Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is a rare inflammatory
|
|
|
- Mervin Chapman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH M.L. White W.L. Hadley Y. Zhang M.A. Dogar Analysis of Central Nervous System Vasculitis with Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of the Normal-Appearing Brain BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is a novel method of studying the brain that creates tissue contrast secondary to water diffusion. Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is a rare inflammatory disease that continues to be difficult to diagnose and evaluate with MR imaging. DWI with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) analysis may demonstrate abnormalities within the brain that would otherwise be undetected by conventional imaging, thus aiding in the diagnosis and evaluation of patients with CNS vasculitis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A retrospective analysis was performed of patients who were diagnosed with CNS vasculitis and had undergone DWI. A total of 15 patients who had DWI with b 1000 were analyzed. Regions of interest were drawn in the anterior, central, and posterior regions of white matter () at 3 levels. Regions of interest were also drawn bilaterally in the caudate heads, putamina, thalami, posterior internal capsules, and the cerebellar. ADC values were measured and compared with 15 healthy controls who were matched for age, sex, and MR imaging scanner. RESULTS: There was a significant increase in the ADC values (P.00625) for the anterior, central, thalami, and posterior internal capsules in patients with CNS vasculitis. CONCLUSION: Diffuse increase in water diffusion was present in the normal-appearing brain in patients with CNS vasculitis, and these abnormalities were not demonstrated by conventional MR imaging sequences. The detection and quantification of ADC abnormalities may provide useful diagnostic information for patients with CNS vasculitis. Central nervous system (CNS) vasculitis is a rare inflammatory disease that affects the arteries and the veins of the brain. 1,2 MR imaging often demonstrates brain lesions in patients with CNS vasculitis. 3-7 However, there are numerous examples of conventional MR imaging not demonstrating lesions in patients with proved vasculitis. 5,6 The limited sensitivity of conventional MR imaging to CNS vasculitis changes is demonstrated by cases in which angiographic abnormalities are present despite normal findings on MR imaging examination. 4,5,7,8 Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) provides a novel method of investigating the brain, which relies on the molecular diffusion of water for tissue contrast. 9 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) analysis allows a quantitative measurement of changes within the brain. Brain analysis using ADCs has been found to demonstrate abnormalities that are not detectable by conventional MR imaging for multiple sclerosis, tuberous sclerosis, Behcet s disease, neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), and the aging brain The detection of abnormalities in the brain by DWI, not otherwise visualized by MR imaging, may help to determine the extent of abnormalities in patients with CNS vasculitis. We evaluated the normal-appearing brain as demonstrated by conventional MR imaging with DWI using ADC analysis to Received April 24, 2006; accepted after revision October 5. From the Department of Radiology (M.L.W., Y.Z.), University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, Neb; the Department of Radiology (W.L.H.), University Hospital of Cleveland/Case Medical Center, Cleveland, Ohio; and the Department of Radiology (M.A.D.), University of Iowa College of Medicine, Iowa City, Iowa. Please address correspondence to Matthew L. White, MD, Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, NE ; matthewwhite@unmc.edu enhance our understanding of the extent and type of changes present in patients with CNS vasculitis. We hypothesized that there would be diffuse abnormalities present within the brain, resulting in increased diffusion and thus increased ADC values. Materials and Methods The medical records were searched by computer for patients with the diagnosis of cerebral vasculitis from 1998 to Since 1998, brain MR imaging has been routinely performed with a DWI sequence. Only cases of inflammatory vasculitis were included. The cases considered to represent vasculitis had to have a clinical diagnosis of vasculitis and 1 of the following: 1) pathologic evidence, 2) classic vasculitis pattern on an angiogram, or 3) clinical course and a response to therapy consistent with vasculitis. 3,15 The diagnosis of vasculitis was based on clinical history and pathology evidence in 6, clinical history and vasculitis pattern on angiograms in 8, and clinical course with response to therapy in 1. The diagnosis was primary CNS vasculitis in 12 patients and vasculitis secondary to sarcoid in 2 patients. There were 15 patients who met our entry criteria (4 men, 11 women; mean, 51.9 years of age; range, years of age). Symptoms in patients had been present from 2 days to 20 days. Eleven patients were imaged within 10 days of the onset of symptoms. The others were imaged after approximately 13, 20, and 45 days of symptoms. Fourteen subjects underwent scanning with 1.5T; and 1, with 3T MR imaging systems. The MR imaging studies are summarized as follows: 9 studies on Signa (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, Wis), 1 study on Magnetom Vision (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany), 2 studies on Symphony (Siemens), 2 studies on Avanto (Siemens), and 1 study on Trio (Siemens). Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) and DWI with b 1000 were performed in all patients. BRAIN ORIGINAL RESEARCH AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28: May
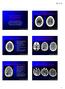
2 Fig 1. A, Regions of interest 1, 2, and 3 represent measurements made in the anterior, central, and posterior in the corona radiata and centrum semiovale. B, The region of interest positions are represented by 4 for the caudate heads, 5 for the putamina, 6 for the posterior internal capsules, and 7 for the thalami. C, Region of interest 8 is positioned in the cerebellar. There was a total of 8 cases that were considered to have vasculitis but were not included in the data analysis. One case had corrupt diffusion source data; 1 case was saved on a storage disk that could no longer be accessed; 1 patient had only MR imaging performed outside our institution, the results of which could not be obtained; and 5 of the vasculitis patients had only follow-up imaging at our institution. Additionally, 3 more patients were excluded as result of not having a true inflammatory vasculitis and/or having a complicated history. One patient was scanned after surgery and radiation therapy for an astrocytoma, and there were 2 patients with Susac Syndrome (a clinical triad of encephalopathy, hearing loss, and retinal arteriolar occlusions). Four-vessel angiography was performed using a digital subtraction technique in all patients. The angiograms were reviewed in a blinded fashion by a neuroradiologist, and the reports were also reviewed. The blinded reviews of the angiograms were all in agreement with the original interpretation. The control subjects were matched for age, sex, and MR imaging scanner. There were 4 male and 11 female controls with a mean of 50.2 years of age (range, years of age). Each control MR imaging was interpreted as having normal findings on brain examination. The indications for examinations of the control subjects included the following: asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss, headaches, anterior communicating artery aneurysm, bilateral upper extremity numbness, paresthesias and facial weakness, acoustic neuroma excision, benign positional vertigo, cerebellar signs and left facial droop, optic disk edema and periphlebitis, peripheral visual field loss, and hemifacial spasm. The primary analysis of the brain consisted of evaluation of the cerebral. Smaller regions of interest were drawn for sampling than those in previous studies secondary to our concern for avoiding partial volume averaging with adjacent CSF, gray matter, or lesions. Regions of interest were drawn bilaterally in the anterior, central, and posterior regions of at each of 3 consecutive levels, with the most caudal level at the superior aspect of the lateral ventricles. These regions corresponded to frontal, frontal-parietal, and parietal. Regions of interest were also drawn bilaterally in the caudate heads, putamina, thalami, posterior internal capsules, and the cerebellar (Fig 1). The regions of interest were drawn to avoid areas of FLAIR and DWI lesions. Similar region-of-interest locations were drawn in patients as well as controls. There was a total of 15 regions of interest for which ADC measurements could not be obtained secondary to lesion locations that did not allow for placement of the region of interest in the patients with CNS vasculitis. The average size of the region of interest in the patients with CNS vasculitis was 44.4 mm 3. The right-sided and left-sided ADC measurements for the 3 levels at which the was measured were averaged together for 1 value to represent each region anterior, central, or posterior. Similarly, the right-sided and left-sided ADC measurements from the caudate heads, putamina, thalami, posterior internal capsules, and the cerebellar were averaged together to obtain 1 measurement for each region. The ADC analysis was performed by using 2-point ADC calculations. 16 Images with b 0 s/mm 2 and b 1000 s/mm 2 were used. ADC maps were generated on an ADW 4.0 workstation (GE Healthcare). The t test was used to compare the average ADCs for each regionof-interest point measured (anterior, central, posterior, caudate heads, putamina, thalami, posterior internal capsules, and the cerebellar ) in the vasculitis subjects with those of healthy controls. A Bonferroni correction was used, making a P value of significant. Results The ADC values in the normal-appearing brain of the patients are summarized in the Table. There was a significant increase in the ADC values (P.00625) for the anterior, central, thalami, and posterior internal capsules (Fig 2). In patients 4 and 5, DWI and FLAIR showed no abnormal findings. Both patients overall demonstrated mild-to-moderate elevation of ADCs compared with the average values of the controls. There were 9 patients with lesions seen on DWI and 12 patients with lesions seen on FLAIR. Only 2 patients demonstrated more lesions on DWI than on FLAIR. There was a total of 75 DWI lesions and 150 FLAIR lesions. Discussion Diagnosing CNS vasculitis continues to be a clinical and radiographic challenge. It has been shown previously that MR 934 White AJNR 28 May
3 ADC in the nonlesional brain of patients Patient/ Age/ Sex Days from Onset to DWI No. of Lesions on DWI/FLAIR Angiographic Findings 1/40/M 7 21/18 Irregular narrowing of anterior, posterior circ. bilaterally 2/46/F 2 6/2 Irregular narrowing of rt. MCA, lt. ACA, and MCA 3/45/F 9 0/1 Segmental stenosis of anterior, posterior circ. bilaterally 4/39/F 5 0/0 Irregular narrowing and serpiginous appearance of rt. PICA Anterior (7.53) (8.09) (7.80) (7.67) 5/74/M 2 0/0 N/A (8.38) 6/58/F 3 2/7 Irregular narrowing of anterior, posterior circ. bilaterally (7.86) 7/56/F 6 5/8 Normal (8.54) 8/54/F 7 0/1 Narrowing and dilation of lt ACA and MCA 9/51/F 6 7/11 Occlusion of lt. ACA and MCA; multiple medium/small (8.28) vessel stenoses 10/48/M 13 5/36 Irregular narrowing of anterior, posterior circ. bilaterally (8.07) 11/51/F 13 13/15 Occlusion in left circ (7.94) 12/52/F 7 0/23 Diffuse vessel caliber variations (7.91) 13/47/F 20 7/8 Stenosis of MCA and PCA bilaterally (8.18) 14/61/M 8 7/17 N/A (8.07) 15/57/F 45 2/3 Irregularity of rt. MCA (8.11) Central (7.87) (7.24) (6.85) (6.59) (7.17) (6.86) (7.32) (6.86) (6.96) (7.91) (768) (7.51) (8.46) (8.10) (7.78) Posterior (7.92) (7.38) (7.45) (7.48) (7.47) (7.75) (7.58) (7.45) (7.86) (6.97) (8.30) (8.18) (8.00) (7.54) ADC ( 10 4 mm 2 /s) Caudate Cerebellar Heads Putamina Thalami Post IC 8.48 (8.48) 7.94 (7.94) (7.84) (7.79) (7.54) (7.41) (7.34) (7.35) (7.73) (6.98) (6.91) (8.56) (8.63) (7.69) (6.59) (6.91) (7.44) (7.51) (7.55) (7.36) (7.59) (7.53) (7.31) (7.41) 8.17 (8.17) (7.89) (7.03) (7.31) (8.57) (7.83) (7.76) 8.13 (8.13) 7.79 (7.79) (7.75) (7.85) (6.88) (7.57) (7.64) (8.21) (7.59) 7.62 (7.62) (8.71) (6.85) (6.71) (6.93) (6.98) (8.00) (7.08) (7.00) (7.34) (7.05) (6.03) (6.36) (6.14) (6.72) (6.40) (7.89) (7.14) (6.92) (5.95) (8.11) (7.96) 8.79 (8.79) (7.80) (7.34) (7.88) (8.01) (8.71) Note: ADC indicates apparent diffusion coefficient; M, male; F, female;, white matter; post IC, posterior internal capsules; ACA, anterior cerebral artery; circ., circulation; rt., right; lt., left; MCA, middle cerebral artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; PICA, posterior inferior cerebellar artery; N/A, not performed; numbers in parentheses are the mean ADC values imaging findings in CNS vasculitis can be negative when abnormalities are present at cerebral angiography. 4-7 Conventional MR imaging findings may even be negative in cases of pathologically proved vasculitis. 17 Also, angiography and biopsy findings can be negative in patients who have CNS vasculitis. 1,3,4,7,17-19 This demonstrates the need for a noninvasive test that can detect abnormalities that may be missed by conventional MR imaging, and even angiography and biopsy. This noninvasive test could potentially be beneficial for both diagnostic and prognostic purposes. DWI uses a contrast mechanism water diffusivity that is unique and quantifiable. 9 This uniqueness of the contrast mechanism allows DWI to demonstrate brain changes that routine MR imaging misses. ADCs increase when water motion increases. However, increased diffusion is a nonspecific finding that can be the result of several mechanisms. DWI with ADC analysis has demonstrated the ability to detect subtle changes throughout the brain. Increased ADC values for normal-appearing brain have been found in multiple sclerosis, tuberous sclerosis, Behcet disease, NF1, and the aging brain Applying ADC analysis to evaluate the brain in patients with CNS vasculitis may reveal otherwise undetectable changes. Our results demonstrate that diffuse changes do occur in the normal-appearing brain in patients with CNS vasculitis. The ADCs were increased throughout the of the corona radiata and centrum semiovale, the thalami, and the posterior internal capsules. The ADC analysis of the brain helped to elucidate the extent of abnormalities that occur in CNS vasculitis. This study demonstrated the ability of ADC measurements to detect brain changes that have not been previously noted. The ADC analysis of the normal-appearing brain may be potentially useful in the diagnostic work-up of patients with suspected CNS vasculitis, given that conventional MR imaging findings may be negative in patients with CNS vasculitis. 4-7 For example, normal MR imaging findings but an abnormality of normal-appearing brain in a patient with suspected CNS vasculitis may be strong evidence for pursuing a more invasive diagnostic test such as brain biopsy. This question needs further evaluation. Even of greater interest would be the possibility that a noninvasive test could help make the diagnosis of CNS vasculitis, and a brain biopsy could be avoided. However, it would be surprising if ADC analysis of the normal-appearing brain in patients suspected of having CNS vasculitis could fulfill that role, given the nonspecific meaning of increased ADCs. We can only hypothesize the meaning of diffuse abnormalities detected by ADC analysis. We would conjuncture that they potentially represent diffuse vasogenic edema, brain destruction (axonal loss), wallerian degeneration, or vascular changes directly due to the vasculitic process. In patients with CNS vasculitis, diffuse pathologic changes in the brain parenchyma include loss of nerve cells, abnormal nerve cells, perivascular lakes of eosinophilic material, and foci of vacuolation. 20 Changes have been found widespread throughout the white and gray matter. 20 At autopsy, diffuse changes of edema, reactive astrocytosis, ischemic change, and hemorrhage have been found. 21 The changes in the posterior internal capsules and the thalami in particular could be due to wallerian degen- AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28: May
4 Fig 2. Comparison of the ADC values (square millimeters per second) between the patients with vasculitis and the healthy controls for anterior (, A), central (B), posterior (C), caudate heads (D), putamina (E), thalami (F), posterior internal capsules (post IC, G), and cerebellar (H). There is a significant increase in the ADC values (P.00625) for the anterior, central, thalami, and post IC in the patients with vasculitis. The horizontal lines indicate the mean ADC values in each group. eration secondary to the tracts of which they consist (the posterior internal capsules) or the numerous connections within them (the thalami). CNS vasculitis is a relatively rare disorder, and this resulted in the number of cases in our series being small. However, given the rarity of the disease, we believe the number of patients in our series is respectable. Not all of our cases are from the same MR imaging scanner, and this may result in an unanticipated bias that we may not have corrected even though we matched our healthy controls by the MR imaging scanner used in the patients with vasculitis. We did use the same b value for all diffusion studies (b 1000). Most of our cases were not pathologically proved, but it has been shown that biopsy can be negative in patients who have CNS vasculitis. 17,19 We were limited in biopsy material available to confirm the diagnosis of CNS vasculitis secondary to the clinical methodologies used at our institution to make the diagnosis of vasculitis. Conclusion We detected changes by ADC analysis of the normal-appearing brain in patients with CNS vasculitis. Further analysis of patients with CNS vasculitis is needed to determine if this 936 White AJNR 28 May
5 information can be used to predict patient diagnosis, acute clinical outcome, or long-term disability. References 1. Calabrese LH, Mallek JA. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system: report of 8 new cases, review of the literature, and proposal for diagnostic criteria. Medicine (Baltimore) 1988;67: Rhodes RH, Madelaire NC, Petrelli M, et al. Primary angiitis and angiopathy of the central nervous system and their relationship to systemic giant cell arteritis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1995;119: Harris KG, Trann DD, Sickels WJ, et al. Diagnosing intracranial vasculitis: the roles of MR and angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1994;15: Greenan TJ, Grossman RI, Goldberg HI. Cerebral vasculitis: MR imaging and angiographic correlation. Radiology 1992;182: Cloft HJ, Phillips CD, Dix JE, et al. Correlation of angiography and MR imaging in cerebral vasculitis. Acta Radiol 1999;40: Wasserman BA, Stone JH, Hellmann DB, et al. Reliability of normal findings on MR imaging for excluding the diagnosis of vasculitis of the central nervous system. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2001;177: Pomper MG, Miller TJ, Stone JH, et al. CNS vasculitis in autoimmune disease: MR imaging findings and correlation with angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1999;20: Meusser S, Rubbert A, Manger B, et al. 99m-Tc-HMPAO-SPECT in diagnosis of early cerebral vasculitis. Rheumatol Int 1996;16: Turner R, Le Bihan D, Maier J, et al. Echo-planar imaging of intravoxel incoherent motion. Radiology 1990;177: Baysal T, Dogan M, Karlidag R, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging in chronic Behcet patients with and without neurological findings. Neuroradiology 2005; 47: Epub 2005 May Engelter ST, Provenzale JM, Petrella JR, et al. The effect of aging on the apparent diffusion coefficient of normal-appearing. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;175: Garaci FG, Floris R, Bozzao A, et al. Increased brain apparent diffusion coefficient in tuberous sclerosis. Radiology 2004;232: Epub 2004 Jun Horsfield MA, Lai M, Webb SL, et al. Apparent diffusion coefficients in benign and secondary progressive multiple sclerosis by nuclear magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 1996;36: Alkan A, Sigirci A, Kutlu R, et al. Neurofibromatosis type 1: diffusion weighted imaging findings of brain. Eur J Radiol 2005;56: Epub 2005 Jun Kissel JT. Neurologic manifestations of vasculitis. Neurol Clin 1989;7: Burdette JH, Elster AD, Ricci PE. Calculation of apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs) in brain using two-point and six-point methods. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998;22: Chu CT, Gray L, Goldstein LB, et al. Diagnosis of intracranial vasculitis: a multi-disciplinary approach. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1998;57: Calabrese LH, Furlan AJ, Cragg LA, et al. Primary angiitis of the central nervous system: diagnostic criteria and clinical approach. Cleve Clin J Med 1992;59: Duna GF, Calabrese LH. Limitations of invasive modalities in the diagnosis of primary angiitis of the central nervous system. J Rheumatol 1995;22: Nurick SW. Blackwood W, Mair WG. Giant cell granulomatous angiitis of the central nervous system. Brain 1972;95: Panda KM, Santosh V, Yasha TC, et al. Primary angiitis of CNS: neuropathological study of three autopsied cases with brief review of literature. Neurol India 2000;48: AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28: May
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics. Disclosures. Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor 4/14/2017
 Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
 Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
Hemodynamic patterns of status epilepticus detected by susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) Poster No.: C-1086 Congress: ECR 014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. AELLEN, E. Abela, R. Kottke, E. Springer,
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis
 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
3D time-of-flight (3D TOF) MR angiography (MRA)
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.A. Deutschmann M. Augustin J. Simbrunner B. Unger H. Schoellnast G.A. Fritz G.E. Klein Diagnostic Accuracy of 3D Time-of-Flight MR Angiography Compared with Digital Subtraction Angiography
ORIGINAL RESEARCH H.A. Deutschmann M. Augustin J. Simbrunner B. Unger H. Schoellnast G.A. Fritz G.E. Klein Diagnostic Accuracy of 3D Time-of-Flight MR Angiography Compared with Digital Subtraction Angiography
Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:291 295, February 1998 Subtraction CT Angiography with Controlled- Orbit Helical Scanning for Detection of Intracranial Aneurysms Satoshi Imakita, Yoshitaka Onishi, Tokihiro Hashimoto,
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke
 Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
Diagnostic improvement from average image in acute ischemic stroke N. Magne (1), E.Tollard (1), O. Ozkul- Wermester (2), V. Macaigne (1), J.-N. Dacher (1), E. Gerardin (1) (1) Department of Radiology,
Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging in the Evaluation of Intracranial Tumors
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 12 Ver. IX (December. 2016), PP 99-104 www.iosrjournals.org Role of Diffusion weighted Imaging
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression
 MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
MR imaging at 3.0 tesla of glossopharyngeal neuralgia by neurovascular compression Poster No.: C-1281 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nishihara 1, T. Noguchi 1, H. Irie 1, K. Sasaguri
Angiographic Correlation of CT Calcification in the Carotid Siphon
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:495 499, March 1999 Angiographic Correlation of CT Calcification in the Carotid Siphon Richard J. Woodcock, Jr, Jonas H. Goldstein, David F. Kallmes, Harry J. Cloft, and C. Douglas
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:495 499, March 1999 Angiographic Correlation of CT Calcification in the Carotid Siphon Richard J. Woodcock, Jr, Jonas H. Goldstein, David F. Kallmes, Harry J. Cloft, and C. Douglas
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS) and CNS
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN High-Resolution MRI Vessel Wall Imaging: Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome and Central Nervous System Vasculitis E.C. Obusez, F. Hui,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN High-Resolution MRI Vessel Wall Imaging: Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Reversible Cerebral Vasoconstriction Syndrome and Central Nervous System Vasculitis E.C. Obusez, F. Hui,
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Kurtosis is a descriptor of the peakedness of a variable relative
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Time Course of Axial and Radial Diffusion Kurtosis of White Matter Infarctions: Period of Pseudonormalization T. Taoka, M. Fujioka, M. Sakamoto, T. Miyasaka, T. Akashi, T. Ochi,
Moyamoya Disease A Vasculopathy and an Uncommon Cause of Recurrent Cerebrovascular Accidents
 Moyamoya Disease A Vasculopathy and an Uncommon Cause of Recurrent Cerebrovascular Accidents Yasmin S. Hamirani, Md 1 *, Mohammad Valikhani, Md 2, Allison Sweney, Ms Iii 2, Hafsa Khan, Md 2, Mohammad Pathan,
Moyamoya Disease A Vasculopathy and an Uncommon Cause of Recurrent Cerebrovascular Accidents Yasmin S. Hamirani, Md 1 *, Mohammad Valikhani, Md 2, Allison Sweney, Ms Iii 2, Hafsa Khan, Md 2, Mohammad Pathan,
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature.
 Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a motor neuron disease
 ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
ORIGINL RESERCH S. Ngai Y.M. Tang L. Du S. Stuckey Hyperintensity of the Precentral Gyral Subcortical White Matter and Hypointensity of the Precentral Gyrus on Fluid-ttenuated Inversion Recovery: Variation
Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:680 687, April 2003 Quantitative Assessment of the Time Course of Infarct Signal Intensity on Diffusion-Weighted Images James D. Eastwood, Stefan T. Engelter, James F. MacFall,
Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice
 Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Vasculitides in Surgical Neuropathology Practice USCAP requires that all faculty in a position to influence or control the content of CME disclose any relevant financial relationship WITH COMMERCIAL INTERESTS
Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia John R. Hesselink, M.D. Causes of Stroke Arterial stenosis Thrombosis Embolism Dissection Hypotension
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging Acute Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia John R. Hesselink, M.D. Causes of Stroke Arterial stenosis Thrombosis Embolism Dissection Hypotension
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
IMAGING IN ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE Timo Krings MD, PhD, FRCP (C) Professor of Radiology & Surgery Braley Chair of Neuroradiology, Chief and Program Director of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology;
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note
 High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
High-resolution T 2 -reversed magnetic resonance imaging on a high-magnetic field system Technical note Yukihiko Fujii, M.D., Ph.D., Naoki Nakayama, M.D., and Tsutomu Nakada, M.D., Ph.D. Departments of
Naoaki Yamada, Satoshi Imakita, and Toshiharu Sakuma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:193 198, February 1999 Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Recent Cerebral Infarctions: A Correlative Study with Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography
 Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
Diagnosis of Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion with Transcranial Color-Coded Real-Time Sonography Kazumi Kimura, Yoichiro Hashimoto, Teruyuki Hirano, Makoto Uchino, and Masayuki Ando PURPOSE: To determine
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
SHORTLY AFTER ITS FIRST DEpiction
 OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
OBSERVATION Seven-Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging New Vision of Microvascular Abnormalities in Multiple Sclerosis Yulin Ge, MD; Vahe M. Zohrabian, MD; Robert I. Grossman, MD Background: Although the role
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1240 1245, August 2002 Case Report Pituitary Apoplexy: Early Detection with Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Jeffrey M. Rogg, Glenn A. Tung, Gordon Anderson, and Selina Cortez Summary:
Cerebrovascular Disease
 Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Neuropathology lecture series Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O 2 consumption (resting):
Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Remission of diffusion lesions in acute stroke magnetic resonance imaging F. A. Fellner 1, M. R. Vosko 2, C. M. Fellner 1, D. Flöry 1 1. AKH Linz, Institute of Radiology, Austria. 2.
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
MR Assessment of Myelination in Infants and Children: Usefulness of Marker Sites
 731 MR ssessment of Myelination in Infants and Children: Usefulness of Marker Sites C. Roger ird 1 Mary Hedberg urton P. Drayer Paul J. Keller Richard. Flom John. Hodak retrospective study was made of
731 MR ssessment of Myelination in Infants and Children: Usefulness of Marker Sites C. Roger ird 1 Mary Hedberg urton P. Drayer Paul J. Keller Richard. Flom John. Hodak retrospective study was made of
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:692 698, May 2004 Water Diffusion Compartmentation at High b Values in Ischemic Human Brain Pierre Brugières, Philippe Thomas, Anne Maraval, Hassan Hosseini, Catherine Combes,
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum
 Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:186-190 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.186 Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Presenting as Rhombencephalitis: An Atypical Case Presentation Joonseok
Intracranial Atherosclerosis Versus Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: a Case Report
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.3031 Intracranial Atherosclerosis Versus Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: a Case Report Joshua A. Ronen 1, Aileen Nguyen 2, Jerrica N. Mueller
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.3031 Intracranial Atherosclerosis Versus Primary Angiitis of the Central Nervous System: a Case Report Joshua A. Ronen 1, Aileen Nguyen 2, Jerrica N. Mueller
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:243 247, February 2002 Case Report Astroblastoma: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation and Distinction from Ependymoma John D. Port, Daniel J. Brat, Peter C. Burger, and Martin G.
Stroke imaging. Why image stroke patients? Stroke. Treatment of infarct. Methods for infarct diagnosis. Treatment of infarct.
 Stroke imaging Stroke Infarct: -Arterial thrombosis/embolus -Hypoxic/ischemic -Venous thrombosis Non-traumatic hemorrhage: -Intracerebral -Subarachnoid Johan Wikström MD PhD Associate Professor of Radiology
Stroke imaging Stroke Infarct: -Arterial thrombosis/embolus -Hypoxic/ischemic -Venous thrombosis Non-traumatic hemorrhage: -Intracerebral -Subarachnoid Johan Wikström MD PhD Associate Professor of Radiology
I t is increasingly recognised that arterial cerebral infarction
 F252 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does cranial ultrasound imaging identify arterial cerebral infarction in term neonates? F Cowan, E Mercuri, F Groenendaal, L Bassi, D Ricci, M Rutherford, L de Vries... See end of
F252 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does cranial ultrasound imaging identify arterial cerebral infarction in term neonates? F Cowan, E Mercuri, F Groenendaal, L Bassi, D Ricci, M Rutherford, L de Vries... See end of
Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2508 2513, November/December 2005 Surface Appearance of the Vertebrobasilar Artery Revealed on Basiparallel Anatomic Scanning (BPAS) MR Imaging: Its Role for Brain MR Examination
acute-onset, severe, recurrent reversible vasoconstriction
 1 RCVS A clinical and radiologic syndrome Characterized by acute-onset, severe, recurrent headache and reversible vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries RCVS accounts for most benign thunderclap headaches"
1 RCVS A clinical and radiologic syndrome Characterized by acute-onset, severe, recurrent headache and reversible vasoconstriction of the cerebral arteries RCVS accounts for most benign thunderclap headaches"
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in Biopsy-Proven Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
 Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging in iopsy-proven reutzfeldt-jakob Disease Hyo-heol Kim, MD 1 Kee-Hyun hang, MD 1 In han Song, PhD 1 Sang Hyun Lee, MD 1 ae Ju Kwon, MD 1 Moon Hee Han, MD 1 Sang-Yun Kim, MD
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine are potentially catastrophic.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with Brain MR Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 12, No. 2, pp. 105 110, 2013 2013 Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine doi:10.2463/mrms.2012-0044 MAJOR PAPER Ring-shaped Lateral Ventricular Nodules Detected with
OBSERVATION. Postpartum Angiopathy With Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy
 Postpartum Angiopathy With Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Aneesh B. Singhal, MD OBSERVATION Background: Postpartum angiopathy (PPA) is a cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome of uncertain cause
Postpartum Angiopathy With Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Aneesh B. Singhal, MD OBSERVATION Background: Postpartum angiopathy (PPA) is a cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome of uncertain cause
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Study Determining Correlation between Histopathological Diagnosis and MRI Findings of Posterior Fossa Tumors Srinivasarao S. Gummadidala 1, B. Jyothi 2 1 Assistant Professor,
Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging
 Case Reports Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging Koichi Nomura 1, Masahiro Mishina 1,SeijiOkubo 1, Satoshi Suda
Case Reports Long-term Observation of Lateral Medullary Infarction due to Vertebral Artery Dissection Assessed with Multimodal Neuroimaging Koichi Nomura 1, Masahiro Mishina 1,SeijiOkubo 1, Satoshi Suda
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging has been reported to be a sensitive and specific method in the diagnosis of disease of the sub-
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1698 1703, October 2001 Imaging of Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage with a Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Sequence in an Animal Model: Comparison with Non Contrast-Enhanced CT
Neuropathology lecture series. III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease. Physiology of cerebral blood flow
 Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Neuropathology lecture series III. Neuropathology of Cerebrovascular Disease Physiology of cerebral blood flow Brain makes up only 2% of body weight Percentage of cardiac output: 15-20% Percentage of O
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
AMSER Case of the Month: March 2019
 AMSER Case of the Month: March 2019 62 year-old male with left-sided weakness Ashley Graziano OMS IV, Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine Erik Yannone MD, Charles Q. Li MD, Warren Chang MD, Matthew
AMSER Case of the Month: March 2019 62 year-old male with left-sided weakness Ashley Graziano OMS IV, Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine Erik Yannone MD, Charles Q. Li MD, Warren Chang MD, Matthew
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT
 Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
Detectability of unruptured intracranial aneurysms on thinslice non-contrast-enhanced CT Poster No.: C-9 Congress: ECR 5 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Nakadate, Y. Iwasa, M. Kishino, U. Tateishi;
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease
 CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
CT perfusion in Moyamoya disease Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. C. Lam, C. P. Tsang, K. K. Wong, R. LEE ; HK, Hong Kong/HK Keywords: Hemodynamics / Flow dynamics,
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Cerebral aneurysms A case study
 August 2001 Cerebral aneurysms A case study Heather L. Hinds, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient 57yr old woman History of migraines Presents with persistent headache several months duration different
August 2001 Cerebral aneurysms A case study Heather L. Hinds, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient 57yr old woman History of migraines Presents with persistent headache several months duration different
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
Magnetic Resonance Angiography of Primary Varicella Vasculitis: Report of Two Cases
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 9:491 496 (1999) Clinical Note Magnetic Resonance Angiography of Primary Varicella Vasculitis: Report of Two Cases Larry A. Kramer, MD, 1 * Carlos Villar-Cordova,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 9:491 496 (1999) Clinical Note Magnetic Resonance Angiography of Primary Varicella Vasculitis: Report of Two Cases Larry A. Kramer, MD, 1 * Carlos Villar-Cordova,
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine
 Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
Vivek R. Deshmukh, MD Director, Cerebrovascular and Endovascular Neurosurgery Chairman, Department of Neurosurgery Providence Brain and Spine Institute The Oregon Clinic Disclosure I declare that neither
Reduced Caliber of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Normal Finding with Ipsilateral Absence or Hypoplasia of the A1 Segment
 Reduced Caliber of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Normal Finding with Ipsilateral Absence or Hypoplasia of the A1 Segment Arthur G. Kane, William P. Dillon, A. James Barkovich, David Norman, Christopher
Reduced Caliber of the Internal Carotid Artery: A Normal Finding with Ipsilateral Absence or Hypoplasia of the A1 Segment Arthur G. Kane, William P. Dillon, A. James Barkovich, David Norman, Christopher
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors
 Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC mapping in the differentiation of intraventricular brain tumors Poster No.: C-2652 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: M. Gavrilov, T.
Blood Supply. Allen Chung, class of 2013
 Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Blood Supply Allen Chung, class of 2013 Objectives Understand the importance of the cerebral circulation. Understand stroke and the types of vascular problems that cause it. Understand ischemic penumbra
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Cerebral arterial stenoses can be caused by a wide range of
 Evaluation of Hyperintense Vessels on FLAIR MRI for the Diagnosis of Multiple Intracerebral Arterial Stenoses Daniela Iancu-Gontard, MD; Catherine Oppenheim, MD, PhD; Emmanuel Touzé, MD; Eric Méary, MD;
Evaluation of Hyperintense Vessels on FLAIR MRI for the Diagnosis of Multiple Intracerebral Arterial Stenoses Daniela Iancu-Gontard, MD; Catherine Oppenheim, MD, PhD; Emmanuel Touzé, MD; Eric Méary, MD;
Usefulness of Intracranial CT Angiography with Spiral CT in Brain Death - A Preliminary Report -
 Usefulness of Intracranial CT Angiography with Spiral CT in Brain Death - A Preliminary Report - Jong-Ho Park, M.D., Hong-Ki Song, M.D., Dae-Young Yoon, M.D. Department of Neurology and Radiology*, Hallym
Usefulness of Intracranial CT Angiography with Spiral CT in Brain Death - A Preliminary Report - Jong-Ho Park, M.D., Hong-Ki Song, M.D., Dae-Young Yoon, M.D. Department of Neurology and Radiology*, Hallym
MRI in MS. MRI in multiple sclerosis. MS T2 Lesions: Pathology. Brain lesions Morphology Matters. Sagittal FLAIR Morphology Matters
 MRI in multiple sclerosis MRI in MS Rohit Bakshi, MD, MA Breakstone Professor of Neurology & Radiology Director, Laboratory for Neuroimaging Research Senior Neurologist, MS Center Brigham & Women s Hospital
MRI in multiple sclerosis MRI in MS Rohit Bakshi, MD, MA Breakstone Professor of Neurology & Radiology Director, Laboratory for Neuroimaging Research Senior Neurologist, MS Center Brigham & Women s Hospital
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma
 Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
Application of three-dimensional angiography in elderly patients with meningioma Poster No.: C-0123 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: X. Han, J. Chen, K. Shi; Haikou/CN Keywords: Neuroradiology
MRI OF THE THALAMUS. Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI
 1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
Sawada J, Orimoto R, Misu T, Katayama T, Aizawa H, Asanome A, Takahashi K, Saito T, Anei R, Kamada K, Miyokawa N, Takahashi T, Fujihara K, Hasebe N.
 Mult Scler (2014.9) 20(10):1413-1416. A case of pathology-proven neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with Sjögren syndrome manifesting aphasia and apraxia due to a localized cerebral white matter lesion.
Mult Scler (2014.9) 20(10):1413-1416. A case of pathology-proven neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder with Sjögren syndrome manifesting aphasia and apraxia due to a localized cerebral white matter lesion.
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism
 Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
Epidermiology Early pulmonary embolism Sitang Nirattisaikul Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 3 rd most common cause of cardiovascular death in the United States, following ischemic heart
In some patients with pituitary macroadenoma, visual acuity
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.M. Tokumaru I. Sakata H. Terada S. Kosuda H. Nawashiro M. Yoshii Optic Nerve Hyperintensity on T2-Weighted Images among Patients with Pituitary Macroadenoma: Correlation with Visual
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 04/26/2014 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 108 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 04/26/2014 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 108 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Initial symptom or syndrome: (1) FOCAL WEAKNESS OR NUMBNESS
 View the referenced DVD patient cases, especially if few hospital or clinic patients are encountered for any one symptom or syndrome. The DVD patient cases are referenced by initial symptom or syndrome
View the referenced DVD patient cases, especially if few hospital or clinic patients are encountered for any one symptom or syndrome. The DVD patient cases are referenced by initial symptom or syndrome
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
