-KAHN, CLARENCE J. PODORE, AND I. ARTHUR MIRSKY (From The May Institute for Medical Research,' The Jewish Hospital,
UROPEPSIN EXCRETION BY MAN. II. UROPEPSIN EXCRETION BY HEALTHY MEN"12 By ROBERT H. BROH-KAHN, CLARENCE J. PODORE, AND I. ARTHUR MIRSKY (From The May Institute for Medical Research,' The Jewish Hospital,
Using a technique by which it is possible to study gastro-intestinal absorption
 531 J. Physiol. (I956) I34, 53I-537 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE BY THE INTACT RAT BY P. C. REYNELL AND G. H. SPRAY From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Oxford (Received 30 May
531 J. Physiol. (I956) I34, 53I-537 THE ABSORPTION OF GLUCOSE BY THE INTACT RAT BY P. C. REYNELL AND G. H. SPRAY From the Nuffield Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Oxford (Received 30 May
Histologically the pyloric glands and the glands of Brunner in the. Ivy(7) and his co-workers seem to believe, at the present time, in the
 6I2.323[6I2.33 6I2.OI5.2I THE SMALL INTESTINE AND GASTRIC SECRETION. (With special reference to Brunner's Glands.) BY MARGARET M. MURRAY. (From the Department of Physiology, Bedford College.) EVIDENCE
6I2.323[6I2.33 6I2.OI5.2I THE SMALL INTESTINE AND GASTRIC SECRETION. (With special reference to Brunner's Glands.) BY MARGARET M. MURRAY. (From the Department of Physiology, Bedford College.) EVIDENCE
ASYNCHRONOUS POSTGANGLIONIC FIRING FROM THE CAT SUPERIOR CERVICAL SYMPATHETIC GANGLION TREATED WITH NEOSTIGMINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 20, 214-220. ASYNCHRONOUS POSTGANGLIONIC FIRING FROM THE CAT SUPERIOR CERVICAL SYMPATHETIC GANGLION TREATED WITH NEOSTIGMINE BY C. TAKESHIGE AND R. L. VOLLE From the Department
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 20, 214-220. ASYNCHRONOUS POSTGANGLIONIC FIRING FROM THE CAT SUPERIOR CERVICAL SYMPATHETIC GANGLION TREATED WITH NEOSTIGMINE BY C. TAKESHIGE AND R. L. VOLLE From the Department
closely resembling that following an antidromic impulse [Eccles and
 185 6I2.833. 96 REFLEX INTERRUPTIONS OF RHYTHMIC DISCHARGE. By E. C. HOFF, H. E. HOFF AND D. SHEEHAN1. (New Haven, Conn.) (From the Laboratory of Physiology, Yale University School of Medicine.) (Received
185 6I2.833. 96 REFLEX INTERRUPTIONS OF RHYTHMIC DISCHARGE. By E. C. HOFF, H. E. HOFF AND D. SHEEHAN1. (New Haven, Conn.) (From the Laboratory of Physiology, Yale University School of Medicine.) (Received
BINOCULAR DEPTH PERCEPTION IN SMALL-ANGLE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 662. BINOCULAR DEPTH PERCEPTION IN SMALL-ANGLE STRABISMUS* BY E. J. NAYLOR AND A. STANWORTH Department of Ophthalmology, University of Manchester MEASUREMENTS of the binocular
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1959) 43, 662. BINOCULAR DEPTH PERCEPTION IN SMALL-ANGLE STRABISMUS* BY E. J. NAYLOR AND A. STANWORTH Department of Ophthalmology, University of Manchester MEASUREMENTS of the binocular
PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS. Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. Office: 2B 84
 PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Quantitative aspects of drugs By the end of this lecture, you should: Determine quantitative
PHARMACODYNAMICS II QUANTITATIVE ASPECTS OF DRUGS Ali Alhoshani, B.Pharm, Ph.D. ahoshani@ksu.edu.sa Office: 2B 84 Quantitative aspects of drugs By the end of this lecture, you should: Determine quantitative
6. Unusual and Influential Data
 Sociology 740 John ox Lecture Notes 6. Unusual and Influential Data Copyright 2014 by John ox Unusual and Influential Data 1 1. Introduction I Linear statistical models make strong assumptions about the
Sociology 740 John ox Lecture Notes 6. Unusual and Influential Data Copyright 2014 by John ox Unusual and Influential Data 1 1. Introduction I Linear statistical models make strong assumptions about the
Oxytocic activity. It is stated that 1 c.c. of oxytocin contains 12 units. single, multivalent, active principle, or whether a number of active
 SOME PROPERTIES OF THE SEPARATED ACTIVE PRINCIPLES OF THE PITUITARY (POSTERIOR LOBE). BY J. H. GADDUM (National Institute for Medical Research). EXTRACTS of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland have
SOME PROPERTIES OF THE SEPARATED ACTIVE PRINCIPLES OF THE PITUITARY (POSTERIOR LOBE). BY J. H. GADDUM (National Institute for Medical Research). EXTRACTS of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland have
THE RELATION BETWEEN SEDATION AND BODY TEMPERATURE IN THE MOUSE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1957), 12, 245. THE RELATION BETWEEN SEDATION AND BODY TEMPERATURE IN THE MOUSE BY A. W. LESSIN AND M. W. PARKES From the Biological Laboratories, Research Department, Roche Products
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1957), 12, 245. THE RELATION BETWEEN SEDATION AND BODY TEMPERATURE IN THE MOUSE BY A. W. LESSIN AND M. W. PARKES From the Biological Laboratories, Research Department, Roche Products
Class 5 the neurotransmitters (drugs)
 Victoria September 7th 2017 Class 5 the neurotransmitters (drugs) psychopharmacology: study of the effects of a drug on behavior pharmacokinetics: study of the fate / movement of substances administered
Victoria September 7th 2017 Class 5 the neurotransmitters (drugs) psychopharmacology: study of the effects of a drug on behavior pharmacokinetics: study of the fate / movement of substances administered
augmentation of contractions which was followed by depression. Addition of Hajdu & McDowall (1949) showed that when the contractions of the isolated
 225 J. Physiol. (I954) I25, 225-23I THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON THE RAT DIAPHRAGM PREPARATION DEPRESSED BY EXCESS POTASSIUM BY KATHARINE A. MONTAGU From the Department of Physiology, King's College, London
225 J. Physiol. (I954) I25, 225-23I THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON THE RAT DIAPHRAGM PREPARATION DEPRESSED BY EXCESS POTASSIUM BY KATHARINE A. MONTAGU From the Department of Physiology, King's College, London
THE EFFECT OF SODIUM INTAKE ON THE URINARY HISTAMINE IN ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 453-462. THE EFFECT OF SODIUM INTAKE ON THE URINARY HISTAMINE IN ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS BY T. BJURO AND H. WESTLING* From the Department of Clinical Physiology, University
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 453-462. THE EFFECT OF SODIUM INTAKE ON THE URINARY HISTAMINE IN ADRENALECTOMIZED RATS BY T. BJURO AND H. WESTLING* From the Department of Clinical Physiology, University
ance of the sugar, until at plasma levels of 140 mgm. per cent the creatinine/sugar clearance ratio
 THE RENAL EXCRETION OF CREATININE IN MAN BY JAMES A. SHANNON 1 (From The Department of Physiology, New York University College of Medicine, New York City) In a previous paper the evidence on the excretion
THE RENAL EXCRETION OF CREATININE IN MAN BY JAMES A. SHANNON 1 (From The Department of Physiology, New York University College of Medicine, New York City) In a previous paper the evidence on the excretion
Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction
 SimVessel: Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction The virtual SimVessel Laboratory is for recordings of smooth muscle contractions of small muscle stripes of different
SimVessel: Physiology and pharmacology of smooth muscle contractions a brief introduction The virtual SimVessel Laboratory is for recordings of smooth muscle contractions of small muscle stripes of different
*.bbbb *. * *,,sn. instrumentally and the results to be read as the ballistic deflection. University College, London.)
 THE SUPERNORMAL PHASE IN MUSCULAR CONTRACTION. BY TAKEO KAMADA. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) 6I2.7414 THE isometric response of a muscle to a single
THE SUPERNORMAL PHASE IN MUSCULAR CONTRACTION. BY TAKEO KAMADA. (From the Department of Physiology and Biochemistry, University College, London.) 6I2.7414 THE isometric response of a muscle to a single
THE UPTAKE OF PHOSPHATE BY EXCISED MYCORRHIZAL ROOTS OF THE BEECH
 [296] THE UPTAKE OF PHOSPHATE BY EXCISED MYCORRHIZAL ROOTS OF THE BEECH VII. ACTIVE TRANSPORT OE ^^P FROM FUNGUS TO HOST DURING UPTAKE OE PHOSPHATE EROM SOLUTION BY J. L. HARLEY AND J. K. BRIERLEY Department
[296] THE UPTAKE OF PHOSPHATE BY EXCISED MYCORRHIZAL ROOTS OF THE BEECH VII. ACTIVE TRANSPORT OE ^^P FROM FUNGUS TO HOST DURING UPTAKE OE PHOSPHATE EROM SOLUTION BY J. L. HARLEY AND J. K. BRIERLEY Department
SHORT AND LONG MEMORIES IN OCTOPUS AND THE INFLUENCE OF THE VERTICAL LOBE SYSTEM
 J. Exp. Biol. (1970), 53. 385-393 385 With 4 text-figures fprinted in Great Britain SHORT AND LONG MEMORIES IN OCTOPUS AND THE INFLUENCE OF THE VERTICAL LOBE SYSTEM BY J. Z. YOUNG Department of Anatomy,
J. Exp. Biol. (1970), 53. 385-393 385 With 4 text-figures fprinted in Great Britain SHORT AND LONG MEMORIES IN OCTOPUS AND THE INFLUENCE OF THE VERTICAL LOBE SYSTEM BY J. Z. YOUNG Department of Anatomy,
Pharmacodynamics Dr. Iman Lec. 2
 Pharmacodynamics Dr. Iman Lec. 2 Inverse agonist: drug that produces effects which are opposite to those of the agonist, e.g. β carbolines bind to benzodiazepine receptor leading to stimulation and anxiety
Pharmacodynamics Dr. Iman Lec. 2 Inverse agonist: drug that produces effects which are opposite to those of the agonist, e.g. β carbolines bind to benzodiazepine receptor leading to stimulation and anxiety
ANALYSIS OF THE CENTRAL RESPIRATORY ACTION OF
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1956), 11, 15. ANALYSS OF THE ENTRAL RESPRATORY ATON OF NALORPHNE N DEEREBRATE DOGS BY FREDERK F. KAO AND JULUS BELFORD From the State University of New York, ollege of Medicine at
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1956), 11, 15. ANALYSS OF THE ENTRAL RESPRATORY ATON OF NALORPHNE N DEEREBRATE DOGS BY FREDERK F. KAO AND JULUS BELFORD From the State University of New York, ollege of Medicine at
A METHOD FOR MEASURING THE ACTIVITY OF COMPOUNDS WITH AN ACTIVITY LIKE VITAMIN K AGAINST INDIRECT ANTICOAGULANTS IN RATS
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959),14, 14. A MTHOD FOR MASURING TH ACTIVITY OF COMPOUNDS WITH AN ACTIVITY LIK VITAMIN K AGAINST INDIRCT ANTICOAGULANTS IN RATS BY J. LOWNTHAL AND J. D. TAYLOR From the Department
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1959),14, 14. A MTHOD FOR MASURING TH ACTIVITY OF COMPOUNDS WITH AN ACTIVITY LIK VITAMIN K AGAINST INDIRCT ANTICOAGULANTS IN RATS BY J. LOWNTHAL AND J. D. TAYLOR From the Department
REVERSAL OF NICOTINE ACTION ON THE INTESTINE BY ATROPINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1951), 6, 31 1. REVERSAL OF NICOTINE ACTION ON THE INTESTINE BY ATROPINE BY N. AMBACHE AND J. EDWARDS From the Medical Research Council, Ophthalmological Research Unit, Institute Ophthalmology,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1951), 6, 31 1. REVERSAL OF NICOTINE ACTION ON THE INTESTINE BY ATROPINE BY N. AMBACHE AND J. EDWARDS From the Medical Research Council, Ophthalmological Research Unit, Institute Ophthalmology,
THE MECHANISM OF THE EMETIC ACTION OF SODIUM SALICYLATE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 45-50. THE MECHANISM OF THE EMETIC ACTION OF SODIUM SALICYLATE BY K. P. BHARGAVA, OM CHANDRA AND D. R. VERMA' From the Upgraded Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 21, 45-50. THE MECHANISM OF THE EMETIC ACTION OF SODIUM SALICYLATE BY K. P. BHARGAVA, OM CHANDRA AND D. R. VERMA' From the Upgraded Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics,
The Neurotransmitters
 The Neurotransmitters Thursday September 7, 2017 Notes By: Jeffrey Vocabulary Pharmacokinetics The study of the movement of administered substances within the body Psychopharmacology The study of how drugs
The Neurotransmitters Thursday September 7, 2017 Notes By: Jeffrey Vocabulary Pharmacokinetics The study of the movement of administered substances within the body Psychopharmacology The study of how drugs
6I :6I2.I83 BY ALISON S. DALE. concluded that the apparent vaso-constriction obtained by F r6 hli c h and
 6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
6I2.313.87:6I2.I83 A REVERSED ACTION OF THE CHORDA TYMPANI ON THE VENOUS OUTFLOW FROM THE SUBMAXILLARY GLAND. BY ALISON S. DALE. (From the Physiological Laboratory, Cambridcgel.) INTRODUCTORY. FROiHLICH
(ethanol) suggests that it is similar to the diuresis following ingestion of water.
 435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
435 J. Physiol. (I946) I04, 435-442 6I2.464.I THE EFFECT OF ETHYL ALCOHOL AND SOME OTHER DIURETICS ON CHLORIDE EXCRETION IN MAN BY M. GRACE EGGLETON AND ISABEL G. SMITH, From the Physiology Department,
J. Physiol. (I957) I37, I4I-I53
 141 J. Physiol. (I957) I37, I4I-I53 EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE AND ADRENALINE ON THE ATRIAL RHYTHM IN THE HEART-LUNG PREPARATION BY J. H. BURN, A. J. GUNNING AND J. M. WALKER From the Department of Pharmacology,
141 J. Physiol. (I957) I37, I4I-I53 EFFECTS OF NORADRENALINE AND ADRENALINE ON THE ATRIAL RHYTHM IN THE HEART-LUNG PREPARATION BY J. H. BURN, A. J. GUNNING AND J. M. WALKER From the Department of Pharmacology,
Diversion of bile and pancreatic juices from the duodenum to the jejunum has
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. EFFECT OF EXCLUSION, ACIDIFICATION, AND EXCISION OF THE DUODENUM ON GASTRIC ACID SECRETION AND THE PRODUCTION
GASTROENTEROLOGY Copyright 1969 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 56, No.4 Printed in U.S.A. EFFECT OF EXCLUSION, ACIDIFICATION, AND EXCISION OF THE DUODENUM ON GASTRIC ACID SECRETION AND THE PRODUCTION
(Received 16 July 1976)
 J. Phyeiol. (1977), 270, pp. 29-36 29 With 5 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain THE SECRETION OF PEPSIN BY T. KONDO* AND D. F. MAGEEt From the Creighton University School of Medicine, Department of
J. Phyeiol. (1977), 270, pp. 29-36 29 With 5 text-ftgure8 Printed in Great Britain THE SECRETION OF PEPSIN BY T. KONDO* AND D. F. MAGEEt From the Creighton University School of Medicine, Department of
