Inferior quality of RSA during paradoxical sleep in rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus
|
|
|
- Crystal Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 362 Brain Research, 97 (1975) Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam - Printed in The Netherlands Inferior quality of RSA during paradoxical sleep in rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus I. URBAN AND D. DE WIED Rudolf Magnus Institute for Pharmacology, University of Utrecht, Medical Factdty, Utrecht (Tile Netherlands) (Accepted June 1st, 1975) Vasopressin and vasopressin analogues are involved in memory consolidation. Posterior lobectomized rats 15 and rats with hereditary 12 diabetes insipidus (DI) have severe disturbances in maintaining conditioned avoidance behavior. Memory impairment of hereditary DI rats can be readily shown in a one-trial learning situation iv. Vasopressin and vasopressin analogues normalize behavioral deficits in posterior lobectomized and hereditary DI rats15,17. A number of behavioral and electrophysiological studies have indicated that paradoxical sleep (PS) and hippocampal theta activity, termed rhythmic slow activity (RSA), are related to memory consolidation processes. Post-trial PS deprivation interfered with response retention in mice and rats 2,4,s. Humans deprived of PS showed inferior scores in verbal retention 1. In addition, an increase in the amount of post-trial theta activity was reported in rats with superior retention of conditioned avoidance response v. This activity, which reflects an activation along midbrain limbic pathways3, 6, accompanies the initiation of movements 5,az and dominates the hippocampus in stage of PS 11. If the RSA during PS is a correlate of the functional state of midbrain limbic structures which is essential for consolidation processes, and if these are controlled by vasopressin or vasopressin analogues, one might expect differences in either quality and/or quantity of RSA during PS in vasopressin deprived animals. The present study reports experiments on qualitative aspects of the RSA during PS in Brattleboro strain rats with hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. Two homozygous (HO-DI) and heterozygous (HE-DI) male rats weighing between 2 and 300 g were implanted with chronic electrodes in the dorsal hippocampus and the neck muscles to record RSA and the electromygram respectively. Two weeks after surgery, 5 habituation sessions were given to each animal in a sound attenuating experimental cage followed by 10 experimental sessions of 3 h duration per animal. During 4 of these sessions each rat received placebo only (0.5 ml of saline solution) and in the remaining sessions desglycinamide-8-arginine vasopressin (DG- AVP) was given (1 and 2/~g/100 body weight) subcutaneously. The RSA was recorded during PS. The total time of PS of the individual animals under the respective treatments was divided into 100-sec analysis epochs. The averaged power spectrum per
2 mean percent of power/hz i I I I I I ~. = homozygous o--o heterozygous N=32 Fig. 1. Differences in hippocampal RSA between heterozygous and homozygous, hereditary diabetes insipidus rats during paradoxical sleep. epoch was computed and stored on paper tape. In addition, subsequent parameters were computed and stored to characterize each spectrum: the 'peak frequency', and the 'mean frequency' and the 'spectrum width' at the level of half peak amplitude with corresponding frequencies. In the final analysis the mean of the averaged spectra was calculated according to animal or treatment and transformed to the percentage of power/hz. To illustrate the global difference in spectra of RSA of HO-DI and HE-DI rats, the data in both groups were pooled and expressed as the mean percentage of power/hz. The spectral parameters were similarly pooled with respect to treatment or animals and their means were compared using the Student's t-test. The localization of the recording electrodes was histologically verified at the end of the experiments. As shown on Fig. 1 the major difference in frequency content of the RSA during PS is confined to the band of Hz. The RSA of HO-DI animals contains lower frequencies than that of HE-DI rats. These relatively large differences can be followed in most of the spectral parameters summarized in Table I. The mean 'peak frequency' of HO-DI rats is 1 Hz and the 'mean frequency' 0.5 Hz lower than that of HE-DI animals. No significant differences exist in the 'spectrum width' parameter except that the corresponding frequencies were significantly shifted to the left on the frequency scale. This indicates that the increase in amount of lower frequencies in homozygous individuals indeed occurs at the cost of higher frequency components. The pattern of RSA of HE-DI rats strongly resembles that of Wistar rats. The effect of a single injection of DG-AVP is illustrated in Fig. 2. In a dosedependent manner, 1 and 2 #g of the peptide/100 g body weight enhanced the generation of RSA of higher frequencies in HO-DI animals. Table II summarizes the changes in spectral parameters in one animal obtained after treatment with 2 doses of DG- AVP. The higher dose almost normalizes the RSA except for the 'peak frequency' parameter which remained significantly below that of HE-DI rats (Table III). These preliminary results show that there are differences in quality of the RSA during PS between HO-DI and HE-DI rats. The fact that the RSA generating substrate does not readily produce high frequency theta components might be explained
3 364 TABLE I DIFFERENCES IN SPECTRAL PARAMETERS OF RSA BETWEEN HETEROZYGOUS AND HOMOZYGOUS DIABETES INSIPIDUS RATS DURING PARADOXICAL SLEEP Dl-homozygous DI-heterozygous P level ± S.D., N= 32 -if± S.D., N= 30 Mean frequency in Hz 7.6 ± ± 0.04 P < Peak frequency in Hz 6.8 ± ± 0.4 P < ½ peak amplitude 0.7 ± ± 0.3 n.s. Frequencies at ½ peak amplitude 6.4± ± ± ±0.4 P < either by a disturbed Na + and K + balance or by assuming a more specific role of vasopressin in membrane processes and transmission. The hypokalemia and hypernatremia which have been found in HO-DI rats a,l, however, are not responsible for the abnormal electrophysiological activity. Treatment with DG-AVP, an analogue of vasopressin which does not ameliorate the symptoms of the diabetes insipidus 16, almost completely normalized RSA. Core temperature is also known to influence the frequency content of RSA in rats 14. According to our observation HO-DI rats do not exhibit hypothermia. So far only quantitative differences in the amount of RSA or RAT DH1 100 percent of power/hz RAT DH ? Hz o--4 plocebo ~--~l~jg DG-AVP ~2~Jg DG-AVP N=16 Fig. 2. Effect of DG-AVP treatment on hippocampal RSA of homozygous diabetes insipidus rats during paradoxical sleep.
4 365 TABLE II EFFECT OF DG-AVP TREATMENT ON SPECTRAL PARAMETERS O17 RSA DURING PARADOXICAL SLEEP IN HOMOZYGOUS DIABETES INSIPIDUS RATS Placebo DG-A VP 1 t~g/lo0 g DG-A VP 2 ttg/lo0 g Mean frequency in Hz 7.7 ± 0.08 Peak frequency in Hz ½ peak amplitude 0.6 ± 0.3 Frequencies at ½ peak amplitude 7.2 ± ~: ± ± 0.4** 7.5 ± 0.2*** 0.8 i ± "- 7.1 ± 0.3"**- 7.6 ± 0.4* *** P < 0.1 > * P < ** P < *** P < TABLE III COMPARISON OF SPECTRAL PARAMETERS OF RSA DURING PARADOXICAL SLEEP IN THE HETEROZYGOUS AND HOMOZYGOUS DIABETES INSIPIDUS RATS, TREATED WITH DG-AVP Heterozygous Homozygous (2) ± P level DG-A VP 2 ttg/lo0 g Mean frequency in Hz :k 0.1 n.s. Peak frequency in Hz 7.8 ± ± 0.2 P < 0.05 ½ peak amplitude 0.7 ~ ± 0.3 n.s. Frequencies at ½ peak amplitude 7.1 ± ~k ± ± 0.3 n.s. PS have been demonstrated to interfere with consolidation processesl,z,4,7, s. The quantitative aspect of the RSA was not specifically investigated in the present study. It may well be that both quality and quantity are equally important in consolidation processes. Experiments are in progress to elucidate this problem. However, the in- ferior quality of RSA during PS in the absence of vasopressin and the beneficial effect of vasopressin treatment support the hypothesis derived from previous studies that vasopressin plays an important role in the consolidation of learned responses. 1 EMPSON, J. A. C., AND CLARKE, P. R. F., Rapid eye movements and remembering, Nature (Lond.), 227 (1970) FISrmEIN, V., Disruptive effects of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation on long-term memory, Physiol. Behav., 6 (1971) GREEN, J. D., AND ARDUINI, A. J., Hippocampal electrical activity in arousal, J. Neurophysiol., 17 (1954) HENNEVIN, E., LECONTE, P., ET BLOCH, V., Augmentation du sommeil paradoxal provoqu6e par l'acquisition, l'extinction et la r6acquisition d'un apprentissage ~t r6inforcement positif, Brain Research, 70 (1974)
5 366 5 KAMP, A., LOPES DA SILVA, F. H., AND STORM VAN LEEUWEN, W., Hippocampal frequency shifts in different behavioral situations, Brain Research, 31 (1971) KLEMM, W. R., Correlation of hippocampal theta rhythm, muscle activity and brain stem reticular formation activity, Commun. Behav. BioL, 5 (1970) LANFIELD, P. W., McGAUGH, J. L., AND TUSk, R. J., Theta rhythm: a temporal correlate of memory storage process in the rat, Science, 175 (1972) LECONTE, P., HENNEVIN, E., AND BOLCH, V., Duration of paradoxical sleep necessary for the acquisition of conditioned avoidance in rat, PhysioL Behav., 13 (1974) MOHRING, B., MOHRING, J., DUADA, G., AND HACK, D., Potassium deficiency in rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus, Amer. J. Physiol., 227 (1974) MOHRING, J., SCH/JMIG, A., BECKNER, H., AND MOHRING, B., ADH-induced potassium retention in rats with genetic diabetes insipidus, Life Sci., 11 (1972) PARMEGIANI, P. L., AND ZANNO, G., A study on the bioelectrical rhythms of cortical and subcortical structures during activated sleep, Arch. ital. Biol., 101 (1963) VALTIN, H., Hereditary hypothalamic diabetes insipidus in rats (Brattleboro strain), Amer. J. Med., 42 (1967) VANDERWOLF~ C. H., Hippocampal electrical activity and voluntary movement, Psychol. Rev., 78 (1971) WHISHAW, I. Q., AND VANDERWOLE~ C. H., Hippocampal EEG and behavior: changes in amplitude and frequency of RSA (theta rhythm) associated with spontaneous and learned movement patterns in rats and cats, Behav. Biol., 8 (1973) WIeD, D. DE, The influence of the posterior and intermediate lobe of pituitary and pituitary peptides on the maintenance of a conditioned avoidance response in rats, Int. J. Neuropharmacol., 4 (1965) WIED, D. DE, GREVEN, H. M., LANDE, S. AND WITTER, A., Dissociation of the behavioral and endocrine effects of lysine vasopressin by tryptic digestion, Brit. J. Pharmacol., 45 (1972) WIED, D. DE, BOHUS, B., AND WIMERSMA GREIDANUS, TJ. B. VAN, Memory deficit in rats with hereditary diabetes insipidus, Brain Research, 85 (1975)
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HIPPOCAMPAL THETA ACTIVITY AND RUNNING SPEED IN THE RAT. W. L. McFarland H. Teitelbaum E. K. Hedges
 AFRRI SCIENTIFIC REPORT AFRRI SR74-6 APRIL 1974 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HIPPOCAMPAL THETA ACTIVITY AND RUNNING SPEED IN THE RAT W. L. McFarland H. Teitelbaum E. K. Hedges CO ARMED FORCES RADIOBIOLOGY RESEARCH
AFRRI SCIENTIFIC REPORT AFRRI SR74-6 APRIL 1974 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HIPPOCAMPAL THETA ACTIVITY AND RUNNING SPEED IN THE RAT W. L. McFarland H. Teitelbaum E. K. Hedges CO ARMED FORCES RADIOBIOLOGY RESEARCH
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may have as many as 200,000
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR
 Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
Physiology Unit 2 CONSCIOUSNESS, THE BRAIN AND BEHAVIOR In Physiology Today What the Brain Does The nervous system determines states of consciousness and produces complex behaviors Any given neuron may
DISTURBANCES IN SLEEP-WAKING PATTERN AND CORTICAL DESYNCHRONIZATION AFTER LATERAL HYPOTHALAMIC DAMAGE: EFFECT OF THE SIZE OF THE LESION
 ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 19B0, SO: 01-91 Short communication DISTURBANCES IN SLEEP-WAKING PATTERN AND CORTICAL DESYNCHRONIZATION AFTER LATERAL HYPOTHALAMIC DAMAGE: EFFECT OF THE SIZE OF THE LESION W. TROJNIAR,
ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 19B0, SO: 01-91 Short communication DISTURBANCES IN SLEEP-WAKING PATTERN AND CORTICAL DESYNCHRONIZATION AFTER LATERAL HYPOTHALAMIC DAMAGE: EFFECT OF THE SIZE OF THE LESION W. TROJNIAR,
EEG, ECG, EMG. Mitesh Shrestha
 EEG, ECG, EMG Mitesh Shrestha What is Signal? A signal is defined as a fluctuating quantity or impulse whose variations represent information. The amplitude or frequency of voltage, current, electric field
EEG, ECG, EMG Mitesh Shrestha What is Signal? A signal is defined as a fluctuating quantity or impulse whose variations represent information. The amplitude or frequency of voltage, current, electric field
Modelling the relation of body temperature and sleep: importance of the circadian rhythm in skin temperature
 Modelling the relation of body temperature and sleep: importance of the circadian rhythm in skin temperature EUS J.W. VAN SOMEREN NETHERLANDS INSTITUTE FOR BRAIN RESEARCH, AMSTERDAM A close relation between
Modelling the relation of body temperature and sleep: importance of the circadian rhythm in skin temperature EUS J.W. VAN SOMEREN NETHERLANDS INSTITUTE FOR BRAIN RESEARCH, AMSTERDAM A close relation between
HIPPOCAMPAL SLOW RHYTHMS IN ONGOING BEHAVIOUR AND DURING CLASSICAL CONDITIONING*
 -=------ 6 Februarie 1971 S.-A. MEDIESE TYDSKRIF 135 HIPPOCAMPAL SLOW RHYTHMS IN ONGOING BEHAVIOUR AND DURING CLASSICAL CONDITIONING* R. C. ALBINO AND K. CAIGER, Psychology Department, University of Natal,
-=------ 6 Februarie 1971 S.-A. MEDIESE TYDSKRIF 135 HIPPOCAMPAL SLOW RHYTHMS IN ONGOING BEHAVIOUR AND DURING CLASSICAL CONDITIONING* R. C. ALBINO AND K. CAIGER, Psychology Department, University of Natal,
Spectral Analysis of EEG Patterns in Normal Adults
 Spectral Analysis of EEG Patterns in Normal Adults Kyoung Gyu Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Ewha Medical Research Center, Ewha Womans University Medical College, Background: Recently, the
Spectral Analysis of EEG Patterns in Normal Adults Kyoung Gyu Choi, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurology, Ewha Medical Research Center, Ewha Womans University Medical College, Background: Recently, the
EEG WORKSHOP Nonepileptiform Abnormalities
 EEG WORKSHOP Nonepileptiform Abnormalities Kamornwan Katanyuwong MD Chiangmai University Hospital EST: 20th July 2010 EEG reading Age Background Epileptiform Non epileptiform Activation procedure normal
EEG WORKSHOP Nonepileptiform Abnormalities Kamornwan Katanyuwong MD Chiangmai University Hospital EST: 20th July 2010 EEG reading Age Background Epileptiform Non epileptiform Activation procedure normal
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Matrix Energetics Research Brainwaves and Heart waves Research on Matrix Energetics in Action
 Matrix Energetics Research Brainwaves and Heart waves Research on Matrix Energetics in Action QEEG (quantitative electroencephalography) and HRV (heart rate variability analysis) tests revealed Dr. Richard
Matrix Energetics Research Brainwaves and Heart waves Research on Matrix Energetics in Action QEEG (quantitative electroencephalography) and HRV (heart rate variability analysis) tests revealed Dr. Richard
Introduction. H. van Lier, 1 A. M. L. Coenen, 1 and W. H. I. M. Drinkenburg 2 1
 The Journal of Neuroscience, March 15, 2003 23(6):2459 2465 2459 Behavioral Transitions Modulate Hippocampal Electroencephalogram Correlates of Open Field Behavior in the Rat: Support for a Sensorimotor
The Journal of Neuroscience, March 15, 2003 23(6):2459 2465 2459 Behavioral Transitions Modulate Hippocampal Electroencephalogram Correlates of Open Field Behavior in the Rat: Support for a Sensorimotor
Neurophysiology & EEG
 Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
Neurophysiology & EEG PG4 Core Curriculum Ian A. Cook, M.D. Associate Director, Laboratory of Brain, Behavior, & Pharmacology UCLA Department of Psychiatry & Biobehavioral Sciences Semel Institute for
Exploratory Whisking by Rat Is Not Phase Locked to the Hippocampal Theta Rhythm
 6518 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 14, 2006 26(24):6518 6522 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Exploratory Whisking by Rat Is Not Phase Locked to the Hippocampal Theta Rhythm Rune W. Berg, 1 Diane Whitmer,
6518 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 14, 2006 26(24):6518 6522 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Exploratory Whisking by Rat Is Not Phase Locked to the Hippocampal Theta Rhythm Rune W. Berg, 1 Diane Whitmer,
Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves
 SICE Annual Conference 27 Sept. 17-2, 27, Kagawa University, Japan Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves Seiji Nishifuji 1, Kentaro Fujisaki 1 and Shogo Tanaka 1 1
SICE Annual Conference 27 Sept. 17-2, 27, Kagawa University, Japan Effects of Light Stimulus Frequency on Phase Characteristics of Brain Waves Seiji Nishifuji 1, Kentaro Fujisaki 1 and Shogo Tanaka 1 1
Post-Training Vasopressin Injections May Facilitate or Delay Shuttle-Box Avoidance Extinction
 BEHAVIORAL AND NEURAL BIOLOGY 36, 211-228 (1982) Post-Training Vasopressin Injections May Facilitate or Delay Shuttle-Box Avoidance Extinction J. J. HAGAN,I B. BOHUS, AND D. DE WIED 2 Rudolf Magnus Institute
BEHAVIORAL AND NEURAL BIOLOGY 36, 211-228 (1982) Post-Training Vasopressin Injections May Facilitate or Delay Shuttle-Box Avoidance Extinction J. J. HAGAN,I B. BOHUS, AND D. DE WIED 2 Rudolf Magnus Institute
Urine Volume and Osmolality Changes During Dreaming Sleep in Man*
 X Urine Volume and Osmolality Changes During Dreaming Sleep in Man* A. J. Mandell, 6. Chaffey, P. Sri 11, M. P. Mandell, J. Rodnick, R. T. Rubin and R. Sheff Biochemical Correlates Laboratory Departments
X Urine Volume and Osmolality Changes During Dreaming Sleep in Man* A. J. Mandell, 6. Chaffey, P. Sri 11, M. P. Mandell, J. Rodnick, R. T. Rubin and R. Sheff Biochemical Correlates Laboratory Departments
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Electroencephalography Improves the Prediction of Functional Outcome in the Acute Stage of Cerebral Ischemia
 1968 Electroencephalography Improves the Prediction of Functional Outcome in the Acute Stage of Cerebral Ischemia J.P.M. Cillessen, MD; A.C. van Huffelen, MD; LJ. Kappelle, MD; A. Algra, MD; J. van Gijn,
1968 Electroencephalography Improves the Prediction of Functional Outcome in the Acute Stage of Cerebral Ischemia J.P.M. Cillessen, MD; A.C. van Huffelen, MD; LJ. Kappelle, MD; A. Algra, MD; J. van Gijn,
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
doi: 10.1038/nature06310 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION www.nature.com/nature 1 www.nature.com/nature 2 www.nature.com/nature 3 Supplementary Figure S1 Spontaneous duration of wake, SWS and REM sleep (expressed
Modules 7. Consciousness and Attention. sleep/hypnosis 1
 Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Modules 7 Consciousness and Attention sleep/hypnosis 1 Consciousness Our awareness of ourselves and our environments. sleep/hypnosis 2 Dual Processing Our perceptual neural pathways have two routes. The
Beyond the Basics in EEG Interpretation: Throughout the Life Stages
 Beyond the Basics in EEG Interpretation: Throughout the Life Stages Steve S. Chung, MD, FAAN Chairman, Neuroscience Institute Director, Epilepsy Program Banner University Medical Center University of Arizona
Beyond the Basics in EEG Interpretation: Throughout the Life Stages Steve S. Chung, MD, FAAN Chairman, Neuroscience Institute Director, Epilepsy Program Banner University Medical Center University of Arizona
HTPPOCAMPAL THETA ACTIVITY IN THE ACUTE PRETRIGEMINAI, CAT
 ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1976, 36: 517-534 HTPPOCAMPAL THETA ACTIVITY IN THE ACUTE PRETRIGEMINAI, CAT T. RADIL-WEISS, B. ZERNICKI and A. MICHALSKI Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental
ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1976, 36: 517-534 HTPPOCAMPAL THETA ACTIVITY IN THE ACUTE PRETRIGEMINAI, CAT T. RADIL-WEISS, B. ZERNICKI and A. MICHALSKI Department of Neurophysiology, Nencki Institute of Experimental
Limbic system outline
 Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Sleep stages. Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM)
 Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
Sleep stages Awake Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 Rapid eye movement sleep (REM) Slow wave sleep (NREM) EEG waves EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES
 HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
HYPOTHALAMIC ELECTRICAL ACTIVITIES PRODUCED BY FACTORS CAUSING DISCHARGE OF PITUITARY HORMONES TERUO NAKAYAMA* Institute of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Nagoya It is known that electrical
Introduction to EEG del Campo. Introduction to EEG. J.C. Martin del Campo, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada
 Introduction to EEG J.C. Martin, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada What is EEG? A graphic representation of the difference in voltage between two different cerebral locations plotted over
Introduction to EEG J.C. Martin, MD, FRCP University Health Network Toronto, Canada What is EEG? A graphic representation of the difference in voltage between two different cerebral locations plotted over
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs
 Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
Effects of acute ketamine infusion on visual working memory encoding: a study using ERPs Corinna Haenschel Psychology, City University London, UK Partly Funded by: the Welsh Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
Characterization of Sleep Spindles
 Characterization of Sleep Spindles Simon Freedman Illinois Institute of Technology and W.M. Keck Center for Neurophysics, UCLA (Dated: September 5, 2011) Local Field Potential (LFP) measurements from sleep
Characterization of Sleep Spindles Simon Freedman Illinois Institute of Technology and W.M. Keck Center for Neurophysics, UCLA (Dated: September 5, 2011) Local Field Potential (LFP) measurements from sleep
Principles of Science
 Principles of Science measurements must be repeatable hypothesis falsifiable rational associations and inferences tools are imperfect communications are honest and transparent clean up mistakes, especially
Principles of Science measurements must be repeatable hypothesis falsifiable rational associations and inferences tools are imperfect communications are honest and transparent clean up mistakes, especially
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL. Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program)
 SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep)
 EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
EEG and some applications (seizures and sleep) EEG: stands for electroencephalography and is a graphed representation of the electrical activity of the brain. EEG is the recording of electrical activity
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition. Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT
 Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
Hippocampal mechanisms of memory and cognition Matthew Wilson Departments of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Biology MIT 1 Courtesy of Elsevier, Inc., http://www.sciencedirect.com. Used with permission.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Systems Neuroscience November 29, Memory
 Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Systems Neuroscience November 29, 2016 Memory Gabriela Michel http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html Forms of memory Different types of learning & memory rely on different brain structures
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Introduction to Neurofeedback. Penny Papanikolopoulos
 Introduction to Neurofeedback Penny Papanikolopoulos Our World is.. The Marvelous World of the Brain Senses, Perception, Cognitions, Images, Emotions, Executive functions etc. Are all regulated by the
Introduction to Neurofeedback Penny Papanikolopoulos Our World is.. The Marvelous World of the Brain Senses, Perception, Cognitions, Images, Emotions, Executive functions etc. Are all regulated by the
Seizure onset can be difficult to asses in scalp EEG. However, some tools can be used to increase the seizure onset activity over the EEG background:
 This presentation was given during the Dianalund Summer School on EEG and Epilepsy, July 24, 2012. The main purpose of this introductory talk is to show the possibilities of improved seizure onset analysis
This presentation was given during the Dianalund Summer School on EEG and Epilepsy, July 24, 2012. The main purpose of this introductory talk is to show the possibilities of improved seizure onset analysis
The Nervous System. Neuron 01/12/2011. The Synapse: The Processor
 The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
The Nervous System Neuron Nucleus Cell body Dendrites they are part of the cell body of a neuron that collect chemical and electrical signals from other neurons at synapses and convert them into electrical
Anxiolytic Drugs and Altered Hippocampal Theta Rhythms: The Quantitative Systems Pharmacological Approach
 Anxiolytic Drugs and Altered Hippocampal Theta Rhythms: The Quantitative Systems Pharmacological Approach Péter Érdi perdi@kzoo.edu Henry R. Luce Professor Center for Complex Systems Studies Kalamazoo
Anxiolytic Drugs and Altered Hippocampal Theta Rhythms: The Quantitative Systems Pharmacological Approach Péter Érdi perdi@kzoo.edu Henry R. Luce Professor Center for Complex Systems Studies Kalamazoo
Index. Behaviour, posthypnotic see Posthypnotic behaviour
 Index Amnesia, posthypnotic see Posthypnotic amnesia Analgesia, hypnotic see Pain Animal hypnosis, 4 duration of, affected by caffeine and X-rays, 71-72 as emotional reaction, 69 emotional stress, role
Index Amnesia, posthypnotic see Posthypnotic amnesia Analgesia, hypnotic see Pain Animal hypnosis, 4 duration of, affected by caffeine and X-rays, 71-72 as emotional reaction, 69 emotional stress, role
EFFECT OF POTASSIUM ON PLASMA RENIN CONCENTRATION IN THE PRESENCE AND ABSENCE OF ADH (BRATTLEBORO RAT MODEL)
 EFFECT OF POTASSIUM ON PLASMA RENIN CONCENTRATION IN THE PRESENCE AND ABSENCE OF ADH (BRATTLEBORO RAT MODEL) Emma Fernandez-Repollet, Susan Opava-Stitzer, and Manuel Martinez-Maldonado Department of Physiology
EFFECT OF POTASSIUM ON PLASMA RENIN CONCENTRATION IN THE PRESENCE AND ABSENCE OF ADH (BRATTLEBORO RAT MODEL) Emma Fernandez-Repollet, Susan Opava-Stitzer, and Manuel Martinez-Maldonado Department of Physiology
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events
 The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events Summary of Updates in Version 2.1 July 1, 2014 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring that The AASM Manual
The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events Summary of Updates in Version 2.1 July 1, 2014 The American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM) is committed to ensuring that The AASM Manual
DIFFERENTIAL EFFECT OF THE DAMAGE TO THE LATERAL HYPOTHALAMIC AREA ON HIPPOCAMPAL THETA RHYTHM DURING WAKING AND PARADOXICAL SLEEP
 ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1989, 49: 153-169 DIFFERENTIAL EFFECT OF THE DAMAGE TO THE LATERAL HYPOTHALAMIC AREA ON HIPPOCAMPAL THETA RHYTHM DURING WAKING AND PARADOXICAL SLEEP E JURKOWLANIEC, W. TROJNIAR, T.
ACTA NEUROBIOL. EXP. 1989, 49: 153-169 DIFFERENTIAL EFFECT OF THE DAMAGE TO THE LATERAL HYPOTHALAMIC AREA ON HIPPOCAMPAL THETA RHYTHM DURING WAKING AND PARADOXICAL SLEEP E JURKOWLANIEC, W. TROJNIAR, T.
High Frequency Oscillations in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
 High Frequency Oscillations in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Paolo Federico MD, PhD, FRCPC Departments of Clinical Neurosciences and Diagnostic Imaging University of Calgary 7 June 2012 Learning Objectives Understand
High Frequency Oscillations in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Paolo Federico MD, PhD, FRCPC Departments of Clinical Neurosciences and Diagnostic Imaging University of Calgary 7 June 2012 Learning Objectives Understand
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9
 Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Chemical Control of Behavior and Brain 1 of 9 I) INTRO A) Nervous system discussed so far 1) Specific 2) Fast B) Other systems extended in space and time 1) Nonspecific 2) Slow C) Three components that
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms
 Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
Sleep, Dreaming and Circadian Rhythms People typically sleep about 8 hours per day, and spend 16 hours awake. Most people sleep over 175,000 hours in their lifetime. The vast amount of time spent sleeping
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Sleep)
 EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Sleep) Slow-Wave Sleep: What Is it? All of us can relate to feeling sleepy, foggy-headed and hungry after a night of poor sleep. The answer to why we feel this way can be found
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Sleep) Slow-Wave Sleep: What Is it? All of us can relate to feeling sleepy, foggy-headed and hungry after a night of poor sleep. The answer to why we feel this way can be found
Inception, Total Recall, & The Brain: An Introduction to Neuroscience Part 2. Neal G. Simon, Ph.D. Professor Dept. of Biological Sciences
 Inception, Total Recall, & The Brain: An Introduction to Neuroscience Part 2 Neal G. Simon, Ph.D. Professor Dept. of Biological Sciences http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wfmlgeh dije Summary from September
Inception, Total Recall, & The Brain: An Introduction to Neuroscience Part 2 Neal G. Simon, Ph.D. Professor Dept. of Biological Sciences http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wfmlgeh dije Summary from September
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings
 Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
Entrainment of neuronal oscillations as a mechanism of attentional selection: intracranial human recordings J. Besle, P. Lakatos, C.A. Schevon, R.R. Goodman, G.M. McKhann, A. Mehta, R.G. Emerson, C.E.
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE. Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D.
 SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
SLEEP DISORDERS IN HUNTINGTON S DISEASE Gary L. Dunbar, Ph.D. Executive Director, Field Neurosciences Institute Co-Director, Program in Neuroscience Central Michigan University Pre-Talk Test 1. Which type
Genetic variation in EEG activity during sleep in inbred mice
 Genetic variation in EEG activity during sleep in inbred mice PAUL FRANKEN, ALAIN MALAFOSSE, AND MEHDI TAFTI Biochemistry and Neurophysiology Unit, Department of Psychiatry, University of Geneva, CH-1225
Genetic variation in EEG activity during sleep in inbred mice PAUL FRANKEN, ALAIN MALAFOSSE, AND MEHDI TAFTI Biochemistry and Neurophysiology Unit, Department of Psychiatry, University of Geneva, CH-1225
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07)
 NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
NEURAL MECHANISMS OF SLEEP (p.1) (Rev. 3/21/07) 1. Revisitation of Bremer s 1936 Isolated Brain Studies Transected the brain: a. Cut between the medulla and the spinal cord ( encephale isole ) Note: recall
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122
 EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
EEG Sleep Circadian rhythms Learning Objectives: 121, 122 Zoltán Lelkes Electroencenphalography Hans Berger pen time amplifier electrodes 1 The waves of the EEG gamma > 30 Hz beta: 13-30 Hz Mental activity:
Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms
 203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
203 Continuing Medical Education Basic Mechanism for Generation of Brain Rhythms Wei-Hung Chen Abstract- Study of the basic mechanism of brain rhythms adds to our understanding of the underlying processes
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG
 Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
Protocol for Rat Sleep EEG Subjects Male Spraue Dawley rats weihin 250-300 rams at the time of surery are used. Food and water are available ad libitum throuhout the experiment. Rats are roup housed prior
AUTOCORRELATION AND CROSS-CORRELARION ANALYSES OF ALPHA WAVES IN RELATION TO SUBJECTIVE PREFERENCE OF A FLICKERING LIGHT
 AUTOCORRELATION AND CROSS-CORRELARION ANALYSES OF ALPHA WAVES IN RELATION TO SUBJECTIVE PREFERENCE OF A FLICKERING LIGHT Y. Soeta, S. Uetani, and Y. Ando Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kobe
AUTOCORRELATION AND CROSS-CORRELARION ANALYSES OF ALPHA WAVES IN RELATION TO SUBJECTIVE PREFERENCE OF A FLICKERING LIGHT Y. Soeta, S. Uetani, and Y. Ando Graduate School of Science and Technology, Kobe
Lecture 8. Arousal & Sleep. Cogs17 * UCSD
 Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Lecture 8 Arousal & Sleep Cogs17 * UCSD Arousal in the Brain Stimulated by sensory input Initiated, maintained endogenously Basal Forebrain Delivers ACh throughout cortex Arousal in the Brain Lateral Hypothalamus
Restoring Communication and Mobility
 Restoring Communication and Mobility What are they? Artificial devices connected to the body that substitute, restore or supplement a sensory, cognitive, or motive function of the nervous system that has
Restoring Communication and Mobility What are they? Artificial devices connected to the body that substitute, restore or supplement a sensory, cognitive, or motive function of the nervous system that has
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4084
 Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
I. Q. WHISHAW. Department of Psychology University of Lethbridge Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada and C. H. VANDERWOLF
 BEHAVIORAL BIOLOGY, 8, 461-484 (1973), Abstract No. I156R Hippocampal EEG and Behavior: Changes in Amplitude and Frequency of RSA (Theta Rhythm) Associated With Spontaneous and Learned Movement Patterns
BEHAVIORAL BIOLOGY, 8, 461-484 (1973), Abstract No. I156R Hippocampal EEG and Behavior: Changes in Amplitude and Frequency of RSA (Theta Rhythm) Associated With Spontaneous and Learned Movement Patterns
Declarative memory includes semantic, episodic, and spatial memory, and
 Gallo Taste Learning and Memory in Aging Milagros Gallo, PhD Declarative memory includes semantic, episodic, and spatial memory, and in humans involves conscious recall. 1 Visual recognition memory is
Gallo Taste Learning and Memory in Aging Milagros Gallo, PhD Declarative memory includes semantic, episodic, and spatial memory, and in humans involves conscious recall. 1 Visual recognition memory is
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
Submitted report on Sufi recordings at AAPB 2013 in Portland. Not for general distribution. Thomas F. Collura, Ph.D. July, 2013
 Submitted report on Sufi recordings at AAPB 2013 in Portland Not for general distribution. Thomas F. Collura, Ph.D. July, 2013 Summary of EEG findings The intent of the EEG monitoring was to see which
Submitted report on Sufi recordings at AAPB 2013 in Portland Not for general distribution. Thomas F. Collura, Ph.D. July, 2013 Summary of EEG findings The intent of the EEG monitoring was to see which
SLEEP, SLEEP DEPRIVATION, AND PERFORMANCE
 30722 Sleep 5.qxd 6/27/2003 2:16 PM Page 567 SLEEP, SLEEP DEPRIVATION, AND PERFORMANCE Sleep Regulation in the Djungarian Hamster: Comparison of the Dynamics Leading to the Slow-Wave Activity Increase
30722 Sleep 5.qxd 6/27/2003 2:16 PM Page 567 SLEEP, SLEEP DEPRIVATION, AND PERFORMANCE Sleep Regulation in the Djungarian Hamster: Comparison of the Dynamics Leading to the Slow-Wave Activity Increase
Chapter 7. Discussion and impact
 Chapter 7 Discussion and impact 225 Affective pathology is a complex construct which encompasses a pathological disturbance in primary emotions, rapidly shifting from neutral to intense perception, associated
Chapter 7 Discussion and impact 225 Affective pathology is a complex construct which encompasses a pathological disturbance in primary emotions, rapidly shifting from neutral to intense perception, associated
Sleep-Dependent Oscillations in the Human Hippocampus and Neocortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 26, 2003 23(34):10897 10903 10897 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Sleep-Dependent Oscillations in the Human Hippocampus and Neocortex Jose L. Cantero, 1 Mercedes Atienza,
The Journal of Neuroscience, November 26, 2003 23(34):10897 10903 10897 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Sleep-Dependent Oscillations in the Human Hippocampus and Neocortex Jose L. Cantero, 1 Mercedes Atienza,
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS
 37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
37 ON-LINE REPOSITORY MATERIAL DIFFERENCES IN SLEEP-INDUCED HYPOXIA BETWEEN A/J AND DBA/2J MOUSE STRAINS Arnon E. Rubin, Vsevolod Y. Polotsky, Alex Balbir, Jerry A. Krishnan, Alan R. Schwartz, Philip L.
Objectives. brain pacemaker circuits role of inhibition
 Brain Rhythms Michael O. Poulter, Ph.D. Professor, Molecular Brain Research Group Robarts Research Institute Depts of Physiology & Pharmacology, Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine
Brain Rhythms Michael O. Poulter, Ph.D. Professor, Molecular Brain Research Group Robarts Research Institute Depts of Physiology & Pharmacology, Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus)
 EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus) Introduction 17 subjects were tested to measure effects of a Brain.fm focus session on cognition. With 4 additional subjects, we recorded EEG data during baseline and while
EEG Analysis on Brain.fm (Focus) Introduction 17 subjects were tested to measure effects of a Brain.fm focus session on cognition. With 4 additional subjects, we recorded EEG data during baseline and while
A Study of Smartphone Game Users through EEG Signal Feature Analysis
 , pp. 409-418 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.11.39 A Study of Smartphone Game Users through EEG Signal Feature Analysis Jung-Yoon Kim Graduate School of Advanced Imaging Science, Multimedia &
, pp. 409-418 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijmue.2014.9.11.39 A Study of Smartphone Game Users through EEG Signal Feature Analysis Jung-Yoon Kim Graduate School of Advanced Imaging Science, Multimedia &
EEG anomalies in Attention- Deficit/Hyperactivity disorder: linking brain and behaviour.
 EEG anomalies in Attention- Deficit/Hyperactivity disorder: linking brain and behaviour. Adam R. Clarke a, Robert J. Barry a, Rory McCarthy b, Mark Selikowitz b a School of Psychology, and Brain & Behaviour
EEG anomalies in Attention- Deficit/Hyperactivity disorder: linking brain and behaviour. Adam R. Clarke a, Robert J. Barry a, Rory McCarthy b, Mark Selikowitz b a School of Psychology, and Brain & Behaviour
Circadian rhythm and Sleep. Radwan Banimustafa MD
 Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Circadian rhythm and Sleep Radwan Banimustafa MD Homeostasis Maintenance of equilibrium by active regulation of internal states: Cardiovascular function (blood pressure, heart rate) Body temperature Food
Non epileptiform abnormality J U LY 2 7,
 Non epileptiform abnormality S U D A J I R A S A K U L D E J, M D. C H U L A L O N G KO R N C O M P R E H E N S I V E E P I L E P S Y C E N T E R J U LY 2 7, 2 0 1 6 Outline Slow pattern Focal slowing
Non epileptiform abnormality S U D A J I R A S A K U L D E J, M D. C H U L A L O N G KO R N C O M P R E H E N S I V E E P I L E P S Y C E N T E R J U LY 2 7, 2 0 1 6 Outline Slow pattern Focal slowing
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma
 Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
EEG History. Where and why is EEG used? 8/2/2010
 EEG History Hans Berger 1873-1941 Edgar Douglas Adrian, an English physician, was one of the first scientists to record a single nerve fiber potential Although Adrian is credited with the discovery of
EEG History Hans Berger 1873-1941 Edgar Douglas Adrian, an English physician, was one of the first scientists to record a single nerve fiber potential Although Adrian is credited with the discovery of
vasopressin in an uncontrolled trial on patients with DI (Crawford, Kennedy & Hill, 1960), rats with
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1977), 59, 11-16 POTNTIATION OF TH RSPONS TO VASOPRSSIN (PITRSSIN) BY TRATMNT WITH A COMBINATION OF CHLORPROPAMID AND CHLOROTHIAZID IN BRATTLBORO RATS WITH HRDITARY HYPOTHALAMIC DIABTS
Br. J. Pharmac. (1977), 59, 11-16 POTNTIATION OF TH RSPONS TO VASOPRSSIN (PITRSSIN) BY TRATMNT WITH A COMBINATION OF CHLORPROPAMID AND CHLOROTHIAZID IN BRATTLBORO RATS WITH HRDITARY HYPOTHALAMIC DIABTS
Prevention of Acetylcholine-Induced Atrial Fibrillation. Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D. and Koroku HASHIMOTO, M.D.
 Prevention of Acetylcholine-Induced Atrial Fibrillation by Electric Pacing Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D. and Koroku HASHIMOTO, M.D. SUMMARY The sinus node artery of 10 dog hearts was auto-perfused with blood
Prevention of Acetylcholine-Induced Atrial Fibrillation by Electric Pacing Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D. and Koroku HASHIMOTO, M.D. SUMMARY The sinus node artery of 10 dog hearts was auto-perfused with blood
(Accepted July 30, 1996)
 NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 19, No. 2 115 SYNTHETIC ACTH ANALOGUE SEMAX DISPLAYS NOOTROPIC-LIKE ACTIVITY IN HUMANS A.Ya. Kaplan, A.G. Kochetova, V.N. Nezavibathko, T.V. Rjasina, Ashmarin
NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 19, No. 2 115 SYNTHETIC ACTH ANALOGUE SEMAX DISPLAYS NOOTROPIC-LIKE ACTIVITY IN HUMANS A.Ya. Kaplan, A.G. Kochetova, V.N. Nezavibathko, T.V. Rjasina, Ashmarin
GLOSSARY OF TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH TENS
 GLOSSARY OF TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH TENS ATP Adenosine Triphosphate that helps to promote protein synthesis. Accommodation Becoming accustomed to stimulation resulting in nerve and muscle fatigue. Acute
GLOSSARY OF TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH TENS ATP Adenosine Triphosphate that helps to promote protein synthesis. Accommodation Becoming accustomed to stimulation resulting in nerve and muscle fatigue. Acute
PSD Analysis of Neural Spectrum During Transition from Awake Stage to Sleep Stage
 PSD Analysis of Neural Spectrum During Transition from Stage to Stage Chintan Joshi #1 ; Dipesh Kamdar #2 #1 Student,; #2 Research Guide, #1,#2 Electronics and Communication Department, Vyavasayi Vidya
PSD Analysis of Neural Spectrum During Transition from Stage to Stage Chintan Joshi #1 ; Dipesh Kamdar #2 #1 Student,; #2 Research Guide, #1,#2 Electronics and Communication Department, Vyavasayi Vidya
PEER REVIEW FILE. Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author)
 PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) Movement-related theta rhythm in the hippocampus is a robust and dominant feature of the local field potential of experimental
PEER REVIEW FILE Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) Movement-related theta rhythm in the hippocampus is a robust and dominant feature of the local field potential of experimental
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
TWO TYPES OF PATTERN OF HIPPOCAMPAL ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY INDUCED BY STIMULATION OF HYPOTHALAMUS AND SURROUNDING PARTS OF RABBIT'S BRAIN
 TWO TYPES OF PATTERN OF HIPPOCAMPAL ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY INDUCED BY STIMULATION OF HYPOTHALAMUS AND SURROUNDING PARTS OF RABBIT'S BRAIN Shizuo TORII* Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Toho University,
TWO TYPES OF PATTERN OF HIPPOCAMPAL ELECTRICAL ACTIVITY INDUCED BY STIMULATION OF HYPOTHALAMUS AND SURROUNDING PARTS OF RABBIT'S BRAIN Shizuo TORII* Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, Toho University,
The role of amplitude, phase, and rhythmicity of neural oscillations in top-down control of cognition
 The role of amplitude, phase, and rhythmicity of neural oscillations in top-down control of cognition Chair: Jason Samaha, University of Wisconsin-Madison Co-Chair: Ali Mazaheri, University of Birmingham
The role of amplitude, phase, and rhythmicity of neural oscillations in top-down control of cognition Chair: Jason Samaha, University of Wisconsin-Madison Co-Chair: Ali Mazaheri, University of Birmingham
AUXILIARIES AND NEUROPLASTICITY
 AUXILIARIES AND NEUROPLASTICITY Claudio Babiloni, Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Foggia (UNIFG), Italy UNIFG structured personnel involved Prof. Claudio Babiloni (Coordinator),
AUXILIARIES AND NEUROPLASTICITY Claudio Babiloni, Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Sciences, University of Foggia (UNIFG), Italy UNIFG structured personnel involved Prof. Claudio Babiloni (Coordinator),
BCIA NEUROFEEDBACK CERTIFICATION PROGRAM
 BCIA NEUROFEEDBACK CERTIFICATION PROGRAM Instructor: Cynthia Kerson, PhD (26 BCIA F2F Hours 10 Self-paced Hours Accredited Instruction) Level: Introductory to Intermediate Practice Gap: Neurofeedback is
BCIA NEUROFEEDBACK CERTIFICATION PROGRAM Instructor: Cynthia Kerson, PhD (26 BCIA F2F Hours 10 Self-paced Hours Accredited Instruction) Level: Introductory to Intermediate Practice Gap: Neurofeedback is
EEG Electrode Placement
 EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
EEG Electrode Placement Classifying EEG brain waves Frequency: the number of oscillations/waves per second, measured in Hertz (Hz) reflects the firing rate of neurons alpha, beta, theta, delta Amplitude:
Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats
 Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
Physiol. Res. 64: 263-267, 2015 SHORT COMMUNICATION Subconvulsive Dose of Kainic Acid Transiently Increases the Locomotor Activity of Adult Wistar Rats V. RILJAK 1, D. MAREŠOVÁ 1, J. POKORNÝ 1, K. JANDOVÁ
McLaughlin, K. A., Fox, N. A., Zeanah, C. H., Sheridan, M. A., Marshall, P., & Nelson, C. A. (2010). Delayed maturation in brain electrical activity
 McLaughlin, K. A., Fox, N. A., Zeanah, C. H., Sheridan, M. A., Marshall, P., & Nelson, C. A. (2010). Delayed maturation in brain electrical activity partially explains the association between early environmental
McLaughlin, K. A., Fox, N. A., Zeanah, C. H., Sheridan, M. A., Marshall, P., & Nelson, C. A. (2010). Delayed maturation in brain electrical activity partially explains the association between early environmental
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1
 Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Possible Functional Roles of Paradoxical Sleep
 Symposia: E. The Physiological Role of Sleep 216 and that there is no causal relation between the two phenomena, which may be just parallel processes. P ARMEGGAN: could agree on this if integration were
Symposia: E. The Physiological Role of Sleep 216 and that there is no causal relation between the two phenomena, which may be just parallel processes. P ARMEGGAN: could agree on this if integration were
Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions
 Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2001, 61: 175-179 Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions El bieta Szel¹g 1, Krystyna Rymarczyk 1 and Ernst Pöppel 2 1 Department
Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2001, 61: 175-179 Conscious control of movements: increase of temporal precision in voluntarily delayed actions El bieta Szel¹g 1, Krystyna Rymarczyk 1 and Ernst Pöppel 2 1 Department
Effect of Acute and Chronic Heat Exposure on Frequency of EEG Components in Different Sleep-Wake State in Young Rats
 Effect of Acute and Chronic Heat Exposure on Frequency of EEG Components in Different Sleep-Wake State in Young Rats Rakesh Kumar Sinha *1 and Amit Kumar Ray 2 1 Dept. of Biomedical Instrumentation, Birla
Effect of Acute and Chronic Heat Exposure on Frequency of EEG Components in Different Sleep-Wake State in Young Rats Rakesh Kumar Sinha *1 and Amit Kumar Ray 2 1 Dept. of Biomedical Instrumentation, Birla
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX:
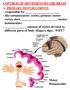 CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX: - responsible for - like somatosensory cortex, primary motor cortex show (motor homunculus) - amount of cortex devoted to different parts of body
