MRI and CT of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma in Children: A Report From Children s Oncology Group Study ARST0332
|
|
|
- Aldous Rolf Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
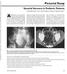
1 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Pediatric Imaging Original Research Kiran Sargar 1,2 Simon. Kao 1 Sheri L. Spunt 3 Douglas S. Hawkins 4 David M. Parham 5 heryl offin 6 M. eth Mcarville 7 Sargar K, Kao S, Spunt SL, et al. Keywords: RST0332, hildren s Oncology Group, T, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, MRI, pediatrics DOI: /JR Received October 5, 2014; accepted after revision January 22, This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants and U ). 1 Department of Radiology, University of Iowa ollege of Medicine, 200 Hawkins Dr, Iowa ity, I ddress correspondence to S.. Kao (simon-kao@uiowa.edu). 2 Present address: Department of Radiology, Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, St Louis, MO. 3 Department of Pediatrics, Stanford University School of Medicine, Palo lto,. 4 Department of Pediatrics, Seattle hildren s Hospital, Seattle, W. 5 Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, hildren s Hospital of Los ngeles and University of Southern alifornia, Keck School of Medicine, Los ngeles,. 6 Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN. 7 Department of Radiological Sciences, St. Jude hildren s Research Hospital, Memphis, TN. JR 2015; 205: X/15/ merican Roentgen Ray Society MRI and T of Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcoma in hildren: Report From hildren s Oncology Group Study RST0332 OJETIVE. The purpose of this article is to determine the MRI and T features of lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma in children. MTERILS ND METHODS. We retrospectively analyzed images of 11 pediatric patients with low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma from a phase 3 clinical trial of nonrhabdomyosarcoma soft-tissue sarcoma (hildren s Oncology Group Protocol RST0332). MRI and T were performed in 10 and four patients, respectively. Location, size, margin, and composition on imaging were correlated with pathologic findings. RESULTS. Tumors were located in the extremities in nine patients, and one tumor each was located in the tongue and lung. Tumors were deep in seven patients and superficial in four patients. ll tumors were well defined, solitary, and nonmetastatic at presentation. Tumors were complex solid-cystic in eight patients and completely solid in three patients. On T1-weighted images, all tumors had at least some areas hypointense to muscles, and six had a split-fat sign. On STIR or T2-weighted images, eight tumors had areas hypointense to adjacent muscle, and eight tumors had fluid signal intensity. On contrast-enhanced MRI studies, eight tumors had thick enhancing internal septations, and three had peripheral nodular gyriform enhancement. When we correlated imaging to pathologic findings, areas with hypointense signal intensity on both T1- and T2-weighted images were likely related to fibrous component; areas with fluid signal intensity on T2-weighted images were likely related to myxoid component. On T, all four tumors were hypodense to muscle, and one tumor showed punctate calcific foci. ONLUSION. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma is hypodense to muscle on T. MRI may identify both fibrous and myxoid components of this rare pediatric soft-tissue sarcoma. L ow-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma is a rare soft-tissue sarcoma characterized by a relatively benign histologic profile, with fibrous paucicellular and myxoid hypervascular zones [1]. In the short term (< 5 years), low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma has an indolent clinical behavior but also a tendency for late local recurrence and metastasis [2]. It is more common in young and middle-aged adults but has increasingly been recognized in the pediatric population. lthough in most cases it is localized to deep soft tissues of the extremities, these tumors can be seen in superficial subcutaneous tissues. The latter location is more commonly seen in children than in adults. On cytogenetic studies, these tumors have a t(7;16)(q34;p11) translocation [1]. ross-sectional imaging, such as T and MRI, has played a crucial role in the detection, evaluation of local extent, and staging of soft-tissue tumors. The hildren s Oncology Group recently completed a 5-year multiinstitutional trial (protocol RST0332) to investigate a riskbased strategy for therapy of patients younger than 30 years with nonrhabdomyosarcoma soft-tissue sarcoma. Of the 551 eligible patients enrolled, 18 received a histologic diagnosis of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. ecause of the rarity of this tumor, there is a paucity of literature describing its imaging features. The purpose of our study was to determine whether the T and MRI features of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma may suggest this diagnosis before biopsy in pediatric patients. Materials and Methods The study cohort comprised patients with low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma who were enrolled in the hildren s Oncology Group protocol RST0332 between February 2007 and February The protocol was HIP compliant and approved by institutional review boards at each par- 414 JR:205, ugust 2015
2 TLE 1: ombined MRI and T Features in 11 Pediatric Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcomas Features Value Shape, round to oval 11 (100) Morphologic features omplex solid cystic 8 (73) Solid 3 (27) Location Intramuscular 6 (55) Subcutaneous 4 (36) Deep (lung) 1 (9) Lower extremity 5 (45) Upper extremity 4 (36) Tongue muscles 1 (9) Diameter (cm), median (range) 6 (2 12) Margin ircumferentially well defined 9 (82) Relatively well defined 1 (9) Infiltrating 1 (9) Involvement of adjacent structures one 1 (9) Skin 1 (9) Vessels 2 (18) Note Except where noted otherwise, data are number (%) of fibromyxoid sarcomas. ticipating institution. ll subjects or their guardians signed informed consent or assent as appropriate. ll tumors were reviewed centrally by two expert pediatric pathologists to confirm the histologic subtypes of nonrhabdomyosarcoma soft-tissue sarcoma. Of the 18 subjects with low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, 11 underwent MRI or T of the primary tumor before tumor resection. T and MR images of these 11 subjects were reviewed retrospectively by a study radiologist central reviewer and a pediatric radiology fellow. MR images were obtained in 10 subjects (Table 1), three of whom also underwent contrast-enhanced MDT with coronal and sagittal reconstructions. One subject underwent only T of the primary tumor. Demographics, clinical data, and pathology reports were reviewed, and pathologic findings were correlated with imaging findings to the extent possible. linical and imaging evidence for local recurrence and metastasis were sought during a 5-year planned follow-up period. MRI The standard MRI protocol included unenhanced T1-weighted and fat-saturated T2-weighted or STIR axial and coronal, unenhanced T1-weighted fat-saturated axial, and contrast-enhanced fatsaturated T1-weighted axial and coronal sequences. dditional sagittal images were acquired in some subjects to better show the tumor extent. On MR images, the radiologist reviewers assessed the anatomic location, size, shape, margin, homogeneity, and signal intensity patterns on T1- weighted and STIR or T2-weighted fat-saturated sequences; contrast enhancement patterns on T1-weighted fat-saturated sequences; and peritumoral edema, hemorrhage, necrosis, and depth of involvement (skin, muscle, bone, joint, and neurovascular invasion). Tumor dimensions were measured in the cephalocaudal, transverse, and anteroposterior planes. Four terms were used to visually classify the tumor margin: circumferentially well-defined when we were able to appreciate well-demarcated margins in over 90% of the tumor surface, relatively well-defined when well-demarcated margins were seen in 70 90% of the tumor surface, discrete mass with poorly defined margins when well-demarcated margins were seen in less than 70% of the tumor surface and there was no infiltration of surrounding structures, and infiltrating margins when tumor was clearly seen invading adjacent structures. Tumor signal homogeneity was classified subjectively on both T1- and T2-weighted images as homogenous when more than 95% of the tumor volume showed uniform signal intensity, as mildly inhomogeneous when 75 95% of the tumor volume showed uniform signal intensity, as moderately inhomogeneous when 50 75% of the tumor volume showed uniform signal intensity, and as complex when less than 50% of the tumor volume showed uniform signal intensity. On T1-weighted MR images, we classified signal intensity of tumor components into four categories: hypointense in areas where tumor had Fig year-old boy with low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma arising in lung. xial T image of chest with lung window shows tumor that is hypodense (36 HU) compared with muscles (63 HU) on mediastinal window (not included) in anterior segment of left lower lobe. signal intensity less than that of adjacent muscles, isointense in areas with signal intensity the same as that of muscles, areas with signal intensity brighter than that of muscles but less bright than that of subcutaneous fat, and areas with signal intensity equal to that of fat. On STIR or T2-weighted fat-saturated images, we classified the signal intensity of tumor components into four categories: hypointense in areas with signal intensity less than that of adjacent muscles, isointense in areas with signal intensity the same as that of muscles, areas brighter than muscles but less bright than fluid, and areas with signal intensity as bright as that of fluid. cystic mass was defined as having a homogeneous hypointense signal on T1-weighted images and homogeneous hyperintense signal, similar to that of fluid, on T2-weighted images, with no enhancing component on contrast-enhanced images. complex cystic mass was defined as having predominantly cystic signal with some enhancing solid components or internal septations. solid mass was defined as having inhomogeneous (predominantly iso- to hypointense) signals on T1-weighted images and inhomogeneous (iso- to hyperintense, but less than fluid) signal on T2-weighted images with enhancement on contrast-enhanced images. We also evaluated contrast enhancement in tumors by comparing unenhanced and contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fat-saturated images. Tumors with peritumoral regions having T1-hypointense and T2-hyperintense signals were designated to exhibit peritumoral edema. reas with T1-hyperintense signal and T2-hyperintense or T2-hypointense signal that did not suppress on fat-saturated images were characterized as internal hemorrhage. Nonenhancing areas within the tumor were characterized as necrosis. We also evaluated invasion of surrounding structures, such as muscles, vessels, bones, nerves, and joints. JR:205, ugust
3 TLE 2: MRI Features of 10 Pediatric Low-Grade Fibromyxoid Sarcomas Imaging Sequence, Feature No. (%) of Fibromyxoid Sarcomas Unenhanced T1-weighted sequence, predominant signal intensity Hypointense 3 (30) Isointense 6 (60) Hyperintense 1 (10) STIR and T2-weighted fat-saturated sequence, predominant signal intensity Hypointense 1 (10) Isointense 5 (50) Hyperintense 4 (40) ontrast enhanced Degree of enhancement Minimal 3 (30) Moderate 7 (70) Intense 0 Pattern of enhancement Homogeneous 0 Inhomogeneous 7 (70) Peripheral nodular gyriform 3 (30) T The anatomic location, size, shape, margin, homogeneity, and density of tumors were assessed on contrast-enhanced T images. We categorized density of the tumor as hypodense (less than that of adjacent muscle), isodense (equal to that of muscle), and hyperdense (more than that of adjacent muscle). reas of calcification and hyperdense hemorrhage within the tumor and the presence and pattern of contrast enhancement were recorded. Pathologic Review In this study, the gross specimens were not available for radiologic-pathologic correlation. ll tumors were, however, reviewed centrally by two expert pediatric pathologists to confirm the histologic subtypes of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. The gross and microscopic pathologic features of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma were obtained from reports issued by local institutions. Results Subjects ranged in age from 3 to 18 years with a median of 13 years. The male-to-female ratio was 2.6:1. ll 11 low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas were nonmetastatic at presentation. There was no evidence of local recurrence or metastasis in our subjects during short-term follow-up of years (median, 2.7 years). Table 1 summarizes the combined MRI and T findings. y MRI and T, nine tumors were circumferentially well defined (> 90% of the tumor surface). Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma was located in the lower extremity in five patients, the D Fig year-old girl with left tongue mass., xial T1-weighted image of neck shows predominantly hypointense mass (arrow) involving tongue muscles on left side., xial T2-weighted image shows mass with predominantly dark signal intensity (arrow), most likely corresponding to fibrous component., xial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fat-saturated image shows inhomogeneous peripheral nodular gyriform enhancement of mass (arrow). D, xial contrast-enhanced T image of face shows mild enhancement of hypodense mass in muscles of tongue on left side. Note tiny calcific focus (arrow) along medial aspect of mass. upper extremity in four patients, and in the tongue muscles and the lung in one patient each. There was involvement of the pelvic region in two of the three lower extremity tumors. Of the four upper extremity tumors, three were located in the region of the shoulder girdle and one was in the upper arm. Two unusual locations were the lung (Fig. 1) and tongue muscles (Fig. 2). On MRI and T, 416 JR:205, ugust 2015
4 Fig. 3 3-year-old boy with left shoulder tumor. Sagittal contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fatsaturated image of left shoulder reveals moderate peripheral nodular gyriform enhancement of tumor with nonenhancing central component, mostly from fibrosis (hypointense on T2-weighted image, not shown). Notice that mass (arrow) is invading scapula, with extension anterior to scapula. the maximum diameter of tumor was 2 12 cm with a median of 6 cm. In nine low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas, the margin was circumferentially well defined (well-demarcated margins in > 90% of the tumor surface), and one of the tumors was relatively well defined (well-demarcated margins in 70 90% of the tumor surface). Infiltrating margins were seen in one of the tumors involving muscles of the shoulder (Fig. 3). MRI (10 Subjects) None of the low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas appeared uniformly homogeneous on T1- and T2-weighted images. Two tumors showed mild inhomogeneity, four showed moderate inhomogeneity, and four had a complex appearance. On T1-weighted images, all low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas had at least some areas with signal intensity less than that of adjacent muscle and equal to that of cortical bone. In six tumors (Table 2), the predominant signal intensity was isointense to muscle (Fig. 4). In three tumors, the predominant signal intensity was hypointense to muscles but more than that of the cortical bone (Fig. 5). One of the tumors showed predominant signal intensity greater than that of muscle but less than that of the subcutaneous fat. Five of the six tumors located in the intramuscular compartment of the extremities showed a splitfat sign (Fig. 5). None of the tumors showed hemorrhagic components. On STIR or T2-weighted fat-saturated images, eight low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas had at least some hypointense areas (Table 2). Eight tumors had areas of fluid signal intensity. Four tumors had predominant signal intensity equal to that of fluid (Fig. 6). In five tumors, the predominant signal intensity was equal to that of muscle (Fig. 5). Of the three completely solid tumors, two were isointense and one was hypointense to muscle on fluidsensitive sequences. Peritumoral edema (Fig. 5) was present in seven cases. Thick (> 3 mm) internal septations were seen in four tumors. On contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fatsaturated images, all 10 low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas revealed mild-to-moderate inhomogeneous contrast enhancement. Thick enhancing internal septations were seen in four sarcomas. reas with T1 and T2 hypointensity and areas with fluid signal on STIR or fat-saturated T2-weighted images showed variable enhancement. In three tumors with a completely solid appearance, peripheral nodular gyriform enhancement was seen (Figs. 2 and 3). one involvement of the scapula was seen in association with a tumor arising from the infraspinatus muscle (Fig. 3). Skin involvement was seen in one tumor in the inguinal-scrotal region. Vascular encasement involving small branches of major extremity vessels was seen in two tumors located in the deep muscular compartment. None of the tumors showed joint or obvious nerve encasement. T (Four Patients) On contrast-enhanced T, all four lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcomas were hypodense to adjacent muscles. Tumors were located in the subcutaneous plane in two subjects, in the lung parenchyma in one patient, and in the tongue muscles in one patient. ll four tumors showed mild inhomogeneous contrast enhancement (Figs. 2 and 7). The tumor involving the tongue had internal punctate calcific foci (Fig. 2). Pathologic Review (11 Patients) ecause gross tumor specimens were not available for central pathologic review, pathology reports from the local institutions of the excised tumors were reviewed. ll tumors were described as well circumscribed, round to oval, and gray-white with a whorled appearance without hemorrhage. The maximum diameter of tumor varied by report, from 2 to 12 cm, with a median of 6 cm. On microscopy, tumors showed two distinct zones a paucicellular fibrous zone and a hypervascu- Fig year-old boy with right elbow tumor., xial T1-weighted image of right elbow shows slightly hyperintense mass in biceps muscle with hypointense areas (arrow) along lateral aspect of mass., xial T2-weighted fat-saturated image reveals solid predominantly T2-hyperintense mass in biceps muscle with few internal hypointense areas (arrow)., xial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fat-saturated image shows moderate inhomogeneous enhancement of tumor with less enhancement of T2-hypointense area shown in panel, consistent with fibrosis. JR:205, ugust
5 Fig year-old girl with thigh tumor., oronal T1-weighted image of right femur shows predominantly hypointense solid tumor involving right iliopsoas muscle. Notice split-fat sign (arrow) along lateral aspect of mass., oronal T2-weighted fat-saturated image of right femur shows that tumor is predominantly hypointense to surrounding muscles. Notice that tumor is abutting right common femoral vessels (arrow). Thin bright rim of peritumoral edema is best seen at superior and inferolateral aspects between inhomogeneous tumor and dark fat., ontrast-enhanced coronal T1-weighted fat-saturated image of right femur shows moderately inhomogeneous peripheral nodular enhancement of tumor. Note that areas that are hypointense on T1- and T2-weighted sequences enhance less than other areas, consistent with fibrosis. lar myxoid zone with an abrupt transition between these zones. Some tumors contained hyalinizing spindle cells with giant rosettes. Fascicular and whorled arrangements were noted in all tumors. In most tumors, mitotic figures were less than 10 per 10 high-power fields, and cellular atypia was rare. No areas of necrosis or hemorrhage were identified. This finding was correlated with the lack of high-density hemorrhage on MRI and T. ytogenetic studies were performed in five tumors, all of which showed the characteristic t(7;16)(q34;p11) translocation. The resection margin was negative in all patients, except in one tumor arising from the left shoulder. Discussion Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma was first described in 1987 and was initially thought to exhibit bland histologic features but aggressive clinical behavior. Subsequently, many studies revealed that low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma usually has a relatively benign course and occurs most commonly in young and middleaged adults. n increasing number of cases have been reported in pediatric patients [1, 3]. On histologic analysis, these tumors have a low mitotic rate, two distinct zones (myxoid and fibrous), bland regular spindle cells, and a swirling or whorled pattern [2]. Myxoid zones are typically hypercellular with prominent vascularity, whereas fibrous zones are hypocellular [1, 2]. The transition between myxoid and fibrous zones may be gradual or abrupt [1]. Hyalinized spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes is now considered to be a variant of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma that also shows collagen rosettes [1, 3, 4]. ytogenetic studies show that the t(7;16)(q34;p11) translocation results in a chimeric fusion protein derived from the FUS gene on chromosome 16p11 and the F2H7 gene on 17q33 being seen in both low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma and hyalinized spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes [1]. ll low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas are positive for Muc-4, an immunohistochemical marker that is very sensitive for the diagnosis of this tumor [5]. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas are also positive for vimentin, actins, D 68, and epithelial membrane antigen and negative for D34, keratins, and S-100 protein [1]. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas are commonly located in the lower extremity, shoulder, trunk, inguinal regions, upper extremity, and vulvovaginal regions [1 3]. In our study, most tumors were seen in the lower and upper extremities, including the shoulder. Two unusual locations in our study were in the lung parenchyma and tongue musculature. Lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma is commonly deep and intramuscular in young and middleaged adults. In the pediatric population, a superficial subcutaneous location has been reported to be more common (37%), compared with less than 10% in large series including all ages [1]. In our pediatric cohort, deep intramuscular (6/11 [55%]) and subcutaneous locations (4/11 [36%]) were observed. The reported median size of tumor ranges from 4.2 to 9.4 cm, which is in agreement with a median size of 6 cm seen in our study. On imaging, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas are solitary and well circumscribed at presentation, but they tend to present as multiple infiltrating masses at recurrence [6]. ll of the tumors in our study were solitary at presentation and most were well circumscribed and round to oval in shape. On MRI, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma is inhomogeneous owing to two distinct internal zones: myxoid and fibrous. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma has been reported to show areas of low signal intensity on both T1- and T2-weighted sequences because of 418 JR:205, ugust 2015
6 the fibrous component [7 11]. In our study, most of the tumors had an inhomogeneous appearance on T1- and T2-weighted images. In all tumors, we found internal components that were hypointense to muscle on T1- weighted images. In agreement with prior reports, we found that most T1-hypointense foci (8/10 [80%]) were also hypointense on T2-weighted images, likely corresponding to fibrous tissue. On T, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas have low-attenuation components that are hypodense to the skeletal muscle, likely due to the myxoid component and extracellular matrix [6, 8, 10, 11]. Though calcification has been reported in these tumors, it is not very common [6, 7, 11, 12] and was seen in only one tumor in our study. We observed a complex solid-cystic appearance in most (9/11 [82%]) of the tumors in our study. The complex solid-cystic appearance is probably related to the histologic profile of the tumor, in which myxoid zones appear cystic and fibrous zones appear as solid nodular or septate areas. somewhat similar imaging appearance in the form of intralesional nodules with hyperintense signal had previously been reported in lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma [6]. few tumors in our study (3/11 [27%]) were entirely solid but no tumor was entirely cystic. The split-fat sign on T1-weighted images was seen in 50% (5/10) of our subjects with an intramuscular tumor. None of the prior studies or case reports has reported this finding in low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. However, this sign was seen in three cases on review of the T1-weighted images included in some case reports [12 14]. The split-fat sign (best appreciated on T1-weighted images) represents a rim of fat surrounding a tumor, such as a peripheral nerve sheath tumor, that is located in the intermuscular space. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcomas are considered to be malignant fibroblastic neoplasms. It is not surprising that low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma that occurs in muscles may exhibit this sign. On fluid-sensitive sequences, a distinct gyriform pattern with multiple folded layers of predominantly low-signal-intensity areas mimicking brain gyri was reported in a prior study [6]. We observed a similar gyriform pattern in two tumors that were completely solid. Peritumoral edema was seen on T2-weighted images in 70% (7/10) of our subjects. This imaging feature has not previously been described or seen on images in previous case reports. However, most of the images from prior reports did not include a fat-suppressed T2-weighted or STIR sequence. In our study, vascular encasement of small branches of major extremity vessels was seen in two subjects, and bone and skin invasion were observed in two different subjects. Though areas of internal hemorrhage Fig year-old boy with right groin mass., xial T1-weighted image of pelvis shows hypointense mass (arrow) in subcutaneous plane of right groin., On axial T2-weighted fat saturation image, mass shows almost entirely fluid signal intensity. Notice T2-hypointense nodular component (arrow) along posterior margin of mass., xial contrast-enhanced T1-weighted fat-saturated image shows peripheral enhancement with nonenhancing central component in this complex cystic mass. Notice nodular enhancement (arrow) along posterior margin of mass. Synovial sarcoma should be considered in differential diagnosis of soft-tissue tumors with cystic appearance. have been reported in low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma [14], no tumor in our study showed imaging evidence of hemorrhage. On T1-weighted fat-saturated contrast-enhanced studies, low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma has been reported to show inhomogeneous contrast enhancement, reflecting the two distinct internal zones with varying vascularity [6, 13]. ll tumors in our study showed inhomogeneous contrast enhancement. Tumors with a complex solid-cystic appearance showed either enhancing solid components Fig year-old boy with left shoulder tumor. oronal contrast-enhanced T scan reveals slightly hypodense mass in left supraclavicular region with thin peripheral rim (arrow) that is isodense to surrounding muscles. Histologic examination shows solid mass without cystic or necrotic changes. JR:205, ugust
7 or enhancing thick (> 3 mm) internal septations. s on the fluid-sensitive sequences, the two tumors that were entirely solid showed a gyriform enhancement pattern on contrastenhanced T1-weighted fat-saturated images. reas with hypointense signal on T1- and T2-weighted images showed variable contrast enhancement, from minimal to intense. This finding may be a reflection of the degree of fibroblastic activity versus frank fibrosis in these tumors, similar to that observed in desmoid tumors [15]. reas with fluid signal intensity on STIR or T2-weighted images showed variable enhancement, likely related to the degree of vascularity of the myxoid component of the tumor. Differential diagnoses for low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma of the extremity and trunk in the pediatric population include rhabdomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, Ewing sarcoma family tumors, nerve sheath tumors, and solitary fibrous tumor. part from some cystic synovial sarcomas, these tumors usually appear solid on imaging and show inhomogeneous contrast enhancement. Rhabdomyosarcoma, myxoid neurofibroma, primitive neuroectodermal tumors, and synovial sarcoma can be distinguished from low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma by the absence of fibrous tissue and, therefore, lack of T1- and T2-hypointense areas. Solitary fibrous tumors can mimic lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma, although they lack the T2-bright myxoid component. Studies with short-term follow-up have shown that, if widely excised, these tumors have relatively low local recurrence (9%) and metastatic (6%) rates. These studies also report that the local recurrence rate of superficial tumors is the same as that of deep tumors, although metastases occurred less frequently with superficial tumors [1, 3]. In contrast, prior studies with long-term follow-up have shown that low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma has high local recurrence (68%) and metastatic (41%) rates [2]. ecause these tumors have an indolent nature, they may recur up to 15 years after completion of therapy, with a median time to recurrence of about 3.5 years [2]. The lung, pleura, and chest wall are the most commonly reported sites of metastasis, followed by bone and liver [2]. Neither local recurrence nor metastasis was found in our subjects during short-term follow-up of years (median, 2.7 years). ecause low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma may recur many years after treatment, long-term follow-up is recommended. Limitations of our study included a relatively small sample despite a 5-year data collection period from all hildren s Oncology Group institutions, underscoring the rarity of this cancer in children and young adults. ecause of the nature of data collection for this study, an exact spatial correlation between radiologic and gross pathologic appearances of the tumor was not possible. However, local pathologic descriptions of the excised tumors provided valuable information regarding tumor composition, which could be correlated to imaging features. nother study limitation is the relatively short-term follow-up of our subjects. onclusion Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma is a rare soft-tissue neoplasm that is increasingly being recognized in pediatric populations. MRI features of a complex solid-cystic tumor with fibrotic tissue that appears hypointense to muscle on T1- and T2-weighted images and exhibits a variable degree of enhancement can be very helpful in suggesting this diagnosis before biopsy. Solid-cystic lesions show enhancement of solid components or thick internal septations. Tumors that are predominantly solid may show peripheral nodular gyriform enhancement. reas with fluid signal intensity on STIR or T2-weighted images may show variable enhancement likely related to the vascularized myxoid component of the tumor. In our study, all tumors underwent complete surgical resection with negative margins (except in one) and showed no evidence of local recurrence or metastasis on short-term follow-up. References 1. illings SD, Giblen G, Fanburg-Smith J. Superficial low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (Evans tumor): a clinicopathologic analysis of 19 cases with a unique observation in the pediatric population. m J Surg Pathol 2005; 29: Evans HL. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: a clinicopathologic study of 33 cases with long-term follow-up. m J Surg Pathol 2011; 35: Folpe L, Lane KL, Paull G, Weiss SW. Lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma and hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes: a clinicopathologic study of 73 cases supporting their identity and assessing the impact of high-grade areas. m J Surg Pathol 2000; 24: Guillou L, enhattar J, Gengler, et al. Translocation-positive low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: clinicopathologic and molecular analysis of a series expanding the morphologic spectrum and suggesting potential relationship to sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma a study from the French Sarcoma Group. m J Surg Pathol 2007; 31: Doyle L, Moller E, Dal in P, Fletcher D, Mertens F, Hornick JL. MU4 is a highly sensitive and specific marker for low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. m J Surg Pathol 2011; 35: Hwang S, Kelliher E, Hameed M. Imaging features of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (Evans tumor). Skeletal Radiol 2012; 41: rnaoutoglou, Lykissas MG, Gelalis ID, et al. Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: a case report and review of the literature. J Orthop Surg Res 2010; 5:49 8. Kim SY, Kim MY, Hwang YJ, et al. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: T, sonography, and MR findings in 3 cases. J Thorac Imaging 2005; 20: Lee J, Park WS, Jin JM, Ha W, Lee SH. Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma in thigh. lin Orthop Surg 2009; 1: Lin J, Wang J, Yu LJ, Ying XL. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: a clinicopathological analysis of 9 cases [in hinese]. Zhonghua ing Li Xue Za Zhi 2009; 38: Maeda E, Ohta S, Watadani T, Goto, Nakajima, Ohtomo K. Imaging findings of thoracic lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma: report of three cases. Jpn J Radiol 2009; 27: Torriani M, Etchebehere M, mstalden EM, Ouellette H. Magnetic resonance imaging of lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma. linics (Sao Paulo) 2006; 61: Miyake M, Tateishi U, Maeda T, et al. T and MRI features of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma in the shoulder of a pediatric patient. Radiat Med 2006; 24: Kim SK, Jee WH, Lee W, hung YG. Haemorrhagic low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: MR findings in two young women. r J Radiol 2011; 84:e146 e Mcarville M, Hoffer F, delman S, Khoury JD, Li, Skapek SX. MRI and biologic behavior of desmoid tumors in children. JR 2007; 189: JR:205, ugust 2015
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
Evening Specialty Conference Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology. Diagnostic pitfalls in bone and soft tissue pathology
 Evening Specialty Conference Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology. Case 1 Elizabeth G Demicco, MD, PhD Mount Sinai Hospital, New York Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners
Evening Specialty Conference Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology. Case 1 Elizabeth G Demicco, MD, PhD Mount Sinai Hospital, New York Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners
Newer soft tissue entities
 Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
MRI and Biologic Behavior of Desmoid Tumors in Children
 MRI of Desmoid s Pediatric Imaging Original Research M. Beth McCarville 1,2 Fredric A. Hoffer 1,2 C. Scott Adelman 1 Joseph D. Khoury 3 Chenghong Li 4 Stephen X. Skapek 5,6 McCarville MB, Hoffer FA, Adelman
MRI of Desmoid s Pediatric Imaging Original Research M. Beth McCarville 1,2 Fredric A. Hoffer 1,2 C. Scott Adelman 1 Joseph D. Khoury 3 Chenghong Li 4 Stephen X. Skapek 5,6 McCarville MB, Hoffer FA, Adelman
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis
 Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts
 Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided Core Needle Biopsy: A Case Report 1
 Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided ore Needle iopsy: ase Report 1 Sang Kwon Lee, M.D., Sun Young Kwon, M.D. 2 We report here on a case of nodular fasciitis (NF) that was diagnosed by
Nodular Fasciitis of the Face Diagnosed by US-Guided ore Needle iopsy: ase Report 1 Sang Kwon Lee, M.D., Sun Young Kwon, M.D. 2 We report here on a case of nodular fasciitis (NF) that was diagnosed by
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors
 The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
MRI Features in the Differentiation of Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors and Neurofibromas
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Wasa et al. MRI of Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors and Neurofibromas Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Junji Wasa 1 Yoshihiro Nishida 1 Satoshi Tsukushi
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Wasa et al. MRI of Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors and Neurofibromas Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Junji Wasa 1 Yoshihiro Nishida 1 Satoshi Tsukushi
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling
 Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 5 Number 2 MRI Of Locally Recurrent Soft Tissue Tumors Of The Musculoskeletal System C Costelloe, A Yasko, W Murphy, R Kumar, V Lewis, P Lin, R Stafford,
Musculoskeletal Sarcomas
 Musculoskeletal Sarcomas Robert C. Orth, M.D., Ph.D. Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 9:01:18 AM No disclosures Page 1 xxx00.#####.ppt
Musculoskeletal Sarcomas Robert C. Orth, M.D., Ph.D. Edward B. Singleton Department of Pediatric Radiology Texas Children s Hospital Page 0 xxx00.#####.ppt 9/23/2012 9:01:18 AM No disclosures Page 1 xxx00.#####.ppt
Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation
 246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
246) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 113 (2012) No. 3, p. 246 250 Solitary Fibrous Tumor of the Kidney with Massive Retroperitoneal Recurrence. A Case Presentation Sfoungaristos S., Papatheodorou M., Kavouras
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hun et al. MRI of Skeletal Muscle Lymphoma Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hang Woo hun 1 Won-Hee Jee 1 Hye Jung Park 1 Yeo Joo Kim 1 Jeong-Mi Park 1
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hun et al. MRI of Skeletal Muscle Lymphoma Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research hang Woo hun 1 Won-Hee Jee 1 Hye Jung Park 1 Yeo Joo Kim 1 Jeong-Mi Park 1
Fun with Fat. General Rules. Case
 Fun with Fat General Rules Imaging: location (deep vs. superficial) Superficial lesions are seldom liposarcomas Deep lesions may be benign or malignant Myxoid stroma is common in benign and malignant lesions
Fun with Fat General Rules Imaging: location (deep vs. superficial) Superficial lesions are seldom liposarcomas Deep lesions may be benign or malignant Myxoid stroma is common in benign and malignant lesions
Case 2. Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset
 Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Original Report. The Reverse Segond Fracture: Association with a Tear of the Posterior Cruciate Ligament and Medial Meniscus
 Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Eva M. Escobedo 1 William J. Mills 2 John. Hunter 1 Received July 10, 2001; accepted after revision October 1, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, University of Washington Harborview Medical enter, 325 Ninth
Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee
 Soft Tissue Sarcoma Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Soft Tissue Sarcoma Collective term for an unusual and diverse
Soft Tissue Sarcoma Presley Regional Trauma Center Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, Tennessee Soft Tissue Sarcoma Collective term for an unusual and diverse
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis
 Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
Case 9087 Retropharyngeal nodular fasciitis Santiago I 1; Cavalheiro F 2; Noruégas MJ 3; Sanches MC3 1 Hospital Infante D. Pedro, Aveiro, Portugal 2 Hospitais da Universidade de Coimbra, Portugal 3 Hospital
A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 4/2000 A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura ALİ KEMAL UZUNLAR 1, MEHMET YALDIZ 1, İBRAHİM H. ÖZERCAN 2, FAHRİ YILMAZ 1, AKIN E. BALCI 3 1
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol.30 / No. 4/2000 A case of giant benign localized fibrous tumor of the pleura ALİ KEMAL UZUNLAR 1, MEHMET YALDIZ 1, İBRAHİM H. ÖZERCAN 2, FAHRİ YILMAZ 1, AKIN E. BALCI 3 1
Imaging Features of Alveolar Soft- Part Sarcoma: A Report From Children s Oncology Group Study ARST0332
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research McCarville et al. Imaging Features of lveolar Soft-Part Sarcoma Pediatric Imaging Original Research M. eth McCarville 1 Sofia Muzzafar 1 Simon C. Kao 2 Cheryl M. Coffin
Pediatric Imaging Original Research McCarville et al. Imaging Features of lveolar Soft-Part Sarcoma Pediatric Imaging Original Research M. eth McCarville 1 Sofia Muzzafar 1 Simon C. Kao 2 Cheryl M. Coffin
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Retroperitoneal Sarcomas - A pictorial review
 Retroperitoneal Sarcomas - A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1409 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Douraghi-Zadeh, K. L. Shahabuddin, R. H. Thomas, E. Moskovic; London/UK Keywords:
Retroperitoneal Sarcomas - A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1409 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Douraghi-Zadeh, K. L. Shahabuddin, R. H. Thomas, E. Moskovic; London/UK Keywords:
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities
 University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
University Journal of Surgery and Surgical Specialities Volume 1 Issue 1 2015 EXTRA SKELETAL MESENCHYMAL CHONDROSARCOMA :A CASE REPORT Rajaraman R Subbiah S Navin Naushad Kilpaulk Medical College Abstract:
Pediatric Soft-Tissue Sarcomas. Beth McCarville, MD St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, Tn
 Pediatric Soft-Tissue Sarcomas Beth McCarville, MD St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, Tn Overview Histologic classifications Characteristic imaging features Helpful clinical characteristics
Pediatric Soft-Tissue Sarcomas Beth McCarville, MD St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, Tn Overview Histologic classifications Characteristic imaging features Helpful clinical characteristics
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 3/ Issue 46/Sep 22, 2014 Page 11296
 CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
CT SPECTRUM OF GIANT RETROPERITONEAL LIPOSARCOMAS WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION Shashikumar M. R 1, Rajendra Kumar N. L 2, C. P. Nanjaraj 3, Nishanth R. K 4, Vishwanath Joshi 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
CASE REPORT PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE.
 PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
PLEOMORPHIC LIPOSARCOMA OF PECTORALIS MAJOR MUSCLE IN ELDERLY MAN- CASE REPORT & REVIEW OF LITERATURE. M. Madan 1, K. Nischal 2, Sharan Basavaraj. C. J 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: M. Madan, K. Nischal,
Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1
 Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1 Received July 1, 2002; accepted after revision November
Takayuki Ohguri 1 Takatoshi Aoki 1 Masanori Hisaoka 2 Hideyuki Watanabe 1 Katsumi Nakamura 1 Hiroshi Hashimoto 2 Toshitaka Nakamura 3 Hajime Nakata 1 Received July 1, 2002; accepted after revision November
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Intramuscular Myxoma: Characteristic MR Imaging Features
 Laura W. ancroft 1 Mark J. Kransdorf 1 David M. Menke 2 Mary I. O Connor 3 William C. Foster 4 Received September 17, 2001; accepted after revision October 30, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
Laura W. ancroft 1 Mark J. Kransdorf 1 David M. Menke 2 Mary I. O Connor 3 William C. Foster 4 Received September 17, 2001; accepted after revision October 30, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic,
M. Beth McCarville 1,2, Sheri L. Spunt 3,4, Stephen X. Skapek 3,4, Alberto S. Pappo 3 5
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.194.244 on 12/04/17 from IP address 37.44.194.244. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Synovial Sarcoma in Pediatric Patients M. eth McCarville
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.194.244 on 12/04/17 from IP address 37.44.194.244. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Synovial Sarcoma in Pediatric Patients M. eth McCarville
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
MR Imaging of Fibroma of the Tendon Sheath. of fibroma of the tendon sheath is
 Michael G. Fox 1,2 Mark J. Kransdorf 1,3 Laura W. ancroft 1 Jeffrey J. Peterson 1 Donald J. Flemming 4,5 Received ugust 9, 2002; accepted after revision October 24, 2002. The opinions and assertions contained
Michael G. Fox 1,2 Mark J. Kransdorf 1,3 Laura W. ancroft 1 Jeffrey J. Peterson 1 Donald J. Flemming 4,5 Received ugust 9, 2002; accepted after revision October 24, 2002. The opinions and assertions contained
Brief History. Identification : Past History : HTN without regular treatment.
 Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Brief History Identification : Name : 陳 x - Admission : 94/10/06 Gender : male Age : 75 y/o Chief Complaint : Urinary difficulty for months. Past History : HTN without regular treatment. Brief History
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Spectrum of MRI Findings of Synovial Sarcoma
 Spectrum of MRI Findings of Synovial Sarcoma Poster No.: C-1523 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Molina, J. Llauger Rosselló, J. Palmer Sancho, G. M. 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 Santandreu,
Spectrum of MRI Findings of Synovial Sarcoma Poster No.: C-1523 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Molina, J. Llauger Rosselló, J. Palmer Sancho, G. M. 1 1 2 1 3 1 1 Santandreu,
5/10. Pathology Soft tissue tumors. Farah Bhani. Mohammed Alorjani
 5/10 Pathology Soft tissue tumors Mohammed Alorjani Farah Bhani Slides are included in this sheet. Objectives: Soft tissue tumors 1. Describe soft tissue tumors. 2. Understand the classification of soft
5/10 Pathology Soft tissue tumors Mohammed Alorjani Farah Bhani Slides are included in this sheet. Objectives: Soft tissue tumors 1. Describe soft tissue tumors. 2. Understand the classification of soft
Special slide seminar
 Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
CONSULTATION DURING SURGERY / NOT A FINAL DIAGNOSIS. FROZEN SECTION DIAGNOSIS: - A. High grade sarcoma. Wait for paraffin sections results.
 Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
Pathology Report Date: 3/5/02 A, B. Biopsy right distal femur- high grade spindle cell sarcoma Immunohistochemistry studies are pending to further classify the nature of the tumor. CONSULTATION DURING
Mark D. Murphey, MD, FACR
 Fundamental Concepts of Musculoskeletal Neoplasm: CT and MRI Mark D. Murphey, MD, FACR Important Features in Evaluation of Musculoskeletal Masses Differential diagnosis Preoperative assessment and staging
Fundamental Concepts of Musculoskeletal Neoplasm: CT and MRI Mark D. Murphey, MD, FACR Important Features in Evaluation of Musculoskeletal Masses Differential diagnosis Preoperative assessment and staging
Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma of the Knee: a Case Report with Radiographic and MRI Finding
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:259-263 Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma of the Knee: a Case Report with Radiographic and MRI Finding Seung Hyun Lee 1,2, In Sook Lee 1,2, You Seon Song 1,2,
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:259-263 Calcifying Aponeurotic Fibroma of the Knee: a Case Report with Radiographic and MRI Finding Seung Hyun Lee 1,2, In Sook Lee 1,2, You Seon Song 1,2,
Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON
 Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Presentation outline Background and epidemiology of sarcomas Sarcoma classification Sarcoma
Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Presentation outline Background and epidemiology of sarcomas Sarcoma classification Sarcoma
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
Using T2-Weighted Sequences to More Accurately Characterize Breast Masses Seen on MRI
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Ultrasound Evaluation of Costochondral Abnormalities in Children Presenting With Anterior Chest Wall Mass
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Supakul and Karmazyn Ultrasound of ostochondral bnormalities Pediatric Imaging Original Research Nucharin Supakul 1 oaz Karmazyn Supakul N, Karmazyn Keywords: anterior
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Supakul and Karmazyn Ultrasound of ostochondral bnormalities Pediatric Imaging Original Research Nucharin Supakul 1 oaz Karmazyn Supakul N, Karmazyn Keywords: anterior
Tumors of Adipose Tissue Tumors Epidemiology Clinical Features. Morphology. Mature Adipocytes Separated by delicate fibrous septa
 Tumors of Adipose Tissue Lipoma Liposarcoma Most commonly happens in female The most common soft tissue tumor o Originates from matured Adipocytes Most commonly happes at the 4 th and 5 th decade of life
Tumors of Adipose Tissue Lipoma Liposarcoma Most commonly happens in female The most common soft tissue tumor o Originates from matured Adipocytes Most commonly happes at the 4 th and 5 th decade of life
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: Available online at: Case Study
 International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
CTA/MRA of Pediatric Hepatic Masses Radiology-Pathology Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº70, pág. 41-50, Abr.-Jun., 2006 CTA/MRA of Pediatric Hepatic Masses Radiology-Pathology Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº70, pág. 41-50, Abr.-Jun., 2006 CTA/MRA of Pediatric Hepatic Masses Radiology-Pathology Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Normal Sonographic Anatomy
 hapter 2:The Liver DUNSTAN ABRAHAM Normal Sonographic Anatomy Homogeneous, echogenic texture (Figure 2-1) Measures approximately 15 cm in length and 10 12.5 cm anterior to posterior; measurement taken
hapter 2:The Liver DUNSTAN ABRAHAM Normal Sonographic Anatomy Homogeneous, echogenic texture (Figure 2-1) Measures approximately 15 cm in length and 10 12.5 cm anterior to posterior; measurement taken
MRI IN THE CHARACTERIZATION OF SEMINOMATOUS AND NONSEMINOMATOUS GERM CELL TUMORS OF THE TESTIS
 MRI IN THE CHARACTERIZATION OF SEMINOMATOUS AND NONSEMINOMATOUS GERM CELL TUMORS OF THE TESTIS Ambesh Deshar *, Gyanendra KC and Zhang Lopsang *Department of Medical Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, First
MRI IN THE CHARACTERIZATION OF SEMINOMATOUS AND NONSEMINOMATOUS GERM CELL TUMORS OF THE TESTIS Ambesh Deshar *, Gyanendra KC and Zhang Lopsang *Department of Medical Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, First
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences
 Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Describe the typical imaging findings of GIST at initial
Imaging of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST) Amir Reza Radmard, MD Assistant Professor Shariati hospital Tehran University of Medical Sciences Describe the typical imaging findings of GIST at initial
Sonography of Pediatric Superficial Lumps and Bumps: Illustrative Examples from Head to Toe
 Sonography of Pediatric Superficial Lumps and umps: Illustrative Examples from Head to Toe nmol Gupta ansal, MD Henrietta Kotlus Rosenberg, MD, FCR, FP Mount Sinai Hospital Icahn School of Medicine at
Sonography of Pediatric Superficial Lumps and umps: Illustrative Examples from Head to Toe nmol Gupta ansal, MD Henrietta Kotlus Rosenberg, MD, FCR, FP Mount Sinai Hospital Icahn School of Medicine at
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
A case of pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma
 Jichi Medical University Journal Chio Shuto Kuniyasu Soda Takayoshi Yoshida Fumio Konishi Abstract We report a very rare case of a pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma in the parietal peritoneum of the
Jichi Medical University Journal Chio Shuto Kuniyasu Soda Takayoshi Yoshida Fumio Konishi Abstract We report a very rare case of a pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma in the parietal peritoneum of the
IAEA Pediatric Radiation Oncology Training Dr Laskar Version 1 June SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA (Non Rhabdomyosarcoma)
 SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA (Non Rhabdomyosarcoma) Soft Tissue structures Fat, Muscles, Fibrous tissue, Blood vessels, Supporting cells of peripheral nervous system Soft Tissue Sarcomas:- embryologically arise
SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA (Non Rhabdomyosarcoma) Soft Tissue structures Fat, Muscles, Fibrous tissue, Blood vessels, Supporting cells of peripheral nervous system Soft Tissue Sarcomas:- embryologically arise
The Radiology Assistant : Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions
 Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Bone tumor - ill defined osteolytic tumors and tumor-like lesions Henk Jan van der Woude and Robin Smithuis Radiology department of the Onze Lieve Vrouwe Gasthuis, Amsterdam and the Rijnland hospital,
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Surgery for Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma, Presenting Two Radiologically and Pathologically Distinctive Patterns
 Surgery for Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma, Presenting Two Radiologically and Pathologically Distinctive Patterns Manabu Hoshi 1, Seiichi Matsumoto 1, Jun Manabe 1, Taisuke Tanizawa 1, Toshio Shigemitsu
Surgery for Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma, Presenting Two Radiologically and Pathologically Distinctive Patterns Manabu Hoshi 1, Seiichi Matsumoto 1, Jun Manabe 1, Taisuke Tanizawa 1, Toshio Shigemitsu
Part 1. Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013
 Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology
 Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine 1921 Original
Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine 1921 Original
LAC + USC.
 Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
ACCME/Disclosures ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS. Tumor types with ALK rearrangements. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. Jason L.
 Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Synovial Sarcoma In The Anterior Abdominal Wall Of A Young Nigerian Female: Case Report.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 28 Number 2 Synovial Sarcoma In The Anterior Abdominal Wall Of A Young Nigerian Female: Case Report. M Akunekwe, D Milner, Jr, B Camazine Citation M Akunekwe,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 28 Number 2 Synovial Sarcoma In The Anterior Abdominal Wall Of A Young Nigerian Female: Case Report. M Akunekwe, D Milner, Jr, B Camazine Citation M Akunekwe,
59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain
 December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care
 Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care Introduction Soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity are common and most
Ultrasound screening of soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity - a BSG guide for ultrasonographers and primary care Introduction Soft tissue masses in the trunk and extremity are common and most
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the. Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue
 The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue Tumors of the Head and Neck Joaquín J. García MD and Andrew L. Folpe MD Department
The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue Tumors of the Head and Neck Joaquín J. García MD and Andrew L. Folpe MD Department
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Soft tissue lipomas, lipoma variants and liposarcomas: MRI evaluation and review of literature
 Soft tissue lipomas, lipoma variants and liposarcomas: MRI evaluation and review of literature Poster No.: R-0122 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. A. Tandon,
Soft tissue lipomas, lipoma variants and liposarcomas: MRI evaluation and review of literature Poster No.: R-0122 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. A. Tandon,
Imaging of Liposarcoma: Classification, Patterns of Tumor Recurrence, and Response to Treatment
 Special Article Pictorial Essay O Regan et al. Imaging of Liposarcoma Special Article Pictorial Essay Kevin N. O Regan 1 Jyothi Jagannathan Katherine Krajewski Katherine Zukotynski Frederico Souza Andrew
Special Article Pictorial Essay O Regan et al. Imaging of Liposarcoma Special Article Pictorial Essay Kevin N. O Regan 1 Jyothi Jagannathan Katherine Krajewski Katherine Zukotynski Frederico Souza Andrew
Research Article A Clinicopathological Analysis of Soft Tissue Sarcoma with Telangiectatic Changes
 Sarcoma Volume 2015, Article ID 740571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/740571 Research Article A Clinicopathological Analysis of Soft Tissue Sarcoma with Telangiectatic Changes Hiroshi Kobayashi,
Sarcoma Volume 2015, Article ID 740571, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/740571 Research Article A Clinicopathological Analysis of Soft Tissue Sarcoma with Telangiectatic Changes Hiroshi Kobayashi,
Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh
 Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Upsala J Med sci 109: 261 265, 2004 Scrotum-like protrusion of lipoma arising from the proximal thigh Report of two cases Koshi Hattori, 1 Masahito Hatori, 1 Mika Watanabe, 2 Toshihisa Osanai, 3 Shoichi
Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:51-55 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.1.51 Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:51-55 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.1.51 Extraosseous Ewing s Sarcoma Presented as a Rectal Subepithelial Tumor: Radiological and Pathological Features
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Original Report. Imaging Features of Fat Necrosis. Lai Peng Chan 1 R. Gee 2 Ciaran Keogh 2 Peter L. Munk 2
 Lai Peng Chan 1 R. Gee 2 Ciaran Keogh 2 Peter L. Munk 2 Received September 16, 2002; accepted after revision pril 29, 2003. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Outram Rd.,
Lai Peng Chan 1 R. Gee 2 Ciaran Keogh 2 Peter L. Munk 2 Received September 16, 2002; accepted after revision pril 29, 2003. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Outram Rd.,
Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin
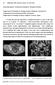 J1 Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin Atsuji Matsuyama 1, Masamichi Nakayama 2, Masanori Hisaoka 1 1 Department of Pathology & Oncology, School of Medicine, University of Occupational & Environmental
J1 Myxoid soft tissue tumor in the loin Atsuji Matsuyama 1, Masamichi Nakayama 2, Masanori Hisaoka 1 1 Department of Pathology & Oncology, School of Medicine, University of Occupational & Environmental
CT Findings of Surgically Resected Pleomorphic Carcinoma of the Lung in 30 Patients
 Kim et al. CT of Pleomorphic Carcinoma of the Lung Chest Imaging Clinical Observations Tae Sung Kim 1 Joungho Han 2 Kyung Soo Lee 1 Yeon Joo Jeong 1 Seo Hyun Kwak 1 Hong Sik Byun 1 Myung Jin Chung 1 Hojoong
Kim et al. CT of Pleomorphic Carcinoma of the Lung Chest Imaging Clinical Observations Tae Sung Kim 1 Joungho Han 2 Kyung Soo Lee 1 Yeon Joo Jeong 1 Seo Hyun Kwak 1 Hong Sik Byun 1 Myung Jin Chung 1 Hojoong
Recurrent Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle: A Case Report
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 211~215, 2012 Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle / 211 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.211 Recurrent Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle:
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 3, pp 211~215, 2012 Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle / 211 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.3.211 Recurrent Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Psoas Muscle:
Radiology-Pathology Conference
 July 31, 2009 Radiology-Pathology Conference Daniel T Ginat, M.D., M.S. Sharlin Johnykutty,, M.D. Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2009 URMC Radiology Page 1 of
July 31, 2009 Radiology-Pathology Conference Daniel T Ginat, M.D., M.S. Sharlin Johnykutty,, M.D. Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2009 URMC Radiology Page 1 of
of Thyroid Lesions Comet Tail Crystals
 2 Ultrasound Features of Thyroid Lesions There are many different features indicating a certain benign or malignant tumor type, but many of these are overlapping signs. Combining several features is considered
2 Ultrasound Features of Thyroid Lesions There are many different features indicating a certain benign or malignant tumor type, but many of these are overlapping signs. Combining several features is considered
Malignant fat-forming solitary fibrous tumor (lipomatous hemangiopericytoma) in the neck: Imaging and histopathological findings of a case
 Malignant fat-forming solitary fibrous tumor (lipomatous hemangiopericytoma) in the neck: Alice Duarte de Carvalho 1, Lucas Faria Abrahão-Machado 2, Cristiano Ribeiro Viana 2, Renato de Castro Capuzzo
Malignant fat-forming solitary fibrous tumor (lipomatous hemangiopericytoma) in the neck: Alice Duarte de Carvalho 1, Lucas Faria Abrahão-Machado 2, Cristiano Ribeiro Viana 2, Renato de Castro Capuzzo
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors
 An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
An Overview of Genital Stromal Tumors By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel School of Medicine
