Advanced Pediatric Emergency Medicine Assembly
|
|
|
- Hillary Hodge
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (+)Charles Macias, MD, FACEP Associate Professor of, Section of Emergency Medicine, Baylor College of Medicine; Director, Evidence Based Outcomes Center and Center for Clinical Effectiveness, Baylor College of Medicine and Texas Children's Hospital, Houston, Texas Advanced Pediatric Emergency Medicine Assembly March New York, NY Best Practices in the ED Management of Status Asthmaticus The management of status asthmaticus in the pediatric population can be challenged by controversies in the choice of novel therapies to treat severe asthma. In this session, the optimal management of status asthmaticus will be discussed for which evidence suggests best practices. Additionally, research in the comparative effectiveness of other therapies will be discussed. OBJECTIVES Discuss first and second line therapy principles of management for status asthmaticus Describe the role of rescue therapies with NIPPV and HFNC in the management of severe asthma Discuss the role of heliox in improving work of breathing Describe pharmacological third line therapies: theophylline, IV beta agonists 3/26/ :00 AM-11:45 AM Grand Ballroom TH-24 DISCLOSURES: (+) No significant financial relationships to disclose
2 Best practices in the ED management of status asthmaticus ACEP Advanced PEM Assembly March 26, 2015 Charles G. Macias MD, MPH Chief Clinical Systems Integration Officer, Texas Children s Director, Evidence Based Outcomes Center and Center for Clinical Effectiveness Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Houston, Texas Overview To discuss existing evidence supporting diagnostic and treatment recommendations for acute severe asthma To delineate best treatment strategies for children experiencing acute severe asthma: comparative effectiveness of treatment strategies To describe the role of knowledge translation and quality improvement in severe acute asthma management in children: best practices Page 1 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:35 PM 1
3 Scope of discussion 593,000 ED visits 2.3% of all ED visits in 2006 ED visits cost 5x PCP visits Akinbami 2009; Kennedy Ann All Asthma Immunol 2003 Affects 22 million persons in the US (NHIS 2005)!0 million children in the US ever diagnosed (Vital Health Stat. 2009) Asthma ED visits Acute Severity Best practices in ED acute severe asthma Mild: 70% predicted; dyspnea with activity; tachypnea Moderate: 40 69% predicted; dyspnea interferes/ limits activity Severe: <40% pred; dyspnea at rest; LT: <25%; can t speak; perspiring NAEPP 2011 Page 2 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:35 PM 2 Domains of management 1. Airway edema: Treat inflammation 2. Airway smoothmuscle hypertrophy, hyperplasia, and bronchoconstriction: treat airway obstruction Page 3 Adapted from National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report. Guidelines for the Diagnosis xxx00.#####.ppt and Management 2/25/2015 of Asthma. 12:36:35 PM August
4 Treat airway obstruction 2. AIRWAY HYPERRESPONSIVENESS Inflammation CLINICAL SYMPTOMS AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION Page 4 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:35 PM 3. Airway remodeling: coupled with above maintain arterial oxygen saturation Page 5 Adapted from National Asthma Education and Prevention Program. Expert Panel Report. Guidelines for the Diagnosis xxx00.#####.ppt and Management 2/25/2015 of Asthma. 12:36:35 PM August
5 Infants/children vs adults Infants/young children vs adults: greater peripheral airway resistance further extension of airway smooth muscle into the peripheral airways less elastic recoil disadvantage of the diaphragm Become hypoxemic more readily (VQ characteristics) decreased SaO2 an early sign of severe airway obstruction Sao2<92% RA 1hr after initial tx indicator of hospitalization for small infants (Connett and Lenney 1993; Geelhoed et al. 1994; Sole et al. 1999) Page 6 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:35 PM Vocal cord dysfunction (VCD) Consider in the difficult to treat May also be induced by similar triggers Abnormal VC adduction by indirect/direct visualization Variable flattening of the inspiratory flow loop Elite athletes prone to EIB and VCD Exercise related breathlessness Treatment: speech therapy and relaxation techniques Page 7 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:35 PM 4
6 The goals have not changed: Adequate arterial oxygen saturation with supplemental oxygen Relief of airflow obstruction Reduction of airway inflammation Page 8 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:35 PM Airway smooth muscle mechanics ß 2 agonist ß 2 AR G protein coupled receptors Parasympathetic tone Corticosteroids Activates adenyl cyclase cellular camp ACh receptor X Anticholinergic MgSO 4 -Inhibit myosin light chain kinase -Inhibit intracellular Ca ++ release -Reduced Ca ++ entry into cell -Sequester intracellular Ca ++ Activation of PKA Ca ++ dependent K + channels Decreased contractility (smooth muscle relaxation) 5
7 Bronchodilators: beta agonists 1. Coupling Uncoupling 2. efficiency Sequestration 3. Downregulation ß 2 agonist ß 2 AR G protein coupled receptors Decreased contractility (smooth muscle relaxation) Expression of receptors Types of agonists Full agonists Isoproterenol Epinephrine Partial agonists Albuterol Terbutaline Number of receptors improves clinical efficacy Page 11 6
8 Continuous vs intermittent beta agonist Wide therapeutic index Data: limited trials Dosing: Pediatric trials: 15 mg/hour NAEPP guidelines: 0.5mg/kg/hour Few limit dosing to per/kg dosing making pediatric dose similar Page 12 Systematic review on continuous therapy: 165 RCTs Pulmonary function: Continuous: significant improvements in PEFR, FEV1 and % Predicted FEV1 2-3 improvements but not in 60 Secondary: Decreased admission (RR 0.68; NNTT 10) Pronounced in the higher severity group Tolerability similar No differences in side-effects Caution in extrapolating to young children Camargo C Cochrane Database of Sys Rev 2003 Page 13 7
9 GINA: Manage asthma exacerbations Repetitive administration of rapid-acting inhaled beta2 agonist MDI with spacer is most cost effective and efficient No evidence to support the use of IV beta2 agonists Evidence supports the use of continuous therapy Epinephrine- subcutaneous or IM not indicated for acute asthma Page 14 Levalbuterol: early data Percent patients admitted % Racemic Albuterol (2.50 mg) *P= %* Levalbuterol (1.25 mg) 482 patient 1-18 yrs Faster improvement in levalbuterol Difference in denominator (6 nebs) Carl J Pediatr 2003 Page 15 8
10 Levalbuterol: ED comparative effectiveness 129 children 2-14 yrs Moderate to severe No difference in clinical score or % change in baseline FEV1 Quereshi Annals of Emerg Med 2005 Page 16 Levalbuterol continuous nebulization Double blind RCT 6-18 yrs 81 children failed ED therapy No difference in median time for continuous therapy or in adverse effects: HR and K+ Andrews et al. J Peds 2009 Page 17 9
11 Levalbuterol ED based RCT 6-17yrs (n=99) >FEV1 improvement and clinical score after 1 hour with 7.5mg of RAC No differences in HR, RR, O2 saturation or admission rates Meta analysis: Cochrane 7 trials, 1625 patients of all ages Low to high quality of evidence No difference in improvement measures (% change FEV1 and CAS), no difference in adverse effects (N/V, headache/jitteriness, nervousness/tremor) Pediatric cardiology patients (CHD, SVT, cardiomyopathy) Wilkinson et at J Asthma 2011 Jat et al. Pulm Pharmacol Ther patients (42 RAC, 40 levalbuterol, 10 both) HR increase of approximately 6.5 beats per minute with equivalency in both groups Kelly et al Ann Pharmacotherap 2013 Page 18 Anticholinergic: ipratropium bromide CNS ACh ACh ACh Blocks pulmonary muscarinic receptors Page 19 10
12 Evidence for ipratropium RCT: acute severe (n=175) 3 arms? hospitalizations Schuh et al, J Pediatr 1995 Meta analysis 20 trials, 2697 children Most 3x 250mcg or 2x500mcg Hospitalization: RR0.73 Overall NNTB: 16 Trends to greater effect with tx intensity/higher severity Griffith Cochrane 2013 Plotnick Cochrane 2003 NNTB:7 severe only Page 20 Ipratropium bromide Severe asthma: Improves pulmonary function, CAS, SaO2 Reduces hospitalizations 1-3 x 500 mcg doses during 1st hour of treatment Variation in evidence/outcomes in ascertainment of groups (severity) and criterion standards for disposition No evidence for efficacy when used alone Page 21 11
13 Airway smooth muscle mechanics ß 2 agonist ß 2 AR Corticosteroids Page 22 Systemic glucocorticosteroids Multiple equivalent regimens Oral prednisone/olone (1-2 mg/kg, max 40-60mg) x 3-10d Parenteral route equivalent to oral prednisone IM dexamethasone acetate (n=32) Gries et al, J Pediatr, 2000 IM dexamethasone acetate (0.6 mg/kg) (n=88) Gordon et al, Pediatr Emerg Care, 2000 Oral dexamethasone (2 doses, 0.6 mg/kg) equivalent to 5 day prednisone for outcome of unscheduled follow-up Greenberg et al,, 2008 Met analysis of 6 ED RCTs to compare IM or oral dexamethasone to 5 day course of oral prednisone or prednisolone; patients receiving dexamethasone less likely to vomit (no difference in 5d relapse) Keeney 2013 Page 23 12
14 Systemic glucocorticosteroids Improving efficiency of care delivery Evaluated the effect of early delivery (within 60 minutes) of triage Early admission reduced odds of admission and length of treatment Bhoqal Ann Emerg Med, 2012 Treatment with corticosteroids within 60 minutes decreased LOS by 25min Davis J Asthma, 2012 Optimal use of steroids in severe asthma has yet to be determined Effect of corticosteroids appears more pronounced in steroid naïve and more severe Early and consistent use of steroids, reserving IV for profound dyspnea, decreased LOC, intubated or in respiratory failure, vomiting Page 24 Knowledge translation: applying QI Strong evidence supporting early administration of systemic corticosteroids Decreased LOS Decreased hospitalization Improved clinical scores Page 25 13
15 EC: Early Administration of steroids Expanding evidence based practice Provider and staff inservicing Clinical decision support Bridging a continuum for home dose Page 26 Airway smooth muscle mechanics ß 2 agonist G protein coupled receptors ß 2 AR Activates adenyl cyclase cellular camp MgSO 4 -Inhibit myosin light chain kinase -Inhibit intracellular Ca ++ release -Reduced Ca ++ entry into cell -Sequester intracellular Ca ++ Activation of PKA Ca ++ dependent K + channels Decreased contractility (smooth muscle relaxation) 14
16 Magnesium sulfate postulated mechanisms modulates Ca ++ channel ion movement direct effect on smooth muscle inhibition of histamine release airway anti-inflammatory effect IV bolus mg/kg to 2 g (20 minute infusion) bronchodilatory effect in 2 minutes after infusion plateau minutes, lasts 1-2 hours untoward: mild BP depression, flushing, tachycardia, bradycardia, muscle weakness Page 28 IV Magnesium in children Meta analysis of 5 RCTs with 182 children Moderate to severe Pulmonary function and clinical scores improved Cheuk Arch Dis Child 2005 Page 29 Cochrane
17 Magnesium Adult study of PEFR<50%: 1109 ( 6 years) at 34 UK hospitals Randomized to IV magnesium, nebulized magnesium or placebo control Weak support for IV on hospital admission outcome but none on PEFR or work of breathing Concluded that nebulized magnesium was not more effective than placebo Goodacre Health Technol Assess 2014 Systematic review suggests IV magnesium reduces hospital admission (NNT=7) Heterogeneity of ascertainment for treatment failure prior to magnesium Kew Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2014 Page 30 Magnesium in adults and children Meta analysis of 16 studies of which 3 included pediatrics and 4 were exclusively pediatrics No clear evidence nebulized magnesium improved pulmonary function or reduced admissions When restricted to 3 trials, in those with severe asthma (FEV1<50%), possible improved lung function Powell Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012 Teasing out children from mixed populations seems to provide more evidence for improved pulmonary function and reduction of admissions with IV magnesium but not nebulized magnesium Shan Respir Med 2013 Page 31 16
18 Magnesium MAGNEsium Trial in children (nebulized) RCT with 3 doses of magnesium for 1 hour (151 mg) 508 children 2-15Assessment of the Yun Asthma Severity Score (ASS) Small statistical gain in score with magnesium Larger effect size with acute severe asthma with shorter duration of symptoms Powell Health Technol Assess 2013 Overall, no clear evidence in 20 years of data that magnesium produces significant side effects in children with acute asthma Stronger evidence for IV than nebulized, but even larger effect size for both IV and nebulized in children with severe acute asthma For children whose FEV1 fails to improve to >60% after 1 hour of care Page 32 Heliox Gas 7x lighter than air, combined with oxygen, a low density air Lowers the resistance to gas flow and turbulent flow Potentially decreases the work of breathing by permitting an increase in ventilation Perceived benefits Improved deposition of airway particles to the distal airways Up to 50% more drug may be delivered Delivery L/min 65:35 to 80:20 helium:oxygen Page 33 17
19 Heliox Reduction in clinical score and pulsus paradoxus by 10mm Hg (n=18) Kudukis et al. J Pediatr 1997 No change in pulmonary function or score (n=11) Carter et al. Chest 1996 Continuous albuterol + hi-flow Helium (240/20 min) Improved pulmonary score using video assessment and trend towards reduced hospitalization (n=30) Kim et al No change in clinical asthma score (n=41) Rivera et al. Am J Emerg Med 2006 No change in clinical asthma score or LOS (n=42) Bigham et al. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2010 Page 34 Heliox Meta analysis of 10 RCTs (3 with children) Mean duration of treatment 120 minutes Most use 70:30 mix of helium:oxygen Improvement difference was 17.3% better for PEF % change with heliox vs oxygen 17/2% mean difference with severe vs moderate-to-severe Lower hospitalization rate (25 vs 36%) Pediatric subgroup: Decrease in clinical scores demonstrating decreased asthma severity Rodrigo Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2014 Page 35 18
20 THE KITCHEN SINK Page 36 Ketamine Induction of bronchodilitation Preventing reuptake of circulating catecholamines Blocking calcium influx Reduction of vagally mediated bronchoconstriction RCT in pediatric patients 0.2 mg/kg bolus Followed by 0.5 mg/kg/hr x 2 hrs No difference in treatment arms Allen Ann Emerg Med PI Score Improvement in PI score Ketamine Placebo Time of infusion Page 37 19
21 Aminophylline No apparent reduction in symptoms, number of txs or LOS Travers Cochrane Database Syst Rev Page Aminophylline Dosing/management practice patterns: 6 mg/kg over 30 min followed by a maintenance dose of mg/kg/h Drug levels are obtained every 6 h during aminophylline infusion Therapeutic level 10 mcg/ml Toxic level 18 Adapted from Dalabih Chest 2012 Toxicity: vomiting*, tremor, headache Meta analysis including pediatrics studies demonstrate no benefit comparing IV beta(2) agonists versus IV aminophylline Mitra Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2012 Page 39 20
22 Terbutaline IV beta (2) agonist (partial agonist) Safety with some cases of elevated CKMB, hypokalemia, tachycardia and mild fall in DBP Stephanopoulos Crit Care Med 1998; Kambalapalli Acta Pediatrica 2005 Retrospective chart review of 120 subjects admitted to PICU 35 late start vs 85 early initiation: 60 vs 16% required mechanical ventilation Doymaz Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2014 Page 40 Terbutaline Prospective: shortened PICU stays with standardized doses Double blind RCT of 49 children Carroll Pediatr Pulmonol 2006 Trend to improvement in clinical score over the first 24 hours 38 vs 52 hours of continuous nebs for terbutaline vs placebo group Bogie Pedatr Emerg Care 2007 TCH dose: 0.5 mcg/kg/min continuous increase by 0.5 mcg/kg/min may require 3-6 mcg/kg/min Page 41 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM 21
23 NIPPV: Bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) Benefits: May improve the delivery of bronchodilators to small airways Decreases workload/fatigue (decrease inspiratory muscle activity) Treatment to prevent hypercarbic and/or hypoxemic respiratory failure Methods: Inspiratory positive airway pressure max 20 cm H2O Expiratory positive airway pressure max 10 cm H2O Published cases in adults/children with sedation utilizing ketamine (mask intolerance) Page 42 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM NIPPV: Bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) PED QI program:165 children 20 kg (lower range 7.5kg and 7 months of age) 5% discharged from the ED, 2% intubated, 39% terminated BiPAP in ED Williams Intensive Care Med 2011 Safe, well tolerated, improvement in clinical score Prospective observational report of 72 PICU patients without control group Decreased clinical score, HR, RR: intubation rate 4% Mayordomo-Colunga Pediatr Pulmonol 2011 Retrospective review (n=83) 88% tolerated, 10% rescued from PICU admission Beers Am J Emerg Med 2007 Unblinded RCT (n=20) Improved clinical score and RR; only 11% (vs 50% of standard group) required adjunct therapies Basnet Pediatr Crit Care Med 2012 Page 43 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM 22
24 High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Allows >2L/min of flow through NC with control of temperature, humidity and O2 blend; provides indeterminate amount of positive airway pressure Retrospective cohort study of 498 cases in the PED (15% asthma) Failure more likely with triage RR>90% age; PCO2>50mmHg; initial venous ph<7.3 Kelly Pediatr Emerg Care 2013 Retrospective review of HFNC for acute respiratory insufficiency in PED to PICU; utilizing an asthma subgroup Infant/toddler flow max 7L/min; pediatric max 8L/min; adult max 50L/min 87 patients when HFNC not available, intubation rate 5% 99 patients when HFNC available, 9% use, 5% intubation rate 172 patients when HFNC policy in place, 23% use, 0.6% intubation rate (p=0.03) Wing Pediatr Emerg Care 2012 Page 44 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM Clinical standards Guidelines or pathways Consistency of strategy for the patient Common respiratory assessment score Provide process to enhance efficiency for the providers Engage stakeholders outside the division for smooth transitions Allow analytics for understanding comparative effectiveness in your own setting Page 45 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM 23
25 Page 46 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM Page 47 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM 24
26 Clinical standards Improving outcomes Common language throughout the system has allowed more rapid transfer Reduced intubation rates Decreased admission rates Decreased LOS Improved patient outcomes Page 48 xxx00.#####.ppt 2/25/ :36:37 PM Questions? 25
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack. Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus
 Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Supplementary Medications during asthma attack Prof. Dr Finn Rasmussen PhD. DrMedSc. Near East University Hospital North Cyprus Conflicts of Interest None Definition of Asthma Airway narrowing that is
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis. Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine
 Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
Wheezy? Easy Peasy! The Emergent Management of Asthma & Bronchiolitis Maneesha Agarwal MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics & Emergency Medicine Asthma Defined National Asthma Education and Prevention
10/6/2014. Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement. Disclosure. Objectives for this talk.
 Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Tommy s Story: An Overview of Asthma Mangement Clifton C. Lee, MD, FAAP, FHM Associate Professor of Pediatrics Chief, Pediatric Hospital Medicine Children s Hospital of Richmond at VCU Disclosure Obviously,
Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update. Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch
 Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch Acknowledgements BTS/SIGN guidelines GINA guidelines NAEPP guidelines
Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Children 2012 Update Sharon Kling Dept Paediatrics & Child Health University of Stellenbosch Acknowledgements BTS/SIGN guidelines GINA guidelines NAEPP guidelines
PEDIATRIC ACUTE ASTHMA SCORE (P.A.A.S.) GUIDELINES. >97% 94% to 96% 91%-93% <90% Moderate to severe expiratory wheeze
 Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
Inclusion: Children experiencing acute asthma exacerbation 24 months to 18 years of age with a diagnosis of asthma Patients with a previous history of asthma (Consider differential diagnosis for infants
Pediatric Respiratory Disease: A Model for the Future of Emergency Medicine Research
 Pediatric Respiratory Disease: A Model for the Future of Emergency Medicine Research Joseph J. Zorc, MD, MSCE Mark Fishman Professor, Department of Pediatrics Perelman School of Medicine, University of
Pediatric Respiratory Disease: A Model for the Future of Emergency Medicine Research Joseph J. Zorc, MD, MSCE Mark Fishman Professor, Department of Pediatrics Perelman School of Medicine, University of
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline
 Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
Asthma Care in the Emergency Department Clinical Practice Guideline Inclusion: 1) Children 2 years of age or older with a prior history of wheezing, and 2) Children less than 2 years of age with likely
AT TRIAGE. Alberta Acute Childhood Asthma Pathway: Evidence based* recommendations For Emergency / Urgent Care
 1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
1 1 Should the child be placed into the Pathway? Asthma Clinical Score (PRAM) Inclusion Children 1 year and 18 years of age who present with wheezing and respiratory distress, and have been diagnosed by
2/12/2015. ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang. Asthma General Information. Asthma General Information
 ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
ASTHMA & COPD The Yin &Yang Arizona State Association of Physician Assistants March 6, 2015 Sedona, Arizona Randy D. Danielsen, PhD, PA-C, DFAAPA Dean & Professor A.T. Still University Asthma General Information
Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma
 Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma Talk Outline Case Delivery of bronchodilators Meter-dose inhalers and spacers Continuous nebulization
Acute Wheezing Emergencies: From Young to Old! Little Wheezers in the ED: Managing Acute Pediatric Asthma Talk Outline Case Delivery of bronchodilators Meter-dose inhalers and spacers Continuous nebulization
Recurrent wheezing illnesses 24.9% Similar to Australia Above global averages
 Prof Mike South Department of General Medicine Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Australia www.mikesouth.org.au Asthma is very common in Australia Approx 25% children have recurrent wheezing illnesses
Prof Mike South Department of General Medicine Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne Australia www.mikesouth.org.au Asthma is very common in Australia Approx 25% children have recurrent wheezing illnesses
Lecture Notes. Chapter 3: Asthma
 Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 3: Asthma Objectives Define asthma and status asthmaticus List the potential causes of asthma attacks Describe the effect of asthma attacks on lung function List the clinical features
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network
 Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Robert Kruklitis, MD, PhD Chief, Pulmonary Medicine Lehigh Valley Health Network Robert.kruklitis@lvh.com Correlation of a Asthma pathophyisology with basic science Asthma (Physiology) Bronchodilators
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II
 Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Emily DiMango, MD Asthma II Director John Edsall/John Wood Asthma Center Columbia University Medical Center HP 2000 Goal: 2.25/1,000 Comparison of Asthma Hospitalization Rates in Children Aged 0-14 in
Objectives. Case Presentation. Respiratory Emergencies
 Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Respiratory Emergencies Objectives Describe how to assess airway and breathing, including interpreting information from the PAT and ABCDEs. Differentiate between respiratory distress, respiratory failure,
Asthma and COPD in the ICU
 Asthma and COPD in the ICU Prescott Woodruff, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Medicine in Residence Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine Acute Exacerbations of Asthma Asthma exacerbations
Asthma and COPD in the ICU Prescott Woodruff, MD, MPH Assistant Professor Medicine in Residence Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine Acute Exacerbations of Asthma Asthma exacerbations
Asthma. No financial relationships with a commercial interest to disclose
 Asthma in the ED Emily Rose, MD FAAP FAAEM FACEP Assistant Professor of Clinical Emergency Medicine Keck School of Medicine of USC LA County + USC Medical Center No financial relationships with a commercial
Asthma in the ED Emily Rose, MD FAAP FAAEM FACEP Assistant Professor of Clinical Emergency Medicine Keck School of Medicine of USC LA County + USC Medical Center No financial relationships with a commercial
The adult therapeutic substitution protocol follows:
 Therapeutic Substitution of Albuterol - Implemented 1/15/2013 After years of evaluation, comparative studies have not consistently demonstrated clinical or safety advantages of levalbuterol over racemic
Therapeutic Substitution of Albuterol - Implemented 1/15/2013 After years of evaluation, comparative studies have not consistently demonstrated clinical or safety advantages of levalbuterol over racemic
Episode 79 Pediatric Asthma
 Reliable Validated Measures of Pediatric Asthma Episode 79 Pediatric Asthma With Dr. Dennis Scolnik & Dr. Sanjay Mehta Prepared by Dr. Anton Helman, April 2016 Pediatric Asthma Severity Indicators life-threatening
Reliable Validated Measures of Pediatric Asthma Episode 79 Pediatric Asthma With Dr. Dennis Scolnik & Dr. Sanjay Mehta Prepared by Dr. Anton Helman, April 2016 Pediatric Asthma Severity Indicators life-threatening
1. What is delayed sequence intubation? Can it be used for severe Asthma exacerbation? 2. What about pregnancy and Asthma is so important?
 Chapter 073 Asthma Episode Overview 1. 10 different causes of a wheeze. 2. List 8 risk factors for death from asthma 3. List 6 objective findings of severe asthma 4. 10 therapies for an acute severe asthma
Chapter 073 Asthma Episode Overview 1. 10 different causes of a wheeze. 2. List 8 risk factors for death from asthma 3. List 6 objective findings of severe asthma 4. 10 therapies for an acute severe asthma
Emergency Department Protocol Initiative
 Emergency Department Protocol Initiative ACUTE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT TOOLKIT March 2006 Provincial Emergency Services Project PHYSICIAN ORDER TEMPLATE FOR CTAS LEVEL 1 ASTHMA ADULT PEDIATRIC Date: Site: Arrival
Emergency Department Protocol Initiative ACUTE ASTHMA MANAGEMENT TOOLKIT March 2006 Provincial Emergency Services Project PHYSICIAN ORDER TEMPLATE FOR CTAS LEVEL 1 ASTHMA ADULT PEDIATRIC Date: Site: Arrival
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations. Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa
 Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
Predicting, Preventing and Managing Asthma Exacerbations Heather Zar Department of Paediatrics & Child Health University of Cape Town South Africa Asthma exacerbations Predicting exacerbation recognising
Printed copies of this document may not be up to date, obtain the most recent version from
 Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Acute Severe Asthma Document Control Information Author E Randle Author Position CATS Consultant Document Owner E Polke Document Owner Position Co-ordinator
Children s Acute Transport Service Clinical Guidelines Acute Severe Asthma Document Control Information Author E Randle Author Position CATS Consultant Document Owner E Polke Document Owner Position Co-ordinator
ASTHMA. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology. Diagnosis. IAP UG Teaching slides
 BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
BRONCHIAL ASTHMA ASTHMA Epidemiology Pathophysiology Diagnosis 2 CHILDHOOD ASTHMA Childhood bronchial asthma is characterized by Airway obstruction which is reversible Airway inflammation Airway hyper
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications
 The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
The Acute & Maintenance Treatment of Asthma via Aerosolized Medications Douglas S. Gardenhire, EdD, RRT-NPS, FAARC Associate Professor and Chairman Department of Respiratory Therapy Objectives Define Asthma.
Asthma Management in ICU. by DrGary Au From KWH
 Asthma Management in ICU by DrGary Au From KWH Overview of Asthma Pathophysiology Therapeutic options Medical treatment NPPV Mechanical ventilation Salvage therapy ~ 235 million people worldwide were affected
Asthma Management in ICU by DrGary Au From KWH Overview of Asthma Pathophysiology Therapeutic options Medical treatment NPPV Mechanical ventilation Salvage therapy ~ 235 million people worldwide were affected
Management of acute asthma in children in emergency department. Moderate asthma
 152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
152 Moderate asthma SpO2 92% No clinical features of severe asthma NB: If a patient has signs and symptoms across categories, always treat according to their most severe features agonist 2-10 puffs via
Exacerbations. Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark
 1st WAO Allied Health Session - Asthma: Diagnosi Exacerbations Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark The health professional that care for patients with asthma exacerbation must be able to Identificafy
1st WAO Allied Health Session - Asthma: Diagnosi Exacerbations Ronald Dahl, Aarhus University Hospital, Denmark The health professional that care for patients with asthma exacerbation must be able to Identificafy
Significance. Asthma Definition. Focus on Asthma
 Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
Focus on Asthma (Relates to Chapter 29, Nursing Management: Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases, in the textbook) Asthma Definition Chronic inflammatory disorder of airways Causes airway hyperresponsiveness
COPD. Breathing Made Easier
 COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
COPD Breathing Made Easier Catherine E. Cooke, PharmD, BCPS, PAHM Independent Consultant, PosiHleath Clinical Associate Professor, University of Maryland School of Pharmacy This program has been brought
Rapid Effects of Inhaled Corticosteroids in Acute Asthma Gustavo J. Rodrigo, MD.
 Rapid Effects of Inhaled Corticosteroids in Acute Asthma Gustavo J. Rodrigo, MD WWW.chestjournal.org Background: Current reviews on the use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) for acute asthma underestimated
Rapid Effects of Inhaled Corticosteroids in Acute Asthma Gustavo J. Rodrigo, MD WWW.chestjournal.org Background: Current reviews on the use of inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) for acute asthma underestimated
Nguyen Tien Dung A/Prof. PhD. MD Head of Pediatric Department - Bach Mai Hospital
 Nguyen Tien Dung A/Prof. PhD. MD Head of Pediatric Department - Bach Mai Hospital A girl patient 11 years old admitted to Bach mai Hospital at 4h15, 12nd November because of difficult breathing She has
Nguyen Tien Dung A/Prof. PhD. MD Head of Pediatric Department - Bach Mai Hospital A girl patient 11 years old admitted to Bach mai Hospital at 4h15, 12nd November because of difficult breathing She has
SCVMC RESPIRATORY CARE PROCEDURE
 Page 1 of 8 Rev. - 11/99, 11/05, 4/11 R-NC - 08/99,08/00, 04/03,10/08,04/09, 07/11, 6/12 B7180-43 OBJECTIVE Continuous Nebulization allows for continuous, controlled drug delivery to the lung, avoiding
Page 1 of 8 Rev. - 11/99, 11/05, 4/11 R-NC - 08/99,08/00, 04/03,10/08,04/09, 07/11, 6/12 B7180-43 OBJECTIVE Continuous Nebulization allows for continuous, controlled drug delivery to the lung, avoiding
Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health.
 Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health Background: These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and
Treatment of Acute Asthma Exacerbations in Adults in the Primary Care or Urgent Care Setting Clinical Practice Guideline MedStar Health Background: These guidelines are provided to assist physicians and
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators
 I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
I. Subject: Continuous Aerosolization of Bronchodilators II. Indications: A. Acute airflow obstruction in which treatment with an aerosolized bronchodilator is desired for an extended period of time, i.e.
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA. Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED
 RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
RESPIRATORY PHARMACOLOGY - ASTHMA Primary Exam Teaching - Westmead ED Sympathomimetic agents MOA: relax airway smooth muscle and inhibit broncho constricting mediators from mast cells May also inhibit
COPD: A Renewed Focus. Disclosures
 COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
COPD: A Renewed Focus Heath Latham, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Disclosures No Business Interests No Consulting No Speakers Bureau No Off Label Use to Discuss
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: bronchial_thermoplasty 10/2010 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Bronchial thermoplasty
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: bronchial_thermoplasty 10/2010 3/2018 3/2019 3/2018 Description of Procedure or Service Bronchial thermoplasty
Quality Design Limitations Inconsistency Indirectness Imprecision studies. Other. considerations Heliox Control (95% Absolute
 Question 7: In the child with asthma exacerbation in the ED, should heliox driven albuterol vs. oxygen or room air driven albuterol be used to prevent hospitalization, decrease time in the ED or improve
Question 7: In the child with asthma exacerbation in the ED, should heliox driven albuterol vs. oxygen or room air driven albuterol be used to prevent hospitalization, decrease time in the ED or improve
Asthma Management for the Athlete
 Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Asthma Management for the Athlete Khanh Lai, MD Assistant Professor Division of Pediatric Pulmonary and Sleep Medicine University of Utah School of Medicine 2 nd Annual Sports Medicine Symposium: The Pediatric
Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. By: Lillian Han
 Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: Lillian Han Background: Respiratory anesthetic emergencies are the most common complications during the administration of anesthesia
Respiratory Anesthetic Emergencies in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery By: Lillian Han Background: Respiratory anesthetic emergencies are the most common complications during the administration of anesthesia
a. Will not suppress respiratory drive in acute asthma
 Status Asthmaticus & COPD with Respiratory Failure - Key Points M.J. Betzner MD FRCPc - NYEMU Toronto 2018 Overview This talk is about the sickest of the sick patients presenting with severe or near death
Status Asthmaticus & COPD with Respiratory Failure - Key Points M.J. Betzner MD FRCPc - NYEMU Toronto 2018 Overview This talk is about the sickest of the sick patients presenting with severe or near death
Course Handouts & Disclosure
 COPD: Disease Trajectory and Hospice Eligibility Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources Hospice Education Network Course Handouts & Disclosure To download presentation
COPD: Disease Trajectory and Hospice Eligibility Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources Hospice Education Network Course Handouts & Disclosure To download presentation
Sample. Affix patient label within this box.
 Instructions for completing orders: Determine PRAM Clinical Score as per the Alberta Acute Childhood Asthma Pathway for Emergent/Urgent Care and select orders based on PRAM Score. Custom orders can be
Instructions for completing orders: Determine PRAM Clinical Score as per the Alberta Acute Childhood Asthma Pathway for Emergent/Urgent Care and select orders based on PRAM Score. Custom orders can be
On completion of this chapter you should be able to: discuss the stepwise approach to the pharmacological management of asthma in children
 7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
7 Asthma Asthma is a common disease in children and its incidence has been increasing in recent years. Between 10-15% of children have been diagnosed with asthma. It is therefore a condition that pharmacists
Asthma. Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital. Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence,
 Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Asthma Rachel Miller, MD, FAAAAI Director Allergy and Immunology New York Presbyterian Hospital Figure 1 Asthma Prevalence, 1980-2000 * Gap between 1995-1996 and 1997 indicates a break in trend due to
Lecture Notes. Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
 Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Lecture Notes Chapter 4: Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Objectives Define COPD Estimate incidence of COPD in the US Define factors associated with onset of COPD Describe the clinical features
Sample. Affix patient label within this box.
 Instructions for completing orders Complete pages 1-3 for General Inpatient Orders. All pathway compatible orders (indicated by ) within the General Inpatient Orders will be followed automatically. Optional
Instructions for completing orders Complete pages 1-3 for General Inpatient Orders. All pathway compatible orders (indicated by ) within the General Inpatient Orders will be followed automatically. Optional
12/18/2017. Disclosures. Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Chapter 7. Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Chapter 7 Anticholinergic (Parasympatholytic) Bronchodilators Clinical Indications for Use Indication for anticholinergic bronchodilator COPD maintenance Indication for combined anticholinergic and β-agonist
Physician Orders Pediatric: LEB ED Asthma Plan
 LEB ED Triage Standing SOB/Wheeze Asthma Non Categorized Criteria: Patients greater than 2 years of age with a history of asthma or airway active disease or two or more previous illnesses treated with
LEB ED Triage Standing SOB/Wheeze Asthma Non Categorized Criteria: Patients greater than 2 years of age with a history of asthma or airway active disease or two or more previous illnesses treated with
MANAGEMENT OF AN ACUTE EPISODE OF ASTHMA IN CHILDREN
 MANAGEMENT OF AN ACUTE EPISODE OF ASTHMA IN CHILDREN Dr. Ebor Jacob 1, Dr. Manivachagan 2, Dr. Amith Balachandran 3 1 Professor, 2 Associate Professor, Paediatric ICU, Christian Medical College, Vellore.
MANAGEMENT OF AN ACUTE EPISODE OF ASTHMA IN CHILDREN Dr. Ebor Jacob 1, Dr. Manivachagan 2, Dr. Amith Balachandran 3 1 Professor, 2 Associate Professor, Paediatric ICU, Christian Medical College, Vellore.
Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience
 Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience 8th Annual North Regional Respiratory Care Conference Minnesota & Wisconsin Societies for Respiratory Care Mayo Civic
Metered Dose Inhalers with Valved Holding Chamber: A Pediatric Hospital Experience 8th Annual North Regional Respiratory Care Conference Minnesota & Wisconsin Societies for Respiratory Care Mayo Civic
Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
RSPT 2317 Clinical Indications Theophylline management of asthma and COPD treatment of apnea of prematurity (AOP) diuretic (obsolete use) classified as a bronchodilator, but is weaker than β agonists effects
From the Text. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. Clinical Indications. RSPT 2317 Methylxanthines
 From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
From the Text RSPT 2217 Gardenhire Chapter 8 Key Terms and Definitions page 151 Xanthine Derivatives Used as Bronchodilators Table 8-1; page 152 Adverse Reactions Seen with Theophylline Box 8-1; page 157
Drug Class Review on Quick-relief Medications for Asthma
 Drug Class Review on Quick-relief Medications for Asthma Preliminary Scan Report #3 November 2013 The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality has not yet seen or approved this report The purpose of
Drug Class Review on Quick-relief Medications for Asthma Preliminary Scan Report #3 November 2013 The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality has not yet seen or approved this report The purpose of
Respiratory Pharmacology. Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France
 Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
Respiratory Pharmacology Manuel Otero Lopez Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Paris, France Programme Bronchomotor tone Drugs and factors influencing airway
In 2005, the prevalence of asthma in the. Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations
 Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations SUSAN M. POLLART, MD, MS; REBEKAH M. COMPTON, MSN, FNP-C; and KURTIS S. ELWARD, MD, MPH University of Virginia Health System, Charlottesville, Virginia Asthma exacerbations
Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbations SUSAN M. POLLART, MD, MS; REBEKAH M. COMPTON, MSN, FNP-C; and KURTIS S. ELWARD, MD, MPH University of Virginia Health System, Charlottesville, Virginia Asthma exacerbations
Asthma in the Athlete
 Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
Asthma in the Athlete Jorge E. Gomez, MD Associate Professor Texas Children s Hospital Baylor College of Medicine Assist Team Physician UH Understand how we diagnose asthma Objectives Be familiar with
US max daily dose i Food and Drug Administration [2]
![US max daily dose i Food and Drug Administration [2] US max daily dose i Food and Drug Administration [2]](/thumbs/88/115964542.jpg) APPENDIX 2 etable 1. Regulatory limits on total daily dose for asthma medications Drugs Canadian max daily dose i Health Canada [1] US max daily dose i Food and Drug Administration [2] European max daily
APPENDIX 2 etable 1. Regulatory limits on total daily dose for asthma medications Drugs Canadian max daily dose i Health Canada [1] US max daily dose i Food and Drug Administration [2] European max daily
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma :
 Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
Medicine Dr. Kawa Lecture 4 - Treatment of asthma : Avoiding allergens. Hyposensitization :Subcutaneous injections of inially very small, but gradually increasing doses of allergens (desensitization or
LRI Children s Hospital
 LRI Children s Hospital Asthma Management in Children On-going Care after Admission to Ward Staff relevant to: Medical & Nursing staff providing asthma management care to Children within UHL Children s
LRI Children s Hospital Asthma Management in Children On-going Care after Admission to Ward Staff relevant to: Medical & Nursing staff providing asthma management care to Children within UHL Children s
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre
 PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
Steven Berkowitz, DVM Chief, Emergency and Critical Care Saint Francis Veterinary Center
 Steven Berkowitz, DVM Chief, Emergency and Critical Care Saint Francis Veterinary Center Outline Anatomy Common Diseases Interventions Oxygen Therapy Medications Nebulization Coupage Respiratory Tract
Steven Berkowitz, DVM Chief, Emergency and Critical Care Saint Francis Veterinary Center Outline Anatomy Common Diseases Interventions Oxygen Therapy Medications Nebulization Coupage Respiratory Tract
UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE
 UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE FLORIDA CHAPTER ACP MEETING 2016 Himangi Kaushal, M.D., F.A.C.P. Program Director Memorial Healthcare System Internal Medicine Residency DISCLOSURES None OBJECTIVES Review some
UPDATE IN HOSPITAL MEDICINE FLORIDA CHAPTER ACP MEETING 2016 Himangi Kaushal, M.D., F.A.C.P. Program Director Memorial Healthcare System Internal Medicine Residency DISCLOSURES None OBJECTIVES Review some
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR) for ED Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbation
 Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR) for ED Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbation PI: Brian Driver, MD Checklist Reviewed Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Confirm pertinent exclusion criteria with PMP Engage
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR) for ED Management of Acute Asthma Exacerbation PI: Brian Driver, MD Checklist Reviewed Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria Confirm pertinent exclusion criteria with PMP Engage
Asthma Exacerbation Management in Children. Kong-Sang Wan, MD,PhD 温港生醫師 台北市聯合醫院仁愛院區小兒科
 Asthma Exacerbation Management in Children Kong-Sang Wan, MD,PhD 温港生醫師 台北市聯合醫院仁愛院區小兒科 Hypocapnia & respiratory alkalosis due to increase resp. rate Symptom classification Severe persistent - day: continue
Asthma Exacerbation Management in Children Kong-Sang Wan, MD,PhD 温港生醫師 台北市聯合醫院仁愛院區小兒科 Hypocapnia & respiratory alkalosis due to increase resp. rate Symptom classification Severe persistent - day: continue
GINA. At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference. for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years. Updated 2017
 GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
GINA At-A-Glance Asthma Management Reference for adults, adolescents and children 6 11 years Updated 2017 This resource should be used in conjunction with the Global Strategy for Asthma Management and
Treatment. Assessing the outcome of interventions Traditionally, the effects of interventions have been assessed by measuring changes in the FEV 1
 58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
58 COPD 59 The treatment of COPD includes drug therapy, surgery, exercise and counselling/psychological support. When managing COPD patients, it is particularly important to evaluate the social and family
Is reslizumab effective in improving quality of life and asthma control in adolescent and adult patients with poorly controlled eosinophilic asthma?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is reslizumab effective in improving
+ Asthma and Athletics
 + Asthma and Athletics Shaylon Rettig, MD, MBA Champion Sports Medicine + Financial Disclosure Dr. Shaylon Rettig has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. + Asthma
+ Asthma and Athletics Shaylon Rettig, MD, MBA Champion Sports Medicine + Financial Disclosure Dr. Shaylon Rettig has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. + Asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children
 Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Tips on managing asthma in children Dr Ranjan Suri Consultant in Respiratory Paediatrics Bupa Cromwell Hospital Clinics: Friday (pm) Asthma in Children Making the diagnosis Patterns of childhood asthma
Acute Asthma in Adults and Children
 Guideline for The Management of Administered by the Alberta Medical Association Acute Asthma in Adults and Children This guideline has been adapted from the CAEP guidelines for Acute Asthma Management
Guideline for The Management of Administered by the Alberta Medical Association Acute Asthma in Adults and Children This guideline has been adapted from the CAEP guidelines for Acute Asthma Management
Objectives. Asthma in Primary Care. Definition. Epidemiology. Pathophysiology
 Objectives Asthma in Primary Care Jed Grant, PA-C Program Director, SJVC PA Program Staff PA, AMCH Emergency Department Apply the NAEPP guideline measures of severity and control including current impairment
Objectives Asthma in Primary Care Jed Grant, PA-C Program Director, SJVC PA Program Staff PA, AMCH Emergency Department Apply the NAEPP guideline measures of severity and control including current impairment
REVIEW AMINOPHYLLINE. Background
 REVIEW AMINOPHYLLINE Background The current 13 th edition of the WHO Model Essential Medicines List (dated April 2003) includes aminophylline on the Complementary List. The listing is as shown below (together
REVIEW AMINOPHYLLINE Background The current 13 th edition of the WHO Model Essential Medicines List (dated April 2003) includes aminophylline on the Complementary List. The listing is as shown below (together
TORCH: Salmeterol and Fluticasone Propionate and Survival in COPD
 TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
TORCH: and Propionate and Survival in COPD April 19, 2007 Justin Lee Pharmacy Resident University Health Network Outline Overview of COPD Pathophysiology Pharmacological Treatment Overview of the TORCH
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Diagnosis, Assessment, Monitoring and Pharmacological Treatment of Asthma Magnitude of Asthma - India Delhi Childhood asthma: 10.9% Adults: 8% Other Cities 3 to 18% Chhabra SK et al Ann Allergy Asthma
Respiratory Pharmacology
 Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Allergy Targets of allergies Type I Histamine Leukotrienes Prostaglandins Bradykinin Hypersensitivity reactions Asthma Characterised by Triggered by Intrinsic Extrinsic (allergic) Mediators Result Early
Clinical guideline for acute wheeze & asthma in children 5 years and over Hospital care
 Clinical guideline for acute wheeze & asthma in children years and over Hospital care Airedale NHS Trust Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS Bradford and Airedale DOB: A&E/Hospital : Weight:
Clinical guideline for acute wheeze & asthma in children years and over Hospital care Airedale NHS Trust Bradford Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust NHS Bradford and Airedale DOB: A&E/Hospital : Weight:
A Clinical Guideline for the use of Intravenous Aminophylline in Acute Severe Asthma in Children
 For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job titles of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by: Assessed and approved by the:
For Use in: By: For: Division responsible for document: Key words: Name and job titles of document author: Name and job title of document author s Line Manager: Supported by: Assessed and approved by the:
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
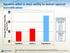 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Asthma in Day to Day Practice
 Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
Asthma in Day to Day Practice VIJAY.K.VANAM Financial relationships: Disclosures Employed at Mercy Medical Center, Mason City. Nonfinancial relationships: I receive no financial gain from any pharmaceutical
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER
 MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
MAYA RAMAGOPAL M.D. DIVISION OF PULMONOLOGY & CYSTIC FIBROSIS CENTER 16 year old female with h/o moderate persistent asthma presents to the ED after 6 hours of difficulty breathing, cough, and wheezing
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma
 Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Asthma Asthma is a complex disorder characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperresponsiveness, and an underlying inflammation.
The Crashing Pediatric Patient: Stopping the Fall
 The Crashing Pediatric Patient: Stopping the Fall I can t breathe... 4 year old BIBA from school with sudden severe resp distress Hx of asthma, food allergies Judith Klein, MD FACEP Assistant Professor
The Crashing Pediatric Patient: Stopping the Fall I can t breathe... 4 year old BIBA from school with sudden severe resp distress Hx of asthma, food allergies Judith Klein, MD FACEP Assistant Professor
Asthma/wheeze management plan
 Asthma/wheeze management plan Name of Patient Date of Birth NHS Number GP surgery Telephone Next appointment Children s Assessment unit/ward telephone Out of hours call 111 Open access Y/N Until date Some
Asthma/wheeze management plan Name of Patient Date of Birth NHS Number GP surgery Telephone Next appointment Children s Assessment unit/ward telephone Out of hours call 111 Open access Y/N Until date Some
Emergency Department Guideline. Asthma
 Emergency Department Guideline Inclusion criteria: Patients 2 years old with: o Known history of asthma or wheezing responsive to bronchodilators presenting to the ED with cough, wheeze, shortness of breath,
Emergency Department Guideline Inclusion criteria: Patients 2 years old with: o Known history of asthma or wheezing responsive to bronchodilators presenting to the ED with cough, wheeze, shortness of breath,
Despite many advances in the
 Single-dose intravenous salbutamol bolus for managing children with acute severe asthma in the emergency department: Reanalysis of data* Gary J. Browne, FRACP, FACEM; Lawrence T. Lam, MApp, PsyMPH Objective:
Single-dose intravenous salbutamol bolus for managing children with acute severe asthma in the emergency department: Reanalysis of data* Gary J. Browne, FRACP, FACEM; Lawrence T. Lam, MApp, PsyMPH Objective:
Early Studies. Then, the Meta-analysis. Recent Studies Al-Ansari. Recent Studies Luo University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio
 Pediatrics Grand Rounds Objectives Review the available literature on the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in the treatment of acute viral bronchiolitis Review proposed mechanism(s) of action and safety
Pediatrics Grand Rounds Objectives Review the available literature on the use of nebulized hypertonic saline in the treatment of acute viral bronchiolitis Review proposed mechanism(s) of action and safety
PM-03 PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS. Protocol SECTION: PM-03 PROTOCOL TITLE: PED ALLERGY/ANAPHYLAXIS REVISED: 01MAY2018
 SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
SECTION: PROTOCOL TITLE: REVISED: 01MAY2018 BLS SPECIFIC CARE: See General Pediatric Care Protocol PM-1 - Determine patient s color category on length based resuscitation tape (Broselow Tape) Epi Pen Protocol
Anticholinergic therapy for acute asthma in children(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Anticholinergic therapy for acute asthma in children(review) TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB.
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Anticholinergic therapy for acute asthma in children(review) TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB TeohL,CatesCJ,HurwitzM,AcworthJP,vanAsperenP,ChangAB.
Knowledge Translation and Emergency Medicine. Eddy Lang Jeremy Grimshaw Michael Brown
 Knowledge Translation and Emergency Medicine Eddy Lang Jeremy Grimshaw Michael Brown Knowledge Translation The exchange, synthesis and application of research evidence within a complex system of relationships
Knowledge Translation and Emergency Medicine Eddy Lang Jeremy Grimshaw Michael Brown Knowledge Translation The exchange, synthesis and application of research evidence within a complex system of relationships
INPATIENT ASTHMA CARE PROTOCOL
 INPATIENT ASTHMA CARE PROTOCOL When ordered by a physician, an eligible child 2 years of age or older who is admitted to the General Pediatric Inpatient Unit at the Children s Hospital of Georgia with
INPATIENT ASTHMA CARE PROTOCOL When ordered by a physician, an eligible child 2 years of age or older who is admitted to the General Pediatric Inpatient Unit at the Children s Hospital of Georgia with
Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease
 Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
Hong Kong Journal of Emergency Medicine Nebulizer versus inhaler with spacer for beta-agonist treatment in acute bronchospastic disease β GPC Lee, WY Sung, HT Fung, CW Kam Objectives: To compare the efficacy
The Office of Evidence Based Practice, 2011 Center of Clinical Effectiveness. Importance. Quality. No of studies
 Question 6: In the child with asthma exacerbation in the ED should magnesium sulfate IV be used prevent hospitalization, decrease time in the ED, and improve pulmonary function? GRADEprofiler Table: Rowe
Question 6: In the child with asthma exacerbation in the ED should magnesium sulfate IV be used prevent hospitalization, decrease time in the ED, and improve pulmonary function? GRADEprofiler Table: Rowe
Asthma training. Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital
 Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma training Mike Levin Division of Asthma and Allergy Red Cross Hospital Introduction Physiology Diagnosis Severity Treatment Control Stage 3 of guidelines Acute asthma Drug delivery Conclusion Overview
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing
 Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Asthma Management Updates: A Focus on Long-acting Muscarinic Antagonists and Intermittent Inhaled Corticosteroid Dosing Diana M. Sobieraj, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor University of Connecticut School
Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(4): 353-59 Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma Praveen Aggarwal*, Onkar Singh**, Jyoti P Wali***, Rohini Handa*, Sada N Dwivedi****, Ashutosh Biswas*****,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE JIACM 2002; 3(4): 353-59 Efficacy of Nebulised Ipratropium in Acute Bronchial Asthma Praveen Aggarwal*, Onkar Singh**, Jyoti P Wali***, Rohini Handa*, Sada N Dwivedi****, Ashutosh Biswas*****,
Asthma. chapter 7. Overview
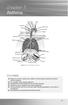 chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
chapter 7 Asthma Sinus Sinus Sinus Right lung Adenoids Tonsils Pharynx Epiglottis Oesophagus Right bronchus Nasal cavity Oral cavity Tongue Larynx Trachea Ribs Left bronchus Diaphragm Bronchiole Pleura
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
