The value of magnetic resonance
|
|
|
- Easter Walsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Neurobiol. Exv. 1996, 56: The value of magnetic resonance - imaging in diagnosis and monitoring of treatment in Monika ~ekiesiriska-~i~atowska', Jerzy ~alecki' and Zbigniew stelmasiak2 '~e~artment of Diagnostic Imaging, Central Railway Hospital and Medical Centre for Postgraduate Education, 2 Bursztynowa St., Warsaw; 2~cientific and Clinical Centre for Demyelinating Diseases, Lublin, Poland Abstract. We analysed MR examinations of 277 patients with multiple sclerosis. White matter hyperintensities in brain were found in 270 of them. The most frequently they were found in periventricular white matter (in 100% of cases), in subcortical localization (52.2%) and in the corpus callosum (44.4%). MR examination allows to estimate the activity of the disease on the basis of the presence of oedema around the plaques and their contrast enhancement with gadopentetate dimeglumine (Gd-DTPA). 17.8% of all cases showed the signs of the acute phase of MS. About one-third of all cases were accompanied by cortical brain atrophy (the most often seen in the frontal lobes), subcortical brain atrophy was less frequent (one-sixth). In about two-third of all cases the corpus callosum atrophy was found. The analysis of follow-up MR examinations of 83 patients taking part in a,iouble-blind placebo-controlled trial of a new immunosupressive drug. ladribine showed that patients from the placebo group were more ~omplianto any changes of the plaques. Decrease of the plaques size was found mainly in women. No correlation between the patients age and the plaques changes was established. Key words: magnetic resonance (MR), multiple sclerosis (MS), white matter hyperintensisties, plaques, brain atrophy, cladribine (2-CDA)
2 172 M. Bekiesiriska-Figatowska et al. INTRODUCTION More than 400 persons with a mean age of 30 years fall ill with multiple sclerosis in Poland every year. Demyelination of nerve fibres causes the multifocal damage of the CNS. The etiopathogenesis of MS has not been established so far. The most probable theories assume the influence of viral, genetic and autoimrnunological factors. Considering varied clinical picture and difficulties in differential diagnosis it seems to be quite obvious that these patients are often referred to magnetic resonance examinations, sometimes with omission of computerized tomography (CT) which in majority of cases reveals no specific abnormalities. The MR method improves diagnostic possibilities in MS and allows to detect plaques in the spinal cord as well as in brain. The purpose of this study was to establish MR symptomatology of MS and to estimate its value in monitoring of treatment of MS. METHODS Subjects Magnetic resonance examinations of 277 patients (17 l women, 106 men) were evaluated for the distribution of MS lesions. The mean age was years (range years). Eighty three patients (5 1 women, 32 men) took part in a double-blind placebo-controlled trial of cladribine. Their mean age was 36.5 (range years). Apparatus Magnetic resonance imaging was performed on a 0.5 T machine (Toshiba MRT5OA) and on a 1.5 T machine (Magnetom Siemens) with a standard head coil. Procedure MR imaging was performed according to the following protocol: slices in two planes (axial and sa- gittal) with slice thickness of 7.5 and 5 mm using spin echo (SE) technique including TI-weighted images (TR 500 or 600 ms, TE 20 or 15 ms), PDweighted (TR 3,000 or 2,500 ms, TE 30 or 15 ms) and T2-weighted (TR 3,000 or 2,500 ms, TE 120 or 90 ms). 81 patients were examined twice: before and after 6 courses of treatment. Cladribine and placebo were administered subcutaneously 5 mg daily for 5 days. Statistical analysis was performed by means of Pearsons correlation coefficients. P values smaller than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. RESULTS Hyperintensive lesions were shown on PD- and T2-weighted images in 270 of 277 patients (97.5 %). The most frequently they were shown in periventricular white matter (in 100% of cases), in subcortical localization (52.2%) and in the corpus callosum (44.4%). The less frequently - in brain cortex (only in one case - 0.4%) (Table I). Plaques could be clearly seen on TI-weighted images as the hypointense foci in only % of all cases. They were imperceptible or easy to overlook on TI-weighted images in 61.9% which shows the poor usefulness of the unenhanced TI-weighted images in MS lesions detection. TI-weighted images are usually abnormal in acute phase and in long standing cases. Localization of plaques TABLE I Localization Number of patients % periventricular subcortical corpus callosum brain stem internal capsule cerebellum basal ganglia brain cortex
3 MRI in MS 173 TABLE I1 Cortical atrophy of the CNS Atrophy of the cortex of Number of patients % of the group of patients of all the patients with atrophy frontal lobes parietal lobes temporal lobes cerebellum occipital lobes no atrophy In 12 patients MR examination was performed after the intravenous administration of contrast medium - Gd-DTPA. The enhancement of the acute plaques was observed on TI-weighted images in all of them. In 48 cases oedema around the plaques was shown on PD- and T2-weighted images. The signs of the acute phase of MS were visualised in 17.8% of all patients. These signs are the result of the increased blood-brain barrier permeability. In 82.2% of patients the plaques were chronic. In majority of cases white matter hyperintensities were focal (69.6%). Only in 1.9% of all cases they were confluent. In 28.5% both focal and confluent lesions were observed. Confluent changes were found around the anterior and posterior parts of the lateral ventricles. The shrinkage of chronic lesions accounts for the ventricular dilatation found in long standing cases of MS. In our material subcortical brain atrophy was visualised in 16.7%. Cortical brain atrophy was observed more frequently: in 37% (Table 11). The brain MR imaging sign most specific for MS probably is an abnormal corpus callosum. Callosal atrophy can be encountered relatively early in the disease, in the absence if clinical disability. It was found in 64.9% of our patients. Only in 98 cases the results of CT examinations were available, 68 of them were normal. Only in 15 cases hypodense foci were found on CT. In 22 - TABLE I11 The results of CT examinations Result of CT Number of patients % normal abnormal atrophy hypodense foci atrophy and hypodense foci MR versus CT TABLE IV Results CT - number MR - number of the examinations of patients of patients normal 68 0 abnormal cortical and/or subcortical atrophy callosal atrophy 0 47 focal changes 15 98
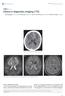
4 174 M. Bekiesiriska-Figatowska et al. brain atrophy was shown. Callosal lesions and atrophy cannot be demonstrated by means of CT (Tables 111 and IV). Perhaps the most important outcome of the last 10 years research is that MRI has emerged as a highly sensitive and independent marker of disease activity that can be used in the context of trials of experimental treatments. In our case the study group consisted of 83 patients with relapsing-remitting MS, randomised to receive placebo or a new immunosupressive drug 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine (cladribine, 2-CDA). The patients were followedup both clinically and with MRI. The patients receiving placebo turned out to be more compliant to any changes (increaseldecrease of the numberlsize) of the plaques. It was statistically significant Fig. 1. Typical periventricular localization of plaques. PDweighted image, axial plane. (P= ). The most encouraging finding was that the number of new plaques was twice as big in the placebo group (8) as in the cladribine group (4) diseases may at times resemble patients with MS to - not significant because of small numbers. the extent that they satisfy the clinical criteria for Dicrease of plaques size was found mainly in definite MS. MR plays an important role in diagnoswomen. No correlation between age of the patients ing these diseases and differentiating them from MS and plaques changes was established. DISCUSSION Magnetic resonance imaging has had an enormous impact on medicine. It has revolutionized the investigation of neurological disorders in general and multiple sclerosis in particular. It is now basic diagnostic method in MS beside anamnesis and physical examination, evoked potentials and cerebro-spinal fluid electrophoresis (oligoclonal bands). None of these methods alone is sufficient to reach the absolutely sure diagnosis. That is why it is very important to use all of them (David et al. 1990, Paolino et al. 1990). The preponderance of MR is underlined in cases of clinically probable MS (Paolino et al. 1990) and as far as the evaluation of disease activity and progression is concerned (Baum et al. 1990, Weinshenker and Nelson 1990). Some authors consider MR (sensitivity 97%) as much more sensitive than evoked potentials (46-89%) but less thancsf electrophoresis (Baumhefner Fig. 2. Plaques in cervical part of spinal cord (a). T2- et al. 1990). Patients with certain other neurologic weighted image, sagittal plane.
5 MRI in MS 175 Fig. 3. T2-weighted images, sagittal plane. A, atrophy of the corpus callosum. B, normal corpus callosum. (Rudick et al. 1986). Hyperintense (PD- and T2-W) lesions in brain (Fig. 1) and/or in spinal cord (Fig.2) and the clinical data lead to the suspicion of MS. One has to take into account that lesions of the type seen in MS may occur also in other diseases, e.g. hypertension, migraine, Alzheimer's disease, encephalitis, vasculitis and in normal ageing (Yetkin et al , Barkhof 1992). Nevertheless there are certain specific features on brain MR images which can make a diagnosis of MS more probable. There must be at least 3 hyperintense foci.. The finding of lesions greater than 5 mm, abutting the bodies of lateral ventricles and in the infratentorial region is specific for MS (Offenbacher et al. 1993). Lack of hyperintensities in brain does not exclude MS (Mushlin et al. 1993) - the lesions may be present only in spinal cord or in optic nerves. Analysing our material we found that the periventricular region is the most common localization of plaques and that callosal atrophy (Fig. 3) is more specific for MS than cortical and subcortical brain atrophy. This confirms the previous literature reports (Gean-Martin et al. 1991, Barkhof 1992, Cendrowski 1993, Thorpe, Miller 1994). We also found very small frequency of cortical lesions which is consistent with other reports (Ormerod et al. 1987, Cendrowski 1993) although it has also been suggested that cortical plaques are much more frequent (Barkhof 1992). The poor usefulness of T 1 -weighted images (except when the contrast medium is administered) has been reported by the other authors (Runge et al. 1984, Koopmans et al. 1989) as well as the presence of focal and confluent lesions (Koopmans et al. 1989). The only imaging possibility available before the era of magnetic resonance - computerized tomography - did not (in majority of cases) reveal any abnormalities in patients with multiple sclerosis. Hypodense foci found in some cases are not specific for this disease. CT can only show brain atrophy but is unable to visualise callosal atrophy. The sensitivity and specificity of MR is much higher. It shows plaques not only in brain but also in spinal cord and even in optic nerves (Sosnowski et al. 1993) thanks to its great resolution. The role of MR in treatment monitoring in MS has already been reported (Barkhof 1992, Thorpe, Miller 1994). Autoimmune processes seem to have a major role in etiopathogenesis of MS. Cladribine is an imunosupressive drug, a highly specific antilymphocyte agent. It has been used with success in treatment of lymphoid leukaemias, notably hairy cell leukaemia and non-hodgkin lymphomas. It has also been used in treatment of chronic progressive
6 176 M. Bekiesiriska-Figatowska et al. MS by Sipe et al. who concluded that it influences favourably the course of chronic progressive MS (Sipe et al. 1994). REFERENCES Barkhof F. (1992) Gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. VU University Press, Amsterdam, 166 p. Baum K., Nehrig C., Schorner W., Girke W. (1990) Long term follow-up of MS: disease activity detected clinically and by MRI. Acta Neurol. Scand. 82: Baumhefner R.W., Tourtelotte W.W., Syndulko K., Waluch V., Ellison G.W., Myers L.W., Cohen S.N., Osborne M., Shapshak P. (1990) Quantitative MS plaque assessment with MRI. Its correlation with clinical parameters, evoked potentials and intra-blood-brain barrier IgG synthesis. Arch. Neurol. 47: Cendrowski W. (1993) Multiple sclerosis. PZWL, Warszawa, 275 p. David P., Ristori G., Elia M., Bartoli A., Ciervo A., Massaro A.R., Carbone G. (1990) Multiple sclerosis. Magnetic resonance imaging, evoked potentials and cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Acta Neurol. Napoli. 12: Gean-Martin A.D., Vezina L.G., Marton K.J. (1991) Abnormal corpus callosum: a sensitive and specific indicator of MS. Neuroradiology 180: Koopmans R.A., Li D.K.B., Oger J.J.F., Mayo J., PatyD.W. (1989) The lesion of MS: imaging of acute and chronic stages. Neurology 39: Mushlin A.I., Detsky AS., Phelps C.E., O'Connor P.W., Kido D.K., Kucharczyk W., Giang D.W., Mooney C., Tansey C.M., Hall W.J. (1993) The accuracy of MR imaging in patients with suspected MS. JAMA 269: Offenbacher H., Fazekas F., Schmidt R., Freidl W., Flook E., Payer F. (1993) Assessment of MRI criteria of a diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 43: Ormerod I.E.C., Miller D.H., McDonald W.I. (1987) The role of NMR imaging in the assessment of multiple sclerosis and isolated neuroradiological lesions: a quantitative study. Brain 110: Paolino E., Granieri E., Tola M.R., Govoni V., Cassetta J., Monetti V.C., Carreras M. (1990) The combineduse of instrumental and laboratory examinations in MS. Is the diagnostic facilitation real? Riv. Neurol. 60: Rudick R.A., Schiffer R.B., Schwetz K.M., Herndon R.M. (1986) Multiple sclerosis: the problem of incorrect diagnosis. Arch. Neurol. 43: Runge V.M., Price A.C., Kirsheer H.S., Allen J.H., Partain C.L., Iames A.E. (1984) Magnetic resonance imaging of multiple sclerosis: a study of pulse-technique efficacy. AJNR 5: Sipe J.C., Romine J.S., Kozio J.A., McMillan R., Zyroff J., Beutler E. (1994) Cladribine in treatment of chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. Lancet 344: Sosnowski P., Ziemianski A,, Paprzycki W. (1993) WartoSC MR w diagnostyce przypadk6w zapalenia nenvu wzrokowego. Rez. Magn. Med. 1: Thorpe J.W., Miller D.H. (1994) MRI: its application and impact. Int. MSJ. 1: Weinshenker B.G., Nelson R. (1990) The Second Canadian Conference on MS. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 17: Yetkin F.Z., Haughton V.M., Papke R.A., Fischer M.E., Rao S.M. (1991) Multiple sclerosis: specificity of MR for diagnosis. Radiology 178: Paper presented at the 2nd International Congress of the Polish Neuroscience Society; Session: Neuroimaging
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis
 APRIL 2002 103 Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis Beside the ability to detect the Olga Ciccarelli and David H. Miller NMR Unit, Institute of Neurology, University College London, Queen Square,
APRIL 2002 103 Magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis Beside the ability to detect the Olga Ciccarelli and David H. Miller NMR Unit, Institute of Neurology, University College London, Queen Square,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Infratentorial Lesions Predict Long-term Disability in Patients With Initial Findings Suggestive of Multiple Sclerosis Arjan Minneboo, MD; Frederick Barkhof, MD; Chris H. Polman,
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:702 706, April 2000 Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis Mar Tintoré, Alex
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:702 706, April 2000 Isolated Demyelinating Syndromes: Comparison of Different MR Imaging Criteria to Predict Conversion to Clinically Definite Multiple Sclerosis Mar Tintoré, Alex
MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update
 MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update Poster No.: C-0285 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Valls Masot, A. M. Quiles Granado, J. Puig Alcántara, L. RamióTorrentà,
MRI diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: an update Poster No.: C-0285 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Valls Masot, A. M. Quiles Granado, J. Puig Alcántara, L. RamióTorrentà,
The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis
 September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Clinical and research application of MRI in diagnosis and monitoring of multiple sclerosis
 24-25 February 2016 - Siena, Italy Clinical and research application of MRI in diagnosis and monitoring of multiple sclerosis IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org How
24-25 February 2016 - Siena, Italy Clinical and research application of MRI in diagnosis and monitoring of multiple sclerosis IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org How
Clinical, Laboratory and Radiological Predictors of Outcome in Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
 Ashraf A. Aboelsafa et al. Clinical, Laboratory and Radiological Predictors of Outcome in Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Ashraf A. Aboelsafa, Ehab A. Elseidy, Ehab S. Mohammed Department of Neuropsychiatry,
Ashraf A. Aboelsafa et al. Clinical, Laboratory and Radiological Predictors of Outcome in Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis Ashraf A. Aboelsafa, Ehab A. Elseidy, Ehab S. Mohammed Department of Neuropsychiatry,
A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1931 1938, November/December 1999 A Comparison of MR Imaging with Fast-FLAIR, HASTE-FLAIR, and EPI-FLAIR Sequences in the Assessment of Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Massimo
Neuroradiology Original Research
 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO), or Devic s disease, is a rare
 Case Report Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) Abstract NMO is a is a rare entity which involves the central nervous system acting as an inflammatory process by attacking the optic nerve (ON) and longitudinally
Case Report Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) Abstract NMO is a is a rare entity which involves the central nervous system acting as an inflammatory process by attacking the optic nerve (ON) and longitudinally
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome
 A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology
 General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
Reactivation of herpesvirus under fingolimod: A case of severe herpes simplex encephalitis
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Reactivation of herpesvirus under fingolimod: A case of severe herpes
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 Reactivation of herpesvirus under fingolimod: A case of severe herpes
Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:813 820, May 1999 Relevance of Hypointense Lesions on Fast Fluid- Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Images as a Marker of Disease Severity in Cases of Multiple Sclerosis Marco Rovaris,
Application of the McDonald MRI Criteria in Multiple Sclerosis
 Original Article 647 Application of the McDonald MRI Criteria in Multiple Sclerosis Ling-Ling Chan, 1 MBBS, FRCR, FAMS, Yih-Yian Sitoh, 2 MBBS, FRCR, June Chong, 3 MBBS, ABR, Siew-Ju See, 4 MBBS, MRCP,
Original Article 647 Application of the McDonald MRI Criteria in Multiple Sclerosis Ling-Ling Chan, 1 MBBS, FRCR, FAMS, Yih-Yian Sitoh, 2 MBBS, FRCR, June Chong, 3 MBBS, ABR, Siew-Ju See, 4 MBBS, MRCP,
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
Myelitis. Case 2. History. Examination. Mahtab Ghadiri
 Case 2 Myelitis Mahtab Ghadiri History A 42-year-old man presented to the emergency department with altered sensation in the lower limbs and difficulty ambulating. He first noted paresthesia in his feet
Case 2 Myelitis Mahtab Ghadiri History A 42-year-old man presented to the emergency department with altered sensation in the lower limbs and difficulty ambulating. He first noted paresthesia in his feet
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Update
 MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Update E. Torage Shivapour, M.D. Clinical Professor Department of Neurology University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics Disclosures I do not have any disclosures. Multiple Sclerosis Most
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS Update E. Torage Shivapour, M.D. Clinical Professor Department of Neurology University of Iowa Hospitals & Clinics Disclosures I do not have any disclosures. Multiple Sclerosis Most
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist
 mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
mr brain volume analysis using brain assist This Paper describes the tool named BrainAssist, which can be used for the study and analysis of brain abnormalities like Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD), Heterotopia
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
MRI in Differential Diagnosis. CMSC, June 2, Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE
 MRI in Differential Diagnosis CMSC, June 2, 2016 Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC Disclosures Speaking, consulting, and/or
MRI in Differential Diagnosis CMSC, June 2, 2016 Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC Disclosures Speaking, consulting, and/or
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome)
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 45-50 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome) Chien-Chuan Huang Tai-Yuan Chen Tai-Ching Wu Yu-Kun Tsui Te-Chang Wu Wen-Sheng Tzeng Chien-Jen Lin Department
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 45-50 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome) Chien-Chuan Huang Tai-Yuan Chen Tai-Ching Wu Yu-Kun Tsui Te-Chang Wu Wen-Sheng Tzeng Chien-Jen Lin Department
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Hot Topics Multiple Sclerosis. Natalie Parks, MD, FRCPC Assistant Professor, Dalhousie University June 27, 2018
 Hot Topics Multiple Sclerosis Natalie Parks, MD, FRCPC Assistant Professor, Dalhousie University June 27, 2018 Disclosures Natalie Parks has received compensation from Biogen, EMD Serono, Roche, and Sanofi
Hot Topics Multiple Sclerosis Natalie Parks, MD, FRCPC Assistant Professor, Dalhousie University June 27, 2018 Disclosures Natalie Parks has received compensation from Biogen, EMD Serono, Roche, and Sanofi
Periventricular T2-hyperintense lesions: does the number matter in CIS?
 Periventricular T2-hyperintense lesions: does the number matter in CIS? Dott.ssa Caterina Lapucci Department of Neuroscience, Rehabilitation, Ophthalmology. Genetics, Maternal and Child Health (DINOGMI)
Periventricular T2-hyperintense lesions: does the number matter in CIS? Dott.ssa Caterina Lapucci Department of Neuroscience, Rehabilitation, Ophthalmology. Genetics, Maternal and Child Health (DINOGMI)
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Clinical, Neurodiagnostic, and MR Findings in Children with Spinal and Brain Stem Multiple Sclerosis
 Clinical, Neurodiagnostic, and MR Findings in Children with Spinal and Brain Stem Multiple Sclerosis Charles M. Glasier, Mark B. Robbins, Patricia C. Davis, Elizenda Ceballos, and Stephen R. Bates PURPOSE:
Clinical, Neurodiagnostic, and MR Findings in Children with Spinal and Brain Stem Multiple Sclerosis Charles M. Glasier, Mark B. Robbins, Patricia C. Davis, Elizenda Ceballos, and Stephen R. Bates PURPOSE:
Low sensitivity of McDonald MRI criteria in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis among Asians
 Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 129 133 Low sensitivity of McDonald MRI criteria in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis among Asians 1 Heng-Thay CHONG MRCP, 1 Norlisah RAMLI FRCR, 2 Kwang-Ho LEE MD, 2 Byung-Joon
Neurology Asia 2006; 11 : 129 133 Low sensitivity of McDonald MRI criteria in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis among Asians 1 Heng-Thay CHONG MRCP, 1 Norlisah RAMLI FRCR, 2 Kwang-Ho LEE MD, 2 Byung-Joon
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Brain MRI Findings of Carbon Disulfide Poisoning
 Brain MRI Findings of Carbon Disulfide Poisoning Joo Hee Cha, MD 1, 2 Sam Soo Kim, MD 2 Heon Han, MD 2 Rok Ho Kim, MD 3 Sang Hyuk Yim, MD 4 Mi Jung Kim, MD 5 Objective: To evaluate the findings of brain
Brain MRI Findings of Carbon Disulfide Poisoning Joo Hee Cha, MD 1, 2 Sam Soo Kim, MD 2 Heon Han, MD 2 Rok Ho Kim, MD 3 Sang Hyuk Yim, MD 4 Mi Jung Kim, MD 5 Objective: To evaluate the findings of brain
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has the potential to
 Frequency and Location of Microbleeds in Patients With Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage Gudrun Roob, MD; Anita Lechner, MD; Reinhold Schmidt, MD; Erich Flooh, MSc; Hans-Peter Hartung, MD; Franz Fazekas,
Frequency and Location of Microbleeds in Patients With Primary Intracerebral Hemorrhage Gudrun Roob, MD; Anita Lechner, MD; Reinhold Schmidt, MD; Erich Flooh, MSc; Hans-Peter Hartung, MD; Franz Fazekas,
Idiopathic Inflammatory Demyelinating Diseases of the Brainstem
 Idiopathic Inflammatory Demyelinating Diseases of the Brainstem 1 A. Rovira-Cañellas, 2 A. Rovira-Gols, 1 J. Sastre-Garriga, 1 C. Auger, 1 J. Munuera, 1 X. Montalban 1 Hospital Vall d Hebron, Barcelona.
Idiopathic Inflammatory Demyelinating Diseases of the Brainstem 1 A. Rovira-Cañellas, 2 A. Rovira-Gols, 1 J. Sastre-Garriga, 1 C. Auger, 1 J. Munuera, 1 X. Montalban 1 Hospital Vall d Hebron, Barcelona.
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an inflammatory disease of the central nervous. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT UPDATE Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Salvatore Q. Napoli, MD, * Rohit Bakshi, MD * *Partners, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Boston, MA, Center for Neurological
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT UPDATE Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Salvatore Q. Napoli, MD, * Rohit Bakshi, MD * *Partners, Multiple Sclerosis Center, Boston, MA, Center for Neurological
Corpus callosum index and long-term disability in multiple sclerosis patients
 J Neurol (2010) 257:1256 1264 DOI 10.1007/s00415-010-5503-x ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Corpus callosum index and long-term disability in multiple sclerosis patients Özgür Yaldizli Ramin Atefy Achim Gass Dietrich
J Neurol (2010) 257:1256 1264 DOI 10.1007/s00415-010-5503-x ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION Corpus callosum index and long-term disability in multiple sclerosis patients Özgür Yaldizli Ramin Atefy Achim Gass Dietrich
Neuroimaging and Other Biomarkers. MRI for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment Decisions in MS
 Neuroimaging and Other Biomarkers MRI for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment Decisions in MS Eric Klawiter, MD MSc Massachusetts General Hospital May 30, 2014 Disclosures and Funding Disclosures: Consulting
Neuroimaging and Other Biomarkers MRI for Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment Decisions in MS Eric Klawiter, MD MSc Massachusetts General Hospital May 30, 2014 Disclosures and Funding Disclosures: Consulting
Correlation of Magnetization Transfer Ratio
 Correlation of Magnetization Transfer Ratio with Clinical Disability in Multiple Sclerosis A. Gass, MD, G. J. Barker, PhD, D. Kidd, MRCP, J. W. Thorpe, MRCP, D. MacManus, DCR, A. Brennan, DCR, P. S. Tofts,
Correlation of Magnetization Transfer Ratio with Clinical Disability in Multiple Sclerosis A. Gass, MD, G. J. Barker, PhD, D. Kidd, MRCP, J. W. Thorpe, MRCP, D. MacManus, DCR, A. Brennan, DCR, P. S. Tofts,
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Adrenoleukodystrophy
 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Adrenoleukodystrophy 2011 NHLBI Pediatric Workshop Sept. 14, 2011 Paul Orchard, M.D. Division of Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant University of Minnesota
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Adrenoleukodystrophy 2011 NHLBI Pediatric Workshop Sept. 14, 2011 Paul Orchard, M.D. Division of Pediatric Blood and Marrow Transplant University of Minnesota
CHAIR SUMMIT 7TH ANNUAL #CHAIR2014. Master Class for Neuroscience Professional Development. September 11 13, Westin Tampa Harbour Island
 #CHAIR2014 7TH ANNUAL CHAIR SUMMIT Master Class for Neuroscience Professional Development September 11 13, 2014 Westin Tampa Harbour Island Sponsored by #CHAIR2014 Use of MRI in Clinical Decision- Making
#CHAIR2014 7TH ANNUAL CHAIR SUMMIT Master Class for Neuroscience Professional Development September 11 13, 2014 Westin Tampa Harbour Island Sponsored by #CHAIR2014 Use of MRI in Clinical Decision- Making
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
MRI Atlas of MS Lesions
 MRI Atlas of MS Lesions M. A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue MRI Atlas of MS Lesions With the collaboration of A. Gass, S. Haller, L. Kappos, J. Kesselring, J.-I. Kira, K. Weier 123 Prof. Dr. med. Mohammad Ali
MRI Atlas of MS Lesions M. A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue MRI Atlas of MS Lesions With the collaboration of A. Gass, S. Haller, L. Kappos, J. Kesselring, J.-I. Kira, K. Weier 123 Prof. Dr. med. Mohammad Ali
gadolinium-dtpa for detection of MRI
 540 50ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1995;59:540-544 SHORT REPORT Neurology M Filippi V Martinelli B Colombo N Canal G Comi Neuroradiology, Scientific Institute Ospedale San Raffaele,
540 50ournal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1995;59:540-544 SHORT REPORT Neurology M Filippi V Martinelli B Colombo N Canal G Comi Neuroradiology, Scientific Institute Ospedale San Raffaele,
Clinically isolated syndromes (CIS) may
 RECOGNIZING AND MANAGING THE CLINICALLY ISOLATED SYNDROME* Steven L. Galetta, MD ABSTRACT Clinically isolated demyelinating syndromes, such as optic neuritis, transverse myelitis, and brain-stem disorders,
RECOGNIZING AND MANAGING THE CLINICALLY ISOLATED SYNDROME* Steven L. Galetta, MD ABSTRACT Clinically isolated demyelinating syndromes, such as optic neuritis, transverse myelitis, and brain-stem disorders,
MR Volume Estimation of Subcortical Brain Lesions and Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Simple and Accurate Stereologic Method
 MR Volume Estimation of Subcortical Brain Lesions and Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Simple and Accurate Stereologic Method O. J. M. Vogels, J. C. M. Zijlmans, M. A. van t Hof, H. O. M. Thijssen, and
MR Volume Estimation of Subcortical Brain Lesions and Ventricular Cerebrospinal Fluid: A Simple and Accurate Stereologic Method O. J. M. Vogels, J. C. M. Zijlmans, M. A. van t Hof, H. O. M. Thijssen, and
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling chronic demyelinating disease
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rhombencephalitis due to Listeria
 cta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rhombencephalitis due to Listeria monocytogenes
cta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Rhombencephalitis due to Listeria monocytogenes
Multiple Sclerosis vs Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in Childhood
 Multiple Sclerosis vs Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in Childhood Steven David Brass, MD, Zografos Caramanos, BA, Carlos Santos, MD, Marie-Emmanuelle Dilenge, MD, Yves Lapierre, MD, and Bernard Rosenblatt,
Multiple Sclerosis vs Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in Childhood Steven David Brass, MD, Zografos Caramanos, BA, Carlos Santos, MD, Marie-Emmanuelle Dilenge, MD, Yves Lapierre, MD, and Bernard Rosenblatt,
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Comparison of MERGE and Axial T2-Weighted Fast Spin-Echo Sequences for Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions in the Cervical Spinal Cord
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Carrera J-P, Forrester N, Wang E, et al. Eastern equine encephalitis
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Carrera J-P, Forrester N, Wang E, et al. Eastern equine encephalitis
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica in Singapore
 Case Reports 26 Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica in Singapore Koh Yeow Hoay, Pavanni Ratnagopal Abstract Introduction: Neuromyelitis optica (NMO)
Case Reports 26 Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica in Singapore Koh Yeow Hoay, Pavanni Ratnagopal Abstract Introduction: Neuromyelitis optica (NMO)
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans
 PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
PRESERVE: How intensively should we treat blood pressure in established cerebral small vessel disease? Guide to assessing MRI scans Inclusion Criteria Clinical syndrome Patients must have clinical evidence
Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis
 43ème CONGRÈS ANNUEL de la Société Française de NeuroRadiologie 30 mars au 1 er avril 2016 Novotel Paris Tour Eiffel Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Àlex Rovira Unitat de Neurorradiología.
43ème CONGRÈS ANNUEL de la Société Française de NeuroRadiologie 30 mars au 1 er avril 2016 Novotel Paris Tour Eiffel Spinal cord MR imaging in Multiple Sclerosis Àlex Rovira Unitat de Neurorradiología.
Cite this article as: BMJ, doi: /bmj c (published 24 March 2006)
 Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: systematic review Penny Whiting, Roger Harbord, Caroline Main, Jonathan J Deeks, Graziella Filippini, Matthias Egger, Jonathan
Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: systematic review Penny Whiting, Roger Harbord, Caroline Main, Jonathan J Deeks, Graziella Filippini, Matthias Egger, Jonathan
Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy
 Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy Poster No.: C-2190 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Puiu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Neuroradiology brain,
Cerebral MRI as an important diagnostic tool in temporal lobe epilepsy Poster No.: C-2190 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Puiu, D. Negru; Iasi/RO Keywords: Neuroradiology brain,
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy
 Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
ORIGINAL RESEARCH E. Matsusue S. Sugihara S. Fujii T. Kinoshita T. Nakano E. Ohama T. Ogawa Cerebral Cortical and White Matter Lesions in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis with Dementia: Correlation with MR
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Multiple Sclerosis (MS) AUC
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Multiple Sclerosis (MS) AUC Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with the following clinical presentations or diagnoses: 09/04/2018
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Multiple Sclerosis (MS) AUC Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with the following clinical presentations or diagnoses: 09/04/2018
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175)
 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Study New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People Sergio Carmona 1, Sandra Barbosa 1 and Maria Laura Ortube 2 * 1 Department of Neuro-ophthalmology, Hospital
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Study New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People Sergio Carmona 1, Sandra Barbosa 1 and Maria Laura Ortube 2 * 1 Department of Neuro-ophthalmology, Hospital
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation
 MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
MR Signal Intensity of the Optic Radiation Mika Kitajima, Yukunori Korogi, Mutsumasa Takahashi, and Komyo Eto PURPOSE: To determine whether a hyperintense layer adjacent to the lateral ventricle on T2-
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Student Lab #: Date. Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System)
 Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Central Nervous System Practical Exam. Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells. 1. Please identify the flagged structure.
 Central Nervous System Practical Exam Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells 1. Please identify the flagged structure. 2. Please identify the flagged structure. 3. Please identify the flagged structure. 4. A
Central Nervous System Practical Exam Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells 1. Please identify the flagged structure. 2. Please identify the flagged structure. 3. Please identify the flagged structure. 4. A
Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype
 MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity. Overview
 Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
The Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Checklist
 The Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Checklist A clinician s guide to evaluating brain MRI in a patient with improbable multiple sclerosis. By Ilya Kister, MD, FAAN Paraphrasing W.B. Matthews about dizziness,
The Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Checklist A clinician s guide to evaluating brain MRI in a patient with improbable multiple sclerosis. By Ilya Kister, MD, FAAN Paraphrasing W.B. Matthews about dizziness,
Severe central and peripheral paraneoplastic demyelination associated with tumours of the ovaries
 DOI 10.1007/s00381-015-2731-5 CASE REPORT Severe central and peripheral paraneoplastic demyelination associated with tumours of the ovaries Elzbieta Jurkiewicz 1 & Katarzyna Kotulska 2 & Katarzyna Nowak
DOI 10.1007/s00381-015-2731-5 CASE REPORT Severe central and peripheral paraneoplastic demyelination associated with tumours of the ovaries Elzbieta Jurkiewicz 1 & Katarzyna Kotulska 2 & Katarzyna Nowak
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis. imaging (MRI) provides
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Bas Jasperse, MD; Arjan Minneboo, MD; Vincent de Groot, MD; Nynke F. Kalkers, MD, PhD; Paul E.
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Determinants of Cerebral Atrophy Rate at the Time of Diagnosis of Multiple Sclerosis Bas Jasperse, MD; Arjan Minneboo, MD; Vincent de Groot, MD; Nynke F. Kalkers, MD, PhD; Paul E.
MRI in Multiple Sclerosis Features of Cerebral Atrophy with special focus on Multiple Sclerosis. E.W. Radue K. Bendfeldt Till Sprenger
 MRI in Multiple Sclerosis Features of Cerebral Atrophy with special focus on Multiple Sclerosis E.W. Radue K. Bendfeldt Till Sprenger Medical Image Analysis Center University Hospital Basel www. miac.ch
MRI in Multiple Sclerosis Features of Cerebral Atrophy with special focus on Multiple Sclerosis E.W. Radue K. Bendfeldt Till Sprenger Medical Image Analysis Center University Hospital Basel www. miac.ch
Hemiparetic multiple sclerosis
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1990;53:675-680 The National Hospital for Nervous Diseases, Queen Square, London J Cowan I E C Ormerod P Rudge Correspondence to: Dr Ormerod, The National
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1990;53:675-680 The National Hospital for Nervous Diseases, Queen Square, London J Cowan I E C Ormerod P Rudge Correspondence to: Dr Ormerod, The National
Yin-Hui Siow MD, FRCPC Director of Nuclear Medicine Southlake Regional Health Centre
 Yin-Hui Siow MD, FRCPC Director of Nuclear Medicine Southlake Regional Health Centre Today Introduction to CT Introduction to MRI Introduction to nuclear medicine Imaging the dementias The Brain ~ 1.5
Yin-Hui Siow MD, FRCPC Director of Nuclear Medicine Southlake Regional Health Centre Today Introduction to CT Introduction to MRI Introduction to nuclear medicine Imaging the dementias The Brain ~ 1.5
MRI Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica
 July 2009 MRI Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica Jenna Nolan, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Our Patient: Initial Presentation J.H. is a 29 year-old woman who presents with acute vision
July 2009 MRI Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica Jenna Nolan, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Our Patient: Initial Presentation J.H. is a 29 year-old woman who presents with acute vision
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1803 1808, November/December 1999 Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Marco Bozzali, Maria A. Rocca, Giuseppe Iannucci,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1803 1808, November/December 1999 Magnetization-Transfer Histogram Analysis of the Cervical Cord in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis Marco Bozzali, Maria A. Rocca, Giuseppe Iannucci,
Coexisting MS and Lhermitte-Duclos Disease
 Coexisting MS and Lhermitte-Duclos Disease Bria K. Casperson 1, Victor Anaya-Baez 1, Stephen S. Kirzinger 2, Ronald Sattenberg 1, Jens O. Heidenreich 1* 1. Department of Radiology, School of Medicine,
Coexisting MS and Lhermitte-Duclos Disease Bria K. Casperson 1, Victor Anaya-Baez 1, Stephen S. Kirzinger 2, Ronald Sattenberg 1, Jens O. Heidenreich 1* 1. Department of Radiology, School of Medicine,
