Regression Equations for Spirometry in Children Aged 6 to 17 Years in Delhi Region
|
|
|
- Lesley Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Short Communication Regression Equations for Spirometry in Children Aged 6 to 17 Years in Delhi Region S.K. Chhabra 1, V.K. Vijayan 2, M. Rahman 3, V. Mittal 1 and P.D. Singh 1 Departments of Cardio-respiratory Physiology 1, Former Director 2 and Biostatistics 3, Viswanathan Chest Hospital, Vallabhbhai Patel Chest Institute, University of Delhi, Delhi, India ABSTRACT Background. Most of the studies carried out in India to develop regression equations for spirometry in children are now several years-to-decades old and had used equipment and measurement protocols that have since changed. Prediction equations using the current standardisation protocols for spirometry are not available. The lung health of the population may have changed too. Objective. To develop regression equations for spirometry for children aged 6 to 17 years of north Indian origin in Delhi region. Methods. School children of north Indian origin, as determined by mother tongue and parentage, aged 6 to 17 years were screened by a health questionnaire and physical examination and those found normal underwent spirometry according to the standardised procedure recommended by the American Thoracic Society/ European Respiratory Society (ATS/ERS) task force in Pearson s correlation analysis was carried out to identify the predictor variables for spirometric parameters. Prediction equations were developed using the multiple linear regression procedure. The independent variables were entered in sequence of height, age and weight. R 2, adjusted R 2 and R 2 change, standard errors of the estimate (SEE), and estimates of regression coefficients were obtained and the goodness of fit was examined. Results. Data was obtained in 365 boys and 305 girls. Forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in one second ( ), peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR), forced expiratory flow rate at 50% and 75% exhalation of vial capacity ( and ) and mean forced expiratory flow rate over the middle 50% of the vital capacity (F ) showed moderate to strong correlations with age, height and weight in both boys and girls. In both genders, the equations explained very high variability of FVC, and PEFR as shown by the R 2 values. The explained variability for flow rates was lesser, with that for being the least. Conclusions. Regression equations for spirometry variables for children of north Indian origin in Delhi region have been developed. These represent the first such effort from India after the publication of the ATS/ERS task force 2005 guidelines on standardisation of spirometry. [Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 2012;54:59-63] Key words: Pulmonary function, Spirometry, Normals, Children, Delhi, Regression equations. INTRODUCTION Pulmonary function is influenced by anthropometric, gender, environmental, genetic, socio-economic and technical factors. To predict pulmonary function, variations with anthropometric variables, sex and race have been studied extensively and documented in the western literature. A few studies from different parts of India 1-9 have provided information on pulmonary function in children and its determinants and prediction equations have been described. The studies have varied in sample size, instrumentation and results. In general, boys have been found to have larger vital capacities and height is the most important determinant with variable contributions from age, weight and some other physical measurements. Technological advancements have resulted in greater automation and newer methods of electronic measurements. The measurement protocols have been revised over time. The latest standardisation of spirometry was carried out by a joint task force of the American Thoracic Society and the European Respiratory Society (ATS/ERS) and published in the year Most of the above Indian studies were carried out several years-to-decades ago with equipment and measurement protocols that have changed. Thus, these may no longer be valid. This is likely to affect interpretation of data. Correct interpretation of pulmonary function data requires [Received: September 5, 2011; accepted after revision: December 20, 2011] Correspondence and reprint requests: Dr S.K. Chhabra, Professor and Head, Department of Cardio-respiratory Physiology, Vallabhbhai Patel Chest Institute, University of Delhi, Delhi , India; skchhabra@mailcity.com
2 60 Regression Equations for Spirometry in Children S.K. Chhabra et al use of locally developed prediction equations. Equations using the current standardisation protocols for spirometry have not been developed in India. Ethnic variations in pulmonary function are well known. This precludes development of a single equation for all Indians. There is an urgent need to develop these equations for different regions of the country. Delhi is a cosmopolitan city in the northern region of the country. We, therefore, carried out a study to develop regression equations for spirometry in children aged 6 to 17 years of north Indian origin in Delhi region. We present here a brief communication of the study carried so that these can be applied in practice at the earliest. A detailed evaluation and comparative analysis with previous Indian studies as well as with equations from other countries will be presented subsequently. MATERIAL AND METHODS The study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee. It was carried out in children in a school selected randomly from a list of schools in Delhi. The school caters to a wide area of Delhi and the children are drawn from a very wide socio-economic spectrum. Hence, it approximates a representative sample. All the children from ages 6 to 17 years were eligible for inclusion provided they had been in Delhi for more than half of their life. Additionally, the mother tongue was required to be Hindi, Urdu or Punjabi, the predominant languages in this region, and both parents had to be of north Indian origin to limit the confounding effects of ethnic variation. A demonstration of the testing procedure was given to familiarise the children with pulmonary function testing. For each age, a target of 15 to 20 boys and girls with technically acceptable tests was set and consecutive eligible children were included till the sample requirement was met. This number was based on statistical considerations of numbers required for linear regression procedures, previously published studies 1-9 and feasibility. A questionnaire was designed in English and Hindi was answered by either parent. It had several sections as follows: cover letter from Principal, information sheet, consent form and questionnaire about the health status. Children with completely filled-up questionnaires with written consent for participation were included. Those judged to be normal from the questionnaire responses were again examined by the investigators in the school to confirm that they were eligible for inclusion. The exclusion criteria included current or past history of any chronic respiratory, cardiac or other system disease, thoracic cage abnormality, any current acute illness, recent chest infection (within 6 weeks), current smokers or with environmental tobacco smoke exposure, and unwilling parents/children. Age in completed years, gender, standing height to the nearest centimeter without shoes and weight rounded off to the nearest kilogram were recorded at the time of the testing. Weight was measured wearing light clothing and no footwear to the nearest 0.5 Kg using an electronic scale that was calibrated on a weekly basis with known weights. Height was measured with the children standing erect with head in the Frankfurt plane and ankles pressed against a wall on which a measuring tape had been fixed. Spirometry was carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the ATS/ERS task force. 10 The spirometer with a heated Lily screen pneumotach (Medisoft Micro 5000, Belgium) was calibrated daily. The manoeuvers were performed in the sitting position with a nose-clip applied. The children was asked to inhale completely and rapidly with a pause of <1 s at total lung capacity (TLC) and exhale with maximum force until no more air was expelled out while maintaining an upright posture. At the completion of expiration and on signal from the technician, the subject was asked to inhale completely. The manoeuvers was monitored on the computer screen. Throughout the procedure, loud verbal encouragement was given to obtain the expiratory and inspiratory manoeuvers completely with maximal force. The procedure was monitored for compliance with the acceptability and repeatability criteria recommended by the ATS/ERS task Force. 10 At least three acceptable and two repeatable efforts were obtained. The highest values of FVC, and PEFR were selected. The flow rates, forced expiratory flow rate at 50% and 75% exhalation of vital capacity ( and ) and mean forced expiratory flow rates over the middle 50% of the vital capacity( ) were obtained from the best curve, i.e. the one with the highest sum of FVC and. Statistical Analysis Statistical analysis was carried out using statistical package for the social sciences (SPSS) 16.0 and GraphPad Prism 4.01 softwares. Analysis was carried out separately in boys and girls. In the present study, the dependent variables were FVC,, PEFR,, F and F. Pearson s correlation analysis was carried out to identify the predictor variables. Prediction equations were developed using the multiple linear regression procedure. Linear and nonlinear models were developed and the former was selected based on criteria of simplicity and ease of clinical application, high predictive capability (R 2 ) and yield of smallest residuals. The independent variables were entered in the sequence of height, age and weight. Models were constructed including one (height), two (height and
3 2012;Vol.54 The Indian Journal of Chest Diseases & Allied Sciences 61 age) and three predictor variables (height, age and weight) and R 2, adjusted R 2 and R 2 change on entering each predictor variable were calculated for each model. If the R 2 change at each step was significant and there was a substantial improvement in the predictive ability, the model was accepted. If not, the model at the previous step was accepted. Standard errors of the estimate (SEE) were calculated and analysis of variance was carried out for each model to evaluate the significance of the regression equation. Estimates of regression coefficients were obtained and their significance was determined by student s t test. The goodness of fit was examined by testing for independence of predictor variables (by examining the tolerance statistics and VIF values), normality and equal variances of the residuals (by residuals normality plot), and linear type relationship between the predictors and the outcome variable (by Q-Q plots). Unusual and influential observations were examined. These included outliers, points with high leverage and high influence. Analysis was repeated excluding these observations to determine their impact on the models and the original models were retained if the effect on the equations was small and inconsequential. RESULTS Acceptable data was obtained in 365 boys and 305 girls. The ages and the anthropometric data (mean±sd) in the two genders were respectively: age (years), 11.53±3.37 and 11.74±3.23 (p>0.05); height (m), 1.49±0.18 and 1.45±0.14 (p<0.01); weight (Kg), 44.56±18.42 and 40.97±13.82 (p<0.01); and body mass index (Kg/m 2 ) 19.04±4.43 and 18.75±3.91 (p>0.05). The age distribution is shown in table 1. The median, (range) and interquartile ranges (IQR) in boys were as follows: age (years): 11, (6 to 17), IQR: 9 to 14; height (m): 1.5, (1.09 to 1.91), IQR: 1.35 to 1.65; weight (Kg): Table 1. Age distribution of the children Age (in years) (n) (n=365) (n=305) 6 (62) (28) (39) (71) (47) (96) (44) (60) (59) (59) (59) (46) , (15 to 98), IQR: 28 to 58. The median, (range) and IQR in girls were as follows: age (years): 11, (6 to 17), IQR: 9 to 15; height (m): 1.48, (1.09 to 1.7), IQR: 1.35 to 1.58; weight (Kg): 41, (15 to 78), IQR: 30 to 51. The pulmonary functions of boys and girls were compared for the entire sample (Table 2). FVC, and PEFR were significantly higher among boys. However, the flow rates,, and were not significantly different. Table 3 shows the correlations of FVC and with age, height and weight in boys and girls. Table 4 shows the correlations of PEFR,,, and with age, height and weight in boys and girls. The regression equations developed are given in table 5. The equation is expressed as follows: Spirometric parameter = Constant + (β Coefficient for height x height in cm) + (β Coefficient for age x age in years) + (β Coefficient for weight x weight in Kg) The SEE is provided for calculation of the lower limits of normal. As /FVC was found to be independent of age and height in boys, and had only a weak correlation with age in girls, no equations were developed for this parameter. Table 2. Pulmonary function distribution in boys and girls for the whole sample Spirometry Gender Mean±SD Median Range Interquartile Parameter Range FVC 2.88±1.09 * to to ± to to ±0.94 * to to ± to to 2.64 PEFR 5.47±2.02 ** to to ± to to ±1.10 ns to to ± to to ±1.24 ns to to ± to to ±0.75 ns to to ± to to 1.92 FVC=Forced vital capacity; =Forced expiratory volume in one second; PEFR=Peak expiratory flow rate; =Mean forced expiratory flow rate over the middle 50% of the vital capacity; and =Forced expiratory flow rates at 50% and 75% exhalation of vital capacity; *=p<0.001; **=p<0.01; ns=not significant, p>0.05
4 62 Regression Equations for Spirometry in Children S.K. Chhabra et al Table 3. Pearson s correlation coefficients (r) for FVC and with age, height and weight FVC FVC Age r=0.89 r=0.89 r=0.85 r=0.87 Height r=0.92 r=0.92 r=0.88 r=0.86 Weight r=0.86 r=0.842 r=0.84 r=0.83 DISCUSSION We have presented prediction equations for various spirometry parameters for children of north Indian origin in Delhi region between the ages of 6 to 17 years. These are derived from spirometry carried out as per the current standardised protocol recommended by the ATS/ERS task force. 10 The FVC,, PEFR,,, and showed moderate to strong correlations with age, height and weight in both boys and girls. The /FVC was not correlated Table 4. Pearson s correlation coefficients (r) for PEFR,, and F with age, height and weight 75 PEFR PEFR Age r=0.87 r=0.81 r=0.77 r=0.77 r=0.82 r=0.73 r=0.70 r=0.62 Height r=0.87 r=0.82 r=0.77 r=0.69 r=0.81 r=0.76 r=0.70 r=0.64 Weight r=0.78 r=0.71 r=0.69 r=0.60 r=0.74 r=0.68 r=0.66 r=0.55 p<0.000 p< p< p< Table 5. Regression equations for spirometry parameters Spirometry Constant β Coefficient for β Coefficient for β Coefficient for Standard Error R 2 Parameter Height Age Weight of Estimate FVC PEFR FVC PEFR Equation: Spirometric parameter = Constant + (β Coefficient for height x height in cm) + (β Coefficient for age x age in years) + (β Coefficient for weight x weight in Kg) Descriptive statistics for /FVC is presented in table 6. The 5 th percentile can be used to define the lower limit of normal. with age or height in boys, and with height in girls, though it showed a weak correlation with age in the latter. Table 6. Descriptive statistics for /FVC ratio Gender Mead±SD 5 th percentile 50 th percentile 95 th percentile 84.41± ±
5 2012;Vol.54 The Indian Journal of Chest Diseases & Allied Sciences 63 In both boys and girls, the equations explained very high variability of FVC, and PEFR as shown by the R 2 values. However, the explained variability for flow rates was lesser, with that for being the least. The very high values for R 2 for FVC and are also the reason why the interpretation algorithms for spirometry are based exclusively on these two parameters. The FVC and are the only parameters for which reproducibility criteria have been defined 10 and the flow rates have less precision. Effects of environmental exposures including environmental tobacco smoke and outdoor air pollution, physical activity and conditioning, nutritional factors, genetics and respiratory infections are extremely difficult to capture and therefore never factored in any model. In addition, pulmonary function has inherent variability on repeated testing. Therefore, pulmonary function parameters usually have a high standard deviation and consequently wide range of 95% confidence limits for defining normalcy. It is remarkable that among all the predictors, height alone explained a major part of variability. Inclusion of age, and weight in some equations, explained a small additional variability as shown by the R 2 change. Thus, in boys, for FVC and, all the three predictor variables were retained in the equations while for PEFR,, and, only height and age were included. For girls, weight was retained in the equations for FVC,, PEFR and. For all the parameters, the adjusted R 2 values were very close to R 2 implying that if the equation was derived from the population rather than the sample, we would get similar results. These equations are the first effort from India after the recent standardisation of spirometry 10 and indeed one of the few available globally. Revision of prediction equations was long overdue as technology and measurement protocols have changed and also to determine if lung health in population is changing due to changes in nutritional status, environmental exposures and rates of early childhood respiratory infections. The previous studies from India, with city and year, were: Bhattacharya and Banerjee 1 (Delhi, 1966), Jain and Ramiah 2 (Delhi, 1967), Vohra et al 3 (Ahmedabad, 1984), Malik and Jindal 4 (Chandigarh, 1985), Kumar et al 5 (Patiala, 1992), Gupta et al 6 (Delhi, 1993), Chowgule et al 7 (Mumbai, 1995), RajKappor et al 8 (Rohtak, 1997) and Vijayan et al 9 (Chennai, 2000). The present study has a few limitations. A wider selection from several schools would have provided a more representative sample. However, the selected school caters to a very wide socio-economic spectrum, and therefore, may be viewed as being fairly representative of Delhi. In order to ensure ethnic homogeneity, we included only children whose parents were of north Indian origin. A multicentric study with participation of other cities of the region was not feasible because of limited resources. Therefore, while the equations predict pulmonary function of children of north Indian origin, we suggest that the equations may also be validated in other north Indian states in further studies. A chest radiograph would have confirmed normalcy. However, this was not feasible in a field study. A careful and detailed history and examination by the physicians, however, ensured that only normal children were included. These equations should be helpful in interpretation of spirometric data, and thus, in the management of respiratory diseases such as asthma in children. Equipments used in most pulmonary clinics use softwares that carry western prediction equations and are not valid for Indian population. These equations would allow manufacturers to provide Indian equations in the softwares. The equations described by us have been developed for northern parts of the country. As ethnic differences are important, each region needs to develop such equations following the standardised protocols and strict quality control. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The project titled Pulmonary Function in Normal Children in Delhi Region: Development of Reference Standards for Spirometry was approved and funded by the Indian Council of Medical Research. The support of the Council is gratefully acknowledged. REFERENCES 1. Bhattacharya AK, Banerjee S. Vital capacity in children and young adults of India. Indian J Med Res 1966;54: Jain SK, Ramiah TJ. Prediction of ventilatory norms in healthy boys 7-14 years age. Indian J Med Res 1967;55: Vohra RS, Shah SC, Shah GS. Pulmonary functions in normal children. Indian Pediatr 1984;21: Malik SK, Jindal SK. Pulmonary function tests in healthy children. Indian Pediatr 1985;22: Kumar A, Pannu BK, Manchanda KC, Singh KD, Lahal SS. Pulmonary function tests in healthy male Punjabi children. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 1992;34: Gupta CK, Mishra G, Mehta SC, Prasad J. On the contribution of height to predict lung volumes, capacities and diffusion in healthy schoolchildren of years. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 1993;35: Chowgule RV, Shetye VM, Parmar JR. Lung function tests in normal Indian children. Indian Pediatr 1995;32: RajKappor, Mahajan KK, Mahajan A. Ventilatory lung function tests in schoolchildren of 6-13 years. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 1997;39: Vijayan VK, Reetha AM, Kuppurao KV, Venkatesan P, Thilakavathy S. Pulmonary function in normal south Indian children aged 7 to 19 years. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 2000;42: Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos F, Casaburi R, Coates A, et al. Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J 2005;26:
Prediction Equations for Spirometry in Adults from Northern India
 Original Article Prediction Equations for Spirometry in Adults from Northern India S.K. Chhabra 1, R. Kumar 3, U. Gupta 1, M. Rahman 2 and D.J. Dash 1 Department of Cardiorespiratory Physiology 1 and Biostatistics
Original Article Prediction Equations for Spirometry in Adults from Northern India S.K. Chhabra 1, R. Kumar 3, U. Gupta 1, M. Rahman 2 and D.J. Dash 1 Department of Cardiorespiratory Physiology 1 and Biostatistics
Comparison of Different Spirometry Reference Equations in Predicting Lung Function in Sri Lankan School Children
 Original Article Comparison of Different Spirometry Reference Equations in Predicting Lung Function in Sri Lankan School Children G Liyanage 1 *, BDW Jayamanne 2, Aaqiff M 3 1 Department of Paediatrics
Original Article Comparison of Different Spirometry Reference Equations in Predicting Lung Function in Sri Lankan School Children G Liyanage 1 *, BDW Jayamanne 2, Aaqiff M 3 1 Department of Paediatrics
/FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan
 Article FEV 1, FVC, FEV 1 /FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan Meenakshi Sharma 1, Rambabu Sharma 2, Neelam Singh 3, Kusum Gaur 4 Abstract Background: The knowledge of pulmonary
Article FEV 1, FVC, FEV 1 /FVC ratio in children of 7-14 years of age from Western Rajasthan Meenakshi Sharma 1, Rambabu Sharma 2, Neelam Singh 3, Kusum Gaur 4 Abstract Background: The knowledge of pulmonary
PREDICTION EQUATIONS FOR LUNG FUNCTION IN HEALTHY, LIFE TIME NEVER-SMOKING MALAYSIAN POPULATION
 Prediction Equations for Lung Function in Healthy, Non-smoking Malaysian Population PREDICTION EQUATIONS FOR LUNG FUNCTION IN HEALTHY, LIFE TIME NEVER-SMOKING MALAYSIAN POPULATION Justin Gnanou, Brinnell
Prediction Equations for Lung Function in Healthy, Non-smoking Malaysian Population PREDICTION EQUATIONS FOR LUNG FUNCTION IN HEALTHY, LIFE TIME NEVER-SMOKING MALAYSIAN POPULATION Justin Gnanou, Brinnell
Indian Journal of Basic & Applied Medical Research; September 2013: Issue-8, Vol.-2, P
 Original article: Study of pulmonary function in different age groups Dr.Geeta J Jagia*,Dr.Lalita Chandan Department of Physiology, Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai, India *Author for correspondence: drgrhegde@gmail.com
Original article: Study of pulmonary function in different age groups Dr.Geeta J Jagia*,Dr.Lalita Chandan Department of Physiology, Seth GS Medical College, Mumbai, India *Author for correspondence: drgrhegde@gmail.com
Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot Malhi, B.R. Srinivas and Lata Kumar
 Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
Comparison of Improvement in Quality of Life Score with Objective Parameters of Pulmonary Function in Indian Asthmatic Children Receiving Inhaled Corticosteroid Therapy Meenu Singh, Joseph L. Mathew, Prabhjot
EFFECT OF SMOKING ON BODY MASS INDEX: A COMMUNITY-BASED STUDY
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE. EFFECT OF SMOKING ON BODY MASS INDEX: A COMMUNITY-BASED STUDY Pragti Chhabra 1, Sunil K Chhabra 2 1 Professor, Department of Community Medicine, University College of Medical Sciences,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. EFFECT OF SMOKING ON BODY MASS INDEX: A COMMUNITY-BASED STUDY Pragti Chhabra 1, Sunil K Chhabra 2 1 Professor, Department of Community Medicine, University College of Medical Sciences,
Spirometric protocol
 Spirometric protocol Spirometry is the most common of the Pulmonary Function Test, that measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled.
Spirometric protocol Spirometry is the most common of the Pulmonary Function Test, that measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled.
Getting Spirometry Right It Matters! Performance, Quality Assessment, and Interpretation. Susan Blonshine RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC
 Getting Spirometry Right It Matters! Performance, Quality Assessment, and Interpretation Susan Blonshine RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC Objectives Sample Title Recognize acceptable spirometry that meets the start
Getting Spirometry Right It Matters! Performance, Quality Assessment, and Interpretation Susan Blonshine RRT, RPFT, AE-C, FAARC Objectives Sample Title Recognize acceptable spirometry that meets the start
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Prasad B K
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(5E):1854-1858 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(5E):1854-1858 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Pulmonary Function Testing
 In the Clinic Pulmonary Function Testing Hawa Edriss MD, Gilbert Berdine MD The term PFT encompasses three different measures of lung function: spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity. In this
In the Clinic Pulmonary Function Testing Hawa Edriss MD, Gilbert Berdine MD The term PFT encompasses three different measures of lung function: spirometry, lung volumes, and diffusion capacity. In this
Interpretation of Spirometry: Selection of Predicted Values and Defining Abnormality
 Review Article Interpretation of Spirometry: Selection of Predicted Values and Defining Abnormality S.K. Chhabra Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Vallabhbhai Patel Chest Institute, University of Delhi,
Review Article Interpretation of Spirometry: Selection of Predicted Values and Defining Abnormality S.K. Chhabra Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Vallabhbhai Patel Chest Institute, University of Delhi,
Prediction models for peak expiratory flow rate in Indian population aged years
 Research Article Prediction models for peak expiratory flow rate in Indian population aged 18 25 years Prakash Kumar Nayak 1, Sudeep Satpathy 1, Magna Manjareeka 1, Priyadarsini Samanta 1, Jayanti Mishra
Research Article Prediction models for peak expiratory flow rate in Indian population aged 18 25 years Prakash Kumar Nayak 1, Sudeep Satpathy 1, Magna Manjareeka 1, Priyadarsini Samanta 1, Jayanti Mishra
behaviour are out of scope of the present review.
 explained about the test, a trial may be done before recording the results. The maneuver consists initially of normal tidal breathing. The subject then inhales to maximally fill the lungs. This is followed
explained about the test, a trial may be done before recording the results. The maneuver consists initially of normal tidal breathing. The subject then inhales to maximally fill the lungs. This is followed
Spirometric evaluation of pulmonary functions of medical students in Nepal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASIAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Spirometric evaluation of pulmonary functions of medical students in Nepal G. B. Nepal 1, P. K. L. Das 2, A. Bhaila 3 1,3 Lecturer, Department of Physiology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ASIAN JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Spirometric evaluation of pulmonary functions of medical students in Nepal G. B. Nepal 1, P. K. L. Das 2, A. Bhaila 3 1,3 Lecturer, Department of Physiology,
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
Measurement of peak expiratory flow rate values in healthy school going children between 6 and 12 years attending urban schools in Chennai
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Durairaj P et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Nov;4(6):2002-2007 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Durairaj P et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2017 Nov;4(6):2002-2007 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Original Research Article DOI:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2008; 52 (4) : 383 388 CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS ANURADHA R. JOSHI*, RATAN SINGH AND A. R. JOSHI Department of Physiology,
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2008; 52 (4) : 383 388 CORRELATION OF PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS WITH BODY FAT PERCENTAGE IN YOUNG INDIVIDUALS ANURADHA R. JOSHI*, RATAN SINGH AND A. R. JOSHI Department of Physiology,
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh
 BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2005; VOL 29 (3) : 93-98 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh JU MAZUMDER 1, S AHMED 2, AH MOLLAH 3, ARML KABIR 4,
BANGLADESH J CHILD HEALTH 2005; VOL 29 (3) : 93-98 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children Aged 6-15 Years in a School of Dhaka City, Bangladesh JU MAZUMDER 1, S AHMED 2, AH MOLLAH 3, ARML KABIR 4,
Evaluation of Lung diffusing capacity for Carbonmonoxide. (DLco) in healthy adolescents ABSTRACT
 Evaluation of Lung diffusing capacity for Carbonmonoxide (DLco) in healthy adolescents AMJAD F. AHMADP P ABSTRACT In pulmonary function tests (PFT), the selection of prediction equation for lung diffusing
Evaluation of Lung diffusing capacity for Carbonmonoxide (DLco) in healthy adolescents AMJAD F. AHMADP P ABSTRACT In pulmonary function tests (PFT), the selection of prediction equation for lung diffusing
Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics
 8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
Bedi et al: PEFR in children
 Original Article A study of peak expiratory flow rate in normal healthy children of Punjab Bedi U 1, Dang BK 2 ABSTRACT Background: Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) recording is an 1 Dr Upneet Bedi Associate
Original Article A study of peak expiratory flow rate in normal healthy children of Punjab Bedi U 1, Dang BK 2 ABSTRACT Background: Peak expiratory flow rate (PEFR) recording is an 1 Dr Upneet Bedi Associate
Comparative Study on the Peak Expiratory Flow Rate of School Children(10 14 years) in the Union Territory of Puducherry
 International Journal of Research in Social Sciences Vol. 8 Issue 7, July 2018, ISSN: 2249-2496 Impact Factor: 7.081 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
International Journal of Research in Social Sciences Vol. 8 Issue 7, July 2018, ISSN: 2249-2496 Impact Factor: 7.081 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
Understanding the Basics of Spirometry It s not just about yelling blow
 Understanding the Basics of Spirometry It s not just about yelling blow Carl D. Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Technical Director - Pulmonary Function Labs and Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine -
Understanding the Basics of Spirometry It s not just about yelling blow Carl D. Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Technical Director - Pulmonary Function Labs and Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine -
Office Based Spirometry
 Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)1, 14-18 Scott Klosterman, DO; Woodson Crenshaw, OMS4 Spartanburg Regional Family Medicine Residency Program; Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine - Virginia Campus
Osteopathic Family Physician (2014)1, 14-18 Scott Klosterman, DO; Woodson Crenshaw, OMS4 Spartanburg Regional Family Medicine Residency Program; Edward Via College of Osteopathic Medicine - Virginia Campus
Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 4 Number 2 Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pulmonary Medicine Volume 4 Number 2 Difference Between The Slow Vital Capacity And Forced Vital Capacity: Predictor Of Hyperinflation In Patients With Airflow Obstruction
Dr. T. Bhuvaneswari * Original Research Article. Abstract
 Original Research Article Diabetes mellitus alteres the pulmonary function test parameters among the patients attending regular check-up in tertiary care hospital in and around Chennai - Evidencebased
Original Research Article Diabetes mellitus alteres the pulmonary function test parameters among the patients attending regular check-up in tertiary care hospital in and around Chennai - Evidencebased
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING. By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS)
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS CATEGORIES Spirometry Lung volumes
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING By: Gh. Pouryaghoub. MD Center for Research on Occupational Diseases (CROD) Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS CATEGORIES Spirometry Lung volumes
This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Study Design and Setting This is a cross-sectional analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) data 2007-2008, 2009-2010, and 2011-2012. The NHANES is
Study of dynamic lung parameters in bronchial Asthma
 20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
20; 4(1): 312-317 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 20; 4(1): 312-317 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 20-11-2017 Accepted: 21-12-2017 Dr. Madhuchhanda Pattnaik Associate
ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print) *Corresponding author Shubhankar Mishra
 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2015; 3(5):429-433 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2015; 3(5):429-433 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
LUNG FUNCTIONS IN MALNOURISHED CHILDREN AGED FIVE TO ELEVEN YEARS
 LUNG FUNCTIONS IN MALNOURISHED CHILDREN AGED FIVE TO ELEVEN YEARS M.M.A. Faridi Pratibha Gupta Anupam Prakash ABSTRACT Lung functions including FVC, FEV 1, PEFR, %FEV 1 /FVC and Empey Index were measured
LUNG FUNCTIONS IN MALNOURISHED CHILDREN AGED FIVE TO ELEVEN YEARS M.M.A. Faridi Pratibha Gupta Anupam Prakash ABSTRACT Lung functions including FVC, FEV 1, PEFR, %FEV 1 /FVC and Empey Index were measured
How to Perform Spirometry
 Purpose How to Perform Spirometry This guideline provides recommendations regarding best practice to support high quality spirometry practice for KINNECT Pre-Employment Medicals. Scope This guideline provides
Purpose How to Perform Spirometry This guideline provides recommendations regarding best practice to support high quality spirometry practice for KINNECT Pre-Employment Medicals. Scope This guideline provides
Evaluation of efficacy and utility of spirometry data in elderly
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20185109 Evaluation of efficacy
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20185109 Evaluation of efficacy
SPIROMETRY. Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: Copyright CARE Medical ltd
 SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual can
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 34(2), September October 2015; Article No. 24, Pages: Role of Spirometry in Diagnosis of Respiratory Diseases
 Review Article Role of Spirometry in Diagnosis of Respiratory Diseases Dipti Mohapatra 1, Tapaswini Mishra 1, Manasi Behera 1, Nibedita Priyadarsini 1, Arati Mohanty 1, *Prakash Kumar Sasmal 2 1 Department
Review Article Role of Spirometry in Diagnosis of Respiratory Diseases Dipti Mohapatra 1, Tapaswini Mishra 1, Manasi Behera 1, Nibedita Priyadarsini 1, Arati Mohanty 1, *Prakash Kumar Sasmal 2 1 Department
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Spirometry: Introduction
 Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Spirometry: Introduction Dr. Badri Paudel 1 2 GMC Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air the patient can expel from the lungs after a maximal expiration.
Pulmonary Functions in Punjabi Type 2 Diabetics: Based on Chronicity of Disease
 Pulmonary Functions in Punjabi Type 2 Diabetics: Based on Chronicity of Disease Navkaran Shergill and Ashok Kumar Abstract Aim: To observe pulmonary functions in two groups of Punjabi population, group
Pulmonary Functions in Punjabi Type 2 Diabetics: Based on Chronicity of Disease Navkaran Shergill and Ashok Kumar Abstract Aim: To observe pulmonary functions in two groups of Punjabi population, group
CHILD HEALTH AND DEVELOPMENT STUDY
 CHILD HEALTH AND DEVELOPMENT STUDY 9. Diagnostics In this section various diagnostic tools will be used to evaluate the adequacy of the regression model with the five independent variables developed in
CHILD HEALTH AND DEVELOPMENT STUDY 9. Diagnostics In this section various diagnostic tools will be used to evaluate the adequacy of the regression model with the five independent variables developed in
Assessment of Bronchodilator Response in Various Spirometric Patterns
 Original Article 2013 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Assessment of Bronchodilator Response in Various Spirometric Patterns Amir Houshang
Original Article 2013 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran ISSN: 1735-0344 TANAFFOS Assessment of Bronchodilator Response in Various Spirometric Patterns Amir Houshang
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C
 MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
MSRC AIR Course Karla Stoermer Grossman, MSA, BSN, RN, AE-C Explain the importance of objective measures in the management of asthma Explain the different types of objective measures used in the management
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
COMPREHENSIVE RESPIROMETRY
 INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist, District Early Intervention Programme National Health Mission, Ambikapur, Chattisgarh, India
 (Volume2, Issue6) Available online at www.ijarnd.com Evaluation of Peak Expiratory Flow Rate and Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second in Indian Children with Suspected Asthma Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist,
(Volume2, Issue6) Available online at www.ijarnd.com Evaluation of Peak Expiratory Flow Rate and Forced Expiratory Volume in One Second in Indian Children with Suspected Asthma Dr. Akanksha Kaushal Physiotherapist,
Association between carrying school bags and lung functions among elementary school children in Al Hilla City,2015
 Association between carrying school bags and lung functions among elementary school children in Al Hilla City,2015 Prof. Dr. Hasan Alwan Baiee Sarah Ala'a Abbas Babylon University All over the world there
Association between carrying school bags and lung functions among elementary school children in Al Hilla City,2015 Prof. Dr. Hasan Alwan Baiee Sarah Ala'a Abbas Babylon University All over the world there
APPENDIX D REFERENCE AND PREDICTIVE VALUES FOR PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE (PEFR)
 APPENDIX D REFERENCE AND PREDICTIVE VALUES FOR PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE (PEFR) Lung function is related to physical characteristics such as age and height. In order to assess the Peak Expiratory Flow
APPENDIX D REFERENCE AND PREDICTIVE VALUES FOR PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATE (PEFR) Lung function is related to physical characteristics such as age and height. In order to assess the Peak Expiratory Flow
BETTER SPIROMETRY. Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: Copyright CARE Medical ltd
 BETTER SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual
BETTER SPIROMETRY Marijke Currie (CRFS) Care Medical Ltd Phone: 0800 333 808 Email: sales@caremed.co.nz What is spirometry Spirometry is a physiological test that measures the volume of air an individual
PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATES AMONG WOMEN EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT COOKING FUELS IN RURAL INDIA
 Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATES AMONG WOMEN EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT COOKING FUELS IN RURAL INDIA Sukhsohale D Neelam 1, Narlawar W Uday 2, Thakre S Sushama 1 and Ughade
Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health PEAK EXPIRATORY FLOW RATES AMONG WOMEN EXPOSED TO DIFFERENT COOKING FUELS IN RURAL INDIA Sukhsohale D Neelam 1, Narlawar W Uday 2, Thakre S Sushama 1 and Ughade
Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement
 Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
Shortness of breath THEME Spirometry: an essential clinical measurement BACKGROUND Respiratory disease is common and amenable to early detection and management in the primary care setting. Spirometric
SPIROMETRY METHOD. COR-MAN IN / EN Issue A, Rev INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark
 SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT)
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT) Objectives: By the end of the present lab, students should be able to: 1. Record lung volumes and capacities and compare them with those of a typical person of the same gender,
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT) Objectives: By the end of the present lab, students should be able to: 1. Record lung volumes and capacities and compare them with those of a typical person of the same gender,
M easurement of lung function is a well established part
 1021 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Feasibility of measuring lung function in preschool children W Nystad, S O Samuelsen, P Nafstad, E Edvardsen, T Stensrud, J J K Jaakkola... See end of article for authors affiliations...
1021 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Feasibility of measuring lung function in preschool children W Nystad, S O Samuelsen, P Nafstad, E Edvardsen, T Stensrud, J J K Jaakkola... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Patient assessment - spirometry
 Patient assessment - spirometry STEP 1 Learning objectives This module will provide you with an understanding of spirometry and the role it plays in aiding the diagnosis of lung diseases, particularly
Patient assessment - spirometry STEP 1 Learning objectives This module will provide you with an understanding of spirometry and the role it plays in aiding the diagnosis of lung diseases, particularly
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 3/12/2018
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
What do pulmonary function tests tell you?
 Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 12 Page December 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.45 Study of effect of obesity on Pulmonary
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i12.45 Study of effect of obesity on Pulmonary
DIAGNOSTIC ACCREDITATION PROGRAM. Spirometry Quality Control Plan
 DIAGNOSTIC ACCREDITATION PROGRAM Spirometry Quality Control Plan Table of Contents Introduction...1 Spirometry Definitions and Requirements...2 Spirometry Requirements... 2...4 Daily Quality Control (see
DIAGNOSTIC ACCREDITATION PROGRAM Spirometry Quality Control Plan Table of Contents Introduction...1 Spirometry Definitions and Requirements...2 Spirometry Requirements... 2...4 Daily Quality Control (see
S P I R O M E T R Y. Objectives. Objectives 2/5/2019
 S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
S P I R O M E T R Y Dewey Hahlbohm, PA-C, AE-C Objectives To understand the uses and importance of spirometry testing To perform spirometry testing including reversibility testing To identify normal and
Spirometry in primary care
 Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
Spirometry in primary care Wednesday 13 th July 2016 Dr Rukhsana Hussain What is spirometry? A method of assessing lung function Measures volume of air a patient can expel after a full inspiration Recorded
OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AND PULMONARY FUNCTION OF WORKERS OF CARPET INDUSTRIES AND SAWMILLS, LALITPUR, NEPAL
 Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AND PULMONARY FUNCTION OF WORKERS OF CARPET INDUSTRIES AND SAWMILLS, LALITPUR, NEPAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
Asian Journal of Medical Science, Volume-5(2014) OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AND PULMONARY FUNCTION OF WORKERS OF CARPET INDUSTRIES AND SAWMILLS, LALITPUR, NEPAL ORIGINAL ARTICLE,Vol-5 No.2 http://nepjol.info/index.php/ajms
Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology
 Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Clinical and radiographic predictors of GOLD-Unclassified smokers in COPDGene
 Clinical and radiographic predictors of GOLD-Unclassified smokers in COPDGene Emily S. Wan, John E. Hokanson, James R. Murphy, Elizabeth A. Regan, Barry J. Make, David A. Lynch, James D. Crapo, Edwin K.
Clinical and radiographic predictors of GOLD-Unclassified smokers in COPDGene Emily S. Wan, John E. Hokanson, James R. Murphy, Elizabeth A. Regan, Barry J. Make, David A. Lynch, James D. Crapo, Edwin K.
Physiology lab (RS) First : Spirometry. ** Objectives :-
 Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
Physiology lab (RS) ** Objectives :- 1. Spirometry in general. 2. Spirogram (volumes and capacities). 3. The importance of vital capacity in diagnosis. 4. Flow volume loop. 5. Miss Arwa s part (the practical
SUMMARY THIS IS A PRINTED COPY OF AN ELECTRONIC DOCUMENT. PLEASE CHECK ITS VALIDITY BEFORE USE.
 i SUMMARY ZENECA PHARMACEUTICALS FINISHED PRODUCT: ACTIVE INGREDIENT: ACCOLATE zafirlukast (ZD9188) Trial title (number): A Dose-ranging, Safety and Efficacy Trial with Zafirlukast (ACCOLATE ) in the Treatment
i SUMMARY ZENECA PHARMACEUTICALS FINISHED PRODUCT: ACTIVE INGREDIENT: ACCOLATE zafirlukast (ZD9188) Trial title (number): A Dose-ranging, Safety and Efficacy Trial with Zafirlukast (ACCOLATE ) in the Treatment
Peak expiratory flow rate and its correlation with body surface area in healthy school children
 2014; 3(4): 397-401 Available online at: www.jsirjournal.com Research Article ISSN 2320-4818 JSIR 2014; 3(4): 397-401 2014, All rights reserved Received: 11-09-2014 Accepted: 22-09-2014 Dr. K. Vijay Krishna
2014; 3(4): 397-401 Available online at: www.jsirjournal.com Research Article ISSN 2320-4818 JSIR 2014; 3(4): 397-401 2014, All rights reserved Received: 11-09-2014 Accepted: 22-09-2014 Dr. K. Vijay Krishna
Lung function testing
 ACTIVITY BRIEF Lung function testing The science at work Common respiratory complaints include asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Peak flow meters and spirometers can be used by health
ACTIVITY BRIEF Lung function testing The science at work Common respiratory complaints include asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). Peak flow meters and spirometers can be used by health
Spirometry: FEVER DISEASE DIABETES HOW RELIABLE IS THIS? 9/2/2010 BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools
 SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
SPIROMETRY PRINCIPLES, PROCEDURE AND QA Spirometry: Dr. Rahul Kodgule CHEST RESEARCH FOUNDATION, PUNE FEVER ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE DIABETES BUT WHAT WE PRACTICE: Spirometers are objective tools to diagnose
Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children and Adolescents of Korean Chinese in Northeast China
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Respiratory Diseases http://dx.doi.org/0./jkms.0...9 J Korean Med Sci 0; : 9-7 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children and Adolescents of Korean Chinese in Northeast China Kui Feng,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Respiratory Diseases http://dx.doi.org/0./jkms.0...9 J Korean Med Sci 0; : 9-7 Spirometric Standards for Healthy Children and Adolescents of Korean Chinese in Northeast China Kui Feng,
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY. A. Definition of Spirometry
 UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
Pulmonary Function Tests. Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist
 Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Pulmonary Function Tests Mohammad Babai M.D Occupational Medicine Specialist www.drbabai.com Pulmonary Function Tests Pulmonary Function Tests: Spirometry Peak-Flow metry Bronchoprovocation Tests Body
Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District
 Original Research Article Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District V. Sivagangailakshmi 1*,
Original Research Article Comparison of pulmonary function between smokers and non-smokers among out patients of Raja Muthaiah Medical College and Hospital, Cuddalore District V. Sivagangailakshmi 1*,
Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide measurements between NIOX MINO â electrochemical and Ecomedics chemiluminescence analyzer
 Respiratory Medicine (2008) 102, 1667e1671 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed SHORT COMMUNICATION Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide measurements between
Respiratory Medicine (2008) 102, 1667e1671 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/rmed SHORT COMMUNICATION Comparison of exhaled nitric oxide measurements between
The Relationship Between FEV 1 and Peak Expiratory Flow in Patients With Airways Obstruction Is Poor*
 Original Research PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING The Relationship Between FEV 1 and Peak Expiratory Flow in Patients With Airways Obstruction Is Poor* Ashutosh N. Aggarwal, MD, FCCP; Dheeraj Gupta, MD, FCCP;
Original Research PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING The Relationship Between FEV 1 and Peak Expiratory Flow in Patients With Airways Obstruction Is Poor* Ashutosh N. Aggarwal, MD, FCCP; Dheeraj Gupta, MD, FCCP;
To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry
 Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article To assess the pulmonary impairment in treated pulmonary tuberculosis patients using spirometry Dhipu Mathew 1, Kirthana G 2, Krishnapriya R 1, Srinivasan R 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Regan EA, Lynch DA, Curran-Everett D, et al; Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) Investigators. Clinical and radiologic disease in smokers with normal spirometry. Published
Supplementary Online Content Regan EA, Lynch DA, Curran-Everett D, et al; Genetic Epidemiology of COPD (COPDGene) Investigators. Clinical and radiologic disease in smokers with normal spirometry. Published
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Lung Function Reference Values in Chinese Children and Adolescents in Hong Kong I. Spirometric Values and Comparison with Other Populations
 Lung Function Reference Values in Chinese Children and Adolescents in Hong Kong I. Spirometric Values and Comparison with Other Populations MARY S. M. IP, EVA M. KARLBERG, JOHAN P. E. KARLBERG, KEITH D.
Lung Function Reference Values in Chinese Children and Adolescents in Hong Kong I. Spirometric Values and Comparison with Other Populations MARY S. M. IP, EVA M. KARLBERG, JOHAN P. E. KARLBERG, KEITH D.
Breathing and pulmonary function
 EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS
 Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Pulmonary function studies in young healthy Malaysians of Kelantan, Malaysia
 Indian J Med Res 134, November 2011, pp 653-657 Pulmonary function studies in young healthy Malaysians of Kelantan, Malaysia Amit Bandyopadhyay * School of Health Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Kelantan,
Indian J Med Res 134, November 2011, pp 653-657 Pulmonary function studies in young healthy Malaysians of Kelantan, Malaysia Amit Bandyopadhyay * School of Health Sciences, University Sains Malaysia, Kelantan,
Received: 23 rd Nov-2012 Revised: 02 nd Dec-2012 Accepted: 03 rd Dec-2012 Research article
 Received: 23 rd Nov-2012 Revised: 02 nd Dec-2012 Accepted: 03 rd Dec-2012 Research article A STUDY OF CHANGES IN PULMONARY FUNCTION WITH ADVANCING AGE AND THE EFFECT OF SMOKING IN MALES OF NORTH KERALA
Received: 23 rd Nov-2012 Revised: 02 nd Dec-2012 Accepted: 03 rd Dec-2012 Research article A STUDY OF CHANGES IN PULMONARY FUNCTION WITH ADVANCING AGE AND THE EFFECT OF SMOKING IN MALES OF NORTH KERALA
COMPARISON BETWEEN INTERCOSTAL STRETCH AND BREATHING CONTROL ON PULMONARY FUNCTION PARAMETER IN SMOKING ADULTHOOD: A PILOT STUDY
 COMPARISON BETWEEN INTERCOSTAL STRETCH AND BREATHING CONTROL ON PULMONARY FUNCTION PARAMETER IN SMOKING ADULTHOOD: A PILOT STUDY Shereen Inkaew 1 Kamonchat Nalam 1 Panyaporn Panya 1 Pramook Pongsuwan 1
COMPARISON BETWEEN INTERCOSTAL STRETCH AND BREATHING CONTROL ON PULMONARY FUNCTION PARAMETER IN SMOKING ADULTHOOD: A PILOT STUDY Shereen Inkaew 1 Kamonchat Nalam 1 Panyaporn Panya 1 Pramook Pongsuwan 1
Correlation of Nutritional Status and Peak Expiratory Flow Rate in Normal South Indian Children Aged 6 to 10 Years
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 2, Issue 3 (Nov.- Dec. 2012), PP 11-16 Correlation of Nutritional Status and Peak Expiratory Flow Rate in Normal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 2, Issue 3 (Nov.- Dec. 2012), PP 11-16 Correlation of Nutritional Status and Peak Expiratory Flow Rate in Normal
SPIROMETRY. Performance and Interpretation for Healthcare Professionals. Faculty of Respiratory Physiology IICMS. Version 1 April 2015
 SPIROMETRY Performance and Interpretation for Healthcare Professionals Faculty of Respiratory Physiology IICMS Version 1 April 2015 Authors: Maria Mc Neill & Geraldine Nolan www.iars.ie Contents Page Background
SPIROMETRY Performance and Interpretation for Healthcare Professionals Faculty of Respiratory Physiology IICMS Version 1 April 2015 Authors: Maria Mc Neill & Geraldine Nolan www.iars.ie Contents Page Background
Spirometry Technique Maximizing Effort, Comprehension & Coordination
 Spirometry Technique Maximizing Effort, Comprehension & Coordination Carl Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Director - Pulmonary Function Labs & Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine - Mayo Clinic College
Spirometry Technique Maximizing Effort, Comprehension & Coordination Carl Mottram, RRT RPFT FAARC Director - Pulmonary Function Labs & Rehabilitation Associate Professor of Medicine - Mayo Clinic College
#8 - Respiratory System
 Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
CHANGES IN THE SHAPE OF THE MAXIMAL EXPIRATORY FLOW-VOLUME CURVE FOLLOWING WEIGHT LOSS IN OBESE FEMALES. Taylor C. Burns.
 CHANGES IN THE SHAPE OF THE MAXIMAL EXPIRATORY FLOW-VOLUME CURVE FOLLOWING WEIGHT LOSS IN OBESE FEMALES By Taylor C. Burns Honors Thesis Appalachian State University Submitted to The Honors College in
CHANGES IN THE SHAPE OF THE MAXIMAL EXPIRATORY FLOW-VOLUME CURVE FOLLOWING WEIGHT LOSS IN OBESE FEMALES By Taylor C. Burns Honors Thesis Appalachian State University Submitted to The Honors College in
CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT
 Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Circular Instruction 195 CIRCULAR INSTRUCTION REGARDING ESTABLISHMENT OF IMPAIRMENT DUE TO OCCUPATIONAL LUNG DISEASE FOR THE PURPOSES OF AWARDING PERMANENT DISABLEMENT COMPENSATION FOR OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES
Prediction equations for pulmonary function values in healthy children in Mashhad city, North East Iran
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prediction equations for pulmonary function values in healthy children in Mashhad city, North East Iran Syad Saleh Tabatabaie 1, Mohammad Hossein Boskabady 1,2, Sakinah Shah Mohammadi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prediction equations for pulmonary function values in healthy children in Mashhad city, North East Iran Syad Saleh Tabatabaie 1, Mohammad Hossein Boskabady 1,2, Sakinah Shah Mohammadi
#7 - Respiratory System
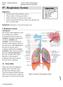 #7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
#7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
Lung Function Basics of Diagnosis of Obstructive, Restrictive and Mixed Defects
 Lung Function Basics of Diagnosis of Obstructive, Restrictive and Mixed Defects Use of GOLD and ATS Criteria Connie Paladenech, RRT, RCP, FAARC Benefits and Limitations of Pulmonary Function Testing Benefits
Lung Function Basics of Diagnosis of Obstructive, Restrictive and Mixed Defects Use of GOLD and ATS Criteria Connie Paladenech, RRT, RCP, FAARC Benefits and Limitations of Pulmonary Function Testing Benefits
Pulmonary Function Testing. Ramez Sunna MD, FCCP
 Pulmonary Function Testing Ramez Sunna MD, FCCP Lecture Overview General Introduction Indications and Uses Technical aspects Interpretation Patterns of Abnormalities When to perform a PFT 1. Evaluation
Pulmonary Function Testing Ramez Sunna MD, FCCP Lecture Overview General Introduction Indications and Uses Technical aspects Interpretation Patterns of Abnormalities When to perform a PFT 1. Evaluation
Tobacco Smoking in India: Prevalence, Quit-rates and Respiratory Morbidity
 Original Article Tobacco Smoking in India: Prevalence, Quit-rates and Respiratory Morbidity S.K. Jindal 1, A.N. Aggarwal 1, K. Chaudhry 2, S.K. Chhabra 3, G.A. D Souza 4, D. Gupta 1, S.K. Katiyar 5, R.
Original Article Tobacco Smoking in India: Prevalence, Quit-rates and Respiratory Morbidity S.K. Jindal 1, A.N. Aggarwal 1, K. Chaudhry 2, S.K. Chhabra 3, G.A. D Souza 4, D. Gupta 1, S.K. Katiyar 5, R.
Correlation between abdominal muscle strength and pulmonary function in subjects with low back pain
 Original Research Article Correlation between abdominal muscle strength and pulmonary function in subjects with low back pain Ruchi Patel 1*, Megha Sheth 2, Neeta Vyas 3 1 P.G. Student, 2 Lecturer, 3 Principal
Original Research Article Correlation between abdominal muscle strength and pulmonary function in subjects with low back pain Ruchi Patel 1*, Megha Sheth 2, Neeta Vyas 3 1 P.G. Student, 2 Lecturer, 3 Principal
Using Spirometry to Rule Out Restriction in Patients with Concomitant Low Forced Vital Capacity and Obstructive Pattern
 44 The Open Respiratory Medicine Journal, 2011, 5, 44-50 Using Spirometry to Rule Out Restriction in Patients with Concomitant Low Forced Vital Capacity and Obstructive Pattern Open Access Imran Khalid
44 The Open Respiratory Medicine Journal, 2011, 5, 44-50 Using Spirometry to Rule Out Restriction in Patients with Concomitant Low Forced Vital Capacity and Obstructive Pattern Open Access Imran Khalid
International Journal of Biomedical and Advance Research 318
 International Journal of Biomedical and Advance Research 318 PRE AND POST-EXERCISE CHANGES IN CARDIO-PULMONARY FUNCTIONS IN HEALTHY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF GULBARGA DISTRICT Malipatil B.S * and Mohammed Ehtesham
International Journal of Biomedical and Advance Research 318 PRE AND POST-EXERCISE CHANGES IN CARDIO-PULMONARY FUNCTIONS IN HEALTHY SCHOOL CHILDREN OF GULBARGA DISTRICT Malipatil B.S * and Mohammed Ehtesham
Increased difference between slow and forced vital capacity is associated with reduced exercise tolerance in COPD patients
 Yuan et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2014, 14:16 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Increased difference between slow and forced vital capacity is associated with reduced exercise tolerance in COPD patients Wei
Yuan et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2014, 14:16 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Increased difference between slow and forced vital capacity is associated with reduced exercise tolerance in COPD patients Wei
