MEN1 Gene Mutation and Reduced Expression Are Associated With Poor Prognosis in Pulmonary Carcinoids
|
|
|
- Cecil Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JCEM ONLINE Advances in Genetics Endocrine Research MEN1 Gene Mutation and Reduced Expression Are Associated With Poor Prognosis in Pulmonary Carcinoids Dorian R. A. Swarts, Aldo Scarpa, Vincenzo Corbo, Wim Van Criekinge, Manon van Engeland, Gaia Gatti, Mieke E. R. Henfling, Mauro Papotti, Aurel Perren, Frans C. S. Ramaekers, Ernst-Jan M. Speel,* and Marco Volante* Departments of Molecular Cell Biology (D.R.A.S., M.E.R.H., F.C.S.R.) and Pathology (E.-J.M.S., M.v.E.), GROW School for Oncology and Developmental Biology, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, The Netherlands; Applied Research on Cancer-NET Research Centre and Department of Pathology and Diagnostics (A.S., V.C.), University and Hospital Trust of Verona, Verona, Italy; Laboratory of Bioinformatics and Computational Genomics (W.V.C.), Ghent University, Belgium; Department of Oncology (G.G., M.P., M.V.), Division of Pathology, University of Turin at San Luigi Hospital, Orbassano, Torino, Italy; and Department of Pathology (A.P.), University of Bern, Bern, Switzerland Context: MEN1 gene alterations have been implicated in lung carcinoids, but their effect on gene expression and disease outcome is unknown. Objective: Our objective was to analyze MEN1 gene and expression anomalies in lung neuroendocrine neoplasms and their correlations with clinicopathologic data and disease outcome. Design: We examined 74 lung neuroendocrine neoplasms including 58 carcinoids and 16 highgrade neuroendocrine carcinomas (HGNECs) for MEN1 mutations (n 70) and allelic losses (n 69), promoter hypermethylation (n 65), and mrna (n 74) expression. Results were correlated with disease outcome. Results: MEN1 mutations were found in 7 of 55 (13%) carcinoids and in 1 HGNEC, mostly associated with loss of the second allele. MEN1 decreased expression levels correlated with the presence of mutations (P.0060) and was also lower in HGNECs than carcinoids (P.0024). MEN1 methylation was not associated with mrna expression levels. Patients with carcinoids harboring MEN1 mutation and loss had shorter overall survival (P.039 and P.035, respectively) and low MEN1 mrna levels correlated with distant metastasis (P.00010) and shorter survival (P.0071). In multivariate analysis, stage and MEN1 allelic loss were independent predictors of prognosis. Conclusion: Thirteen percent of pulmonary carcinoids harbor MEN1 mutation associated with reduced mrna expression and poor prognosis. Also in mutation-negative tumors, low MEN1 gene expression correlates with an adverse disease outcome. Hypermethylation was excluded as the underlying mechanism. (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 99: E374 E378, 2014) ISSN Print X ISSN Online Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2014 by the Endocrine Society Received July 8, Accepted November 12, First Published Online November 25, 2013 Pulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms (NENs) include well-differentiated carcinoids, classified into typical carcinoid (TC) and atypical carcinoid (AC) subtypes, with a relatively favorable prognosis (1, 2), and aggressive highgrade neuroendocrine carcinomas (HGNECs), ie, largecell neuroendocrine carcinoma (LCNEC) and small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). Lung carcinoids occur in 5% of patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 1 syndrome with MEN1 germline mutations (3). MEN1 mutations have been re- * E.-J.M.S. and M.V. contributed equally to the manuscript. Abbreviations: AC, atypical carcinoid; HGNEC, high-grade neuroendocrine carcinoma; LCNEC, large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma; MEN, multiple endocrine neoplasia; MSP, methylation-specific PCR; NEN, neuroendocrine neoplasia; NGS, next-generation sequencing; SCLC, small-cell lung cancer; TC, typical carcinoid. E374 jcem.endojournals.org J Clin Endocrinol Metab, February 2014, 99(2):E374 E378 doi: /jc
2 doi: /jc jcem.endojournals.org E375 ported in approximately 16% of sporadic lung carcinoids (4 6) but are exceptional in HGNECs (7, 8). Allelic losses of the MEN1 locus are detected more frequently ( 36%) than gene mutations (5), suggesting that alternative mechanisms might lead to MEN1 gene inactivation. So far, the association of MEN1 gene alterations with clinical follow-up has not been reported in lung NENs. Here we report a comprehensive analysis of MEN1 alterations, methylation status, and transcriptional expression in 74 lung NENs. Results are compared with tumor characteristics and clinical outcome. Statistical analysis Correlations between MEN1 data and follow-up were determined using IBM SPSS Statistics (version ; IBM) setting the P values cutoff for significance at.05. Differences in mean MEN1 mrna levels were determined by Student s t test, and the optimal cutoff point was determined using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Associations between clinical and molecular parameters were calculated using logistic and linear regression, Fisher s exact, or 2 tests, as appropriate. Associations between relative expression levels of MEN1 and other genes were calculated using Pearson s correlation. Survival curves were created by the Kaplan-Meier method and compared using the log-rank test. The prognostic value of age at diagnosis, histopathology, sex, smoking status, tumor diameter, and MEN1 mutation, deletion, and gene expression were tested in univariate and multivariate settings using Cox regression. Only variables with a P value.10 in univariate analyses were included in multivariate analyses. Materials and Methods Tissue samples Seventy-four sporadic lung NENs (34 TCs, 23 ACs, 1 unclassified carcinoid, 9 LCNECs, 6 SCLCs, and 1 mixed LCNEC- SCLC), including 71 with follow-up (median 52 months), were studied. Institutional review board approval for the study was obtained by each contributing center following local ethical requirements. Nine neuroendocrine cell lines were included for MEN1 mrna expression analysis. MEN1 mutational analysis The entire coding region and splice junctions of MEN1 were analyzed on tumor and matched normal DNA by Sanger sequencing, as described (9) (Supplemental Table 1A). MEN1 deletion analysis Fluorescent in situ hybridization on frozen sections was performed using the MEN1 locus BAC probe CTD , and centromere probes for chromosomes 1, 11, 3, and 7 as described (10). Quantitative real-time PCR Quantitative real-time PCR was performed using mrna on MEN1, menin interactors JUND and MLL, and menin targets HOXC8, P18, P21, and P27, using primers listed in Supplemental Table 1B. Expression levels were normalized to ACTB and CYPA housekeeping genes as described (11). Methylation-specific PCR and next-generation sequencing MEN1 promoter methylation analysis was performed on all cases by nested methylation-specific PCR (MSP) (Supplemental Table 1C) and by next-generation sequencing (NGS) on methyl- CpG binding domain-immunoprecipitated DNA of 10 primary carcinoids and carcinoid cell lines NCI-H720 and NCI-H727 (focusing on the MEN1 gene). Results MEN1 gene mutations and deletions are more frequent in ACs MEN1 mutations were searched in 70 tumors, including 7 previously published cases (5). Eight cases (11%) showed nonsynonymous somatic alterations: 2 of 32 TCs (6%), 5 of 23 ACs (22%), and 1 of 7 LCNECs (14%). Mutations included 3 small deletions, 3 single-nucleotide substitutions, and 2 insertions (Supplemental Tables 2 and 3). Patient 35 showed the same MEN1 mutations in the primary tumor and 2 distant metastases removed 8 and 10 years later. Ploidy status and MEN1 deletion were analyzed by fluorescent in situ hybridization in 69 tumors (Table 1 and Figure 1, A C). Most carcinoids were disomic, whereas HGNECs were more frequently polysomic. Among carcinoids, 8 of 57 (14%, 1 TC and 7 ACs) showed MEN1 allelic loss. In HGNECs, MEN1 was deleted in 3 of 12 cases (25%). MEN1 deletion was more frequent in ACs than in TCs (P.0060) and was significantly associated with the presence of mutations in both the total group of NENs (P.0022) and in carcinoids (P.0063) (Supplemental Table 3). MEN1 gene expression is heterogeneous in lung NENs Quantitative RT-PCR performed on all 74 NENs showed that relative MEN1 expression levels in lung NENs ranged from to 0.85, generally lower than exocrine pancreas (mean 0.58; Figure 1D) but higher than normal lung (mean 0.078). A gradual decrease in mean MEN1 expression values was apparent from TCs to ACs and HGNECs (Figure 1, D and E). Similarly, MEN1 expression levels in SCLC NCI-H69 and LCNEC NCI- H460 cell lines were lower than in lung carcinoid NCI- H720 and NCI-H727 cells (Figure 1D). MEN1 gene expression levels were inversely correlated to the presence of mutations and deletions (Supplemental Table 3) in the
3 E376 Swarts et al The MEN1 Gene in Lung Carcinoids J Clin Endocrinol Metab, February 2014, 99(2):E374 E378 Table 1. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of Clinical Data and MEN1 Parameters Correlated With Outcome of Patients With Pulmonary NENs Lung NENs, P Values Carcinoids, P Values Univariate Multivariate a Univariate Multivariate a Age at diagnosis.0003 NS.0021 NS Diameter.086 NI NS NI Histopathology NS Sex.049 NS NS NI Smoking status NS NI NS NI Stage.0002 NS MEN1 deletion.013 NS MEN1 mutation.060 NI.050 NI MEN1 gene expression NS Abbreviations: NI, not included in multivariate analysis; NS, not significant. a Only parameters displaying a P value.05 are included in multivariate analysis, and in the final model all P values needed to be.05. complete group of lung NENs (P.0060) and carcinoids (P.025). No correlation between MEN1 methylation and gene expression Because low MEN1 expression levels were present in tumors with neither MEN1 mutation nor deletion, we analyzed MEN1 promoter methylation by MSP. No methylation-specific product was seen in 65 primary NENs, cell lines, and 15 normal lungs from noncancer patients. NGS in 10 primary carcinoids and lung carcinoid cell lines NCI- H720 and NCI-H727 showed some methylation signals in MEN1 promoter region and gene body but not at the locus used for MSP analysis (Supplemental Figure 1). No methylation signals were found in CpG islands. There were no differences in methylation between samples with high and low MEN1 mrna levels. Deregulation of MEN1 is associated with metastatic disease and poor prognosis MEN1 gene mutations and deletions and decreased gene expression were associated with the presence of distant metastasis in both the total group of NENs and the carcinoids subgroup but were not related to sex, age, and smoking status (Supplemental Table 4). In particular, MEN1 mrna levels were significantly lower in patients with distant metastasis and/or patients who died from their tumor, both in the entire group (0.162 vs 0.318, P.00080) and within the carcinoid subgroup (Figure 1E). Univariate survival analysis showed in both the complete group of NENs and the carcinoid subgroup that age, histopathology, stage, presence of MEN1 deletions, and decreased gene expression were significantly associated with higher risk of death (Table 1). At multivariate survival analysis, histopathology and decreased MEN1 gene expression in lung NENs overall and stage and MEN1 deletion in the carcinoid subgroup retained statistical significance. Kaplan-Meier survival analysis confirmed that the 15-year overall survival of lung carcinoids was significantly shorter in patients with MEN1 mutation (Figure 1F), decreased mrna levels (Figure 1G), and deletion (P.035). Menin interactors and target genes Within the complete set of NENs, MEN1 gene expression was correlated with that of its interactors JUND (P.016) and MLL (P.026) but not of its targets HOXC8, P18, P21, and P27. Significant associations between MEN1 deletion and low HOXC8 expression (P.010) and low P18 gene expression (P.017) were also found. MEN1 mutational status and menin protein expression were not associated with mrna levels of interactors and downstream targets. In the complete group of NENs, as well as within carcinoids, lower levels of P18 expression (P.0074 and P.0011, respectively) were associated with lower 15-year survival. Discussion Our study on pulmonary NENs shows that the presence of MEN1 mutation and/or a lower MEN1 gene expression is associated with distant metastasis and lower 15-year survival in both the entire cohort of NENs and lung carcinoids considered separately. MEN1 mutations were found in 13% of carcinoids (7 of 55), in line with previous reports (4, 5), with most mutations occurring in ACs. All mutations were of the lossof-function type, and most mutated cases also displayed deletion of the second MEN1 locus. Only 1 of 15 HGNECs was mutated, confirming that MEN1 mutations do not play a major role in HGNECs (7, 8).
4 doi: /jc jcem.endojournals.org E377 Figure 1. MEN1 gene alterations and expression in lung NENs and association with survival. A C, Fluorescence in situ hybridization for the MEN1 locus (in red), showing a case with an MEN1 mutation but retention of 2 copies of the MEN1 gene (A) and 2 cases with MEN1 mutation and associated loss of the MEN1 locus (B and C), the latter in the presence of 2 copies of chromosome 7 (centromeric probe of chromosome 7 in green). D, Scatterplots showing the relative mrna expression values of MEN1 for TCs, ACs, LCNECs, SCLCs, neuroendocrine (NE) cancer cell lines, and normal tissues compared with the geometric mean of the expression levels of the housekeeping genes ACTB and CYPA. The horizontal bars represent the mean expression values. E, Differences between the mean values SD of MEN1 gene expression levels between the total group of carcinoids (TC/AC) and NE carcinomas (LCNEC/SCLC) (left; 95% confidence interval, to ) and of carcinoid patients (TC/AC) with a favorable (Fav) and a poor disease outcome (right; 95% confidence interval, ). F and G, Kaplan-Meier analyses depicting 15-year overall survival in the group of carcinoids according to the presence of MEN1 gene mutations (F, dotted line) or MEN1 gene expression levels below the cutoff point of (G, dotted line). promoter with MSP analysis, whereas methylated regions outside the CpG island were identified by methyl-cpg binding domain sequencing. However, such methylation was not associated with reduced MEN1 mrna levels, suggesting that MEN1 hypermethylation unlikely underlies MEN1 downregulation. MEN1 gene alterations and reduced expression were significantly associated with tumor stage, presence of distant metastases, and patient survival. At multivariate analysis, decreased MEN1 gene expression was an independent predictor of disease outcome in both the complete group of NENs and in the group of carcinoids alone. This finding seems specific for lung NENs because it is not observed in pancreatic NENs (10). The mechanisms underlying the role of MEN1 gene loss of function and the acquisition of clinical aggressiveness in lung carcinoids deserves further investigation. We identified correlations between MEN1 and JUND/MLL mrna levels but not with menin targets P18, P21, and P27, suggesting that lung-specific mechanisms might be active, such as the E-cadherin/ -catenin pathway, which interacts with menin and is frequently deregulated in lung NENs (7). In conclusion, our comprehensive overview of MEN1 molecular alterations in lung NENs demonstrates a significant association between MEN1 gene deregulation and clinical aggressiveness in lung carcinoids and postulates different mechanisms of gene regulation in well-differentiated and poorly differentiated NENs. The large majority of neoplasms with the wild-type MEN1 gene had high mrna levels. However, not all cases with low mrna levels harbored mutations or deletions, indicating that other mechanisms might unbalance MEN1 expression in these tumors. No hypermethylation was seen in CpG islands within the MEN1 Acknowledgments We thank the following people who have provided us with tumor material: Jos Broers, Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Maastricht University, The Netherlands; Thomas Rudolph, De-
5 E378 Swarts et al The MEN1 Gene in Lung Carcinoids J Clin Endocrinol Metab, February 2014, 99(2):E374 E378 partment of Pathology, University of Bern, Switzerland; Matthijs van Oosterhout and Kees Seldenrijk, Department of Pathology, Sint Antonius Hospital, Nieuwegein, The Netherlands; Loes van Velthuysen, Division of Pathology, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. In addition, we thank Kim Wouters and Jürgen Veeck, Department of Pathology, Maastricht University Medical Centre, for help with the MSP and the Biobix genome browser, respectively. We also thank Annick Haesevoets, Department of Molecular Cell Biology and Pathology, Maastricht University Medical Centre, for technical assistance; Robert-Jan van Suylen, Department of Pathology, Jeroen Bosch Hospital, s-hertogenbosch; and Erik Thunnissen, Department of Pathology, Free University Medical Centre, Amsterdam, for performing reclassification of carcinoid tumors; and Anne-Marie Dingemans, Department of Pulmunology, Maastricht University Medical Centre, Maastricht, The Netherlands, for acquiring clinical follow-up data. Address all correspondence and requests for reprints to: Prof Aldo Scarpa, MD, PhD, Applied Research on Cancer-NET Research Centre and Department of Pathology and Diagnostics, University of Verona, Policlinico G. B. Rossi, Piazzale L. A. Scuro 10, Verona, Italy. aldo.scarpa@univr.it. Current affiliation for D.R.A.S.: Department of Biology, University of York, York, United Kingdom. This work was supported by grants from the Italian Association for Cancer Research (AIRC) (Grant IG to M.V.; Grant to A.S.), the Italian Cancer Genome Project (FIRB RBAP10AHJB to A.S.), and the Jan Dekkerstichting and Ludgardine Bouwmanstichting (Grant 2010_010 to D.R.A.S. and E.-J.M.S.). Disclosure Summary: W.V.C. is employed as CSO in Mdx- Health., E.-J.M.S. has received honoraria from the Speakers Bureau of Pfizer and Lilly and is a consultant/advisory board member of Pfizer. References 1. Beasley MB, Thunnissen FB, Hasleton PhS, et al. Carcinoid tumour. In: Travis WD, Brambilla E, Muller-Harmelink HK, Harris CC, editors. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the lung, pleura, thymus and heart. Lyon: IARC Press, 2004: Granberg D, Eriksson B, Wilander E, et al. Experience in treatment of metastatic pulmonary carcinoid tumors. Ann Oncol. 2001;12: Sachithanandan N, Harle RA, Burgess JR. Bronchopulmonary carcinoid in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Cancer. 2005;103: Debelenko LV, Brambilla E, Agarwal SK, et al. Identification of MEN1 gene mutations in sporadic carcinoid tumors of the lung. Hum Mol Genet. 1997;6: Görtz B, Roth J, Krähenmann A, et al. Mutations and allelic deletions of the MEN1 gene are associated with a subset of sporadic endocrine pancreatic and neuroendocrine tumors and not restricted to foregut neoplasms. Am J Pathol. 1999;154: Veschi S, Lattanzio R, Aceto GM, et al. Alterations of MEN1 and E-cadherin/ -catenin complex in sporadic pulmonary carcinoids. Int J Oncol Debelenko LV, Swalwell JI, Kelley MJ, et al. MEN1 gene mutation analysis of high-grade neuroendocrine lung carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2000;28: Haruki N, Yatabe Y, Travis WD, et al. Characterization of highgrade neuroendocrine tumors of the lung in relation to menin mutations. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2000;91: Corbo V, Dalai I, Scardoni M, et al. MEN1 in pancreatic endocrine tumors: analysis of gene and protein status in 169 sporadic neoplasms reveals alterations in the vast majority of cases. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2010;17: Swarts DR, Claessen SM, Jonkers YM, van Suylen RJ, Dingemans AM, de Herder WW, de Krijger RR, Smit EF, Thunnissen FB, Seldenrijk CA, Vink A, Perren A, Ramaekers FC, Speel EJ. Deletions of 11q22.3-q25 are associated with atypical lung carcinoids and poor clinical outcome. Am J Pathol. 2011;179: Swarts DR, Henfling ME, Van Neste L, et al. CD44 and OTP are strong prognostic markers for pulmonary carcinoids. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:
Enterprise Interest. Pfizer, Roche, BMS, MSD, Novartis
 Enterprise Interest Pfizer, Roche, BMS, MSD, Novartis Beyond the WHO 2015 classification of lung neuroendocrine tumours Genomics of lung NETs & identification of biomarkers for prognosis and therapy Prof.
Enterprise Interest Pfizer, Roche, BMS, MSD, Novartis Beyond the WHO 2015 classification of lung neuroendocrine tumours Genomics of lung NETs & identification of biomarkers for prognosis and therapy Prof.
Lung neuroendocrine tumors: pathological characteristics
 Review Article Lung neuroendocrine tumors: pathological characteristics Luisella Righi 1, Gaia Gatti 1, Marco Volante 1, Mauro Papotti 2 1 Department of Oncology, San Luigi Hospital, Orbassano, Italy;
Review Article Lung neuroendocrine tumors: pathological characteristics Luisella Righi 1, Gaia Gatti 1, Marco Volante 1, Mauro Papotti 2 1 Department of Oncology, San Luigi Hospital, Orbassano, Italy;
The Impact of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNC)
 The Impact of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNC) Disclosure None Background Torino, Italy LCNC Rare tumor (2% to 3% all resected primary lung cancers) Preoperative
The Impact of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Pulmonary Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNC) Disclosure None Background Torino, Italy LCNC Rare tumor (2% to 3% all resected primary lung cancers) Preoperative
Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung
 Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung M Papotti, L Righi, & M Volante University of Turin at San Luigi Hospital TORINO NETs OF THE LUNG Menu - Spectrum of NE lung tumors - CARCINOID TUMORS - SCLC /LCNEC
Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the lung M Papotti, L Righi, & M Volante University of Turin at San Luigi Hospital TORINO NETs OF THE LUNG Menu - Spectrum of NE lung tumors - CARCINOID TUMORS - SCLC /LCNEC
Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell lung Cancer (NSCLC) By CISH Technique
 Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
Small cell lung cancer and large cell neuroendocrine tumours interobserver variability. Michael den Bakker Erasmus MC
 Small cell lung cancer and large cell neuroendocrine tumours interobserver variability Michael den Bakker Erasmus MC PPC London 2007 WEB presentation Pulmonary pathology Club presentation, London, November
Small cell lung cancer and large cell neuroendocrine tumours interobserver variability Michael den Bakker Erasmus MC PPC London 2007 WEB presentation Pulmonary pathology Club presentation, London, November
Nanda Horeweg, Carlijn M. van der Aalst, Erik Thunnissen, Kristiaan Nackaerts, Carla Weenink, Harry J.M. Groen, Jan-Willem J.
 Characteristics of lung cancers detected in the randomized NELSON lung cancer screening trial Nanda Horeweg, Carlijn M. van der Aalst, Erik Thunnissen, Kristiaan Nackaerts, Carla Weenink, Harry J.M. Groen,
Characteristics of lung cancers detected in the randomized NELSON lung cancer screening trial Nanda Horeweg, Carlijn M. van der Aalst, Erik Thunnissen, Kristiaan Nackaerts, Carla Weenink, Harry J.M. Groen,
Insulinoma-associated protein (INSM1) is a sensitive and specific marker for lung neuroendocrine tumors in cytologic and surgical specimens
 Insulinoma-associated protein (INSM1) is a sensitive and specific marker for lung neuroendocrine tumors in cytologic and surgical specimens Kartik Viswanathan, M.D., Ph.D New York Presbyterian - Weill
Insulinoma-associated protein (INSM1) is a sensitive and specific marker for lung neuroendocrine tumors in cytologic and surgical specimens Kartik Viswanathan, M.D., Ph.D New York Presbyterian - Weill
Pleomorphic carcinoma of the lung: which CT findings predict poor prognosis?
 Pleomorphic carcinoma of the lung: which CT findings predict poor prognosis? Poster No.: C-1887 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Fujisaki, T. Aoki, S. Kinoshita, Y. Hayashida, Y.
Pleomorphic carcinoma of the lung: which CT findings predict poor prognosis? Poster No.: C-1887 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Fujisaki, T. Aoki, S. Kinoshita, Y. Hayashida, Y.
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Association of molecular status and organs with metastases at diagnosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
 Association of molecular status and organs with metastases at diagnosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Chantal Kuijpers* 1,2, Lizza Hendriks 3, Jules Derks 3, Anne-Marie Dingemans
Association of molecular status and organs with metastases at diagnosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Chantal Kuijpers* 1,2, Lizza Hendriks 3, Jules Derks 3, Anne-Marie Dingemans
gliomas. Fetal brain expected who each low-
 Supplementary Figure S1. Grade-specificity aberrant expression of HOXA genes in gliomas. (A) Representative RT-PCR analyses of HOXA gene expression in human astrocytomas. Exemplified glioma samples include
Supplementary Figure S1. Grade-specificity aberrant expression of HOXA genes in gliomas. (A) Representative RT-PCR analyses of HOXA gene expression in human astrocytomas. Exemplified glioma samples include
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis
 The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
The 16th KJC Bioinformatics Symposium Integrative analysis identifies potential DNA methylation biomarkers for pan-cancer diagnosis and prognosis Tieliu Shi tlshi@bio.ecnu.edu.cn The Center for bioinformatics
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 06; 23 December 2016
 SALSA MLPA probemix P417-B2 BAP1 Lot B2-1216. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0215), two reference probes have been added and two target probes have a minor change in length. The BAP1 (BRCA1 associated
SALSA MLPA probemix P417-B2 BAP1 Lot B2-1216. As compared to version B1 (lot B1-0215), two reference probes have been added and two target probes have a minor change in length. The BAP1 (BRCA1 associated
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine. Bei Li, Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club
 Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
Biomarker development in the era of precision medicine Bei Li, 23.08.2016 Interdisciplinary Technical Journal Club The top ten highest-grossing drugs in the United States help between 1 in 25 and 1 in
WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER?
 CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
Neuroendocrine Lung Tumors Myers
 Diagnosis and Classification of Neuroendocrine Lung Tumors Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor Director, Anatomic Pathology & MLabs University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI myerjeff@umich.edu
Diagnosis and Classification of Neuroendocrine Lung Tumors Jeffrey L. Myers, M.D. A. James French Professor Director, Anatomic Pathology & MLabs University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI myerjeff@umich.edu
Chibueze Onyemkpa 1, Alan Davis 1, Michael McLeod 1, Tolutope Oyasiji 1,2. Original Article
 Original Article Typical carcinoids, goblet cell carcinoids, mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinomas, neuroendocrine carcinomas and adenocarcinomas of the appendix: a comparative analysis of survival profile
Original Article Typical carcinoids, goblet cell carcinoids, mixed adenoneuroendocrine carcinomas, neuroendocrine carcinomas and adenocarcinomas of the appendix: a comparative analysis of survival profile
Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
Jpn J Clin Oncol 1997;27(5)305 309 Revisit of Primary Malignant Neoplasms of the Trachea: Clinical Characteristics and Survival Analysis -, -, - - 1 Chest Department and 2 Section of Thoracic Surgery,
CDH1 truncating alterations were detected in all six plasmacytoid-variant bladder tumors analyzed by whole-exome sequencing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 CDH1 truncating alterations were detected in all six plasmacytoid-variant bladder tumors analyzed by whole-exome sequencing. Whole-exome sequencing of six plasmacytoid-variant bladder
Supplementary Figure 1 CDH1 truncating alterations were detected in all six plasmacytoid-variant bladder tumors analyzed by whole-exome sequencing. Whole-exome sequencing of six plasmacytoid-variant bladder
WHO e TNM: Importanza della classificazione nell approccio terapeutico
 WHO e TNM: Importanza della classificazione nell approccio terapeutico Marco Volante Mauro Papotti Dipartimento di Scienze Cliniche e Biologiche Ospedale San Luigi Orbassano, Torino Rare tumors Heterogeneous
WHO e TNM: Importanza della classificazione nell approccio terapeutico Marco Volante Mauro Papotti Dipartimento di Scienze Cliniche e Biologiche Ospedale San Luigi Orbassano, Torino Rare tumors Heterogeneous
Clinical features of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a population-based overview
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG CANCER Clinical features of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a population-based overview Jules L. Derks 1, Lizza E. Hendriks 1, Wieneke A. Buikhuisen 2, Harry J.M. Groen 3, Erik
ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG CANCER Clinical features of large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma: a population-based overview Jules L. Derks 1, Lizza E. Hendriks 1, Wieneke A. Buikhuisen 2, Harry J.M. Groen 3, Erik
Uveal melanoma is the most common primary intraocular
 Genetics Higher Percentage of FISH-Determined Monosomy 3 and 8q Amplification in Uveal Melanoma Cells relate to Poor Patient Prognosis Thomas van den Bosch, 1,2 Jackelien G. M. van Beek, 2,3 Jolanda Vaarwater,
Genetics Higher Percentage of FISH-Determined Monosomy 3 and 8q Amplification in Uveal Melanoma Cells relate to Poor Patient Prognosis Thomas van den Bosch, 1,2 Jackelien G. M. van Beek, 2,3 Jolanda Vaarwater,
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors
 Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors Jaume Capdevila, MD, PhD Vall d'hebron University Hospital Vall d'hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO)
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors Jaume Capdevila, MD, PhD Vall d'hebron University Hospital Vall d'hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO)
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+)
 Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
Virtual Journal Club: Front-Line Therapy and Beyond Recent Perspectives on ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
 Virtual Journal Club: Front-Line Therapy and Beyond Recent Perspectives on ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Reference Slides ALK Rearrangement in NSCLC ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) is a receptor
Virtual Journal Club: Front-Line Therapy and Beyond Recent Perspectives on ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Reference Slides ALK Rearrangement in NSCLC ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) is a receptor
ORIGINAL PAPER. Marginal pulmonary function is associated with poor short- and long-term outcomes in lung cancer surgery
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 37 ~ 42, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.1.37 ORIGINAL PAPER Marginal pulmonary function is associated with poor short- and long-term outcomes in lung cancer surgery Naoki Ozeki, Koji
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 37 ~ 42, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.1.37 ORIGINAL PAPER Marginal pulmonary function is associated with poor short- and long-term outcomes in lung cancer surgery Naoki Ozeki, Koji
Pulmonary resection remains the most effective. Survival in Synchronous vs Single Lung Cancer. Upstaging Better Reflects Prognosis
 Survival in Synchronous vs Single Lung Cancer Upstaging Better Reflects Prognosis Marcel Th. M. van Rens, MD; Pieter Zanen, MD, PhD; Aart Brutel de la Rivière, MD, PhD, FCCP; Hans R. J. Elbers, MD, PhD;
Survival in Synchronous vs Single Lung Cancer Upstaging Better Reflects Prognosis Marcel Th. M. van Rens, MD; Pieter Zanen, MD, PhD; Aart Brutel de la Rivière, MD, PhD, FCCP; Hans R. J. Elbers, MD, PhD;
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק
 Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק 26.06.09 Lecture outlines WHO histological classification Macro/Micro assessment Early diagnosis Minimal pathology Main subtypes SCC, AdCa, LCLC
Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Histopathology ד"ר יהודית זנדבנק 26.06.09 Lecture outlines WHO histological classification Macro/Micro assessment Early diagnosis Minimal pathology Main subtypes SCC, AdCa, LCLC
Life Science Journal 2014;11(7)
 Life Science Journal 4;(7) http://www.lifesciencesite.com Impact of primary tumor resection on response and survival in metastatic breast cancer patients Enas. A. Elkhouly¹, Eman. A. Tawfik ¹, Alaa. A.
Life Science Journal 4;(7) http://www.lifesciencesite.com Impact of primary tumor resection on response and survival in metastatic breast cancer patients Enas. A. Elkhouly¹, Eman. A. Tawfik ¹, Alaa. A.
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 28; 4 January 2018
 SALSA MLPA probemix ME011-B3 Mismatch Repair genes Lot B3-1017 and B3-0715. As compared to the previous version B2 (lot B2-0614), one probe has a small change in length but no change in the sequence detected.
SALSA MLPA probemix ME011-B3 Mismatch Repair genes Lot B3-1017 and B3-0715. As compared to the previous version B2 (lot B2-0614), one probe has a small change in length but no change in the sequence detected.
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Impact of pre-treatment symptoms on survival after palliative radiotherapy An improved model to predict prognosis?
 Impact of pre-treatment symptoms on survival after palliative radiotherapy An improved model to predict prognosis? Thomas André Ankill Kämpe 30.05.2016 MED 3950,-5 year thesis Profesjonsstudiet i medisin
Impact of pre-treatment symptoms on survival after palliative radiotherapy An improved model to predict prognosis? Thomas André Ankill Kämpe 30.05.2016 MED 3950,-5 year thesis Profesjonsstudiet i medisin
Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer. Cheol Min Kang 2018/04/05
 Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Abstract No.: ABS-0075 Clinicopathological Factors Affecting Distant Metastasis Following Loco-Regional Recurrence of breast cancer 2018/04/05 Cheol Min Kang Department of surgery, University of Ulsan
Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer
 Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer Eleftherios P. Diamandis, M.D., Ph.D., FRCP(C) EORTC-NCI-ASCO Meeting,November 16, 2007 Yousef GM, Diamandis EP. Endocr.
Novel Biomarkers (Kallikreins) for Prognosis and Therapy Response in Ovarian cancer Eleftherios P. Diamandis, M.D., Ph.D., FRCP(C) EORTC-NCI-ASCO Meeting,November 16, 2007 Yousef GM, Diamandis EP. Endocr.
Clonal evolution of human cancers
 Clonal evolution of human cancers -Pathology-based microdissection and genetic analysis precisely demonstrates molecular evolution of neoplastic clones- Hiroaki Fujii, MD Ageo Medical Laboratories, Yashio
Clonal evolution of human cancers -Pathology-based microdissection and genetic analysis precisely demonstrates molecular evolution of neoplastic clones- Hiroaki Fujii, MD Ageo Medical Laboratories, Yashio
Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma.
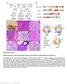 Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Supplementary Figure 1 Breeding scheme, transgenes, histological analysis and site distribution of SB-mutagenized osteosarcoma. (a) Breeding scheme. R26-LSL-SB11 homozygous mice were bred to Trp53 LSL-R270H/+
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to pancreatic cancer
 Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to pancreatic cancer M.G. He, K. Zheng, D. Tan and Z.X. Wang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nuclear Industry 215 Hospital
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to pancreatic cancer M.G. He, K. Zheng, D. Tan and Z.X. Wang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nuclear Industry 215 Hospital
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma
 Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
Original Article Prognostic factors in curatively resected pathological stage I lung adenocarcinoma Yikun Yang 1, Yousheng Mao 1, Lin Yang 2, Jie He 1, Shugeng Gao 1, Juwei Mu 1, Qi Xue 1, Dali Wang 1,
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR
 SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
P53 Gene Deletion Detected By Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization is an Adverse
 Blood First Edition Paper, prepublished online August 31, 2004; DOI 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1363 P53 Gene Deletion Detected By Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization is an Adverse Prognostic Factor for Patients
Blood First Edition Paper, prepublished online August 31, 2004; DOI 10.1182/blood-2004-04-1363 P53 Gene Deletion Detected By Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization is an Adverse Prognostic Factor for Patients
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva
 Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Locoregional treatment Session Oral Abstract Presentation Saulo Brito Silva Background Post-operative radiotherapy (PORT) improves disease free and overall suvivallin selected patients with breast cancer
Patient age and cutaneous malignant melanoma: Elderly patients are likely to have more aggressive histological features and poorer survival
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 7: 1083-1088, 2017 Patient age and cutaneous malignant melanoma: Elderly patients are likely to have more aggressive histological features and poorer survival FARUK TAS
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 7: 1083-1088, 2017 Patient age and cutaneous malignant melanoma: Elderly patients are likely to have more aggressive histological features and poorer survival FARUK TAS
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
The 2015 World Health Organization Classification for Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Practical Approach
 The 2015 World Health Organization Classification for Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Practical Approach Dr. Carol Farver Director, Pulmonary Pathology Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Institute Objectives Discuss
The 2015 World Health Organization Classification for Lung Adenocarcinomas: A Practical Approach Dr. Carol Farver Director, Pulmonary Pathology Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Institute Objectives Discuss
LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY: UPDATE ON NEUROENDOCRINE LUNG TUMORS
 LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY: UPDATE ON NEUROENDOCRINE LUNG TUMORS William D. Travis, M.D. Attending Thoracic Pathologist Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY PULMONARY NE TUMORS CLASSIFICATION
LUNG CANCER PATHOLOGY: UPDATE ON NEUROENDOCRINE LUNG TUMORS William D. Travis, M.D. Attending Thoracic Pathologist Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY PULMONARY NE TUMORS CLASSIFICATION
Analysis on the Characteristics and Prognosis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.5.2205 Characteristics and Prognosis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis on the Characteristics and Prognosis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.5.2205 Characteristics and Prognosis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors RESEARCH ARTICLE Analysis on the Characteristics and Prognosis of Pulmonary Neuroendocrine
Rare Neuroendocrine Tumours and Cancers of Endocrine Organs
 Rare Neuroendocrine Tumours and Cancers of Endocrine Organs 1. Neuroendocrine Tumours 1.1 General Results Table 1. Neuroendocrine Tumours: Incidence, Trends, Survival Flemish Region 2001-2010 Both Sexes
Rare Neuroendocrine Tumours and Cancers of Endocrine Organs 1. Neuroendocrine Tumours 1.1 General Results Table 1. Neuroendocrine Tumours: Incidence, Trends, Survival Flemish Region 2001-2010 Both Sexes
After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
 ESTS METASTASECTOMY SUPPLEMENT Alberto Oliaro, MD, Pier L. Filosso, MD, Maria C. Bruna, MD, Claudio Mossetti, MD, and Enrico Ruffini, MD Abstract: After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
ESTS METASTASECTOMY SUPPLEMENT Alberto Oliaro, MD, Pier L. Filosso, MD, Maria C. Bruna, MD, Claudio Mossetti, MD, and Enrico Ruffini, MD Abstract: After primary tumor treatment, 30% of patients with malignant
Applying Genomics to Cancer 21 st September The Frequency of EGFR mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: The Cardiff Experience
 Applying Genomics to Cancer 21 st September 2015 The Frequency of EGFR mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: The Cardiff Experience Aled Daniels R Butler, R Attanoos, H Davies University Hospital of Wales
Applying Genomics to Cancer 21 st September 2015 The Frequency of EGFR mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma: The Cardiff Experience Aled Daniels R Butler, R Attanoos, H Davies University Hospital of Wales
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD
 RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
Update: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
 ASH 2008 Update: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Improving Patient Response to Treatment with the Addition of Rituximab to Fludarabine-Cyclophosphamide ASH 2008: Update on chronic lymphocytic leukemia CLL-8
ASH 2008 Update: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Improving Patient Response to Treatment with the Addition of Rituximab to Fludarabine-Cyclophosphamide ASH 2008: Update on chronic lymphocytic leukemia CLL-8
A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in The Netherlands
 World J Surg (2018) 42:490 497 DOI 10.1007/s00268-017-4278-y ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in The Netherlands
World J Surg (2018) 42:490 497 DOI 10.1007/s00268-017-4278-y ORIGINAL SCIENTIFIC REPORT A Nationwide Population-Based Study on the Survival of Patients with Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in The Netherlands
Reporting HPV related carcinomas of the head and neck. dr. Nina Zidar Institute of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia
 Reporting HPV related carcinomas of the head and neck dr. Nina Zidar Institute of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia Conflict of interest/funding X None Company: Product royalties
Reporting HPV related carcinomas of the head and neck dr. Nina Zidar Institute of Pathology Faculty of Medicine University of Ljubljana Slovenia Conflict of interest/funding X None Company: Product royalties
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.2995
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with brainstem tumors. (a) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation versus wild-type PPM1D. (b) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation
Supplementary Figure 1 Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with brainstem tumors. (a) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation versus wild-type PPM1D. (b) Comparison of patients with PPM1D mutation
Liquid Biopsy. Jesus Garcia-Foncillas MD PhD. Director
 Liquid Biopsy Jesus Garcia-Foncillas MD PhD Director Main issues about liquid biopsies New paradigm: Precision Medicine Heterogeneity & Dynamics Surrogate mirror for the tumor CTCs in colon cancer ctdna:
Liquid Biopsy Jesus Garcia-Foncillas MD PhD Director Main issues about liquid biopsies New paradigm: Precision Medicine Heterogeneity & Dynamics Surrogate mirror for the tumor CTCs in colon cancer ctdna:
Supplementary. properties of. network types. randomly sampled. subsets (75%
 Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Immunohistochemical Profile of Lung Tumors in Image Guided Biopsies
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1342 Immunohistochemical Profile of Lung Tumors in Image Guided Biopsies T. Pavithra 1 *, A. Dhanalakshmi 1, C. Lalitha 1, K.B. Lavanya 1 and S. Shifa 2 Department
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1342 Immunohistochemical Profile of Lung Tumors in Image Guided Biopsies T. Pavithra 1 *, A. Dhanalakshmi 1, C. Lalitha 1, K.B. Lavanya 1 and S. Shifa 2 Department
Oral Communications & Posters
 Carcinoma uroteliale: Current and future directions of treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder cancer/ Multimodality approach of bladder cancer Oral Communications & Posters CRISTINA MASINI Oncologia Medica
Carcinoma uroteliale: Current and future directions of treatment of Muscle-Invasive Bladder cancer/ Multimodality approach of bladder cancer Oral Communications & Posters CRISTINA MASINI Oncologia Medica
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extent of visceral pleural invasion and the prognosis of surgically resected node-negative non-small cell lung cancer Yangki Seok 1, Ji Yun Jeong 2 & Eungbae
MSI positive MSI negative
 Pritchard et al. 2014 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI positive MSI negative Hypermutated Median: 673 Average: 659.2 Non-Hypermutated Median: 37.5 Average: 43.6 Supplementary Figure 1: Somatic Mutation Burden
Pritchard et al. 2014 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI positive MSI negative Hypermutated Median: 673 Average: 659.2 Non-Hypermutated Median: 37.5 Average: 43.6 Supplementary Figure 1: Somatic Mutation Burden
Oberndofer 1907 Illeal Serotonin Secreting Tumor Carcinoid (Karzinoide)
 GEP-NET Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Oberndofer 1907 Illeal Serotonin Secreting Tumor Carcinoid (Karzinoide) 1 Histogenesis 16 different
GEP-NET Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Oberndofer 1907 Illeal Serotonin Secreting Tumor Carcinoid (Karzinoide) 1 Histogenesis 16 different
Classification of Low-Grade Neuroendocrine Tumors of Midgut and Unknown Origin
 Classification of Low-Grade Neuroendocrine Tumors of Midgut and Unknown Origin SUSANNE VAN EEDEN, MD, PASCAL F. H. J. QUAEDVLIEG, MD, BABS G. TAAL, MD, PHD, G. JOHAN A. OFFERHAUS, MD, PHD, CORNELIS B.
Classification of Low-Grade Neuroendocrine Tumors of Midgut and Unknown Origin SUSANNE VAN EEDEN, MD, PASCAL F. H. J. QUAEDVLIEG, MD, BABS G. TAAL, MD, PHD, G. JOHAN A. OFFERHAUS, MD, PHD, CORNELIS B.
NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATION IN EPITHELIAL TUMORS Marco Volante
 NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATION IN EPITHELIAL TUMORS Marco Volante University of Turin, San Luigi Hospital, Orbassano, Turin, Italy marco.volante@unito.it pure NE tum..a grey zone pure non-ne ca. 0% NE
NEUROENDOCRINE DIFFERENTIATION IN EPITHELIAL TUMORS Marco Volante University of Turin, San Luigi Hospital, Orbassano, Turin, Italy marco.volante@unito.it pure NE tum..a grey zone pure non-ne ca. 0% NE
Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Histological Type. Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer. Nottingham Tenovus Primary Breast Cancer Study. Survival (%) Ian Ellis
 Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological Type
Morphological and Molecular Typing of breast Cancer Ian Ellis Molecular Medical Sciences, University of Nottingham Department of Histopathology, Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust Histological Type
Frequencies of actionable mutations and survival in variants of invasive adenocarcinoma of lung
 Original Article Frequencies of actionable mutations and survival in variants of invasive adenocarcinoma of lung Zhengbo Song 1,2 *, Tangfeng Lv 1 *, Yiping Zhang 2, Yong Song 1 1 Department of Respiratory
Original Article Frequencies of actionable mutations and survival in variants of invasive adenocarcinoma of lung Zhengbo Song 1,2 *, Tangfeng Lv 1 *, Yiping Zhang 2, Yong Song 1 1 Department of Respiratory
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection
 Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
Long term survival study of de-novo metastatic breast cancers with or without primary tumor resection Dr. Michael Co Division of Breast Surgery Queen Mary Hospital The University of Hong Kong Conflicts
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES: Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Glioblastoma 5hmC quantified by paired BS and oxbs treated DNA hybridized to Infinium DNA methylation arrays. Workflow depicts analytic
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Study design.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Study design. Leukopenia was classified as early when it occurred within the first 8 weeks of thiopurine therapy and as late when it occurred more than 8 weeks after the start of
Supplementary Figure 1 Study design. Leukopenia was classified as early when it occurred within the first 8 weeks of thiopurine therapy and as late when it occurred more than 8 weeks after the start of
Factors Affecting Survival in Neuroendocrine Tumors: A 15-Year Single Center Experience
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:00/00/0000 Acceptance:00/00/0000 : A 15-Year Single Center Experience Abdullah Sakin 1 *, Makbule Tambas 2, Saban Secmeler 3, Orçun Can 3, Serdar Arici 3,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:00/00/0000 Acceptance:00/00/0000 : A 15-Year Single Center Experience Abdullah Sakin 1 *, Makbule Tambas 2, Saban Secmeler 3, Orçun Can 3, Serdar Arici 3,
Evaluation of the efficacy of cisplatin etoposide and the role of thoracic radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation in LCNEC
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG CANCER Evaluation of the efficacy of cisplatin etoposide and the role of thoracic radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation in LCNEC Arsela Prelaj 1, Sara Elena Rebuzzi 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE LUNG CANCER Evaluation of the efficacy of cisplatin etoposide and the role of thoracic radiotherapy and prophylactic cranial irradiation in LCNEC Arsela Prelaj 1, Sara Elena Rebuzzi 2,
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor
 Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Elizabeth H. Moore, MD Personalized Medicine: Lung Biopsy and Tumor Mutation Testing Genomic testing has resulted in a paradigm shift in the
Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis
 5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
5/17/13 Refining Prognosis of Early Stage Lung Cancer by Molecular Features (Part 2): Early Steps in Molecularly Defined Prognosis Johannes Kratz, MD Post-doctoral Fellow, Thoracic Oncology Laboratory
Gastrinoma: Medical Management. Haley Gallup
 Gastrinoma: Medical Management Haley Gallup Also known as When to put your knife down Gastrinoma Definition and History Diagnosis Historic Management Sporadic vs MEN-1 Defining surgical candidates Nonsurgical
Gastrinoma: Medical Management Haley Gallup Also known as When to put your knife down Gastrinoma Definition and History Diagnosis Historic Management Sporadic vs MEN-1 Defining surgical candidates Nonsurgical
Characterization of Patients with Poor-
 Characterization of Patients with Poor- Risk Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Hamieh L 1 *, McKay RR 1 *, Lin X 2, Simantov R 2, Choueiri TK 1 *Equal contributions 1 Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston,
Characterization of Patients with Poor- Risk Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Hamieh L 1 *, McKay RR 1 *, Lin X 2, Simantov R 2, Choueiri TK 1 *Equal contributions 1 Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston,
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
SCOPE TODAYS SESSION. Case 1: Case 2. Basic Theory Stuff: Heavy Stuff. Basic Questions. Basic Questions
 MONDAY TEACHING SCOPE TODAYS SESSION Case 1: Basic Questions Case 2 Basic Questions Basic Theory Stuff: AJCC TNM + Stage Group for Carcinoid of the Appendix Management of Carcinoid of the Appendix (NCCN)
MONDAY TEACHING SCOPE TODAYS SESSION Case 1: Basic Questions Case 2 Basic Questions Basic Theory Stuff: AJCC TNM + Stage Group for Carcinoid of the Appendix Management of Carcinoid of the Appendix (NCCN)
Tumor necrosis is a strong predictor for recurrence in patients with pathological T1a renal cell carcinoma
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 125-130, 2015 Tumor necrosis is a strong predictor for recurrence in patients with pathological T1a renal cell carcinoma KEIICHI ITO 1, KENJI SEGUCHI 1, HIDEYUKI SHIMAZAKI 2, EIJI TAKAHASHI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 9: 125-130, 2015 Tumor necrosis is a strong predictor for recurrence in patients with pathological T1a renal cell carcinoma KEIICHI ITO 1, KENJI SEGUCHI 1, HIDEYUKI SHIMAZAKI 2, EIJI TAKAHASHI
Marcel Th. M. van Rens, MD; Aart Brutel de la Rivière, MD, PhD, FCCP; Hans R. J. Elbers, MD, PhD; and Jules M. M. van den Bosch, MD, PhD, FCCP
 Prognostic Assessment of 2,361 Patients Who Underwent Pulmonary Resection for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, Stage I, II, and IIIA* Marcel Th. M. van Rens, MD; Aart Brutel de la Rivière, MD, PhD, FCCP; Hans
Prognostic Assessment of 2,361 Patients Who Underwent Pulmonary Resection for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, Stage I, II, and IIIA* Marcel Th. M. van Rens, MD; Aart Brutel de la Rivière, MD, PhD, FCCP; Hans
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) is an
 JCEM ONLINE Advances in Genetics Endocrine Care Higher Risk of Aggressive Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in MEN1 Patients With MEN1 Mutations Affecting the CHES1 Interacting MENIN Domain Detlef K. Bartsch,
JCEM ONLINE Advances in Genetics Endocrine Care Higher Risk of Aggressive Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors in MEN1 Patients With MEN1 Mutations Affecting the CHES1 Interacting MENIN Domain Detlef K. Bartsch,
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 30; 06 June 2017
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
Impact of Prognostic Factors
 Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
Melanoma Prognostic Factors: where we started, where are we going? Impact of Prognostic Factors Staging Management Surgical intervention Adjuvant treatment Suraj Venna, MD Assistant Clinical Professor,
Research Article Prognostic Implication of Predominant Histologic Subtypes of Lymph Node Metastases in Surgically Resected Lung Adenocarcinoma
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 64568, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/64568 Research Article Prognostic Implication of Predominant Histologic Subtypes of Lymph Node Metastases in Surgically
BioMed Research International, Article ID 64568, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/.55/24/64568 Research Article Prognostic Implication of Predominant Histologic Subtypes of Lymph Node Metastases in Surgically
Thymic neoplasms are the most common tumors of
 Thymic Carcinoma: A Multivariate Analysis of Factors Predictive of Survival in 290 Patients Benny Weksler, MD, Rajeev Dhupar, MD, MBA, Vishal Parikh, BS, Katie S. Nason, MD, MPH, Arjun Pennathur, MD, and
Thymic Carcinoma: A Multivariate Analysis of Factors Predictive of Survival in 290 Patients Benny Weksler, MD, Rajeev Dhupar, MD, MBA, Vishal Parikh, BS, Katie S. Nason, MD, MPH, Arjun Pennathur, MD, and
CTC in clinical studies: Latest reports on GI cancers
 CTC in clinical studies: Latest reports on GI cancers François-Clément Bidard, MD PhD GI cancers are characterized by Multimodal treatment strategies Treatments are adapted to tumor burden & prognosis
CTC in clinical studies: Latest reports on GI cancers François-Clément Bidard, MD PhD GI cancers are characterized by Multimodal treatment strategies Treatments are adapted to tumor burden & prognosis
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript World J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 February 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics
 The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics Manon van Engeland, PhD Dept. of Pathology GROW - School for Oncology & Developmental Biology Maastricht University Medical
The silence of the genes: clinical applications of (colorectal) cancer epigenetics Manon van Engeland, PhD Dept. of Pathology GROW - School for Oncology & Developmental Biology Maastricht University Medical
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29; 31 July 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
MAPK Pathway. CGH Next Generation Sequencing. Molecular Tools in Care of Patients with Pigmented Lesions 7/20/2017
 Molecular Tools in Care of Patients with Pigmented Lesions Tammie Ferringer, MD Geisinger Medical Center, Danville, PA tferringer@geisinger.edu DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Tammie Ferringer,
Molecular Tools in Care of Patients with Pigmented Lesions Tammie Ferringer, MD Geisinger Medical Center, Danville, PA tferringer@geisinger.edu DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Tammie Ferringer,
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
