NEUROENDOSCOPY VAMSI KRISHNA YERRAMNENI
|
|
|
- Solomon French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NEUROENDOSCOPY VAMSI KRISHNA YERRAMNENI
2 INTRODUCTION The field of neuroendoscopy began with great promise. This new modality hold the potential to allow neurosurgeons to visualize anatomical structures never before studied in live patients. The perspective would be unique, a magnified view of the ventricular system viewed from within its walls.
3 HISTORY Max Nitze credited with designing first to device an endoscope this was a crude device composed of a series of lenses with an illumination source at the tip. First neurosurgical endoscopic procedure was performed by L Espinasse. In 1910, he used cystoscope to perform fulguration of the choroid plexus in two infants with hydrocephalus. In 1922, Walter Dandy described the use of an endoscope to perform choroid plexectomy. Dandy reported the first ventriculostomy for the treatment of hydrocephalus fenestration of the lamina terminalis via a craniotomy and a transfrontal approach. In 1923, Fay and Grant were able to visualize and photograph successfully the interior of the ventricles of a child with hydrocephalus by using a cystoscope. That same year, Mixter performed the first successful ETV by using a urethroscope in a 9-month-old girl with obstructive hydrocephalus.
4 HIST CONT. In 1932, Dandy again reported use of an endoscope for choroid plexectomy. In 1934, Putnam described cauterization of the choroid plexus with an endoscopic device. The procedure was performed 12 times in seven patients, was successful in at least three cases, and resulted in two deaths. 9 years later Putnam reported his series of endoscopic choroid plexectomy in 42 patients. There were 10 perioperative deaths.15 patients failed to respond, although 17 had successful relief of increased intracranial pressure.
5 CONT Scarff described his initial results after using a novel endoscope equipped with a mobile cauterizing electrode, an irrigation system that prevented collapse of the ventricles, and a movable operating tip that could be used to perforate the floor of the third ventricle. He punctured the floor of the third ventricle in one patient and achieved dramatic results: a 3-cm decrease in head circumference 6 weeks postoperatively.
6 HISTORY In 1947, McNickle - percutaneous method of performing third ventriculostomy in patients with both obstructive and communicating hydrocephalus. Initially he used a 19-gauge needle and an endoscope for visualization. Despite the numerous reports that demonstrated the potential utility of neuroendoscopy, the field never gained favor in general neurosurgical practice. The fact was that poor magnification and illumination made neuroendoscopy difficult and unreliable.
7 TECHNOLOGICAL BREAKTHROUGHS New Lens Type. In 1966, Hopkins and Storz developed a rigid endoscope that used a new type of lens, the SELFOC lens. Conventional lenses have a uniform refractive index, The SELFOC lens used gradient index glass that had a refractive index that varied with the radial dimension of the lens. Conventional endoscopes required the careful placement of a series of relay and field lenses to construct an appropriate image. This new technology essentially obviated the need for the relay lenses while preserving light transmission. These lenses also created a wider effective field of vision.
8 INVENTION OF CCD S. In 1969, George Smith and Willard Boyle invented the first CCDs at Bell Laboratories. The CCDs usually a silicon chip, which are capable of converting optical data into electrical current. Chargecoupling refers to the manner in which the electronic charges are stored and transmitted. The CCDs are ideal for use in low-light environments and were readily incorporated into the system s apparatus, resulting in both improved quality of the transmitted images and decreased size of the endoscopic systems.
9 FIBREOPTICS.. first used in the 1950s and 1960s, and refined further in the 1970s. allowed the light source to be separated from the rest of the endoscope. In1963 Scarff described the first use of a fiber lighting system with an external light source for ventriculoscopy. These advances, which brought together brighter light sources and cameras with improved resolution, the two key components of any endoscope, were an important part of the rediscovery of neuroendoscopy.
10 REDISCOVERY OF NEUROENDOSCOPY In 1978, Vries described his experience treating five patients with hydrocephalus, in whom he performed ETVs by using a fiberoptic endoscope.. In1990 Jones and colleagues described a 50% shunt-free success rate for ETV in 24 patients with various forms of hydrocephalus. Four years later, Jones and coworkers had improved their success rate to 61% in a series of 103 patients. Currently ETV is primarily used to treat obstructive hydrocephalus.
11 INSTRUMENT DESIGN
12 3 CHIP CCD CAMERA
13
14
15
16 Comparison of rigid and flexible scopes Rlgid scopes Flexible scope Advantges Better image Steerability higher resolution Application in spine Wider view, Better colour Better light transmission Light weight of disposable scopes Disadvantages Less maneuverable Poor image Not applicble in Spine. Pixel granules Narrower view Less true colour Worse light Smaller working channel Limited selection of scopes and instruments
17 AREAS OF NEUROENDOSCOPY The endoscope is currently being used for all types of neurosurgically treatable disorders: intraventricular tumors, skull base tumors, craniosynostosis, degenerative spine disease, intracranial cysts, rare subtypes of hydrocephalus.
18 INDICATIONS OF ETV Non-communicating hydrocephalus Congenital lesions stenosis of aqueduct of Sylvius obstruction of foramen of Monro atresia of foramina of Luschka & Magendie Dandy-Walker cyst
19 WELL ACCEPTED INDICATIONS Aqueductal stenosis Arachnoid cyst & ass. hydrocephalus Neoplastic etiology e.g. tectal plate tumors Intraventricular neurocysticercosis Dandy Walker syndrome and its variants
20 RELATIVE INDICATIONS Patients with repeated shunt infections Post-meningitic hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus following intraventricular hemorrhage
21 THIRD VENTRICULOSTOMY PROCEDURE A trephanation was performed in the Kocher point. When a neuroendoscope is introduced to a lateral cerebral ventricle, it is necessary to identify the foramen of Monro, which is surrounded by the choroid plexus and septal and thalamostriate veins. The correct point for the third ventriculostomy is the socalled hypophysiomamillary triangle (an area between the infundibular recess and mamillary bodies) away from the bifurcation of the basilar artery and the portal circulation of the hypophysis.
22 ETV There are different techniques to perforate the bottom of the third ventricle. The perforation can be made with the use of sharp instruments such as a very thin neuroendoscope itself or coagulation. Both methods are connected with increased risk of injury to the basilar artery. The third ventriculostomy can be made with the use of Fogarty's catheters. The crucial point is to perforate Liliequist's membrane. Hemostasis done with bipolar cautery probes.
23 ETV FAILURE Follow-up for 5-6 years Maximum incidence of failure: first 1-2 months No failure reported after 5 yrs. Early : within 4 wks Non-absorption from arachnoid granulation despite good MRI flow Delayed : after 4 wks Stoma closure gliosis / scarring (6-15%) No MRI flow Jones et al Min. Inv. Tech NS 1993 Siamin et al Childs Nervous System 2001 Cinalli et al Min. JNS 1999
24 ETV FAILURE Failure rate 10-40% Primary technical failure: difficult perforation, 2 nd membrane imperforation Secondary technical failure: Stoma closure gliosis / scarring CSF absorption failure Major complication <2% CSF leak Meningitis <1% Damage to hypothalamus: DI, SIADH Injury to vessels e.g. basilar artery injury
25 CONT. Etiology (Most imp. Factor) Previous meningitis Ass. myelomeningocele Shunt infection Repeated shunt malfunction Chiari malformation Technical: imperforated 2 nd membrane
26 NEUROENDOSCOPY VS SHUNT In infants suffering from chronic noncommunicating hydrocephalus after effective neuroendoscopic procedures, the rate of head circumference growth does not decrease, which is very different in comparison with infants treated by shunt implantation. The rate of head circumference growth in infants after neuroendoscopic procedures does not constantly increase as a function of time following the operative treatment, despite the fact that, in some children of the group, the head circumference could become higher according to the percentile chart. There are significant differences after an effective neuroendoscopic procedure between the rate of head growth in neonates, which is lower, and in infants, which is higher. In children suffering from chronic hydrocephalus, the observed decrease in ventricular size after neuroendoscopic procedures is smaller than after shunt implantation. In infants suffering from Chiari II malformation, after neuroendoscopic operative treatment, the average ventricular size is larger than in other children.
27 FOURTH VENTRICLE NCC EXCISION A relative contraindication to resection of cisternal cysts is the presence of significant inflammation, demonstrated by extensive enhancement of the cisterns and cysts on MR images. In these cases, the arachnoid and cyst walls are often opaque and indistinguishable, making exploration and removal of the cysts difficult and hazardous. If surgical exploration is considered, a low threshold for converting from the excision to placement of a shunt must be maintained.
28 ENDOSCOPIC TNTS
29 ENDOSCOPIC SHUNT PLACEMENT Goal is to place the ventricular catheter tip away from the choroid plexus. Small diameter endoscope as stylet with in the ventricular catheter may allow more accurate catheter positioning with in the ventricles. May decrease the chances of completely missing the ventricles. But does nt improve the surgical outcome once the tip is with in the ventricles.
30 ENDOSCOPIC REPAIR OF CSF RHINORRHEA: Anterior skull base defects are repaired. Intrathecal fluroscein administration helps in localising the defect. Endoscope passed through nostrils and fibrous tissue excised and graft placement done
31 ENDOSCOPIC COLLOID CYST EXCISION Ventricular enlargement renders the endoscopic intervention easier; The lesions are approached via a transcortical, transventricular, and transforaminal route. In general, the entry point should be located opposite the dominant hemisphere. In case of asymmetric ventricular dilation, the approach is via the wider ventricle. However, an asymmetric foramen of Monro with asymmetric covering of the cyst by the fornices is more important. Of course, the route of access with the least potential for fornix damage should be chosen. For accurate planning of the ideal approach, neuronavigation is indispensable Usually, the burr hole is placed behind the hairline and as far laterally (approximately 5-6 cm paramedian) as possible to allow straight access without damage to the caudate nucleus and fornix.
32 COLLOID CYST. Total cyst extirpation is attempted but not at the expense of severe hemorrhage. In these cases, the best option seems to be to coagulate the residual part of the cyst wall. However, the question remains whether small remnants of the capsule that may be left in place cause cyst recurrence.
33 SPINAL ENDOSCOPY The evolution of minimally invasive spine surgery dates from the 1929 report by Dandy (, in which he described removal of loose cartilage from the intervertebral disc. In 1931, Burman introduced the concept of myeloscopy for direct spinal cord observation. In 1934, Mixter and Barr reported an open hemilaminectomy with intraoperative discotomy for treatment of intervertebral disc rupture into the spinal canal. \In 1938, Pool (expanded on Burman's work and reported myeloscopic inspection of the dorsal nerve roots of the cauda equina. In 1942, Pool introduced the concept of intrathecal endoscopy and reported the results of more than 400 myeloscopic procedures.
34 CONT Myeloscopy fell out of favor for a time because of the morbidity associated with insertion of a large-bore scope into the neural cavity. The state of spinal endoscopy remained essentially the same until Ooi et alused an endoscope to examine the intrathecal space before surgery. Color photographs were taken during the procedure and were later correlated with the findings noted during the open procedure. Using improved technology, Ooi et al. were able to describe pathological features in greater detail, including chronic arachnoiditis and nerve root excursion during claudication associated with lumbar spinal stenosis. In 1989, Stoll et al. described epiduroscopy with a fiberoptic scope as an adjunct to open surgical procedures. As part of a FDA-approved study, a multicenter evaluation of 60 patients, for observation of the epidural space, was performed. No complications were observed during the study.
35 KAMBIN S TRIANGLE Percutaneous lumabar disc surgery is performed through the triangular working zone, or Kambin's triangle- This triangular zone is defined by the exiting nerve root or spinal nerve. The nerve makes up the hypotenuse of the triangle and therefore defines the anterior and superior safe working margins. The nerve makes an angle of 40 degrees with the dura as it exits under the pedicle. The hypotenuse is an average of 23 mm long. The longer leg is defined inferi-orly by the superior endplate of the distal vertebrae and measures 18.9 mm on average. The shorter leg of the triangle is defined by the superior articular facet of the distal vertebrae and usually measures 12.3 mm..
36
37 Patient Positioning Prone with abdomen free (Wilson Frame or Andrews table) Spine Flexed Depending on surgeon preference, microscope can be placed on either side of patient.
38 Guide Wire Placement Spinal needle is placed into paraspinous musculature 1.5cm off of midline at the appropriate level confirmed using lateral fluoroscopy The spinal needle is removed and a vertical incision is made at the puncture site The guide wire is placed through the incision and directed toward the inferior aspect of superior lamina under lateral fluoroscopy
39 Initial Dilator Insertion Insert initial cannulated soft tissue dilator over the guide wire Once the fascia is penetrated remove guide wire and advance the dilator down to the inferior edge of superior lamina Confirm placement of initial dilator using lateral lateral flouroscopy Use the initial dilator to palpate the lamina in both the coronal and sagital planes The tip of the dilator is used to sweep the paraspinal musculature off the laminar edge This maneuver affirms coronal placement and expedites soft tissue removal
40
41 The laminar edge is identified and the ligamentum flavum is detached from the undersurface of the lamina with a curved curette Soft Tissue Removal Soft tissue over the lamina and interlaminar space is removed with a pituitary rongeur It is essential to remove all soft tissue exposed in the operative corridor in order to maximize the working space within the Tubular Retractor
42 Medial Laminotomy A hemilaminotomy / medial facetotomy is performed with a Kerrison punch or high speed drill. Effective utilization of lateral fluoroscopy will help tailor the necessary dissection to access specific pathology If the pathology is beyond the confines of the Tubular Retractor, the retractor can be move or angled over the pathology by a process known as wanding. Wanding allows the surgeon to place the objects of interest in the center of the operative corridor
43 Ligamentum Removal The ligamentum flavum is opened with an angled curette. The curette is placed under the remaining superior lamina where the ligament is thin The ligament is penetrated with a curette utilizing a twisting motion. It is pealed back caudally and dorsally, then resected with a Kerrison punch
44 Nerve Root Identification The dura and traversing nerve root are identified The nerve root is retracted medially utilizing a Penfield dissector, Love style or suction retractor The volar epidural space can be explored and epidural veins can be cauterized
45 Discectomy An annulotomy can be performed with the Sheathed Annulotomy Knife while protecting the nerve root with the retractor
46 MICROENDOSCOPIC DISCECTOMY reduction of tissue trauma. Less duration of hosp. stay The ability to visualize the nerve root and disc disease directly, and allowing bony decompression (i.e., spinal and lateral recess stenosis).
47 ENDOSCOPIC SPINAL SURGERY Endoscopic Posterior Cervical Laminoforaminotomy ; This muscle-splitting approach is effective in limiting postoperative pain and muscle spasms while maintaining the integrity of midline posterior muscular and ligamentous attachments to the spine Anterior Cervical Foraminotomy ; The anterior cervical foraminotomy procedure is effective for unilateral radicular symptoms and can be performed on an outpatient basis
48 THORACOSCOPIC PROCEDURES Thoracoscopic Procedures ; The potential complications are similar to those associated with open thoracotomy, although the incidence varies. There is a reduced incidence of post-thoracotomy pain, intercostal neuralgia, pulmonary dysfunction, and scapular dysfunction associated with a thoracoscopic compared with an open thoracotomy approach. Complications may arise from many factors, including anesthesia, patient positioning, port placement and access, and manipulation of instruments, with injury to the lung parenchyma and thoracic vascular structures.
49 THORACOSCOPIC DISSECTOMY The anatomic dissection of the spine was essentially identical to the steps for thoracic discectomy using open thoracotomy. A cavity was drilled in the dorsal vertebral body and disc space to provide enough space to insert tools, to avoid manipulation of the spinal cord, and to expose normal dura rostral and caudal to the herniated disc. The cavity was pyramidal or hemispherical for small- to moderate-sized disc herniations and rectangular for larger herniations. The spinal cord and nerve roots were decompressed microsurgically under direct visualization using endoscopic spine tools with calibrated shafts and fine-angled tips.
50 THORACOSCOPIC SYMPATHECTOMY For palmar hyperhidrosis, the T2 ganglion and associated nerve of Kuntz were identified visually, isolated surgically, and divided with endoscopic cautery scissors. The associated nerve of Kuntz was found in fewer than 5% of patients. Axillary hyperhidrosis was present, the T3 and T4 ganglions were isolated. The sympathetic chain was transected in situ, creating a gap of 5 mm or more between the cut ends. The effectiveness of sympathectomy was gauged by monitoring palmar temperature for more than a 1 C increase in temperature after the sympathetic chain was transected
51 THORACOSCOPIC SYMPATHECTOMY A number of complications can result from thoracic endoscopic sympathectomy; they include compensatory hyperhidrosis syndrome (CHS), Horner's syndrome, intercostal neuralgia, pneumothorax, gustatory sweating vascular injury. increased sweating in non-denervated areas,
52 OTHER PROCEDURES Thoracoscopic-assisted Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Fractures Complications that can occur during anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF)
53 ENDOSCOPICALLY ASSISTED TRANSORAL-TRANSPHARYNGEAL APPROACH TO THE CRANIOVERTEBRAL JUNCTION By use of the 30-degree-angled endoscope, clivus can be visualised without the need for extensive palatal splitting. A broader field of view is obtained using the endoscope, and the lateral and inferior fields can be visualised well by rotating the endoscope. enable us to avoid performing extended maxillotomies in in patients requiring more aggressive procedures would have been necessary if microscopic technique were used. avoids splitting the soft palate. Minimizing the swallowing difficulty that sometimes results from this maneuver.
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy. Dr Kanwaljeet Garg
 Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy Dr Kanwaljeet Garg Introduction Endoscopic third ventriculostomyis a technique to treat non communicating hydrocephalus. Involves making a hole in the floor of the third
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy Dr Kanwaljeet Garg Introduction Endoscopic third ventriculostomyis a technique to treat non communicating hydrocephalus. Involves making a hole in the floor of the third
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Decompression (IG-MLD) for File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: image-guided_minimally_invasive_decompression_for_spinal_stenosis
Corporate Medical Policy Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Decompression (IG-MLD) for File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: image-guided_minimally_invasive_decompression_for_spinal_stenosis
Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures
 9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
9 Cervical Posterior surgical procedures are those procedures that have been in use for a long time with established efficacy in the treatment of radiculopathy and myelopathy caused by pathologies including
Surgical Technique Guide
 MIS Access System Surgical Technique Guide and Product Catalogue introduction contents This surgical technique guide describes the new SPOTLIGHT TM Access System that permits 3-dimensional visualisation
MIS Access System Surgical Technique Guide and Product Catalogue introduction contents This surgical technique guide describes the new SPOTLIGHT TM Access System that permits 3-dimensional visualisation
T.L.I.F. Surgical Technique. Featuring the T.L.I.F. SG Instruments, VG2 PLIF Allograft, and the MONARCH Spine System.
 Surgical Technique T.L.I.F. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Featuring the T.L.I.F. SG Instruments, VG2 PLIF Allograft, and the MONARCH Spine System. CONSULTING SURGEON Todd Albert, M.D. Rothman
Surgical Technique T.L.I.F. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Featuring the T.L.I.F. SG Instruments, VG2 PLIF Allograft, and the MONARCH Spine System. CONSULTING SURGEON Todd Albert, M.D. Rothman
Surgical Technique. TraXis. Precision. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Spacer. The Art & Science of Spine Surgery
 Surgical Technique Precision TraXis Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Spacer The Art & Science of Spine Surgery Table of Contents Introduction 3 Indications 4 Key Instruments 5 Surgical Technique
Surgical Technique Precision TraXis Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Spacer The Art & Science of Spine Surgery Table of Contents Introduction 3 Indications 4 Key Instruments 5 Surgical Technique
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With lumbar spinal stenosis
 Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Decompression for Spinal (701126) (Formerly Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression for Spinal ) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/17 Next Review Date:
Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Decompression for Spinal (701126) (Formerly Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression for Spinal ) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/17 Next Review Date:
1. Introduction: 3. Surgical Procedures. 2. Indications. 3.a. Surgical Instruments. 3.b. Patient Positioning. 3.c. Surgical Technique
 1. Introduction: Luiz Pimenta M.D., Larry T. Khoo M.D. ANTERIOR MICROENDOSCOPIC DISCECTOMY AND FUSION FOR THE CERVICAL SPINE Minimally invasive spine surgery by means of an endoscopic technique has gained
1. Introduction: Luiz Pimenta M.D., Larry T. Khoo M.D. ANTERIOR MICROENDOSCOPIC DISCECTOMY AND FUSION FOR THE CERVICAL SPINE Minimally invasive spine surgery by means of an endoscopic technique has gained
Akihito Minamide, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Wakayama Medical University, Wakayama, JAPAN
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUES/DECISION -MAKING IN CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Cervico-Thoracic Junction Pathology Radiculopathy Akihito Minamide, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Wakayama Medical University,
SURGICAL TECHNIQUES/DECISION -MAKING IN CERVICAL SPINE SURGERY: Cervico-Thoracic Junction Pathology Radiculopathy Akihito Minamide, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Wakayama Medical University,
T.L.I.F. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
 T.L.I.F. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cover Surgical Header Technique Sub Guide header Introduction (T.L.I.F. ) technique has gained wide acceptance Additionally, the T.L.I.F. procedure avoids
T.L.I.F. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Cover Surgical Header Technique Sub Guide header Introduction (T.L.I.F. ) technique has gained wide acceptance Additionally, the T.L.I.F. procedure avoids
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
The rise of minimally invasive techniques
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E S Minimally Invasive Foraminotomy of the Cervical Spine: Improving Technique and Expanding Indications Laura A. Snyder, MD Justin C. Clark, MD Luis M. Tumialán, MD The minimally
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E S Minimally Invasive Foraminotomy of the Cervical Spine: Improving Technique and Expanding Indications Laura A. Snyder, MD Justin C. Clark, MD Luis M. Tumialán, MD The minimally
Populations Interventions Comparators Outcomes Individuals: With lumbar spinal stenosis
 Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Decompression for Spinal (701126) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/18 Next Review Date: 07/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 07/13, 07/14, 07/15,
Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Decompression for Spinal (701126) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 10/01/18 Next Review Date: 07/19 Preauthorization No Review Dates: 09/10, 07/11, 07/12, 07/13, 07/14, 07/15,
Technique Guide. ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty.
 Technique Guide ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Table of Contents Introduction Overview 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications and Contraindications 5 Product Information
Technique Guide ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Table of Contents Introduction Overview 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications and Contraindications 5 Product Information
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
1105 two (2) vertebrae... 1, add on per additional vertebra
 SPINE STAGE OPERATIONS Staged operations shall be paid at 100% for the first stage and 85% for the second stage. Where the second stage pays a higher fee 100% shall be paid and the first stage shall be
SPINE STAGE OPERATIONS Staged operations shall be paid at 100% for the first stage and 85% for the second stage. Where the second stage pays a higher fee 100% shall be paid and the first stage shall be
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE MANUAL. InterFuse T
 1 CONTENTS InterFuse T Product Description 3 Indications for Use 3 X-Ray Marker Locations 4 Product Specifications 4 Instrument Set 5 Step 1 Preoperative Planning 8 Patient Positioning 8 Step 2 Disc Removal
1 CONTENTS InterFuse T Product Description 3 Indications for Use 3 X-Ray Marker Locations 4 Product Specifications 4 Instrument Set 5 Step 1 Preoperative Planning 8 Patient Positioning 8 Step 2 Disc Removal
Current Spine Procedures
 SPINE BOOT CAMP: WHAT YOU DON T KNOW MAY COST YOU! David Abraham, M.D. The Reading Neck and Spine Center Reading, PA Current Spine Procedures Epidural/Transforaminal Injections Lumbar Procedures Laminectomy
SPINE BOOT CAMP: WHAT YOU DON T KNOW MAY COST YOU! David Abraham, M.D. The Reading Neck and Spine Center Reading, PA Current Spine Procedures Epidural/Transforaminal Injections Lumbar Procedures Laminectomy
5. COMMON APPROACHES. Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2.
 5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
5. COMMON APPROACHES Each of the described approaches is also demonstrated on supplementary videos, please see Appendix 2. 5.1. LATERAL SUPRAORBITAL APPROACH The most common craniotomy approach used in
ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty.
 ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
ARCH Laminoplasty System. Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
Compression of the lumbar nerve roots and subsequent leg
 INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE Lumbar Decompression Using a Tubular Retractor System Sapan D. Gandhi, BS,* Christopher K. Kepler, MD, MBA,w and D. Greg Anderson, MDw Summary: Spinal stenosis and intervertebral
INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE Lumbar Decompression Using a Tubular Retractor System Sapan D. Gandhi, BS,* Christopher K. Kepler, MD, MBA,w and D. Greg Anderson, MDw Summary: Spinal stenosis and intervertebral
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS
 LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
LUMBAR SPINAL STENOSIS Always occurs in the mobile segment. Factors play role in Stenosis Pre existing congenital or developmental narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal Translation of one anatomic segment
THORACOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF SPINE TUMORS
 1. Introduction: THORACOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF SPINE TUMORS 3. Surgical Procedures: 81 Endoscopic surgical techniques are used in many disciplines after its first usage in gastroenterological interventions.
1. Introduction: THORACOSCOPIC MANAGEMENT OF SPINE TUMORS 3. Surgical Procedures: 81 Endoscopic surgical techniques are used in many disciplines after its first usage in gastroenterological interventions.
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF INCIDENTAL DURAL TEARS IN MICROENDOSCOPIC LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY: INCIDENCE AND OUTCOMES
 A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF INCIDENTAL DURAL TEARS IN MICROENDOSCOPIC LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY: INCIDENCE AND OUTCOMES Takahiro Tsutsumimoto, Mutsuki Yui, Masashi Uehara, Hiroki Ohba, Hiroshi Ohta, Hidemi
A PROSPECTIVE STUDY OF INCIDENTAL DURAL TEARS IN MICROENDOSCOPIC LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION SURGERY: INCIDENCE AND OUTCOMES Takahiro Tsutsumimoto, Mutsuki Yui, Masashi Uehara, Hiroki Ohba, Hiroshi Ohta, Hidemi
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
NewBridge. Laminoplasty Fixation INTERNATIONAL EDITION
 NewBridge L A M I N O P L A S T Y F I X A T I O N S Y S T E M Laminoplasty Fixation INTERNATIONAL EDITION Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 2 PRE-OPERATIVE 3 OPERATIVE 10 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 12 PART NUMBERS
NewBridge L A M I N O P L A S T Y F I X A T I O N S Y S T E M Laminoplasty Fixation INTERNATIONAL EDITION Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 2 PRE-OPERATIVE 3 OPERATIVE 10 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE 12 PART NUMBERS
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
MEDICAL HISTORY CHIRO PHYSICAL
 Overview of Spinal Injection Procedures Blake A. Johnson, MD, FACR 1 PATIENT MANAGEMENT EVALUATION TREATMENT P.T. MEDICAL CHIRO S SURGICAL Effective treatment requires a precise diagnosis! HISTORY PHYSICAL
Overview of Spinal Injection Procedures Blake A. Johnson, MD, FACR 1 PATIENT MANAGEMENT EVALUATION TREATMENT P.T. MEDICAL CHIRO S SURGICAL Effective treatment requires a precise diagnosis! HISTORY PHYSICAL
mild Devices Kit - Instructions for Use
 INDICATION FOR USE The Vertos mild Devices are specialized surgical instruments intended to be used to perform lumbar decompressive procedures for the treatment of various spinal conditions. CONTENTS AND
INDICATION FOR USE The Vertos mild Devices are specialized surgical instruments intended to be used to perform lumbar decompressive procedures for the treatment of various spinal conditions. CONTENTS AND
Initial Clinical Outcomes of Percutaneous Full- Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Using an Interlaminar Approach at the L4-L5
 Pain Physician 2017; 20:E507-E512 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Initial Clinical Outcomes of Percutaneous Full- Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Using an Interlaminar Approach at the L4-L5 Jun-ichiro
Pain Physician 2017; 20:E507-E512 ISSN 2150-1149 Retrospective Evaluation Initial Clinical Outcomes of Percutaneous Full- Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy Using an Interlaminar Approach at the L4-L5 Jun-ichiro
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: axial_lumbosacral_interbody_fusion 6/2009 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Axial Lumbosacral Interbody Fusion File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: axial_lumbosacral_interbody_fusion 6/2009 10/2017 10/2018 10/2017 Description
Codes for Back and Spinal Procedures
 20930 Allograft for spine surgery only; morselized 20931 Allograft for spine surgery only; structural 20936 Autograft for spine surgery only (includes harvesting the graft); local (eg, ribs, spinous process,
20930 Allograft for spine surgery only; morselized 20931 Allograft for spine surgery only; structural 20936 Autograft for spine surgery only (includes harvesting the graft); local (eg, ribs, spinous process,
Adult - Cerebrovascular. Adult - Cranio-Cervical Junction. Adult - Epilepsy. Adult - Hydrocephalus
 list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
22110 vertebral segment; cervical vertebral segment; thoracic vertebral segment; lumbar
 The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
PROCEDURES WE PERFORM
 PROCEDURES WE PERFORM Decompression, Stabilization, and More North American Spine offers a family of advanced, minimally invasive procedures that are highly effective in treating most forms of chronic
PROCEDURES WE PERFORM Decompression, Stabilization, and More North American Spine offers a family of advanced, minimally invasive procedures that are highly effective in treating most forms of chronic
VTI INTERFUSE T SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FORWARD THINKING FOR THE BACK. 1/20
 VTI INTERFUSE T SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FORWARD THINKING FOR THE BACK. 1/20 CONTENTS InterFuse T Product Description Indications for Use X-Ray Marker Locations Product Specifications Instrument Set 3 4 5 STEP
VTI INTERFUSE T SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FORWARD THINKING FOR THE BACK. 1/20 CONTENTS InterFuse T Product Description Indications for Use X-Ray Marker Locations Product Specifications Instrument Set 3 4 5 STEP
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine...2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion. An introduction to
 An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
An introduction to ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion This booklet provides general information on ACDF. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
This procedure lacks scientific evidence of effectiveness, and is not covered.
 ARBenefits Approval: 09-21-2011 Effective Date: 01-01-2012 Revision Date: Code(s): 0275T Medical Policy Title: Minimally Invasive, Image-Guided Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Document: ARB0186
ARBenefits Approval: 09-21-2011 Effective Date: 01-01-2012 Revision Date: Code(s): 0275T Medical Policy Title: Minimally Invasive, Image-Guided Lumbar Decompression for Spinal Stenosis Document: ARB0186
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
O PE RATIV E TE C HN IQ U E. ProView. Expandable Retractor System U.S. EDITION
 O PE RATIV E TE C HN IQ U E ProView M I N I M A L A C C E S S P O R TA L ( M A P ) S Y S T E M Expandable Retractor System U.S. EDITION Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 9 PART NUMBERS
O PE RATIV E TE C HN IQ U E ProView M I N I M A L A C C E S S P O R TA L ( M A P ) S Y S T E M Expandable Retractor System U.S. EDITION Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION 2 OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE 9 PART NUMBERS
Uncosectomy Facilitated Cervical Foraminotomy using a new high-speed shielded curved device
 Uncosectomy Facilitated Cervical Foraminotomy using a new high-speed shielded curved device Pierre Bernard, M.D. (1), Michal Tepper, Ph.D. (2), Ely Ashkenazi, M.D. (3) (1) Centre Aquitain du Dos, Hôpital
Uncosectomy Facilitated Cervical Foraminotomy using a new high-speed shielded curved device Pierre Bernard, M.D. (1), Michal Tepper, Ph.D. (2), Ely Ashkenazi, M.D. (3) (1) Centre Aquitain du Dos, Hôpital
VERTEBRIS cervical Full-endoscopic Spinal Instrumentation. Vertebris
 VERTEBRIS cervical Full-endoscopic Spinal Instrumentation Vertebris 2 VERTEBRIS cervical, full-endoscopic techniques Table of contents Vertebris VERTEBRIS cervical 4 Introduction 4 The full-endoscopic
VERTEBRIS cervical Full-endoscopic Spinal Instrumentation Vertebris 2 VERTEBRIS cervical, full-endoscopic techniques Table of contents Vertebris VERTEBRIS cervical 4 Introduction 4 The full-endoscopic
ARCH Laminoplasty System
 Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty ARCH Laminoplasty System Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Dedicated System for Open-door Laminoplasty ARCH Laminoplasty System Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Technique Guide. Insight Retractor. Minimal invasive access system to the posterior thoracolumbar spine.
 Technique Guide Insight Retractor. Minimal invasive access system to the posterior thoracolumbar spine. Table of Contents Introduction Insight Retractor 2 AO Principles 4 Indications and Contraindications
Technique Guide Insight Retractor. Minimal invasive access system to the posterior thoracolumbar spine. Table of Contents Introduction Insight Retractor 2 AO Principles 4 Indications and Contraindications
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: Page 1 of 11
 Page 1 of 11 Content Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Clinical Indications Lumbar Spine Surgery Lumbar Spine Surgery Description Indication Coding Lumbar Spinal Fusion (single level)surgery
Page 1 of 11 Content Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination Clinical Indications Lumbar Spine Surgery Lumbar Spine Surgery Description Indication Coding Lumbar Spinal Fusion (single level)surgery
CSF. Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System
 Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
Cerebrospinal Fluid(CSF) System By the end of the lecture, students must be able to describe Physiological Anatomy of CSF Compartments Composition Formation Circulation Reabsorption CSF Pressure Functions
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
VTI INTERFUSE S SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FORWARD THINKING FOR THE BACK.
 VTI INTERFUSE S SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FORWARD THINKING FOR THE BACK. CONTENTS InterFuse S Product Description Indications for Use X-Ray Marker Locations and Product Specifications Instrument Set 3 4 5-7 STEP
VTI INTERFUSE S SURGICAL TECHNIQUE FORWARD THINKING FOR THE BACK. CONTENTS InterFuse S Product Description Indications for Use X-Ray Marker Locations and Product Specifications Instrument Set 3 4 5-7 STEP
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
PARADIGM SPINE. Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion. Interlaminar Stabilization
 PARADIGM SPINE Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Interlaminar Stabilization 2 A UNIQUE MIS ALTERNATIVE TO PEDICLE SCREW FIXATION The Gold Standard The combined use of surgical decompression and different
PARADIGM SPINE Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion Interlaminar Stabilization 2 A UNIQUE MIS ALTERNATIVE TO PEDICLE SCREW FIXATION The Gold Standard The combined use of surgical decompression and different
Synovial cyst of spinal facet
 Case report CHUN C. KAO, M.D., STEFAN S. WINKLER, M.D., AND J. H. TURNER, M.D. Sections of Neurosurgery, Radiology, and Pathology, Madison Veterans Administration Hospital, and University of Wisconsin,
Case report CHUN C. KAO, M.D., STEFAN S. WINKLER, M.D., AND J. H. TURNER, M.D. Sections of Neurosurgery, Radiology, and Pathology, Madison Veterans Administration Hospital, and University of Wisconsin,
PARADIGM SPINE. Brochure. coflex-f Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion
 PARADIGM SPINE Brochure coflex-f Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion coflex-f THE UNIQUE, MINIMALLY INVASIVE FUSION DEVICE The coflex-f implant is designed to deliver surgeon confidence and patient satisfaction.
PARADIGM SPINE Brochure coflex-f Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion coflex-f THE UNIQUE, MINIMALLY INVASIVE FUSION DEVICE The coflex-f implant is designed to deliver surgeon confidence and patient satisfaction.
Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh. Razi kittaneh. Maher hadidi
 1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
1 Yara saddam & Dana Qatawneh Razi kittaneh Maher hadidi LECTURE 10 THORAX The thorax extends from the root of the neck to the abdomen. The thorax has a Thoracic wall Thoracic cavity and it is divided
LUMBAR POSTERIOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE SYSTEM. Surgical Technique
 LUMBAR POSTERIOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE SYSTEM Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med M.U.S.T. Mini Open Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale
LUMBAR POSTERIOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE SYSTEM Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med M.U.S.T. Mini Open Surgical Technique Joint Spine Sports Med CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale
Surgical Privileges Form: "Neurosurgery" Clinical Privileges Request. Requested (To be completed by the applicant) Not Recommended (For committee use)
 Surgical Form: Clinical Request "Neurosurgery" Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. the applicant) CATEGORY I: Core : 1. Interpretation of
Surgical Form: Clinical Request "Neurosurgery" Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. the applicant) CATEGORY I: Core : 1. Interpretation of
ISPUB.COM. Lumbar Sympathectomy by Laser Technique. S Kantha, B Kantha METHODS AND MATERIALS
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Minimally Invasive Spinal Technology Volume 1 Number 2 Lumbar Sympathectomy by Laser Technique S Kantha, B Kantha Citation S Kantha, B Kantha. Lumbar Sympathectomy by
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Minimally Invasive Spinal Technology Volume 1 Number 2 Lumbar Sympathectomy by Laser Technique S Kantha, B Kantha Citation S Kantha, B Kantha. Lumbar Sympathectomy by
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Central Region Clinical Claim Edit
 Subject: Laminotomy (Hemilaminectomy) with Decompression of Nerve Root(s), Including Partial Facetectomy, Foraminotomy and/or Excision of Herniated Intervertebral Disc, Reexploration, Single Interspace-Lumbar
Subject: Laminotomy (Hemilaminectomy) with Decompression of Nerve Root(s), Including Partial Facetectomy, Foraminotomy and/or Excision of Herniated Intervertebral Disc, Reexploration, Single Interspace-Lumbar
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
5/19/2017. Interspinous Process Fixation with the Minuteman G3. What is the Minuteman G3. How Does it Work?
 Interspinous Process Fixation with the Minuteman G3 LLOYDINE J. JACOBS, MD CASTELLVI SPINE MEETING MAY 13, 2017 What is the Minuteman G3 The world s first spinous process plating system that is: Minimally
Interspinous Process Fixation with the Minuteman G3 LLOYDINE J. JACOBS, MD CASTELLVI SPINE MEETING MAY 13, 2017 What is the Minuteman G3 The world s first spinous process plating system that is: Minimally
Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression (IG-MLD) for Spinal Stenosis. Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.107 Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression (IG-MLD) for Spinal Stenosis Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed
MP 7.01.107 Image-Guided Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression (IG-MLD) for Spinal Stenosis Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12/2013 Original Policy Date 12/2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed
Spinal Interventional Pain Management and Lumbar Spine Surgery
 Spinal Interventional Pain Management and Lumbar Spine Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.024 01/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/22/2014
Spinal Interventional Pain Management and Lumbar Spine Surgery Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.06.024 01/01/2014 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/22/2014
Surgical techniques and procedures for cerebrovascular surgery. Surgery for the AVF at the cranio-cervical junction and high cervical spine
 VS-1 Surgery for the AVF at the cranio-cervical junction and high cervical spine Hiroyuki Kinouchi University of Yamanashi, Department of Neurosurgery Dural AVFs have been recognized as common type of
VS-1 Surgery for the AVF at the cranio-cervical junction and high cervical spine Hiroyuki Kinouchi University of Yamanashi, Department of Neurosurgery Dural AVFs have been recognized as common type of
Traditionally, lumbar stenosis is treated with an
 technical note J Neurosurg Spine 24:602 607, 2016 Percutaneous biportal endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: a technical note and preliminary clinical results Jin Hwa Eum, MD, 1 Dong Hwa
technical note J Neurosurg Spine 24:602 607, 2016 Percutaneous biportal endoscopic decompression for lumbar spinal stenosis: a technical note and preliminary clinical results Jin Hwa Eum, MD, 1 Dong Hwa
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
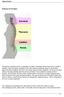 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
Lumbar disc reherniation after transforaminal lumbar endoscopic discectomy
 Original Article Page 1 of 5 Lumbar disc reherniation after transforaminal lumbar endoscopic discectomy Thomas A. Kosztowski, David Choi, Jared Fridley, Michael Galgano, Ziya Gokaslan, Adetokunbo Oyelese,
Original Article Page 1 of 5 Lumbar disc reherniation after transforaminal lumbar endoscopic discectomy Thomas A. Kosztowski, David Choi, Jared Fridley, Michael Galgano, Ziya Gokaslan, Adetokunbo Oyelese,
Index 377 Index A Alajouanine, T. H., 6 Ancient medicine, management of back and leg pain, 1 3 Anesthesia, microendoscopic discectomy, 364, 365 minima
 Index 377 Index A Alajouanine, T. H., 6 Ancient medicine, management of back and leg pain, 1 3 Anesthesia, microendoscopic discectomy, 364, 365 minimally invasive lumbar surgery, 75, 76 percutaneous transpedicular
Index 377 Index A Alajouanine, T. H., 6 Ancient medicine, management of back and leg pain, 1 3 Anesthesia, microendoscopic discectomy, 364, 365 minimally invasive lumbar surgery, 75, 76 percutaneous transpedicular
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF)
 Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Royal Oak IBFD System Surgical Technique Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Preoperative Planning Preoperative planning is necessary for the correct selection of lumbar interbody fusion devices.
Neurosurgical Techniques
 Neurosurgical Techniques Neurosurgical Techniques Laminectomy for the Removal of Spinal Cord Tumors J. GRAFTON LOVE, M.D. Section of Neurologic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota
Neurosurgical Techniques Neurosurgical Techniques Laminectomy for the Removal of Spinal Cord Tumors J. GRAFTON LOVE, M.D. Section of Neurologic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
Thoracoscopic surgical resection of thoracic neurogenic tumors
 Neurosurg Focus 7 (5):Article 1, 1999 Thoracoscopic surgical resection of thoracic neurogenic tumors Patrick P. Han, M.D., and Curtis A. Dickman, M.D. Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological
Neurosurg Focus 7 (5):Article 1, 1999 Thoracoscopic surgical resection of thoracic neurogenic tumors Patrick P. Han, M.D., and Curtis A. Dickman, M.D. Division of Neurological Surgery, Barrow Neurological
Chapter 4 Section 20.1
 Surgery Chapter 4 Section 20.1 Issue Date: August 29, 1985 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(c)(2) and (c)(3) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE CODES 61000-61626, 61680-62264, 62268-62284, 62290-63048, 63055-64484, 64505-64595,
Surgery Chapter 4 Section 20.1 Issue Date: August 29, 1985 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(c)(2) and (c)(3) 1.0 CPT 1 PROCEDURE CODES 61000-61626, 61680-62264, 62268-62284, 62290-63048, 63055-64484, 64505-64595,
EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018
 EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018 Marc J. Levine, MD Rothman Institute Director Spine Surgery Program
EVALUATE, TREAT AND WHEN TO REFER RED FLAGS Mid Atlantic Occupational Regional Conference and Environmental Medicine October 6, 2018 Marc J. Levine, MD Rothman Institute Director Spine Surgery Program
Chapter 4 Section 20.1
 Surgery Chapter 4 Section 20.1 Issue Date: August 29, 1985 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(c)(2) and (c)(3) Copyright: CPT only 2006 American Medical Association (or such other date of publication of CPT). All
Surgery Chapter 4 Section 20.1 Issue Date: August 29, 1985 Authority: 32 CFR 199.4(c)(2) and (c)(3) Copyright: CPT only 2006 American Medical Association (or such other date of publication of CPT). All
M.I.S. MAKE IT SMART IN ONE SYSTEM. Surgical Technique. Hip Knee Spine Navigation
 M.I.S. MAKE IT SMART IN ONE SYSTEM Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation M.U.S.T. Mini Open Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation 2 C O N T E N T S 1 INTRODUCTION 4 2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5
M.I.S. MAKE IT SMART IN ONE SYSTEM Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation M.U.S.T. Mini Open Surgical Technique Hip Knee Spine Navigation 2 C O N T E N T S 1 INTRODUCTION 4 2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE 5
REFERENCE DOCTOR Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Transforaminal / Interlaminar. Hyeun Sung Kim, MD, PhD,
 Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Transforaminal / Interlaminar Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean
Percutaneous Endoscopic Discectomy Transforaminal / Interlaminar Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean
How I do it: percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for lumbar disk herniation
 Acta Neurochirurgica (2018) 160:2473 2477 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3723-5 HOW I DO IT - SPINE DEGENERATIVE How I do it: percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for lumbar disk herniation
Acta Neurochirurgica (2018) 160:2473 2477 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3723-5 HOW I DO IT - SPINE DEGENERATIVE How I do it: percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy for lumbar disk herniation
Procedure Coding Made Simple Five principles will help you capture appropriate charges for spine surgeries.
 Coding/Billing By Kim Pollock, MS, RN, MBA, CPC Procedure Coding Made Simple Five principles will help you capture appropriate charges for spine surgeries. It seems like coding spine cases is as complicated
Coding/Billing By Kim Pollock, MS, RN, MBA, CPC Procedure Coding Made Simple Five principles will help you capture appropriate charges for spine surgeries. It seems like coding spine cases is as complicated
Visualization of Sacral Nerve Roots via Percutaneous Intraspinal Navigation (PIN) V
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2420 2424, October 2005 Technical Note Visualization of Sacral Nerve Roots via Percutaneous Intraspinal Navigation (PIN) V Takuya Fujimoto, Brian P. Giles, Robert E. Replogle,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2420 2424, October 2005 Technical Note Visualization of Sacral Nerve Roots via Percutaneous Intraspinal Navigation (PIN) V Takuya Fujimoto, Brian P. Giles, Robert E. Replogle,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,900 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
A Patient s Guide to Cervical Foraminotomy
 A Patient s Guide to Cervical Foraminotomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Cervical Foraminotomy 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Shoulder Subacromial Decompression. 15 CPT & Coding Issues for Orthopedic & Spine ASC Facilities. 15 CPT & Coding Issues for Orthopedics and Spine
 Orthopedics and Spine 12th Annual Orthopedic, Spine & Pain Management- Driven ASC The Future of Spine Conference by Becker s ASC Review & Becker s Spine Review Speaker Stephanie Ellis, R.N., CPC Ellis
Orthopedics and Spine 12th Annual Orthopedic, Spine & Pain Management- Driven ASC The Future of Spine Conference by Becker s ASC Review & Becker s Spine Review Speaker Stephanie Ellis, R.N., CPC Ellis
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
L8 Spine System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Add: No.1-8, Tianshan Road, Xinbei District, Changzhou, Jiangsu, China
 Add: No.-8, Tianshan Road, Xinbei District, Changzhou, Jiangsu, China 23022 Tel: 0086 59 8595556 Fax: 0086 59 859555 Http://www.kanghui.com Add: F25, Shanghai International Pharmaceutical Trad & Exhibition
Add: No.-8, Tianshan Road, Xinbei District, Changzhou, Jiangsu, China 23022 Tel: 0086 59 8595556 Fax: 0086 59 859555 Http://www.kanghui.com Add: F25, Shanghai International Pharmaceutical Trad & Exhibition
 The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION
 AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
AN INTRODUCTION TO PCF POSTERIOR CERVICAL FUSION This booklet provides general information on the Posterior Cervical Fusion (PCF) surgical procedure for you to discuss with your physician. It is not meant
Microendoscope-assisted posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a technical note
 Original Study Microendoscope-assisted posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a technical note Hirohiko Inanami 1, Fumiko Saiki 1, Yasushi Oshima 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inanami Spine and Joint
Original Study Microendoscope-assisted posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a technical note Hirohiko Inanami 1, Fumiko Saiki 1, Yasushi Oshima 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inanami Spine and Joint
