NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
|
|
|
- Peregrine Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves Skull base Orbits TMJ s Soft tissue neck Nasopharynx/Face Sinus Glomus Tumor Brachial Plexus Cervical spine Thoracic spine Lumbar spine Sacrum Spine screen MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
2 Page 2 SIEMENS--Please uncheck the MTC box on T1 pre and post contrast brain imaging 06/07/17 MRI Brain without contrast for stroke (Use in the workup for stroke or TIA) FOV-230 5mm DWI/ADC axial FOV-230 5mm DWI/ADC coronal FOV-230 5mm T2 AX FOV-230 5mm T2 COR FOV-230 5mm FLAIR AX FS FOV-230 5mm GRAD HEMO FOV-230 5mm MRI Brain without contrast FOV-230 5mm DWI/ADC FOV-230 5mm T2 AX FOV-230 5mm T2 COR FOV-230 5mm FLAIR AX FS FOV-230 5mm GRAD HEMO FOV-230 5mm MRI Brain with/without contrast FOV-230 5mm DWI/ADC axial FOV-230 5mm Add Coronal DWI/ADC coronal if for stroke FOV-230 5mm DWI/ADC for GRAD HEMO FOV-230 5mm stroke/tia workup T2 COR FOV-230 5mm FLAIR AX FS FOV-230 5mm T1 AX FOV-230 5mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR) FOV-230 use water excitation keep isotropic 0.9 mm T2 AX FOV-230 5mm T1 AX POST FOV-230 5mm **IF YOU SEE A TUMOR, run the MPRAGE in the axial plane instead of the sagittal plane MRI Brain for seizures-preferred w/wo contrast
3 Page 3 MPRAGE SAG pre FOV mm DWI/ADC FOV-230 5mm 3D SAG T2 SPACE (dark fluid) (through mid-line) FOV-230 1mm ***perform axial and coronal MPR 3x1 T2 COR THIN (perpendicular to temporal lobe) FOV-230 3mm GRAD HEMO FOV-230 5mm T1 AX FOV-230 5mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR) 0.9 mm use water excitation keep isotropic T2 AX FOV-230 5mm T1 AX POST 5mm **IF you see a tumor, run the MPRAGE in the axial plane instead of the sagittal plane MRI Brain for MS-preferred w/wo contrast FOV-230 5mm DWI/ADC FOV-230 5mm 3D SAG T2 SPACE (dark fluid) (through mid-line) FOV-230 1mm GRAD HEMO FOV-230 5mm T1 AX FOV-230 3mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR) 0.9mm keep isotropic! use water excitation FOV 230 T2 AX FOV-230 5mm T1 AX POST FOV-230 3mm ***Do AX and COR MPR from SAG SPACE 3mm X 1mm **IF you see a tumor, run the MPRAGE in the axial plane instead of the sagittal plane MRI Brain for Pineal Gland-preferred w/wo contrast DWI/ADC (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm FLAIR AX FS (whole brain) FOV-230 5mm GRAD HEMO (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm
4 Page 4 THIN (MID LINE STRUCTURES) FOV-200 3mm T2 SAG THIN (MID LINE STRUCTURES) FOV-200 3mm T1 AX (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR) FOV mm keep isotropic! Use water excitation T2 AX (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 AX POST (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm *****IF you see a tumor, run the MPRAGE in the axial plane instead of the sagittal plane MRI Sella-preferred w/wo contrast THIN FOV-150 3mm T1 COR THIN FOV-150 3mm T2 COR THIN FOV 160 3mm T1 COR PRE 30 sec long 256x192 FOV 160 3mm ETL-3 HALF DOSE FOLLOWED BY SALINE BOLUS T1 COR DYNAMIC POST COPIED TO T1 COR PRE T1 COR DYNAMIC POST T1 COR DYNAMIC POST T1 COR DYNAMIC POST T1 COR DYNAMIC POST COPIED TO T1 COR PRE COPIED TO T1 COR PRE COPIED TO T1 COR PRE COPIED TO T1 COR PRE T1 COR THIN POST FOV-150 3mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR 5x5 and 3x3) FOV 230 keep isotropic! use water excitation THIN POST FOV-150 **** START SCAN IMMEDIATELY FOLLOWING INJECTION-use injector when possible ***You do not need to run the dynamic sequences if there is a obvious mass arising from the sella or if the patient has had previous pituitary surgery ***IF the referring orders a brain as well please add in the following sequences at no charge T2 AX FLAIR AX FS DIFFUSION *****IF you see a tumor, run the MPRAGE in the axial plane instead of the sagittal plane MRI FAST Scan for Hydrocephalus Single Shot TSE T2 Imaging (HASTE) in the axial, sagittal, and coronal planes matrix size, ; FOV 24; TR/TE/turbo factor, 1500 ms/120 ms/76; 5-mm section thickness;
5 Page 5 approximately 25 sections Total imaging time, approximately 90 seconds MRA/MRV MRA Brain only 3D TOF AX MRA Brain with and without contrast (Dr. Heck's follow up aneurysm coil) 3D TOF AX FL3D PRE FL3D POST ***We should only be giving contrast on MRA brain for Dr. Heck or Dr. Brown UNLESS the referring physician or the insurance company insist on doing the exam w/wo contrast MRV Brain-preferred with and without contrast 2D TOF (oblique Sagittal) PHASE SAG PHASE AX PHASE COR 3D SAG MPRAGE (Do COR MPR) FOV mm keep isotropic use water excitation ****IF THE PATIENT IS NOT SCHEDULED FOR AN MRI BRAIN AS WELL please include the following T2 AXIAL MRA brain with contrast only THE FOLLOWING EXAM WILL BE RARE AND IS ONLY TO BE USED WHEN THE REFERRING PHYSICIAN
6 Page 6 OR THE INSURANCE COMPANY INSISTS ON BEING SPECIFIC WITH REGARDS TO MRA Brain with contrast only FL3D PRE Administer 1 ml contrast 3D TOF AX Administer remaining contrast to equal weight based dose FL3D POST MRA Carotids with and without contrast 3D TOF (MIP right and left carotid together, rotate R/L) FL3D PRE T1 AX FS (COVER FROM 1 inch ABOVE SKULL BASE TO TOP OF STERNUM) FL3D POST (MIP right and left carotid together and separately, rotate R/L)
7 Page 7 ***Coverage on contrast enhanced sequence is from aortic arch to include COW MRA carotids without contrast 2D TOF (MIP right and left carotid together) 3D TOF (MIP right and left carotid together and separately) T1 AX FS (COVER FROM 1 inch ABOVE SKULL BASE TO TOP OF STERNUM) MRI 8th Nerve-preferred w/wo contrast DWI/ADC (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm FLAIR AX FS (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm 3D T2 AX (Post Fossa) FOV mm max REPLACE THE ABOVE SEQUENCE WITH THE FOLLOWING IF ABLE 3D CISS (Post Fossa) FOV max T1 AX THIN (Post Fossa) FOV-180 3mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR 5x5 & 3x3) FOV mm keep isotropic! Use water excitation T2 AX (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 AX FS POST (Post Fossa) FOV-180 3mm **Perform a COR MPR (2X1) on 3D sequence after cutting down to the IAC's **IF you see a tumor, run the MPRAGE in the axial plane instead of the sagittal plane MRI Cranial Nerves-preferred w/wo contrast (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 AX (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm FLAIR AX FS (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm DWI/ADC (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm
8 Page 8 T1 COR coverage below FOV-230 3mm 3D T2 AX (Post Fossa) FOV mm max REPLACE THE ABOVE SEQUENCE WITH THE FOLLOWING IF ABLE 3D CISS (Post Fossa) FOV mm max MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR 5x5 & 3x3) FOV mm keep isotropic! Use water excitation T2 AX (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 COR FS THIN (Post Fossa) FOV-180 3mm COVERAGE FOR CRANIAL NERVES 1st-6th--nerve cover from above optic chiasm through pons 7th nerve--cover 8th nerve region through parotid gland 9th-12th nerve--cover lower pons through tongue base INDICATIONS FOR CRANIAL NERVES Nerves 1-6 visual/pupillary problems facial/jaw pain orbital numbness Nerve 7 Ramsey Hunt Syndrome Bell's Palsy Nerve 8 Hearing loss dizziness Tinnitus Nerves 9-12 Swallowing difficulty **IF you see a tumor, run the MPRAGE in the axial plane instead of the sagittal plane MRI PARANASAL SINUS-Use for anosmia (whole brain) FOV mm T2 AX (whole brain) FOV mm T1 AX THIN (Sinus) FOV mm T1 COR THIN (Sinus) FOV mm T2 COR FS THIN (Sinus) FOV mm T2 AX FS THIN (Sinus) FOV mm
9 Page 9 MPRAGE SAG POST FOV mm keep isotropic! use water excitation T1 AX FS THIN POST (sinus) FOV mm T1 COR FS THIN POST (sinus) FOV mm Cover from tip of nose to the brain stem and superior border of frontal sinus to the level of the lower lip Cover all sinuses including a cut above the frontal sinuses on axials MRI Skull Base (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 AX (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm STIR AX (through skull base) FOV-200 3mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR) FOV mm keep isotropic! use water excitation T1 AX (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 COR FS (through skull base) FOV-200 3mm T1 AX FS (through skull base) FOV-200 3mm ******Axials--cover mandible through top of frontal sinus ******Coronals--cover dorsal pons through mid maxilary sinus MRI Orbits-preferred w/wo contrast DWI/ADC (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm FLAIR AX FS (Whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 AX THIN FOV-180 3mm T1 COR THIN FOV-180 3mm T2 COR FS THIN FOV-180 3mm T2 AX FS THIN FOV-200 3mm MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR) FOV mm keep isotropic use water excitation T1 AX FS THIN POST FOV-180 3mm
10 Page 10 T1 COR FS THIN POST FOV-180 3mm ***If referring physician orders a MRI brain also, you will perform the entire brain protocol and charge an additional study MRI TMJ'S T1 COR (mouth closed) 120 FOV 3mm PD/T2 SAG (mouth closed) 120 FOV 3mm ***open mouth to comfortable position PD/T2 SAG (mouth open) 120 FOV 3mm GRE SAG (one slice each side) 120 FOV 3mm ***repeat gradient at various degrees while patient closes mouth *****Create CINE file from gradient sequences to show ROM *****If using dual echo sequences separate PD and T2 into individual folders MRI Soft Tissue Neck (USE FOR PAROTID GLAND) preferred w/wo contrast T1 AX FOV-220 5mm T2 AX FOV-220 5mm T1 COR FOV-220 5mm T2 SAG FS FOV-220 5mm Midline to include both sides of tongue STIR COR FOV-250 5mm T1 AX POST FOV-220 5mm T1 COR FS POST FOV-220 5mm MRI Nasopharynx/Face FOV-220 5mm T1 AX FOV-220 3mm STIR AX FOV-220 5mm T2 COR THIN FOV-200 3mm cover anterior face through floor of anterior skull base MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR) keep isotropic! FOV mm use water excitation T1 AX FS FOV-220 3mm T1 COR FS FOV-220 3mm ******Axials--cover mandible through top of frontal sinus ******Coronals--cover dorsal pons through mid maxillary sinus
11 Page 11 MRI Glomus Tumor (Use for pulsitile tinnitus) FLAIR AX FS (whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T2 AX FS (whole brain) FOV-200 5mm DWI/ADC (whole brain) FOV-230 5mm T1 AX THIN (Post Fossa-include down to C2) FOV-180 3mm 3D TOF AX (COW-include down to C2) MPRAGE SAG POST (Do COR MPR 5x5 and 3x3) FOV mm keep isotropic! Use water excitation T1 AX THIN POST(Post Fossa-include down to C2) FOV-180 3mm ***The carotids have been dropped from the glomus tumor protocol-only do carotids if referring physician specifically asks for them MRI Brachial Plexus-prefered w/wo contrast T1 AX (scan bilaterally) T1 COR STIR AX T1 AX POST T1 COR FS POST FS POST *****scan unilaterally except for T1 AX *****AX coverage-c5 through level of axilla *****SAG coverage-glenoid of affected side through opposite side of spine MRI Cervical Spine T2 SAG SPACE SAG 0.9mm TE->120 ***Do axial MPR at 2mmX2mm from base of skull through T2 GRE AX **** see comments below ****If giving contrast add T1 AX PRE (copy to T2 AX) FS POST T1 AX POST ******* Axial coverage is C2-T1 ******** Add T2 AX if myelopathy or if you see abnormal signal in the cord
12 Page 12 ***Run T2 axial INSTEAD of MEDIC if there is a large amount of metal artifact from surgery MRI Thoracic Spine COUNTER 3mm slices T2 SAG 3mm slices 3mm slices SPACE SAG **Do axial MPR 3mmx3mm entire thoracic spine TE> mm T2 AX ("stack" through entire thoracic spine) 5mm-6mm **If giving contrast add T1 AX PRE (copy to T2 AX) FS POST 3mm slices T1 AX POST ******Counter must include C1 (without distortion) and Thoracic marker MRI Lumbar Spine-radiologists preference to perform w/wo if patient has has surgery within 10 years SPACE SAG TE-> mm ***** Do AX MPR 3mmx3mm entire lumbar spine-also do 4mmx4mm SAG MPR T1 AX (scan L3-4, L4-5, L5-S1 disc spaces) T2 AX (scan L3-4, L4-5, L5-S1 disc spaces) FS POST T1 AX POST ***If you do NOT have the ability to do a 3D sagittal sequence (SPACE) you must scan L2-L3, L3-L4, L4-L5, L5-S1 disc spaces axially MRI Spine for MS ***When scanning multiple studies for Multiple Sclerosis you can OMIT the SPACE sequence. Be certain to run the following in each ordered spinal exam. DO NOT forget to add the T2 sagittal in the lumbar region since we do not routinely perform the T2 sagittal. T2 SAG T1 AX T2 AX FS POST T1 AX POST
13 Page 13 MRI Sacrum T1 COR (parallel to sacrum) TE STIR COR (parallel to sacrum) PD FS SAG TE 45 T1 AX (perpendicular to sacrum) TE T2 FS AX MRI Sacrum w/wo T1 COR (parallel to sacrum) TE STIR COR (parallel to sacrum) T1 AX (perpendicular to sacrum) TE T2 FS AX FS FS (perpendicular to sacrum) T1 AX FS MRI Lumbosacral plexus-charge pelvis w/wo T1 AX STIR AX T2 COR SPACE T1 COR T2 SAG STIR COR T1 AX FS T1 COR FS ***Axials are straight, coronals are parallel to the sacrum ***COVERAGE IS BILATERAL FROM L3 TO TOP OF HIPS MRI Spine Screen Cervical spine
14 Page 14 T2 SAG Thoracic spine T2 SAG Lumbar spine T2 SAG ****You do NOT need to scan axials except in RARE cases of signifigant cord compression ****You do not need to do the SPACE sequence
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018)
 MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies
 Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards
 I s s u e 3 1 - M a rc h 2 0 0 7 F i e l d Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards Drs. Mukherji, Parmar create Achieva 3.0T ExamCards
I s s u e 3 1 - M a rc h 2 0 0 7 F i e l d Strength Publication for the Philips MRI Community University of Michigan continues fine-tuning neuro ExamCards Drs. Mukherji, Parmar create Achieva 3.0T ExamCards
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less)
 Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Pediatric CT Protocols (18 years old or less) Ped1: Head CT Ped2: Cervical spine CT Ped3: Sinus CT Ped4: Neck CT Ped5: Chest CT Ped6: Abdomen and pelvis CT Ped7: Thoracic or lumbar spine CT Ped8: Extremity
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels
 CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
CT of the Head, Spine, and Cerebral Vessels Objectives Determine specific imaging plane used to acquire or reformat CT scan, i.e. sagittal, coronal, transverse, and offaxis or oblique. Assess and evaluate
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
ORDERING GUIDELINES: MRI
 ORDERING GUIDELINES: MRI GENERAL INFORMATION: Pregnant Patients May undergo an MRI exam at any stage of pregnancy if the risk-benefit ratio to the patient warrants the study be performed. Present data
ORDERING GUIDELINES: MRI GENERAL INFORMATION: Pregnant Patients May undergo an MRI exam at any stage of pregnancy if the risk-benefit ratio to the patient warrants the study be performed. Present data
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS
 BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS Updated 03/14/2018 Routine Bilateral w/wo Silicone Breast Implant Post Biopsy Additional View Right Unilateral w/wo Left Unilateral w/wo Saline Breast Implant Biopsy Breast (Bilateral
BREAST MRI PROTOCOLS Updated 03/14/2018 Routine Bilateral w/wo Silicone Breast Implant Post Biopsy Additional View Right Unilateral w/wo Left Unilateral w/wo Saline Breast Implant Biopsy Breast (Bilateral
Body MRI General Comments
 Body MRI General Comments 1. All body imaging should be performed on a 1.5 T magnet unless body habitus necessitates the larger bore of the 3 T. 2. DWI is now considered standard protocol for all solid
Body MRI General Comments 1. All body imaging should be performed on a 1.5 T magnet unless body habitus necessitates the larger bore of the 3 T. 2. DWI is now considered standard protocol for all solid
Can SCMR CMR protocol recommendations
 Can SCMR CMR protocol recommendations V1.3 - April 2009 CanSCMR CMR Protocol and SOP Recommendation 2009 (15 minutes) 2 Planning of LV fct. real time multiple axes Realtime 3 cine long axis 6 long axes
Can SCMR CMR protocol recommendations V1.3 - April 2009 CanSCMR CMR Protocol and SOP Recommendation 2009 (15 minutes) 2 Planning of LV fct. real time multiple axes Realtime 3 cine long axis 6 long axes
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol. for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS. David K.B.
 Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
Consortium of MS Centres Guidelines Revised Standardized MRI Protocol for the Diagnosis and Follow-up of MS David K.B. Li MD FRCPC Indianapolis, Indiana May 27, 2015 Disclosure I have received research
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018)
 General Guidelines 1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE o Vibe / Lava o
General Guidelines 1.5T MRI BODY PROTOCOLS (Updated 3/26/2018) NEVER hesitate to reach out to a radiologist for guidance! Siemens / GE terminology, other abbreviations: o HASTE / SSFSE o Vibe / Lava o
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T
 BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
BODY MRI PROTOCOLS 1.5T Table of Contents Non Specific...3-5 Renals.....6-8 Adrenals.....9-11 Pancreas..12-14 Liver 15-17 Liver No Gad.18-21 Liver Eovist..22-24 Liver Iron Quant 25-29 MRCP.30-34 ENTEROGRAPHY.35-38
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
GUIDELINES FOR. Advanced. Imaging Studies
 GUIDELINES FOR Advanced Imaging Studies Locations Herrin Hospital Memorial Hospital of Carbondale St. Joseph Memorial Hospital 201 S 14th Street Herrin, IL 62948 618.942.2171 ext 35400 General Radiography*
GUIDELINES FOR Advanced Imaging Studies Locations Herrin Hospital Memorial Hospital of Carbondale St. Joseph Memorial Hospital 201 S 14th Street Herrin, IL 62948 618.942.2171 ext 35400 General Radiography*
CPT CODES. Ph: (307) Fax: (307) CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00
 Ph: (307) 382-4282 Fax: (307) 382-4291 CPT CODES CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00 74150 Abdomen w/o contrast $ 809.00 74160 Abdomen w/ contrast $1175.00 w/ contrast: $1262.00 74170 Abdomen w_w/o contrast $1324.00
Ph: (307) 382-4282 Fax: (307) 382-4291 CPT CODES CATSCAN IV Contrast: 87.00 74150 Abdomen w/o contrast $ 809.00 74160 Abdomen w/ contrast $1175.00 w/ contrast: $1262.00 74170 Abdomen w_w/o contrast $1324.00
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow
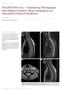 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging MAGNETOM Aera Combining Throughput and Highest Quality Spine Imaging in an Optimized Clinical Workflow Johan Dehem, M.D. VZW Jan Yperman, Ieper, Belgium Cervical spine imaging
MRI ANATOMICAL GUIDE Please include BUN Creatinine levels of all patients 60 and older or with H/O Renal Failure. Lab work is current within 3 months.
 Head & Neck Brain Alzheimer's Dz Stroke/CVA No MRI Brain w/o 70551 Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Suspected MS Tumor/mass/Cancer Seizures Cranial Nerve Lesions H Infection/ Abscess
Head & Neck Brain Alzheimer's Dz Stroke/CVA No MRI Brain w/o 70551 Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Suspected MS Tumor/mass/Cancer Seizures Cranial Nerve Lesions H Infection/ Abscess
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
05/02/ CPT Preauthorization Groupings Effective May 2, Computerized Tomography (CT) Abdomen 6. CPT Description SEGR CT01
 Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Preauthorization Groupings CPT
Computerized Tomography (CT) 6 & 101 5 Upper Extremity 11 Lower Extremity 12 Head 3 Orbit 1 Sinus 2 Neck 4 7 Cervical Spine 8 Thoracic Spine 9 Lumbar Spine 10 Colon 13 CPT Preauthorization Groupings CPT
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
screening; including image post processing CT, heart; without contrast material; with Requires authorization
 0042T Cerebral perfusion analysis using CT; with ; including of parametric maps with determination of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time 74263 Computed tomographic (CT) colonography,
0042T Cerebral perfusion analysis using CT; with ; including of parametric maps with determination of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and mean transit time 74263 Computed tomographic (CT) colonography,
MRI enters Emergency Department for fast, confident decisions
 MRI enters Emergency Department for fast, confident decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2016 www.philips.com/fieldstrength When MRI is the preferred choice, ED patients can
MRI enters Emergency Department for fast, confident decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - November 2016 www.philips.com/fieldstrength When MRI is the preferred choice, ED patients can
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA
 Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
Tips and Tricks of State of the art MRA Mayil Krishnam, MD,MBA, MRCP,FRCR(UK) Professor of Radiology Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine Objectives Technical
ACR MRI Accreditation Program. ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update. Educational Objectives. ACR accreditation. History. New Modular Program
 ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire
 Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Anatomy 2 nd Paper. Past Papers
 Anatomy 2 nd Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
Anatomy 2 nd Paper Past Papers September 2010 April 2010 September 2009 April 2009 September 2008 April 2008 September 2007 April 2007 September 2006 May 2006 September 2005 April 2005 September 2004 April
Stroke / CVA TIA Trauma Dizziness Headaches. Acoustic Neuroma Syrinx Visual Change Vascular Lesions (AVM) Elevated Prolactin Vertigo Bell s palsy
 Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
Head Brain Alzheimer s Mental Status Change Confusion Dementia Memory Loss Dizziness Headaches MRI Brain w/o 70551 Tumor / Mass / Cancer Cranial Nerve Lesions HIV Infection Suspected MS Neurofibromatosis
UPPER EXTREMITY
 UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
Routine Guide EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION. 14x17 CW* 14x17LW 14x17LW. 14x17LW 14x17LW 14x17LW
 EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging
 Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
Keep Imaging Simple: An Introduction To Neuroimaging Meghan Elkins, OD, FAAO Please silence all mobile devices and remove items from chairs so others can sit. Unauthorized recording of this session is
W/ (2) (3) (4) (5) (5) (6) (6) CTA
 Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
Index Abdomen W/ and W/Out (2) Abdomen Pelvis W/Out (3) Abdomen Pelvis W/ (4) Pelvis W/ (5) Chest W/Out (5) Chest/Abdomen/Pelvis W/ (6) Chest W/ (6) CTA ( 7-8) Neuro (8-9) Musculoskeletal (10) Trauma (11)
Contrast Guidelines for Common CT/CTA & MRI/MRA
 Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir. HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi
 Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Semiotics in Radiology
 Adelino Santos Health Technology College Coimbra, Portugal Collaboration of António Agudo Student of Radiology College of Health Technology Coimbra, Portugal What are the most important points to evaluate
Adelino Santos Health Technology College Coimbra, Portugal Collaboration of António Agudo Student of Radiology College of Health Technology Coimbra, Portugal What are the most important points to evaluate
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Special Instructions
 FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
FDA and ACR guidelines are as follows: Special Instructions Safety concerning NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCA) Prior to administering MRI contrast (GBCA), any patient who answers yes to
EXAMS_ Page 1/5 SORTED - NUMERIC
 BIOPSY 19103L-MR MV MR Guided Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77021, 10022, 19295, 90772, A4550, 99000 19103L-ST MV Stereotactic Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77031, 10022, 19295, 90772,
BIOPSY 19103L-MR MV MR Guided Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77021, 10022, 19295, 90772, A4550, 99000 19103L-ST MV Stereotactic Breast Biopsy, Vac Assist - LT 19103, 77031, 10022, 19295, 90772,
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions
 Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
Direct visualization of nerves can influence surgery decisions FieldStrength MRI magazine User experiences - April 2018 www.philips.com/fieldstrength Northern Fukushima MRI team adds 3D NerveVIEW sequence
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego. MR Angiography. Techniques & Applications. John R. Hesselink, M.D.
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego MR Angiography Techniques & Applications John R. Hesselink, M.D. Vascular Imaging Arterial flow void Flow enhancement Gadolinium enhancement Vascular
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review
 AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review Modality Body Part CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT
AIM 2014 CPT Radiology & Cardiac Codes Requiring Review Modality Body Part CT Head 1 70480 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; w/o contrast 1 CT Head 1 70481 CT orbit, sella or posterior fossa; with CT
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire
 Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Personalized Solutions. MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides
 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW
 INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
INDEPENDENT LEARNING: DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL FOOTBALL LEAGUE: ANATOMICAL FACTORS TO CONSIDER IN REVIEW CDC REPORT - CAUSES OF DISABILITY, 2005 REVIEW QUESTIONS ABOUT DISC HERNIATION IN THE NATIONAL
Nervous & Skeletal Systems. Virtual Science University
 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Spine. After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Positioning for Exams of the Spine. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-15. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify: 4-1. Identify
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 4 Positioning for Exams of the Spine. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 4-1 through 4-15. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to identify: 4-1. Identify
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Part II: MRI v. Metal
 Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
Orthopedic Hardware Imaging Trent Roth, MD And Lauren Ladd, MD Indiana University School of Medicine IU Health Physicians-Radiology Recap: Imaging Techniques Radiography Standard for initial and surveillance
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
HBA THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014
 HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
HBA 531 - THE BODY Head & Neck Written Examination October 23, 2014 Name: NOTE 2: When asked to trace nerve, artery, or vein pathways, do so by using arrows, e.g., structure a structure b structure c...
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Class Time: 9/12,10-10,11-21 Days: Listed Saturdays 1p-4p Room:HS208. Office Phone: Home Phone:
 Semester/Year: FALL 2015 CASPER COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS RDTK 1920 H1 Computed Tomography Procedures I Lecture Hours: 3 Lab Hours: 0 Credit Hours: 3 Class Time: 9/12,10-10,11-21 Days: Listed Saturdays 1p-4p
Semester/Year: FALL 2015 CASPER COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS RDTK 1920 H1 Computed Tomography Procedures I Lecture Hours: 3 Lab Hours: 0 Credit Hours: 3 Class Time: 9/12,10-10,11-21 Days: Listed Saturdays 1p-4p
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
We Accept Care Credit
 We Accept Care Credit Standard Fee Schedule Valid 1-Jan-18 to 1-July-18 **Prices Subject to Change, Call 702-222-3544 For Verification** Exam CPT PAYMENT IN FULL AT TIME OF SERVICE EKG 93000 35 TREADMILL
We Accept Care Credit Standard Fee Schedule Valid 1-Jan-18 to 1-July-18 **Prices Subject to Change, Call 702-222-3544 For Verification** Exam CPT PAYMENT IN FULL AT TIME OF SERVICE EKG 93000 35 TREADMILL
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
FOLLICULAR / OVULATION STUDY USG HIP JOINT (LEFT) USG HIP JOINT (RIGHT) USG KNEE JOINT (LEFT) USG KNEE JOINT (RIGHT) USG KUB USG MUSKULOSKELETAL USG
 RADIOLOGY TESTS SONOGRAPHY,COLOR DOPPLER 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN TWINS 3D/4D USG PELVIS ABDOMEN & PELVIS USG ABDOMEN UPPER USG ANKLE JOINT (LEFT) USG ANKLE JOINT (RIGHT) USG B SCAN BREAST
RADIOLOGY TESTS SONOGRAPHY,COLOR DOPPLER 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN 3D/4D ANAMOLY SCAN TWINS 3D/4D USG PELVIS ABDOMEN & PELVIS USG ABDOMEN UPPER USG ANKLE JOINT (LEFT) USG ANKLE JOINT (RIGHT) USG B SCAN BREAST
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for oral contrast**
 MRB AB01AMR 01aAbdomen (with dynamics) + Pelvis (pre/post) A74183 A72197 Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for
MRB AB01AMR 01aAbdomen (with dynamics) + Pelvis (pre/post) A74183 A72197 Indications: Abdomen and pelvis for malignancy. If there is history of small bowel or mesentery tumor, see "contrast" section for
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013
 Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
Vascular CT Protocols
 Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Vascular CT Protocols V 1D: Chest and abdominal CT angiogram (aortic dissection protocol) V 1T: Chest CT angiogram (aortic trauma protocol) V 2: Abdominal and pelvis CT angiogram (aortic aneurysm protocol)
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
