Contrast-Enhanced CT with Knowledge-Based Iterative Model Reconstruction for the Evaluation of Parotid Gland Tumors: A Feasibility Study
|
|
|
- Evangeline Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck pissn eissn Korean J Radiol 2018;19(5): Contrast-Enhanced CT with Knowledge-Based Iterative Model Reconstruction for the Evaluation of Parotid Gland Tumors: A Feasibility Study Chae Jung Park, MD, Ki Wook Kim, MD, Ho-Joon Lee, MD, Myeong-Jin Kim, MD, PhD, Jinna Kim, MD, PhD All authors: Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea Objective: The purpose of this study was to determine the diagnostic utility of low-dose CT with knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction (IMR) for the evaluation of parotid gland tumors. Materials and Methods: This prospective study included 42 consecutive patients who had undergone low-dose contrastenhanced CT for the evaluation of suspected parotid gland tumors. Prior or subsequent non-low-dose CT scans within 12 months were available in 10 of the participants. Background noise (BN), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) were compared between non-low-dose CT images and images generated using filtered back projection (FBP), hybrid iterative reconstruction (idose 4 ; Philips Healthcare), and knowledge-based IMR. Subjective image quality was rated by two radiologists using five-point grading scales to assess the overall image quality, delineation of lesion contour, image sharpness, and noise. Results: With the IMR algorithm, background noise (IMR, 4.24 ± 3.77; idose 4, 8.77 ± 3.85; FBP, ± 4.06; p = [IMR vs. idose 4 ] and p < [IMR vs. FBP]) was significantly lower and SNR (IMR, ± 7.49; idose 4, ± 3.29; FBP, 7.33 ± 2.03; p = [IMR vs. idose 4 ] and p < [IMR vs. FBP]) was significantly higher compared with the other two algorithms. The CNR was also significantly higher with the IMR compared with the FBP (25.76 ± vs ± 3.18, p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in BN, SNR, and CNR between low-dose CT with the IMR algorithm and nonlow-dose CT. Subjective image analysis revealed that IMR-generated low-dose CT images showed significantly better overall image quality and delineation of lesion contour with lesser noise, compared with those generated using FBP by both reviewers 1 and 2 (4 vs. 3; 4 vs. 3; and 3 4 vs. 2; p < 0.05 for all pairs), although there was no significant difference in subjective image quality scores between IMR-generated low-dose CT and non-low-dose CT images. Conclusion: Iterative model reconstruction-generated low-dose CT is an alternative to standard non-low-dose CT without significantly affecting image quality for the evaluation of parotid gland tumors. Keywords: Knowledge-based iterative reconstruction; Filtered back projection; Computed tomography; Parotid tumor; Parotid gland; Radiation dosage; Image reconstruction; Image quality Received September 9, 2017; accepted after revision February 10, This study was supported by a faculty research grant of Yonsei University College of Medicine ( ). Corresponding author: Jinna Kim, MD, PhD, Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 50-1 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemun-gu, Seoul 03722, Korea. Tel: (822) Fax: (822) jinna@yuhs.ac This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. INTRODUCTION Parotid gland tumors constitute approximately 3% of all head and neck tumors (1), with a majority of patients presenting with a palpable mass in the pre-auricular region. For patients with suspected parotid gland tumors, CT can easily confirm the presence of a parotid mass and assess the extent of tumor to facilitate the determination of benign or malignant nature of the tumor for appropriate treatment selection. However, streak artifacts caused by various dental restorations on CT often interfere with the evaluation of Copyright 2018 The Korean Society of Radiology 957
2 Park et al. the parotid gland and Stensen duct. Furthermore, they increase the difficulty of evaluation of masses originating in the deep lobe of the gland, which lies anterior to the styloid process of the temporal bone and lateral to the parapharyngeal fat (2). Technological advances have continued to improve the quality of CT images, with a noticeable progression in CT reconstruction algorithms, particularly iterative reconstruction techniques (3). The most recently introduced knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction (IMR) system has been used for CT imaging of various body parts, with several advantages such as better image quality and decreased noise and radiation dose, compared with previous CT reconstruction algorithms (4-7). The purpose of this study was to assess the diagnostic utility of low-dose CT using the IMR algorithm in patients with parotid gland tumors and compare the CT images with those obtained via other reconstruction algorithms and with non-low-dose CT. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients This prospective clinical study was approved by our Institutional Review Board, and informed consent was obtained from each patient. Between November 2015 and July 2016, 42 consecutive patients (16 males and 26 females) with suspected parotid gland tumors who were scheduled to undergo contrast-enhanced CT were enrolled in this study. In addition, after retrospective review of these patients, prior or subsequent non-low-dose CT images within 12 months were available in 10 patients (5 males and 5 females), who were included for the comparison of imaging parameters using the reconstruction methods and non-low-dose CT images. However, subsequent non-lowdose CT images after surgery were not included. The median patient age was 50.5 years (range, years), and the median body mass index (BMI) was 23.4 kg/m 2 (range, kg/m 2 ). Overall, 36 patients underwent surgical excision or biopsy for their parotid gland masses, and the final histopathological diagnoses were: benign non-neoplastic lesions in two, benign neoplasms in 28, and malignancy in 6. The specific histological types included lymphoepithelial cyst (n = 1), branchial cleft cyst (n = 1), pleomorphic adenoma (n = 23), Warthin tumor (n = 3), basal cell adenoma (n = 1), myoepithelioma (n = 1), mucoepidermoid carcinoma (n = 1), salivary duct carcinoma (n = 1), and lymphoma (n = 4). The remaining six patients were diagnosed with acute parotitis (n = 3), pneumoparotid (n = 1), and lipoma (n = 2) on the basis of imaging findings without further diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. The mean size of the 38 measurable masses on CT images was 22.6 ± 9.6 mm (range, mm). Image Acquisition and Reconstruction All studies were performed using a 256-row multidetector CT scanner (Brilliance ict scanner; Philips Healthcare, Cleveland, OH, USA) at our institution. CT images were acquired at a manually fixed peak tube voltage of 100 kvp, with automated Z-axis dose modulation using a scout image (DoseRight; Philips Healthcare). The maximal tube current was limited to 150 mas, and the effective mas ranged from 77 mas to 131 mas. The field of view was 180 mm, with a matrix of 512 x 512. Other scanning parameters were as follows: detector configuration, 128 x mm; pitch, 0.601; tube rotation time, 0.5 seconds; and acquisition mode, helical. All patients underwent contrast-enhanced CT in the supine position using a neck CT protocol. Contiguous images of the neck were acquired in the axial plane from the orbital floor to the suprasternal notch. A total of ml of the iodinated contrast medium iobitridol (Xenetix 300; Guerbet, Roissy, France) was intravenously administered at a flow rate of 2 ml/s using an automated injector, followed by injection of 40 ml of 0.9% saline solution at the same flow rate. Contrast-enhanced CT scans were obtained at seconds after the initiation of contrast agent administration. Three axial image datasets were created by reconstructing the identical raw projection dataset using three different algorithms, namely filtered back projection (FBP), idose 4 level 3 (a fourth-generation hybrid iterative reconstruction algorithm supplied by Philips Healthcare), and IMR level 1. The idose 4 and IMR algorithms include levels 1 7 and levels 1 3, respectively, with a higher level providing greater noise reduction. All reconstructed section thicknesses were 3 mm. Concurrent non-low-dose CT images in 10 patients were obtained with various scanners and vendors, suggesting variation in parameters. They consisted of a helical scan at a tube voltage of 120 kvp and mas ranging from 90 mas to 150 mas. FBP reconstruction algorithms were used. To evaluate the radiation dose, the CT dose index volume (CTDI vol, described in mgy) and dose length product (DLP, 958
3 CT with IMR for the Evaluation of Parotid Gland Tumors described in mgy-cm) were recorded, according to the dose report (8). Objective Image Analyses Objective image assessment was conducted by measuring the background noise (BN), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) as quantitative image parameters on a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) workstation (Centricity RA 1000; GE Healthcare, Chicago, IL, USA). A head and neck radiologist with 6 years of experience recorded the average attenuation values (V) and standard deviation (SD) of Hounsfield units (HU) by placing a circular or ovoid region of interest measuring approximately 10 mm in diameter in the two empty spaces bilaterally on the head (Air), masseter muscle (MM), and internal jugular vein (IJV) at the same level of the parotid gland mass (Fig. 1). The measurement was repeatedly conducted for each of the three image datasets, and BN, SNR, and CNR were calculated using the following formulae: BN = SDAir right + SDAir left 2 sufficient, 4 = good, 5 = excellent), delineation of tumor (ranging from 1 = no visual delineation to 5 = perfect delineation of tumor), image sharpness (ranging from 1 = distinct blurring to 5 = no apparent image blurring), and image artifact and noise (ranging from 1 = extensive image artifact and noise to 5 = no apparent artifact and noise) (9). Statistical Analysis All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 20.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). All recorded data were presented as means ± SDs. Quantitative imaging parameters (BN, SNR, and CNR) and subjective image assessment for the low-dose CT with three reconstruction algorithms and non-low-dose CT were compared using Friedman tests, followed by Wilcoxon signed-rank tests. Interobserver agreement for the subjective image analyses was calculated using Cohen s kappa statistics with quadratic weighting, and estimation of the overall kappa was based on the study of Landis and Koch (10) as follows: slight agreement (0 0.20), fair agreement ( ), moderate agreement ( ), substantial agreement ( ), and almost perfect agreement ( ) (10). A p value of < SNR = VMM BN CNR = VIJV - VMM SDMM Subjective Image Analyses Using a PACS workstation, two radiologists with 15 years and 4 years of experience, respectively, independently assessed 4 axial image sets displayed on 4 monitors concurrently in 10 patients for whom non-low-dose CT was available. Three axial image sets displayed on 3 monitors were also assessed in the remaining 32 patients for whom non-low-dose CT was not available. In addition to the default preselected window settings (window width of 350 HU, window level of 60 HU), the radiologists were allowed to change the window width and level for optimal viewing conditions. The image sets of each patient were displayed randomly to each radiologist. Both radiologists were blinded to the patient data, clinical information, and image reconstruction technique. For each image dataset, each radiologist graded the overall image quality (1 = non-diagnostic, 2 = poor, 3 = Fig. 1. Assessment of objective image quality at parotid gland level. Regions of interest were drawn to bilaterally measure SD of air (background noise) and attenuation of masseter muscle and internal jugular vein for estimation of signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-tonoise ratio. SD = standard deviation 959
4 Park et al. Table 1. Results of Objective Analyses of Reconstruction Techniques for CT in Evaluation of Parotid Gland Masses Parameters BN SNR CNR Low-dose CT FBP ± ± ± 3.18 idose ± ± ± 6.54 IMR 4.24 ± ± ± Non low-dose CT 9.4 ± ± ± Comparison (p value) FBP vs. idose FBP vs. IMR < 0.001* < 0.001* < 0.001* FBP vs. non-low-dose CT * idose 4 vs. IMR 0.037* 0.011* idose 4 vs. non-low-dose CT IMR vs. non-low-dose CT *p < 0.05, SNR measured at MM, CNR between MM and internal jugular vein. BN = background noise, CNR = contrast-to-noise ratio, FBP = filtered back projection, idose 4 = hybrid iterative reconstruction, IMR = knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction, MM = masseter muscle, SNR = signal-to-noise ratio 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS The results of the objective image analyses are summarized in Table 1. The mean BN value was significantly lower with the IMR algorithm than with the FBP (4.24 ± 3.77 vs ± 4.06, p < 0.001) and idose 4 algorithm (4.24 ± 3.77 vs ± 3.85, p = 0.037), while the mean SNR value was significantly higher with the IMR algorithm than with the FBP (23.93 ± 7.49 vs ± 2.03, p < 0.001) and idose 4 algorithms (23.93 ± 7.49 vs ± 3.29, p = 0.011). The mean CNR value was significantly higher with the IMR algorithm, compared with that of FBP (25.76 ± vs ± 3.18, p < 0.001), although there was no significant difference in the CNR value between the IMR and idose 4 algorithms (25.76 ± vs ± 6.54, p = 0.602). Furthermore, while lower BN and higher SNR and CNR values were obtained in IMR-generated low-dose CT, compared with non-low-dose CT, there were no statistically significant differences between them (9.4 ± 12.75, p = 0.268; ± 6.66, p = 0.171; and ± 11.23, p = 1.000, respectively). The results of subjective image analyses are shown in Table 2. The four groups were compared using Friedman test, with similar or better subjective image quality scores for low-dose CT using an IMR algorithm compared with those obtained with low-dose CT using FBP and idose 4 algorithms, as well as with non-low-dose CT, with regard to overall image quality, delineation of tumor, and image artifact and noise (IMR vs. other three algorithms, 4 vs. 3 4, 4 vs. 3 4, and 3 4 vs. 2 3) (Figs. 2, 3). However, there was no significant difference in subjective image quality scores for all pairs among the four groups, except in the comparison of FBP vs. IMR algorithms, according to Wilcoxon signed-rank tests following Friedman tests (p = 0.028, 0.002, and for reader 1 and p = 0.021, 0.011, and for reader 2, respectively). Meanwhile, according to only reader 2, the score for image sharpness was significantly lower for the low-dose CT with IMR and idose 4 algorithm than for FBP (p = and p = 0.021, respectively), although there was no significant difference in the score for image sharpness between low-dose CT using the three reconstruction algorithms and non-low-dose CT images for reader 1. Interobserver agreements for the subjective image analyses were moderate to substantial for all parameters (overall image quality: ĸ = 0.46, delineation of the tumor contour: ĸ = 0.58, image sharpness: ĸ = 0.67, and artifact and noise: ĸ = 0.57). The average CTDI vol and DLP values with low-dose CT were 3.78 ± 0.94 mgy and ± mgy-cm, respectively. The average CTDI vol was 73.71% lower (3.78 mgy vs mgy) for low-dose CT than for non-low-dose CT with various scanners (Table 3). DISCUSSION In the present study, we compared the image quality of low-dose CT with IMR and non-low-dose CT with conventional reconstruction in patients with parotid gland masses. Our results demonstrated that low-dose CT with 960
5 CT with IMR for the Evaluation of Parotid Gland Tumors Table 2. Results of Subjective Analyses of Reconstruction Techniques for CT in Evaluation of Parotid Gland Masses Low-Dose CT* Comparison 2 (P) Non-Low- Comparison 1 Interobserver Parameters Readers FBP idose 4 IMR Dose CT* (P) Agreement IMR vs. Non-Low- Dose CT idose 4 vs. Non-Low- Dose CT idose 4 vs. IMR FBP vs. Non-Low- Dose CT FBP vs. FBP vs. idose 4 IMR R1 3 (2 4) 4 (3 4) 4 (3 4) 4 (2 5) R2 3 (2 3) 4 (3 4) 4 (3 4) 4 (2 5) Overall image quality R1 3 (2 4) 3 (2 4) 4 (4 5) 3 (2 5) R2 3 (2 4) 4 (3 5) 4 (4 5) 4 (1 5) < Delineation of tumor R1 4 (2 4) 3 (2 4) 2 (2 4) 3 (1 5) Image sharpness R2 4 (3 4) 3 (3 4) 2 (2 3) 4 (1 5) R1 2 (1 4) 3 (2 3) 4 (2 4) 3 (1 4) R2 2 (1 2) 3 (2 4) 3 (2 4) 3 (2 3) Noise and artifacts *Values indicate median (range), p < 0.05 indicates that there was/were pair/pairs showing significant difference for six pairs in four different data sets according to Friedman test, p values indicate comparison results for six pairs in four different data sets according to Wilcoxon signed-rank tests following Friedman tests, Values indicate kappa scores. knowledge-based IMR yielded comparable objective and subjective measures of image quality, compared with nonlow-dose CT as well as other reconstruction algorithms, and this finding was consistent with the results of previous studies (4-7). Recently, several studies have reported the advantages of the IMR algorithm for CT evaluation of other body parts (11,12). We decided to assess the utility of this technique for parotid gland imaging, which is susceptible to interference by streak artifacts derived from dental amalgam restorations that are frequently observed on CT images reconstructed with FBP algorithms (2). Furthermore, image contrast is another important parameter to determine the precise extent of the mass on CT, because the majority of parotid gland tumors are pleomorphic adenomas, which show poor contrast enhancement on CT images obtained 30 seconds after contrast administration and are difficult to detect against the background of parotid gland tissue (13). Although the conventional FBP technique is the most widely used CT reconstruction algorithm because of fast and efficient reconstruction, it can result in image deterioration due to systemic geometric distortion and streak artifacts with insufficient data collection (14). With rapid advances in computer technologies, iterative reconstruction algorithms represent an innovation characterized by repeated modification processes with multiple iteration correction steps. This technique has dramatically improved the overall image quality through noise reduction and adequate resolution (3, 15). IMR is the latest knowledgebased or model-based iterative reconstruction algorithm offered by Philips Healthcare. It optimizes the image reconstruction process by reflecting image and data statistics and systemic models. Therefore, the IMR algorithm requires a longer reconstruction time. However, we used the latest processors with greater computational capacity in the present study, which yielded an average reconstruction time of approximately 5 minutes only, which is acceptable for clinical use. In the present study, we performed objective and subjective image analyses using several imaging parameters. Among the quantitative imaging parameters, CNR describes the extent to which differences in attenuation between two different regions increase above the pixel-to-pixel variations (16). Thus, CNR represents an excellent image quality parameter for the detection of low-contrast lesions. In the present study, CNR was significantly higher for low-dose CT with IMR algorithm compared with FBP reconstruction, and 961
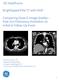
6 Park et al. greatly aids the detection and characterization of parotid masses, considering that different tumors with different cell types and enhancement patterns develop in the parotid gland. In addition, we assessed artifacts and noise together, and found that low-dose CT with IMR resulted in significantly lesser overall noise and artifacts, compared A B C Fig year-old woman with right parotid gland mass. Three axial image sets reconstructed using FBP (A), idose 4 (B), and IMR (C) algorithms. Compared with FBP- and idose 4 -reconstructed images, significant decrease in streak artifacts related to dental amalgam was observed in parotid area with better conspicuity and definition of tumor margins in iterative model-reconstructed image. However, iterative model-reconstructed image showed relatively poor image sharpness, compared with FBP- and idose 4 -reconstructed images. FBP = filtered back projection, idose 4 = hybrid iterative reconstruction, IMR = knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction A B C D Fig year-old man with left parotid gland mass. Four axial image sets of low-dose CT reconstructed using FBP (A), idose 4 (B), and knowledge-based IMR (C) algorithms and non-low-dose CT (D). Compared with FBP- and idose 4 -reconstructed images as well as non-low-dose CT, there is significant decrease in noise associated with parotid region and significantly better contrast and characterization of tumor in iterative model-reconstructed image. Parotid tissue appears blotchy and pixelated in iterative model-reconstructed image. 962
7 CT with IMR for the Evaluation of Parotid Gland Tumors Table 3. Radiation Dose in Low-Dose and Non-Low-Dose CT Scan Parameters Low-Dose CT Non-Low-Dose CT CTDI vol (mgy) 3.78 ± ± 6.43 DLP (mgy-cm) ± ± CTDI vol = CT dose index volume, DLP = dose length product with other reconstruction algorithms and non-low-dose CT, which was especially apparent with streak artifacts caused by dental amalgam restorations interfering with the evaluation of the parotid gland and Stensen duct. While the average score of subjective imaging parameters for overall image quality and delineation of the parotid mass was significantly higher with IMR compared with FBP, probably due to significant noise reduction, image sharpness was worse in CT with the IMR algorithm, compared with FBP and non-low-dose CT in the present study. This result might be associated with distinct image features obtained using iterative reconstruction techniques, such as a unique plastic texture and a blotchy, pixelated appearance, as reported previously (17). Among the various image quality optimization methods applied for iterative reconstruction, the total variation minimization method has been widely used (18). However, it inevitably results in excessive smoothing of images because of its basic assumption. Therefore, a characteristic texture of CT images reconstructed using iterative reconstruction techniques may be observed in the form of oversmoothing in edge regions and a blotchy, pixelated appearance in nonedge regions (19), which might affect the image sharpness. Nevertheless, we believe that the unique image texture obtained with IMR might not affect or may only slightly affect the accurate diagnosis of parotid galnd masses with IMR in this study. Previous phantom studies demonstrated that IMR enables a dose reduction of 60 80%, compared with FBP (20). In the present study, the mean DLP for CT performed at 100 kvp with the IMR algorithm was ± mgy-cm, and this was approximately 74% lower than the values obtained for CT performed at 120 kvp with the FBP algorithm at our institution. This result indicates that IMR undoubtedly offers further radiation dose reduction, compared with other reconstruction techniques, without severely compromising the image quality. This study has several limitations. First, the image quality was analyzed on the basis of semiquantitative and qualitative parameters, and phantom experiments provide more accurate and comprehensive information about the image quality using various physical metrics, such as the modulation transfer function, section sensitivity profile, and noise power spectrum (21, 22). Second, although reviewers were blinded during subjective image analyses, they may be able to distinguish the four image sets because of the unique image texture obtained with IMR, resulting in assessment bias. Third, we failed to compare the diagnostic performance indicators (such as sensitivity and specificity) for the reconstruction algorithms because all patients carried parotid gland masses. Finally, only 42 patients were included in the study and non-low-dose CT was available only in 10 patients. Future studies with larger sample sizes determined by statistical power analysis are necessary to elucidate our findings. In conclusion, despite unique plastic texture and blotchy pixelated appearance of images with IMR algorithm, CT evaluation with knowledge-based IMR is a feasible alternative to non-low-dose CT, without significantly affecting image quality in patients with parotid gland tumors. REFERENCES 1. Lin CC, Tsai MH, Huang CC, Hua CH, Tseng HC, Huang ST. Parotid tumors: a 10-year experience. Am J Otolaryngol 2008;29: Barrett JF, Keat N. Artifacts in CT: recognition and avoidance. Radiographics 2004;24: Geyer LL, Schoepf UJ, Meinel FG, Nance JW Jr, Bastarrika G, Leipsic JA, et al. State of the art: iterative CT reconstruction techniques. Radiology 2015;276: Halpern EJ, Gingold EL, White H, Read K. Evaluation of coronary artery image quality with knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction. Acad Radiol 2014;21: Khawaja RDA, Singh S, Blake M, Harisinghani M, Choy G, Karaosmanoglu A, et al. Ultra-low dose abdominal MDCT: using a knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction technique for substantial dose reduction in a prospective clinical study. Eur J Radiol 2015;84: Park SB, Kim YS, Lee JB, Park HJ. Knowledge-based iterative model reconstruction (IMR) algorithm in ultralow-dose CT for evaluation of urolithiasis: evaluation of radiation dose reduction, image quality, and diagnostic performance. Abdom Imaging 2015;40: Ryu YJ, Choi YH, Cheon JE, Ha S, Kim WS, Kim IO. Knowledgebased iterative model reconstruction: comparative image quality and radiation dose with a pediatric computed tomography phantom. Pediatr Radiol 2016;46: Shrimpton PC, Hillier MC, Lewis MA, Dunn M. National survey of doses from CT in the UK: Br J Radiol 2006;79: Jessen KA, Panzer W, Shrimpton PC, Bongartz G, Gelejins J, Tosi G, et al. EUR 16262: European guidelines on quality 963
8 Park et al. criteria for computed tomography. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977;33: Hu Y, Pan S, Zhao X, Guo W, He M, Guo Q. Value and clinical application of orthopedic metal artifact reduction algorithm in CT scans after orthopedic metal implantation. Korean J Radiol 2017;18: Lim HJ, Chung MJ, Shin KE, Hwang HS, Lee KS. The impact of iterative reconstruction in low-dose computed tomography on the evaluation of diffuse interstitial lung disease. Korean J Radiol 2016;17: Choi DS, Na DG, Byun HS, Ko YH, Kim CK, Cho JM, et al. Salivary gland tumors: evaluation with two-phase helical CT. Radiology 2000;214: Shepp LA, Logan BF. The Fourier reconstruction of a head section. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1974;21: Seibert JA. Iterative reconstruction: how it works, how to apply it. Pediatr Radiol 2014;44 Suppl 3: Hendrick RE. Breast MRI: fundamentals and technical aspects. New York, NY: Springer Science & Business Media, Yasaka K, Katsura M, Akahane M, Sato J, Matsuda I, Ohtomo K. Model-based iterative reconstruction for reduction of radiation dose in abdominopelvic CT: comparison to adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction. Springerplus 2013;2: Sidky EY, Pan X. Image reconstruction in circular conebeam computed tomography by constrained, total-variation minimization. Phys Med Biol 2008;53: Qi H, Chen Z, Zhou L. CT image reconstruction from sparse projections using adaptive TpV regularization. Comput Math Methods Med 2015;2015: Mehta D, Thompson R, Morton T, Dhanantwari A, Shefer E. Iterative model reconstruction: simultaneously lowered computed tomography radiation dose and improved image quality. Med Phys Int J 2013;2: Boone JM. Determination of the presampled MTF in computed tomography. Med Phys 2001;28: Siewerdsen JH, Cunningham IA, Jaffray DA. A framework for noise-power spectrum analysis of multidimensional images. Med Phys 2002;29:
Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose?
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Optimizing radiation dose by varying age at pediatric temporal bone CT
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 1, 2015 Optimizing radiation dose by varying age at pediatric temporal bone CT Daichi Noto, 1 Yoshinori Funama, 2a Mika Kitajima, 3 Daisuke
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 1, 2015 Optimizing radiation dose by varying age at pediatric temporal bone CT Daichi Noto, 1 Yoshinori Funama, 2a Mika Kitajima, 3 Daisuke
Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK. John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean
 Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean Why a new dose survey? Number of enquires received concerning the current NDRL Concern that could
Doses from Cervical Spine Computed Tomography (CT) examinations in the UK John Holroyd and Sue Edyvean Why a new dose survey? Number of enquires received concerning the current NDRL Concern that could
Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost 1, Jean Chalaoui 1, Louis-Mathieu Stevens 2,3, Nicolas Noiseux 2,3, Carl Chartrand-Lefebvre 1,3
 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Imaging with CT Angiography and Iterative Reconstruction: Quantitave Evaluation of Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Imaging with CT Angiography and Iterative Reconstruction: Quantitave Evaluation of Radiation Dose Reduction and Image Quality Simon Nepveu 1, Irina Boldeanu 1, Yves Provost
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT. Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
 ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
ESTABLISHING DRLs in PEDIATRIC CT Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine CT Dose Indices CTDI INTRODUCTION CTDI 100, CTDI w, CTDI vol
X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT
 Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Computed Tomography-Basic Principles and Good Practice X-Ray & CT Physics / Clinical CT INSTRUCTORS: Dane Franklin, MBA, RT (R) (CT) Office hours will be Tuesdays from 5pm to 6pm CLASSROOM: TIME: REQUIRED
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use?
 Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
Doses from pediatric CT examinations in Norway Are pediatric scan protocols developed and in daily use? Eva Godske Friberg * Norwegian Radiation Protection Authority, P.O. Box, Østerås, Norway Abstract.
A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (17): 7683-7687 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on CT pulmonary angiography at low kv and low-concentration contrast medium using iterative reconstruction. Yanhe
PMP. Original Article. Introduction. Hee Jung Kim, Sung Yong Park, Young Hee Park, Ah Ram Chang
 Original Article PMP Progress in Medical Physics 28(1), March 217 https://doi.org/1.14316/pmp.217.28.1.27 pissn 258-4445, eissn 258-4453 Dosimetric Effects of Low Dose 4D CT Using a Commercial Iterative
Original Article PMP Progress in Medical Physics 28(1), March 217 https://doi.org/1.14316/pmp.217.28.1.27 pissn 258-4445, eissn 258-4453 Dosimetric Effects of Low Dose 4D CT Using a Commercial Iterative
Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically
 Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research
Cardiac CT Lowering the Dose Dramatically U. Joseph Schoepf, MD, FAHA, FSCBT MR, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director of Cardiovascular Imaging Disclosures Consultant for / research
Survey of patients CT radiation dose in Jiangsu Province
 Original Article Page 1 of 6 Survey of patients CT radiation dose in Jiangsu Province Yuanyuan Zhou 1, Chunyong Yang 1, Xingjiang Cao 1, Xiang Du 1, Ningle Yu 1, Xianfeng Zhou 2, Baoli Zhu 1, Jin Wang
Original Article Page 1 of 6 Survey of patients CT radiation dose in Jiangsu Province Yuanyuan Zhou 1, Chunyong Yang 1, Xingjiang Cao 1, Xiang Du 1, Ningle Yu 1, Xianfeng Zhou 2, Baoli Zhu 1, Jin Wang
Acknowledgments. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Lung Nodule Detection. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Chest CT Protocols. Chest CT Protocols
 Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT
 Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Original Article Thoracic Imaging
 Original Article Thoracic Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1179 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(6):1179-1186 Size-Specific Dose Estimation In the Korean Lung Cancer
Original Article Thoracic Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1179 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(6):1179-1186 Size-Specific Dose Estimation In the Korean Lung Cancer
A more accurate method to estimate patient dose during body CT examinations with tube current modulation
 A more accurate method to estimate patient dose during body CT examinations with tube current modulation Poster No.: C-0738 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Kawaguchi 1, Y. Matsunaga
A more accurate method to estimate patient dose during body CT examinations with tube current modulation Poster No.: C-0738 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Kawaguchi 1, Y. Matsunaga
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
8/3/2016. Consultant for / research support from: Astellas Bayer Bracco GE Healthcare Guerbet Medrad Siemens Healthcare. Single Energy.
 U. Joseph Schoepf, MD Prof. (h.c.), FAHA, FSCBT-MR, FNASCI, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director, Division of Cardiovascular Imaging Consultant for / research support from: Astellas
U. Joseph Schoepf, MD Prof. (h.c.), FAHA, FSCBT-MR, FNASCI, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director, Division of Cardiovascular Imaging Consultant for / research support from: Astellas
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches
 Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
To Shield or Not to Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D.
 To Shield or Not to Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D. Disclosures Consultant to: Nuance, Inc. Page 2 Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT has increased in women vulnerable to cancer induction by radiation.
To Shield or Not to Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D. Disclosures Consultant to: Nuance, Inc. Page 2 Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT has increased in women vulnerable to cancer induction by radiation.
Comparative Analysis of Radiation Dose and Image Quality Between Thyroid Shielding and Unshielding During CT Examination of the Neck
 Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Young Hen Lee 1 Eun-tae Park 1 Pyong Kon Cho 1 Hyung Suk Seo 1 Bo-Kyung Je 1 Sang-il Suh 2 Kyung-Sook
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Young Hen Lee 1 Eun-tae Park 1 Pyong Kon Cho 1 Hyung Suk Seo 1 Bo-Kyung Je 1 Sang-il Suh 2 Kyung-Sook
354 Korean J Radiol 9(4), August 2008
 Review of Failed CT Phantom Image Evaluations in 2005 and 2006 by the CT Accreditation Program of the Korean Institute for Accreditation of Medical Image Hye Jung Park, MD 1 Seung Eun Jung, MD 1, 2 Young
Review of Failed CT Phantom Image Evaluations in 2005 and 2006 by the CT Accreditation Program of the Korean Institute for Accreditation of Medical Image Hye Jung Park, MD 1 Seung Eun Jung, MD 1, 2 Young
CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations. Sarah Bell
 CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations Sarah Bell Sarah.bell14@nhs.net Outline 1. Introduction 2. Aims and Objectives 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion 6. Conclusions 7. References Introduction
CT Optimisation for Paediatric SPECT/CT Examinations Sarah Bell Sarah.bell14@nhs.net Outline 1. Introduction 2. Aims and Objectives 3. Methods 4. Results 5. Discussion 6. Conclusions 7. References Introduction
CT of the chest with model-based, fully iterative reconstruction: comparison with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction
 Ichikawa et al. BMC Medical Imaging 2013, 13:27 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access CT of the chest with model-based, fully iterative reconstruction: comparison with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction
Ichikawa et al. BMC Medical Imaging 2013, 13:27 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access CT of the chest with model-based, fully iterative reconstruction: comparison with adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction
Radiation Dose Reduction: Should You Use a Bismuth Breast Shield?
 Radiation Dose Reduction: Should You Use a Bismuth Breast Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. Michael V. Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT
Radiation Dose Reduction: Should You Use a Bismuth Breast Shield? Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. Michael V. Yester, Ph.D. University of Alabama at Birmingham Breast Radiation on CT Use of chest CT
CT SCAN PROTOCOL. Shoulder
 CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
CT SCAN PROTOCOL Shoulder Purpose and Summary CT images made with this protocol are used to provide the orthopedic surgeon with a detailed 3D anatomical reconstruction of the patient s scapula and proximal
The Computed Tomography Examination
 CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS The Computed Tomography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Computed Tomography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive
CONTENT SPECIFICATIONS The Computed Tomography Examination The purpose of The American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT ) Computed Tomography Examination is to assess the knowledge and cognitive
Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose??
 Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose?? William P. Shuman MD, FACR FSCBTMR Department of Radiology University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Boston, October 10, 2012 Conflict of Interest
Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose?? William P. Shuman MD, FACR FSCBTMR Department of Radiology University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Boston, October 10, 2012 Conflict of Interest
Fused monochromatic imaging acquired by single source dual energy CT in hepatocellular carcinoma during arterial phase: an initial experience
 Original Article Fused monochromatic imaging acquired by single source dual energy CT in hepatocellular carcinoma during arterial phase: an initial experience Shun-Yu Gao, Xiao-Peng Zhang, Yong Cui, Ying-Shi
Original Article Fused monochromatic imaging acquired by single source dual energy CT in hepatocellular carcinoma during arterial phase: an initial experience Shun-Yu Gao, Xiao-Peng Zhang, Yong Cui, Ying-Shi
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING. Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
SPECIFIC PRINCIPLES FOR DOSE REDUCTION IN HEAD CT IMAGING Rajiv Gupta, MD, PhD Neuroradiology, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School OUTLINE 1 st Presentation: Dose optimization strategies
Journal of Radiology and Imaging
 Journal of Radiology and Imaging An Open Access Publisher http://dx.doi.org/10.14312/2399-8172.2017-2 Original research Open Access Reduction of radiation dose in adult CT-guided musculoskeletal procedures
Journal of Radiology and Imaging An Open Access Publisher http://dx.doi.org/10.14312/2399-8172.2017-2 Original research Open Access Reduction of radiation dose in adult CT-guided musculoskeletal procedures
Ask EuroSafe Imaging. Tips & Tricks. CT Working Group. Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose
 Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nancy, FR) Mika Kortesniemi (HUS Medical Imaging
Ask EuroSafe Imaging Tips & Tricks CT Working Group Optimization of scan length to reduce CT radiation dose Alban Gervaise (Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Nancy, FR) Mika Kortesniemi (HUS Medical Imaging
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR
 Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Ultralow Dose Chest CT with MBIR Ella A. Kazerooni, M.D. Professor & Director Cardiothoracic Radiology Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs University of Michigan Disclosures Consultant: GE Healthcare
Gender differences in CT calcium scoring: A phantom study
 Gender differences in CT calcium scoring: A phantom study Nicholas Petrick, Qin Li, Benjamin Berman, Marios A Gavrielides, Rongping Zeng, Berkman Sahiner CDRH/OSEL/DIDSR U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Gender differences in CT calcium scoring: A phantom study Nicholas Petrick, Qin Li, Benjamin Berman, Marios A Gavrielides, Rongping Zeng, Berkman Sahiner CDRH/OSEL/DIDSR U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement
 Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with 64-MD-CT Angiography
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 805-809, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net B-Flow, Power Doppler and Color Doppler Ultrasound in the Assessment of Carotid Stenosis: Comparison with
Radiation Dose Reduction with Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction for Pediatric CT 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Sarabjeet Singh,
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Sarabjeet Singh,
Improved image quality of low-dose thoracic CT examinations with a new postprocessing software*
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 11, NUMBER 3, Summer 2010 Improved image quality of low-dose thoracic CT examinations with a new postprocessing software* Anne Catrine Traegde Martinsen,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 11, NUMBER 3, Summer 2010 Improved image quality of low-dose thoracic CT examinations with a new postprocessing software* Anne Catrine Traegde Martinsen,
Toshiba Aquillion 64 CT Scanner. Phantom Center Periphery Center Periphery Center Periphery
 Comparison of radiation dose and imaging performance for the standard Varian x-ray tube and the Richardson Healthcare ALTA750 replacement tube for the Toshiba Aquillion CT scanners. by Robert L. Dixon,
Comparison of radiation dose and imaging performance for the standard Varian x-ray tube and the Richardson Healthcare ALTA750 replacement tube for the Toshiba Aquillion CT scanners. by Robert L. Dixon,
Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements
 Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements Jonas Andersson Medical Physicist, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Sciences University Hospital of Norrland, Umeå Sweden Contents The Computed
Computed tomography Acceptance testing and dose measurements Jonas Andersson Medical Physicist, Ph.D. Department of Radiation Sciences University Hospital of Norrland, Umeå Sweden Contents The Computed
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC
 CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Acknowledgments John Boone, PhD Michael McNitt-Grey,
CURRENT CT DOSE METRICS: MAKING CTDI SIZE-SPECIFIC Keith Strauss, MSc, FAAPM, FACR Cincinnati Children s Hospital University of Cincinnati College of Medicine Acknowledgments John Boone, PhD Michael McNitt-Grey,
STRUCTURED EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS EFFECTIVE: JANUARY 1, 2016
 Computed Tomography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled with selected clinical experiences,
Computed Tomography The purpose of structured education is to provide the opportunity for individuals to develop mastery of discipline-specific knowledge that, when coupled with selected clinical experiences,
Uozu city/jp, Minatoku, Tokyo/JP Bones, Extremities, CT, Surgery, Physics, Artifacts, Image verification /ecr2014/C-0462
 Metal Artifact Reduction Algorithm enablesreduce metal artifacts and improvement of diagnosis in the postoperative Pedicle screws implant for Spinal Fusion: A Phantom Study Poster No.: C-0462 Congress:
Metal Artifact Reduction Algorithm enablesreduce metal artifacts and improvement of diagnosis in the postoperative Pedicle screws implant for Spinal Fusion: A Phantom Study Poster No.: C-0462 Congress:
Reduced exposure using asymmetric cone beam processing for wide area detector cardiac CT
 Reduced exposure using asymmetric cone beam processing for wide area detector cardiac CT The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Reduced exposure using asymmetric cone beam processing for wide area detector cardiac CT The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Institutional review board approval was obtained prior to the start of this study.
 Lower Limb Alignment and Length Measurements - Comparison of Computed Tomography, Upright Full-Length Conventional Radiography and Upright Biplanar Linear-Low Dose X-ray Scanner Poster No.: C-1382 Congress:
Lower Limb Alignment and Length Measurements - Comparison of Computed Tomography, Upright Full-Length Conventional Radiography and Upright Biplanar Linear-Low Dose X-ray Scanner Poster No.: C-1382 Congress:
Case Report pissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2012;67(4): INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 Focal Fat Deposition Developed in the Segment IV of the Liver Following Gastrectomy Mimicking a Hepatic Metastasis: Two Case Reports 1 위절제술후에간의제 4 분절에서발생한간전이를닮은국소지방침윤 : 두증례보고
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 Focal Fat Deposition Developed in the Segment IV of the Liver Following Gastrectomy Mimicking a Hepatic Metastasis: Two Case Reports 1 위절제술후에간의제 4 분절에서발생한간전이를닮은국소지방침윤 : 두증례보고
Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric
 Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
Translating Protocols Across Patient Size: Babies to Bariatric Cynthia H. McCollough, PhD, FACR, FAAPM Professor of Radiologic Physics Director, CT Clinical Innovation Center Department of Radiology Mayo
Outcomes in the NLST. Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening
 Outcomes in the NLST Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening Denise R. Aberle, MD Professor of Radiology and Bioengineering David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 Disclosures I have
Outcomes in the NLST Health system infrastructure needs to implement screening Denise R. Aberle, MD Professor of Radiology and Bioengineering David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 Disclosures I have
Research Article Usefulness of Nonenhanced Computed Tomography for Diagnosing Urolithiasis without Pyuria in the Emergency Department
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 810971, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/810971 Research Article Usefulness of Nonenhanced Computed Tomography for Diagnosing Urolithiasis without
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 810971, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/810971 Research Article Usefulness of Nonenhanced Computed Tomography for Diagnosing Urolithiasis without
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Original Article INTRODUCTION
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.720 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):720-727 Radiation Dose Reduction of Chest CT with Iterative Reconstruction in Image
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.720 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):720-727 Radiation Dose Reduction of Chest CT with Iterative Reconstruction in Image
Performance of Half-dose Chest Computed Tomography in Lung Malignancy Using an Iterative Reconstruction Technique
 https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.1.47 KMJ Original Article Performance of Half-dose Chest Computed Tomography in Lung Malignancy Using an Iterative Reconstruction Technique Hee Kang 1, Jung Gu Park
https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2017.32.1.47 KMJ Original Article Performance of Half-dose Chest Computed Tomography in Lung Malignancy Using an Iterative Reconstruction Technique Hee Kang 1, Jung Gu Park
BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging. Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes
 BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes 1 Outline Introduction K-Edge Imaging Patient imaging at the European synchrotron Medical Phase Contrast
BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes 1 Outline Introduction K-Edge Imaging Patient imaging at the European synchrotron Medical Phase Contrast
Invivo Dosimetry for Mammography with and without Lead Apron Using the Glass Dosimeters
 Original Article PROGRESS in MEDICAL PHYSICS Vol. 26, No. 2, June, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.2.93 Invivo Dosimetry for Mammography with and without Lead Apron Using the Glass Dosimeters
Original Article PROGRESS in MEDICAL PHYSICS Vol. 26, No. 2, June, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.2.93 Invivo Dosimetry for Mammography with and without Lead Apron Using the Glass Dosimeters
Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer
 Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT
 GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 39/ May 14, 2015 Page 6787
 ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Original Article Thoracic Imaging
 Original Article Thoracic Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.803 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):803-808 Radiological Report of Pilot Study for the Korean Lung Cancer
Original Article Thoracic Imaging https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.803 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2018;19(4):803-808 Radiological Report of Pilot Study for the Korean Lung Cancer
State of the art and future development for standardized estimation of organ doses in CT
 State of the art and future development for standardized estimation of organ doses in CT March 2015 William J. O Connel, Dr. Ph, Senior Medical Physicist Imagination at work. Agenda Introduction Duke Florida
State of the art and future development for standardized estimation of organ doses in CT March 2015 William J. O Connel, Dr. Ph, Senior Medical Physicist Imagination at work. Agenda Introduction Duke Florida
Ultra-Low-Dose Sparse-View Quantitative CT Liver Perfusion Imaging
 ADVANCES IN BRIEF Ultra-Low-Dose Sparse-View Quantitative CT Liver Perfusion Imaging Esmaeil Enjilela 1, Ting-Yim Lee 1,2, Jiang Hsieh 4, Amol Murjoomdar 3, Errol Stewart 1, Mark Dekaban 1, Feng Su 1,
ADVANCES IN BRIEF Ultra-Low-Dose Sparse-View Quantitative CT Liver Perfusion Imaging Esmaeil Enjilela 1, Ting-Yim Lee 1,2, Jiang Hsieh 4, Amol Murjoomdar 3, Errol Stewart 1, Mark Dekaban 1, Feng Su 1,
Certainty. lives in layers. Philips IQon Spectral CT. Computed tomography
 Computed tomography Certainty *The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services requires United States hospitals that treat Medicare patients to participate in the national Hospital Consumer Assessment of
Computed tomography Certainty *The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services requires United States hospitals that treat Medicare patients to participate in the national Hospital Consumer Assessment of
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients
 128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
doi: /j.anl
 doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2006.07.001 Synchronous unilateral parotid gland neoplasms of three different histological types Shuho Tanaka 1, Keiji Tabuchi 1, Keiko Oikawa 1, Rika Kohanawa 1, Hideki Okubo 1, Dai
doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2006.07.001 Synchronous unilateral parotid gland neoplasms of three different histological types Shuho Tanaka 1, Keiji Tabuchi 1, Keiko Oikawa 1, Rika Kohanawa 1, Hideki Okubo 1, Dai
Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax
 Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax Poster No.: C-0013 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Z. Dejian 1, X. Zhuodong 2, J. Hui 2, L. Xiao 3 ;
Application of CARE kv and SAFIRE in Contrast-Enhanced CT Examination on Thorax Poster No.: C-0013 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Z. Dejian 1, X. Zhuodong 2, J. Hui 2, L. Xiao 3 ;
Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis
 GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
Accounting for Imaging Dose
 Accounting for Imaging Dose High Profile Over-exposures Lead to Growing Concern FDA issues warning in October 2009-209 patients exposed to 8 times typical dose for CT brain perfusion scan (3-4 Gy) - Some
Accounting for Imaging Dose High Profile Over-exposures Lead to Growing Concern FDA issues warning in October 2009-209 patients exposed to 8 times typical dose for CT brain perfusion scan (3-4 Gy) - Some
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes
 Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
Triple Rule-out using 320-row-detector volume MDCT: A comparison of the wide volume and helical modes Poster No.: C-0488 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit E.-J. Kang,
Estimated Radiation Dose Associated With Low-Dose Chest CT of Average-Size Participants in the National Lung Screening Trial
 Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Larke et al. Estimated Radiation Dose for Low-Dose Chest CT Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Frederick J. Larke 1 Randell L. Kruger 2
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Larke et al. Estimated Radiation Dose for Low-Dose Chest CT Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Frederick J. Larke 1 Randell L. Kruger 2
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Vardhanabhuti et al. Three Algorithms to Assess Standard- and Low-Dose Chest CT Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Varut Vardhanabhuti 1,2 Robert
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Vardhanabhuti et al. Three Algorithms to Assess Standard- and Low-Dose Chest CT Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Varut Vardhanabhuti 1,2 Robert
Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out (tro) examination
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):21898-21905 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015005 Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):21898-21905 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015005 Original Article Application of flash dual-source CT at low radiation dose and low contrast medium dose in triple-rule-out
Purpose. Methods and Materials
 Comparison of iterative and filtered back-projection image reconstruction techniques: evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography Poster No.: C-1644 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific
Comparison of iterative and filtered back-projection image reconstruction techniques: evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography Poster No.: C-1644 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific
An Introduction to Dual Energy Computed Tomography
 An Introduction to Dual Energy Computed Tomography Michael Riedel University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Introduction The idea of computed tomography (CT) was first introduced in the
An Introduction to Dual Energy Computed Tomography Michael Riedel University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Introduction The idea of computed tomography (CT) was first introduced in the
At present, CT of the brain is the imaging technique of choice
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PATIENT SAFETY Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage in CT: Benefits of Sinogram-Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction Techniques B. Bodelle, E. Klein, N.N.N. Naguib, R.W. Bauer, J.M. Kerl, F. Al-Butmeh,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PATIENT SAFETY Acute Intracranial Hemorrhage in CT: Benefits of Sinogram-Affirmed Iterative Reconstruction Techniques B. Bodelle, E. Klein, N.N.N. Naguib, R.W. Bauer, J.M. Kerl, F. Al-Butmeh,
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic)
 Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
Improved Imaging of the Cervico-Thoracic Junction in Computed Tomography
 Yonsei Med J 49(1):84-89, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.1.84 Improved Imaging of the Cervico-Thoracic Junction in Computed Tomography Pyong Kon Cho, 1,5 Young Hen Lee, 1 You Hyun Kim, 2 Jong Hak Choi, 2
Yonsei Med J 49(1):84-89, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.1.84 Improved Imaging of the Cervico-Thoracic Junction in Computed Tomography Pyong Kon Cho, 1,5 Young Hen Lee, 1 You Hyun Kim, 2 Jong Hak Choi, 2
Abdominal CT protocol s influence on postoperative follow-up of lesions detection associated with gastrointestinal tumours
 Original Article on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Abdominal CT protocol s influence on postoperative follow-up of lesions detection associated with gastrointestinal tumours Jing-Feng Zhang
Original Article on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Abdominal CT protocol s influence on postoperative follow-up of lesions detection associated with gastrointestinal tumours Jing-Feng Zhang
Real-time elastography of parotid gland masses: the value of strain ratio for the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors
 Realtime elastography of parotid gland masses: the value of strain ratio for the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors Poster No.: C09 Congress: ECR 05 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M.
Realtime elastography of parotid gland masses: the value of strain ratio for the differentiation of benign from malignant tumors Poster No.: C09 Congress: ECR 05 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M.
THE TUFFEST STUFF CT REGISTRY REVIEW Live Lecture Seminar SATURDAY CURRICULUM
 1. The CT Imaging Chain-10 major components & their functions a. The x-ray tube b. Generator c. Filter d. Pre-patient collimator e. Pre-detector collimator f. Detector system g. Analog to digital converter
1. The CT Imaging Chain-10 major components & their functions a. The x-ray tube b. Generator c. Filter d. Pre-patient collimator e. Pre-detector collimator f. Detector system g. Analog to digital converter
Comparison of CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB
 Comparison of CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB Poster No.: C-0757 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Yoon, H. Soohee; Changwon-si/KR Thorax, Lung, Respiratory system,
Comparison of CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB Poster No.: C-0757 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Yoon, H. Soohee; Changwon-si/KR Thorax, Lung, Respiratory system,
BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam
 GE Healthcare BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam Michael Swack, MD Diagnostic Radiologist Irvington Radiologists, PC
GE Healthcare BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam Michael Swack, MD Diagnostic Radiologist Irvington Radiologists, PC
Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES
 DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-601 Original Research THE USE OF REFORMATTED CONE BEAM CT IMAGES IN ASSESSING MID-FACE TRAUMA, WITH A FOCUS ON THE ORBITAL FLOOR FRACTURES RALUCA ROMAN 1, MIHAELA HEDEȘIU 1, FLOAREA
Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System features of follicular thyroid adenoma and carcinoma: a single-center study
 Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System features of follicular thyroid adenoma and carcinoma: a single-center study Jung Won Park 1, Dong Wook Kim 1, Donghyun Kim 1, Jin Wook Baek 1, Yoo Jin Lee
Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System features of follicular thyroid adenoma and carcinoma: a single-center study Jung Won Park 1, Dong Wook Kim 1, Donghyun Kim 1, Jin Wook Baek 1, Yoo Jin Lee
Artifact reduction strategies for prosthetic heart valve CT imaging
 Int J Cardiovasc Imaging (2012) 28:2099 2108 DOI 10.1007/s10554-012-0041-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Artifact reduction strategies for prosthetic heart valve CT imaging Jesse Habets Petr Symersky Tim Leiner Bas A.
Int J Cardiovasc Imaging (2012) 28:2099 2108 DOI 10.1007/s10554-012-0041-5 ORIGINAL PAPER Artifact reduction strategies for prosthetic heart valve CT imaging Jesse Habets Petr Symersky Tim Leiner Bas A.
FDG-18 PET/CT - radiation dose and dose-reduction strategy
 FDG-18 PET/CT - radiation dose and dose-reduction strategy Poster No.: C-1856 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit P. Nicholson, S. McSweeney, K. O'Regan; Cork/IE Radiation
FDG-18 PET/CT - radiation dose and dose-reduction strategy Poster No.: C-1856 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit P. Nicholson, S. McSweeney, K. O'Regan; Cork/IE Radiation
Yang Hou 1, Jiahe Zheng 1, Yuke Wang 1, Mei Yu 1, Mani Vembar 2, Qiyong Guo 1 * Abstract. Introduction
 Optimizing Radiation Dose Levels in Prospectively Electrocardiogram-Triggered Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Using Iterative Reconstruction Techniques: A Phantom and Patient Study Yang Hou 1,
Optimizing Radiation Dose Levels in Prospectively Electrocardiogram-Triggered Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography Using Iterative Reconstruction Techniques: A Phantom and Patient Study Yang Hou 1,
Measurement error of spiral CT Volumetry:
 Measurement error of spiral CT Volumetry: Influence of Low Dose CT Technique 1 Tae Gyu Lee, M.D. 2, Myung Jin Chung, M.D., Sung Bum Cho, M.D. 2, Jae Min Cho, M.D., Seog Joon Kim, M.D. 2, Sang Hyun Baik,
Measurement error of spiral CT Volumetry: Influence of Low Dose CT Technique 1 Tae Gyu Lee, M.D. 2, Myung Jin Chung, M.D., Sung Bum Cho, M.D. 2, Jae Min Cho, M.D., Seog Joon Kim, M.D. 2, Sang Hyun Baik,
Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures
 Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures Collin, David; Dunker, Dennis; Gothlin, Jan H.; Geijer, Mats Published in: Acta Radiologica
Observer variation for radiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging of occult hip fractures Collin, David; Dunker, Dennis; Gothlin, Jan H.; Geijer, Mats Published in: Acta Radiologica
SURGERY OF THE HAND. Basosquamous Carcinoma of the Hand in a Radiologist with Prolonged Radiation Exposure INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT CASE REPORT
 CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2016;21(3):162-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.3.162 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Basosquamous
CASE REPORT pissn 1598-3889 eissn 2234-0998 J Korean Soc Surg Hand 2016;21(3):162-166. http://dx.doi.org/10.12790/jkssh.2016.21.3.162 JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN SOCIETY FOR SURGERY OF THE HAND Basosquamous
Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT
 Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT Junfu Liang 1,2, Hui Wang 1, Lei Xu 1, Li Dong 1, Zhanming
Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT Junfu Liang 1,2, Hui Wang 1, Lei Xu 1, Li Dong 1, Zhanming
Taller-Than-Wide Sign of Thyroid Malignancy: Comparison Between Ultrasound and CT
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Yoon et al. Taller-Than-Wide Sign of Thyroid Malignancy Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Soo Jeong Yoon 1 Dae Young Yoon 1,2
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Yoon et al. Taller-Than-Wide Sign of Thyroid Malignancy Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Soo Jeong Yoon 1 Dae Young Yoon 1,2
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research
 Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Sagara et al. Abdominal CT With Low Versus Routine Dose Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Yoshiko Sagara 1 Amy K. Hara 2 William Pavlicek
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Sagara et al. Abdominal CT With Low Versus Routine Dose Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Yoshiko Sagara 1 Amy K. Hara 2 William Pavlicek
SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report
 www.siemens.com/healthcare SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report Table of contents 1 Dosimetry and imaging performance report 5 1.1 Dose information 5 1.1.1 General
www.siemens.com/healthcare SOMATOM Drive System Owner Manual Dosimetry and imaging performance report Table of contents 1 Dosimetry and imaging performance report 5 1.1 Dose information 5 1.1.1 General
CT Quality Control Manual FAQs
 CT Quality Control Manual FAQs General Question: How often will the QC Manual be updated and how will those updates be communicated? Answer: The ACR CT Physics Subcommittee will review any comments, issues
CT Quality Control Manual FAQs General Question: How often will the QC Manual be updated and how will those updates be communicated? Answer: The ACR CT Physics Subcommittee will review any comments, issues
Feasibility of Iterative Model Reconstruction for Unenhanced
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Yuji Iyama, MD Takeshi Nakaura, MD Ayumi Iyama, MD Masafumi Kidoh, MD Kazuhiro Katahira, MD Seitaro Oda, MD Daisuke
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Yuji Iyama, MD Takeshi Nakaura, MD Ayumi Iyama, MD Masafumi Kidoh, MD Kazuhiro Katahira, MD Seitaro Oda, MD Daisuke
Measurement of organ dose in abdomen-pelvis CT exam as a function of ma, KV and scanner type by Monte Carlo method
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 1(4): 187-194 Measurement of organ dose in abdomen-pelvis CT exam as a function of ma, KV and scanner type by Monte Carlo method M.R. Ay 1, M. Shahriari 2, S. Sarkar 3, P.
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 1(4): 187-194 Measurement of organ dose in abdomen-pelvis CT exam as a function of ma, KV and scanner type by Monte Carlo method M.R. Ay 1, M. Shahriari 2, S. Sarkar 3, P.
MEDICAL UNIVERSITY of SOUTH CAROLINA
 U. Joseph Schoepf, MD Prof. (h.c.), FAHA, FSCBT-MR, FNASCI, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director, Division of Cardiovascular Imaging MEDICAL UNIVERSITY of SOUTH CAROLINA Disclosures
U. Joseph Schoepf, MD Prof. (h.c.), FAHA, FSCBT-MR, FNASCI, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director, Division of Cardiovascular Imaging MEDICAL UNIVERSITY of SOUTH CAROLINA Disclosures
