Optic Disc Ovality in Primary School Children in Beijing
|
|
|
- Job Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Anatomy and Pathology/Oncology Optic Disc Ovality in Primary School Children in Beijing Yin Guo, 1,2 Li Juan Liu, 2 Liang Xu, 2 Yan Yun Lv, 1 Ping Tang, 1 Yi Feng, 1 Jin Qiong Zhou, 2 Meng Meng, 1 and Jost B. Jonas 2,3 1 Tongren Eye Care Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China 2 Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China 3 Department of Ophthalmology, Medical Faculty, Mannheim of Ruprecht-Karls-University, Seegartenklinik Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany Correspondence: Liang Xu, Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology, 17 Hougou Lane, Chong Wen Men, Beijing, China; xlbio1@163.com. Yin Guo, Tongren Eye Care Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, No. 1 Dongjiaominxiang Street, Dongcheng District, Beijing, China; trguoyin@gmail.com. Submitted: February 1, 2015 Accepted: June 4, 2015 Citation: Guo Y, Liu LJ, Xu L, et al. Optic disc ovality in primary school children in Beijing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015;56: DOI: /iovs PURPOSE. The purpose of this study was to assess the ovality of the optic disc and its associations with myopia-related factors in primary school children in Beijing. METHODS. This longitudinal school-based study included 382 grade 1 children and 299 grade 4 children who were followed for 2 years. Study participants underwent a comprehensive eye examination including autorefractometry, ocular biometry, and fundus photography. RESULTS. Fundus photographs were available for 562 children (82.5%). The mean optic disc ovality (maximal-to-minimal disc diameter) was (range, ). Oval discs defined by an ovality of 1.33 were detected in 37 children (prevalence: 6.6%; 95% confidence interval: ). In multivariate linear regression analysis, higher optic disc ovality index was significantly associated with older age (P ¼ 0.001), female sex (P ¼ 0.005), larger parapapillary beta zone (P < 0.001), and shorter time spent indoors with studying (P ¼ 0.003) and was marginally significant (P ¼ 0.057), with greater increase in myopic refractive error from 2011 to From 2011 to 2013, myopic refractive error increased in the oval optic disc group by diopters compared to diopters in the nonoval disc group. CONCLUSIONS. The prevalence of oval optic discs in Beijing school children was markedly higher than in the elderly Beijing Eye Study population (6.6% vs. 0.36%), paralleling the higher prevalence of myopia in school children. The association between oval optic discs and less time spent indoors with studying after adjusting for longitudinal change in myopic refractive error, age, sex and parapapillary beta zone may warrant further exploration of external factors associated with oval optic discs. Keywords: myopia progression, ocular biometry, oval optic discs An oval-shaped optic disc represents the oblique insertion of the optic nerve into the ocular globe. 1 The prevalence of oval-shaped optic discs and their associations with myopia, in particular with high myopia, have been reported in previous studies In a longitudinal study of 1227 children, Samarawickrama et al. 11 found an oval disc prevalence in 37% of their study participants. The prevalence of oval-shaped optic discs was associated with more marked myopic refractive error, higher cylindrical refractive error, and longer axial length. Although previous studies were focused on oval optic discs, only few investigations, besides the study by Samarawickrama et al. 11 addressed the prevalence and associations of oval optic discs in children In addition, the definition of an oval disc varied among studies. Samarawickrama et al. 11 defined an oval or tilted optic disc to be present when one margin of the optic disc was raised above the opposite margin as seen from stereoscopic photographs, using a stereoscopic viewer. Other studies usually applied optic disc measurements and used minimal-to-maximal disc diameter ratio or vertical and horizontal disc diameters to define an oval disc shape. Because of the marked increase in the prevalence and severity of axial myopia in the young generation in East Asia and Southeast Asia and, because oval optic discs were associated with axial myopia, assessment of the prevalence and associated factors of oval discs may be of special interest in children, especially in China One would be particularly interested in identifying features in children which may predispose to an eventual myopic shift. Knowledge of such features also would be of potential help in elucidating factors influencing the axial elongation of the eyes of children. We therefore conducted this study to examine the prevalence of oval optic discs in school children from Beijing and to explore their associations with other parameters. METHODS The study included children who attended primary schools (grades 1 and 4) in a rural region and an urban area of greater Beijing. 17,18 The Human Research Ethics Committee of the Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, approved the study protocol, and informed written consent according to the Declaration of Helsinki was obtained from at least one parent per child after explaining the study to parents and children. Ophthalmologic examinations of the children included noncycloplegic autorefractometry (autorefractor KR-8900, Topcon, Tokyo, Japan) and measurement of best corrected visual Copyright 2015 The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, Inc. iovs.arvojournals.org j ISSN:
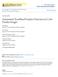
2 Optic Disc Ovality and Myopia Development IOVS j July 2015 j Vol. 56 j No. 8 j 4548 FIGURE. Oval optic nerve head in 2011 (left) and in 2013 (right) (same magnification); white arrows ¼ parapapillary beta zone; black arrows ¼ optic disc border; blue vertical bars (same length) ¼ vertical disc diameter unchanged; horizontal black bars (same length) ¼ horizontal disc diameter in 2013 (shorter in 2013 than in 2011); green horizontal bars (same length) ¼ horizontal width of parapapillary beta zone in 2011 (shorter in 2011 than in 2013). acuity by subjective refractometry. Spherical equivalent refractive error was calculated as spherical refractive error þ1/2 cylindrical refractive error. We also performed an examination of ocular motility, slit-lamp based biomicroscopy assessment of the anterior and posterior ocular segments, and nonmydriatic digital fundus photography (458; CR-DGI camera; Canon, Inc., Tokyo, Japan). Optical low-coherence reflectometry (Lenstar model LS900 optical biometer; Haag-Streit, Koeniz, Switzerland) was applied to measure central corneal thickness, corneal curvature, anterior chamber depth, lens thickness, and axial length of the right eyes of all subjects. All examinations were carried out by trained ophthalmologists and optometrists. The axial length-to-anterior corneal curvature (AL/CC) ratio, also known as axial length-to-corneal radius (AL/CR) ratio, was used as additional surrogate for refractive error. 19 In a standardized interview and referring to the whole previous year, the parents were asked how long the children needed to get to school and how they went (by foot, bicycle, bus, or private car); how much time during school breaks was spent outdoors; and how much time was spent with what kind of sports or with leisure during the week and during the weekends (see Supplementary Table S1). The total time spent outdoors was summarized as time spent in any activity outdoors. Parents were also asked about the time the children spent indoors, including the time spent watching television and playing with electronic devices (see Supplementary Table S2). The average time spent daily on these activities was calculated using the formula: [{(hours spent on a weekday) 3 5 þ (hours spent on a weekend day) 3 2}/7]. We also inquired about birth weight, mother s age at birth, whether the children were breast fed, smoking habits and alcohol consumption of father and mother, level of education and profession of both parents, size of the house the family inhabited (in m 2 ), monthly family income, and occurrence of myopia in the parents. Optic disc photographs were defined as assessable if the optic disc margin could be clearly identified. Using disc photographs and ImageJ version 1.43u software ( nih.gov/ij/; provided in the public domain by the National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA), we measured the horizontal, vertical, and minimal and maximal optic disc diameters and optic disc areas. The optic disc shape was assessed by its ovality factor, measured as the maximal-tominimal optic disc diameter ratio. 20 Similar to previous studies, an oval optic disc was defined as an optic nerve head with an ovality of 1.33 (Fig.). 21 The parapapillary region was differentiated into an alpha zone and a beta zone. 18 The alpha zone was characterized by irregular pigmentation. On its outer side, it was bounded by the retina, and by the beta zone on its inner side, or if there was no beta zone, with the peripapillary ring of the optic disc margin. Features of the beta zone included thinning of the chorioretinal tissues with good visibility of the large choroidal vessels and the sclera. Magnification by ImageJ system was Combined with the magnification factor 31.4 of the fundus camera, total magnification was We then corrected for the magnification by the optic medium of the eye, applying the method of Littmann, using either axial length measurements or refractive error measurements. 22 Measurements were made by a trained ophthalmologist (YG), supervised by two optic nerve head specialists (LX, JBJ). The panel of the two optic nerve head specialists convened at intervals of 1 to 2 months to supervise the main examiner (YG) by checking the results obtained on randomly selected study participants and to discuss the results obtained on images selected by the main examiner. Two years after the baseline examination, the children were invited to be re-examined using the same techniques. 23 Inclusion criterion for the present study was the availability of fundus photographs of sufficient quality to assess the optic discs. Statistical analysis was performed using commercially available statistical software (SPSS version 22.0; SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA; for Windows; Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). Parameters were presented as means 6 standard deviations. Normal distribution of the parameters was examined by
3 Optic Disc Ovality and Myopia Development IOVS j July 2015 j Vol. 56 j No. 8 j 4549 applying the Kolmogorov-Smirnoff test. Associations between disc ovality and other ocular and systemic parameters were examined first in univariate analysis and then in multivariate analysis. To examine associations between the prevalence of oval optic discs and other parameters such as refractive error, socioeconomic parameters, and indoor activity, the chi-square test was applied for categorical variables and a logistic regression analysis for continuous variables. After univariate analysis of potential associations, we performed a stepwise multivariate analysis with prevalence of oval optic discs as the dependent variable and, as independent variables, all parameters that showed a significant association with the main parameters in univariate analysis. Odds ratios (OR) were calculated and 95% confidence intervals (CI) were presented. All P values were 2-sided and were considered statistically significant when the values were less than RESULTS The study included 681 children, consisting of 382 students (56.1%) from grade 1 with a mean age of years (range, 5 8 years) and 299 students (43.9%) from grade 4 with a mean age of years (range, 8 13 years). Of these 681 children, fundus photographs of sufficient quality to assess the optic nerve head were available for 562 children (82.5%). The children with acceptable fundus photographs, compared to the children without those photographs, were significantly older ( years of age versus years of age; P < 0.001), had longer axial lengths ( mm versus mm; P ¼ 0.005), a higher AL/CC ratio ( vs ; P < 0.001), and were more myopic ( diopters versus diopters; P < 0.001). Of the 681 students examined at baseline in 2011, 542 individuals (79.6%) returned for a follow-up examination in In the period from 2011 to 2013, the mean refractive error became more myopic, from diopters by diopters, mean axial length increased from mm by mm, and mean AL/CC ratio increased from by At baseline examination in 2011, the mean optic disc ovality (minimal-to-maximal disc diameter ratio) was (median: 1.16; range, ). Oval optic discs were detected in 37 of 562 children (prevalence: 6.6%; 95% CI: ). In univariate analysis, the optic disc ovality was significantly associated with older age (P < 0.001; correlation coefficient r: 0.19), female sex (P < 0.001; r: 0.18), urban region of habitation (P < 0.001; r: 0.17), physical versus intellectual occupation of the father (P < 0.001; r: 0.16) and mother (P ¼ 0.005; r: 0.15), more myopic refractive error (P ¼ 0.02; r: 0.10), higher AL/CC ratio (P ¼ 0.01; r: 0.11), greater increase in myopic refractive error from 2011 to 2013 (P ¼ 0.02; r: 0.12), smaller change in cylindrical refractive error from 2011 to 2013 (P ¼ 0.02; r: 0.11), larger parapapillary alpha zone (P ¼ 0.002; r: 0.13) and larger parapapillary beta zone (P < 0.001; r: 0.28), smaller horizontal optic disc diameter (P < 0.001; r: 0.51), larger vertical optic disc diameter (P < 0.001; r: 0.24), smaller optic cup diameter (P < 0.001; r: 0.15), and smaller neuroretinal rim area (P < 0.001; r: 0.18). It was not significantly associated with body mass index (P ¼ 0.83), birth weight (P ¼ 0.16), breast feeding of the child during infancy (P ¼ 0.32), maternal age at birth (P ¼ 0.95), alcohol consumption (P ¼ 0.24) and smoking (P ¼ 0.79) by the mother during pregnancy, time spent outdoors (P ¼ 0.18), time spent with indoors studying (P ¼ 0.20), vertical optic cup diameter (P ¼ 0.74), cylindrical refractive error (P ¼ 0.14), change in AL/CC ratio (P ¼ 0.34), best corrected visual acuity (logmar) (P ¼ 0.26), central corneal thickness (P ¼ 0.13), corneal curvature radius (P ¼ 0.10), paternal myopia (P ¼ 0.66), maternal myopia (P ¼ 0.50), and body weight (P ¼ 0.15) (Table 1). In multivariate linear regression analysis, higher optic disc ovality index remained significant (overall correlation coefficient r: 0.42); associated with older age (P ¼ 0.001), female sex (P ¼ 0.005) and larger parapapillary beta zone (P < 0.001), shorter time spent indoors studying (P ¼ 0.003), and marginally significantly (P ¼ 0.057) associated with greater increase in myopic refractive error from 2011 to 2013 (Table 2). If the study population was stratified by the presence of an oval optic disc in 2011, the mean refractive error at the initial examination was diopters in the oval optic disc group and diopters in the nonoval optic disc group. The increase in myopic refractive error was diopters in the oval optic disc group compared to diopters in the nonoval group. In univariate analysis, presence of oval optic discs was significantly associated with older age (P ¼ 0.001), female sex (P ¼ 0.004), heavier body weight (P ¼ 0.002), taller body height (P ¼ 0.02), higher body mass index (P ¼ 0.04), physical versus intellectual occupation of the father (P < 0.001) and mother (P < 0.001), more myopic refractive error (P ¼ 0.01), larger cylindrical refractive error (P ¼ 0.048), larger change in cylindrical refractive error (P ¼ 0.02), higher AL/CC ratio (P < 0.001), larger parapapillary beta zone (P < 0.001), shorter vertical optic disc diameter (P < 0.001), and smaller vertical optic cup diameter (P < 0.001). It was not significantly associated with region of habitation (P ¼ 0.10), best corrected visual acuity (P ¼ 0.54), change in myopic refractive error from 2011 to 2013 (P ¼ 0.55), axial length (P ¼ 0.08), higher change in AL/CC ratio (P ¼ 0.05), parapapillary alpha zone (P ¼ 0.06), horizontal optic disc diameter (P ¼ 0.78), vertical optic cup diameter (P ¼ 0.06), and neuroretinal rim area (P ¼ 0.43) (Table 3). Multivariate regression analysis included the presence of oval optic discs as dependent variable and all those parameters as independent variables which were (defined here as P value of <0.10) associated with the presence of oval optic disc in the univariate analysis. In the final model, presence of oval optic discs remained significantly associated with older age (P ¼ 0.03; OR: 1.31 [95% CI: ]), larger beta zone parapapillary atrophy (P < 0.001; OR: 12.8 [95% CI: ]), and smaller cylindrical refractive error (P ¼ 0.04; OR: 0.38 [95% CI: ]). DISCUSSION In our school-based study population, the prevalence of oval optic discs, defined as a maximal-to-minimal disc diameter ratio of 1.33 was 6.6%. A higher optic disc ovality was significantly associated with older age (P ¼ 0.001), female sex (P ¼ 0.005), larger parapapillary beta zone (P < 0.001), shorter time spent indoors studying (P ¼ 0.003), and marginal significance (P ¼ 0.057) associated with greater increase in myopic refractive error from 2011 to 2013 (Table 1). In univariate analysis, the presence of oval optic discs was additionally associated with higher AL/CC ratio and more myopic refractive error. The prevalence of oval optic discs of 6.6% in our study population was higher than the prevalence reported in the Australian population-based Blue Mountains Eye Study 6 of an elderly population with a prevalence of oval or tilted discs of 1.6%, and it was higher than in the elderly population of the Beijing Eye Study with an oval optic disc prevalence of 0.36%. 6,21 The oval optic disc prevalence in our study was lower than that in a recent study from Singapore by Samarawickrama et al. 11 with a prevalence of 37%. Reasons for the differences between the prevalence rates of oval optic
4 Optic Disc Ovality and Myopia Development IOVS j July 2015 j Vol. 56 j No. 8 j 4550 TABLE 1. Univariate Analysis Associations Between Optic Disc Ovality Factor and Ocular and Systemic Parameters Parameter P Value Standardized Regression Coefficient Regression Coefficient 95% CI Age, y < to Sex < to Maternal myopia 0.50 Paternal myopia 0.66 Birth weight, kg 0.16 Maternal age at birth, y 0.95 Breast feeding of the child 0.32 Mother s occupation (blue collar/white collar) to Father s occupation (blue collar/white collar) < to Alcohol consumption by mother during pregnancy 0.24 Smoking by mother during pregnancy 0.79 Body weight, kg 0.15 Body mass index, kg/m Urban/rural region of habitation < to Time spent outdoors to 0.01 Time spent indoors studying to 0.10 Ocular parameters Corneal curvature radius, mm 0.10 Central corneal thickness, lm 0.13 Axial length/corneal curvature radius ratio to Refractive error, D to Cylindrical refractive error, D 0.14 Increase in myopic refractive error (2011 to 2013) to Change in cylindrical refractive error (2011 to 2013) to Change in AL/CC ratio 0.34 Area of parapapillary alpha zone, mm to Area of parapapillary beta zone, mm 2 < to Best corrected visual acuity 0.26 Horizontal optic disc diameter, mm < to Vertical optic disc diameter, mm < to Horizontal optic cup diameter, mm < to Vertical optic cup diameter, mm 0.74 Neuroretinal rim area, mm 2 < to discs between the studies may have been differences in the prevalence of myopia, with a lower prevalence of myopia in the elderly populations from Beijing and Australia and higher myopia prevalence in the school children from Singapore and Beijing, and differences in the definition of oval optic discs. In the Singapore Cohort Study of Risk Factors for Myopia, 11 optic disc tilting or ovality was diagnosed when an optic disc margin was raised above the opposite margin as seen on stereoscopic optic disc photographs. In other studies, a minimal-to-maximal optic disc diameter ratio of 0.8 (equivalent to a maximal-tominimal optic disc diameter ratio of 1.25), 24 a minimal-tomaximal optic disc diameter ratio of 0.7 (equivalent to a maximal-to-minimal optic disc diameter ratio of 1.43), 21 or values of a minimal-to-maximal optic disc diameter ratio between 0.7 and 0.8 were used to define an oval optic disc. 25 In univariate analysis in our study, a higher optic disc ovality and, subsequently, a higher prevalence of oval optic discs were related to more marked myopia, in agreement with previous studies. 6,21,26,27 Interestingly, multivariate analysis revealed that in our study population, the prevalence of oval optic discs and the disc ovality were no longer associated with myopia or with axial length after adjusting for older age, female sex, larger area of parapapillary beta zone, and shorter time spent indoors studying. Adding axial length (P ¼ 0.15) or refractive error (P ¼ 0.64) to the model did not reveal significant associations. If the change in refractive error was added, the association with the disc ovality was marginally significant (P ¼ 0.06) (Table 1). It suggests that in our study population, factors associated with older age, female sex, and potentially with life style may have had a stronger influence on TABLE 2. Multivariate Linear Regression Analysis of the Association Between Optic Disc Ovality Factor (Maximal/Minimal Disc Diameter) and Ocular and Systemic Parameters in Primary School Children in Beijing Parameter P Value Standardized Regression Coefficient Beta Regression Coefficient B 95% CI for B Variance Inflation Factor Age, y to Sex, boys/girls to ,00 Parapapillary beta zone, mm 2 < to Time spent indoors with studying, h to Refractive error, D, in year 2013 versus in year to
5 Optic Disc Ovality and Myopia Development IOVS j July 2015 j Vol. 56 j No. 8 j 4551 TABLE 3. Parameters Associated With the Presence of Oval Optic Discs (Univariate Analysis) Parameter P Value Regression Coefficient B Odds Ratio 95% CI Age, y Sex Urban/rural region Body weight, kg Body height, cm Body mass index, kg/m Refractive error, D Best corrected visual acuity 0.54 Axial length, mm 0.08 Increase in myopic refractive error (year 2011 to year 2013) 0.55 Area of beta zone, mm 2 < Area of alpha zone, mm Horizontal optic disc diameter, mm 0.78 Vertical optic cup diameter, mm 0.06 Neuroretinal rim area, mm Parental parameters Occupation (physical/intellectual) of the father < Occupation (physical/intellectual) of the mother < optic disc shape than axial length or myopic refractive error had. One may assume that the association between oval optic discs and parapapillary beta zone was secondary to the strain exerted on the temporal parapapillary region by the abnormal shape, and presumably by the abnormal rotation of the optic nerve head in eyes with ovally configured optic discs. Optic discs which appear to be oval in the ophthalmoscopic view are often rotated around the vertical optic disc axis, leading to a perspective shortening of the horizontal disc diameter. Due to this vertical optic disc rotation, the nasal edge of the optic disc, compared to its temporal margin, is more prominent so that the definition of an oval or tilted optic disc as applied in the Singapore Cohort Study of Risk Factors for Myopia is fulfilled. 11 In a parallel manner, the perspective shortening of the horizontal disc diameter increases the ratio of the maximal disc diameter (usually the vertical disc diameter) to the minimal disc diameter (then the horizontal disc diameter). 28 It remains unclear whether the observed association between higher optic disc ovality and shorter time spent indoors studying after adjusting for other factors such as older age, female sex, larger parapapillary beta zone, and greater increase in myopic refractive error from 2011 to 2013, was primary or secondary. It raises the question of which factors determine the axial elongation of the growing globe in children and adolescents. Interestingly, in our study population the progression of myopia in children with oval optic discs was marginally, significantly (P ¼ 0.056) greater than that in children without oval optic discs after adjusting for factors such as older age, female sex, and larger parapapillary beta zone (Table 1). If further studies confirm this trend, one may argue whether the presence of an oval optic disc or a high disc ovality could serve to predict future progression of myopia. In a recent investigation by Kim et al., 10 the longitudinal change in the optic nerve head shape in children with incipient myopia was associated with an increase in myopia, although the magnitude of disc ovality was not proportional to the amount of the myopic shift. Further studies could be conducted to clarify the mechanism underlying myopic progression and explain the observed differences between children with myopic oval optic discs and those without oval optic discs. Interestingly, the prevalence of oval optic discs in our young study population (prevalence: 6.6%) was markedly higher than in the adult population of the Beijing Eye Study (prevalence: 0.36%), with a mean age of years (range, years). 21 Both of the populations did not markedly differ in refractive error ( diopters [range, 7.38 to þ7.25 diopters]) of our study population versus diopters (range, 22.0 to þ7.50 diopters); Beijing Eye Study population, axial length of mm [range, mm] vs mm (range, mm) and mean AL/CC ratio ( vs ). Because the supervising panel for the assessment of oval optic discs in both studies consisted of the same members (LX, JBJ), it is unlikely that the marked differences in prevalence of oval optic discs between both of the Chinese groups of different ages were due mainly to a measurement artifact. In view of the marked differences in age between both age groups and because the prevalence of oval optic discs increased with older age in our study, one may assume that the differences in the prevalence of oval optic discs between the study populations will further increase when the children of our study grow older. Potential limitations of our study should be mentioned. First, the study was not population-based so that the possibility of a selection bias existed. Second, refractometry was not performed under cycloplegic conditions, so that involuntary accommodation during refractometry may have covered latent hyperopia. Instead of cycloplegic refractometry, however, we measured axial length and corneal curvature and took the ratio of both parameters as surrogate for refractive error. Third, a 2-year follow-up period might have been too short to determine longitudinal changes. Fourth, the study depended on the accuracy of answers to the standardized questionnaire given by the parents in the interview. Although a test of plausibility was performed in the sense that the total amount of time spent outdoors and indoors had to make sense in terms of the total time available, the reliability of the answers could not truly be assessed. Fifth, because optical coherence tomographic (OCT) images of the optic nerve head were not available, the study assessed the optic disc shape only in a 2-dimensional manner. An ophthalmoscopically oval optic disc, however, can just be the distorted perspective image of a normally shaped optic nerve head. 28 If the position of the optic disc shifted from a location close to
6 Optic Disc Ovality and Myopia Development IOVS j July 2015 j Vol. 56 j No. 8 j 4552 the center of the posterior pole to a location at the nasal side of the eye globe wall, the ophthalmoscopic view will no longer meet the optic disc in a perpendicular but at an oblique angle. As also pointed out in a previous study, this viewing of the optic disc in an oblique angle will lead to a change in the two-dimensionally assessed optic disc shape: The vertical disc diameter will remain unchanged, whereas the horizontal disc diameter in the 2-dimensional measurement will become shorter. 29,30 In that constellation, the vertical disc diameter is the maximal diameter, and the horizontal disc diameter is the minimal disc diameter. Subsequently, the disc shape changes from a circular shape to a vertically oval shape. It reflects the rotation of the optic disc image around the vertical disc axis. The optic disc can rotate also around the horizontal axis with the superior disc pole compared with the inferior disc pole coming closer to the cornea. Finally, the optic disc can rotate around the sagittal axis, in which case the maximal disc diameter is orientated in an oblique angle to the horizontal and in which the vertical disc diameter is shorter than the maximal disc diameter. 28,30 The disc rotation around the sagittal axis does not lead to a perspective distortion of the ophthalmoscopic optic disc image. In clinical practice, often a combination of a rotation around all three axes can be present. In summary, rotation of optic nerve heads may preclude the accurate characterization of their real shape and size from 2- dimensional fundus photographs, requiring instead 3-dimension imaging, such as OCT. Sixth, the main goal of the study was to assess associations between optic disc shape (and the presence of abnormally shaped optic discs as defined by the ovality) and other ocular and systemic parameters, with special reference to myopia. We did not measure the orientation of the optic disc as defined by the angle between the maximal disc diameter and the horizontal. Future studies may determine that angle and may then differentiate between optic disc which were rotated mostly around the vertical axis and optic discs which were rotated predominantly around the horizontal axis. One could then address the question whether vertically rotated discs as compared to horizontally rotated discs show a stronger or weaker correlation with axial myopia associated parameters. In conclusion, ovally configured optic discs occurred in approximately 7 of 100 Beijing school children. This prevalence was higher than in adults in Beijing or in Australia, and it was lower than in Singaporean school children. It is consistent with the association between oval optic discs and axial myopia and the myopic shift taking place in the young generations in East Asia. The association between oval optic discs and the ophthalmoscopic parapapillary beta zone may be explained by the rotation of the optic disc around its vertical axis in eyes with oval optic discs potentially leading to a strain on the temporal disc margin. The association between a higher optic disc oval shape and less time spent indoors studying after adjusting for older age, female sex, larger parapapillary beta zone, and greater increase in myopic refractive error over two years may warrant further exploration of external factors potentially associated with ovalshaped optic discs. Acknowledgments Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants and and National Key Technology R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology Grants 2012BAH05F05 and 2013BAH19F04. Disclosure: Y. Guo, None; L.J. Liu, None; L. Xu, None; Y.Y. Lv, None; P. Tang, None; Y. Feng, None; J.Q. Zhou, None; M. Meng, None; J.B. Jonas, None References 1. Apple DJ, Rabb MF, Walsh PM. Congenital anomalies of the optic disc. Surv Ophthalmol. 1982;27: Hwang YH, Yoo C, Kim YY. Characteristics of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in eyes with myopic optic disc tilt and rotation. J Glaucoma. 2012;21: Hwang YH, Yoo C, Kim YY. Myopic optic disc tilt and the characteristics of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma. 2012;21: Lim L, Gazzard G, Chan YH, et al. Corneal biomechanics, thickness and optic disc morphology in children with optic disc tilt. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008;92: Nakazawa M, Kurotaki J, Ruike H. Longterm findings in peripapillary crescent formation in eyes with mild or moderate myopia. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008;86: Vongphanit J, Mitchell P, Wang JJ. Population prevalence of tilted optic disks and the relationship of this sign to refractive error. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;133: Vongphanit J, Mitchell P, Wang JJ. Prevalence and progression of myopic retinopathy in an older population. Ophthalmology. 2002;109: Xu L, Li Y, Wang S, et al. Characteristics of highly myopic eyes: the Beijing Eye Study. Ophthalmology. 2007;114: Lai TY, Fan DS, Lai WW, Lam DS. Peripheral and posterior pole retinal lesions in association with high myopia: a crosssectional community-based study in Hong Kong. Eye (Lond). 2008;22: Kim TW, Kim M, Weinreb RN, et al. Optic disc change with incipient myopia of childhood. Ophthalmology. 2012;119: Samarawickrama C, Mitchell P, Tong L, et al. Myopia-related optic disc and retinal changes in adolescent children from Singapore. Ophthalmology. 2011;118: Morgan I, Rose K. How genetic is school myopia? Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005;24: Lin LL, Shih YF, Hsiao CK, Chen CJ. Prevalence of myopia in Taiwanese schoolchildren: 1983 to Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2004;33: Seet B, Wong TY, Tan DT, et al. Myopia in Singapore: taking a public health approach. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001;85: Pan CW, Ramamurthy D, Saw SM. Worldwide prevalence and risk factors for myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2012;32: Morgan IG, Ohno-Matsui K, Saw SM. Myopia. Lancet. 2012; 379: Guo Y, Liu LJ, Xu L, et al. Outdoor activity and myopia among primary students in rural and urban regions of Beijing. Ophthalmology. 2013;120: Guo Y, Liu LJ, Xu L, et al. Parapapillary beta zone in primary school children in Beijing: associations with outdoor activity. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55: Grosvenor T, Scott R. Role of the axial length/corneal radius ratio in determining the refractive state of the eye. Optom Vis Sci. 1994;71: Jonas JB, Kling F, Grundler AE. Optic disc shape, corneal astigmatism, and amblyopia. Ophthalmology. 1997;104: You QS, Xu L, Jonas JB. Tilted optic discs: The Beijing Eye Study. Eye (Lond). 2008;22: Littmann H. Zur Bestimmung der wahren Größe eines Objektes auf dem Hintergrund des lebenden Auges. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1982;180: Guo Y, Liu LJ, Xu L, et al. Myopic shift and outdoor activity among primary school children: one-year follow-up study in Beijing. PLoS One. 2013;8:e75260.
7 Optic Disc Ovality and Myopia Development IOVS j July 2015 j Vol. 56 j No. 8 j Tay E, Seah SK, Chan SP, et al. Optic disk ovality as an index of tilt and its relationship to myopia and perimetry. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;139: How AC, Tan GS, Chan YH, et al. Population prevalence of tilted and torted optic discs among an adult Chinese population in Singapore: the Tanjong Pagar Study. Arch Ophthalmol. 2009;127: Brazitikos PD, Safran AB, Simona F, Zulauf M. Threshold perimetry in tilted disc syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108: Park KA, Park SE, Oh SY. Long-term changes in refractive error in children with myopic tilted optic disc compared to children without tilted optic disc. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013;54: Dai Y, Jonas JB, Ling Z, Sun X. Ophthalmoscopic-perspectively distorted optic disc diameters and real disc diameters. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci In press. 29. Jonas JB, Gusek GC, Guggenmoos-Holzmann I, Naumann GOH. Variability of the real dimensions of normal optic discs. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1988;226: Dai Y, Jonas JB, Ling Z, Sun XH. Unilateral peripapillary intrachoroidal cavitation and optic disc rotation. Retina. 2015; 35:
Parapapillary Gamma Zone and Axial Elongation Associated Optic Disc Rotation: The Beijing Eye Study
 Anatomy and Pathology/Oncology Parapapillary Gamma Zone and Axial Elongation Associated Optic Disc Rotation: The Beijing Eye Study Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Ya Xing Wang, 1 Qi Zhang, 1 Yuan Yuan Fan, 3 Liang
Anatomy and Pathology/Oncology Parapapillary Gamma Zone and Axial Elongation Associated Optic Disc Rotation: The Beijing Eye Study Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Ya Xing Wang, 1 Qi Zhang, 1 Yuan Yuan Fan, 3 Liang
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements in Myopia Using Optical Coherence Tomography Dennis L. del Rosario, MD and Mario M. Yatco, MD University of Santo
Risk Factors of Myopic Shift among Primary School Children in Beijing, China: A Prospective Study
 633 Research Paper Ivyspring International Publisher International Journal of Medical Sciences 2015; 12(8): 633-638. doi: 10.7150/ijms.12133 Risk Factors of Myopic Shift among Primary School Children in
633 Research Paper Ivyspring International Publisher International Journal of Medical Sciences 2015; 12(8): 633-638. doi: 10.7150/ijms.12133 Risk Factors of Myopic Shift among Primary School Children in
도시초등학교 4 학년의굴절이상과안계측치변화
 도시초등학교 4 학년의굴절이상과안계측치변화 1119 1120 Table 1. Comparison of uncorrected visual acuity using logmar between March and December [No. of eyes (%)] March December Difference p-value Total Uncorrected visual acuity
도시초등학교 4 학년의굴절이상과안계측치변화 1119 1120 Table 1. Comparison of uncorrected visual acuity using logmar between March and December [No. of eyes (%)] March December Difference p-value Total Uncorrected visual acuity
Paraxial Schematic Eye Models for 7- and 14-Year-Old Chinese Children
 Anatomy and Pathology/Oncology Paraxial Schematic Eye Models for 7- and 14-Year-Old Chinese Children Shi-Ming Li, 1 Ningli Wang, 1 Yuehua Zhou, 1 Si-Yuan Li, 1 Meng-Tian Kang, 1 Luo-Ru Liu, 2 He Li, 2
Anatomy and Pathology/Oncology Paraxial Schematic Eye Models for 7- and 14-Year-Old Chinese Children Shi-Ming Li, 1 Ningli Wang, 1 Yuehua Zhou, 1 Si-Yuan Li, 1 Meng-Tian Kang, 1 Luo-Ru Liu, 2 He Li, 2
Myopic Shift and Outdoor Activity among Primary School Children: One-Year Follow-Up Study in Beijing
 among Primary School Children: One-Year Follow-Up Study in Beijing Yin Guo 1, Li Juan Liu 2, Liang Xu 2 *, Ping Tang 1, Yan Yun Lv 1, Yi Feng 1, Meng Meng 1, Jost B. Jonas 2,3 1 Tongren Eye Care Center,
among Primary School Children: One-Year Follow-Up Study in Beijing Yin Guo 1, Li Juan Liu 2, Liang Xu 2 *, Ping Tang 1, Yan Yun Lv 1, Yi Feng 1, Meng Meng 1, Jost B. Jonas 2,3 1 Tongren Eye Care Center,
Distribution and Severity of Myopic Maculopathy Among Highly Myopic Eyes
 Clinical and Epidemiologic Research Distribution and Severity of Myopic Maculopathy Among Highly Myopic Eyes Ou Xiao, 1 Xinxing Guo, 1,2 Decai Wang, 1 Monica Jong, 3,4 Pei Ying Lee, 5 Linxing Chen, 1 Ian
Clinical and Epidemiologic Research Distribution and Severity of Myopic Maculopathy Among Highly Myopic Eyes Ou Xiao, 1 Xinxing Guo, 1,2 Decai Wang, 1 Monica Jong, 3,4 Pei Ying Lee, 5 Linxing Chen, 1 Ian
Incidence of myopia and biometric characteristics of premyopic eyes among Chinese children and adolescents
 Li et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:178 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0836-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Incidence of myopia and biometric characteristics of premyopic eyes among Chinese children and adolescents
Li et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:178 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0836-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Incidence of myopia and biometric characteristics of premyopic eyes among Chinese children and adolescents
Advances in OCT Murray Fingeret, OD
 Disclosures Advances in OCT Murray Fingeret, OD Consultant Alcon, Allergan, Bausch & Lomb, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Diopsys, Heidelberg Engineering, Reichert, Topcon Currently Approved OCT Devices OCT Devices
Disclosures Advances in OCT Murray Fingeret, OD Consultant Alcon, Allergan, Bausch & Lomb, Carl Zeiss Meditec, Diopsys, Heidelberg Engineering, Reichert, Topcon Currently Approved OCT Devices OCT Devices
RETINAL NERVE FIBER LAYER
 CLINICAL SCIENCES The Effect of Scan Diameter on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurement Using Stratus Optic Coherence Tomography Giacomo Savini, MD; Piero Barboni, MD; Michele Carbonelli, MD;
CLINICAL SCIENCES The Effect of Scan Diameter on Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness Measurement Using Stratus Optic Coherence Tomography Giacomo Savini, MD; Piero Barboni, MD; Michele Carbonelli, MD;
Original Article Correlation of axial length and corneal curvature with diopter in eyes of adults with anisometropia
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13639-13643 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010322 Original Article Correlation of axial length and corneal curvature with diopter in eyes of adults with anisometropia
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13639-13643 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010322 Original Article Correlation of axial length and corneal curvature with diopter in eyes of adults with anisometropia
Generational difference of refractive error in the baseline study of the Beijing Myopia Progression Study
 1 Beijing Ophthalmology and Visual Science Key Lab, Beijing Tongren Eye Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China 2 The Affiliated Eye Hospital and School of Optometry
1 Beijing Ophthalmology and Visual Science Key Lab, Beijing Tongren Eye Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China 2 The Affiliated Eye Hospital and School of Optometry
T he optic disc as the bottleneck of the whole visual
 189 CLINICAL SCIENCE Optic disc morphology in south India: the Vellore Eye Study J B Jonas, R Thomas, R George, E Berenshtein, J Muliyil... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
189 CLINICAL SCIENCE Optic disc morphology in south India: the Vellore Eye Study J B Jonas, R Thomas, R George, E Berenshtein, J Muliyil... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Science & Technologies
 STANDARD COMPUTERIZED PERIMETRY IN FUNCTION OF DIAGNOSTIC GLAUCOMA Iljaz Ismaili, 1 Gazepov Strahil, 2, Goshevska Dashtevska Emilija 1 1 University Eye Clinic,Skopje 2 Clinical Hospital, Shtip Abstract
STANDARD COMPUTERIZED PERIMETRY IN FUNCTION OF DIAGNOSTIC GLAUCOMA Iljaz Ismaili, 1 Gazepov Strahil, 2, Goshevska Dashtevska Emilija 1 1 University Eye Clinic,Skopje 2 Clinical Hospital, Shtip Abstract
Parapapillary Atrophy and Retinal Vessel Diameter in Nonglaucomatous Optic Nerve Damage
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32, No. 11, October 1991 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Parapapillary Atrophy and Retinal Vessel Diameter in Nonglaucomatous
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32, No. 11, October 1991 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Parapapillary Atrophy and Retinal Vessel Diameter in Nonglaucomatous
Scanning Laser Tomography to Evaluate Optic Discs of Normal Eyes
 Scanning Laser Tomography to Evaluate Optic Discs of Normal Eyes Hiroshi Nakamura,* Toshine Maeda,* Yasuyuki Suzuki and Yoichi Inoue* *Eye Division of Olympia Medical Clinic, Tokyo, Japan; Department of
Scanning Laser Tomography to Evaluate Optic Discs of Normal Eyes Hiroshi Nakamura,* Toshine Maeda,* Yasuyuki Suzuki and Yoichi Inoue* *Eye Division of Olympia Medical Clinic, Tokyo, Japan; Department of
Body Height, Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Open-Angle Glaucoma. The Beijing Eye Study 2011
 Body Height, Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Open-Angle Glaucoma. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1, Qi Sheng You 1, Xiaobin Xie 3, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Body Height, Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure and Open-Angle Glaucoma. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1, Qi Sheng You 1, Xiaobin Xie 3, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Ophthalmoscopic Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head JOST B. JONAS, MD, WIDO M. BUDDE, MD, AND SONGHOMITRA PANDA-JONAS, MD
 SURVEY OF OPHTHALMOLOGY VOLUME 43 NUMBER 4 JANUARY FEBRUARY 1999 MAJOR REVIEW Ophthalmoscopic Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head JOST B. JONAS, MD, WIDO M. BUDDE, MD, AND SONGHOMITRA PANDA-JONAS, MD Department
SURVEY OF OPHTHALMOLOGY VOLUME 43 NUMBER 4 JANUARY FEBRUARY 1999 MAJOR REVIEW Ophthalmoscopic Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head JOST B. JONAS, MD, WIDO M. BUDDE, MD, AND SONGHOMITRA PANDA-JONAS, MD Department
Myopia has emerged as a major health issue in east Asia,
 Clinical and Epidemiologic Research What Factors are Associated with Myopia in Young Adults? A Survey Study in Taiwan Military Conscripts Yin-Yang Lee, 1,2 Chung-Ting Lo, 3 Shwu-Jiuan Sheu, 4,5 and Julia
Clinical and Epidemiologic Research What Factors are Associated with Myopia in Young Adults? A Survey Study in Taiwan Military Conscripts Yin-Yang Lee, 1,2 Chung-Ting Lo, 3 Shwu-Jiuan Sheu, 4,5 and Julia
The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation
 C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
C L I N I C A L S C I E N C E The Effect of Pupil Dilation on Scanning Laser Polarimetry With Variable Corneal Compensation Amjad Horani, MD; Shahar Frenkel, MD, PhD; Eytan Z. Blumenthal, MD BACKGROUND
The evaluation of the optic nerve and retinal nerve
 Five rules to evaluate the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer for glaucoma Murray Fingeret, O.D., a,b Felipe A. Medeiros, M.D., c Remo Susanna, Jr, M.D., d and Robert N. Weinreb, M.D. c a Department
Five rules to evaluate the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer for glaucoma Murray Fingeret, O.D., a,b Felipe A. Medeiros, M.D., c Remo Susanna, Jr, M.D., d and Robert N. Weinreb, M.D. c a Department
Measurement of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Eyes Using 3D OCT-1000 Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
 pissn: 111-8942 eissn: 292-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 212;26(4):255-259 http://dx.doi.org/1.3341/kjo.212.26.4.255 Original Article Measurement of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Eyes Using 3D OCT-1 Spectral
pissn: 111-8942 eissn: 292-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 212;26(4):255-259 http://dx.doi.org/1.3341/kjo.212.26.4.255 Original Article Measurement of Choroidal Thickness in Normal Eyes Using 3D OCT-1 Spectral
Optic Nerve: Clinical Examination
 Optic Nerve: Clinical Examination Marcelo T. Nicolela 2 Core Messages Optic disc evaluation is of fundamental importance in the management of glaucoma. Clinical examination of the optic disc is best performed
Optic Nerve: Clinical Examination Marcelo T. Nicolela 2 Core Messages Optic disc evaluation is of fundamental importance in the management of glaucoma. Clinical examination of the optic disc is best performed
An overview of the myopia problem in China
 Preface Page 1 of 5 An overview of the myopia problem in China It is now generally accepted that several locations in East and Southeast Asia, specifically the Republic of Korea, Japan, Singapore, mainland
Preface Page 1 of 5 An overview of the myopia problem in China It is now generally accepted that several locations in East and Southeast Asia, specifically the Republic of Korea, Japan, Singapore, mainland
Parapapillary Retinal Vessel Diameter in Normal and Glaucoma Eyes
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 30, No. 7, July 1989 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Parapapillary Retinal Vessel Diameter in Normal and Glaucoma Eyes
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 30, No. 7, July 1989 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Parapapillary Retinal Vessel Diameter in Normal and Glaucoma Eyes
Morphologic Predictive Factors for Development of Optic Disc Hemorrhages in Glaucoma METHODS
 Morphologic Predictive Factors for Development of Optic Disc Hemorrhages in Glaucoma Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Peter Martus, 3 Wido M. Budde, 1 and Jochen Hayler 1 From the 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Eye
Morphologic Predictive Factors for Development of Optic Disc Hemorrhages in Glaucoma Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Peter Martus, 3 Wido M. Budde, 1 and Jochen Hayler 1 From the 1 Department of Ophthalmology and Eye
Ocular Biometric Measurements In Emmetropic And Myopic Malaysian Children - A Population-Based Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ocular Biometric Measurements In Emmetropic And Myopic Malaysian Children - A Population-Based Study Azura Ramlee, MS Ophthalmology, Goh Pik Pin, MS Ophthalmology, Clinical Research Centre,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Ocular Biometric Measurements In Emmetropic And Myopic Malaysian Children - A Population-Based Study Azura Ramlee, MS Ophthalmology, Goh Pik Pin, MS Ophthalmology, Clinical Research Centre,
A Formula to Predict Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Measurements Based on Time Domain OCT Measurements
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(5):369-377 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.5.369 Original Article A Formula to Predict Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(5):369-377 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.5.369 Original Article A Formula to Predict Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, September: 67-72, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Macular Ganglion Cell Complex Measurement Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography in Glaucoma
Analysis of Peripapillary Atrophy Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
 Analysis of Peripapillary Atrophy Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Analysis of Peripapillary Atrophy Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Children: The Gobi Desert Children Eye Study
 Glaucoma Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Children: The Gobi Desert Children Eye Study Chun-Yan Wang, 1 Yan-Fei Zheng, 1 Bin Liu, 1 Zi-Wei Meng, 1 Fei Hong, 1 Xiao-xia Wang, 1 Xiao-Juan Wang, 1 Lagan
Glaucoma Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Children: The Gobi Desert Children Eye Study Chun-Yan Wang, 1 Yan-Fei Zheng, 1 Bin Liu, 1 Zi-Wei Meng, 1 Fei Hong, 1 Xiao-xia Wang, 1 Xiao-Juan Wang, 1 Lagan
Ocular Hypertension: General Characteristics and Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure. The Beijing Eye Study 2011
 Ocular Hypertension: General Characteristics and Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1., Qi Sheng You 1, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Ocular Hypertension: General Characteristics and Estimated Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure. The Beijing Eye Study 2011 Jost B. Jonas 1,2., Ningli Wang 3., Ya Xing Wang 1., Qi Sheng You 1, Diya Yang 3, Liang
Recent studies have suggested that the pattern of loss of
 Influence of Cilioretinal Arteries on Neuroretinal Rim and Parapapillary Atrophy in Glaucoma Wido M. Budde 1,2 and Jost B. Jonas 1,2 PURPOSE. The pattern of neuroretinal rim loss and increase in the area
Influence of Cilioretinal Arteries on Neuroretinal Rim and Parapapillary Atrophy in Glaucoma Wido M. Budde 1,2 and Jost B. Jonas 1,2 PURPOSE. The pattern of neuroretinal rim loss and increase in the area
Academic achievement, close up work parameters, and myopia in Singapore military conscripts
 Br J Ophthalmol 2001;85:855 860 855 Department of Community, Occupational and Family Medicine, National University of Singapore, 16 Medical Drive, Singapore 117597, Republic of Singapore S-M Saw K-S Chia
Br J Ophthalmol 2001;85:855 860 855 Department of Community, Occupational and Family Medicine, National University of Singapore, 16 Medical Drive, Singapore 117597, Republic of Singapore S-M Saw K-S Chia
This study was limited to those discs in which all 3 THE CRESCENT
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 16-20 The tilted disc DAVID DORRELL From the Department of Neuro-Ophthalmology, National Hospitals for Nervous Diseases, Queen Square, London SUMMARY Sixty tilted
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 16-20 The tilted disc DAVID DORRELL From the Department of Neuro-Ophthalmology, National Hospitals for Nervous Diseases, Queen Square, London SUMMARY Sixty tilted
Relationship of Hypertropia and Excyclotorsion in Superior Oblique Palsy
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2013;27(1):39-43 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2013.27.1.39 Relationship of Hypertropia and Excyclotorsion in Superior Oblique Palsy Original Article
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2013;27(1):39-43 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2013.27.1.39 Relationship of Hypertropia and Excyclotorsion in Superior Oblique Palsy Original Article
Clinical Approach To Refractive Errors. Dr. Faizur Rahman Associate Professor Peshawar Medical College
 Clinical Approach To Refractive Errors Dr. Faizur Rahman Associate Professor Peshawar Medical College Learning objectives By the end of this lecture the students would be able to; Correlate optics with
Clinical Approach To Refractive Errors Dr. Faizur Rahman Associate Professor Peshawar Medical College Learning objectives By the end of this lecture the students would be able to; Correlate optics with
Follow up of focal narrowing of retinal arterioles in glaucoma
 Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:285 289 285 Department of Ophthalmology and Eye Hospital, Friedrich-Alexander- University Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany K I Papastathopoulos J B Jonas Correspondence to:
Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:285 289 285 Department of Ophthalmology and Eye Hospital, Friedrich-Alexander- University Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany K I Papastathopoulos J B Jonas Correspondence to:
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Conversion of Ocular Hypertensives into Glaucoma: A Retrospective Study Aditi Singh 1, Shibi
Relationship Between Structure
 Original Article Relationship Between Structure and Function of the Optic Nerve Head-Glaucoma versus Normal Dr Savita Bhat, Dr Anna Elias, Dr Siddharth Pawar, Dr S.J. Saikumar, Dr Alpesh Rajput, superior,
Original Article Relationship Between Structure and Function of the Optic Nerve Head-Glaucoma versus Normal Dr Savita Bhat, Dr Anna Elias, Dr Siddharth Pawar, Dr S.J. Saikumar, Dr Alpesh Rajput, superior,
Change of b-zone Parapapillary Atrophy During Axial Elongation: Boramae Myopia Cohort Study Report 3 METHODS
 Glaucoma Change of b-zone Parapapillary Atrophy During Axial Elongation: Boramae Myopia Cohort Study Report 3 Kyoung Min Lee, 1,2 Ho-Kyung Choung, 1,2 Martha Kim, 3 Sohee Oh, 4 and Seok Hwan Kim 1,2 1
Glaucoma Change of b-zone Parapapillary Atrophy During Axial Elongation: Boramae Myopia Cohort Study Report 3 Kyoung Min Lee, 1,2 Ho-Kyung Choung, 1,2 Martha Kim, 3 Sohee Oh, 4 and Seok Hwan Kim 1,2 1
The increasing prevalence of myopia in junior high school students in the Haidian District of Beijing, China: a 10-year population-based survey
 Li et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:88 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0483-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The increasing prevalence of myopia in junior high school students in the Haidian District of Beijing,
Li et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:88 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0483-6 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The increasing prevalence of myopia in junior high school students in the Haidian District of Beijing,
Myopia and Near Work Activity in Maderassa Children in Karachi
 Original Article Myopia and Near Work Activity in Maderassa Children in Tahir Masaud Arbab, Saeed Iqbal, Sami ur Rehman Khan, Manzoor A Mirza. Pak J Ophthalmol 2008, Vol. 24 No. 3..............................................................................
Original Article Myopia and Near Work Activity in Maderassa Children in Tahir Masaud Arbab, Saeed Iqbal, Sami ur Rehman Khan, Manzoor A Mirza. Pak J Ophthalmol 2008, Vol. 24 No. 3..............................................................................
The optic nerve head as a foramen in the ocular coats
 BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW Optic Nerve Head Histopathology in High Axial Myopia Jost B. Jonas, MD,*w Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, MD,z and Songhomitra Panda-Jonas, MDw Purpose: To describe particularities of the optic
BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW Optic Nerve Head Histopathology in High Axial Myopia Jost B. Jonas, MD,*w Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, MD,z and Songhomitra Panda-Jonas, MDw Purpose: To describe particularities of the optic
Observation of Posterior Precortical Vitreous Pocket Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography
 Anatomy and Pathology Observation of Posterior Precortical Vitreous Pocket Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Hirotaka Itakura, Shoji Kishi, Danjie Li, and Hideo Akiyama Department of Ophthalmology,
Anatomy and Pathology Observation of Posterior Precortical Vitreous Pocket Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Hirotaka Itakura, Shoji Kishi, Danjie Li, and Hideo Akiyama Department of Ophthalmology,
S uperior segmental optic hypoplasia (SSOH), also termed
 910 CLINICAL SCIENCE Optical coherence tomography of superior segmental optic hypoplasia K Unoki, N Ohba, W F Hoyt... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Kazuhiko Unoki, MD,
910 CLINICAL SCIENCE Optical coherence tomography of superior segmental optic hypoplasia K Unoki, N Ohba, W F Hoyt... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Kazuhiko Unoki, MD,
Bilateral Microphthalmos Associated with Papillomacular Fold, Severe Hyperopia and Steep Cornea
 Bilateral Microphthalmos Associated with Papillomacular Fold, Severe Hyperopia and Steep Cornea Mojtaba Abrishami, MD 1 Alireza Maleki, MD 2 Ali Hamidian-Shoormasti, MD 3 Mostafa Abrishami, MD 4 Abstract
Bilateral Microphthalmos Associated with Papillomacular Fold, Severe Hyperopia and Steep Cornea Mojtaba Abrishami, MD 1 Alireza Maleki, MD 2 Ali Hamidian-Shoormasti, MD 3 Mostafa Abrishami, MD 4 Abstract
Intro to Glaucoma/2006
 Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
Intro to Glaucoma/2006 Managing Patients with Glaucoma is Exciting Interesting Challenging But can often be frustrating! Clinical Challenges To identify patients with risk factors for possible glaucoma.
The effect of optic disc diameter on vertical cup to disc ratio percentiles in a population based cohort: the Blue Mountains Eye Study
 766 SCIENTIFIC REPORT The effect of optic disc diameter on vertical cup to disc ratio percentiles in a population based cohort: the Blue Mountains Eye Study J G Crowston, C R Hopley, P R Healey, A Lee,
766 SCIENTIFIC REPORT The effect of optic disc diameter on vertical cup to disc ratio percentiles in a population based cohort: the Blue Mountains Eye Study J G Crowston, C R Hopley, P R Healey, A Lee,
Research Article A Meta-Analysis for Association of Maternal Smoking with Childhood Refractive Error and Amblyopia
 Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 8263832, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8263832 Research Article A Meta-Analysis for Association of Maternal Smoking with Childhood Refractive Error and Amblyopia
Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 8263832, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8263832 Research Article A Meta-Analysis for Association of Maternal Smoking with Childhood Refractive Error and Amblyopia
Myopia affects 1.6 billion people worldwide and 2.5 billion
 Clinical and Epidemiologic Research Prevalence of Refractive Errors in a Multiethnic Asian Population: The Singapore Epidemiology of Eye Disease Study Chen-Wei Pan, 1 Ying-Feng Zheng, 2,3 Ainur Rahman
Clinical and Epidemiologic Research Prevalence of Refractive Errors in a Multiethnic Asian Population: The Singapore Epidemiology of Eye Disease Study Chen-Wei Pan, 1 Ying-Feng Zheng, 2,3 Ainur Rahman
Thickness Changes in the Fovea and Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Depend on the Degree of Myopia
 Thickness Changes in the Fovea and Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Depend on the Degree of Myopia Sung-Won Choi, MD, Seok-Joon Lee, MD Department of Ophthalmology, Wonju Christian Hospital. Yonsei
Thickness Changes in the Fovea and Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Depend on the Degree of Myopia Sung-Won Choi, MD, Seok-Joon Lee, MD Department of Ophthalmology, Wonju Christian Hospital. Yonsei
Parafoveal Scanning Laser Polarimetry for Early Glaucoma Detection
 Yamanashi Med. J. 18(1), 15~ 20, 2003 Original Article Parafoveal Scanning Laser Polarimetry for Early Glaucoma Detection Satoshi KOGURE, Yoshiki TODA, Hiroyuki IIJIMA and Shigeo TSUKAHARA Department of
Yamanashi Med. J. 18(1), 15~ 20, 2003 Original Article Parafoveal Scanning Laser Polarimetry for Early Glaucoma Detection Satoshi KOGURE, Yoshiki TODA, Hiroyuki IIJIMA and Shigeo TSUKAHARA Department of
Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in Highly Myopic Eyes following Cataract Surgery
 Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in Highly Myopic Eyes following Cataract Surgery Fedra Hajizadeh, MD 1 Mohammad Riazi Esfahani, MD 1,2 Hooshang Faghihi, MD 3 Mehdi Khanlari, MD 4 Abstract Purpose:
Optical Coherence Tomography Findings in Highly Myopic Eyes following Cataract Surgery Fedra Hajizadeh, MD 1 Mohammad Riazi Esfahani, MD 1,2 Hooshang Faghihi, MD 3 Mehdi Khanlari, MD 4 Abstract Purpose:
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: , 2013
 268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
268 Comparison of optic nerve morphology in eyes with glaucoma and eyes with non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography YUXIN YANG 1, HAITAO ZHANG 1,
Based on the studies by Goldmann and Schmidt 1 and Ehlers. Central Corneal Thickness Correlated with Glaucoma Damage and Rate of Progression
 Central Corneal Thickness Correlated with Glaucoma Damage and Rate of Progression Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Andrea Stroux, 3,4 Isabel Velten, 1 Anselm Juenemann, 1 Peter Martus, 3 and Wido M. Budde 1,2 PURPOSE.
Central Corneal Thickness Correlated with Glaucoma Damage and Rate of Progression Jost B. Jonas, 1,2 Andrea Stroux, 3,4 Isabel Velten, 1 Anselm Juenemann, 1 Peter Martus, 3 and Wido M. Budde 1,2 PURPOSE.
* Şükrü Bayraktar, MD, Zerrin Bayraktar, MD, and Ömer Faruk Yilmaz, MD
 Journal of Glaucoma 10:163 169 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Influence of Scan Radius Correction for Ocular Magnification and Relationship Between Scan Radius With Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Journal of Glaucoma 10:163 169 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Influence of Scan Radius Correction for Ocular Magnification and Relationship Between Scan Radius With Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Assessment of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Changes by Cirrus High-definition Optical Coherence Tomography in Myopia
 Divya Singh et al Original REASEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10028-1223 Assessment of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Changes by Cirrus High-definition Optical Coherence Tomography in Myopia 1 Divya Singh, 2 Sanjay
Divya Singh et al Original REASEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10028-1223 Assessment of Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Changes by Cirrus High-definition Optical Coherence Tomography in Myopia 1 Divya Singh, 2 Sanjay
Prevalence of Myopia and its Association with Body Stature and Educational Level in 19-Year-Old Male Conscripts in Seoul, South Korea
 Clinical and Epidemiologic Research Prevalence of Myopia and its Association with Body Stature and Educational Level in 19-Year-Old Male Conscripts in Seoul, South Korea Su-Kyung Jung, 1,4 Jin Hae Lee,
Clinical and Epidemiologic Research Prevalence of Myopia and its Association with Body Stature and Educational Level in 19-Year-Old Male Conscripts in Seoul, South Korea Su-Kyung Jung, 1,4 Jin Hae Lee,
Prescription of atropine eye drops among children diagnosed with myopia in Taiwan from 2000 to 2007: a nationwide study
 (2013) 27, 418 424 & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-222X/13 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Prescription of atropine eye drops among children diagnosed with myopia in Taiwan
(2013) 27, 418 424 & 2013 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-222X/13 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Prescription of atropine eye drops among children diagnosed with myopia in Taiwan
Macular Thickness and Amblyopia
 Original Article Macular Thickness and Amblyopia Zhale Rajavi 1, MD; Hossein Moghadasifar 1, MD; Mohadese Feizi 1, MD; Narges Haftabadi 1, MS Reza Hadavand 1, BS; Mehdi Yaseri 2,3, PhD; Kourosh Sheibani
Original Article Macular Thickness and Amblyopia Zhale Rajavi 1, MD; Hossein Moghadasifar 1, MD; Mohadese Feizi 1, MD; Narges Haftabadi 1, MS Reza Hadavand 1, BS; Mehdi Yaseri 2,3, PhD; Kourosh Sheibani
Recent decades have seen a rapid rise in the
 LIGHT EXPOSURE AND CHILDHOOD MYOPIA There is evidence in many countries globally that the prevalence of myopia is on the rise. Advances in measurement technology now allow many environmental factors potentially
LIGHT EXPOSURE AND CHILDHOOD MYOPIA There is evidence in many countries globally that the prevalence of myopia is on the rise. Advances in measurement technology now allow many environmental factors potentially
Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness parameters in myopic population using scanning laser polarimetry (GDxVCC)
 Dada T et al Original article Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness parameters in myopic population using scanning laser polarimetry (GDxVCC) Dada T1, Aggarwal A1, Bali SJ2, Sharma A1, Shah
Dada T et al Original article Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness parameters in myopic population using scanning laser polarimetry (GDxVCC) Dada T1, Aggarwal A1, Bali SJ2, Sharma A1, Shah
OtticaFisiopatologica
 Anno quindicesimo dicembre 2010 How to assess the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness Antonio Ferreras Miguel Servet University Hospital, Zaragoza. Aragón Health Sciences Institute University of Zaragoza
Anno quindicesimo dicembre 2010 How to assess the retinal nerve fiber layer thickness Antonio Ferreras Miguel Servet University Hospital, Zaragoza. Aragón Health Sciences Institute University of Zaragoza
Seiji T. Takagi, Yoshiyuki Kita, Asuka Takeyama, and Goji Tomita. 1. Introduction. 2. Subjects and Methods
 Ophthalmology Volume 2011, Article ID 914250, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/914250 Clinical Study Macular Retinal Ganglion Cell Complex Thickness and Its Relationship to the Optic Nerve Head Topography in Glaucomatous
Ophthalmology Volume 2011, Article ID 914250, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/914250 Clinical Study Macular Retinal Ganglion Cell Complex Thickness and Its Relationship to the Optic Nerve Head Topography in Glaucomatous
Noel de Jesus Atienza, MD, MSc and Joseph Anthony Tumbocon, MD
 Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
Original Article Philippine Journal of OPHTHALMOLOGY Diagnostic Accuracy of the Optical Coherence Tomography in Assessing Glaucoma Among Filipinos. Part 1: Categorical Outcomes Based on a Normative Database
Optic Disc Evaluation: Is the Optic Disc Glaucomatous and Has it Progressed?
 Optic Disc Evaluation: Is the Optic Disc Glaucomatous and Has it Progressed? Jody Piltz-Seymour, M.D. Clinical Professor Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Wills Glaucoma Service Valley
Optic Disc Evaluation: Is the Optic Disc Glaucomatous and Has it Progressed? Jody Piltz-Seymour, M.D. Clinical Professor Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Wills Glaucoma Service Valley
Case Report Peripapillary Intrachoroidal Cavitation in Myopia Evaluated with Multimodal Imaging Comprising (En-Face) Technique
 Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 890876, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890876 Case Report Peripapillary Intrachoroidal Cavitation in Myopia Evaluated with Multimodal
Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 890876, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/890876 Case Report Peripapillary Intrachoroidal Cavitation in Myopia Evaluated with Multimodal
Comparison of Optic Disc Topography Measured by Retinal Thickness Analyzer with Measurement by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II
 Comparison of Optic Disc Topography Measured by Retinal Analyzer with Measurement by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II Noriko Itai*, Masaki Tanito*, and Etsuo Chihara* *Senshokai Eye Institute, Uji, Kyoto,
Comparison of Optic Disc Topography Measured by Retinal Analyzer with Measurement by Heidelberg Retina Tomograph II Noriko Itai*, Masaki Tanito*, and Etsuo Chihara* *Senshokai Eye Institute, Uji, Kyoto,
Evaluation of myopia on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Spectralis optical coherence tomography
 2716 Evaluation of myopia on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Spectralis optical coherence tomography YI ZHA, JINFEI ZHUANG, DA LIN, WANGQIANG FENG, HAIHUA ZHENG and JIANQIU CAI Ophthalmology
2716 Evaluation of myopia on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Spectralis optical coherence tomography YI ZHA, JINFEI ZHUANG, DA LIN, WANGQIANG FENG, HAIHUA ZHENG and JIANQIU CAI Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology. Caring For Your Eyes. Jurong Medical Centre
 Ophthalmology Caring For Your Eyes Jurong Medical Centre Your eyes and you At Jurong Medical Centre, we have a dedicated team of ophthalmologists that specialise in treating a wide range of acute and chronic
Ophthalmology Caring For Your Eyes Jurong Medical Centre Your eyes and you At Jurong Medical Centre, we have a dedicated team of ophthalmologists that specialise in treating a wide range of acute and chronic
International Journal of Ophthalmic Research
 International Journal of Ophthalmic Research Online Submissions: http://www.ghrnet.org/index./ijor/ doi:10.17554/j.issn.2409-5680.2017.03.55 Int. J. Ophthalmic Res 2017 June; 3(2): 226-230 ISSN 2409-5680
International Journal of Ophthalmic Research Online Submissions: http://www.ghrnet.org/index./ijor/ doi:10.17554/j.issn.2409-5680.2017.03.55 Int. J. Ophthalmic Res 2017 June; 3(2): 226-230 ISSN 2409-5680
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a new noninvasive
 Use of Optical Coherence Tomography to Assess Variations in Macular Retinal Thickness in Myopia Marcus C. C. Lim, 1 Sek-Tien Hoh, 1 Paul J. Foster, 1,2 Tock-Han Lim, 3,4 Sek-Jin Chew, 1 Steve K. L. Seah,
Use of Optical Coherence Tomography to Assess Variations in Macular Retinal Thickness in Myopia Marcus C. C. Lim, 1 Sek-Tien Hoh, 1 Paul J. Foster, 1,2 Tock-Han Lim, 3,4 Sek-Jin Chew, 1 Steve K. L. Seah,
Elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) is a major risk factor for
 Glaucoma The Association between Retinal Vessel Diameter and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Asymmetric Normal Tension Glaucoma Patients Joon Mo Kim, 1 Mo Sae Kim, 2 Hyo Ju Jang, 1 Ki Ho Park, 3
Glaucoma The Association between Retinal Vessel Diameter and Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Asymmetric Normal Tension Glaucoma Patients Joon Mo Kim, 1 Mo Sae Kim, 2 Hyo Ju Jang, 1 Ki Ho Park, 3
Efficacy of Photorefractive Keratectomy for Military Pilot Recruitment in an Asian Air Force
 Efficacy of Photorefractive Keratectomy for Military Pilot Recruitment in an Asian Air Force Brian See, Gerard Nah, Wee Hoe Gan, Robin Low AsMA Annual Scientific Meeting 2013 Chicago, IL, USA Disclosure
Efficacy of Photorefractive Keratectomy for Military Pilot Recruitment in an Asian Air Force Brian See, Gerard Nah, Wee Hoe Gan, Robin Low AsMA Annual Scientific Meeting 2013 Chicago, IL, USA Disclosure
Changes in Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness after Pattern Scanning Laser Photocoagulation in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(3):220-225 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.3.220 Original Article Changes in Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness after
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2014;28(3):220-225 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2014.28.3.220 Original Article Changes in Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness after
Differences between Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy and Open Angle Glaucoma with Altitudinal Visual Field Defect
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2015;29(6):418-423 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.29.6.418 Original Article Differences between Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2015;29(6):418-423 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2015.29.6.418 Original Article Differences between Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
Snoring and Glaucoma. Ya Xing Wang 1, Liang Xu 1 *, Jian Jun Li 1, Hua Yang 1, Ya Qin Zhang 1, Jost B. Jonas 1,2 * Abstract.
 Ya Xing Wang 1, Liang Xu 1 *, Jian Jun Li 1, Hua Yang 1, Ya Qin Zhang 1, Jost B. Jonas 1,2 * 1 Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital University of Medical Science, Beijing,
Ya Xing Wang 1, Liang Xu 1 *, Jian Jun Li 1, Hua Yang 1, Ya Qin Zhang 1, Jost B. Jonas 1,2 * 1 Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital University of Medical Science, Beijing,
著者最終稿 (author final version) post.
 Title Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplas Health Care Project Participants( Author(s) YAMAMOTO, Tetsuya Citation [Japanese journal of ophthalmolog [583] Issue Date 2004-11-01 Rights Version 著者最終稿 (author
Title Superior Segmental Optic Hypoplas Health Care Project Participants( Author(s) YAMAMOTO, Tetsuya Citation [Japanese journal of ophthalmolog [583] Issue Date 2004-11-01 Rights Version 著者最終稿 (author
Ganglion cell complex scan in the early prediction of glaucoma
 Original article in the early prediction of glaucoma Ganekal S Nayana Super Specialty Eye Hospital and Research Center, Davangere, Karnataka, India Abstract Objective: To compare the macular ganglion cell
Original article in the early prediction of glaucoma Ganekal S Nayana Super Specialty Eye Hospital and Research Center, Davangere, Karnataka, India Abstract Objective: To compare the macular ganglion cell
Automated Tessellated Fundus Detection in Color Fundus Images
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Proceedings of the Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis International Workshop 2016 Proceedings Oct 21st, 2016 Automated Tessellated Fundus Detection in Color Fundus
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Proceedings of the Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis International Workshop 2016 Proceedings Oct 21st, 2016 Automated Tessellated Fundus Detection in Color Fundus
Myopia and Glaucoma. Kazuhisa Sugiyama Nagahisa Yoshimura Editors
 Myopia and Glaucoma Kazuhisa Sugiyama Nagahisa Yoshimura Editors 123 Myopia and Glaucoma ThiS is a FM Blank Page Kazuhisa Sugiyama Nagahisa Yoshimura Editors Myopia and Glaucoma Editors Kazuhisa Sugiyama
Myopia and Glaucoma Kazuhisa Sugiyama Nagahisa Yoshimura Editors 123 Myopia and Glaucoma ThiS is a FM Blank Page Kazuhisa Sugiyama Nagahisa Yoshimura Editors Myopia and Glaucoma Editors Kazuhisa Sugiyama
EPIDEMIOLOGY. SECTION EDITOR: LESLIE HYMAN, PhD. Prevalence and Characteristics of Myopic Retinopathy in a Rural Chinese Adult Population
 EPIDEMIOLOGY SECTION EDITOR: LESLIE HYMAN, PhD Prevalence and Characteristics of Myopic Retinopathy in a Rural Chinese Adult Population The Handan Eye Study Li Qin Gao, MD; Wu Liu, MD; Yuan Bo Liang, MD,
EPIDEMIOLOGY SECTION EDITOR: LESLIE HYMAN, PhD Prevalence and Characteristics of Myopic Retinopathy in a Rural Chinese Adult Population The Handan Eye Study Li Qin Gao, MD; Wu Liu, MD; Yuan Bo Liang, MD,
PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH PREVALENCE OF GLAUCOMA AMONG FISHERMEN COMMUNITY OF MUNDRA TALUKA OF KUTCH DISTRICT- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY Sanjay Upadhyay 1, Jayantilal Shah 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 Associate Professor,
R&M Solutions
 Mohamed Hosny El-Bradey, MD., Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, Tanta University. Wael El Haig, MD., Professor of Ophthalmology. Zagazeeg University. 1 Myopic CNV is considered the most common vision
Mohamed Hosny El-Bradey, MD., Assistant Professor of Ophthalmology, Tanta University. Wael El Haig, MD., Professor of Ophthalmology. Zagazeeg University. 1 Myopic CNV is considered the most common vision
MATERIALS AND METHODS
 Glaucoma Analysis of Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Distribution in Normal Young Adults Seung Woo Hong, 1,2 Myung Douk Ahn, 2 Shin Hee Kang, 1,3 and Seong Kyu Im 1,4 PURPOSE. To determine the anatomic
Glaucoma Analysis of Peripapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Distribution in Normal Young Adults Seung Woo Hong, 1,2 Myung Douk Ahn, 2 Shin Hee Kang, 1,3 and Seong Kyu Im 1,4 PURPOSE. To determine the anatomic
M yopia is a growing public health problem with visual,
 341 CLINICAL SCIENCE Utility values and myopia in teenage school students S-M Saw, G Gazzard, K-G Au Eong, D Koh... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Seang-Mei Saw, Department
341 CLINICAL SCIENCE Utility values and myopia in teenage school students S-M Saw, G Gazzard, K-G Au Eong, D Koh... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Seang-Mei Saw, Department
Bitemporal visual field defects mimicking chiasmal compression in eyes with tilted disc syndrome
 Optometry (2009) 80, 232-242 Bitemporal visual field defects mimicking chiasmal compression in eyes with tilted disc syndrome Joseph W. Sowka, O.D., a and Vincent V. Luong, B. Optom. b a Nova Southeastern
Optometry (2009) 80, 232-242 Bitemporal visual field defects mimicking chiasmal compression in eyes with tilted disc syndrome Joseph W. Sowka, O.D., a and Vincent V. Luong, B. Optom. b a Nova Southeastern
Il contributo dell'angio-oct: valutazione integrata della componente nervosa e vascolare della malattia glaucomatosa
 SIMPOSIO G.O.A.L. - LE NUOVE FRONTIERE DIAGNOSTICHE E LE LINEE DI INDIRIZZO AMBULATORIALI DEL GLAUCOMA Coordinatore e moderatore: D. Mazzacane Presidente: L. Rossetti Il contributo dell'angio-oct: valutazione
SIMPOSIO G.O.A.L. - LE NUOVE FRONTIERE DIAGNOSTICHE E LE LINEE DI INDIRIZZO AMBULATORIALI DEL GLAUCOMA Coordinatore e moderatore: D. Mazzacane Presidente: L. Rossetti Il contributo dell'angio-oct: valutazione
S Morishita, T Tanabe, S Yu, M Hangai, T Ojima, H Aikawa, N Yoshimura. Clinical science
 Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan Correspondence to: Dr T Tanabe, Department of Ophthalmology, The Tazuke Kofukai Medical Institute,
Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan Correspondence to: Dr T Tanabe, Department of Ophthalmology, The Tazuke Kofukai Medical Institute,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE RISK FACTORS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF ANGLE CLOSURE GLAUCOMA IN EYES WITH SHALLOW ANTERIOR CHAMBER
 RISK FACTORS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF ANGLE CLOSURE GLAUCOMA IN EYES WITH SHALLOW ANTERIOR CHAMBER Sundeep 1, Niveditha H 2, Pooja Patil 3, N V V Himamshu 4, Vinutha B V 5, Liji P 6, M S Smitha Gowda 7, Nivedhitha
RISK FACTORS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF ANGLE CLOSURE GLAUCOMA IN EYES WITH SHALLOW ANTERIOR CHAMBER Sundeep 1, Niveditha H 2, Pooja Patil 3, N V V Himamshu 4, Vinutha B V 5, Liji P 6, M S Smitha Gowda 7, Nivedhitha
Possible Errors in the Measurement of Retinal Lesions
 Possible Errors in the Measurement of Retinal Lesions / V. Arnold*]. W. C. Gates j and K. M. Taylor* Purpose. To determine the accuracy of the measurement of structure in the retina from fundus photographs.
Possible Errors in the Measurement of Retinal Lesions / V. Arnold*]. W. C. Gates j and K. M. Taylor* Purpose. To determine the accuracy of the measurement of structure in the retina from fundus photographs.
Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic Syndrome
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 215, Article ID 62372, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/62372 Clinical Study Choroidal Thickness in Eyes with Unilateral Ocular Ischemic
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an imaging
 Glaucoma Adjusting Circumpapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Profile Using Retinal Artery Position Improves the Structure Function Relationship in Glaucoma Yuri Fujino, 1 Takehiro Yamashita, 2 Hiroshi
Glaucoma Adjusting Circumpapillary Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Profile Using Retinal Artery Position Improves the Structure Function Relationship in Glaucoma Yuri Fujino, 1 Takehiro Yamashita, 2 Hiroshi
Structural changes of the anterior chamber following cataract surgery during infancy
 Structural changes of the anterior chamber following cataract surgery during infancy Matthew Nguyen, Emory University Marla Shainberg, Emory University Allen Beck, Emory University Scott Lambert, Emory
Structural changes of the anterior chamber following cataract surgery during infancy Matthew Nguyen, Emory University Marla Shainberg, Emory University Allen Beck, Emory University Scott Lambert, Emory
Generally, myopia is a condition of the eye that makes it
 Glaucoma Effect of Myopia on the Progression of Primary Open- Angle Glaucoma Jin Young Lee, 1 Kyung Rim Sung, 1 Seungbong Han, 2 and Jung Hwa Na 1 1 Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, University
Glaucoma Effect of Myopia on the Progression of Primary Open- Angle Glaucoma Jin Young Lee, 1 Kyung Rim Sung, 1 Seungbong Han, 2 and Jung Hwa Na 1 1 Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, University
Prevalence and Associations of Incomplete Posterior Vitreous Detachment in Adult Chinese: The Beijing Eye Study
 Prevalence and Associations of Incomplete Posterior Vitreous Detachment in Adult Chinese: The Beijing Eye Study Lei Shao 1, Liang Xu 2, Qi Sheng You 2, Ya Xing Wang 2, Chang Xi Chen 2, Hua Yang 2, Jin
Prevalence and Associations of Incomplete Posterior Vitreous Detachment in Adult Chinese: The Beijing Eye Study Lei Shao 1, Liang Xu 2, Qi Sheng You 2, Ya Xing Wang 2, Chang Xi Chen 2, Hua Yang 2, Jin
Peripapillary circle of Zinn Haller revealed by fundus fluorescein angiography
 British Journal of Ophthalmology 1997;81:663 667 663 Department of Ophthalmology, School of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea M-K Ko D-S Kim Y-K Ahn Correspondence to: Myung-Kyoo Ko, MD, Department
British Journal of Ophthalmology 1997;81:663 667 663 Department of Ophthalmology, School of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea M-K Ko D-S Kim Y-K Ahn Correspondence to: Myung-Kyoo Ko, MD, Department
Influence of Myopic Disc Shape on the Diagnostic Precision of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph
 Influence of Myopic Disc Shape on the Diagnostic Precision of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph Yoshio Yamazaki,* Keiji Yoshikawa, Shiho Kunimatsu, Nobuyuki Koseki, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Shun Matsumoto and Makoto
Influence of Myopic Disc Shape on the Diagnostic Precision of the Heidelberg Retina Tomograph Yoshio Yamazaki,* Keiji Yoshikawa, Shiho Kunimatsu, Nobuyuki Koseki, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Shun Matsumoto and Makoto
