Indian J Med Res 117, April 2003, pp R. Guleria, T.R. Singh, S. Sinha, A.K. Padhy*, K. Gupta* & J.N. Pande
|
|
|
- Toby Strickland
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 158 INDIAN J MED RES, APRIL 2003 Indian J Med Res 117, April 2003, pp Effect of inhalation of salbutamol, beclomethasone dipropionate & ipratropium bromide on mucociliary clearance in some patients with chronic stable bronchial asthma R. Guleria, T.R. Singh, S. Sinha, A.K. Padhy*, K. Gupta* & J.N. Pande Departments of Medicine & *Nuclear Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India Received August 16, 2002 Background & objectives: Asthma is now regarded as an inflammatory disease and bronchial inflammation may disrupt mucociliary function. Inhaled drugs may act by improving mucociliary function. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of salbutamol, ipratropium bromide and beclomethasone on mucociliary clearance in patients with chronic stable asthma and to compare the efficacy of these drugs on mucociliary clearance. Methods: Ten patients with chronic stable asthma were enrolled in the study, but two patients did not complete the study. Patients with bronchial asthma were chosen on clinical grounds. 99m Tc phytate radioaerosol generated through a nebulizer, was given to each patient on four days. After each administration the radioactivity over the thorax was constantly measured in sequential frame mode for 120 min. Radioactivity in the thorax was also measured after 24 h. A base-line pulmonary function test with reversibility was obtained. Salbutamol, ipratropium bromide, beclomethasone dipropionate and placebo inhalation were given randomly to each patient on four days. Results: The mean age of patients (n=8) was 36±9.3 yr and mean duration of symptoms was 5±6.6 yr. There was no visual impression that mucociliary clearance was enhanced with any of the drugs. The time activity curves did not show any visually recognisable change in slope. In only one patient the curve tended to show a steeper slope with ipratropium inhalation. In the rest of the patients the curves showed no difference at all with medication when compared with placebo. All the quantitative indices analyzed by two-way ANOVA at the end of one and two hours were comparable for the three test drugs and placebo. None of the three test drugs demonstrated statistically significant mucociliary clearance effect compared with placebo. However, the temporal difference in airways clearance efficiency (ACE) was significant with beclomethasone and ipratropium bromide. Interpretation & conclusion: Inhalation of any of the three drugs tested did not produce any immediate improvement in mucociliary clearance as compared to placebo in patients with stable bronchial asthma suggesting the need for further studies using higher doses of drugs for longer duration in a large sample. Key words Beclomethasone dipropionate - bronchial asthma - ipratropium bromide - mucociliary clearance - radioaerosol - salbutamol Mucociliary clearance is one of the most important defenses of the respiratory tract for the removal of inhaled particles, endogenous cellular debris, and excess secretions from the 158
2 GULERIA et al : MUCOCILIARY CLEARANCE IN CHRONIC STABLE BRONCHIAL ASTHMA 159 tracheobronchial tree 1. The effect of pharmacological agents on the clearance of airways secretions has been debatable. Whether β 2 agonists increase mucociliary clearance in the lungs in vivo is still an unanswered question as studies undertaken are few and the results are conflicting 2-4. Similarly the effect of anti-inflammatory agent on mucociliary clearance is not known. It is presumed that bronchial inflammation may disrupt mucociliary function. It is also possible that increased bronchial inflammation and decreased mucociliary clearance may interact and be mutually exacerbating. Steroid therapy in bronchial asthma helps in recovery by bringing about the resolution of airway inflammation. Oral glucocorticoid therapy has been documented to improve peripheral airways mucus clearance in stable asthma 5. The effect of inhaled steroids on mucociliary clearance is unclear and needs evaluation. Ipratropium bromide, an anticholingergic drug, has been used effectively in the treatment of stable bronchial asthma. One study 6 has demonstrated facilitated clearance following the administration of the drug in healthy subjects. Its effect on mucociliary clearance in bronchial asthma has also been investigated 7,8. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the effect of β 2 agonist (salbutamol), anticholinergic drug (ipratropium bromide) and steroid (beclomethasone) inhalation on mucociliary clearance in patients of stable bronchial asthma. Material & Methods Ten patients with chronic stable asthma attending the Medicine outpatients Department and Chest Clinic of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), New Delhi were enrolled for the study; two patients did not complete the study. The sample was a sample of convenience. Each patient underwent 4 studies on 4 days with a 24h follow up recording. A total of 36 studies was done. As there were resource constraints and each patient work up was quite exhaustive only 10 patients were studied. The study was conducted during 1995 to Patients with bronchial asthma were chosen on clinical grounds. They included non smoking adults with paroxysms of dyspnoea, wheezing and cough, who improved with drug therapy. Chronic stable asthma was defined as patients who were symptom free, had not had a paroxysmal dyspnoeic attack for at least 6 wk prior to the study and were on minimum maintenance bronchodilators. Patients with associated right ventricular failure, arrhythmia, valvular disease etc., and those with respiratory failure and associated acute illness such as febrile illness and acute respiratory tract infection were excluded from the study. Written informed consent for participation in the study was obtained from all the patients. Details of the patients including age, sex, weight, height, history of dyspnoea, cough, wheezing and smoking habits and treatment were recorded. The findings of physical examination were also recorded in a proforma. A chest X-ray was obtained. Patients were advised to stop all the drugs 12 h before the study which was carried out on outpatient basis. Routine spirometry was done with an electronic rolling seal spirometer (PK Morgan, UK). Salbutamol (100 µg/puff), ipratropium bromide (20 µg/puff), beclomethasone dipropionate (100 µg/puff) and placebo inhalation were given to each patient at random on four separate days. Radioaerosol inhalation lung cine-scintigraphy: This was done in the Department of Nuclear Medicine as follows. After a preliminary physical examination on day one to make sure that the patient did not have symptomatic bronchospasm, the patient was made to sit comfortably in a chair and relax for 10 min. 99m Tc phytate radioaerosol generated through BARC (Bhaba Atomic Research Centre, Mumbai) nebuliser was given through a mouth piece during resting tidal volume breathing. The radioaerosol solution used contained 20 mci of radioactivity (half life of 99m Tc is 6 h). The size of aerosol produced by the BARC nebuliser was 0.84 micron in activity median aerodynamic diameter (AMAD) with a geometric standard deviation of Patients were asked to inhale the aerosol for about 3 min so that about 2 mci i.e., one-tenth of the total preparation was deposited inside the thorax. Immediately after this, the patient was given a puff of the test medication from a meter dose inhaler
3 160 INDIAN J MED RES, APRIL 2003 approximately at mid lung volume while performing a slow inspiration from functional residual capacity to total lung capacity in the same sitting position. About 10 sec of breath holding was observed after complete inhalation. The manoeuvre was repeated twice over one minute or so with some quiet breath intervals. Care was taken to see that the proper technique was used while the inhaler was used. Placebo inhaler was used before the procedure to ensure adequate inhalation technique. The patient was then immediately made to lie comfortably in the supine position on the examination table under the Gamma camera. Radioactivity in the thorax was continuously measured in sequential frame mode from anteriorly for 120 min. A total of 120, 60-second frames were stored in the computer. At the end of the recording period, a static emission image was obtained. During the procedure aerosol deposition patterns in the lungs were inspected and, for quantitative analysis the 120 frames were sequentially divided into 8 parts, each representing a sequential 15 min process consisting of 15 original frames. These sequential 15 frames were combined to make one frame. Thus eight new frames were made out of 120 frames in all. Radioactivity in the first new frame covering the initial 15 min after radioaerosol inhalation was the basis for the subsequent calculation and comparison. The patient was called the next day to measure the radioactivity that remained in the thorax at the end of 24 h to find the alveolar deposition ratio. Data analysis: Following correction for background radioactivity and after obtaining a physically half-life corrected time activity curve from the right lung, visual inspection of the time activity curve was done and the following quantitative parameters to assess mucociliary clearance were calculated for each 15 min period for the ciliated airways in the right lung. The left lung was excluded because of possible contamination of radioactivity from the stomach. Considering A = Radioactivity in the extrapulmonary ciliated airway at time t. B = Radioactivity in the intrapulmonary ciliated airways at time t. C = Radioactivity in the poorly ciliated or non ciliated airways and/or the alveoli. T = Total radioactivity. Total radioactivity at o time, To = Ao + Bo + Co In actual calculation the radioactivity in the compartment A was not taken into consideration by obviating measurement of radioactivity in the mediastinal portion. In this case, To = Bo + Co. Because the radioactivity in the alveolar compartment is not cleared, the radioactivity remaining in the lungs at 24 h is defined as the alveolar deposition, Co should be equal to Ct at 24 h. Hence, the equation is To = Bo + Co= Bo + Ct The various parameters to evaluate intrapulmonary mucociliary clearance are shown in Table I. Statistical methods: The data were recorded in a pre deigned proforma and managed on an excel worksheet. All the entries were checked for any error. The quantitative variables were assessed for approximate normality and these were summarized by mean and standard deviation in each group. After checking the variance stability and normality, two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare mean values of quantitative variables between the main effects of drug groups and the time and drug interaction. Since the change in the cine-scintigraphic quantitative parameters was not normally distributed, Kruskal wallis one-way ANOVA followed by Wilcoxon rank sum test with Boneferroni correction were used to compare the various parameters in groups. In this study, P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Results Demographic profile: Of the 10 patients included, 8 (5 males and 3 females) completed the study. The mean age was 36±9.3 yr; all were non smokers, and mean duration of symptoms were 5±6.6 yr. The pulmonary function test showed mean FVC 83±19.8 per cent of predicted, mean FEV ±25.3 per cent of predicted and FEV 1 /FVC per cent was 79.3±20.2.
4 GULERIA et al : MUCOCILIARY CLEARANCE IN CHRONIC STABLE BRONCHIAL ASTHMA 161 Table I. Various parameters to evaluate intrapulmonary mucociliary clearance LRR (%) = Tt X 100 To = amount of radioactivity remaining in the lungs at the time t relative to the total radioactivity initially deposited ADR (%) = Bt X 100 = Tt - Co X 100 To To = percentage of radioactivity initially deposited that has occupied the ciliated airways by time t ARR (%) = Bt X 100 = Tt - Co X 100 Bo To - Co = percentage of radioactivity initially deposited on the ciliated airways that has retained by time t ACE (%) = Bo - Bt X 100 Bo = ARR = percentage of radioactivity deposited on the ciliated airways that has already cleared by time t AIDR (%) = Co / To X 100 Ratio (ALDR) (%) = percentage of the total initial radioactivity deposited in the non-ciliated alveolar space relative to the total radioactivity deposited in the lung LRR, lung retention ratio; ADR, airway deposition ratio; ARR, airway retention ratio; ACE, airways clearance efficiency; AIDR, alveolar deposition; Tt, amount of radioactivity in the lung at time t; To, total amount of radioactivity initially deposited in lung i.e., at time O; Bt, amount of radioactivity present in pulmonary ciliated airways i.e., at time t; Bo, amount of radioactivity initially deposited in pulmonary ciliated airways i.e., at time O; Co, amount of radioactivity initially deposited in non ciliated alveolar space i.e., at time O Radioaerosol inhalation lung cine scintigraphy: There was no visual impression that mucociliary clearance was enhanced with any of the drugs. Time activity curves The time activity curves did not show any visually recognisable change in slope. In one patient the curve tended to show a steeper slope with ipratropium. In the rest of the patients the curves showed no difference when compared with those of placebo or the other drugs. Quantitative indices All the quantitative indices analysed by two-way ANOVA at the end of one and 2 h in asthmatic patients were comparable for placebo and the three test-drug (Table II). However, the temporal differences in all parameters were significant with beclomethasone and ipratropium bromide (Table III). Discussion The study is largely comparable in methodology to those by Isawa et al 9,10 and Lafortuna et al 4. We did continuous recording of radioaerosol clearance for the test period to alleviate any discrepancies in the result that might arise from repositioning of the patients before the Gamma camera. Also, unlike the previous workers 4,9,10 we examined the clearance effect on a separate day with the placebo. This was based on the assumption that giving placebo and test drug on the same day would take a longer time and hence there was a greater chance of getting an error due to inadvertent movement of the patient. Secondly, as there were three test drugs the whole study consisting of the combination of test drug and placebo would have become more cumbersome. Mossberg et al 11 found that tracheobronchial clearance of rapidly inhaled 99 m Tc-labelled Teflon particles in patients with asthma was the same as that in healthy non smokers. Foster et al 12 however noted considerable reduction in the mucus clearance and tracheal mucus velocity in asthmatic patients with symptoms; while Bateman et al 13 showed that mucociliary clearance was significantly poor in asthmatics than in the healthy control groups. Pavia et al 14 and Pakes et al 15 also found impaired mucociliary clearance in asthmatics both in mild, stable disease and in remission, relative to normal volunteers. The degree of impairment of the mucociliary clearance may be related to the degree of severity of the asthmatic attack although cause or effect could not be established. These studies suggest that impairment of mucociliary clearance occurs in stable asthmatics and it possibly increases as the disease worsens.
5 162 INDIAN J MED RES, APRIL 2003 Table II. Radioaerosol lung cine scintigraphic quantitative parameters in bronchial asthma of patients at 1 and 2 h Parameter Placebo Salbutamol Beclomethosone lpratropium LRR 1st h 87.16± ± ± ±9.94 2nd h 75.66± ± ± ±13.08 ADR 1st h 50.66± ± ± ± nd h 39.40± ± ± ±23.05 ARR 1st h 78.58±l6.2l 69.08± ± ±9.77 2nd h 63.97± ± ± ±13.30 ACE 1st h 21.42± ± ± ±9.77 2nd h 35.92± ± ± ±13.29 LRR, lung retention ratio; ADR, airway deposition ratio; ARR, airway retention ratio; ACE, airway clearance efficiency All values are in percentage. Values are shown as mean±sd (n=8) Table III. Change in radioaerosol lung cine scintigraphic quantitative parameters from 1st to 2nd h Parameter Placebo Salbutamol Beclomethosone lpratropium LRR 11.5± ± ±12.4* 9.6±12.2* ADR 11.2± ± ±11.6* 6.8±11.6* ARR -4.7± ± ±11.7* 13.2±10.1* ACE -14.5± ± ±11.7* -14.1±10.2* *P<0.05; LRR, lung retention ratio; ADR, airway deposition ratio; ARR, airway retention ratio; ACE, airway clearance efficiency Values are shown as mean±sd (n=8) It is unclear from the literature whether mucociliary clearance increases with inhaled medication. Studies of the effect of salbutamol on mucociliary clearance in bronchial asthma are limited. In 1986 Isawa et al 9 demonstrated a minimal but significant bronchodilatation followed 7 days treatment with oral salbutamol, but the treatment did not induce any recognisable changes either in the deposition pattern of inhaled aerosol or in mucociliary clearance. Mortensen et al 2 demonstrated significantly increased mucociliary clearance in asthmatics and healthy subjects. They however found no benefit with a dry powder inhaler. We did not find any significant improvement with salbutamol inhalation in the present study. Previous studies on the effect of the ipratropium bromide on mucociliary clearance in healthy subjects 6,16-18 and in patients with bronchial asthma 7,15 have also not shown any significant change. In humans ipratropium is believed not to alter the volumetric and rheologic properties of secretions and it is believed that it does not adversely affect their clearance from the lungs 8. In our study we failed to show improved mucociliary clearance with 40 µg of ipratropium. In only one patient was a steep slope in the time activity curve observed which may not be considered significant because none of the other patients showed any difference in the curves when compared with those of placebo and the other drugs. Perhaps studies on larger number of patients with higher dose of ipratropium might be more indicative. Corticosteroids, by virtue of their ability to suppress inflammation, are acknowledged to play a major role in the management of asthma. It has been suggested that the steroids may improve the mucociliary clearance in patients with airway disease 19. However, studies are very limited. The
6 GULERIA et al : MUCOCILIARY CLEARANCE IN CHRONIC STABLE BRONCHIAL ASTHMA 163 antigen induced fall in tracheal mucus velocity was prevented when budesonide was given in experimental animals 3. It has also been suggested that a delayed improvement in mucociliary clearance in response to oral glucocorticocoid therapy may occur. This is supported by the study of Agnew et al 5. In conclusion, salbutamol, ipratropium bromide and beclomethasone inhalation did not show any immediate improvement in mucociliary clearance over placebo in patients with stable bronchial asthma. It is possible that long-term use may improve mucociliary clearance. Further studies using higher doses of drug for longer durations and on a larger number of patients are required. References 1. Messina MS, O Riordan TG, Smaldone GC. Changes in mucociliary clearance during acute exacerbations of asthma. Am Rev Respr Dis 1991; 143 : Mortensen J, Groth S, Lange P, Hermansen F. Effect of terbutaline on mucociliary clearance in asthmatic and healthy subjects after inhalation from a pressurised inhaler and a dry powder inhaler. Thorax 1991; 46 : O Riordan TG, Mao Y, Otero R, Lopez J, Sabater JR, Abraham WM. Budesonide affects allergic mucociliary dysfunction. J Appl Physiol 1998; 85 : Lafortuna CL, Fazio F. Acute effect of inhaled salbutamol on mucociliary clearance in health and chronic bronchitis. Respiration 1984; 45 : Agnew JE Bateman JR, Pavia D, Clarke SW. Peripheral airways mucus clearance in stable asthma is improved by oral corticosteroid therapy. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir 1984; 20 : Matthys H, Muller M, Konietzko N, Adam WE. Tracheobronchial clearance studies with and without Sch 1000 using 99m Technetium sulphate ( 99m Tc) particles. Postgrad Med J 1975; 51 (Suppl 7) : Bell JA, Bluestein BM, Danta I, Wanner A. Effect of inhaled ipratropium bromide on tracheal mucociliary transport in bronchial asthma. Mt Sinai J Med 1984; 51 : Stresemann E. Total airway resistance (R t ), sputum volume and rheology in patients with chronic bronchitis following treatment with Sch 1000 MDI and placebo. Postgrad Med J 1975; 51 (Suppl 7) : Isawa T, Teshima T, Hirano T, Ebina A, Konno K. Effect of oral salbutamol on mucociliary clearance mechanisms in the lungs. Tohoku J Exp Med 1986; 150 : Isawa T, Teshima T, Hirano T, Ebina A, Anazawa Y, Konno K. Effect of bronchodilation on the deposition and clearance of radioaerosol in bronchial asthma in remission. J Nucl Med 1987; 28 : Mossberg B, Strandberg K, Philipson K, Camner P. Tracheobronchial clearance in bronchial asthma: response to beta-adrenoceptor stimulation. Scand J Respir Dis 1976; 57 : Foster WM, Langenback EG, Bergofsky EH. Lung mucociliary function in man: interdependence of bronchial and tracheal mucus transport velocities with lung clearance in bronchial asthma and healthy subjects. Ann Occup Hyg 1982; 26 : Bateman JRM, Pavia D, Sheahan NF, Agnew JE, Clarke SW. Impaired tracheobronchial clearance in patients with mild stable asthma. Thorax 1983; 38 : Pavia D, Bateman JR, Sheahan NF, Agnew JE, Clarke SW. Tracheobronchial mucociliary clearance in asthma: impairment during remission. Thorax 1985; 40 : Pakes GE, Brogden RN, Heel RC, Speight TM, Avery GS. Ipratropium bromide: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in asthma and chronic bronchitis. Drugs 1980; 20 : Francis RA, Thomson ML, Pavia D, Douglas RB. Ipratropium bromide: mucociliary clearance rate and airway resistance in normal subjects. Br J Dis Chest 1977; 71 : Ruffin RE, Wolff RK, Dolovich MB, Rossman CM, Fitzgerald JD. New house MT. Aerosol therapy with Sch 1000 : a short-term mucociliary clearance in normal and bronchitic subjects and toxicology in normal subjects. Chest 1978; 73 : Konietzko N, Muller N, Adam WE. Studies of mucociliary clearance following the use of ipratropium bromide by healthy individuals and patients with chronic bronchitis. Wien Med Wochenschr 1974; 124 (Suppl 21) : Del Donno M, Bittesnich D, Chetta A, Olivieri D, Lopez-Vidriero MT. The effect of inflammation on mucociliary clearance in asthma: an overview. Chest 2000; 118 : Reprint requests : Dr R. Guleria, Professor, Department of Medicine, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi , India
Lung Physiology and How Aerosol Deposits in the Lungs. 1. Physiological and Anatomical Background
 XA0100097 43 Lung Physiology and How Aerosol Deposits in the Lungs Toyoharu Isawa, M.D. 1. Physiological and Anatomical Background Weibel's morphologic data has been referred to not only for predicting
XA0100097 43 Lung Physiology and How Aerosol Deposits in the Lungs Toyoharu Isawa, M.D. 1. Physiological and Anatomical Background Weibel's morphologic data has been referred to not only for predicting
Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients
 Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Thorax 1987;42:457-461 Effect of particle size of bronchodilator aerosols on lung distribution and pulmonary function in patients with chronic asthma D M MITCHELL, M A SOLOMON, S E J TOLFREE, M SHORT,
Tracheobronchial deposition and clearance in small airways in asthmatic subjects
 Eur Respir J, 1996, 9, 1123 1129 DOI: 1.1183/931936.96.961123 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1996 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Tracheobronchial deposition and
Eur Respir J, 1996, 9, 1123 1129 DOI: 1.1183/931936.96.961123 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1996 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Tracheobronchial deposition and
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences
 International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences www.ijmrhs.com Volume 2 Issue 3 July - Sep Coden: IJMRHS Copyright @2013 ISSN: 2319-5886 Received: 23 th May 2013 Revised: 24 th Jun 2013 Accepted:
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Particle Clearance in Human Bronchial Airways: Comparison of Stochastic Model Predictions with Experimental Data
 Ann. occup. Hyg., Vol. 46, Supplement 1, pp. 329 333, 2002 2002 British Occupational Hygiene Society Published by Oxford University Press DOI: 10.1093/annhyg/mef659 Particle Clearance in Human Bronchial
Ann. occup. Hyg., Vol. 46, Supplement 1, pp. 329 333, 2002 2002 British Occupational Hygiene Society Published by Oxford University Press DOI: 10.1093/annhyg/mef659 Particle Clearance in Human Bronchial
Study of dynamic lung parameters in bronchial Asthma
 20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES
 AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
AEROSOL THERAPY: THE PRACTICALITIES Lester I. Harrison, PhD Section Head, Clinical Pharmacokinetics, 3M Pharmaceuticals, 3M Center 270-3S-05, St. Paul, MN, USA 55144 liharrison@mmm.com Introduction: Horses,
The optimal particle size for beta-adrenergic aerosols in mild asthmatics*
 The optimal particle size for beta-adrenergic aerosols in mild asthmatics* Introduction The treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) has improved considerably with the introduction
The optimal particle size for beta-adrenergic aerosols in mild asthmatics* Introduction The treatment of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD) has improved considerably with the introduction
Effect of selective and non-selective beta blockade on pulmonary function and tracheobronchial mucociliary clearance in healthy subjects
 Thorax 1986;41:31-35 Effect of selective and non-selective beta blockade on pulmonary function and tracheobronchial mucociliary clearance in healthy subjects D PAVIA, JRM BATEMAN, AM LENNARD-JONES, JE
Thorax 1986;41:31-35 Effect of selective and non-selective beta blockade on pulmonary function and tracheobronchial mucociliary clearance in healthy subjects D PAVIA, JRM BATEMAN, AM LENNARD-JONES, JE
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis
Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot Malhi, B.R. Srinivas and Lata Kumar
 Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Defining COPD. Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist
 Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
Defining COPD Georgina Grantham Community Respiratory Team Leader/ Respiratory Nurse Specialist Defining COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a common, preventable and treatable disease
DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES:
 TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
TITLE: Tiotropium Compared with Ipratropium for Patients with Moderate to Severe Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Review of the Clinical Effectiveness DATE: 09 December 2009 CONTEXT AND POLICY
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Nonbronchodilator pulmonary effects
 Nonbronchodilator pulmonary effects Effect of β-adrenergic agonists on mucociliary clearance William D. Bennett, PhD Chapel Hill, NC The mucociliary clearance apparatus, an important defense mechanism
Nonbronchodilator pulmonary effects Effect of β-adrenergic agonists on mucociliary clearance William D. Bennett, PhD Chapel Hill, NC The mucociliary clearance apparatus, an important defense mechanism
Dose-response comparison of ipratropium bromide from a metered-dose inhaler and by jet nebulisation
 Thorax 1983;38:297-301 Dose-response comparison of ipratropium bromide from a metered-dose inhaler and by jet nebulisation SA GOMM, NP KEANEY, LP HUNT, SC ALLEN, TB STRETTON From the Department ofrespiratory
Thorax 1983;38:297-301 Dose-response comparison of ipratropium bromide from a metered-dose inhaler and by jet nebulisation SA GOMM, NP KEANEY, LP HUNT, SC ALLEN, TB STRETTON From the Department ofrespiratory
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 3.01 ANTIASTHMATICS 3.01a BETA 2 AGONIST ASTHMA, CHRONIC BRONCHITIS & EMPHYSEMA Salbutamol Inhaler 100ug/dose [Albuterol] (Ventolin) Salbutamol Sulphate Respirator Solution 0.5% (5mg/ml),
TORCH: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate and Survival in COPD
 TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease By: Dr. Fatima Makee AL-Hakak () University of kerbala College of nursing Out lines What is the? Overview Causes of Symptoms of What's the difference between and asthma?
History & Development
 RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
RSPT 2317 Anticholinergic Bronchodilators () History & Development Prototypical parasympatholytic agent is atropine an alkaloid found naturally in the plants Atropa belladona (nightshade) and Datura species
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
G. Boyd on behalf of a UK Study group
 Eur Respir J, 1995, 8, 1494 1498 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.95.08091494 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1995 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Salmeterol xinafoate in
Eur Respir J, 1995, 8, 1494 1498 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.95.08091494 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1995 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Salmeterol xinafoate in
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD. Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton
 Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Life-long asthma and its relationship to COPD Stephen T Holgate School of Medicine University of Southampton Definitions COPD is a preventable and treatable disease with some significant extrapulmonary
Respiratory Therapy. Medical/Scientific/General Background
 Respiratory Therapy Medical/Scientific/General Background Marketing Europe Dr. Rainer Jakobs PMM Europe 1 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM Europe RT Medical/Scientific/General Background 2 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM
Respiratory Therapy Medical/Scientific/General Background Marketing Europe Dr. Rainer Jakobs PMM Europe 1 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM Europe RT Medical/Scientific/General Background 2 Dr. Rainer Jakobs, PMM
Indian Journal of Basic & Applied Medical Research; September 2013: Issue-8, Vol.-2, P
 Original article: Study of pulmonary function in different age groups Dr.Geeta J Jagia*,Dr.Lalita Chandan Department of Physiology, Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai, India *Author for correspondence: drgrhegde@gmail.com
Original article: Study of pulmonary function in different age groups Dr.Geeta J Jagia*,Dr.Lalita Chandan Department of Physiology, Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai, India *Author for correspondence: drgrhegde@gmail.com
Effect of an extension tube on the bronchodilator efficacy of terbutaline delivered from a metered dose inhaler
 Thorax, 1980, 35, 552-556 Effect of an extension tube on the bronchodilator efficacy of terbutaline delivered from a metered dose inhaler S A GOMM, N P KEANEY, N J P WINSEY, AND T B STRETTON From the Department
Thorax, 1980, 35, 552-556 Effect of an extension tube on the bronchodilator efficacy of terbutaline delivered from a metered dose inhaler S A GOMM, N P KEANEY, N J P WINSEY, AND T B STRETTON From the Department
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(4): 353-59 Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma Praveen Aggarwal*, Onkar Singh**, Jyoti P Wali***, Rohini Handa*, Sada N Dwivedi****, Ashutosh Biswas*****,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(4): 353-59 Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma Praveen Aggarwal*, Onkar Singh**, Jyoti P Wali***, Rohini Handa*, Sada N Dwivedi****, Ashutosh Biswas*****,
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO
 ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
ASTHMA PROTOCOL CELLO Leiden May 2011 1 Introduction This protocol includes an explanation of the clinical picture, diagnosis, objectives, non medical and medical therapy and a scheme for inhaler dosage.
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline Management of COPD Pocket Guide MODULE A: MAAGEMET OF COPD 1 2 Patient with suspected or confirmed COPD presents to primary care [ A ] See sidebar A Perform brief clinical
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Regan EA, Lynch DA, Curran-Everett D, et al; Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) Investigators. Clinical and radiologic disease in smokers with normal spirometry. Published
Supplementary Online Content Regan EA, Lynch DA, Curran-Everett D, et al; Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) Investigators. Clinical and radiologic disease in smokers with normal spirometry. Published
Study No.: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period: Study Design: Centres: Indication: Treatment: Objectives: Primary Outcome/Efficacy Variable:
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
Outline FEF Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications?
 Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
Reduced FEF25-75 in asthma. What does it mean and what are the clinical implications? Fernando Holguin MD MPH Director, Asthma Clinical & Research Program Center for lungs and Breathing University of Colorado
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Spirometry: FEVER DISEASE DIABETES HOW RELIABLE IS THIS? 9/2/2010 BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools
 SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System
 Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
Medications Affecting The Respiratory System Overview Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. It is an intermittent and reversible airflow obstruction that affects the bronchioles. The
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY. This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma.
 ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
ADULT ASTHMA GUIDE SUMMARY This summary provides busy health professionals with key guidance for assessing and treating adult asthma. Its source document Asthma and Respiratory Foundation NZ Adult Asthma
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Roflumilast (Daxas) for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease August 2009 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
Effect of manual percussion on tracheobronchial clearance in patients with chronic airflow obstruction and excessive tracheobronchial secretion
 Thorax 1986;41:448-452 Effect of manual percussion on tracheobronchial clearance in patients with chronic airflow obstruction and excessive tracheobronchial secretion CP VAN DER SCHANS, DA PERS, DS POSTMA
Thorax 1986;41:448-452 Effect of manual percussion on tracheobronchial clearance in patients with chronic airflow obstruction and excessive tracheobronchial secretion CP VAN DER SCHANS, DA PERS, DS POSTMA
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
COPD. Helen Suen & Lexi Smith
 COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
COPD Helen Suen & Lexi Smith What is COPD? Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a non reversible, long term lung disease Characterized by progressively limited airflow and an inability to perform full
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Community COPD Service Protocol
 Community COPD Service Protocol Acknowledgements This protocol is based on the following documents: 1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults
Community COPD Service Protocol Acknowledgements This protocol is based on the following documents: 1. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in adults
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with Boehringer Ingelheim s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data.
 abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
abcd Clinical Study Synopsis for Public Disclosure This clinical study synopsis is provided in line with s Policy on Transparency and Publication of Clinical Study Data. The synopsis which is part of the
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE
 RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
RESPIRATORY CARE IN GENERAL PRACTICE Definitions of Asthma and COPD Asthma is due to inflammation of the air passages in the lungs and affects the sensitivity of the nerve endings in the airways so they
A Study on Effect of Cement Dust on Pulmonary Function Test in Construction Workers
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE A Study on Effect of Cement Dust on Pulmonary Function Test in Construction Workers Amey Paranjape Assistant Professor, Department of TB & Chest, B.K.L.Walawalkar Rural Medical
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE A Study on Effect of Cement Dust on Pulmonary Function Test in Construction Workers Amey Paranjape Assistant Professor, Department of TB & Chest, B.K.L.Walawalkar Rural Medical
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 4, April-2016 1644 Interpretation of Bronchodilator Response for Assessment of Airway Obstruction. Dr.S. meenakshi ABSTRACT:
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Asthma Description. Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways.
 Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
Asthma Asthma Description Asthma is a disease that affects the lungs defined as a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways. Symptoms of asthma In susceptible individuals, this inflammation causes recurrent
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Mannitol dry powder for inhalation (Bronchitol) for cystic fibrosis. April 2008
 Mannitol dry powder for inhalation (Bronchitol) for cystic fibrosis April 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
Mannitol dry powder for inhalation (Bronchitol) for cystic fibrosis April 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not
L. Borgström*, E. Bondesson*, F. Morén**, E. Trofast*, S.P. Newman +
 Eur Respir J, 1994, 7, 69 73 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.94.07010069 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1994 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Lung deposition of budesonide
Eur Respir J, 1994, 7, 69 73 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.94.07010069 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1994 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Lung deposition of budesonide
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL
 THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
THE NEW ZEALAND MEDICAL JOURNAL Vol 120 No 1267 ISSN 1175 8716 Is Salamol less effective than Ventolin? A randomised, blinded, crossover study in New Zealand Catherina L Chang, Manisha Cooray, Graham Mills,
Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients
 Thorax 1988;43:674-678 Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients ANDERS ULLMAN, NILS SVEDMYR From the Department of Clinical
Thorax 1988;43:674-678 Salmeterol, a new long acting inhaled,f2 adrenoceptor agonist: comparison with salbutamol in adult asthmatic patients ANDERS ULLMAN, NILS SVEDMYR From the Department of Clinical
It is recommended that a mask and protective eyewear be worn when providing care to a patient with a cough
 UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
UNIVERSITY HEALTH NETWORK POLICY #: PAGE 1 OF 7 POLICY AND PROCEDURE MANUAL: RESPIRATORY THERAPY DEPT PATIENT CARE SECTION ORIGINAL DATE: 04/03 ISSUED BY: SITE LEADER APPROVED BY: Infection Prevention
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse
 Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
Budesonide treatment of moderate and severe asthma in children: A doseresponse study Soren Pedersen, MD, PhD, and Ove Ramsgaard Hansen, MD Kolding, Denmark Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate
D DAVID PUBLISHING. 1. Introduction
 Journal of Health Science 2 (2014) 591-598 doi: 10.17265/2328-7136/2014.12.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Two Formulations of Ipratropium Bromide (IB) HFA pmdi in Patients with
Journal of Health Science 2 (2014) 591-598 doi: 10.17265/2328-7136/2014.12.004 D DAVID PUBLISHING Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Two Formulations of Ipratropium Bromide (IB) HFA pmdi in Patients with
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Air Flow Limitation. In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation.
 Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Asthma Air Flow Limitation In most serious respiratory disease, a key feature causing morbidity and functional disruption is air flow imitation. True whether reversible, asthma and exercise-induced bronchospasm,
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits
 B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
B/1 Dual-Controller Asthma Therapy: Rationale and Clinical Benefits MODULE B The 1997 National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel guidelines on asthma management recommend a 4-step approach
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness. treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years
 The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
The clinical effectiveness and costeffectiveness of corticosteroids for the treatment of chronic asthma in children under the age of 12 years Submission of evidence from AstraZeneca UK Ltd regarding the
21/03/2011 AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY. Fundamentals of aerosols
 AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Norfolk, UK steve.newman@physics.org
AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY AEROSOL DEPOSITION AND THE ASSESSMENT OF PULMONARY DRUG DELIVERY Steve Newman Scientific Consultant Norfolk, UK steve.newman@physics.org
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized
 DANIEL E. HILLEMAN, PharmD ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To review the role of long-acting bronchodilators in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including the importance of treatment
DANIEL E. HILLEMAN, PharmD ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To review the role of long-acting bronchodilators in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including the importance of treatment
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
Presented by UIC College of Nursing
 Presented by UIC College of Nursing Describe COPD. Identify red flags for a COPD exacerbation. Identify COPD triggers or risk factors. Differentiate between long-acting inhalers and emergency use inhalers.
Presented by UIC College of Nursing Describe COPD. Identify red flags for a COPD exacerbation. Identify COPD triggers or risk factors. Differentiate between long-acting inhalers and emergency use inhalers.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 1/18/2018
 Presented by UIC College of Nursing Describe COPD. Identify red flags for a COPD exacerbation. Identify COPD triggers or risk factors. Differentiate between long acting inhalers and emergency use inhalers.
Presented by UIC College of Nursing Describe COPD. Identify red flags for a COPD exacerbation. Identify COPD triggers or risk factors. Differentiate between long acting inhalers and emergency use inhalers.
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
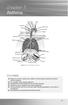 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract
 Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Drugs acting on the respiratory tract Antiasthmatic drugs Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by episodes of reversible airways obstruction due to bronchial hyperresponsiveness;
Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial
 Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial by Vikram Kumar, a P. Ramesh, a Rakesh Lodha, a R. M. Pandey,
Montelukast vs. Inhaled Low-Dose Budesonide as Monotherapy in the Treatment of Mild Persistent Asthma: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled Trial by Vikram Kumar, a P. Ramesh, a Rakesh Lodha, a R. M. Pandey,
SYNOPSIS THIS IS A PRINTED COPY OF AN ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT. PLEASE CHECK ITS VALIDITY BEFORE USE.
 Drug product: Drug substance(s): Document No.: Edition No.: 1 Study code: Accolate Zafirlukast (ZD9188) 9188IL/0138 Date: 02 May 2007 SYNOPSIS A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, -controlled, Parallel
Drug product: Drug substance(s): Document No.: Edition No.: 1 Study code: Accolate Zafirlukast (ZD9188) 9188IL/0138 Date: 02 May 2007 SYNOPSIS A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, -controlled, Parallel
PATIENT INFORMATION Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Fact Sheet
 PATIENT INFORMATION Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Fact Sheet What is COPD? COPD is a general term, which includes the conditions chronic asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is due
PATIENT INFORMATION Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Fact Sheet What is COPD? COPD is a general term, which includes the conditions chronic asthma, chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It is due
Original Article. Hospital, Mahidol University 3) Division of Respiratory Disease and Tuberculosis, Department of Medicine, Faculty of
 Original Article Efficacy of Pursed Lips Breathing with Forced Expiration Techniques and Active Cycle of Breathing Technique on Pulmonary Mucus Clearance in Healthy Subjects J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 22: 247
Original Article Efficacy of Pursed Lips Breathing with Forced Expiration Techniques and Active Cycle of Breathing Technique on Pulmonary Mucus Clearance in Healthy Subjects J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 22: 247
Airway deposition and airway effects of antiasthma drugs delivered from metered-dose inhalers
 Eur Respir J 1997; 10: 2127 2138 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.97.10092127 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 REVIEW Airway deposition
Eur Respir J 1997; 10: 2127 2138 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.97.10092127 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1997 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 REVIEW Airway deposition
Clinical & Experimental Allergy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 1 10 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03814.x c 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd Effect of inhaled dust mite allergen on regional particle deposition and mucociliary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 1 10 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03814.x c 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd Effect of inhaled dust mite allergen on regional particle deposition and mucociliary
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended.
 Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Bricanyl () DK/W/0017/pdWS/001 Rapporteur: Denmark Finalisation procedure
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Bricanyl () DK/W/0017/pdWS/001 Rapporteur: Denmark Finalisation procedure
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of the Dossier. Volume:
 Final Report M/100977/21Final Version () 2. SYNOPSIS A Title of Study: A PHASE IIa, RANDOMISED, DOUBLE-BLIND, MULTIPLE DOSE, PLACEBO CONTROLLED, 3 PERIOD CROSS-OVER, ASCENDING DOSE CLINICAL TRIAL TO ASSESS
Final Report M/100977/21Final Version () 2. SYNOPSIS A Title of Study: A PHASE IIa, RANDOMISED, DOUBLE-BLIND, MULTIPLE DOSE, PLACEBO CONTROLLED, 3 PERIOD CROSS-OVER, ASCENDING DOSE CLINICAL TRIAL TO ASSESS
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide.
 Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Step-down approach in chronic stable asthma: A comparison of reducing dose Inhaled Formoterol/ Budesonide with maintaining Inhaled Budesonide. By: DR MOHD SHAMSUL AMRI Supervisor: Associate Professor Dr
Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment (Hand-Held)
 Small Volume Aerosol Treatment Page 1 of 6 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment To standardize the delivery of inhalation aerosol drug therapy via small volume (hand-held)
Small Volume Aerosol Treatment Page 1 of 6 Purpose Policy Physician's Order Small Volume Nebulizer Treatment To standardize the delivery of inhalation aerosol drug therapy via small volume (hand-held)
Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma
 Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma Dr Andrew Tai FRACP, PhD Paediatric Respiratory and Sleep Specialist Women's and Children's Hospital, Adelaide Approaching the patient Check the diagnosis
Practical Approach to Managing Paediatric Asthma Dr Andrew Tai FRACP, PhD Paediatric Respiratory and Sleep Specialist Women's and Children's Hospital, Adelaide Approaching the patient Check the diagnosis
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
Citation for published version (APA): Schans, C. P. V. D. (1991). Physiotherapy and bronchial mucus transport s.n.
 University of Groningen Physiotherapy and bronchial mucus transport van der Schans, Cees P. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Physiotherapy and bronchial mucus transport van der Schans, Cees P. IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
The FDA Critical Path Initiative
 The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
The FDA Critical Path Initiative Clinical Considerations for Demonstration of Dose-response for Inhaled Corticosteroids - Exhaled Nitric Oxide Model Badrul A. Chowdhury, MD, PhD Director Division of Pulmonary
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Bronchial reactions to the inhalation of high-dose tobramycin in cystic fibrosis
 Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 122 126 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00264002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Bronchial reactions to the
Eur Respir J 2002; 20: 122 126 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.02.00264002 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2002 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 Bronchial reactions to the
Management of acute asthma in children in emergency department. Moderate asthma
 152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation
 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article STUDY OF ASTHMA QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE: AN INSTRUMENT FOR REVIEWING ASTHMA HEALTH EDUCATION AND PROMOTION
Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation www.jpsionline.com Research Article STUDY OF ASTHMA QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE: AN INSTRUMENT FOR REVIEWING ASTHMA HEALTH EDUCATION AND PROMOTION
Respiratory Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 5 February (minutes for web publishing)
 Respiratory Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 5 February 2010 (minutes for web publishing) Respiratory Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology
Respiratory Subcommittee of PTAC meeting held 5 February 2010 (minutes for web publishing) Respiratory Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology
