Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae
|
|
|
- Gwendoline Pearson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; XX; XXX XXX doi: /mrms.mp Published Online: November 29, 2017 MAJOR PAPER Additive Value of 3T 3D CISS Imaging to Conventional MRI for Assessing the Abnormal Vessels of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulae Hiroyuki Uetani 1*, Toshinori Hirai 2, Mika Kitajima 1, Minako Azuma 2, Shigetoshi Yano 3, Hideo Nakamura 3, Keishi Makino 3, Yutaka Kai 4, Yasunori Nagayama 1, Yoshihito Kadota 2, and Yasuyuki Yamashita 1 Introduction: We investigated the additive value of the 3T three-dimensional (3D) constructive interference in steady state (CISS) sequence to conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the evaluation of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae (SDAVF). Materials and Methods: We included 16 consecutive patients (15 men, 1 woman; age range years; mean 64 years) with SDAVF who underwent 3T MRI and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) before treatment. Two neuroradiologists independently evaluated the presence of abnormal vessels on 3D CISS-, - and images ( WI), and contrast-enhanced WI using a 3-point grading system. Interobserver agreement was assessed by calculating the κ coefficient. Results: The SDAVF site was the cervical region in one patient, the thoracic region in 12 patients, the lumbar region in two, and the sacral region in one. For the visualization of abnormal vessels, the mean score was significantly higher for 3D CISS than the other sequences (P < 0.05). In 12 of 16 cases (75%) both readers made definite positive findings on additional 3D-CISS images. Interobserver agreement was excellent for 3D CISS images (κ = 1.0), good for WI (κ = 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI] ) and WI (κ = 0.74; 95% CI ) and moderate for contrast-enhanced WI (CE WI) (κ = 0.50; 95% CI ). Conclusion: For the assessment of abnormal vessels of SDAVF, the 3T 3D CISS sequence adds value to conventional MRI. Keywords: spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae, constructive interfer ence in steady state, magnetic resonance imaging, arteriovenous fistulae, abnormal vessels Introduction Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae (SDAVF) have been underdiagnosed. If not treated adequately, they can lead to considerable morbidity with progressive spinal cord symptoms. 1 SDAVF are predominantly seen in elderly men. 2 Initially, the symptoms and signs of SDAVF can mimic degenerative spine disease or infectious or transverse myelopathy. The symptoms 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University, Honjo, Chuo-ku, Kumamoto, Kumamoto , Japan 2 Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Miyazaki University, Miyazaki, Japan 3 Department of Diagnostic Neurosurgery, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University, Kumamoto, Japan 4 Department of Neurosurgery, Aso Central Hospital, Kumamoto, Japan *Corresponding author, Phone: , Fax: , hama-moto@hotmail.co.jp 2017 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- NoDerivatives International License. Received: July 31, 2017 Accepted: September 15, 2017 can persist for several months before a correct diagnosis is made. 3 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) usually exhibits characteristic findings of intramedullary hyperintensity, variable intramedullary and leptomeningeal enhancement, a mild to moderate mass effect, and tortuous, exuberant vascular flow voids along the dorsal spinal cord, primarily involving the thoracic spinal cord and conus medullaris. 1,4 Tortuous and exuberant vessels were seen in 35 91% of patients on conventional MRI, i.e., - and images ( WI), and on contrast-enhanced WI (CE WI). 2,4,5 However, if the shunt volume is small, they might not be seen on conventional sequences. In the evaluation of SDAVF, coiled or serpentine vascular structures may be better appreciated on heavily than on standard turbo-spin echo sequences. 6,7 The constructive interference in steady state (CISS) sequence can yield high-resolution images with good contrast between cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and intradural vessels. 6 While there are a few case reports documenting the usefulness of CISS sequences for the identification of abnormal Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences 1
2 H. Uetani et al. vessels of SDAVF, 1,6,8 the additive value of three-dimensional (3D) CISS imaging to conventional MRI for the evaluation of SDAVF has not been systematically investigated. The purpose of this study was to assess the additive value of 3T 3D-CISS imaging to conventional MRI for the evaluation of the abnormal vessels of SDAVF. Materials and Methods Study population and MR technique We declare that all human studies have been approved by the Kumamoto University Hospital ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. This retrospective study was approved by the ethics committee, and informed consent was waived. We retrospectively assessed 16 consecutive patients with SDAVF diagnosed on digital subtraction angiography (DSA) at Kumamoto University Hospital. They were 15 men and 1 woman ranging in age from 42 to 81 years (mean 64 years). All scans were acquired on a 3T MR unit (Magnetom Trio; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) with a spinal matrix coil; DSA was performed preoperatively. We examined sagittal slabs on the 3D CISS sequences and conventional sagittal and axial 2D- WI. All images were acquired with a rectangular field of view (FOV) to obtain finer spatial resolution in the phase-encoding direction. The parameters we used were: Sagittal W spin-echo (SE) sequences, TR/TE 600/8.6 ms, 1 excitation, section thickness 3 mm, intersection gap 0.3 mm, FOV mm, matrix , acquisition time = 2 min 54 s; axial W SE sequences, TR/TE eff 600/10 ms, 1 excitation, section thickness 3 or 4 mm, intersection gap 0.3 mm, FOV mm, acquisition time = 3 min 12 s; sagittal W fast SE (FSE) sequence, TR/TEeff 3000/70 ms, 1 excitation, section thickness 3 mm, intersection gap 0.3 mm, FOV mm, matrix , acquisition time = 2 min 16 s; axial W FSE sequences, TR/TE eff 4000/70 ms, 1 excitation, section thickness 3 or 4 mm, intersection gap 0.3 mm, FOV mm, acquisition time = 2 min 24 s; CISS sequence, TR/TE 7.1/2.8 ms, 1 excitation, section thickness 0.5 mm, flip angle 43, FOV 250 mm, matrix , slab thickness = 32 mm, acquisition time = 3 min 43 s. The sagittal and axial contrast-enhanced W SE sequences were acquired with the same parameters as the precontrast MRI scans and the oblique coronal reconstruction CISS images were created with a multiplanar reconstruction technique. DSA technique Diagnostic intra-arterial DSA via a femoral arterial approach was performed in a biplane angiography suite (Allura Xper FD; Philips Healthcare, Best, the Netherlands) by a trained neuroradiologist and/or a neurosurgeon. The angiographic technique included the selective manual injection of 3 5 ml of a 300-mg/ml iodinated nonionic contrast agent into the intended arteries and anteroposterior imaging at a rate of 3 frames/s. The matrix was and the FOV was 42 cm. To obtain 3D images of the vessels injected from the feeder and of the bony structures, we acquired 3D rotational angiographs on the same angiography system. On a dedicated commercially available workstation (Philips Healthcare) we then reconstructed and analyzed the filling run-volume. The 3D images were reconstructed in a matrix with an isotropic voxel size. Image evaluation Two readers with 23 and 21 years of experience in neuroangiography consensually evaluated the entire series of DSA images on a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) workstation. Two other observers with 19 and 18 years of experience in diagnostic neuro-mri who were blinded to clinical information and DSA results independently evaluated the presence of abnormal vessels on 3D CISS images and and CE WI on a PACS workstation. They used a 3-point grading system where grade 3 = definitely positive, grade 2 = probably positive, and grade 1 = equivocal or definitely negative. First, the readers analyzed conventional sequences ( WI), and the 3D CISS images were analyzed 2 weeks later without conventional sequences. Statistical analysis We used κ coefficient to assess the interobserver agreement in each type of sequence; κ < 0.20 = poor, = fair, = moderate, = good, = very good, and κ > 0.90 = excellent. The Friedman test and the Scheffe test were used to evaluate the grading differences of the four types of images. Differences of P < 0.05 were considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Results Tables 1 and 2 shows the summary of clinical findings, MR findings, and grade assessment for the 4 MR sequences in 16 patients with SDAVF. DSA confirmed that the fistulae were located in the cervical region in one-, the thoracic region in 12-, the lumbar region in 2-, and the sacral region in one patient. For the presence of abnormal vessels, 2 readers assigned grade 3 to all 3D CISS images and grade 1 to 14 cases on WI. On reader 1 assigned grade 3 to 3-, grade 2 to 10-, and grade 1 to 3 cases. Reader 2 recorded as grade 3 in 4-, grade 2 in 7-, and grade 1 in 5 cases. On CE WI scans reader 1 scored 3 cases as grade 3, 6 as grade 2, and 7 as grade 1; reader 2 judged one case as grade 3, 4 as grade 2, and 11 as grade 1. Interobserver agreement was excellent for 3D CISS images (κ = 1.0), good for WI (κ = 0.78; 95% confidence interval [CI] ) and WI (κ = 0.74; 95% CI ) and moderate for CE WI (κ = 0.50; 95% CI ). 2 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
3 CISS Imaging of Spinal Dural AVF Table 1 Summary of 16 patients with spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae Case/Age (year)/sex Paresthesias Leg weakness Disturbances in sensation Symptoms Pain Disturbances in gait 1/58/M /75/M /60/M /58/M /73/M /75/F /62/M /78/M /58/M /52/M /78/M /59/M /81/M /42/M /56/M /63/M M, male; F, female. Time from onset to diagnosis (months) Table 2 Summary of MR abnormalities and grade assessment for 4 MR sequences in 16 patients with spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae Case Extent of intramedullary hyperintensity Fistula site Feeder WI WI CE WI CISS R1 R2 R1 R2 R1 R2 R1 R2 1 T3 8 T5 Intercostal a T7 conus T6 Intercostal a T8 conus T7 Intercostal a T4 conus T7 Intercostal a T8 12 T7 Intercostal a T8 11 T9 Intercostal a T5 conus T10 Intercostal a T7 11 T10 Intercostal a T5 conus L3 Lumbar a none C5 Vertebral a T1 10 T2 Intercostal a T4 conus L1 Lumbar a T5 conus T7 Intercostal a T6 conus T6 Intercostal a T7 conus S2 Iliolumbar a T7 conus T11 Intercostal a The presence of abnormal vessels on each sequence was qualitatively evaluated using a 3-point grading system: 3, definitely positive; 2, probably positive; 1, equivocal or definitely negative. C, Cervical; CE contrast-enhanced imaging; CISS, constructive interference in steady state imaging; L, Lumbar; R1, reader 1; R2, reader 2; S, Sacral; T, thoracic; imaging; imaging. Epub ahead of print 3
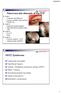
4 H. Uetani et al. Table 3 shows the comparative result of the mean score of the 4 MR sequences. There were statistical significant differences in mean score among 4 MR sequences (P < 0.001). The mean scores were significantly higher for 3D CISS than WI (P < 0.05). There were no statistical significant differences in the mean score among WI. In 12 of 16 cases (75%) both readers reported definite positive findings when 3D CISS images were added (Fig. 1). After the addition of 3D CISS imaging, the judgment of reader 1 changed from grade 1 to grade 3 in 3 (19%) and from grade 2 to grade 3 in 9 (56%) cases. For reader 2 the change was from grade 1 to grade 3 in 5 (31%) and from grade 2 to grade 3 in 7 (44%) cases. Discussion We found that 3D CISS imaging had additive values to conventional MRI for demonstrating the abnormal vessels of SDAVF. We attribute the superiority of the 3D CISS technique over the Table 3 Comparison of the mean score of the 4 MR sequences WI WI CE WI CISS Reader I 1.2 ± ± ± ± 0.0* Reader ± ± ± ± 0.0* *The mean score was significantly higher for CISS than the other sequences (P < 0.05). CE contrast-enhanced imaging; CISS, constructive interference in steady state imaging; imaging; imaging. other sequences to its providing the higher spatial resolution essential for the delineation of the abnormal vessels within the CSF. In contrast to submillimeter sections without intersection gaps on 3D CISS sequences, on SE sequences the section thickness and the intersection gaps are usually 3- or 4 mm. The contiguous thin-slice sections on 3D CISS images facilitated the detection of the detailed structure and extent of the abnormal vessels. Also, the 3D CISS sequence yields better contrast between the CSF and solid structures including the spinal cord, dura mater, nerve roots, and venous structures 9 and there are significantly fewer CSF flow artifacts. According to Haacke et al., 10 3D CISS sequence yields fewer flow artifact than other sequences (e.g. FSE and other gradient-echo techniques) by summing steady state precession fast imaging with steady state precession (FISP) with an alternating-, and reversed FISP (PSIF) with a non-alternating radiofrequency pulse. Spinal DSA is the diagnostic gold standard for SDAVF; it offers the additional advantage of possible simultaneous treatment, but it is invasive and time-consuming. MRI often suggests the diagnosis non-invasively. MRI findings with the highest sensitivity for SDAVF included intramedullary hyperintensity and exuberant and tortuous vessels on either the ventral or the dorsal side of the spinal cord. The specificity of flow voids, but not of hyperintensity, was very high for spinal AVF. 11 Gilbertson et al. 4 found flow voids on 35% of WI- and on 45% of WI scans and Hurst and Grossman 5 detected flow voids on 91% of WI- and 70% of CE WI scans. Based on their literature review, Toossi et al. 11 concluded that flow voids were found on 89% of MRI scans of Fig. 1 A 58-year-old man (Case 9) with a spinal dural arteriovenous fistula (SDAVF). Conventional, including sagittal ( WI) (A), (B), and contrast-enhanced (C) MR imaging shows swelling in the thoracic spinal cord and conus medullaris. WI scans (A) revealed areas with hyperintensity in the spinal cord. Sagittal and coronal 3D constructive interference in steady state (CISS) imaging (D, E) disclosed a tortuous vascular structures (arrows) along the spinal cord. The SDAVF was diagnosed by intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (F). The site of the SDAVF was the third lumbar vertebral level (arrow). Both readers judged this as grade 3 on 3D CISS and grade 1 on conventional MR images for the identification of abnormal vessels. 4 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences
5 CISS Imaging of Spinal Dural AVF patients with SAVF. However, if the shunt volume is small, no abnormal vessels may be observed on conventional sequences. 1,12 In our 3T MRI study, we observed flow voids on 13% of WI- and on 69 81% of WI scans. Krings and Geibprasert 1 suggested that for the identification of abnormal vessels of SDAVF, heavily sequences were more useful than standard WI scans. Morris et al. 8 reported three cases in which MRI with 3D CISS and 3D phase-cycled fast imaging employing steady state acquisition (PC-FIESTA) was useful not only for the documentation but also the localization of difficult-to-find SDAVF. To our knowledge, ours is the first systematic comparison of the usefulness of 3D CISS images and conventional MRI for the evaluation of SDAVF. As the 3D CISS sequence does not require the use of gadolinium-based contrast agents, it avoids the risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. 13 Suspecting the presence of abnormal vessels associated with SDAVF is important for their early diagnosis and following treatment. As the 3D CISS sequence does not involve contrast media and provides useful information about the presence of abnormal vessels associated with SDAVF, it should be added to routine MR studies for SDAVF screening. Our study presents several limitations. First, we evaluated only axial and sagittal planes with the SE images. The combination of sagittal, axial, and coronal SE sequences may have resulted in the detection of more abnormal vessels associated with SDAVF; however, it is time-consuming. Thus, we can t use that for whole spine evaluation in patients with SDAVF in the clinical situation. 3D CISS images can be reconstructed in any desired cross-sections and such reconstructions along a curved or tilted section are especially useful in these patients. Second, although contrast-enhanced 3D gradient-echo sequences may be useful for the evaluation of spinal arteriovenous shunt lesions 14, we did not assess them in this study. Further studies are needed to clarify the usefulness of 3D CISS imaging compared with contrast-enhanced 3D gradient-echo sequences. Third, 3D CISS images couldn t assess the intramedullary abnormalities related with SDAVF. SE WI scans can demonstrate intramedullary signal changes of the spinal cord associated with SDAVF. We think that 3D CISS and SE WI sequences are complementary imaging methods for the evaluation of SDAVF. Finally, we evaluated only the patients with SDAVF using conventional sequences and CISS images. Since 3D CISS image has a high sensitivity for detection of small structures surrounded by CSF, it remains the possibility that redundant nerve roots of the cauda equine and mild dilated normal veins are interpreted as tortuous abnormal veins associated SDAVF. We think that it is important to detect intramedullary hyperintensity and tortuous vessels for diagnosis of SDAVF, therefore the combination coronal reconstruction of 3D CISS and SE WI sequences are useful for the evaluation of SDAVF. Further studies with comparison between patients with SDAVF and spinal canal stenosis are needed to clarify the usefulness of 3D CISS in the clinical setting. Conclusion The 3D CISS sequence is useful for evaluating the abnormal vessels of SDAVF and should be added to routine MR examinations in patients suspected of harboring SDAVF. Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. References 1. Krings T, Geibprasert S. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2009; 30: Jellema K, Tijssen CC, van Gijn J. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: a congestive myelopathy that initially mimics a peripheral nerve disorder. Brain 2006; 129: Cenzato M, Versari P, Righi C, Simionato F, Casali C, Giovanelli M. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulae: analysis of outcome in relation to pretreatment indicators. Neurosurgery 2004; 55: ; discussion Gilbertson JR, Miller GM, Goldman MS, Marsh WR. Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas: MR and myelographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1995; 16: Hurst RW, Grossman RI. Peripheral spinal cord hypointensity on T2 MR images: a reliable imaging sign of venous hypertensive myelopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000; 21: Ramli N, Cooper A, Jaspan T. High resolution CISS imaging of the spine. Br J Radiol 2001; 74: Krings T, Lasjaunias PL, Hans FJ, et al. Imaging in spinal vascular disease. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 2007; 17: Morris JM, Kaufmann TJ, Campeau NG, Cloft HJ, Lanzino G. Volumetric myelographic magnetic resonance imaging to localize difficult-to-find spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg Spine 2011; 14: Hirai T, Korogi Y, Shigematsu Y, et al. Evaluation of syringomyelia with three-dimensional constructive interference in a steady state (CISS) sequence. J Magn Reson Imaging 2000; 11: Haacke EM, Wielopolski PA, Tkach JA, Modic MT. Steadystate free precession imaging in the presence of motion: application for improved visualization of the cerebrospinal fluid. Radiology 1990; 175: Toossi S, Josephson SA, Hetts SW, et al. Utility of MRI in spinal arteriovenous fistula. Neurology 2012; 79: Miller TR, Eskey CJ, Mamourian AC. Absence of abnormal vessels in the subarachnoid space on conventional magnetic resonance imaging in patients with spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Focus 2012; 32:E Yang L, Krefting I, Gorovets A, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and class labeling of gadolinium-based contrast agents by the food and drug administration. Radiology 2012; 265: Akter M, Hirai T, Kitajima M, et al. Type 1 perimedullary arteriovenous fistula with subarachnoid hemorrhage: utility of contrast-enhanced 3D gradient-echo technique. Magn Reson Med Sci 2011; 10: Epub ahead of print 5
Spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas (SDAVF) are the most commonly
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Comparison of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced 3T MR and 64-Row Multidetector CT Angiography for the Localization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas S. Oda, D. Utsunomiya, T. Hirai,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Comparison of Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced 3T MR and 64-Row Multidetector CT Angiography for the Localization of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas S. Oda, D. Utsunomiya, T. Hirai,
Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1932 Role of Three-Dimensional Rotational Angiography in the Treatment of Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Yigit Ozpeynirci 1, Bernd Schmitz 2, Melanie Schick
Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR?
 Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR? Poster No.: C-3378 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J. C. Röper-Kelmayr 1, C. Ginthör 1, D. Flöry 1, R. Chapot
Spinal dural AV fistula: One stop shop imaging with MR? Poster No.: C-3378 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: J. C. Röper-Kelmayr 1, C. Ginthör 1, D. Flöry 1, R. Chapot
Evaluation of Intracranial Vasculatures in Healthy Subjects with Arterial-Spin-Labeling-Based 4D-MR Angiography at 3T
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 335 339, 2016 doi:10.2463/mrms.tn.2015-0081 TECHNICAL NOTE Evaluation of Intracranial Vasculatures in Healthy Subjects with Arterial-Spin-Labeling-Based 4D-MR Angiography
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 15, No. 3, pp. 335 339, 2016 doi:10.2463/mrms.tn.2015-0081 TECHNICAL NOTE Evaluation of Intracranial Vasculatures in Healthy Subjects with Arterial-Spin-Labeling-Based 4D-MR Angiography
SDAVFs are rare acquired vascular lesions predominantly
 CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
CLINICAL REPORT W.J. van Rooij R.J. Nijenhuis J.P. Peluso M. Sluzewski G.N. Beute B. van der Pol Spinal Dural Fistulas without Swelling and Edema of the Cord as Incidental Findings SUMMARY: SDAVFs cause
Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:781 786, April 2000 Peripheral Spinal Cord Hypointensity on T2-weighted MR Images: A Reliable Imaging Sign of Venous Hypertensive Myelopathy Robert W. Hurst and Robert I. Grossman
MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases
 833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
833 MR Imaging of Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations at 0.5 T: Study of 34 Cases D. Dormont 1 F. Gelbert 2 E. Assouline 2 D. Reizine 2 A. Helias 2 M. C. Riche 2 J. Chiras 1 J. Sories 1 J. J. Merland
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Arteriovenous (AV) shunts of the spinal cord and its meninges
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Mull R.J. Nijenhuis W.H. Backes T. Krings J.T. Wilmink A. Thron Value and Limitations of Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography in Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH M. Mull R.J. Nijenhuis W.H. Backes T. Krings J.T. Wilmink A. Thron Value and Limitations of Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography in Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations and Dural Arteriovenous
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
The Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Grading Cervical Neural Foraminal Stenosis Based on Oblique Sagittal Images
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI for Grading Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Chul Hee Han 1 So Yeon Lee 1 Eun
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI for Grading Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Chul Hee Han 1 So Yeon Lee 1 Eun
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Non Contrast MRA. Mayil Krishnam. Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine
 Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Localization and Treatment of Unruptured Paraclinoid Aneurysms: A Proton Density MRI-based Study
 Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.3.180 Original Article Localization and Treatment of Unruptured Paraclinoid
Journal of Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery pissn 2234-8565, eissn 2287-3139, http://dx.doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.3.180 Original Article Localization and Treatment of Unruptured Paraclinoid
Cervical Spondylosis: Three-dimensional Gradient-Echo MR with Magnetization Transfer
 Cervical Spondylosis: Three-dimensional Gradient-Echo MR with Magnetization Transfer Elias R. Melhem, Mark L. Benson, Norman J. Beauchamp, and Roland R. Lee PURPOSE: To compare a three-dimensional Fourier
Cervical Spondylosis: Three-dimensional Gradient-Echo MR with Magnetization Transfer Elias R. Melhem, Mark L. Benson, Norman J. Beauchamp, and Roland R. Lee PURPOSE: To compare a three-dimensional Fourier
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
MAJOR PAPER. Introduction
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; 217 222 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0072 Published Online: October 11, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Benefit of 3T Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Comparison to Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging
Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; 16; 217 222 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2016-0072 Published Online: October 11, 2016 MAJOR PAPER Benefit of 3T Diffusion-weighted Imaging in Comparison to Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
S. Inagawa, N. Yoshimura, Y. Ito; Niigata/JP spinal sacral areteriovenous fistulae, CTA, MRA /ecr2010/C-2581
 Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Localization of sacral spinal arteriovenous fistulae in reference to the dural structure with CTA and MRA of high spatial resolution: A pictorial essay Poster No.: C-2581 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational
Venous Infarction of the Spinal Cord Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: MR Imaging
 739 Venous Infarction of the Spinal Cord Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: MR Imaging Findings E-M. Larsson 1 P. Desai 1 C. W. Hardin 2 J. Story 3 J. R. Jinkins 1 Three patients with spinal dural
739 Venous Infarction of the Spinal Cord Resulting from Dural Arteriovenous Fistula: MR Imaging Findings E-M. Larsson 1 P. Desai 1 C. W. Hardin 2 J. Story 3 J. R. Jinkins 1 Three patients with spinal dural
Cervical Spine: Three-dimensional Fast Spin-Echo MR Imaging Improved Recovery of Longitudinal Magnetization with Driven Equilibrium Pulse 1
 Elias R. Melhem, MD Ryuta Itoh, MD, PhD Paul J. M. Folkers, PhD Index terms: Magnetic resonance (MR), technology, 34.121419 Spinal cord, MR, 341.121419 Spine, MR, 34.121419 Radiology 2001; 218:283 288
Elias R. Melhem, MD Ryuta Itoh, MD, PhD Paul J. M. Folkers, PhD Index terms: Magnetic resonance (MR), technology, 34.121419 Spinal cord, MR, 341.121419 Spine, MR, 34.121419 Radiology 2001; 218:283 288
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
How I do it: Non Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography (syngo NATIVE)
 Clinical How-I-do-it Cardiovascular How I do it: Non Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography (syngo NATIVE) Manuela Rick, Nina Kaarmann, Peter Weale, Peter Schmitt Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany Introduction
Clinical How-I-do-it Cardiovascular How I do it: Non Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography (syngo NATIVE) Manuela Rick, Nina Kaarmann, Peter Weale, Peter Schmitt Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany Introduction
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Cerebral cavernous malformation (CCM) comprise
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.M. de Souza R.C. Domingues L.C.H. Cruz, Jr. F.S. Domingues T. Iasbeck E.L. Gasparetto Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging for the Evaluation of Patients with Familial Cerebral Cavernous
Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization after coil embolization of visceral artery aneurysms
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(1): 64-68 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.883769 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.09.29 Accepted: 2013.01.15 Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2013; 78(1): 64-68 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.883769 CASE REPORT Received: 2012.09.29 Accepted: 2013.01.15 Time-resolved Magnetic Resonance Angiography for assessment of recanalization
CT is generally the preferred imaging technique in the assessment
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.H. Miller T. Walkiewicz R.B. Towbin J.G. Curran Improved Delineation of Ventricular Shunt Catheters Using Fast Steady-State Gradient Recalled-Echo Sequences in a Rapid Brain MR Imaging
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J.H. Miller T. Walkiewicz R.B. Towbin J.G. Curran Improved Delineation of Ventricular Shunt Catheters Using Fast Steady-State Gradient Recalled-Echo Sequences in a Rapid Brain MR Imaging
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
MRI of chronic spinal cord injury
 The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report
 Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
Non-Invasive Follow-up Evaluation of Post-Embolized AVM with Time-Resolved MRA: A Case Report Yong Woon Shim, MD 1 Tae-Sub Chung, MD 1 Won-Suk Kang, MD 1 Jin-Yang Joo, MD 2 Ralph Strecker, MD 3 Juergen
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego. MR Angiography. Techniques & Applications. John R. Hesselink, M.D.
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Comparison of MERGE and Axial T2-Weighted Fast Spin-Echo Sequences for Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions in the Cervical Spinal Cord
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Martin et al. MRI Detection of Multiple Sclerosis Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Original Research Nancy Martin 1 David Malfair 2 Yinshan Zhao
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition
 637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
637 MR Flow Imaging in Vascular Malformations Using Gradient Recalled Acquisition William M. Needell 1 Kenneth R. Maravilla Twenty patients with known or suspected intracranial vascular lesions were evaluated
The Behavior of Pantopaque on MR: In Vivo and In Vitro
 997 The Behavior of Pantopaque on MR: In Vivo and In Vitro Analyses Ira F. Braun 1 John A. Maiko Patricia C. Davis James C. Hoffman, Jr. Louis H. Jacobs MR imaging is considered by many to be the procedure
997 The Behavior of Pantopaque on MR: In Vivo and In Vitro Analyses Ira F. Braun 1 John A. Maiko Patricia C. Davis James C. Hoffman, Jr. Louis H. Jacobs MR imaging is considered by many to be the procedure
CSM is the most common cause of spinal cord dysfunction
 Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Published December 22, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2756 ORIGINAL RESEARCH T. Sato T. Horikoshi A. Watanabe M. Uchida K. Ishigame T. Araki H. Kinouchi Evaluation of Cervical Myelopathy Using Apparent Diffusion
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at the Craniocervical Junction with Perimedullary Venous Drainage
 Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at the Craniocervical Junction with Perimedullary Venous Drainage Mario Mascalchi, Fabio Scazzeri, Daniele Prosetti, Giampiero Ferrito, Fabrizio Salvi, and Nello Quilici Summary:
Dural Arteriovenous Fistula at the Craniocervical Junction with Perimedullary Venous Drainage Mario Mascalchi, Fabio Scazzeri, Daniele Prosetti, Giampiero Ferrito, Fabrizio Salvi, and Nello Quilici Summary:
Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with detachable
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Pierot C. Delcourt F. Bouquigny D. Breidt B. Feuillet O. Lanoix S. Gallas Follow-Up of Intracranial Aneurysms Selectively Treated with Coils: Prospective Evaluation of Contrast-Enhanced
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Pierot C. Delcourt F. Bouquigny D. Breidt B. Feuillet O. Lanoix S. Gallas Follow-Up of Intracranial Aneurysms Selectively Treated with Coils: Prospective Evaluation of Contrast-Enhanced
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME
 Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME Po-An Tai, Yong-Kwang Tu, and Hon-Man Liu 1 Background and purpose: Spinal
Spinal Arteriovenous Malformations SURGICAL TREATMENT OF SPINAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: VASCULAR ANATOMY AND SURGICAL OUTCOME Po-An Tai, Yong-Kwang Tu, and Hon-Man Liu 1 Background and purpose: Spinal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children
 Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Detection of Leptomeningeal CNS Metastases in Children Noah D. Sabin, M.D. Julie H. Harreld M.D. Kathleen J. Helton M.D. Zoltan Patay M.D., Ph.D. St. Jude Children s Research Hospital Memphis, TN Leptomeningeal
Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: MR and Myelographic Findings
 Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: MR and Myelographic Findings Julie R. Gilbertson, Gary M. Miller, Marc S. Goldman, and W. Richard Marsh PURPOSE: To examine the clinical and radiographic findings in
Spinal Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas: MR and Myelographic Findings Julie R. Gilbertson, Gary M. Miller, Marc S. Goldman, and W. Richard Marsh PURPOSE: To examine the clinical and radiographic findings in
Published November 13, 2014 as /ajnr.A4164
 Published November 13, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4164 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Time-Resolved Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography of Spinal Vascular Malformations M. Amarouche, J.L. Hart, A. Siddiqui, T. Hampton,
Published November 13, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4164 ORIGINAL RESEARCH SPINE Time-Resolved Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography of Spinal Vascular Malformations M. Amarouche, J.L. Hart, A. Siddiqui, T. Hampton,
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression
 MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography
 Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
Anatomic Evaluation of the Circle of Willis: MR Angiography versus Intraarterial Digital Subtraction Angiography K. W. Stock, S. Wetzel, E. Kirsch, G. Bongartz, W. Steinbrich, and E. W. Radue PURPOSE:
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
 THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
Three-dimensional FISP Imaging in the Evaluation of Carotid Cavernous Fistula: Comparison with Contrast-Enhanced CT and Spin-Echo MR
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:253 259, February 1998 Three-dimensional Imaging in the Evaluation of Carotid Cavernous Fistula: Comparison with and Toshinori Hirai, Yukunori Korogi, Satoshi Hamatake, Ichiro
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:253 259, February 1998 Three-dimensional Imaging in the Evaluation of Carotid Cavernous Fistula: Comparison with and Toshinori Hirai, Yukunori Korogi, Satoshi Hamatake, Ichiro
Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:13 17, January 2003 Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT Kohsuke Kudo, Satoshi Terae, Takeshi Asano, Masaki Oka, Kenshi Kaneko,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:13 17, January 2003 Anterior Spinal Artery and Artery of Adamkiewicz Detected by Using Multi-Detector Row CT Kohsuke Kudo, Satoshi Terae, Takeshi Asano, Masaki Oka, Kenshi Kaneko,
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal Cord without Evidence of Spinal Cord Herniation or an Intradural Mass
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
AS is the most common cause of the obstructive hydrocephalus.
 Published December 15, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2833 ORIGINAL RESEARCH O. Algin B. Turkbey Evaluation of Aqueductal Stenosis by 3D Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different
Published December 15, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2833 ORIGINAL RESEARCH O. Algin B. Turkbey Evaluation of Aqueductal Stenosis by 3D Sampling Perfection with Application-Optimized Contrasts Using Different
Spinal Arteriovenous Shunts: Angioarchitecture and Historical Changes in Classification
 REVIEW ARTICLE doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0316 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 57, 356 365, 2017 Spinal Arteriovenous Shunts: Angioarchitecture and Historical Changes in Classification Keisuke Takai 1 Online May
REVIEW ARTICLE doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2016-0316 Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 57, 356 365, 2017 Spinal Arteriovenous Shunts: Angioarchitecture and Historical Changes in Classification Keisuke Takai 1 Online May
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Pankaj Sharma, Alok Ranjan, Rahul Lath
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Case Journal Report Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):365-370 Filum terminale http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.365 arteriovenous fistula 365 Arteriovenous Fistula of the Filum
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Case Journal Report Asian Spine J 2014;8(3):365-370 Filum terminale http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2014.8.3.365 arteriovenous fistula 365 Arteriovenous Fistula of the Filum
Neurovascular elements of the PCF
 Level I: Neurovascular elements of the PCF Trigeminal and Abducent Superior cerebellar artery and vein Dandy s vein Level II: Facial and Cochleovestibular AICA and internal auditory artery, veins Level
Level I: Neurovascular elements of the PCF Trigeminal and Abducent Superior cerebellar artery and vein Dandy s vein Level II: Facial and Cochleovestibular AICA and internal auditory artery, veins Level
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine
 NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 3: 49-53, 2013 www.centauro.it Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine K-A. MARDAL 1, G. RUTKOWSKA 1, S. LINGE 1.2, V. HAUGHTON 3 1 Center
NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 3: 49-53, 2013 www.centauro.it Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine K-A. MARDAL 1, G. RUTKOWSKA 1, S. LINGE 1.2, V. HAUGHTON 3 1 Center
Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy
 IJCMR 836 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy Vivek E 1, Abubacker Sulaiman F 2, Srinivasa Mudali K 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Low-back pain (LBP)
IJCMR 836 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Diagnostic Value of 3D Fiesta Sequence in Imaging of Lumbar Radiculopathy Vivek E 1, Abubacker Sulaiman F 2, Srinivasa Mudali K 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Low-back pain (LBP)
Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis
 Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis Poster No.: C-3377 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
Optimized phase contrast MRV technique outperforms timeof-flight in the diagnosis of cerebral venous thrombosis Poster No.: C-3377 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit
Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage posterior surgery: a case report
 Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
Iizuka et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2014, 8:421 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Giant schwannoma with extensive scalloping of the lumbar vertebral body treated with one-stage
Case Report. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUTION
 Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2011; 35: 928-933 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.928 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Cauda Equina Syndrome Caused by Spinal Dural
Case Report Ann Rehabil Med 2011; 35: 928-933 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2011.35.6.928 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Cauda Equina Syndrome Caused by Spinal Dural
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
A quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid flow in post-traumatic syringomyelia
 Paraplegia (1995) 33, 203-207 1995 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 0031-1758/95 $9.00 A quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid flow in post-traumatic syringomyelia
Paraplegia (1995) 33, 203-207 1995 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 0031-1758/95 $9.00 A quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid flow in post-traumatic syringomyelia
Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck
 Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.827 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):827-835 Evaluation of Aqueductal Patency in Patients
Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.827 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):827-835 Evaluation of Aqueductal Patency in Patients
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol. for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS. David K.B.
 Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
SPINAL EPIDURAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: REPORT OF A CASE WITH DISCUSSION OF CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT
 SPINAL EPIDURAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: REPORT OF A CASE WITH DISCUSSION OF CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT Caitlin M. Clark, B.A. and W. Craig Clark, M.D., Ph.D., FAANS, FACS, FICS INTRODUCTION True
SPINAL EPIDURAL ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS: REPORT OF A CASE WITH DISCUSSION OF CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT Caitlin M. Clark, B.A. and W. Craig Clark, M.D., Ph.D., FAANS, FACS, FICS INTRODUCTION True
CARDIAC MRI. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Overview
 CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
Management of spinal dural arteriovenouse fistula
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 4 2017 October-December Article Management of spinal dural arteriovenouse fistula A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion, N. Dobrin, I. Poeată ROMANIA DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0074
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 4 2017 October-December Article Management of spinal dural arteriovenouse fistula A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion, N. Dobrin, I. Poeată ROMANIA DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2017-0074
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Historical perspective
 SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
SPINAL AVM Introduction Vascular malformations of spinal cord are a rare clinical entity, representing 5% of all primary spinal cord lesions, with arteriovenous malformations(avm) & cavernous malformations
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus. Disclosures. Pulsatile Tinnitus: Differential Diagnosis. Pulsatile Tinnitus
 Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy
 Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
Original Study Static and dynamic cervical MRI: two useful exams in cervical myelopathy Lorenzo Nigro 1, Pasquale Donnarumma 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Marika Rullo 2, Antonio Santoro 1, Roberto Delfini 1
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
Diagnosis of Vertebral Artery Ostial Stenosis on Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography: Usefulness of a Thin-Slab MIP Technique
 Diagnosis of Vertebral Artery Ostial Stenosis on Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography: Usefulness of a Thin-Slab MIP Technique Sun Mi Kim 1, Deok Hee Lee 2 Jin Woo Choi 3, Byung Se Choi 4, Hyun Sin In 5 It
Diagnosis of Vertebral Artery Ostial Stenosis on Contrast-Enhanced MR Angiography: Usefulness of a Thin-Slab MIP Technique Sun Mi Kim 1, Deok Hee Lee 2 Jin Woo Choi 3, Byung Se Choi 4, Hyun Sin In 5 It
Extracranial Carotid Arteries: Evaluation with Black Blood MR Angiography
 Robert R. Edelman, MD #{149} Heinrich P. Mattle, MD #{149} Bernd Wallner, MD #{149} Richard Bajakian, MD #{149} Jonathan Kleefield, MD #{149} Craig Kent, MD #{149} John J. Skillman, MD Jeffrey B. Mendel,
Robert R. Edelman, MD #{149} Heinrich P. Mattle, MD #{149} Bernd Wallner, MD #{149} Richard Bajakian, MD #{149} Jonathan Kleefield, MD #{149} Craig Kent, MD #{149} John J. Skillman, MD Jeffrey B. Mendel,
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA
 Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a disabling chronic demyelinating disease
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
Diagn Interv Radiol 2010; 16:106 111 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imaging of active multiple sclerosis plaques: efficiency of contrast-enhanced magnetization transfer
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
Recently, diagnostic imaging methods for spinal
 J Neurosurg Spine 18:398 408, 2013 AANS, 2013 Three-dimensional angioarchitecture of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas, with special reference to the intradural retrograde venous drainage system Clinical
J Neurosurg Spine 18:398 408, 2013 AANS, 2013 Three-dimensional angioarchitecture of spinal dural arteriovenous fistulas, with special reference to the intradural retrograde venous drainage system Clinical
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening. Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006
 Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Blunt Carotid Injury- CT Angiography is Adequate For Screening Kelly Knudson, M.D. UCHSC April 3, 2006 CT Angiography vs Digital Subtraction Angiography Blunt carotid injury screening is one of the very
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging
 Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Morphological changes of the cervical spinal canal and cord due to aging on MR imaging Shigeru Kobayashi, MD,PhD 1, Katsuhiko Hayakawa, MD, PhD 2, Takashi Nakane, MD, PhD 2, Riya Kosaka MD,PhD 3. 1 Department
Perforating arteries originating from the posterior communicating artery: a 7.0-Tesla MRI study
 Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 2986 2992 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1485-4 MAGNETIC RESONANCE Mandy M. A. Conijn Jeroen Hendrikse Jaco J. M. Zwanenburg Taro Takahara Mirjam I. Geerlings Willem P. Th. M. Mali Peter
Eur Radiol (2009) 19: 2986 2992 DOI 10.1007/s00330-009-1485-4 MAGNETIC RESONANCE Mandy M. A. Conijn Jeroen Hendrikse Jaco J. M. Zwanenburg Taro Takahara Mirjam I. Geerlings Willem P. Th. M. Mali Peter
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
Supplementary Online Content Schlaeger R, Papinutto N, Zhu AH, et al. Association between thoracic spinal cord gray matter atrophy and disability in multiple sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. Published online June
