Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy
|
|
|
- August Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21: , April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: MR findings reported in conjunction with spinal dural arteriovenous fistula (SDAVF) include cord swelling, increased T2 signal within the spinal cord, and parenchymal enhancement, each of which is nonspecific. Enlarged vessels on the cord surface, the most specific MR finding, is noted in only half of SDAVF patients. Nevertheless, we have frequently observed MR peripheral hypointensity of the spinal cord in SDAVF on T2- weighted images, which is not characteristic of nonvascular or nonhemorrhagic causes of myelopathy and which has not been described in association with SDAVF. We hypothesized that peripheral cord hypointensity might reliably suggest the diagnosis of SDAVF or other causes of venous hypertensive myelopathy. METHODS: We reviewed the MR findings in 11 consecutive cases of angiographically confirmed symptomatic SDAVF and in four cases of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula with spinal drainage, a lesion that also causes spinal cord deficits mediated by venous hypertensive myelopathy. RESULTS: In each case, T2 hypointensity involving the cord periphery was present. This sign has not been previously described in association with either SDAVF or other causes of venous hypertensive myelopathy. It appears, however, to be a relatively constant imaging feature of SDAVF. CONCLUSION: In the absence of spinal hemorrhage, T2 hypointensity involving the periphery of the spinal cord suggests venous hypertensive myelopathy as a cause of spinal cord dysfunction. Nonhemorrhagic venous hypertensive myelopathy (VHM) results from a small but clinically significant group of vascular lesions affecting the spinal cord that are characterized by arteriovenous shunting. Most often, VHM results from spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas (SDAVFs), acquired lesions in which arteriovenous shunting of blood from radicular arteries drains into the pial veins of the spinal cord (1 5). The clinical significance of VHM lies in its often confusing clinical presentation, which frequently leads to delays in diagnosis (1). Delayed diagnosis combined with the potential to cause devastating neurologic deficits, which are preventable or reversible if diagnosed and treated early, make prompt recognition of VHM essential to prevent permanent disability (6, 7). Diagnosis of VHM constitutes a significant challenge from a radiologic standpoint. MR imaging March 2, 1999; accepted after revision November 2. From the Department of Radiology, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, 3400 Spruce St, Philadelphia, PA Address reprint requests to Robert W. Hurst MD. American Society of Neuroradiology often permits noninvasive diagnosis of VHM caused by SDAVF and has increased its recognition as an important cause of progressive myelopathy. MR findings previously reported with VHM have included cord enlargement, intramedullary enhancement, engorgement of pial veins, and increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images (8 11). We report an additional imaging sign, T2 hypointensity involving the cord periphery, which appears to be frequently present in VHM and to suggest the diagnosis reliably (Fig 1). We attempted to determine whether this sign was a frequent and reliable finding in SDAVF and how it might reflect the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms of VHM. Methods We reviewed 1.5-T MR images of 11 consecutive patients seen at this institution with angiographically confirmed SDAVF. Each patient had clinically symptomatic VHM resulting from the SDAVF. We then analyzed imaging findings in four consecutive patients who were symptomatic from spinal drainage caused by intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. All patients with an intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula also had 781
2 782 HURST AJNR: 21, April 2000 FIG 1. A, Anteroposterior view of spinal angiogram (injection of intercostal artery) shows filling of an SDAVF with pial drainage (arrowheads; arrow indicates catheter tip). B, Sagittal contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (500/11) MR image shows enhancing enlarged pial vessels as well as intrinsic cord enhancement. C, Axial FSE T2-weighted (4500/90) image shows peripheral hypointensity (closed arrow) with increased central cord signal (open arrows). D, Sagittal FSE T2-weighted (2700/85 eff ) image shows enlarged pial vessels, central increased signal, and peripheral hypointense rim (arrows). angiographic confirmation of the fistula and its drainage into the cervical spinal cord. All patients underwent T1-weighted and fast spin-echo (FSE) T2-weighted imaging. Contrast-enhanced sagittal T1- weighted images were obtained in 10 of 11 patients with SDAVF and in all patients with intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Proton density weighted (2500/20), true T2-weighted (2500/80), and gradient-echo (117/20) images were also obtained in one patient with SDAVF and compared with the FSE images. Images were reviewed by both authors in a nonblinded fashion. Results In the SDAVF patients, we identified the following abnormalities on MR images: cord enlargement in six (55%) of 11; increased central cord signal on T2-weighted images in 10 (100%) of 10; visible surface vessels in 10 (91%) of 11 on T2-weighted images and in seven (70%) of 10 on contrast-enhanced images; and parenchymal cord enhancement in nine (90%) of 10 (Fig 2). In addition, each patient had a rim of hypointense signal involving the periphery of the spinal cord on T2-weighted images. While sometimes subtle on FSE T2-weighted images, the finding became much more conspicuous on true T2-weighted and gradient-echo images. It was identified in patients with SDAVF originating from thoracic, lumbar, and sacral levels (Fig 3). In the patients with intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas, MR findings of cord swelling, increased T2 signal involving the central portion of the spinal cord, and cord parenchymal enhancement were present in each case. Abnormal vessels were visible on FSE T2-weighted images in two FIG 2. A, Anteroposterior view of spinal angiogram shows early filling of pial venous drainage (arrowheads) from spinal DAVF (arrow indicates catheter tip). B, Sagittal FSE T2-weighted (5600/100 eff ) MR image shows enlarged pial vessels, central increased cord signal, and rim of peripheral hypointensity (arrowheads).
3 AJNR: 21, April 2000 VENOUS HYPERTENSIVE MYELOPATHY 783 FIG 3. A, Anteroposterior subtracted view of early arterial-phase injection of the left hypogastric artery shows dural AVF (arrow) with sacral feeding vessels. Arrowheads signify draining veins. B, Sagittal contrast-enhanced T1-weighted (400/14) MR image shows intraparenchymal cord enhancement as well as enhancement of enlarged vessels on the cord surface. C, Sagittal FSE T2-weighted (4400/100 eff ) image shows multiple flow voids on the cord surface, increased signal intensity within the central cord, as well as a rim of peripheral hypointensity (arrowheads). (50%) of the four patients and on contrast-enhanced images in 100% of patients. A rim of decreased signal involving the periphery of the spinal cord was also present on FSE T2-weighted images in each patient (Fig 4). Discussion SDAVFs are the most common type of spinal vascular abnormality. These acquired lesions represent arteriovenous shunts involving a small area of dura with afferent supply from a radicular artery. Arterialized drainage from the SDAVF flows into the pial veins of the spinal cord, causing enlargement and engorgement of the cord venous system. The resultant VHM is responsible for the progressive neurologic deficits caused by the lesions. Hemorrhage is not associated with SDAVF (1 5). A number of investigators have examined MR imaging findings in VHM resulting from SDAVF. Reported findings include cord swelling, enlarged pial veins, increased signal intensity on T2-weighted images, and enhancement of the cord parenchyma (8 11). In the largest published study, Gilbertson et al (10) examined MR findings in 66 patients with SDAVF and reported increased T2 signal in the cord (100%), contrast enhancement (88%), cord enlargement (45%), and flow voids on the cord surface (on 35% of T1-weighted images and on 45% of T2-weighted images). The most constantly reported MR finding has been increased signal in the spinal cord parenchyma on T2-weighted images. This finding is, however, extremely nonspecific and may result from infection, inflammatory disorders, demyelinating disease, vasculitis, cord neoplasm, and a host of other sources of spinal cord dysfunction. The MR feature considered most specific for VHM, that of enlarged pial veins, has been reported in less than half the confirmed cases. Our finding of visible spinal vessels in 10 of 11 patients represents an improvement in sensitivity. This may reflect advancements in MR techniques since the publication of previous studies or may simply reflect the smaller number of patients in our group. Nevertheless, hypothesizing the diagnosis of SDAVF on the basis of noninvasive imaging findings remains difficult and requires spinal angiography for confirmation. A feature we observed in all our patients with SDAVF was peripheral hypointensity of the spinal cord on T2-weighted images (Fig 1). This imaging feature has not been previously reported in association with SDAVF or other nonhemorrhagic spinal cord disorders and may be subtle, particularly on FSE images, which minimize susceptibility differences. Nevertheless, the finding was present on gradient-echo as well as on true T2-weighted sequences, both of which considerably increase the conspicuity of peripheral hypointensity over FSE sequences. The sign was present in each patient symptomatic with angiographically confirmed SDAVF and might reflect the presence of VHM.
4 784 HURST AJNR: 21, April 2000 FIG 4. A and B, Late arterial-phase anteroposterior (A) and lateral (B) right vertebral artery injection shows filling of dural arteriovenous fistula (open arrow, B) originating from intradural vertebral artery. Drainage along cervical spinal cord is visible in both views (closed arrows). C, Coronal contrast-enhanced MR image shows intraaxial cervicomedullary enhancement and enlarged pial cervical vein (arrowheads). D and E, Sagittal (3733/100 eff ) (D) and axial (4000/100 eff )(E) T2-weighted images of cervical cord show subpial hypointensity (arrowheads). We also examined patients with intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with spinal venous drainage identical to that seen in patients with SDAVF in whom VHM developed (12 14). We confirmed peripheral T2 hypointensity involving the spinal cord in each of four symptomatic patients with spinal drainage from intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (Fig 4), which supports the conclusion that the sign is associated with the diagnosis of VHM regardless of the inciting lesion. Pathologic changes found in VHM include pial venous engorgement, parenchymal edema, ischemia, and venous infarction (4, 15 18). These features underlie the most commonly identified MR findings, including enlarged surface vessels, cord swelling, and increased T2 signal within the cord. None of these pathologic findings would be expected to decrease spinal cord parenchymal signal on T2-weighted images. We hypothesized that the observed T2 shortening is a result of slow flow of blood containing deoxyhemoglobin within a distended spinal cord capillary and venous system. Pathologic studies of spinal venous hypertension have identified dilatation involving the pial veins on the cord surface that extends retrogradely into the venous system within the cord parenchyma. The surface hypointensity occurs where the effects of venous dilatation and slow flow would be expected to be most prominent. The finding was present in each patient but was more conspicuous in some than in others. The variable conspicuity of the sign may be related to the degree of venous hypertension. Each of our patients had relatively severe spinal cord dysfunction as evidenced by a symptomatic course of at least 1 year and fixed neurologic deficits resulting from the cord VHM. Differences in T2 weighting alter the conspicuity of the sign. The use of FSE sequences minimizes susceptibility differences relative to true T2- weighted images (19, 20). Use of true T2-weighted and gradient-echo sequences results in increased conspicuity of the finding (Fig 5). A second but less likely mechanism for T2 shortening is accumulation of paramagnetic substances within spinal cord parenchyma affected by venous hypertension. Staining for such compounds, including those containing both iron and calcium, has been confirmed in studies of VHM (4, 5, 15, 17, 18, 21). Nevertheless, the hypointensity seen in our patients with VHM was not nearly as marked and
5 AJNR: 21, April 2000 VENOUS HYPERTENSIVE MYELOPATHY 785 FIG 5. A, Sagittal FSE T2-weighted (5417/98) MR image shows increased central cord signal with subtle peripheral hypointensity. B and C, Sagittal proton density weighted (2500/20) (B) and true T2-weighted (2500/80) (C) images show decrease in cord signal intensity (arrows). D, Axial gradient-echo (117/20) image shows increased conspicuity of peripheral hypointensity (arrows). E, Anteroposterior view of left L1 injection shows filling of dural arteriovenous fistula (arrow indicates catheter tip). was more stereotyped than has been reported from paramagnetic effects. None of our patients had hypointensity visible on T1-weighted images. In addition, staining indicated that paramagnetic substances were usually distributed uniformly throughout the spinal cord parenchyma. VHM-associated hypointensity, in contrast, demonstrates exquisite localization to the pial surface. These features suggest that paramagnetic deposition probably played a minor role, if any, in the T2 hypointensity seen in our patients. Hemorrhage, a phenomenon well known to result in T2 shortening, may result from other spinal vascular lesions, such as spinal cord arteriovenous malformations or cavernous malformations, but has not been reported in conjunction with SDAVF. None of our patients had a clinical or radiologic picture that would have suggested spinal hemorrhage. Although not specifically mentioned, the sign may be identified in previously published cases of SDAVF. It may be seen on the FSE T2- weighted image in the study by Bowen et al (8) of MR angiography in SDAVF. Willinsky et al (22), in the investigation of posttreatment MR findings in SDAVF, provided additional evidence for both the presence and origin of peripheral hypointensity. In their study, peripheral hypointensity was seen on the pretreatment T2-weighted MR image but was not evident on the study done 17 months after treatment. The resolution of the sign further supports the conclusion that the hypointensity is due to deoxygenated blood in distended pial veins, which return to a more normal size after obliteration of the fistula. Conclusion Our review of 11 patients with SDAVF and symptomatic VHM reveals that T2 signal loss involving the peripheral portions of the spinal cord is a constant finding. The identical finding in four patients with intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula with spinal drainage, a disorder that also causes symptomatic VHM, suggests that peripheral T2 hypointensity is a reliable marker for the diagnosis of VHM. This MR finding has not been previously reported and, in the presence of increased central cord signal, may suggest a more specific diagnosis of VHM, the most common vascular mechanism of spinal cord dysfunction.
6 786 HURST References 1. Symon L, Kuyama H, Kendall B. Dural arteriovenous malformations of the spine: clinical features and surgical results in 55 cases. J Neurosurg 1984;60: Muraszko K, Oldfield E. Vascular malformations of the spinal cord and dura. Neurosurg Clin North Am 1990;1: Morgan M, Marsh W. Management of spinal dural arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 1989;70: Kim S, Kim R, Choi B. Nontraumatic ischemic myelopathy: a review of 25 cases. Paraplegia 1988;26: Hurst R, Kenyon L, Lavi E, Raps E, Marcotte P. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula: the pathology of venous hypertensive myelopathy. Neurology 1995;45: Niimi Y, Berenstein A, Setton A, Neophytides A. Embolization of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: results and follow-up. Neurosurgery 1997;40: Tacconi L, Lopez I, Symon L. Outcome and prognostic factors in the surgical treatment of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: a long term study. Br J Neurosurg 1997;11: Bowen B, Fraser K, Kochan J, Pattany P, Green B, Quencer R. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation with MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16: DeMarco J, Dillon W, Halbach V, Tsuruda J. Dural arteriovenous fistulas: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiology 1990;175: Gilbertson J, Miller G, Goldman M, Marsh W. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: MR and myelographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16: Isu T, Iwasaki Y, Akino M, Koyanagi I, Abe H. Magnetic resonance imaging in cases of spinal dural arteriovenous fistula. Neurosurgery 1989;24: AJNR: 21, April Brunereau L, Gobin Y, Meder J, Cognard C, Tubiana J, Merland J. Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas with spinal venous drainage: relation between clinical presentation and angiographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1996;17: Chen C, Chen C, Lin T. Enhanced cervical MRI in identifying intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae with spinal perimedullary venous drainage. Neuroradiology 1998;40: Hahnel S, Jensen O, Geletnekyu K. MR appearance of an intracranial dural arteriovenous fistula leading to cervical myelopathy. Neurology 1998;51: Adams J, Duchen L. Greenfield s Neuropathology. New York: Oxford University Press;1992: Hurst R, Hackney D, Goldberg H, Davis R. Reversible arteriovenous malformation-induced venous hypertension as a cause of reversible neurological deficits. Neurosurgery 1992;30: Kim R. Necrotizing myelopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1991; 12: Jellinger K. Pathology of Spinal Vascular Malformations and Vascular Tumors. Berlin: Springer;1978: Gomori J, Grossman R, Goldberg H, Zimmerman R, Bilaniuk L. Intracranial hematomas: imaging by high-field MR. Radiology 1985;157: Thulborn K, Waterton J, Matthews P, Radda G. Oxygenation dependence of the transverse relaxation time of water proteins in whole blood at high field. Biochem Biophys Acta 1982;714: Hughes J. Disorders of the Spine and Spinal Cord. New York: Wiley;1990: Willensky R, terbrugge K, Montanera W, Mikulis D, Wallace C. Posttreatment MR findings in spinal dural arteriovenous malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995;16:
SDAVFs are rare acquired vascular lesions predominantly
 CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: MR and Myelographic Findings
 Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: MR and Myelographic Findings Julie R. Gilbertson, Gary M. Miller, Marc S. Goldman, and W. Richard Marsh PURPOSE: To examine the clinical and radiographic findings in
Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: MR and Myelographic Findings Julie R. Gilbertson, Gary M. Miller, Marc S. Goldman, and W. Richard Marsh PURPOSE: To examine the clinical and radiographic findings in
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
Venous Infarction of the Spinal Cord Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: MR Imaging
 739 Venous Infarction of the Spinal Cord Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: MR Imaging Findings E-M. Larsson 1 P. Desai 1 C. W. Hardin 2 J. Story 3 J. R. Jinkins 1 Three patients with spinal dural
739 Venous Infarction of the Spinal Cord Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: MR Imaging Findings E-M. Larsson 1 P. Desai 1 C. W. Hardin 2 J. Story 3 J. R. Jinkins 1 Three patients with spinal dural
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at the Craniocervical Junction with Perimedullary Venous Drainage
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at the Craniocervical Junction with Perimedullary Venous Drainage Mario Mascalchi, Fabio Scazzeri, Daniele Prosetti, Giampiero Ferrito, Fabrizio Salvi, and Nello Quilici Summary:
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at the Craniocervical Junction with Perimedullary Venous Drainage Mario Mascalchi, Fabio Scazzeri, Daniele Prosetti, Giampiero Ferrito, Fabrizio Salvi, and Nello Quilici Summary:
N-butyl 2-cyanoacrylate Embolization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol : 7, January N-butyl -cyanoacrylate Embolization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae Joon K. Song, Y. Pierre Gobin, Gary R. Duckwiler, Yuichi Murayama, John G. Frazee, Neil A.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol : 7, January N-butyl -cyanoacrylate Embolization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae Joon K. Song, Y. Pierre Gobin, Gary R. Duckwiler, Yuichi Murayama, John G. Frazee, Neil A.
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVF) have long
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Noguchi M. Kubo N. Kuwayama Y. Kamisaki G. Tomizawa K. Kameda H. Kawabe S. Ogawa N. Watanabe S. Endo H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Retrograde Cortical Venous
Historical perspective
 SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Intracranial DAVFs are grouped as benign or aggressive depending
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. guchi N. Kuwayama M. Kubo Y. Kamisaki K. Kameda G. Tomizawa H. Kawabe H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Retrograde Cortical Venous Drainage: Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. guchi N. Kuwayama M. Kubo Y. Kamisaki K. Kameda G. Tomizawa H. Kawabe H. Seto Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Retrograde Cortical Venous Drainage: Use of Susceptibility-Weighted
Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1267 1273, August 1998 Dementia Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: The Pathologic Findings of Venous Hypertensive Encephalopathy Robert W. Hurst, Linda J. Bagley, Steven
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME
 Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME Po-An Tai, Yong-Kwang Tu, and Hon-Man Liu 1 Background and purpose: Spinal
Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME Po-An Tai, Yong-Kwang Tu, and Hon-Man Liu 1 Background and purpose: Spinal
Arteriovenous (AV) shunts of the spinal cord and its meninges
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Mull R.J. Nijenhuis W.H. Backes T. Krings J.T. Wilmink A. Thron Value and Limitations of Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography in Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Mull R.J. Nijenhuis W.H. Backes T. Krings J.T. Wilmink A. Thron Value and Limitations of Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography in Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous
Multidisciplinary Management of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas. Clinical Presentation and Long-Term Follow-Up in 49 Patients
 Multidisciplinary Management of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Clinical Presentation and Long-Term Follow-Up in 49 Patients J. Marc C. van Dijk, MD; Karel G. TerBrugge, MD; Robert A. Willinsky, MD;
Multidisciplinary Management of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Clinical Presentation and Long-Term Follow-Up in 49 Patients J. Marc C. van Dijk, MD; Karel G. TerBrugge, MD; Robert A. Willinsky, MD;
Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR?
 Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR? Poster No.: C-3378 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J. C. Röper-Kelmayr 1, C. Ginthör 1, D. Flöry 1, R. Chapot
Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR? Poster No.: C-3378 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J. C. Röper-Kelmayr 1, C. Ginthör 1, D. Flöry 1, R. Chapot
Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; XX; XXX XXX doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0098 Published Online: November 29, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels
Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; XX; XXX XXX doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0098 Published Online: November 29, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Spinal Arteriovenous Shunts: Angioarchitecture and Historical Changes in Classification
 REVIEW ARTICLE doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0316 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 57, 356 365, 2017 Spinal Arteriovenous Shunts: Angioarchitecture and Historical Changes in Classification Keisuke Takai 1 Online May
REVIEW ARTICLE doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0316 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 57, 356 365, 2017 Spinal Arteriovenous Shunts: Angioarchitecture and Historical Changes in Classification Keisuke Takai 1 Online May
Spinal DAVFs are the most common vascular malformations
 Neurosurg Focus 26 (1):E8, 2009 Overview of the current role of endovascular and surgical treatment in spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas Am i r R. De h d a s h t i, M.D., 1 Le o d a n t e B. Da Co s
Neurosurg Focus 26 (1):E8, 2009 Overview of the current role of endovascular and surgical treatment in spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas Am i r R. De h d a s h t i, M.D., 1 Le o d a n t e B. Da Co s
Clinical Features and Outcomes of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations Comparison Between Nidus and Fistulous Types
 Clinical Features and Outcomes of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations Comparison Between Nidus and Fistulous Types Young-Jun Lee, MD, PhD; Karel G. Terbrugge, MD, FRCP(C); Guillaume Saliou, MD, PhD;
Clinical Features and Outcomes of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations Comparison Between Nidus and Fistulous Types Young-Jun Lee, MD, PhD; Karel G. Terbrugge, MD, FRCP(C); Guillaume Saliou, MD, PhD;
Results of the surgical treatment of perimedullary arteriovenous fistulas with special reference to embolization
 Neurosurg Focus 5 (4): Article 9, 1998 Results of the surgical treatment of perimedullary arteriovenous fistulas with special reference to embolization Kazutoshi Hida, M.D., Yoshinobu Iwasaki, M.D., Katsuya
Neurosurg Focus 5 (4): Article 9, 1998 Results of the surgical treatment of perimedullary arteriovenous fistulas with special reference to embolization Kazutoshi Hida, M.D., Yoshinobu Iwasaki, M.D., Katsuya
SPINAL EPIDURAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: REPORT OF A CASE WITH DISCUSSION OF CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT
 SPINAL EPIDURAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: REPORT OF A CASE WITH DISCUSSION OF CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT Caitlin M. Clark, B.A. and W. Craig Clark, M.D., Ph.D., FAANS, FACS, FICS INTRODUCTION True
SPINAL EPIDURAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: REPORT OF A CASE WITH DISCUSSION OF CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT Caitlin M. Clark, B.A. and W. Craig Clark, M.D., Ph.D., FAANS, FACS, FICS INTRODUCTION True
Vascular Malformations
 Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Vascular Malformations LTC Robert Shih Chief of Neuroradiology Walter Reed Medical Center Special thanks to LTC Alice Smith (retired) Disclosures: None. This presentation reflects the personal views of
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Recently, diagnostic imaging methods for spinal
 J Neurosurg Spine 18:398 408, 2013 AANS, 2013 Three-dimensional angioarchitecture of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas, with special reference to the intradural retrograde venous drainage system Clinical
J Neurosurg Spine 18:398 408, 2013 AANS, 2013 Three-dimensional angioarchitecture of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas, with special reference to the intradural retrograde venous drainage system Clinical
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas, also known as. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: outcome and prognostic factors
 Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E11, 2012 Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: outcome and prognostic factors Marco Cenzato, M.D., 1 Alberto Debernardi, M.D., 1 Roberto Stefini, M.D., 2 Giuseppe D Aliberti, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E11, 2012 Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: outcome and prognostic factors Marco Cenzato, M.D., 1 Alberto Debernardi, M.D., 1 Roberto Stefini, M.D., 2 Giuseppe D Aliberti, M.D.,
Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2582 2586, November/December 2005 Case Report Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization Ismail Oran, Mustafa
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2582 2586, November/December 2005 Case Report Treatment of Slow-Flow (Type I) Perimedullary Spinal Arteriovenous Fistulas with Special Reference to Embolization Ismail Oran, Mustafa
Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
 J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
J Neurosurg 101:31 35, 2004 Selective disconnection of cortical venous reflux as treatment for cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas J. MARC C. VAN DIJK, M.D., PH.D., KAREL G. TERBRUGGE, M.D., ROBERT A.
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
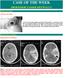 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY A 29 years old male patients presented with proptosis, ecchymoses of the left eye with both subjective and objective bruit
Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula
 Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Case Reports 24 Venous Stroke with Intracranial Dural Arteriovenous Fistula Tzung-Wen Chiang 1,2, Shung-Lon Lai 1, Leang-Kai Chang 2, Yung-Yee Chang 1, Min-Yu Lan 1, Yeh-Lin Kuo 3, Chen-Chung Lu 3, and
Pial arteriovenous fistula of the spine in a child with hemiplegia
 CASE REPORT Pial arteriovenous fistula of the spine in a child with hemiplegia Kazuki Hatayama 1, Shinichiro Goto 1, Ayumi Nishida 2 & Masaru Inoue 1 1 Department of Pediatrics, Okayama Red-Cross Hospital,
CASE REPORT Pial arteriovenous fistula of the spine in a child with hemiplegia Kazuki Hatayama 1, Shinichiro Goto 1, Ayumi Nishida 2 & Masaru Inoue 1 1 Department of Pediatrics, Okayama Red-Cross Hospital,
A.J. Hauer Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae
 A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
A.J. Hauer 27-06-2018 Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulae Dural arteriovenous fistulae (davfs) epidemiology Pathological anastomoses (within the dural leaflets) between meningeal arteries and dural
Spinal intradural arteriovenous fistulas acquired in late adulthood: absent spinal venous drainage in pathogenesis and pathophysiology
 J Neurosurg Spine 3:488 494, 2005 Spinal intradural arteriovenous fistulas acquired in late adulthood: absent spinal venous drainage in pathogenesis and pathophysiology Report of two cases GABRIEL C. TENDER
J Neurosurg Spine 3:488 494, 2005 Spinal intradural arteriovenous fistulas acquired in late adulthood: absent spinal venous drainage in pathogenesis and pathophysiology Report of two cases GABRIEL C. TENDER
Title. CitationNeurologia medico-chirurgica, 49(3): Issue Date Doc URL
 Title Cervical Epidural Arteriovenous Fistula With Radicul Author(s)Kawabori, Masahito; Hida, Kazutoshi; Yano, Shunsuke; CitationNeurologia medico-chirurgica, 49(3): 108-113 Issue Date 2009-03 Doc URL
Title Cervical Epidural Arteriovenous Fistula With Radicul Author(s)Kawabori, Masahito; Hida, Kazutoshi; Yano, Shunsuke; CitationNeurologia medico-chirurgica, 49(3): 108-113 Issue Date 2009-03 Doc URL
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Cavernous Sinus Presenting with Progressive Venous Congestion of the Pons and Cerebrum: Report of one case Soo-Bin Yim, M.D., Jong-Sung Kim, M.D., Yang Kwon,M.D.*, Choong-Gon
Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:34 38, January 2005 Case Report Intradural Spinal Vein Enlargement in Craniospinal Hypotension M. Todd Burtis, John L. Ulmer, Glenn A. Miller, Alexandru C. Barboli, Scott A. Koss,
Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas (davfs) are
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 9:8 9, 8 Timing, severity of deficits, and clinical improvement after surgery for spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas Michael M. Safaee, MD, Aaron J. Clark, MD, PhD,
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 9:8 9, 8 Timing, severity of deficits, and clinical improvement after surgery for spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas Michael M. Safaee, MD, Aaron J. Clark, MD, PhD,
MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition
 637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Published November 13, 2014 as /ajnr.A4164
 Published November 13, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4164 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Time-Resolved Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography of Spinal Vascular Malformations M. Amarouche, J.L. Hart, A. Siddiqui, T. Hampton,
Published November 13, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4164 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Time-Resolved Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography of Spinal Vascular Malformations M. Amarouche, J.L. Hart, A. Siddiqui, T. Hampton,
Sp i n a l davfs are acquired vascular lesions characterized
 Neurosurg Focus 26 (1):E4, 2009 Intracranial subarachnoid hemorrhage resulting from cervical spine dural arteriovenous fistulas: literature review and case presentation Da n i e l R. Fa s s e t t, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 26 (1):E4, 2009 Intracranial subarachnoid hemorrhage resulting from cervical spine dural arteriovenous fistulas: literature review and case presentation Da n i e l R. Fa s s e t t, M.D.,
Variable Appearances of Subacute Intracranial Hematomas on High-Field Spin-Echo MR
 1019 Variable Appearances of Subacute Intracranial Hematomas on High-Field Spin-Echo MR John M. Gomori' 2 Robert I. Grossman' David B. Hackney' Herbert I. Goldberg' Robert A. Zimmerman' Larissa T. Bilaniuk'
1019 Variable Appearances of Subacute Intracranial Hematomas on High-Field Spin-Echo MR John M. Gomori' 2 Robert I. Grossman' David B. Hackney' Herbert I. Goldberg' Robert A. Zimmerman' Larissa T. Bilaniuk'
MRI of chronic spinal cord injury
 The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
Case Report Multidisciplinary management of multiple spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2013;6(9):814-821 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1308023 Case Report Multidisciplinary management of multiple spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae Liang Ge 1*, Rui Feng 2*, Xiaolong
Int J Clin Exp Med 2013;6(9):814-821 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM1308023 Case Report Multidisciplinary management of multiple spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae Liang Ge 1*, Rui Feng 2*, Xiaolong
Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic dural arteriovenous fistula with perimedullary hypertension: case report
 Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
Foreman et al. Chiropractic & Manual Therapies 2013, 21:23 http://www.chiromt.com/content/21/1/23 CHIROPRACTIC & MANUAL THERAPIES CASE REPORT Paraplegia in a chiropractic patient secondary to atraumatic
S. Inagawa, N. Yoshimura, Y. Ito; Niigata/JP spinal sacral areteriovenous fistulae, CTA, MRA /ecr2010/C-2581
 Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological Institute, St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Arizona
 clinical article J Neurosurg 122:876 882, 2015 The role of microscope-integrated near-infrared indocyanine green videoangiography in the surgical treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
clinical article J Neurosurg 122:876 882, 2015 The role of microscope-integrated near-infrared indocyanine green videoangiography in the surgical treatment of intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Recanalization of spinal arteriovenous malformations following embolization
 J Neurosurg 7:74-72, 989 Recanalization of spinal arteriovenous malformations following embolization WALTER A. HALL, M.D., EDWARD H. OLDFIELD, M.D., AND JOHN L. DOPPMAN, M.D. Clinical Neurosurgery Section,
J Neurosurg 7:74-72, 989 Recanalization of spinal arteriovenous malformations following embolization WALTER A. HALL, M.D., EDWARD H. OLDFIELD, M.D., AND JOHN L. DOPPMAN, M.D. Clinical Neurosurgery Section,
Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:2016 2020, November/December 1999 Case Report Three Cases of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula of the Anterior Condylar Vein within the Hypoglossal Canal Robert Ernst, Robert Bulas,
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence
 A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
A New Trend in Vascular Imaging: the Arterial Spin Labeling (ASL) Sequence Poster No.: C-1347 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Hodel, A. GUILLONNET, M. Rodallec, S. GERBER, R. 1
Central Vasomotor Failure in a Patient with Medulla Arteriovenous Fistula
 Case Reports 192 Central Vasomotor Failure in a Patient with Medulla Arteriovenous Fistula Ching-Hwung Lin 1, Yuk-Keung Lo 1, Yuh-Te Lin 1, Jie-Yuan Li 1, Ping-Hong Lai 2, and Yung-Yen Gau 1 Abstract-
Case Reports 192 Central Vasomotor Failure in a Patient with Medulla Arteriovenous Fistula Ching-Hwung Lin 1, Yuk-Keung Lo 1, Yuh-Te Lin 1, Jie-Yuan Li 1, Ping-Hong Lai 2, and Yung-Yen Gau 1 Abstract-
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Intracranial dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) with retrograde
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
ORIGINAL RESEARCH W.J. van Rooij M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas with Cortical Venous Drainage: Incidence, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our purpose
Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Evaluation with MR Angiography
 Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Evaluation with MR Angiography B. C. Bowen, K. Fraser, J. P. Kochan, P. M. Pattany, B. A. Green, and R. M. Quencer PURPOSE: To show that postgadolinium three-dimensional
Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Evaluation with MR Angiography B. C. Bowen, K. Fraser, J. P. Kochan, P. M. Pattany, B. A. Green, and R. M. Quencer PURPOSE: To show that postgadolinium three-dimensional
Researcher 2018;10(3) Management of Vascular Myelopathy.
 Management of Vascular Myelopathy Mustafa El-sayed Mohammed El-sayed 1, Magdy Asaad El-Hawar 1, Wafik Ebrahim Aly 2 and Ahmed Mohammed Abd El-Fatah Deabes 3 1 Neurosurgery Department, Faculty of Medicine,
Management of Vascular Myelopathy Mustafa El-sayed Mohammed El-sayed 1, Magdy Asaad El-Hawar 1, Wafik Ebrahim Aly 2 and Ahmed Mohammed Abd El-Fatah Deabes 3 1 Neurosurgery Department, Faculty of Medicine,
EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Arteriovenous fistula after radiosurgery for multiple CAVM EMBOLIZATION OF ARTERIOVENOUS FISTULA AFTER RADIOSURGERY FOR MULTIPLE CEREBRAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS Chao-Bao Luo, Wan-Yuo Guo, Michael
Craniocervical Junction Venous Anatomy on Enhanced MR Images: The Suboccipital Cavernous Sinus
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1127 1131, June/July 1999 Craniocervical Junction Venous Anatomy on Enhanced MR Images: The Suboccipital Cavernous Sinus Ronald D. Caruso, Arthur E. Rosenbaum, Ja Kwei Chang, and
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1127 1131, June/July 1999 Craniocervical Junction Venous Anatomy on Enhanced MR Images: The Suboccipital Cavernous Sinus Ronald D. Caruso, Arthur E. Rosenbaum, Ja Kwei Chang, and
DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY
 Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
Neuroradiology (2008) 50:1013 1023 DOI 10.1007/s00234-008-0433-3 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY The anterior medullary anterior pontomesencephalic venous system and its bridging veins communicating to the dural
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Spinal DAVFs, perimedullary AVFs, and spinal. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of the spinal arteriovenous fistulas and malformations
 J Neurosurg Spine 19:207 216, 2013 AANS, 2013 Clinical features and treatment outcomes of the spinal arteriovenous fistulas and malformations Clinical article Won-Sang Cho, M.D., 1 Ki-Jeong Kim, M.D.,
J Neurosurg Spine 19:207 216, 2013 AANS, 2013 Clinical features and treatment outcomes of the spinal arteriovenous fistulas and malformations Clinical article Won-Sang Cho, M.D., 1 Ki-Jeong Kim, M.D.,
Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein
 J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
J Radiol Sci 2011; 36: 129-134 Endovascular Treatment of Cavernous Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas by Direct Puncture of Facial Vein Shih-Wei Hsu 1 Yeh-Lin Kuo 1 Min-Hsiung Cheng 2 Department of Diagnostic
Journal of Radiology Case Reports
 Pediatric Holohemispheric Developmental Venous Anomaly: Definitive characterization by 3D Susceptibility Weighted Magnetic Resonance Angiography Michael A. Casey 1, Sourabh Lahoti 2, Ajeet Gordhan 2* 1.
Pediatric Holohemispheric Developmental Venous Anomaly: Definitive characterization by 3D Susceptibility Weighted Magnetic Resonance Angiography Michael A. Casey 1, Sourabh Lahoti 2, Ajeet Gordhan 2* 1.
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
 Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
Transverse-Sigmoid Sinus Dural Arteriovenous Malformations Kenan I. Amautovic, M.D., and Ali F. Krisht, M.D. '-...--- Learning Objectives: After reading this article, the participant should: 1. Have an
7/5/2016. Neonatal high-output cardiac failure. Case 1 POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS
 John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
John Deveikis, M.D. POSTNATAL STRATEGIES FOR CEREBRAL ATERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS JULY, 2016 Neonatal high-output cardiac failure Tachypnea, tachycardia, hypotension, failure to thrive When congenital heart
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
MR Characteristics of Subdural Hematomas and Hygromas at 1.5 T
 687 MR Characteristics of Subdural Hematomas and Hygromas at 1.5 T Edward S. Fobben 1 Robert I. Grossman Scott W. tlas David B. Hackney Herbert I. Goldberg Robert. Zimmerman Larissa T. Bilaniuk MR images
687 MR Characteristics of Subdural Hematomas and Hygromas at 1.5 T Edward S. Fobben 1 Robert I. Grossman Scott W. tlas David B. Hackney Herbert I. Goldberg Robert. Zimmerman Larissa T. Bilaniuk MR images
Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation
 206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
206 Chiriac et al Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation Spontaneous occlusion of a cerebral arteriovenous malformation after subtotal endovascular embolisation A. Chiriac, N. Dobrin*,
(http://thejns.org/doi/abs/ / focus11344)
 Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E3, 2012 Surgical treatment of Type I spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas Alexander E. Ropper, M.D., Bradley A. Gross, M.D., and Rose Du, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E3, 2012 Surgical treatment of Type I spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas Alexander E. Ropper, M.D., Bradley A. Gross, M.D., and Rose Du, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Neurosurgery,
Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:992 996, May 2001 Case Report Spontaneous Closure of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: Report of Three Cases and Review of the Literature Alain Luciani, Emmanuel Houdart, Charbel Mounayer,
DAVFs and AVMs are cerebral vascular malformations
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.T. Le N.J. Fischbein J.B. André C. Wijman J. Rosenberg G. Zaharchuk Identification of Venous Signal on Arterial Spin Labeling Improves Diagnosis of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas and
ORIGINAL RESEARCH T.T. Le N.J. Fischbein J.B. André C. Wijman J. Rosenberg G. Zaharchuk Identification of Venous Signal on Arterial Spin Labeling Improves Diagnosis of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas and
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dural AVFs) constitute 10%
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH N. Horie M. Morikawa N. Kitigawa K. Tsutsumi M. Kaminogo I. Nagata 2D Thick-Section MR Digital Subtraction Angiography for the Assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas BACKGROUND AND
A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging
 Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Neuroradiology (2002) 44: 907 911 DOI 10.1007/s00234-002-0860-5 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY N. Morita M. Harada K. Yoneda H. Nishitani M. Uno A characteristic feature of acute haematomas in the brain on
Embolization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Polyvinyl Alcohol Particles: Experience in 14 Patients
 Embolization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Polyvinyl Alcohol Particles: Experience in 14 Patients Douglas A. Nichols, 1 Daniel A. Rufenacht, 1 Clifford R. Jack, Jr., 1 and GlennS. Forbes 1
Embolization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistula with Polyvinyl Alcohol Particles: Experience in 14 Patients Douglas A. Nichols, 1 Daniel A. Rufenacht, 1 Clifford R. Jack, Jr., 1 and GlennS. Forbes 1
Acute traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) is a devastating
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH B.G. Leypold A.E. Flanders A.S. Burns The Early Evolution of Spinal Cord Lesions on MR Imaging following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: How early spinal cord injury
ORIGINAL RESEARCH B.G. Leypold A.E. Flanders A.S. Burns The Early Evolution of Spinal Cord Lesions on MR Imaging following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: How early spinal cord injury
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
General Data. Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30
 General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
General Data Gender: Female Birthday and age: 1932/11/03, 73 y/o Occupation: house keeper Date of Admission: 2005/03/30 Chief Complain Dizziness and light headache for recent 1 year. Present illness Hypertension
Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations
 J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
J Neurosurg 78: 167-175, 1993 Occlusive hyperemia: a theory for the hemodynamic complications following resection of intracerebral arteriovenous malformations NAYEF R. F. AL-RODHAN, M.D., PH.D., THORALF
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
SPINAL AVM: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES. Presented by : Anuj K Tripathi
 SPINAL AVM: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES Presented by : Anuj K Tripathi SPINAL AVM Spinal vascular malformations represent a rare and insufficiently studied pathological entity Great difficulties
SPINAL AVM: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES Presented by : Anuj K Tripathi SPINAL AVM Spinal vascular malformations represent a rare and insufficiently studied pathological entity Great difficulties
Materials and Methods. A. Biondi, 1 2 J.J. Merland, 1 J.E. Hodes, 1 A. Aymard, 1 and D. Reizine 1
 Aneurysms of Spinal Arteries Associated with Intramedullary Arteriovenous Malformations. II. Results of A V M Endovascular Treatment and Hemodynamic Considerations I A. Biondi, 1 2 J.J. Merland, 1 J.E.
Aneurysms of Spinal Arteries Associated with Intramedullary Arteriovenous Malformations. II. Results of A V M Endovascular Treatment and Hemodynamic Considerations I A. Biondi, 1 2 J.J. Merland, 1 J.E.
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report
 Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
Cerebral DAVF is an acquired abnormal arterialto-venous
 Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E10, 2012 Dural arteriovenous fistulas presenting with brainstem dysfunction: diagnosis and surgical treatment Charles Kulwin, M.D., Bradley N. Bohnstedt, M.D., John A. Scott, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 32 (5):E10, 2012 Dural arteriovenous fistulas presenting with brainstem dysfunction: diagnosis and surgical treatment Charles Kulwin, M.D., Bradley N. Bohnstedt, M.D., John A. Scott, M.D.,
Dural arteriovenous shunts (DAVSs), also called dural
 Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Natural History of Dural Arteriovenous Shunts Michael Söderman, MD, PhD; Ladislav Pavic, MD, PhD; Göran Edner, MD; Staffan Holmin, MD, PhD; Tommy Andersson, MD, PhD Background and Purpose Dural arteriovenous
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Case Report. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUTION
 Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2011; 35: 928-933 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.928 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Cauda Equina Syndrome Caused by Spinal Dural
Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2011; 35: 928-933 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.928 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Cauda Equina Syndrome Caused by Spinal Dural
MR Evaluation of Neurovascular Lesions After Endovascular Occlusion with Detachable Balloons
 523 MR Evaluation of Neurovascular Lesions After Endovascular Occlusion with Detachable Balloons Eddie S. K. Kwan 1 Samuel M. Wolpert 1 R. Michael Scotf Val Runge 1 Three patients with surgically inaccessible
523 MR Evaluation of Neurovascular Lesions After Endovascular Occlusion with Detachable Balloons Eddie S. K. Kwan 1 Samuel M. Wolpert 1 R. Michael Scotf Val Runge 1 Three patients with surgically inaccessible
Management of spinal dural arteriovenouse fistula
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 4 2017 October-December Article Management of spinal dural arteriovenouse fistula A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion, N. Dobrin, I. Poeată ROMANIA DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0074
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 4 2017 October-December Article Management of spinal dural arteriovenouse fistula A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion, N. Dobrin, I. Poeată ROMANIA DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0074
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment
 Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Cerebrovascular Malformations in the Elderly Indications for Treatment Johanna T. Fifi, MD, FAHA, FSVIN Director of Endovascular Ischemic Stroke Assistant Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Radiology
Partially trombosed glomus type spinal arteriovenous malformation case presentation
 442 Gorgan et al Partially trombosed glomus type spinal arteriovenous malformation Partially trombosed glomus type spinal arteriovenous malformation case presentation M.R. Gorgan, Narcisa Bucur, Catioara
442 Gorgan et al Partially trombosed glomus type spinal arteriovenous malformation Partially trombosed glomus type spinal arteriovenous malformation case presentation M.R. Gorgan, Narcisa Bucur, Catioara
Pankaj Sharma, Alok Ranjan, Rahul Lath
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Case Journal Report Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):365-370 Filum terminale http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.365 arteriovenous fistula 365 Arteriovenous Fistula of the Filum
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Case Journal Report Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):365-370 Filum terminale http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.365 arteriovenous fistula 365 Arteriovenous Fistula of the Filum
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are
 TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
TOPIC DURAL FISTULAS DURAL FISTULAS Advances in Surgical Approaches to Dural Fistulas Patrick P. Youssef, MD Albert Jess Schuette, MD C. Michael Cawley, MD Daniel L. Barrow, MD Department of Neurosurgery,
Spinal arteriovenous malformations: new classification and surgical treatment
 Neurosurg Focus 20 (5):E7, 2006 Spinal arteriovenous malformations: new classification and surgical treatment YURI P. ZOZULYA, M.D., PH.D., EUGENE I. SLIN KO, M.D., PH.D., AND IYAD I. AL-QASHQISH, M.D.
Neurosurg Focus 20 (5):E7, 2006 Spinal arteriovenous malformations: new classification and surgical treatment YURI P. ZOZULYA, M.D., PH.D., EUGENE I. SLIN KO, M.D., PH.D., AND IYAD I. AL-QASHQISH, M.D.
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION!
 CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
CASE REPORT MASSIVE EPISTAXIS IN A NEONATE: A SYMPTOM OF VEIN OF GALEN MALFORMATION! Shagufta Wahab 1, Rizwan Ahmad Khan 2, Manjari Thapa Manger 3 1. Radiodiagnosis, Aligarh Muslim University, Aligarh,
Endovascular management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas
 Neurosurg Focus 26 (5):E15, 2009 Endovascular management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas A review Wa l ava n Si va k u m a r, B.S., Ga b r i e l Za d a, M.D., Pa r h a m Ya s h a r, M.D., St e v
Neurosurg Focus 26 (5):E15, 2009 Endovascular management of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas A review Wa l ava n Si va k u m a r, B.S., Ga b r i e l Za d a, M.D., Pa r h a m Ya s h a r, M.D., St e v
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease
 Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
