FieldStrength. Pediatric neuro, MSK, whole body imaging
|
|
|
- Maryann Alaina Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric neuro, MSK, whole body imaging Tokai University reports on benefits of Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit University of Michigan praises Elite Breast solution for biopsies SmartExam for efficient, reproducible shoulder imaging at PAMF Maastricht performs MRA of spinal cord blood vessels FreeWave upgrade for Intera 1.5T boosts throughput
2 Pediatric protocols must adapt coil selection, field of view, and in-plane resolution to children s smaller anatomy. This often adversely affects SNR, and sequences must be refined to remain diagnostic. J. Herman Kan, MD, see page 22 Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright holder. Philips Medical Systems Nederland B.V. reserves the right to make changes in specifications or to discontinue any product, at any time, without notice or obligation, and will not be liable for any consequences resulting from the use of this publication. Printed in the Netherlands FieldStrength is also available via the Internet: Editor-in-chief Karen Janssen Editorial team Petra Beekmans, Ruud de Boer (PhD), Jan De Becker, Andre van Est, Paul Folkers (PhD), Karen Janssen. Contributors Dr. Abidi, Amjad Alkadri (MD), Nancy Babich, Walter Backes (PhD), Tracy Byers, Tom Chenevert (PhD), Ian Crick, Caroline Daly (MD), Frits de Graaf, Jerry Duncan, PJ Early, John Feller (MD), Sue Fowler, Liesbeth Geerts (PhD), Gabriel Gonzalez, Hyun Woo Goo (MD), Greg Harpel, David Hegarty, Dave Hitt, Yutaka Imai (MD, PhD), Marko Ivancevic (PhD), Karen Janssen, James Joers (PhD), Herman Kan (MD), Nozomu Koyama, Kenneth Martin (MD), Peter Morris (PhD), Dr. Naik, Hidetomo Takase, Takayuki Tamura, Marius van Meel. Subscriptions Please register on Correspondence FieldStrength@philips.com or FieldStrength, Philips Healthcare, Building QR 0119 P.O. Box , 5680 DA Best, The Netherlands Notice FieldStrength is published three times per year for users of Philips MRI systems. FieldStrength is a professional magazine for users of Philips medical equipment. It provides the healthcare community with results of scientific studies performed by colleagues. Some articles in this magazine may describe research conducted outside the USA on equipment not yet available for commercial distribution in the USA. Some products referenced may not be licensed for sale in Canada. 2 FieldStrength Issue 38 August 2009
3 In this issue NetForum Visit the NetForum User Community for downloading ExamCards and viewing application tips, clinical cases, extended versions of FieldStrength articles, and more. Reports from our users New MultiTransmit technology advances 3.0T imaging Prof. Imai reports significant benefits for image quality and exam speed on the Achieva 3.0T TX. University of Michigan praises Elite Breast solution for biopsies Dr. Daly, Dr. Chenevert see excellent imaging and simplified biopsy procedures with MammoTrak. SmartExam Shoulder enables efficient, reproducible imaging PAMF combines SmartExam with their high resolution, small FOV exams for high quality, consistent MR images. MRA is powerful tool for imaging spinal cord blood vessels Dr. Backes, Maastricht University Hospital, uses non-invasive MRA as an alternative for imaging spinal cord blood vessels. DMI sees jump in image quality with Achieva XR According to Dr Feller, his busy imaging practice is ready to ramp up to 3.0T at short notice. Upgrade for Intera 1.5T boosts throughput at Hiroshima scanning center According to Takayuki Tamura, a FreeWave upgrade improves imaging and increases throughput and profitability. Hospitals deploy Panorama HFO as an all purpose MRI scanner Panorama HFO serves all MRI needs of both Community Memorial Hospital, Hicksville and Porter Hospital, Valparaiso. Realizing the full potential of a 3.0T MRI system Utilization services use Kaizen Event to improve productivity at Al Zahra Hospital, UAE. Pediatric imaging B-FFE enables superb pediatric neuro imaging Dr Martin, Oakland, uses high resolution, good contrast of B-FFE to visualize small detail in pediatric neuro MR. Asan Medical Center proves the power of pediatric whole body MRI Dr. Goo performs whole body MRI of pediatric patients on Achieva 1.5T and 3.0T. Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Dr Kan, Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital, builds dedicated scans for many different applications in musculoskeletal MRI. Clinical case report DWI of the breast at 3.0T Research Carbon-13 spectroscopy at 7.0T MR news MultiTransmit takes award at ISMRM FieldStrength is going green NetForum news Application tips Tips for acetabular radial hip imaging Calendars Education / Events calendar FieldStrength 3
4 MR news - ISMRM 2009 MultiTransmit takes award at ISMRM Parallel RF transmission technology in clinical 3T imaging attracts attention at the 2009 ISMRM meeting in Honolulu MultiTransmit was well represented in the scientific program at ISMRM 2009, with five presentations by the University of Bonn, explicating their findings in liver, pelvis, breast and spine imaging. The e-poster on clinical results with MultiTransmit was awarded. Winfried Willinek, MD received an award for his e-poster presentation Parallel RF transmission in body MRI for reduced dielectric shading, improved B1 homogeneity and accelerated imaging at 3.0T: Initial clinical experience in 40 patients using MultiTransmit in the Body Imaging category, indicative of the clinical importance of MultiTransmit. Philips lunch symposium a success Dr. Willinek also gave an excellent presentation at the Philips Gold Corporate lunch symposium at ISMRM, in which he emphasized that 3T is mature for all applications, and provides superb image quality. Additionally, he added, MultiTransmit provides the benefits of improved image contrast, consistency and shorter scan times, which results in increased value, particularly in more challenging patients. He substantiated his points with many outstanding clinical cases demonstrating the benefits of Achieva 3.0T TX. ISMRM Other speakers at the attention-getting symposium included Joop van Vaals, PhD, on Philips new developments and research. Prof. Peter Luyten, PhD, of University Medical Center, Utrecht, shared examples of research results from the Philips 7.0T User Group. 4 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
5 Achieva 3.0T TX in Bonn Achieva 3.0T TX event in Bonn The University of Bonn (Germany) has been the fi rst institution in the world to use Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit in a clinical setting. The University recently hosted a special symposium featuring Dr. Willinek, Prof. Klaas Pruessmann (Zurich) and other prominent speakers to formally celebrate the inauguration of its Achieva 3.0T TX. Several members of the press were in attendance, and a segment featuring Dr. Willinek was broadcast on German television. Dear Friends, The highlight at this year s ISMRM was Philips MultiTransmit, introduced at last year s RSNA. Several papers provided excellent clinical evidence of the value of this clever technology. And even the competition mentioned that MultiTransmit is the future of 3.0T imaging. The Philips lunch symposium was a great success, with high attendance and a fascinating presentation by Winfried Willinek, MD, demonstrating the clinical benefi ts of Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit: improved image homogeneity and consistency, better contrast and shorter scan times. This issue of FieldStrength features a report on Achieva 3.0T TX from Tokai University in Japan. It also focuses on pediatric MR imaging, with articles describing different approaches and techniques required for MRI of pediatric patients. I hope you enjoy reading this issue of FieldStrength! ISMRM Tracy W. Byers VP and Business Manager MRI Philips Healthcare USA FieldStrength 5
6 New MultiTransmit technology advances 3.0T imaging Tokai University School of Medicine reports significant benefits for image quality and exam speed on the Achieva 3.0T TX Tokai University School of Medicine has been evaluating the Achieva 3.0T TX with Philips new MultiTransmit technology since last February. Dr. Yutaka Imai, Professor of Radiology and Dean of Tokai University, believes MultiTransmit is an important advancement for 3.0T MRI. Even after just three months, he is committed to ensuring that his next MRI scanner will be another Achieva 3.0T TX, as he considers MultiTransmit essential for the future of 3.0T MRI. Prof. Yutaka Imai MultiTransmit technology embodied in the new Achieva 3.0T TX was developed by Philips to overcome fundamental challenges associated with high-field MRI. The study reports that by using multiple RF sources, MultiTransmit dramatically reduces dielectric shading effects, resulting in significantly better image uniformity and consistency for each and every patient. The power, amplitude, phase and waveform of all RF sources are automatically adjusted for optimal uniformity in each patient s unique anatomy. In addition, local Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) can be reduced, allowing increases in scanning speed by up to 40%. In the first two months after installation, the Department of Radiology at Tokai University School Conventional MultiTransmit Very large ovarian cyst In T2-weighted images of this large ovarian cystadenocarcinoma, the shading caused by fluid in the cyst is considerably reduced by MultiTransmit. 6 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
7 Liver image uniformity In these T2-weighted images of the liver, the shading caused by dielectric effects is dramatically reduced in the Achieva 3.0T TX. MultiTransmit also provides better signal uniformity on the high resolution liver images after administration of EOB at delayed phase. Conventional - T2-Weighted MultiTransmit - T2-Weighted Conventional - EOB delayed MultiTransmit - EOB delayed of Medicine, Kanagawa, Japan scanned both healthy volunteers and patients on its new Achieva 3.0T TX scanner. Initially, Professor Imai and his colleagues made direct comparisons by scanning with and without MultiTransmit. In these comparison studies, the MultiTransmit images were clearly superior, he recalls. The Achieva 3.0T TX has definitely come up to expectations. When imaging large volume masses, the shading that you can sometimes get with traditional high field systems is dramatically reduced. We noticed that consistently from the first scans we did. reduced and the enhanced image quality helps us significantly in diagnosis. Fat suppression is also far more homogeneous than with traditional 3.0T systems, he says. The Tokai radiologists are also using the Achieva 3.0T TX in other areas that have traditionally been challenging at 3.0T, for instance spine, breast, upper abdomen and pelvis. In all application areas we see dramatic improvements in imaging quality and uniformity, says Professor Imai. Imaging challenging anatomies Professor Imai particularly sees benefits for liver imaging and patients with a large amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity. For patients with hepatocellular carcinoma, an MR exam is essential to exclude the possibility of other small lesions being present before surgery. But these are some of the most challenging MR exams, especially at high field strengths due to shading caused by the large amount of ascites surrounding the liver. The same effect is observed with fluid surrounding large ovarian cysts. With MultiTransmit, the dielectric shading is dramatically In the case of cervical spondylosis, for example, we are able to use a 180º refocusing pulse instead of 120º because local SAR is well controlled in the Achieva 3.0T TX. This means that contrast in the cerebrospinal fluid and the spinal cord is markedly improved. In breast imaging too, the RF signal can be adapted on a patient-by-patient basis, leading to greater signal uniformity of bilateral breast tissues and more accurate evaluation of the tumor vessels. We also routinely obtain excellent T2-weighted images of the biliary system and, using MRCP with the Achieva 3.0T TX, we FieldStrength 7
8 T2-weighted MRCP can clearly depict the main pancreatic duct. In general, we find that MultiTransmit also provides far greater contrast between enhanced and unenhanced tissues on T1-weighted post-contrast images. Biliary system and pancreatic duct The T2-weighted coronal image clearly depicts intra-hepatic and common bile ducts with excellent signal uniformity. MRCP shows all courses of the main pancreatic duct. Faster spine and pelvic exams One of the important benefits of MultiTransmit is that it leads to a reduction of local SAR, allowing the system to be driven harder. This allows significant increases in scanning speed without compromising image quality a fact readily appreciated by Professor Imai: We found that scan times could be cut, on average by around 30%, which makes the exams much easier for patients, especially those with painful back or pelvic conditions who may be unable to lie still for too long. In all application areas we see dramatic improvements in imaging quality and uniformity. The future of 3.0T imaging Professor Imai s first experiences with the new Achieva 3.0T TX system demonstrate the clinical benefits of the MultiTransmit technology. The enhanced image uniformity and consistency over a broad range of applications will enable us to employ the benefits of high-field diagnostic MRI in a wider patient population. I believe that this MultiTransmit technology is absolutely essential for the future development of 3.0T imaging, he says. In fact, at Tokai University we are so impressed with MultiTransmit technology that we have no doubt that the next MRI system we invest in will be another Achieva 3.0T TX. Conventional 5:30 min. MultiTransmit 2:35 min. Conventional MultiTransmit Reduced scan time in pelvis Cervical spondylosis In these T2-weighted pelvic scans, MultiTransmit enables a 55% reduction in scan time. The MultiTransmit image clearly shows reduction of flow void and bright CSF in the spinal canal. This is achieved because MultiTransmit enables the use of a 180 refocusing pulse rather than the conventional FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
9 Benign prostatic hypertrophy In the T2-weighted images of the enlarged prostate, multiple bright nodules are visualized in the transition zone. MultiTransmit images provide better T1 contrast in the prostate after administration of Gd-DTPA. Conventional T2-Weighted MultiTransmit T2-Weighted Post contrast Post contrast Rectal and ovarian cancer In this patient with double cancer, rectal cancer is clearly visualized as a bulky mass. The cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary is shown as both cystic and solid components in the tumor. T2-weighted Post contrast T2-weighted Post contrast FieldStrength 9
10 University of Michigan praises Elite Breast solution for biopsies University of Michigan sees excellent imaging and simplified biopsy procedures with MammoTrak combined with their Achieva 3.0T system Caroline Daly, MD Tom Chenevert, PhD Philips Elite Breast, a complete solution for breast MRI includes the dockable MammoTrak patient support, the 16-channel and 7-channel SENSE Breast coils for imaging and biopsy, and DynaCAD Enterprise for MR analysis and for planning biopsies on the MR console. The University of Michigan Health System (UMHS, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA) is the first in the world with the Elite Breast clinical solution on Achieva 3.0T. The University of Michigan Department of Radiology provides radiology services for the University of Michigan Health System, the University Health Service and the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System, and provides more than 500,000 examinations every year. UHMS is performing breast exams and 3-4 breast biopsies each month. UMHS was first in the world to combine Achieva 3.0T with the MammoTrak dockable patient support. The department completed its first 3.0T biopsies with the Achieva 3.0T scanner and the Elite Breast Clinical Solution in late March Caroline Daly, MD, Assistant Professor, University of Michigan Health System Department of Radiology, says the first and subsequent biopsies have gone very smoothly. We ve done three wire localizations and seven needle biopsies so far with the Breast Elite package. The fact that the patient enters the scanner feet-first is a huge advantage. MammoTrak s patient comfort is a major benefit According to Dr. Daly, the biggest advantage of the Elite Breast solution is the patient comfort provided by the MammoTrak patient support. MammoTrak is designed with the patient in mind, with features such as an adjustable headrest and patient-friendly construction materials. It s hard to biopsy patients who are uncomfortable. The fact that the patient enters the scanner feet-first is a huge advantage. Tom Chenevert, PhD, Professor, University of Michigan Health System Department of Radiology, agrees with Dr. Daly. In biopsies in particular, with the cables and IV lines that are required for a vacuum-assisted biopsy, communication with the patient is sometimes difficult. The feet-first position makes this much easier. The dockability of MammoTrak is another advantage. For localization accuracy, the fact that you re docking the trolley with the integrated coil in a known location in the middle of the magnet is very important, particularly at 3.0T, says Dr. Chenevert. In the head-first position, with a potentially moving table, you could have inaccuracies. From a precision point of view, this is the right way to do it. And the MammoTrak slides over the patient table, so as soon as the patient is removed, another patient can be scanned. 10 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
11 We have very high quality diagnostic images, and we ve been very pleased with the set of cases that we ve done so far. Achieva 3.0T with MammoTrak at UMHS. Dr. Daly says that having the patient farther out of the magnet is much easier on the staff, as well as the patient. It s easier to monitor the patient and the cabling that we need to use for the vacuum-assisted device you re not on a tether quite as much, because her head is out of the magnet, whereas before, if you biopsied on the opposite side of the gantry, you needed every inch of cabling to get the needle to the patient. In addition, she says the new lighting feature, which is built into the 7-channel coil, enables better visualization of the breast for biopsy. Coils enable high image quality MammoTrak comes with two versions of a dedicated breast coil. The open design 7-channel SENSE Breast coil with its integrated lighting allows imaging and biopsy. The 16-channel SENSE Breast coil facilitates superb temporal and spatial resolution for improved visualization of small lesions, important for early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Both allow visualization of a large area that includes the axilla. The image quality is lovely, says Dr. Daly. We have optimized our diagnostic scans, and now we re producing very good quality images. In addition, she says the compression paddles allow more compression from the lateral aspect of the breast than the stand-alone 7-channel Breast coil. The new coil facilitates better compression of the breast and less alteration of patient positioning for biopsy. Needle placement system aids biopsy work Dr. Daly uses both the grid system and the pillar system to perform biopsies, because each has its own advantages. I believe the pillar system has more accurate targeting than the grid system in many cases, but the grid is easier and faster to learn and teach to others. There s a smaller chance of making an error with the targeting when using the grid system because there are fewer moving parts. One of the advantages of the pillar system is the ability to angulate. This provides a greater range of accessible lesions, Dr. Chenevert adds. This is especially important in the case of larger women. Efficient biopsy planning with Invivo DynaCAD shows the optimal trajectory to the breast lesion. After needle placement an additional scan is done to monitor the needle placement and position. MR-guided biopsies can be performed with lateral, medial or cranial access. We ve used DynaCAD from the very start for all our biopsies, says Dr. Daly. It s a very easy to use system, and very straightforward. The biopsy planning software is especially well thought out. FieldStrength 11
12 Marker detection Dynamic e-thrive Biopsy procedure DynaCAD is a very easy to use system. The biopsy planning software is especially well thought out. First a sagittal scan is performed for detection of the fiducial markers that DynaCAD uses to calculate the lesion coordinates for performing the biopsy. Then an axial dynamic e-thrive scan is used to visualize the lesion that will be biopsied. Performed on Achieva 3.0T and MammoTrak with 7-channel SENSE Breast coil. Advantages of 3.0T in breast MR Breast imaging at 3.0T presents many advantages compared to 1.5T, including higher signal-to-noise ratio and better spatial resolution for improved lesion conspicuity. The scans are really beautiful, says Dr. Daly. We have very high quality diagnostic images, and we ve been very pleased with the set of cases that we ve done so far. Many of our patients are post-surgical, so that means they could have clips in place, implanted devices or even breast implants, says Dr. Daly. With the higher magnetic field strength, artifacts due to clips may be stronger, which may make 3.0T imaging more challenging. In our opinion the advantages of 3.0T outweigh the challenges. We have encountered some challenges with scanning large breasts, particularly with combined fat and water saturation in the posterior tissues and chest wall, and some pulsation artifact that particularly affects subtracted images. But I m hopeful that we can overcome these challenges in the near future. The dielectric effect can be challenging at 3.0T, agrees Dr. Chenevert, particularly in large breasts where we desire uniformity over a large field-of-view. That said, in our opinion the advantages of 3.0T outweigh these challenges. In addition, now there are technical solutions to these non-uniformities, since fat suppression has been improved significantly by advanced shim routines and the dielectric effect is greatly mitigated by MultiTransmit and the improved magnet design of Achieva 3.0T. Philips ahead of the curve The features of the Achieva 3.0T system, combined with the superb image quality and workflow benefits of the Elite Breast solution are driving the market toward more effective and efficient means of providing breast MRI at 3.0T. Considering the new American Cancer Society recommendations for breast MRI for women at higher risk for breast cancer, Philips is once again ahead of the curve. 12 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
13 Clinical case report DWI of the breast at 3.0T By Thomas Chenevert, PhD, Mark Helvie, MD, Caroline Daly, MD, (University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) and Marko Ivancevic, PhD (Philips Healthcare) Introduction In diffusion-weighted MR images tissue contrast is based on water mobility properties. It is particularly used for visualization of lesions that alter water mobility relative to surrounding tissues. At the University of Michigan we recently introduced diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) to our 3.0T breast MR examination protocol consisting of T1- and T2-weighted sequences and a dynamic 3D T1 gradient echo sequence. The diffusion-weighted sequence The diffusion sequence is evaluated as an efficient way to localize the area of suspicion by way of reduced water mobility secondary to increased cellular density, thereby appearing hyperintense on DWI. The sequence used is an axial 2D singleshot EPI with b factors 0 and 800, 2.5 mm isotropic voxel size, SENSE factor 3, SPAIR fat suppression, 4 averages and a total scan time of 5:23 min. Scanning is currently performed using the 7-channel SENSE Breast coil. Higher channel coils, such as 16-channel SENSE Breast coil, would allow higher SENSE factor for reduced distortion. The isotropic voxels allow for reformatting and MIP display in arbitrary planes. Results The figure shows a 47-year old patient with a malignant lesion in the right breast visible on T1- and T2-weighted images. The lesion is also well depicted on the high b-value DWI axial image and the sagittal reformat of the low b-value. DWI of the breast at 3.0T has clinical potential in the applications of lesion visualization in high-risk patient imaging, diagnostic follow-up and problem solving, as well as assessment of response in women undergoing neoadjuvant treatment. T1-weighted DWI (b=800) T2-weighted Sagittal reformat of DWI (b=0) FieldStrength 13
14 B-FFE enables superb pediatric neuro imaging High resolution, good contrast of B-FFE help optimize pediatric neuro MR to visualize small detail at Oakland Children s Hospital Clinicians at Children s Hospital and Research Center at Oakland (Oakland, California, USA) are using Balanced FFE (B-FFE) in many of their pediatric neuro examinations. It is part of all routine spine exams, and has become the most valuable sequence for diagnosis in almost all the Center s cranial nerve and spinal nerve root imaging. Kenneth Martin, MD Balanced FFE provides high resolution and very strong contrast, almost like a silhouette. Kenneth W. Martin, MD, Associate Director of Neuro Imaging at Children s Hospital and Research Center at Oakland is using a state-of-the-art upgraded Intera 1.5T and the 6-channel SENSE Head coil for his pediatric neuro patients. He began using B-FFE, a balanced gradient echo sequence, in 2003 while imaging patients that were candidates for a cochlear implant. He needed a very clear image of the eighth cranial nerve, which originates from the brain stem, and goes to the inner ear through cerebral spinal fluid. Before that, Dr. Martin s routine sequences had been using slice thicknesses from 3 to 6 mm, making it impossible to visualize a 1 mm nerve within 6 mm of other tissue and fluid. He started using the B-FFE images to identify the cranial nerves and was very impressed with the image quality. This is a very high resolution sequence; we can take extremely thin slices with it, he explains. It s heavily T2-weighted, and it provides very strong contrast, almost like a silhouette. It was during the fine-tuning of the spatial resolution in these cranial nerve studies that he became interested in what else the sequence was capable of. B-FFE helps visualize filum terminale in pediatric spinal canal The very first thing that came to mind is the spine and the tiny little nerve roots that come off the end of the spine, especially the cauda equina, Dr. Martin says. In adults we would be looking for herniated discs that are pressing on those nerves, but in children, we 14 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
15 Nerve root avulsion 3-week-old male with flaccid right arm underwent CSF cisternography of spinal nerve roots. Axial B-FFE images show pseudomeningocele formation and cervical spinal nerve root avulsion indicating Erb palsy. Avulsion of the nerve root within the spinal canal prevents surgical repair, so conservative treatment only. were looking for abnormalities that affect a little band of tissues in the spinal canal called the filum terminale. The filum in children is about 1 mm thick, like cranial nerves, and the spinal canal is about 2 cm across. So we adapted our B-FFE sequence, which had already been tuned to produce very high detail, for sagittal scanning of the spine from top to bottom. This sagittal scan covers the entire spinal cord, all the nerve roots, and, more importantly, the filum terminale with a typical voxel size of 0.48 x 0.48 x 0.5 mm. Suddenly we were seeing things in the spine that were not visible before and flew in the face of what we d been taught, such as our understanding of how the filum terminale develops. Since then, Children s Hospital and Research Center at Oakland has added B-FFE to all spine exams. As an example, there are a group of tumors called dropped metastases that have a propensity to spread through cerebrospinal fluid, and one place they end up is down in the lower spinal canal, says Dr. Martin. When we have a patient with one of these tumors, we scan the spine as part of the routine staging evaluation for the tumor, and we can look for these lesions. So, in addition to applying B-FFE to visualize anomalies of the spinal cord in babies, the hospital now also uses B-FFE for imaging patients with dropped metastases. As it turns out, those are the two main reasons that we image the spine in children, especially the spinal canal itself, says Dr. Martin. Balanced FFE is superb for identifying problems like this. In fact, taking into consideration all the reasons that we image the spine, it s almost always the best sequence that we have. Intraventricular neurocisticercosis 16-year-old female with headache Post contrast Post contrast B-FFE and vomiting. CSF cisternography is performed with B-FFE, 0.3 x 0.3 mm pixels, 1 mm slice thickness. Image shows a third ventricular thin-walled cyst with central nodule and hydrocephalus. High detail in the image provides valuable preoperative information. FieldStrength 15
16 Cisternography in neurofibromatosis 10-year-old patient with neurofibromatosis Type I experiences headache and dizziness. B-FFE image shows hydrocephalus due to two masses within and obstructing the cerebral aqueduct. A flow void through the 3 rd ventriculostomy indicates patency. Pixels 0.3 x 0.3 mm, 1 mm slices. Versatile sequence for pediatric brain and spine Dr. Martin also successfully uses B-FFE for imaging of pediatric dermoid and epidermoid cysts. These are fluid containing cysts, and they image very much like cerebrospinal fluid. So, in some patients you can t see them at all with routine T1- and T2-weighted imaging. We now use B-FFE, which usually makes these cysts very conspicuous. Similarly, arachnoid cysts, which occur within cerebrospinal fluid, are extremely difficult to image because of their thin, lace-like quality. As an example, Dr. Martin mentions a study where on routine sagittal T1- and T2-weighted images the spinal cord looks like it s being pushed in one direction. It could be stuck in one direction, or the patient s spine is curved and it s taking the shortest pathway between two points or it s actually being pushed in that direction, he says. After we ran the B-FFE scan we didn t have to guess anymore about which one of those three things it might be. We can actually see the arachnoid. There are a number of conditions that occur in or near the brain where physicians have experienced similar limitations. But in example after example, says Dr. Martin, B-FFE has shown to be a very versatile imaging sequence. It s not a panacea, and it s not something that we can cover the entire brain with. We use it selectively when we need images with very high detail and where we suspect that a lot of water like cerebrospinal fluid or a cyst is involved. This B-FFE technique is a very potent imaging tool. Children s Hospital and Research Center at Oakland 16 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
17 Extensively optimized exam protocol with B-FFE differentiates Center Most MR imaging centers don t perform this in-depth, but very important scan optimized for children, mainly because they aren t exclusively engaged in pediatric imaging. Some practices simply perform a sagittal T1-weighted post-contrast image of the spine, but at Children s Hospital and Research Center at Oakland, exams include axial and sagittal T2-weigted imaging of the whole spine, axial and sagittal post-contrast T1-weighted imaging of the whole spine, and a B-FFE scan of the cauda equina and filum terminale. On B-FFE images we have found lesions that were stuck to the nerve roots of the cauda equina, which we could not see on any other image type, says Dr. Martin. I can tell you that it makes a tremendous difference in the treatment of a cancer patient. And because the treatment has changed, presumably their outcome has changed as well. As pediatric radiologists, our job is to outperform what anybody else does in imaging for kids, he concludes. This is what makes us get up in the morning and come to work. Whether it s MR or CT or ultrasound, we re going to do the best we can, and we re going to try to do it better than anybody s ever done it before. As pediatric radiologists, our job is to outperform what anybody else does for kids. T2-weighted T1-weighted, post-contrast B-FFE B-FFE Cisternography of caudal thecal sac 12-year-old male with diabetes insipidus. T2-weighted and post-contrast T1-weighted images appear normal. B-FFE images of the cauda equina demonstrate a 3 mm nodule attached to nerve roots. This finding changed the follow up. Final diagnosis of metastatic germ. FieldStrength 17
18 Asan Medical Center proves the power of pediatric whole body MRI New approaches for pediatric whole body MRI help visualize lesions in children Dr. Hyun Woo Goo, Associate Professor of Pediatric Radiology at Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea has been using whole body MRI techniques for diagnosing lesions in children. According to Prof. Goo, the excellent fat suppression of the center s Achieva 1.5T and 3.0T systems contributes significantly to the effectiveness of these new techniques. Prof. Hyun Woo Goo One of the most important applications for whole body MRI in children is the visualization of suspicious lesions. Whole body MRI offers important advantages, the most obvious being absence of ionizing radiation and excellent soft-tissue contrast especially important for children who may have to undergo many follow-up examinations after malignant lesion diagnosis and therapy. Pediatric MRI also presents some challenges, points out Prof. Goo. It s necessary to adapt many parameters to the patient size. Because the patients are smaller, the signal is less and we have to find the right balance between SNR and spatial resolution to reach the sweet spot. In this respect I find the Philips systems particularly good because the platform is so flexible and it s very easy to trade one parameter off against another to get the right balance. Although scan time is longer, the quality of respiratory-triggered images on the Achieva is almost comparable with that of breath-hold scans. STIR is the workhorse Asan Medical Center performs whole body MRI on Achieva 1.5T and 3.0T systems using the Integrated Body coil. Whole body MRI is mainly used for staging in oncology patients, and for follow up after treatment. But pediatricians have quickly realized that whole body MRI is an effective and easy technique and they also refer patients with other indications, for example multiple hemangiomas or systemic diseases like dermatomyositis, explains Prof. Goo. Even in patients with fever of unknown origin, they often request whole body MRI because they recognize that it s a powerful tool. There are also many motion artifacts with children and you need techniques for suppressing these. Respiratory triggering is one such technique and, here again, the Philips systems perform particularly well. Standard pediatric whole body exam COR and SAG 2D STIR min. Pre-contrast 2D T min. Post-contrast FS 3D T1 3-4 min. Dedicated MRI (DWI, Perfusion ) Total Examination Time min. Prof. Goo regards STIR sequences as the workhorse in whole body MRI in children, since good fat suppression is essential for visualizing lesions, especially extra-skeletal lesions. STIR images have very high contrast-to-noise ratio so can easily visualize small subcutaneous nodules, he says. Our protocol starts with coronal and sagittal STIR which takes 15 to 20 minutes. We also add the sagittal STIR sequence for better imaging of lesions in the sternum and spine. If findings are clear, the examination ends with the STIR scans. If further investigation is needed, precontrast 2D T1-weighted and post-contrast fast 18 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
19 1.5T 3.0T STIR DWIBS PET/CT ADC maps Dynamic post-contrast Comparison of 1.5T and 3.0T Due to the higher SNR at 3.0T, image quality is better than at 1.5T. In these 3.0T images, fewer artifacts are observed and very homogeneous signal intensity from the liver, the kidneys and the bowels. T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma in 14-year-old girl Several sites of lymphoma can clearly be seen both in whole body MRI and PET/CT (blue circled). In addition, the coronal STIR image shows an additional hepatic lesion (pink circled), which appears benign on PET/CT. ADC map demonstrates an increased ADC value of the hepatic lesion which is not typical of lymphoma. Dynamic CE T1-weighted MR images are confirmed as benign hemangioma. suppressed 3D T1-weighted scans follow. T1-weighted sequences, which are sensitive to fat, are particularly suitable for adolescents because their bones contain a lot of fatty marrow, says Prof. Goo. T1-weighted imaging is also used to delineate localized fatty marrow changes after radiotherapy and to identify subacute hemorrhage. Finally, dedicated sequences such as DWI or contrast-enhanced imaging may be performed. The STIR sequence is very sensitive but may be less specific. Adding a DWIBS scan is then a very good choice to increase specificity, mentions Prof Goo as an example. The total exam time can thus vary from 15 to about 60 minutes. New approaches for pediatric whole body MRI Prof. Goo and his colleagues at the Asan center have been evaluating alternative ways for performing pediatric whole body MRI to improve SNR and spatial resolution. They have developed a new sliding-coil technique using the tabletop extender and the 16-channel Torso XL coil to provide full-body coverage in 3 stations of children up to 125 cm in length. Even though the 32-channel Body coil covers the whole of the body, pediatric patients usually feel uncomfortable with it. In contrast, with the sliding coil technique, patients feel much more comfortable because the 16-channel coil simply slides over the patient s body, he points out. Recently, Prof. Goo has also started using the Achieva 3.0T for whole body MRI. In general, the RF issues that may occur with adults at 3.0T are largely absent in pediatric patients, so pediatric imaging fully benefits from the higher SNR at 3.0T. Prof. Goo compared 1.5T and 3.0T results using the Integrated Body coil. It s not surprising that we found 3.0T images to have a clearly better SNR. We also saw fewer artifacts and improved homogeneity at 3.0T when we chose a patient with a left-right diameter of less than 45 cm, he says. The better image quality was particularly noticeable in the liver, kidney and bowel areas. FieldStrength 19
20 STIR STIR Bone scintigraphy DWIBS Rhabdomyosarcoma in 8-year-old girl The bone scintigraphy images (right) look entirely normal, while MRI shows a focal hyperintense lesion in the lower thoracic spine. The two suspicious lesions also stand out from the background very clearly in the DWIBS image. 10-year-old with lymphoma Pre-treatment Whole-body DWIBS PET DWIBS DWIBS ADC STIR provides more detail than corresponding PET images. Follow up after 9 days induction chemotherapy shows that the lymphoma involvement is markedly reduced. The very dark nodules involving both kidneys have almost disappeared on the follow up ADC map. ADC maps also show that the bone marrow signal has changed from black to white, which is not conspicuous on STIR images. 20 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
21 Whole body MRI in staging and follow-up exams Children with metastatic tumors often have to undergo all kinds of imaging in a short period of time, and the Asan team tries to find ways to limit the number of exams and the exposure to ionizing radiation. Prof. Goo and co-workers compared whole body MRI with bone scintigraphy in pediatric patients with malignant solid tumors or Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH). Their studies showed significantly better sensitivity for whole body MRI, which supports the conclusions from studies in other centers. In our center we now direct children towards whole body MRI instead of bone scintigraphy, asserts Prof. Goo. The case of whole body MRI versus PET/CT is not so clear cut. Whole body MRI is generally preferred for brain, liver and bone marrow, while PET/CT is preferred for lungs and lymph nodes. Further comparative studies are necessary, but Prof. Goo believes that the two modalities will continue to complement each other. Other strategies Prof. Goo points out that some aspects of whole body MRI require attention. Some believe that whole body MRI is not useful for lung evaluation, but we frequently do see lung nodules on STIR images even if these are very small, says Prof. Goo. Artifacts caused by metallic implants may also hinder image interpretation, but when using STIR, we don t experience this as a problem. However, whole body MRI, particularly STIR, may not always be specific enough so it is important to use additional information, he explains. Prof. Goo makes use of all clinical data available, including clinical history, lesion distribution pattern, findings from other imaging methods, and results from dedicated regional MRI and diffusion/perfusion MRI. DWI, in particular is valuable for initial and follow-up imaging. Finally, we often use whole body DWIBS, a very robust sequence with low distortion and excellent fat suppression. Spatial resolution is also very high in DWIBS images, so you can see more detail than with PET, he says. A growing trend Prof. Goo believes that the number of pediatric whole body MRI examinations will increase in the future driven by the concerns regarding children s exposure to ionizing radiation. In addition, new technical developments like the use of the SENSE Head Spine coil and the slidingcoil technique for whole body imaging of children at Asan both leading to improved SNR and spatial resolution are likely to further spur the growth of pediatric whole body MRI. After 9 days chemotherapy DWIBS ADC STIR References HW Goo, SH Choi, T Ghim, HN Moon, JJ Seo Whole-body MRI of paediatric malignant tumours: comparison with conventional oncological imaging methods Pediatric Radiology (2005) 35: HW Goo, DH Yang, YS Ra, JS Song, HJ Im, JJ Seo, T Ghim, HN Moon Whole-body MR Imaging of Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis: Comparison with Plain Radiography and Bone Scintigraphy Pediatric Radiology (2006) 36: T Takahara, Y Imai, T Yamashita, S Yasuda, S Nasu, M Van Cauteren Diffusion Weighted Whole Body Imaging with Background Body Signal Suppression (DWIBS): Technical Improvement using Free Breathing, STIR and High Resolution 3D Display Radiation Medicine, 22(4), (2004) FieldStrength 21
22 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans for many different applications in musculoskeletal MRI. In the growing field of pediatric musculoskeletal (MSK) imaging, image quality is vital, and special optimizations must be made for child-size anatomy. Pediatric MSK MR imaging can be divided roughly into two segments: sports medicine, predominantly standardized studies; and tumor/infection studies, usually tailored to a specific question and closely monitored by a radiologist to determine if the FOV is adequate to visualize the pathology and whether contrast is necessary. J. Herman Kan, MD. J. Herman Kan, MD, is Assistant Professor of Radiology and Radiological Sciences at Monroe Carell Jr. Children s Hospital at Vanderbilt University (Nashville, Tennessee, USA). He strives to develop optimal pediatric MSK protocols on both the Achieva 3.0T X-series and the Achieva 1.5T. Pediatric MSK imaging requires specially optimized protocols Adult imaging protocols do not always translate well to children. Pediatric MSK protocols must adapt coil selection, field of view (FOV), and in-plane resolution to children s smaller anatomy, says Dr. Kan. This often adversely affects signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and sequences must be refined to remain diagnostic, while getting the child on and off the table quickly, whether sedated or not. When we just halve the FOV, then SNR issues arise. So, other modifications are also made, like SENSE factor, fat suppression, TE and TR, coil choice and more. Knee MRI is probably the most common musculoskeletal MR study we do. If you use adult parameters on a 4-year-old knee, you ll be scanning from the mid tibia to the mid femur. You really need to just focus on the knee itself: about 2 cm above the physis of the distal femur to 1-2 cm below the physis of the proximal tibia. So, the FOV needs to be decreased from around 160 mm for an adult knee to about 80 mm for 4-year-old. In addition, higher spatial resolution is required to delineate the smaller anatomy. When we just halve the FOV and decrease pixel size, then SNR issues arise, Dr. Kan says. So, other modifications are also made, like optimizing the SENSE factor, fat suppression, TE and TR, dealing with chemical shift effects, comparing different coils, comparing 1.5T and 3.0T. 22 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
23 T2 FS coronal We have developed dedicated ExamCards for small, medium and large children, with optimized sequences for each body area. Bare bones protocol is basis in pediatric sports medicine Pediatric and adolescent sports medicine is a rapidly growing field, Dr. Kan says. It is important that radiologists are ready to address this population and create quality images that the orthopedist can trust prior to open and arthroscopic surgical interventions. All pediatric musculoskeletal MRI exams need to include, at a minimum, certain key sequences. You need to start out with this bare bones protocol, explains Dr. Kan. It should have fluid-sensitive sequences in three orientations for visualizing edema and cartilage this may be any combination of fat-suppressed T2-weighted, fat-suppressed PD-weighted and STIR scans. It should include one or two anatomic T1- or PD-weighted sequences to evaluate cartilage, internal derangement and marrow, tailored for whichever body part is being imaged. And a susceptibility sequence, either 3D WATS or 2D FFE, is needed to evaluate for blood products or mineralization. When those basic sequences are established you can add to and deviate from them. Discoid lateral meniscus with bucket handle tear 8-year-old girl with intermittent knee popping. Sports medicine MRI protocol was performed using the SENSE 8-channel Knee coil on Achieva 3.0T. The lateral meniscus is globally enlarged, and the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus contains increased intrasubstance signal and is flipped anteriorly (arrows). Voxel size is 0.25 x 0.31 x 2.5 mm. In addition to high-quality imaging, a child-friendly atmosphere is essential to successful pediatric MR service. Vanderbilt Children s Hospital We have developed dedicated ExamCards in small, medium and large versions, with optimized sequences for each body area that we are imaging. We prefer PDweighted images without fat suppression for evaluating cartilage, and use a combination of PD-weighted and fluid sensitive sequences for visualizing ligaments. At 1.5T, we use STIR as our primary sequence to assess for edema as it provides very homogeneous fat suppression and we have carefully optimized the sequence. At 3.0T we prefer fat-saturated T2-weighted imaging as our workhorse, fluid-sensitive sequence for identifying soft tissue and marrow edema. FieldStrength 23
24 We want to do the study as quickly as possible before the child starts moving and you get non-diagnostic images. Fast scanning especially important in children When using the smaller FOV and optimizing image quality, scan time will increase, explains Dr. Kan. However, pediatric patients generally have short attention spans, and can t always understand directions. So, we want to do the study as quickly as possible before the child starts moving and you get non-diagnostic images. Even if a child is sedated, we want to scan quickly to minimize the sedation time because sedation has its own inherent risks. Therefore, our protocols are tailored to balance the need for fast scanning and high resolution imaging. Dr. Kan intensely optimized the knee exam because it is the most requested exam type. A regular sports medicine knee protocol of about 25 minutes includes sagittal T2-weighted fat-suppressed, PD-weighted and WATS; axial and coronal fat- suppressed PD-weighted; and an optional coronal T1-weighted scan for preschool children. When needed, for instance to avoid sedation, we do a so-called fast knee scan in only 7 to 10 minutes. The resolution will be decreased somewhat, and the study is not necessarily optimized for the size of the child. However, these studies often provide valuable diagnostic information, although less aesthetically pleasing, and we avoid the need for sedation. MSK oncology protocols help determine lesion extent Dr. Kan has a special protocol for imaging skip lesions, separate lesions within the same bone, that may occur in patients with osteosarcoma and Ewing s sarcoma. These skip lesions are important to find, says Dr. Kan, because if these are present, there s a higher chance that the patient has metastases elsewhere. It also changes the surgical planning; instead of just resecting the tumor, the area of skip lesions needs to be removed as well. We routinely do joint-to-joint imaging for all our bone tumor patients with the specific purpose to assess for skip lesions. STIR T2 SPAIR T1 FS SPIR Acute hematogeneous osteomyelitis 9-year-old girl, non-weightbearing, with normal radiographs of the right knee. Infection protocol performed with the SENSE 8-channel Knee coil on Achieva 3.0T. Images show focal marrow edema of the distal femur metaphysis with transphyseal extension (arrows) and juxta-cortical edema (arrowheads). 24 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
25 T2 FS coronal Juvenile idiopathic arthritis 14-year-old girl with bilateral stiffness in the hips. Infection MRI protocol was performed with SENSE Torso coil on Achieva 3.0T. Images show significant subchondral edema in bilateral hips, affecting the acetabulum and femoral heads (arrows), cartilage loss, joint space narrowing, and hypointense foci within hip effusions consistent with rice bodies (arrowheads). For joint-to-joint imaging, Dr. Kan typically acquires a T1-weighted scan with the Integrated Body coil. A small coil that fits the tumor size is used for the remainder of the images to provide higher resolution of the tumor itself. These high resolution images are very important to define each fascial compartment and determine if the tumor extends from one compartment to another, or has invaded neurovascular structures. Other dedicated protocols are made Dr. Kan also uses special protocols for infection, for dermatomyositis and a limited trauma protocol. The limited trauma protocol essentially contains three sequences: fluid-sensitive scans in two planes and a T1-weighted anatomic scan. Child-friendly atmosphere helps achieve good pediatric imaging In addition to high-quality imaging, a child-friendly atmosphere is essential to successful pediatric MR service, says Dr. Kan. The Children s Hospital building is designed around children, and the personnel specializes in children. We have lots of toys and colorful drawings in our waiting area and hallways. We have a child life specialist who works with both child and family to prepare the child for the MR exam. Our staff members love children, and they have the stamina and the patience to help each child have a positive MRI experience. Usually it s a 10-minute study but we can do it in 5 minutes if we have to. For instance, if a child has a calf injury and is non-weightbearing, while plain radiographs are negative, we need to decide whether to put the child in a cast for a radiographically occult (non-visualized) fracture for two to four weeks. In such cases, we can perform a quick, limited MR study, says Dr. Kan. If that is entirely normal, then we know it s not a fracture, and can look for other reasons that the child is nonweightbearing. STIR T2 SPAIR In a current project, Dr. Kan, with the help of Jared Cobb, a graduate student at the Vanderbilt University Imaging Institute of Science, is optimizing imaging of the epiphyseal cartilage in children by using T1 rho research sequences. This is driven by the need to study normal epiphyseal cartilage maturation, evaluating potential growth disturbance related to infection, or to AVN in a very early stage. The T1 rho sequence is sensitive to the amount of proteoglycans within cartilage, and may therefore be useful as a non-invasive exam to assess cartilage quality and development. Radiologically occult proximal tibia fracture 13-year-old boy, non-weightbearing, with normal radiographs of the right leg. Limited trauma exam with SENSE Cardiac coil on Achieva 1.5T shows non-displaced, acute stress fracture (arrow) of the proximal tibia with significant juxtacortical soft tissue edema (arrowheads). FieldStrength 25
26 SmartExam Shoulder enables efficient, reproducible imaging PAMF combines SmartExam with their high resolution, small FOV exams for high quality, consistent MR images Palo Alto Medical Foundation (PAMF, Palo Alto, California, USA) uses SmartExam with its Achieva 3.0T X-series scanner in about 60 shoulder exams per month. Initially, the techs hesitated to rely on SmartExam Shoulder for planning their demanding small FOV, high resolution scans, but after building a proper training database, SmartExam now performs consistently. Gabriel Gonzalez, RT After having used SmartExam for brain, spine and knee, PAMF recently also implemented SmartExam Shoulder. High reproducibility is the biggest advantage says Gabriel Gonzalez, RT, at PAMF. Even with variables due to technologist training, body habitus or surgeries, SmartExam Shoulder is very consistent in planning scans. For follow-up exams, we categorically see a much more detailed comparison to the previous study than before. PAMF s preferences incorporated in database When the ExamCard is started, SmartExam first performs a 3D SmartSurvey to locate the anatomical landmarks in the shoulder. Then it automatically plans the ExamCard s scans according to the site s preferences, including positioning a REST slab over the lungs and a volume shim box for optimized fat suppression. In shoulder studies, PAMF routinely uses small FOV, high matrix scans to focus in on the region of interest, and achieve good visualization of the labrum and the rest of the rotator cuff. Gonzalez was initially concerned that SmartExam Shoulder would have difficulty in accurately positioning the small FOV, as this is quite critical. For follow-up exams, we categorically see a much more detailed comparison to the previous study than before. During the SmartExam training phase the site s techs perform manual planning, and SmartExam stores their preferences in its training database. SmartExam Shoulder looks for a pattern in how techs plan the scans relative to the anatomical landmarks in the shoulder, Gonzalez says. In consecutive scans, it adds to the database. After about 10 patients, SmartExam Shoulder began to make useful planning suggestions. We can either confirm the suggestions, or make slight adjustments, which are saved in the database, explains Gonzalez. SmartExam adjusts for the widely varying angles of the shoulder. It figures out exactly where the anatomical features are, then plans all scans accordingly and runs the ExamCard, says Gonzalez. We now use SmartExam Shoulder routinely and all of our shoulder studies are very accurate and very consistent. No matter what changes their body may have experienced or what position they re in, patients are assured that they will have a study that is easily compared with their previous exam. Better patient care SmartExam does make the technologists job easier, says Gonzalez, but more importantly it allows them to focus on the patient. Shoulder studies, can sometimes make patients feel a little claustrophobic. With SmartExam, we can focus more on patient care rather than planning. As with any new technology, there was a feeling among the techs that it was another step in machines taking over our job, he adds. But we have come to see that there is less room for error now, and we turn in consistently good studies. This is a tool that allows us to provide better patient care. It makes us more useful, more helpful to the patients and enables a high quality shoulder study. 26 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
27 Consistent planning in different patients Despite differences in age, symptoms, patient position, anatomy and pathology, SmartExam Shoulder consistently plans images. Right shoulder SmartExam planning 31-year-old male, possible partial tear and fraying of the bursal aspect of the distal supraspinatus tendon. 73-year-old male, full supraspinatus tendon tear with fluid filled gap and tendinous retraction as well as probable partial tears of infraspinatus and subscapularis tendons. 63-year-old male, prominent tendinosis throughout the supraspinatus and infraspinatus tendons, and high grade partial tear and possible full thickness perforation at the humeral attachment of the supraspinatus tendon. Left shoulder SmartExam planning 26-year-old male, moderate tendinosis and edema at the infraspinatus musculotendinous junction and foot plate indicating inflammation and/or partial tearing. 59-year-old male, post rotator cuff repair with large partial thickness tear of the articular surface of the supraspinatus tendon. 48-year-old male, mild to moderate supraspinatus tendinosis, most pronounced at the greater tuberosity attachment. No rotator cuff tear. FieldStrength 27
28 MRA is powerful tool for imaging spinal cord blood vessels Maastricht University Hospital uses non-invasive MRA as an attractive alternative to catheter angiography in imaging spinal cord blood vessels. Until recently, digital subtraction angiography was considered the only practical method of imaging the very small caliber spinal cord blood vessels. However, the Department of Radiology at Maastricht University Hospital, The Netherlands, has been evaluating MRA as an alternative tool for depicting these vessels with very positive results. Walter Backes, PhD. Before undertaking clinical procedures such as aortic aneurysm surgery and correction of spinal cord vascular malformations, accurate knowledge of the location of blood vessels supplying the spinal cord is essential, explains Walter Backes, PhD, medical physicist at Maastricht University Hospital. The challenge here, however, is that significant variations occur in individual patients spinal cord vascular anatomy. This means that an initial procedure to locate these vessels must always be carried out, because serious complications such as paraplegia could result if a vessel supplying the spinal cord is obstructed or pinched off during surgery. MRA as efficient, non-invasive alternative The standard procedure for localizing these vessels is digital subtraction angiography (DSA), but this has some disadvantages. The Adamkiewicz artery (AKA) for example, one of the largest arteries supplying the spinal cord, can be connected to any one of more than twenty segmental arteries branching off the aorta. Using DSA to locate this artery before surgery to correct an aortic aneurysm is a laborious process that may take several catheterizations and contrast injections, points out Dr. Backes. If you re lucky, the artery might be found on the first or second attempt, but it s not uncommon for patients to have to return several times before the artery is found. of all spinal cord arteries in one scan. They developed dedicated MRA sequences for depicting the spinal arteries and veins, offering an attractive, non-invasive, alternative to DSA. Using these sequences, we can reliably locate the Adamkiewicz artery in just one session, says Dr. Backes. Large FOV, high resolution make MRA ideal for spinal arteries Philips systems offer some important advantages in this application, points out Dr. Backes. They enable a very large FOV which is essential to be able to visualize the Adamkiewicz artery that can originate anywhere along the thoracolumbar spine in combination with the high spatial resolution needed for imaging the tiny blood vessels supplying the spinal cord. Besides for locating the Adamkiewicz artery, the Maastricht clinicians also use their dedicated 1.5T ExamCard to visualize collateral supplies to the Adamkiewicz artery which again may be located anywhere within and sometimes even outside the thoracolumbar region. Patients often have other problems such as arteriosclerosis of the aorta with occlusions of the main tributaries. This means that the main segmental supplier may be blocked and it s necessary before surgery to look for collateral vessels that may be supplying it. Dr. Backes and his colleagues realized that MRA could make this procedure much easier, as MRA allows use of a large FOV that enables visualization Moreover, the technique is valuable for investigating spinal cord abnormalities such as spinal dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) of the spinal cord, in 28 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
29 T2 weighted MRA Collateral supply to Adamkiewicz artery The long arrow shows the Adamkiewicz artery and the arrowheads show the collateral supply vessels. Aortic aneurysm corrected with a graft which results in loss of many of the segmental arteries in the region of interest. MRA was used to visualize the collateral supply before the procedure to minimize the possibilities of complications during surgery. DAVF of the spinal cord Visualization of the spinal cord in a case of dural arteriovenous fi stula (DAVF). The T2-weighted image shows fl ow voids (arrows), and the MRA image visualizes the engorged arterialized vein. Sacral DAVF of spinal cord Patient presented with symptoms of DAVF. Initially five unsuccessful attempts were made to identify the arterial feeder using DSA. The feeder was subsequently identified using MRA as originating low down in the sacral region, which was later confirmed in a sixth DSA examination. This case shows the benefits of MRA. which a spinal vein becomes engorged with arterial blood due to the presence of an arteriovenous shunt. DAVF can often easily be seen on T2-weighted images so you don t need to use MRA for this, explains Dr. Backes. However, these T2-weighted images do not tell you where the fi stulous connection originates. MRA is able to pinpoint non-invasively the arterial feeder of such vascular abnormalities in one imaging session. So, for this too, we fi nd that MRA with its large FOV covering the entire thoracic, lumbar and sacral region is far more effi cient than DSA. MRA easier to use for locating AKA Dr. Backes and his colleagues at Maastricht University Hospital have no doubt that MRA is an extremely useful tool for visualizing the spinal cord blood supply. Our experience shows that MRA is a reliable, reproducible, and patient-friendly imaging technique for detecting the Adamkiewicz artery and for providing valuable information on the location of arterial feeders prior to intervention. The large FOV and the fact that it s non invasive means that in these clinical applications MRA is much easier to use than catheter angiography. References: 1 Mull M, Nijenhuis RJ, Backes WH, Krings T, Wilmink JT, Thron A Value and limitations of contrast-enhanced MR angiography in spinal arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fi stulas AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Aug;28(7): Backes WH, Nijenhuis RJ Advances in spinal cord MR angiography AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Apr;29(4): NetForum Visit NetForum to view or download the ExamCard 1.5T Spinal cord arteries contributed by Dr. Backes, Maastricht 3 Backes WH, Nijenhuis RJ, Mess WH, Wilmink FA, Schurink GW, Jacobs MJ Magnetic resonance angiography of collateral blood supply to spinal cord in thoracic and thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm patients J Vasc Surg Aug;48(2): FieldStrength 29
30 DMI sees jump in image quality with Achieva XR Busy imaging practice is ready to ramp up from 1.5T to 3.0T at short notice Desert Medical Imaging (DMI, Indian Wells, California, USA) installed its Achieva XR rampable MR system just over a year ago. With more than 20 MRI patients a day, DMI s Achieva XR performs a mix of scans that includes neuro, musculoskeletal, breast and cardiovascular at 1.5T. John F. Feller, MD Achieva XR brought us an immediate improvement in image quality John F. Feller, MD, Medical Director and founder of Desert Medical Imaging, says DMI chose the Achieva XR for several reasons, including its flexibility. We can respond quickly if a competing center puts in a 3.0T system. It s a state-of-the-art 1.5T system that we can convert to a 3.0T system in four or five workdays without major renovations. The only thing that needs to happen is the spectrometer and the coils need to be swapped out, says Dr. Feller. He adds that DMI can also ramp up the system to 3.0T when they reach 30 or 35 patients a day and want to improve throughput. We can go from 30-minute slots to 20-minute slots, and continue to grow the practice. It s the only product in the industry with that flexibility. DMI researched the cost effectiveness of buying a 1.5T system and replacing it with a 3.0T later, versus buying a rampable 1.5T system. The Achieva XR is much more cost effective if you re planning on a 3.0T system down the road, says Dr. Feller. The Achieva XR also offers high residual value, with 3.0T X-series components such as the magnet and gradients. Breast studies benefit from high quality images When adding to DMI s Panorama HFO scanner, the most important factor was improving image quality. Image quality is very good on the Achieva XR, says Dr. Feller. We wanted a system with a direct digital spectrometer and at least 16 channels, so we could accommodate the full complement of coils we have. In terms of our SNR calculations, it s our opinion that we got about a 25% improvement in image quality with the Achieva XR. Breast studies, in particular, are benefiting from the addition of the Achieva XR. We have a multidisciplinary breast conference every month, in which we get surgical and pathologic follow-up on all of our cases. The correlation between the surgical and pathologic findings presented at the conference has been very good, says Dr. Feller. DMI is currently performing breast biopsies on the Panorama High Field Open (HFO), using DynaCAD for post processing and DynaLOC for intervention. Their ultimate goal is to add the new Elite Breast solution to the Achieva XR for improved workflow and image quality to take the breast MR program to the next level. Elite Breast incorporates the MammoTrak dockable patient support system, DynaCAD Enterprise, and integrated breast coils for a complete breast solution. SmartExam adds efficiency, reproducibility to common scans DMI uses SmartExam for knee, shoulder, spine, and brain exams. SmartExam is a huge improvement in operational efficiency, says Dr. Feller. In the case of a shoulder, for example, it decreases the number of steps for our techs from 42 to two. And we ve found that our less experienced techs get up to speed more quickly on our most common exams. After an analysis using Philips Utilization software, Dr. Feller discovered that the total time spent on these exams had decreased significantly. SmartExam frees the techs to concentrate on things that need their expertise, instead of spending their valuable time clicking a mouse. 30 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
31 The reproducibility of the exams at DMI has improved, even for experienced technologists. You want to compare apples to apples, not different slice orientation or slices that aren t at the same location, explains Dr. Feller. With SmartExam, the follow-up exams end up being almost exactly the same in terms of positioning and alignment, so that the comparative measurements in the follow-up studies are more accurate. The Achieva XR brought us an immediate improvement in image quality, which has been very consistent ever since, Dr. Feller says. It has been a very stable system, and we ve had very little down time. I m a happy customer. It s a state-of-the-art 1.5T system that we can convert to a 3.0T system in four or five workdays. Left index finger glomus tumor A 36-year-old female with left index finger pain beneath index finger nail bed. There is a 0.4 x 0.7 cm well-circumscribed homogeneously enhancing soft tissue mass interposed between the nail and the distal phalanx of the left index finger highly suggestive of a glomus tumor. There is some associated mild pressure erosion involving the dorsal cortex of the distal phalanx. Achieva XR, 47 mm Microscopy coil. Patient in left lateral decubitus position with left arm flexed about head and hand extended in supine position supra cephalically. FOV was relatively small, averaging 8 x 4 cm. Voxel size averaged at 0.3 x 0.3 mm. T1-weighted B-FFE B-FFE T2-weighted Post contrast Post contrast Right knee patellar tendon rupture A 61-year-old female with right knee anterior pain 5-6 weeks post intraarticular anterior ACL reconstruction surgery utilizing a patella bone-tendon-bone graft. Apart from postoperative changes, the images demonstrate a full thickness tear of the patellar tendon proximally 2 cm distal to the level of the inferior pole of the patella. The torn ends of the patella tendon are retracted 1 cm resulting in patella alta. A moderate sized joint effusion extends through a capsular defect into the subcutaneous fat anteriorly at the level of the patellar tendon rupture. FieldStrength 31
32 Intera 1.5T upgrade boosts throughput at Hiroshima center Contributed by Takayuki Tamura, RT, Department of Radiology, Health Management & Promotion Center, Hiroshima Atomic Bomb Casualty Council Established to care ostensibly for the victims of war, The Health Control/ Promotion Center of the Hiroshima Atomic Bomb Casualty Council (the Center) has transformed into an important medical resource for this vibrant city of one million inhabitants. To meet demand for MRI services, the Center implemented the FreeWave release 2.6 upgrade for its Intera 1.5T system, improving throughput and increasing profitability. Takayuki Tamura, RT The Center was established in 1953 to conduct health management and epidemiological research on behalf of the victims of the 1945 atomic bomb detonation in Hiroshima, Japan. Presently, the Center provides health checks for Hiroshima s citizens, most of whom are referred from various clinics in the city. Consequently, the hospital faced conflicting demands: providing high quality results in a wide range of disciplines during the limited time frame of normal business hours. Since December 2000, the Center operates an Intera 1.5T (Power gradients, release 7). Recently, however, confronted with increasing difficulties in providing more advanced study methods, the Center determined to upgrade the system in an effort to address these challenges most effectively. Upgrade counteracts longer scan times The typical exam time for head and spine was 20 minutes at the Center, while abdominal or extremity studies which comprise about 20% of the total case volume could take as long as 40 to 60 minutes. By shortening these exam times, clinicians anticipated an increase in throughput. See figures showing the estimated profit increase expected with the upgrade, and the monthly case volume realized before and after upgrade. The numbers have steadily increased and are still climbing. ExamCards play critical role A key element of the upgrade option were ExamCards, that contain all the scans required for a complete MRI examination. Using ExamCards which are categorized by study type neutralizes interoperator differences in scanning technique and enhances overall throughput. In addition, ExamCards automatically perform post-processing, thus decreasing most of the technologists post-processing burdens. See examples in figures. 32 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
33 Estimated profi ts expected with the upgrade The Center anticipates a positive return on investment in 3-6 years, with an increased number of examinations possible by virtue of enhanced throughput potential. In addition, the wide variety of available applications will increase examination quality. Monthly case volume comparison Shifts in monthly case volume pre- and post-upgrade, including breakdown data. The upgrade has signifi cantly improved throughput. Auto MIP 3D Myelography 3D B-TFE COR with SPIR, slices of 1 mm thickness Example of ExamCard with Auto MIP The Center set up an automated spine ExamCard. The acquisition of 3D B-TFE coronal images of the spinal cord triggers the automated reconstruction of a 3D myelograph using optimal fi lter algorithm. FieldStrength 33
34 3D T1W TFE, 200 slices of 1 mm thickness Auto MPR VSRAD Volume analysis Example of ExamCard with Auto MPR Acquisition of 3D T1-TFE volumetric brain images, including the hippocampus for diagnosing Alzheimer s disease, triggers automatic reconstruction of three-plane diagnostic images. Before upgrade (R7) After upgrade (R2.6) Fat suppression before and after upgrade The bilateral fat suppressed breast image before upgrade, made with 4-channel SENSE Body coil, demonstrates incomplete fat suppression. After upgrade, the bilateral fat suppressed image is now successfully acquired with the 7-channel SENSE Breast coil. Excellent fat suppression in crural edema study STIR Parallel MIP MobiViews ordered for a close examination of a patient with crural edema. The homogeneous fat suppression in the entire area, from the abdomen to the crura, enhances visualization of the swollen lymph nodes in the inguinal region and edema in the crural region. 34 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
35 FLAIR T2W TSE T1W FFE DWI SSh EPI T1W FFE 3D TOF MRA Brain ExamCard The routine head protocol with SmartExam Brain combines the 16-channel NeuroVascular coil and SENSE enabling acquisition of all images in only 12 minutes. Specialized coils and shimming increase efficiency The upgrade also provided numerous SENSE-supporting coils, which have greatly shortened scan times for joint studies in particular. The Dual coil functionality allows a simultaneous use of the 16-channel NeuroVascular coil and 15-channel Spine coil, eliminating the need to swap coils in head and spine exams, which represent 80% of all studies. This Dual coil capability also obviates patient repositioning that a comprehensive head/spine study would require. These new features contribute significantly to increased throughput at the Center. More improvements expected on flexible scanning platform The upgrade has transformed the Center s capable existing system into a state-of-the art solution with high costbenefit advantages. Popular technologies developed for 3.0T systems are applied to 1.5T machines, which now are achieving virtually perfect image quality and ease-of-use. Additionally, the combination of SENSE Flex S and M coils enabled a wider field FOV range with a higher sensitivity in scanning joints. The 16-channel SENSE XL Torso coil is highly appreciated for its wide coverage, encompassing the liver and bladder in one acquisition. Release 2.6 also enhances magnetic field shimming accuracy. In bilateral breast imaging, 2D shimming a new feature largely facilitates fat suppression in both breasts. Moreover, the combination of e-thrive and SPAIR techniques has enabled excellent fat suppressed images without RF penetration problem. Large coverage scanning Abdominal image of multiple liver cysts acquired with 16-channel SENSE XL Torso coil. This coil provides a very wide sensitivity range. FieldStrength 35
36 Hospitals deploy Panorama HFO as an all purpose MRI scanner Panorama High Field Open scanner serves all MRI needs of both Community Memorial Hospital and Porter Hospital. Community Memorial Hospital and Porter Hospital are two very different facilities. However, both use Panorama HFO as their only MRI system. The Panorama s wide-open patient space makes it a good choice for patients of all sizes and MR needs. Panorama High Field Open MRI appeals to both patients and referring physicians alike with its 360º panoramic viewing angle and spacious 160 cm-wide patient aperture ensuring a comfortable, relaxing MRI experience for anxious, elderly, obese or claustrophobic patients. The large space allows sideways positioning for any patient, assuring that any anatomy (including knee, wrist and shoulder) is always at the isocenter for best image quality. Solenoid Technology coils offer superb coverage and comfort, high SNR and excellent homogeneity. The images benefit from the minimal susceptibility and distortion as well as uncompromised fat saturation at the 1.0T field strength, while providing SNR comparable to 1.5T. Since the majority of patients prefer the open Panorama over any cylindrical system, this helps when marketing a practice directly to the patients. Panorama HFO helps Community Memorial Hospital grow quality MR exams on about 70 patients a month. Many of the patients are referred from the hospital s pain management clinic, orthopedic department and family practice physicians. Rich Wharton (Philips) and MRI technologists Robin Morhart, Angel Stevens, Lori Peglow. Located in a city of about 5,700 residents, Community Memorial Hospital (Hicksville, Ohio, USA) is a critical access hospital with 25 beds. The Panorama was installed in June 2008, and is used to perform high The Panorama s large patient aperture is a plus at Community Memorial. Sue Fowler, RT, Radiology Manager at Community Memorial, says, There are a significant number of patients in our demographic area who are too large for a closed system or who are claustrophobic. If patients are claustrophobic, the technologists can take them to see the unit, which helps to dispel any negative perceptions they might have about closed MR systems and puts them at ease. Our Panorama is the only high field open system available to them in our service area. We re not doing conscious sedation, but we ve had some pediatric patients whose parents have stayed in the room with them, and that has been very calming for the children. 36 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
37 Subacute subdural bleeding T1-weighted An 81-year-old female with history of diabetes presented with headaches, tinnitus. T1-weighed image shows increase in subdural fluid. FLAIR demonstrates small amounts of fluid in the subdural space along the convexity of the brain, consistent with subacute subdural bleeding without mass effect, with reactive meningeal enhancement. FLAIR FLAIR Post contrast T1-weighted T2-weighted PD-weighted T1-weighted Large disc extrusion 40-year-old male with low back pain and right-sided foot drop for several months. Sagittal images demonstrate a large disc extrusion at L4-L5 with spinal stenosis. The axial images demonstrate right paracentral disc hernation compressing the thecal sac and impinging on the right L5 nerve root. T1-weighted T2-weighted The community members overwhelmingly wanted an open MR system. When Community Memorial began the search for an MR system, hospital administrators surveyed their physicians and members of the community. The physicians wanted a 1.5T closed-bore system, citing image quality issues with open-bore systems, says Gregg Harpel, Vice President of Ancillary Services. The community members overwhelmingly wanted an open MR system. When Philips presented the Panorama as a high field open, I was a bit skeptical, as sales representatives claims of image quality can sometimes be a bit inflated. But when we saw it in action, I knew we had the right fit. FieldStrength 37
38 Next, Mr. Harpel and the team discussed it with the hospital s radiology group and medical staff. Once they were on board, we presented the numbers to the Board of Governors and the Township Trustees to get their approval, he says. The success of the project relied heavily on the continued growth of the hospital, so they were a bit apprehensive, but their faith in us has paid off. The high field open system fulfills its promises The Panorama is the Community Memorial s only MRI scanner, and serves all its MR needs. In a small, rural area, two MR systems would be cost-prohibitive. Even with refurbished units, the cost of purchase, maintenance, training and regulatory oversight would not be costeffective, explains Mr. Harpel. More importantly, there would be no added value in having two different machines; we have not run into anything that we cannot do on this magnet. We have not run into anything that we cannot do on this magnet. We have nothing but great things to say about our Panorama, agrees Ms. Fowler. We were very pleased with the entire process from beginning to end. We decided on a turnkey approach, whereby Philips was also in charge of putting together the modular building that would be attached to our hospital, and we believe that was money well spent. One of the highlights was when the huge building for the MR suite came through the streets of our small town to arrive at the hospital. Mr. Harpel says the Panorama has turned out to be a marketing tool for the hospital. We have people coming to our hospital that didn t know we had a hospital a year ago. Not only are they coming for the MRI, but also for other services. The marketing campaign had a residual effect of getting our name out and building our image. Being in Hicksville, many people get an instant mental image of someplace lost in time. The MRI campaign let everyone in the extended area know that we are here and we have top-notch technology. We are very happy with the choice that we made, says Ms. Fowler. With the Panorama we have the best of both worlds: we have a system that s both high field and open. Panorama meets all MR needs at Porter Hospital Nancy Babich Porter Hospital (Valparaiso, Indiana, USA), in comparison, is a large hospital with 250 beds. Nancy Babich, Director of Imaging for Porter Hospital, says Porter has imaged about 7,000 patients on its Panorama HFO since it was installed in late Brain and cardiac imaging is fairly common here, as is imaging of extremities. Because of the openness of the Panorama, and the fact that we work through a central scheduling department, we also get claustrophobic patients who won t or can t go to other facilities. Especially in brain imaging, where the head must be held still, the open sides of the Panorama are a welcome addition to MR exams. For pediatric patients, it s reassuring to have a parent or family member in the MR room with them. In fact at one point we had a mother come and lie next to her child during the scan, says Ms. Babich. Porter has had MR scanners in its facilities for a long time and appreciated both the image quality, and the service on Philips equipment. We needed an open MR, says Ms. Babich, and when we saw the capabilities of the Panorama the removable table, the cardiac capabilities, the high quality images we decided it would answer our needs for both a high field and an open scanner. We decided Panorama HFO would answer our needs for both a high field and an open scanner. 38 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
39 T2-weighted PD-weighted T2 TSE T1 FFE post-contrast Brain Total spine A 33-year-old female complaining of bilateral upper & lower extremity weakness and dizziness. No abnormalities were identified. SENSE.Flex M coil is used for cervical area and Integrated Body coil for thoracic and lumbar areas. Voxel size 1.15 x 1.76 x 4.0 mm in all stations. Panorama HFO exam of a 44-year-old male complaining of dizziness and inability to focus shows a normal brain. Voxel size 0.8 x 100 x 5 mm, scan times 2:58 min. for T2 TSE and 2:12 min. for T1 FFE. The open nature of the scanner and the superb images it creates have differentiated Porter Hospital from others in the area. Panorama is fully capable The Panorama efficiently serves all the hospital s MR needs, she adds. We have not had to turn any patients away or ambulance any patients to a high field scanner, because we haven t encountered any limitations on the Panorama. The open nature of the scanner and the superb images it creates have differentiated Porter Hospital from others in the area, says Dr. Alkadri. People no longer have to travel outside of Porter County to have an open MR exam, he says. A competing hospital recently installed an open scanner, but it s not high field. Amjad Alkadri, MD Amjad Alkadri, MD, Chairman of Imaging at Porter Hospital says that, in his opinion, the quality of the images created with the Panorama is comparable to those from a 1.5T system. The combination of the high field strength and Philips improved coil technology have finally made it possible to create high quality images in an open magnet. A high field open is really an advantage for all patient services in MR, says Dr Alkadri. Before the HFO magnet was introduced, radiologists had to choose between quality and how open the magnet could be. With the HFO magnet, we are now able to offer an open magnet without compromising on image quality. FieldStrength 39
40 Realizing the full potential of a 3.0T MRI system Utilization Services use a Kaizen Event to improve productivity After close to three years using their Achieva 3.0T X-Series, the management of the Al Zahra Hospital in Sharjah, close to Dubai in the United Arab Emirates, observed they had not yet reached the expected return on their investment. They were averaging 62 minutes to examine each patient, the same productivity as they had managed on their previous, 1.0T system. In the second half of 2008, they decided to look at ways to increase the patient throughput. Philips Utilization Services suggested a Kaizen Event to identify and implement improvements in the examinations and the patient change-over times. The Philips specialists were really good and professional at finding out the causes of delays and making recommendations. Kaizen is the Japanese word for change for the better. It is also the term given to a continuing, quality improvement method. But there is a special form, a Kaizen Event, that makes a concentrated effort over a couple of days to achieve a well-defined improvement. Before the Kaizen Event in the Al Zahra hospital, Philips Utilization Services monitored the use of the MRI scanner over three months. This provided data to compare key performance indicators, such as scan times for exams and the ratio between scanning and changeover time, with other private hospitals. The main finding was the long change-over times often because the next patient was not yet available. Identifying and altering inefficient use of time Two Philips workflow consultants and a Philips MR application specialist worked with a team of radiologists, technologists, receptionists and IT staff in a three day Kaizen Event in the hospital, in January Based on the monitoring data, the recommended goal was to shorten the interval between patient appointments to 45 minutes. To do this, the team had to identify opportunities to eliminate or shorten activities, or to transfer them out of the examination room. These were ranked by effectiveness, and the top four were implemented. The Philips specialists were really good and professional at finding out the causes of delays and making recommendations, says Dr. Abidi, Senior Manager, Administration and Quality Control. 40 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
41 We have carried out the recommendations of the team, and have already reduced the process time for MRI from 60 to 40 minutes. While the goal to switch to 45-minute patient scheduling was immediately accomplished manually, the team decided the most sustainable solution was to implement this electronically. During the three days of the Kaizen Event, the hospital IT specialists and the stakeholders from radiology discussed how this could best support the scheduling, and defined the requirements for an update of the scheduling application. They also took this opportunity to implement a few quick wins like an area to include comments to the clinical request, and improved printing. The team also created a temporary second changing-room in the corridor near the MR room the permanent solution was approved for construction and added a second technologist. This reduced average change-over times, measured during the Kaizen Event, from 17 to 8 minutes. The last change tackled during the Event was the consistency of the ExamCards between radiologists. All the radiologists were interviewed, and a local Philips MR specialist continued to work on this after the event. Working toward sustainable improvement We have carried out the recommendations of the team, and have already reduced the process time for MRI from 60 to 40 minutes, confirms Dr. Abidi. We have definitely benefited from their advice, he continues, and we can now handle a minimum of 20 to 21 cases a day, whereas on average we are dealing with 14. The challenge now is to get 5 or 6 more referrals a day from local practitioners to make the most of their productivity gains. Staff at the hospital are already working on marketing the benefits of 3.0T MRI to the referring doctors to achieve this. The Al Zahra is opening a second hospital in Dubai at the end of The Kaizen Event has influenced how they are setting up the new MRI suite too. We are making use of this experience, says Dr. Abidi. We have learned a lot. The Al Zahra Hospital team and Philips consultants gathered during the Kaizen Event. FieldStrength 41
42 Application tips Acetabular radial hip imaging MR hip imaging is routinely performed for assessment of the acetabulum and acetabular labrum. These scans are traditionally acquired in the orthogonally planned axial, coronal and sagittal planes. The results of these scans demonstrate true parallel slices of the acetabulum, acetabular labrum, femoral head and neck, and trochanter anatomies. An additional view can be acquired using radially planned slices for a unique anatomical perspective. Dave Hitt, MR Clinical Development Specialist, USA Marius van Meel, Application Specialist MSK MRI, Netherlands MR imaging of the entire acetabular labrum is difficult due to its complicated location and because it is easily affected by partial volume effects 1. A radial scan acquires slices, centered on a planned radial axis, providing full visualization of the entire acetabular circumference. Orthogonally planned slices compromise this circumference which may cause a partial volume of the anatomy. Radial imaging has been described as more accurate for the diagnosis of acetabular labral lesions, when compared with oblique coronal and oblique axial slices 2. Tip 1: Patient set-up Patient positioning is easily achieved with the patient either headfirst or feet-first on the table. Often this choice is based on the comfort of the patient with receiving an MR scan. There are several options for the coil to use. The actual choice depends largely on availability at the site. Turn the patient s feet inward to pronate the greater trochanters, and support in position with velcro straps wrapped around the feet. Place a sponge in between the ankles to maintain the inward position of feet and toes. Tip 2: Radial protocols In radial protocol planning a radial axis (e.g. right to left) and a radial angle are specified within the protocol. This type of scan could be thought of in terms of a bike wheel, where the axle of the wheel is the radial axis, and the slices are the spokes of the wheel. The scan type, radial axis and slice orientation parameters are selected under the Geometry tab, in addition to the number of slices and radial angle. The number of slices chosen will limit the maximum radial angle possible, and also impact the scan time. A radial scan may be either a multislice (MS) sequence, or a multiple single slice (M2D) sequence. This is specified by the Scan mode parameter under the Contrast tab. 42 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
43 The benefits of a MS radial scan include shorter scan times which will permit a higher resolution matrix to be scanned at the cost of a crosstalk artifact that follows in line with the radial axis. If only the acetabular labrum is evaluated, this crosstalk will not interfere with visualizing the anatomy. Scan mode MS Scan mode M2D The M2D sequence will avoid this crosstalk artifact across the joint, if visualization of the entire acetabulum circumference is needed. However, scan time will be longer, which may require lowering the matrix or reducing the number of slices. Another option to avoid crosstalk would be to use a gradient echo acquisition. Tip 3: Planning the radial scan Planning of the radial scans requires several surveys to correct for the complex anatomical angulations of the acetabulum and provide geometric offsets and angulations for the sequences 3. These offsets and angulations are carried over into the radial sequence in such a fashion that the radial axis is perpendicular to the acetabulum. This planning results in a series of images demonstrating the femoral head, acetabular labrum and acetabulum at incremental angulations. There are several methods of planning a radial scan, but the preferred method makes use of two initial surveys and a radial-setup-survey, as shown below. First, two initial surveys are acquired that should be of such quality that the anatomical detail is clearly demonstrated. These surveys are orthogonal true axial and coronal slices, and may be combined into a multi-stack sequence. Use the axial and coronal slice that best demonstrates the midpoint of the acetabulum to plan a radial-setup-survey with double angulations, see figure. The red arrows indicate the acetabular points for aligning the radial-setup-survey. Initial survey Radial-setup-survey Radial scan Example of radial ExamCard. Note the unique GEO names. FieldStrength 43
44 The radial-setup-survey provides a double angulated view of the femoral head and contains all angulations needed for the radial scan. The radial PD TSE SPAIR images demonstrate the acetabular labrum with the neck of the femur in varying degrees around the acetabulum. Note the labral tear (arrow). The radial slices are centered on the femoral head, with slice 1 in the coronal or 12 o clock position, and the following slices rotated incrementally. Tip 4: Transferring the correct angulations to the radial scan Although using the GEO name of the radial-setup-survey would transport the correct angulations to the radial scan, it would also reset the radial scan back to a parallel acquisition. To prevent this, load the radial-setup-survey in a viewport and click on it, so it highlights with an orange border. Click on the orange info box (red arrow) to extend the information. Now open the radial scan and type in these exact angulations. If the planned radial scan does not resemble the spokes on a wheel, similar to the figure, then change the orientation and/or the radial axis. 44 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
45 Tip 5: ExamCards The angles and offsets of the hip anatomy, from the right to the left side of the body, will change for each unilateral hip planned. By creating a dedicated right and a dedicated left radial hip ExamCard, incorrect angulations will not be traded from one side to the other. Examples of these ExamCards using the SENSE Flex M and SENSE Flex L coils are available on NetForum. Tip 6: Planning in-line with the femoral neck To study the femoral head-neck junction over its full circumference instead of only anteriorly as in the conventional oblique axial method a radial scan may provide more information in subtle cases of FAI Cam type impingement 4. Planning differs slightly from a radial scan for evaluation of the labrum. The radial axis should now be in line with the axis of the femoral neck. To achieve this, use a new radial-setup-survey with a different GEO name (e.g. SurRf). Plan this survey on the initial survey, using the axial and coronal slices that best depict the femoral neck. The radial-setup-survey is planned perpendicular to the femoral neck. The dashed red line indicates the femoral axis to which the radial-setup-survey is perpendicularly aligned. This will provide the correct angulations for the radial scan of the femoral neck. Continue planning as in Tip 4. Acknowledgements Dr. Lipman, MD, Dr. Cheng, MD, Invision Imaging, Honolulu, HI. USA. Dr. Goumas, MD, MPH, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Palo Alto, CA, USA. References 1. I sao Abe, Yoshitada Harada, Kazuhiro Oinuma, Koya Kamikawa, Fuminori Morita, Hideshige Moriya. Acetabular Labrum: Abnormal Findings at MR Imaging in Asymptomatic Hips. Radiology 2000, 216: G. M. J. Poltz, J. Brossmann, M. von Knoch, C. Muhle, M. Heller, J. Hassenpfl ug. Magnetic resonance arthrography of the acetabular labrum: value of radial reconstructions. Arch Orthopaedic Trauma Surgery, 2001, 121, pages NetForum Visit the MRI NetForum user community for downloading radial hip ExamCards or for more application tips. 3. Motoyuki Morii, Toshikazu Kubo, Yasusuke Hirasawa. Radial MRI of the hip with moderate osteoarthritis. Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (British Edition). Vol. 82-B, No. 3, April K.S. Rakhra, P. Beaulé, A.M. Sheikh, D. Allen Comparison of MRI Alpha Angle Measurement Planes in Femoroacetabular Impingement. Paper No th Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society, 2009 FieldStrength 45
46 Carbon-13 spectroscopy at 7.0T of calf muscle and brain Researchers in Nottingham and Nashville are conducting in-vivo 13 C MR studies of glycogen metabolism Carbon-13 ( 13 C) spectroscopy allows researchers to study processes within the body beyond what conventional proton MR can do. When performed at 7.0T, 13 C spectroscopy is yielding a wealth of information on metabolism for Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science, (VUIIS, Nashville, Tennessee, USA) and the Sir Peter Mansfield Magnetic Resonance Center (Nottingham, UK). While conventional MR detects signal from nuclei of hydrogen atoms, mainly in water, multi-nuclear MR spectroscopy (MRS) enables detection of signal from other nuclei with magnetic signals at different frequencies, such as phosphorus-31, fluorine-19, sodium-23, xenon-129 and carbon-13 (1% natural abundance; the most abundant C isotope is carbon -12). 13 C spectroscopy produces spectra that can help monitor certain biochemical processes in the body. At 7.0T, the 13 C spectrum has a larger chemical shift dispersion than at lower field strengths, so is more spread out and peaks are sharper, to allow for easier observation of chemically distinct carbon atoms. The increased SNR also improves visibility of the low-abundance 13 C isotope. Diabetes studies underway at Nottingham Prof. Peter Morris The Sir Peter Mansfield Magnetic Resonance Center has already undertaken 13 C MRS studies at lower field strengths, and expects to obtain better results at 7.0T. Prof. Peter Morris, PhD, says the center is looking at muscles and studying glycogen turnover. This turnover is not only important in exercise physiology, but it s extremely significant in diabetes, which is often seen as a disease of glycogen storage. Simply being able to measure what s happening to these glycogen stores will help us determine how best to replete them. This study s goal is to find a way of actually probing diabetes and its reaction to new classes of drugs designed to increase glycogen stores, so 13 C is a very useful biomarker of whether those drugs are effective. We can separate out the different metabolites in a way that s not possible at lower fields. Neuro 13 C studies to begin soon In another study, 13 C spectroscopy will be used to look at brain metabolism. After administering 13 C-labeled glucose, 13 C spectroscopy can be applied to measure the rates at which the 13 C label is transferred from glucose to glutamate. This is actually a way to measure the rate of energy consumption in that part of the brain, Prof. Morris explains. So in my view this is an indication of brain activity. We may not know exactly what the brain is doing, but we can measure how much energy it s consuming. This work goes hand-in-hand with functional MRI, he adds. Prof. Morris plans to begin this study with healthy young volunteers. But, of course there s good evidence that there are differences in the rates of neurotransmitter turnover in neurodegenerative diseases, as well as effects of aging that we can look at. So we hope to begin with healthy young volunteers, and then to look at different ages and a range of neurodegenerative diseases. 46 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
47 7.0T glycogen spectrum from calf muscle Natural abundance 13 C (left) and 1 H (right) spectra recorded at 7.0T from human calf muscle. The 13 C C1 glycogen peak is clearly visible (inset). 13 C spectroscopy can be applied to measure the rates at which the 13 C label is transferred from glucose to glutamate. Prof. Morris says using the Achieva 7.0T system for multi-nuclear MR spectroscopy has lived up to his expectations. We do see the improvement in sensitivity and the ability to get relatively better homogeneity at higher fi elds than in some of the lower fi eld systems. We realize the advantage of the additional chemical shift dispersion, and can separate out the different metabolites in a way that s not possible at lower fi elds. At 7.0T, they are pulled apart and become much clearer. Vanderbilt investigating glycogen synthesis James Joers, PhD James Joers, PhD, Assistant Professor of Radiology and Radiological Sciences at Vanderbilt University Institute of Imaging Science (VUIIS) is investigating glycogen synthesis from infused 13 C and metabolic changes in the calf muscles of healthy volunteers. Dr. Joers hopes to begin similar research in other groups: people who are obese, people who have had bariatric surgery and people who have complications from obesity. We expect to see signifi cantly less glycogen synthesis in someone with insulin resistance. With bariatric surgery patients, we are less sure what to expect. Changes in intracellular hepatic and muscular lipid levels that are thought to regulate insulin sensitivity most likely change after surgery, thereby having an effect on glucose clearance. However, the metabolic changes due to contributions from surgery and those from the low-calorie diets that occur in conjunction with the surgery are largely unknown. We hope to fi nd out what those metabolic contributions are, and how they manifest themselves in that particular realm of glucose consumption and usage. He and his team are also in the process of developing and refi ning methodologies for studying localized 13 C in the brain at 7.0T. They hope to use both the muscle and brain spectroscopy to examine the metabolic differences between healthy and diseased populations. FieldStrength 47
48 Spectral time course after ingestions of 13 C The spectrum shown in red is the pre-ingestion natural abundance spectrum. The other spectra are measured after ingestion of 13 C labelled glucose. The 13 C spectrum on the right shows the glucose/glycogen region 2.5 hours post-ingestion. First experiments a success I was pleasantly surprised at how well our fi rst experiences at 7.0T went, says Dr. Joers. We received our Philips multinuclear spectroscopy (MNS) upgrade in October of 2008, and within two weeks we were getting natural abundance glycogen signal in a 10-minute scan from a human calf muscle. In the fi rst in-vivo glycogen spectrum we took, the peaks just jumped out. And since the 13 C-infused glucose is still a little pricey, we had used natural abundance levels. Being able to observe the spectrum at such low levels was quite pleasing. In the fi rst in-vivo glycogen spectrum we took from a human calf muscle, the peaks just jumped out. Philips has active role in 7.0T research To enable multinuclear spectroscopy, the Achieva 7.0T systems at both sites are equipped with an additional receiver operating at 13 C frequency, and an RF amplifi er operating at 13 C frequency. In addition, they are using special coils, and have developed some specifi c pulse sequences and higher bandwidth RF waveforms. a valuable platform for feedback and information exchange. The future of 7.0T usability is wide open. The prospects are extremely promising, both for research in spectroscopy and in imaging. Prof. Morris appreciates Philips participation in this type of research. Philips has put a lot of effort into producing the multinuclear spectrometer. They ve also built and refi ned the 13 C coil, and it has pretty much worked right out of the box. We are very pleased with the way it has all come together. Dr. Joers adds, Philips plays its role in the 7.0T research, and the Philips 7.0T user meetings are References: 1 Shulman G.I. Rothman D.L. et al. Quantitation of muscle glycogen-synthesis in normal subject and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by C-13 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. NEJM (4): Petersen K.F. and Shulman G.I. Etiology of insulin resistance. AJM , (Suppl.) 5A:10S-16S. 48 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
49 MR news FieldStrength is going Green: register for version In an effort to be more environmentally friendly, FieldStrength now offers electronic-only subscriptions. When a new FieldStrength issue is available, subscribers to the electronic version will receive an overview. A click on an article of interest will take you to the online version of that article. Online FieldStrength offers more: Image movies when relevant Direct links to NetForum ExamCards PDF versions of selected articles or the full issue Capability to print only the pages that interest you To preview FieldStrength online, go to eldstrength. You can enter a new online subscription or modify your current subscription from print to electronic. FieldStrength readers who do prefer so, can of course, still continue to receive the printed version. Please consider the environment before printing any document. From NetForum With over 13,000 registrations the NetForum Communities are still growing. Within MRI NetForum, ExamCards are the most viewed documents. However, online training modules, web seminars and application tips are also very popular. Benefit and contribute Downloading an ExamCard from NetForum into your own scanner enables you to use an expert protocol without investing development time. If you have developed an ExamCard that consistently provides good results, please share it on NetForum to help others add to their current practice. If you d like to contribute an ExamCard or Clinical Case, please use the Contact form on NetForum or send an to fi eldstrength@philips.com. Register to fully benefit Registered viewers have access to more functionality and content, including ExamCard downloads, online training modules, more application tips, safety training modules and FAQ. Most popular NetForum documents in first half of 2009: 1. ExamCard: 1.5T Non-CE renal/mesenteric MRA - Scottsdale Healthcare 2. Training module: Achieva R ExamCard: 1.5T Full length humerus with dual coils - Scottsdale Healthcare 4. ExamCard: 1.5T TRANCE lower legs 5. ExamCard: 1.5T Breast - University of Chicago NetForum Visit the NetForum User Community for downloading ExamCards and viewing application tips, clinical cases, extended versions of FieldStrength articles, and more. FieldStrength 49
50 Education calendar T AMIGENICS/NIC 3.0T courses Las Vegas, Nevada, USA Info: Colleen Perone, Tel. (+1) Visiting Physician Fellowship Programs Combination of didactic lectures and interactive MRI case reading with experienced 3.0T MR radiologists. Radiology Technologist Practicum Hands-on experience and technical insights. Breast MRI Advanced Breast MRI Workshop Cleveland, Ohio, USA Date: October 8-9 Two-day course for radiologists, technologists. Participants have basic knowledge of MRI, breast imaging. The course combines lectures and the clinical practice of breast MR. Note that class size for this course is limited. Info: The Chicago International Breast Course Chicago, USA Date: October 1-4 Info: education/cme/cibc2009/ Soc. of Breast Imaging Postgraduate course Washington D.C. Date: October Info: Advances in Breast MRI Las Vegas, USA Date: October Info: radiologycme.stanford.edu/2009bmri Musculoskeletal Erasmus Course on Musculoskeletal MRI Bratislava, Slovakya Date: October 5-9 Info: MR Angiography Contrast-enhanced MRA in clinical practice Maastricht, The Netherlands Date: t.b.d. For physicians and radiographers. Includes teaching sessions and volunteer and patient scanning. Info: Tim Leiner, MD, PhD, Workshop MRI of Carotid Atherosclerosis Seattle, Washington, USA Date: September Info: our-research/groups/vil, Cardiac MR Cardiac MR courses at CMR Academy German Heart Institute, Berlin All courses are for cardiologists and radiologists. Some parts will be offered in separate groups. Info: Tel Fellowship Dates: Oct. 19 Nov. 27 and Nov 28 Jan 9 (2010) Intensive course including hands-on training at the German Heart Institute, and reading and partially quantifying over 250 cases Compact course Dates: October CMR diagnostics in theory and practice, including performing examinations and case interpretation. CVMRI Practicum: New Techniques and Better Outcomes St. Luke s Episcopal Hospital, Houston,Texas Date: t.b.d. On principles and practical applications of Cardiac MRI. Info: trose@sleh.com Tel , Fax: International Cardiac MR course Leeds, England Dates: June 15-19, Oct Deals with theoretical principles and practical applications of Cardiac MRI. Daily practical scanning and post-processing sessions in small groups. Info: Mgreen@leedscmr.org Erasmus Course on Cardiovascular MRI Leiden, Netherlands Date: October 8-9 Focuses on clinical applications of cardiac MR. Info: Cardiac MRI Training Washington Hospital Center, Washington, DC, USA Date: Three-month fellowship Info: Pamela Wilson Tel Cardiac MR Imaging in Clinical Practice Leeds, England Date: t.b.d. Designed by cardiologists for cardiology trainees and cardiologists. Includes the basics of CMR methodology and its daily applications. Lectures are presented with fi rmly clinical focus in a case-based format. Info: j.c.beeton@leeds.ac.uk Tel CMR case review Leeds, England Date: October cases in a day intensive course for cardiology or radiology trainees or physicians. Info: j.c.beeton@leeds.ac.uk Tel Cardiovascular MR training courses and fellowships St. Louis, Mo., USA Date: Spring 2010 Lecture format (2.5 days) or lecture plus hands-on (4 days). Also offered are hands-on technologist training courses and three-month fellowships. Info: ctrain.wustl.edu, cme@wustl.edu Tel MR Spectroscopy MR Spectroscopy course (1.5T and 3.0T) Zurich, Switzerland Date: July 6-10, 2009 Theory sessions and daily practical scanning and post-processing sessions in small groups. Info: education-centre, dmeier@ethz.ch Advanced MR Spectroscopy Cleveland, Ohio, USA Dates: September 29 - October 2 Four-day course for clinical scientists, MR engineers, research technologists, physicians, and physicists of Philips MR sites, interested in MR spectroscopy. Participants require basic MR scanning experience. Note that class size for this course is limited Info: vicki.milligan@philips.com NetForum Register on NetForum to have free access to online training modules on use of Philips MR scanners and packages, use of coils, MR safety. 50 FieldStrength Issue 38 Summer 2009
51 General MR Essential Guide to Philips in MRI Different locations, UK Dates: October Specifically designed for Philips users, past, present and future. It is designed to provide a modular approach to accommodate all levels of knowledge Info: lorna.smith@philips.com MRI self-directed visiting fellowship ProScan Education Foundation Cincinnatti, Ohio, USA Date: continuously throughout the year. Info: Visiting_Fellowships-448.html, mrieducation@proscan.com Tel MRI-EDUC North American off-site training courses Dates: upon request Info: lori.hawkins@philips.com Tel Fax: MR Basics Cleveland, Ohio, USA Designed for the novice technologists with little or no previous MR experience. Lectures cover the basic concepts and theory of MRI. This program is entirely didactic and theory based. MR Essentials for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, Ohio, USA This comprehensive course for technologists covers all basic scanning and system functionality. Lectures cover MRI safety, scan parameters, and pulse sequences. MR Advanced for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, Ohio, USA Didactic and hands-on course covering advanced applications including advanced scan parameters, pulse sequences, advanced Neuro, Ortho, Body and Breast imaging techniques. Extended MR WorkSpace for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, Ohio, USA Didactic and hands-on course covering basic system maintenance, EWS functionality, and all MR analysis packages with lectures in Cardiac imaging, fmri and Diffusion Tensor imaging and Fiber Tracking. Cardiac Imaging for Achieva, Intera and Panorama HFO users Cleveland, Ohio, USA Didactic and hand-on course covering all cardiac views, heart valves, Q-flow, coronary arteries and the postprocessing packages on the EWS. Events calendar Date Event Location More information August Highfield MR Symposium Bonn, Germany Aug. 29 Sep. 2 European Society of Cardiology ESC Barcelona, Spain September 1-4 Röntgenveckan Jönköping, Sweden September European Society of Neuroradiology ESNR Athens, Greece September Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society Lisbon, Portugal of Europe CIRSE Sep 29 Oct. 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography MRA Club East Lansing, MI, USA October 1-3 European Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medecine Antalya, Turkey and Biology ESMRMB October 7-11 American Society of Head Neck Radiology ASHNR New Orleans, LA, USA October Journées Françaises de Radiologie JFR Paris, France November 1-5 American Society for Therapeutic Radiology Chicago, IL, USA and Oncology ASTRO November American Heart Association AHA Orlando, FL, USA scientificsessions.americanheart.org Nov. 29 Dec. 4 Radiological Society of North America RSNA Chicago, IL, USA January Arab Health Dubai, UAE May 1-7 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine ISMRM Stockholm, Sweden FieldStrength 51
52 What inspired our MultiTransmit innovation in 3T? No two patients are alike. The Achieva 3.0T TX automatically adjusts to each patient s unique anatomy. Its MultiTransmit parallel RF transmission technology tailors the RF signals to provide consistent high image quality and reduced scan times across a broad range of clinical applications. Make diagnoses based on information that is fast, robust and reliable. It just makes clinical and economic sense. To learn more, please visit us at *Because our innovations are inspired by you.
Publication for the Philips MRI Community. New MultiTransmit technology advances 3.0T imaging
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 New technology advances 3.0T imaging Tokai University School of Medicine reports significant benefits for image quality and
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 New technology advances 3.0T imaging Tokai University School of Medicine reports significant benefits for image quality and
Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 38 Summer 2009 Pediatric MSK imaging benefits from tailored scan protocols Vanderbilt University Children s Hospital builds dedicated scans
FieldStrength. Leuven research is finetuning. whole body staging
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 40 May 2010 Leuven research is finetuning 3.0T DWIBS for whole body staging The University Hospital of Leuven is researching 3.0T whole body
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 40 May 2010 Leuven research is finetuning 3.0T DWIBS for whole body staging The University Hospital of Leuven is researching 3.0T whole body
The first MR with IQ. Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam
 The first MR with IQ Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam Smart Exam reproducibility 2 consistency, and efficiency Philips Intera 1.5T gives you the image quality, patient comfort and range of clinical applications
The first MR with IQ Philips Intera 1.5T With SmartExam Smart Exam reproducibility 2 consistency, and efficiency Philips Intera 1.5T gives you the image quality, patient comfort and range of clinical applications
Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
An excellent fit to expand the imaging center, Prodiva 1.5T
 An excellent fit to expand the imaging center, Prodiva 1.5T FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - December 2017 www.philips.com/fieldstrength High quality MR imaging combined with a simplified,
An excellent fit to expand the imaging center, Prodiva 1.5T FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - December 2017 www.philips.com/fieldstrength High quality MR imaging combined with a simplified,
Fast and easy diagnostic imaging from head to toe
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 50 2014 / 1 Fast and easy diagnostic imaging from head to toe Ingenia 1.5T with dstream provides speed and convenience, IntelliSpace Portal provides flexibility
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 50 2014 / 1 Fast and easy diagnostic imaging from head to toe Ingenia 1.5T with dstream provides speed and convenience, IntelliSpace Portal provides flexibility
MRI to fit your planning. Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration
 MRI to fit your planning Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration MR Imaging that fits Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration allows radiation oncologists to take full advantage of MRI s excellent
MRI to fit your planning Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration MR Imaging that fits Philips Panorama HFO Oncology Configuration allows radiation oncologists to take full advantage of MRI s excellent
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December More patients and high clinical versatility
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 More patients and high clinical versatility Panorama HFO accommodates broader patient group and provides exceptional results
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 More patients and high clinical versatility Panorama HFO accommodates broader patient group and provides exceptional results
Large health system benefits from multiple scanners for breast MRI
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 42 DECEMBER 2010 Large health system benefits from multiple scanners for breast MRI Breast MR and MR-guided biopsy are daily practice at WellStar Health
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 42 DECEMBER 2010 Large health system benefits from multiple scanners for breast MRI Breast MR and MR-guided biopsy are daily practice at WellStar Health
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
FreeWave upgrade enables faster, more powerful imaging
 FreeWave upgrade enables faster, more powerful imaging Western Neurological Associates upgrades Intera 1.5T to Release 2.5 with FreeWave, and sees a significant improvement in image quality and efficiency.
FreeWave upgrade enables faster, more powerful imaging Western Neurological Associates upgrades Intera 1.5T to Release 2.5 with FreeWave, and sees a significant improvement in image quality and efficiency.
Ingenia 3.0T excels in cardiac imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 45 2012/1 Ingenia 3.0T excels in cardiac imaging St. Luke s Episcopal Hospital sees huge advantages in image quality, workflow Publication for the Philips
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 45 2012/1 Ingenia 3.0T excels in cardiac imaging St. Luke s Episcopal Hospital sees huge advantages in image quality, workflow Publication for the Philips
Expanding therapy options for
 MR systems Sonalleve MR-HIFU Expanding therapy options for women s health and oncology 2 Discover the freedom of patient-friendly and non-invasive therapy options Sonalleve MR-HIFU is an innovative therapy
MR systems Sonalleve MR-HIFU Expanding therapy options for women s health and oncology 2 Discover the freedom of patient-friendly and non-invasive therapy options Sonalleve MR-HIFU is an innovative therapy
Herlev radiation oncology team explains what MRI can bring
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 Herlev radiation oncology team explains what MRI can bring The radiotherapy unit at Herlev University Hospital investigates use of MRI for radiotherapy
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 Herlev radiation oncology team explains what MRI can bring The radiotherapy unit at Herlev University Hospital investigates use of MRI for radiotherapy
MultiTransmit 4D brings robustness to 3.0T cardiac imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 44 SUMMER 2011 MultiTransmit 4D brings robustness to 3.0T cardiac imaging Bonn clinicians see a reduction in artifacts and inhomogeneities as a significant
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 44 SUMMER 2011 MultiTransmit 4D brings robustness to 3.0T cardiac imaging Bonn clinicians see a reduction in artifacts and inhomogeneities as a significant
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo
 Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR.
 GE Healthcare PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR. MR Radiation Oncology Suite MAXIMIZE YOUR PRECISION. HELP MINIMIZE PATIENT COMPLICATIONS. Our goal in MR radiation oncology is to
GE Healthcare PINPOINTING RADIATION THERAPY WITH THE PRECISION OF MR. MR Radiation Oncology Suite MAXIMIZE YOUR PRECISION. HELP MINIMIZE PATIENT COMPLICATIONS. Our goal in MR radiation oncology is to
FieldStrength. Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging. SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology. Publication for the Philips MRI Community
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 Tips for abdomen/pelvis oncology imaging SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology This article is part of Field Strength issue 41, September
University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards
 I s s u e 3 1 - M a rc h 2 0 0 7 F i e l d Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards Drs. Mukherji, Parmar create Achieva 3.0T ExamCards
I s s u e 3 1 - M a rc h 2 0 0 7 F i e l d Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards Drs. Mukherji, Parmar create Achieva 3.0T ExamCards
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
Field Strength. Achieva 3.0T excels in wide range of applications. Fletcher Allen Health Care finds many uses for versatile system
 Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Achieva 3.0T excels in wide range of applications Fletcher Allen Health Care finds many uses for versatile system This article is part of Field
Field Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Achieva 3.0T excels in wide range of applications Fletcher Allen Health Care finds many uses for versatile system This article is part of Field
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging
 Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
Echelon Oval provides a robust suite of leading musculoskeletal imaging capabilities for detailed assessment of all anatomy for your most challenging cases. Hitachi Medical Systems America, Inc. 1959 Summit
MR neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves
 Publication for the Philips I Community ISSE 50 2014 / 1 neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves Shandong edical Imaging esearch Institute explores DWIBS for neurography in extremities
Publication for the Philips I Community ISSE 50 2014 / 1 neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves Shandong edical Imaging esearch Institute explores DWIBS for neurography in extremities
Ingenia MR-RT. MR Systems. The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning
 Ingenia MR-RT MR Systems The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning Table of contents Experience the difference MRI makes 3 A comprehensive MR-sim solution 4 Position with precision 6 Tailored
Ingenia MR-RT MR Systems The comprehensive MR-sim solution to fit your planning Table of contents Experience the difference MRI makes 3 A comprehensive MR-sim solution 4 Position with precision 6 Tailored
A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed
 A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed The new Philips Ingenia Elition X solution offers cutting-edge MR imaging techniques,
A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed A revolutionary breakthrough in diagnostic quality and speed The new Philips Ingenia Elition X solution offers cutting-edge MR imaging techniques,
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
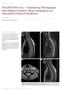 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Ingenia Elition S. 3.0T imaging at your fingertips
 3.0T imaging at your fingertips 3.0T imaging at your fingertips Healthcare is maturing daily setting and adopting new standards in clinical pathways. At the same time, there is a need for high productivity,
3.0T imaging at your fingertips 3.0T imaging at your fingertips Healthcare is maturing daily setting and adopting new standards in clinical pathways. At the same time, there is a need for high productivity,
FieldStrength. Multi-parametric 3.0T MRI provides excellent prostate imaging
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 35 September / October 2008 Multi-parametric 3.0T MRI provides excellent prostate imaging Three different centers show that advances in imaging
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 35 September / October 2008 Multi-parametric 3.0T MRI provides excellent prostate imaging Three different centers show that advances in imaging
BioMatrix Tuners: CoilShim
 MAGNETOM Vida special issue Head and Neck Imaging Clinical 11 BioMatrix Tuners: CoilShim Miriam R. Keil, Ph.D.; Jörg Rothard; Carmel Hayes, Ph.D. Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany A cervical spine
MAGNETOM Vida special issue Head and Neck Imaging Clinical 11 BioMatrix Tuners: CoilShim Miriam R. Keil, Ph.D.; Jörg Rothard; Carmel Hayes, Ph.D. Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany A cervical spine
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
UVM brain MRI protocols upgraded with latest methods
 UVM brain MRI protocols upgraded with latest methods FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - March 2017 UVM appreciates latest neuro MR methods for diagnosing and workflow The MRI staff at University
UVM brain MRI protocols upgraded with latest methods FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - March 2017 UVM appreciates latest neuro MR methods for diagnosing and workflow The MRI staff at University
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors
 Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
ACR MRI Accreditation Program. ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update. Educational Objectives. ACR accreditation. History. New Modular Program
 ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions
 Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Emergency Abdominal MRI Protocols
 2018 SPR Annual Meeting & Postgraduate Course May 15-19, 2018 Nashville, Tennessee Emergency Abdominal MRI Protocols Unni Udayasankar MD Associate Professor Department of Medical Imaging University of
2018 SPR Annual Meeting & Postgraduate Course May 15-19, 2018 Nashville, Tennessee Emergency Abdominal MRI Protocols Unni Udayasankar MD Associate Professor Department of Medical Imaging University of
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology
 Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology & Urology Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital Disclosures
Abdominal MRI Techniques in Pediatric Oncology Jonathan R. Dillman, M.D. Assistant Professor Departments of Radiology & Urology Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital Disclosures
Worldwide Leading Academic Center Gets a Lift in Advanced MR Imaging
 Worldwide Leading Academic Center Gets a Lift in Advanced MR Imaging As one of the largest and most authoritative scientific medical centers in Europe, Erasmus University Medical Center (Rotterdam, Netherlands),
Worldwide Leading Academic Center Gets a Lift in Advanced MR Imaging As one of the largest and most authoritative scientific medical centers in Europe, Erasmus University Medical Center (Rotterdam, Netherlands),
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
FieldStrength. MR-guided prostate biopsy boosts accuracy of diagnosis at Aachen
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology MR-guided prostate biopsy boosts accuracy of diagnosis at Aachen Montreal MR-OR suite enables
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 41 September 2010 SPECIAL ISSUE MR in oncology MR-guided prostate biopsy boosts accuracy of diagnosis at Aachen Montreal MR-OR suite enables
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 肌肉骨骼磁振造影. 本週課程內容 General Technical Considerations 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系
 本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
本週課程內容 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu 肌肉骨骼磁振造影簡介 醫用磁振學 MRM 肌肉骨骼磁振造影 盧家鋒助理教授國立陽明大學生物醫學影像暨放射科學系 alvin4016@ym.edu.tw MRI of the musculoskeletal system (5th/6th edition) Editor: Thomas H. Berquist MD 2 General
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 65. Benign Hepatic Masses
 65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Field Strength. Regional Perfusion Imaging (RPI) matches cerebral arteries to flow territories
 Field Strength Changing how the world looks at MR. Regional Perfusion Imaging (RPI) matches cerebral arteries to flow territories Research groups in Utrecht, Baltimore and Singapore collaborate on this
Field Strength Changing how the world looks at MR. Regional Perfusion Imaging (RPI) matches cerebral arteries to flow territories Research groups in Utrecht, Baltimore and Singapore collaborate on this
Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner. Answers for life.
 Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner Answers for life. 1 ACQUIRE An automated whole breast solution. Reduced acquisition time.
Full ultrasound breast volumes. Faster scans. Streamlined workflow. ACUSON S2000 Automated Breast Volume Scanner Answers for life. 1 ACQUIRE An automated whole breast solution. Reduced acquisition time.
How Much Tesla Is Too Much?
 How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours. Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany
 PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
Functional Orthopedic Imaging Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion. Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy.
 Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Capturing Motion, Flow and Perfusion dynamic volume CT Case Study Brochure Centre University Hospital Nancy http://www.toshibamedicalsystems.com Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation 2013. All rights reserved.
Enhancing diagnostic confidence in the technically difficult patient
 Ultrasound Customer story Enhancing diagnostic confidence in the technically difficult patient Philips Affiniti 70 with PureWave technology Putting Affiniti to the test A study of abdominal exams at Freeman
Ultrasound Customer story Enhancing diagnostic confidence in the technically difficult patient Philips Affiniti 70 with PureWave technology Putting Affiniti to the test A study of abdominal exams at Freeman
Ultrasound - Prostate
 Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Prostate Ultrasound of the prostate uses sound waves to produce pictures of a man s prostate gland and to help diagnose symptoms such as difficulty urinating or an elevated
Scan for mobile link. Ultrasound - Prostate Ultrasound of the prostate uses sound waves to produce pictures of a man s prostate gland and to help diagnose symptoms such as difficulty urinating or an elevated
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI BREAST CANCER. The incidence of getting breast cancer is 1:19 in Malaysia
 Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
Anyone can get breast cancer BREAST MRI KATE Datin Dr Fatimah Moosa Sunway Medical Centre DATIN SERI ENDON KYLIE SIZE DOES NOT MAKE A DIFFERENCE BREAST CANCER The incidence of getting breast cancer is
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
Staging Colorectal Cancer
 Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
Staging Colorectal Cancer CT is recommended as the initial staging scan for colorectal cancer to assess local extent of the disease and to look for metastases to the liver and/or lung Further imaging for
difference in MR oncology
 Melany Atkins, M airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Tom Schrack, ARMRIT, S airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Making a difference in MR oncology imaging Oncologic imaging represents
Melany Atkins, M airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Tom Schrack, ARMRIT, S airfax Radiology onsultants (R) in airfax, VA Making a difference in MR oncology imaging Oncologic imaging represents
MEASUREMENT OF EFFECT SOLID TUMOR EXAMPLES
 MEASUREMENT OF EFFECT SOLID TUMOR EXAMPLES Although response is not the primary endpoint of this trial, subjects with measurable disease will be assessed by standard criteria. For the purposes of this
MEASUREMENT OF EFFECT SOLID TUMOR EXAMPLES Although response is not the primary endpoint of this trial, subjects with measurable disease will be assessed by standard criteria. For the purposes of this
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Westmead Breast Cancer Institute
 Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast MRI? Breast MRI is a technique that uses a magnetic field to create an image of the breast tissue, using hundreds
Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Westmead Breast Cancer Institute What is breast MRI? Breast MRI is a technique that uses a magnetic field to create an image of the breast tissue, using hundreds
Breast Cancer Screening
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
Scan for mobile link. Breast Cancer Screening What is breast cancer screening? Screening examinations are tests performed to find disease before symptoms begin. The goal of screening is to detect disease
The Key to Confidence
 WITH The Key to Confidence The Key to Confidence More detail, better accuracy, greater confidence The G-scan Brio is a revolutionary MRI approach for all musculoskeletal applications, which allows you
WITH The Key to Confidence The Key to Confidence More detail, better accuracy, greater confidence The G-scan Brio is a revolutionary MRI approach for all musculoskeletal applications, which allows you
OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER
 OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER By Dr. John Feller, MD, Radiologist Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA MRI is clinically accepted as the best imaging modality for displaying anatomical
OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER By Dr. John Feller, MD, Radiologist Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA MRI is clinically accepted as the best imaging modality for displaying anatomical
FieldStrength. Elite Clinical Solution enhances breast imaging
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 36 December 2008 Elite Clinical Solution enhances breast imaging Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit RF technology Non-contrast-enhanced MRA
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 36 December 2008 Elite Clinical Solution enhances breast imaging Achieva 3.0T TX with MultiTransmit RF technology Non-contrast-enhanced MRA
For a legacy that lives large: Think Big. Philips CT Big Bore. Computed tomography
 Computed tomography For a legacy that lives large: Think Big Philips CT Big Bore The big question The world of cancer care is rapidly changing. The number of new cancer cases is expected to rise by about
Computed tomography For a legacy that lives large: Think Big Philips CT Big Bore The big question The world of cancer care is rapidly changing. The number of new cancer cases is expected to rise by about
WITH. The Next Step in Office MRI
 WITH The Next Step in Office MRI Introducing S-scan the Next Step in Office MRI Based on extensive customer feedback and years of engineering, Esaote has designed the S-scan with exp Technology, an optimized
WITH The Next Step in Office MRI Introducing S-scan the Next Step in Office MRI Based on extensive customer feedback and years of engineering, Esaote has designed the S-scan with exp Technology, an optimized
Breast MRI Update. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition
 www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Musculoskeletal tumours Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Primary bone tumours 3 Clinical
www.rcr.ac.uk Recommendations for cross-sectional imaging in cancer management, Second edition Musculoskeletal tumours Faculty of Clinical Radiology www.rcr.ac.uk Contents Primary bone tumours 3 Clinical
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Elastography in the. technically difficult patient. EPIQ ultrasound system. Ultrasound
 Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Optimized. clinical pathway. propels high utilization of PET/MR at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital
 Optimized propels high utilization of PET/MR at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital clinical pathway As one of Europe s largest teaching hospitals, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital is renowned for its innovative research
Optimized propels high utilization of PET/MR at Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital clinical pathway As one of Europe s largest teaching hospitals, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital is renowned for its innovative research
Intuitive. Intelligent. Innovative. General Imaging
 Intuitive. Intelligent. Innovative. General Imaging CLARITY CONFIDENCE EASE OF USE 2 Complete flexibility, outstanding quality For robust performance you can rely on for a wide range of clinical tasks,
Intuitive. Intelligent. Innovative. General Imaging CLARITY CONFIDENCE EASE OF USE 2 Complete flexibility, outstanding quality For robust performance you can rely on for a wide range of clinical tasks,
High performance compact ultrasound
 High performance compact ultrasound Philips CX30 CompactXtreme ultrasound system Philips CX30 CompactXtreme Philips CX30 CompactXtreme ultrasound system goes wherever you need it, bringing ultrasound excellence
High performance compact ultrasound Philips CX30 CompactXtreme ultrasound system Philips CX30 CompactXtreme Philips CX30 CompactXtreme ultrasound system goes wherever you need it, bringing ultrasound excellence
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018)
 MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
MRI-PET: Oncologic Applications
 MRI-PET: Oncologic Applications Pablo R. Ros, MD University Hospitals Case Medical Center Case Western Reserve University SCBT-MR Boston, MA October, 2012 Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org Acknowledgement Osman
MRI-PET: Oncologic Applications Pablo R. Ros, MD University Hospitals Case Medical Center Case Western Reserve University SCBT-MR Boston, MA October, 2012 Pablo.Ros@UHhospitals.org Acknowledgement Osman
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) Ultrasound - Abdomen Children s (pediatric) ultrasound imaging of the abdomen is a safe, noninvasive test that uses sound waves to produce a clear picture of
Designed for first-time-right imaging and increased patient comfort for a faster workflow *. Ingenia 1.5T S. MR systems
 1 Premium IQ defined as increased SNR and speed and improved fat-free and motion-free imaging obtained on dstream with ds SENSE, mdixon and MultiVane XD compared to Achieva with SENSE, Dixon and Propeller.
1 Premium IQ defined as increased SNR and speed and improved fat-free and motion-free imaging obtained on dstream with ds SENSE, mdixon and MultiVane XD compared to Achieva with SENSE, Dixon and Propeller.
Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Achieva 7.0T put into action in Alzheimer s disease research
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 43 MaY 2011 Achieva 7.0T put into action in Alzheimer s disease research With its exceptionally high SNR, 7.0T MR is used in research on Alzheimer s disease
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 43 MaY 2011 Achieva 7.0T put into action in Alzheimer s disease research With its exceptionally high SNR, 7.0T MR is used in research on Alzheimer s disease
