Preliminary data on microrna expression profiles in a group of South African patients diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukaemia
|
|
|
- Jayson Hunt
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 386 Preliminary data on microrna expression profiles in a group of South African patients diagnosed with chronic myeloid leukaemia ANDREA PRINSLOO 1, ROGER POOL 1 and CHANTAL VAN NIEKERK 2 Departments of 1 Haematology and 2 Chemical Pathology, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Pretoria and Tshwane Academic Division of The National Health Laboratory Service, Pretoria, Gauteng, South Africa Received November 18, 2016; Accepted March 15, 2017 DOI: /mco Abstract. Micro ribonucleic acids (mirnas) are small functional non coding RNAs that downregulate gene expression at the post transcriptional level. Abnormal expression of specific mirnas has been recorded in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, other non Hodgkin B cell lymphomas, lung cancer and chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML). The aim of this study was to compare mirna expression profiles among patients with newly diagnosed CML, those on established therapy with imatinib mesylate, and healthy individuals. The expression of 88 mirnas was evaluated in a total of nine samples divided into three groups: Group 1 comprised three samples collected from newly diagnosed CML patients; group 2 consisted of three samples collected from patients on therapy; the remaining three samples were collected from healthy volunteers (control group). Total RNA was extracted from whole blood and reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT qpcr) was performed on the LightCycler 480 platform using Human Serum & Plasma mirna PCR Arrays. In group 1, only SNORD44 was downregulated, while hsa mir 372 and hsa mir 375 were found to be significantly upregulated compared with the control group. By contrast, 49 mirnas were significantly upregulated in group 2 compared with the control group. mirnas hsa mir 106b, hsa mir 21, hsa mir 221, hsa mir 10a, hsa mir 193a 5p and hsa mir 30e were expressed in group 2. Therefore, mirna expression profiles differed between the two patient groups. Correspondence to: Mrs. Andrea Prinsloo, Department of Haematology, Faculty of Health Sciences, University of Pretoria and Tshwane Academic Division of The National Health Laboratory Service, 5 Bophelo Road, Prinshof Campus, Private Bag X323, Arcadia, Pretoria 0007, Gauteng, South Africa E mail: andrea.prinsloo@up.ac.za Abbreviations: BCR, breakpoint cluster region; CCyR, complete cytogenetic response; CML, chronic myeloid leukaemia; mirna, microrna; RNA, ribonucleic acid; RT qpcr, reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction; WCC, white cell count Key words: chronic, expression, leukaemia, microrna, myeloid Introduction Chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) is an acquired disease resulting from the malignant transformation of a single stem cell, characterized by anaemia extreme blood granulocytosis and granulocytic immaturity (1). CML is triggered by a reciprocal translocation of the long arms of chromosomes 9 and 22, referred to as the Philadelphia chromosome (2). The breakpoint cluster region (BCR) gene on chromosome 22 and the Abelson murine leukaemia viral oncogene homolog 1 (ABL1) gene on chromosome 9 are involved in this t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation leading to the formation of a new chimeric fusion oncogene, BCR ABL1. Expression of this fusion oncogene produces an abnormal, elongated 8 kb ribonucleic acid (RNA) fragment, which is translated into a unique tyrosine phosphoprotein kinase, considered to be essential for the development of the leukaemic phenotype (1,3). Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec ; Novartis, Basel, Switzerland) has been established as the standard first line therapy for CML (4,5). Response to therapy is defined as optimal, suboptimal, or failure of treatment. Optimal response is defined as follows: Complete haematological response [normal full blood count, minimal cytogenetic response (CyR) at 3 months]; partial cytogenetic response at 6 months; complete CyR (CCyR) at 12 months and major molecular response ( 3 log reduction in BCR ABL1 transcripts) at 18 months (6). MicroRNAs (mirnas) have recently been identified as a class of small functional non coding RNAs of nucleotides (7,8) which bind to the 3' untranslated region of mrnas, downregulating gene expression at the post transcriptional level. Recent research suggests that mirnas may play an important role in the pathology of haematological malignancies (9). mirnas are found in the genomes of C. elegans, Drosophila, mice, as well as humans, often with highly conserved sequences. However, in mammals, no genomic sequences that are perfectly complementary to known mirnas have yet been identified (10). The mirna stem loop precursor, pre mirna, may be transcribed as part of a longer primary RNA termed pri mirna (11). mirnas play critical roles in cellular processes, including metabolism, apoptosis, differentiation and development (8). mirnas are often found in polycistronic clusters containing an average of 2 3 mirnas. These polycistronic
2 PRINSLOO et al: PRELIMINARY DATA ON mirna EXPRESSION PROFILES IN CML 387 clusters are usually located in fragile regions prone to deletions and other molecular damaging alterations (12). mirnas are expressed in specific haematological cell types with a regulatory function in early haematopoietic differentiation, erythropoiesis, granulopoiesis, megakaryopoiesis and lymphoid development (12). An example was the demonstration of a cluster of mirnas found to be transcribed from an intron of the C13 25 open reading frame locus at 13q31 q32. This polycistron (hsa-mir-17-92) is amplified and overexpressed in different types of B cell lymphoma (12). Lymphogenesis was found to be promoted by hsa-mir in a murine stem cell transplantation model (13). In addition, it was determined that this polycistron is also transcriptionally regulated by c MYC, which may be of great significance, as oncogenic variants of ABL1 are upregulated by c MYC expression; furthermore, c MYC is required and acts synergistically with BCR ABL1, resulting in transformation to CML (12). Gordon et al found hsa-mir 10a, hsa-mir 17/92, hsa-mir 150, hsa-mir 203 and hsa-mir 328 to be the most commonly deregulated mirnas in CML (14). A mirna may function as a tumour suppressor or an oncogene (15). An example of this is hsa-mir 17/92, which has been shown to target BCL2, STAT5 and JAK2 (tumour suppressor), as well as the CDK inhibitor CDKN1A (p21), functioning as an oncogene. This cluster of mirnas also exhibits increased expression in the early chronic phase of CML, but not in blast phase (BP), making it a possible therapeutic target. Downregulation of hsa-mir 328 has also been described as a crucial stage of disease progression to BP (15). The present pilot study was performed to determine the mirna expression profiles in a South African population of CML patients compared with the mirna signature in CML described in the literature. This study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of the University of Pretoria (38/2007). Materials and methods Patients. The expression profiles of 88 mirnas were evaluated in nine blood samples, which consisted of samples from three healthy individuals (control group), three newly diagnosed CML patients (group 1) and three CML patients on imatinib mesylate therapy (group 2). The samples were collected from the Department of Medical Oncology at the Steve Biko Academic Hospital in mirna extraction. Whole blood was collected in PAXgene Blood RNA Tube IVD (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) or EDTA BD Vacutainer (Becton Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) collection tubes. The PAXGene Blood mirna kit (Qiagen) was used to extract total RNA from three samples and the mirneasy Mini kit (Qiagen) was used to extract total RNA from the remaining six samples. Extracted products were analysed to ensure adequate quality and purity using the Agilent Bioanalyser (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Reverse transcriptase quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT qpcr). mirnas were transcribed to cdna using Table I. Reaction mix composition. Reagent description Volume (µl) 2X RT 2 qpcr SYBR Green mastermix 1,275 Diluted first strand reaction (1:10) 100 RNase free H 2 O 1,175 Total volume 2,550 RT, reverse transcriptase; qpcr, quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Table II. RT qpcr cycling conditions. Number Duration Temperature Optic of cycles (sec) ( C) detection Off Off Off On RT, reverse transcriptase; qpcr, quantitative polymerase chain reaction. the RT 2 mirna First Strand kit (Qiagen). RT qpcr was performed on the LightCycler 480 platform (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) using Human Serum mirna PCR Arrays (Qiagen), which contained the mirnas associated with CML in the literature. This was the only array at the time recommended for blood and/or blood products. The RT 2 qpcr SYBR Green master mix (Qiagen) was used to amplify the cdna according to the reaction mixture composition and the cycling conditions listed in Tables I and II. Postamplification a melting curve program was run at 95 C for 1 min, 65 C for 2 min followed by C at 2 C/min (data collection step). Data analysis. The relative quantitation method ΔΔ2Cq (16) was used to analyse and normalise the expression profile data. Raw data were captured on an Excel template and uploaded on the free PCR Array Data Analysis Web Portal ( pcrdataanalysis.sabiosciences.com/pcr/arrayanalysis.php; accessed, 22/01/2015) (Qiagen). A cut off cycle threshold (Ct) value of 35 C was used for mirna expression. This cut off value was recommended in the protocol for data analysis by the supplier of the program used. This program automatically calculated the average Ct, ΔCt, as well as the 2 ΔΔCt. Fold changes were then calculated with a 95% confidence interval. The P value was automatically calculated and translated to fold regulation. This was plotted on a volcano plot combining the P value and the fold regulation expression data from the two groups. All reagents and kit protocols were used according to the manufacturer's guidelines, except for the Human Serum mirna PCR Arrays, where total RNA extracted from whole blood instead of serum or plasma was used.
3 388 Figure 1. Volcano plot representing statistical significant fold regulation data from the control group and group 1. FC, fold change. Results Patient characteristics. The mirna expression profiles of 88 mirnas were analysed in a total of 9 patients divided into three different groups. The white cell count (WCC) of the samples was crucial for determining the amount of whole blood to be used for the mirna extraction protocol. The WCC of the newly diagnosed group ranged from to x10 9 /l (median, x10 9 /l). The WCC of the CML patients on therapy ranged from 5.32 to x10 9 /l (median 33.79x10 9 /l). The age of the study population ranged from 16 to 69 years (median, 33 years). The patient sample consisted of five male and four female individuals, including the age matched control group. Differential mirna expression. Compared with the control group, there was a significant decrease in the number of mirnas expressed in newly diagnosed patients and CML patients receiving therapy. Of the 88 mirnas investigated, 50 (56%) were expressed in the control group, 8/88 (9%) were expressed in the newly diagnosed group and 17/88 (19%) were expressed in the group of patients receiving imatinib mesylate therapy. Volcano plots combining the P value (P<0.01) and the fold regulation expression data of the two groups are shown in Figs. 1 and 2. In group 1, only two mirnas (hsa mir 372 and hsa mir 375) were significantly up regulated compared with the control group. By contrast, 49 mirnas were significantly up regulated in group 2. These results suggest that the expression profiles may differ between the two groups of patients. The mirna expression of the three samples in the group of CML patients on therapy (group 2) was separately analysed to determine whether therapy affects mirna expression (data not shown). Although there was a correlation of mirna expression among samples C2, C7 (not in remission) and C9 (achieved CCyR) (6), it should be noted that a number of mirnas were expressed in sample C9 (in CCyR) and not expressed in the other two samples, including hsa mir 122, hsa mir 150, hsa mir 210 and hsa mir 23a. Of these, only hsa mir 23a and hsa mir 150 were also expressed in the control group. Discussion Complete haematological response, CCyR and major molecular response are currently used as prognostic indicators. The
4 PRINSLOO et al: PRELIMINARY DATA ON mirna EXPRESSION PROFILES IN CML 389 Figure 2. Volcano plot representing statistical significant fold regulation data from the control group and group 2. FC, fold change. RT qpcr used to detect and measure BCR ABL transcript levels is required for this classification (6). A growing body of evidence suggests that mirna expression may be used as a prognostic marker. In a study performed on mirna expression in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL), Calin et al (17) observed a significant association between a group of mirnas and the expression of ZAP 70 and the time between diagnosis and initial treatment. The authors believe that mirna expression may be a valuable addition to existing prognostic markers for CLL (17). Cummins and Velculescu alluded to the possibility of using mirnas as early indicators of cancer initiation or progression (18). Wu et al also concluded that mirnas may be used as prognostic markers in cancer (19). The aim of the present study was to compare mirna expression profiles in patients with newly diagnosed CML, those on therapy with imatinib mesylate, and healthy individuals. The mirna expression data demonstrated that a significant number of mirnas were expressed in the control group compared with the other two groups. Our results were consistent with those of Ramkissoon et al (20), in that no hsa mir155 expression was found in healthy individuals, but was present in both groups of CML patients. One discrepant finding was the expression of hsa mir 223 by the malignant cells isolated by Ramkissoon et al (20). We were unable to identify expression of hsa mir223 in either of the two groups of CML patients, whereas their study only focused on expression of mir 142, mir 155, mir 181 and mir 223 (20). Focusing on the samples from the group of patients on therapy (group 2), samples C2 and C7 were from patients who were not in remission at the time. Sample C9 was from a patient who achieved CCyR at the time the sample was collected. Of note, the patient who provided sample C7 was not responding to therapy at the time the sample was collected. The expression profiles of these three samples suggest that hsa mir 122 and hsa mir210 may be used as possible indicators of response to therapy; however, due to the small sample size, definitive conclusions could not be reached. Jose Eneriz et al investigated the expression profiles of 250 mirnas in 8 CML patients, 3 of whom were considered to be resistant to therapy (4), and they identified 19 mirnas differentially expressed between CML patients responding to therapy and those resistant to imatinib mesylate therapy. They found the following 18 mirnas to be downregulated in CML patients not responding to therapy: hsa mir 7, hsa mir 23a, hsamir 26a, hsa mir 29a, hsa mir 29c, hsa mir 30b, hsamir 30c, hsa mir 100, hsa mir 126#, hsa mir 134, hsa mir 141, hsa mir 183, hsa mir 196b, hsa mir 199a, hsa mir 224, hsa mir 326, hsa mir 422b and hsa mir 520a.
5 390 Only hsa mir 191 was upregulated in CML patients resistant to therapy (4). In contrast, our results showed 49 mirnas to be upregulated compared with the 18 mirnas that were downregulated (4). However, the results of both studies were based on small sample sizes. In addition, although both studies had the same objectives, the methodology differed, making comparison difficult. However, the results of both studies suggest that there is a significant difference in the mirna expression profile patterns between the two groups of CML patients. As the sample size of this pilot study was small, more in depth research on a large scale is required to validate these results. Further research in this field is required to elucidate the possible role of mirna expression as a prognostic marker. Novel mirnas may be identified that may be of value as prognostic markers in CML, which may lead to individualized therapy and improved patient outcome. Acknowledgements The authors are grateful to the National Health Laboratory Service Research Trust Fund for funding this study (Grant004_94200) and would especially like to thank the Department of Medical Microbiology for providing access to essential equipment. References 1. Liesveld JL and Lichtman MA: Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia and related disorders. In: Williams Hematology. Kaushansky K, Lichtman MA, Beutler E, Kipps TJ, Seligsohn U and Prchal JT (eds). Mcraw Hill, New York, pp , Schüler F and Dölken G: Detection and monitoring of minimal residual disease by quantitative real time PCR. Clin Chim Acta 363: , Stenthoft J, Pallisgaard N, Kjeldsen E, Holm MS, Nielsen JL and Hokland P: Kinetics of BCR ABL fusion transcript levels in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with STI571 measured by quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction. Eur J Haematol 67: , San José Enériz E, Román Gómez J, Jiménez Velasco A, Garate L, Martin V, Cordeu L, Vilas Zornoza A, Rodríguez Otero P, Calasanz MJ, Prósper F and Agirre X: MicroRNA expression profiling in imatinib resistant chronic myeloid leukemia patients without clinically significant ABL1 mutations. Mol Cancer 8: 69, Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, Deininger M, Silver RT, Goldman JM, Stone RM, et al: Five year follow up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 355: , Hoffbrand AV and Moss PAH: Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. In: Essential Haematology. Wiley Blackwell, United Kingdom pp196, Yeung ML, Bennasser Y and Jeang KT: mirnas in the biology of cancers and viral infections. Curr Med Chem 14: , Georgantas RW III, Hildreth R, Morisot S, Alder J, Liu CG, Heimfeld S, Calin GA, Croce CM and Civin CI: CD34+ hematopoietic stem progenitor cell microrna expression and function: A circuit diagram of differentiation control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: , Lawrie CH: MicroRNAs and haematology: Small molecules, big function. Br J Haematol 137: , Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP, Khrapko K and Kosik KS: A microrna array reveals extensive regulation of micrornas during brain development. RNA 9: , Miska EA, Alvarez Saavedra E, Townsend M, Yoshii A, Sestan N, Rakic P, Constantine Paton M and Horvitz HR: Microarray analysis of microrna expression in the developing mammalian brain. Genome Biol 5: R68, Venturini L, Battmer K, Castoldi M, Schultheis B, Hochhaus A, Muckenthaler MU, Ganser A, Eder M and Scherr M: Expression of the mir polycistron in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood 109: , He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon Cardo C, Lowe SW, Hannon GJ and Hammond SM: A microrna polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435: , Gordon JE, Wong JJ and Rasko JE: MicroRNAs in myeloid malignancies. Brit J of Haematol 162: , Yeh CH, Moles R and Nicot C: Clinical significance of micrornas in chronic and acute human leukemia. Mol Cancer 15: 37, Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene expression data using real time quantitative PCR and the 2( Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25: , Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, et al: A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 353: , Cummins JM and Velculescu VE: Implications of micro RNA profiling for cancer diagnosis. Oncogene 25: , Wu W, Sun M, Zou GM and Chen J: MicroRNA and cancer: Current status and prospective. Int J Cancer 120: , Ramkissoon SH, Mainwaring LA, Ogasawara Y, Keyvanfar K, McCoy JP Jr, Sloand EM, Kajigaya S and Young NS: Hematopoietic specific microrna expression in human cells. Leuk Res 30: , 2006.
MicroRNAs: the primary cause or a determinant of progression in leukemia?
 MicroRNAs: the primary cause or a determinant of progression in leukemia? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
MicroRNAs: the primary cause or a determinant of progression in leukemia? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1)
 MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML
 Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
CML CML CML. tyrosine kinase inhibitor CML. 22 t(9;22)(q34;q11) chronic myeloid leukemia CML ABL. BCR-ABL c- imatinib mesylate CML CML BCR-ABL
 1 Key Wordschronic myeloid leukemiaimatinib mesylate tyrosine kinase inhibitor chronic myeloid leukemia CML imatinib mesylate CML CML CML CML Ph 10 1 30 50 3 5 CML α IFNα Ph Ph cytogenetic response CRmajor
1 Key Wordschronic myeloid leukemiaimatinib mesylate tyrosine kinase inhibitor chronic myeloid leukemia CML imatinib mesylate CML CML CML CML Ph 10 1 30 50 3 5 CML α IFNα Ph Ph cytogenetic response CRmajor
Molecular Hematopathology Leukemias I. January 14, 2005
 Molecular Hematopathology Leukemias I January 14, 2005 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Diagnosis requires presence of Philadelphia chromosome t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation BCR-ABL is the result BCR on chr
Molecular Hematopathology Leukemias I January 14, 2005 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Diagnosis requires presence of Philadelphia chromosome t(9;22)(q34;q11) translocation BCR-ABL is the result BCR on chr
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array
 MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
Imatinib Mesylate in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Local Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Local Experience PC Bee, MMed*, G G Gan, MRCP*, A Teh, FRCP**, A R Haris, MRCP* *Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Local Experience PC Bee, MMed*, G G Gan, MRCP*, A Teh, FRCP**, A R Haris, MRCP* *Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine,
ONE STEP MULTIPLEX RT-PCR FOR BCRlABL GENE IN MALAY PATIENTS DIAGNOSED AS LEUKAEMIA
 ONE STEP MULTIPLEX RT-PCR FOR BCRlABL GENE IN MALAY PATIENTS DIAGNOSED AS LEUKAEMIA 1Rosline H, 1Majdan R, 1Wan Zaidah A, 1Rapiaah M, 1Selamah G, 2A A Baba, 3D M Donald 1Department of Haematology, 2Department
ONE STEP MULTIPLEX RT-PCR FOR BCRlABL GENE IN MALAY PATIENTS DIAGNOSED AS LEUKAEMIA 1Rosline H, 1Majdan R, 1Wan Zaidah A, 1Rapiaah M, 1Selamah G, 2A A Baba, 3D M Donald 1Department of Haematology, 2Department
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute
 Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute Natural History of CML Accumulation of immature myeloid cells New cytogenetic changes Chronic Phase Accelerated Phase
Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute Natural History of CML Accumulation of immature myeloid cells New cytogenetic changes Chronic Phase Accelerated Phase
Molecular Markers. Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC
 Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Objectives. Morphology and IHC. Flow and Cyto FISH. Testing for Heme Malignancies 3/20/2013
 Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes ~ 4.6 -
 Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
Chapter 4 Cellular Oncogenes - 4.2 ~ 4.6 - Many retroviruses carrying oncogenes have been found in chickens and mice However, attempts undertaken during the 1970s to isolate viruses from most types of
The BCR-ABL1 fusion. Epidemiology. At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine
 At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
THE USE OF WT1-QPCR TO MEASURE AND DETECT MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA. Ava Greco
 THE USE OF WT1-QPCR TO MEASURE AND DETECT MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA Ava Greco REVIEW OF LITERATURE What is Leukemia? Abnormal growth of cells in the blood stream Progresses rapidly
THE USE OF WT1-QPCR TO MEASURE AND DETECT MINIMAL RESIDUAL DISEASE IN ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA Ava Greco REVIEW OF LITERATURE What is Leukemia? Abnormal growth of cells in the blood stream Progresses rapidly
JAK2 V617F analysis. Indication: monitoring of therapy
 JAK2 V617F analysis BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
JAK2 V617F analysis BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
mir-17 in imatinib resistance and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
 JBUON 2013; 18(2): 437-441 ISSN: 1107-0625 www.jbuon.com E-mail: info@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE mir-17 in imatinib resistance and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
JBUON 2013; 18(2): 437-441 ISSN: 1107-0625 www.jbuon.com E-mail: info@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE mir-17 in imatinib resistance and response to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
MPL W515L K mutation
 MPL W515L K mutation BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
MPL W515L K mutation BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
When to change therapy? Andreas Hochhaus Universitätsklinikum Jena, Germany
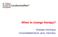 When to change therapy? Andreas Hochhaus Universitätsklinikum Jena, Germany Chromosome 22 Chromosome 9 e1 1b m-bcr M-bcr e1 e2 b1 b5 5 3 BCR ABL 5 3 1a a2 a3 μ -bcr e19 a11 e1a2 b2a2 b3a2 e19a2 p190 bcr-abl
When to change therapy? Andreas Hochhaus Universitätsklinikum Jena, Germany Chromosome 22 Chromosome 9 e1 1b m-bcr M-bcr e1 e2 b1 b5 5 3 BCR ABL 5 3 1a a2 a3 μ -bcr e19 a11 e1a2 b2a2 b3a2 e19a2 p190 bcr-abl
Hematologic and cytogenetic responses of Imatinib Mesylate and significance of Sokal score in chronic myeloid leukemia patients
 ORIGINAL ALBANIAN MEDICAL RESEARCH JOURNAL Hematologic and cytogenetic responses of Imatinib Mesylate and significance of Sokal score in chronic myeloid leukemia patients Dorina Roko 1, Anila Babameto-Laku
ORIGINAL ALBANIAN MEDICAL RESEARCH JOURNAL Hematologic and cytogenetic responses of Imatinib Mesylate and significance of Sokal score in chronic myeloid leukemia patients Dorina Roko 1, Anila Babameto-Laku
MicroRNA-29a Reveals Oncogenic Role on Myeloid Malignancies by Regulating DNMT3A
 MicroRNA-29a Reveals Oncogenic Role on Myeloid Malignancies by Regulating DNMT3A Heba Alkhatabi, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Medical Laboratory Collage of Applied Medical science King Abdul Aziz
MicroRNA-29a Reveals Oncogenic Role on Myeloid Malignancies by Regulating DNMT3A Heba Alkhatabi, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Medical Laboratory Collage of Applied Medical science King Abdul Aziz
Myeloproliferative Disorders - D Savage - 9 Jan 2002
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
 Bioscientia Int. Support Services Dept. Konrad-Adenauer-Strasse 17 55218 Ingelheim Germany Phone 49(0)6132-781-203 49(0)6132-781-224 49(0)6132-781-165 Fax 49(0)6132-781-236 int.support@bioscientia.com
Bioscientia Int. Support Services Dept. Konrad-Adenauer-Strasse 17 55218 Ingelheim Germany Phone 49(0)6132-781-203 49(0)6132-781-224 49(0)6132-781-165 Fax 49(0)6132-781-236 int.support@bioscientia.com
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer. Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee
 MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
MP BCR-ABL1 Testing in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.85 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 10/18/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 8.01.30 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.85 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 10/18/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 8.01.30 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) By DEISSEROTH READ ONLINE
 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) By DEISSEROTH READ ONLINE If searched for the ebook by DEISSEROTH Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) in pdf format, in that case you come on to correct
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) By DEISSEROTH READ ONLINE If searched for the ebook by DEISSEROTH Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) in pdf format, in that case you come on to correct
Leukemia BCR-ABL Fusion Gene Real Time RT-PCR Kit
 Revision No.: ZJ0003 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 Leukemia BCR-ABL Fusion Gene Real Time RT-PCR Kit Cat. No.: TR-0126-02 For use with ABI Prism 7000/7300/7500/7900(96 well); Smart Cycler II; icycler iq 4/iQ
Revision No.: ZJ0003 Issue Date: Aug 7 th, 2008 Leukemia BCR-ABL Fusion Gene Real Time RT-PCR Kit Cat. No.: TR-0126-02 For use with ABI Prism 7000/7300/7500/7900(96 well); Smart Cycler II; icycler iq 4/iQ
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
EVI-1 oncogene expression predicts survival in chronic phase CML patients resistant to imatinib
 EVI-1 oncogene expression predicts survival in chronic phase CML patients resistant to imatinib Mustafa Daghistani Department of Haematology, Imperial College London at Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road,
EVI-1 oncogene expression predicts survival in chronic phase CML patients resistant to imatinib Mustafa Daghistani Department of Haematology, Imperial College London at Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road,
An update on imatinib mesylate therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in a teaching hospital in Malaysia
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(1) : 57 An update on imatinib mesylate therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in a teaching hospital in Malaysia Bee PC 1, MD, MMed, Gan GG 1, MBBS, FRCP, Tai YT 1, MBBS,
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(1) : 57 An update on imatinib mesylate therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in a teaching hospital in Malaysia Bee PC 1, MD, MMed, Gan GG 1, MBBS, FRCP, Tai YT 1, MBBS,
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+)
 Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
"Molecular Monitoring Strategies to Track Response to BCR-ABL Kinase Inhibitors in CML"
 Association of Molecular Pathology USCAP Companion Meeting Sunday, February 12, 2006 7:00 PM Dan Jones, MD, PhD Associate Professor Medical Director, Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory Division of Pathology
Association of Molecular Pathology USCAP Companion Meeting Sunday, February 12, 2006 7:00 PM Dan Jones, MD, PhD Associate Professor Medical Director, Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory Division of Pathology
CML: definition. CML epidemiology. CML diagnosis. CML: peripheralbloodsmear. Cytogenetic abnormality of CML
 MolecularDiagnostic.be Third Scientific Meeting Molecular Diagnostics.be t(9;22) CML: definition Management of CML patients treated with TKI: the place of molecular monitoring Antwerp, December 13 th 11
MolecularDiagnostic.be Third Scientific Meeting Molecular Diagnostics.be t(9;22) CML: definition Management of CML patients treated with TKI: the place of molecular monitoring Antwerp, December 13 th 11
The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Gynecologic Oncology 112 (2009) 55 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Gynecologic Oncology 112 (2009) 55 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients
Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology
 Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body
 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body Jeffrey H Lipton, PhD MD FRCPC Staff Physician, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Professor of Medicine University of Toronto POGO November,
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body Jeffrey H Lipton, PhD MD FRCPC Staff Physician, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Professor of Medicine University of Toronto POGO November,
DETERMINANT VALUE OF THE CYTOGENETIC AND MOLECULAR IMATINIB THERAPEUTIC RESPONSE IN CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
 Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Secţiunea Genetică şi Biologie Moleculară, TOM XIV, 2013 DETERMINANT VALUE OF THE CYTOGENETIC AND MOLECULAR IMATINIB THERAPEUTIC RESPONSE IN CHRONIC
Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Secţiunea Genetică şi Biologie Moleculară, TOM XIV, 2013 DETERMINANT VALUE OF THE CYTOGENETIC AND MOLECULAR IMATINIB THERAPEUTIC RESPONSE IN CHRONIC
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Introduction. Methods Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 BCR/ABL level at 6 months identifies good risk CML subgroup after failing early molecular response at 3 months following imatinib therapy for CML in chronic phase AJH Dennis (Dong Hwan) Kim, 1 * Nada Hamad,
BCR/ABL level at 6 months identifies good risk CML subgroup after failing early molecular response at 3 months following imatinib therapy for CML in chronic phase AJH Dennis (Dong Hwan) Kim, 1 * Nada Hamad,
Expression of Micro-RNA 128 and Let-7b in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cases
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2263 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/05/2018 Acceptance:07/17/2018 Expression of Micro-RNA 128 and Let-7b in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cases
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2263 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/05/2018 Acceptance:07/17/2018 Expression of Micro-RNA 128 and Let-7b in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cases
Cancer and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition
 Cancer and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition 1 Motivation (1) In first world countries cancer is the second most common cause of death after cardiovascular diseases. For most tumors, treatment is limited to surgery,
Cancer and Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition 1 Motivation (1) In first world countries cancer is the second most common cause of death after cardiovascular diseases. For most tumors, treatment is limited to surgery,
Bosulif. Bosulif (bosutinib) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.22 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1,2018 Subject: Bosulif Page: 1 of 5 Last Review
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.22 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1,2018 Subject: Bosulif Page: 1 of 5 Last Review
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
SESSION III: Chronic myeloid leukemia PONATINIB. Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy
 SESSION III: Chronic myeloid leukemia PONATINIB Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy Ponatinib A Pan-BCR-ABL Inhibitor Rationally designed inhibitor of BCR- ABL
SESSION III: Chronic myeloid leukemia PONATINIB Gianantonio Rosti, MD, Department of Hematology, University of Bologna, Italy Ponatinib A Pan-BCR-ABL Inhibitor Rationally designed inhibitor of BCR- ABL
Talpaz M. et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosomepositive leukemias. N Engl J Med (2006) 354;24:
 References Sprycel Talpaz M. et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosomepositive leukemias. N Engl J Med (2006) 354;24:2531-2541. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice
References Sprycel Talpaz M. et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosomepositive leukemias. N Engl J Med (2006) 354;24:2531-2541. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice
Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
 International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
 Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Molecular Response: What is really important? Jeff Szer The Royal Melbourne Hospital PROBABILITY, % PROBABILITY OF SURVIVAL AFTER MYELOABLATIVE TRANSPLANTS FOR CML IN CHRONIC
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Molecular Response: What is really important? Jeff Szer The Royal Melbourne Hospital PROBABILITY, % PROBABILITY OF SURVIVAL AFTER MYELOABLATIVE TRANSPLANTS FOR CML IN CHRONIC
Imatinib Mesylate (Glivec) in Pediatric Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate (Glivec) in Pediatric Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Bahoush Gr, 1 Alebouyeh M, 2 Vossough P 1 1 Pediatric Hematology-Oncology Department, Ali-Asghar Children's Hospital,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate (Glivec) in Pediatric Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Bahoush Gr, 1 Alebouyeh M, 2 Vossough P 1 1 Pediatric Hematology-Oncology Department, Ali-Asghar Children's Hospital,
BCR-ABL1 Kinase Domain Mutation Status (including educational clinical scenario)
 BCR-ABL1 Kinase Domain Mutation Status 171802 (including educational clinical scenario) Issue date: 23rd February 2018 Closing date: 23rd March 2018 Results for the BCR-ABL1 Kinase Domain Mutation Status
BCR-ABL1 Kinase Domain Mutation Status 171802 (including educational clinical scenario) Issue date: 23rd February 2018 Closing date: 23rd March 2018 Results for the BCR-ABL1 Kinase Domain Mutation Status
GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS
 GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS Dra. Margarita Sánchez-Beato Lymphoma Group Molecular Pathology Programme CNIO Agilent Microarray and Sequencing Roadshow,
GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS Dra. Margarita Sánchez-Beato Lymphoma Group Molecular Pathology Programme CNIO Agilent Microarray and Sequencing Roadshow,
Monitor TM assay: comparison with traditional RT-qPCR methods
 Preliminary evaluation of the GeneXpert Dx System for CML patients monitoring through the Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor TM assay: comparison with traditional RT-qPCR methods Silvia Calatroni Division of Hematology
Preliminary evaluation of the GeneXpert Dx System for CML patients monitoring through the Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor TM assay: comparison with traditional RT-qPCR methods Silvia Calatroni Division of Hematology
Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation
 Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction
 www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
The legally binding text is the original French version
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 14 March 2007 SPRYCEL 20 mg, film-coated tablet, blister (377 637-9) SPRYCEL 20 mg, film-coated tablet, bottle (377
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 14 March 2007 SPRYCEL 20 mg, film-coated tablet, blister (377 637-9) SPRYCEL 20 mg, film-coated tablet, bottle (377
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
screening procedures Disease resistant to full-dose imatinib ( 600 mg/day) or intolerant to any dose of imatinib
 Table S1. Study inclusion and exclusion criteria Inclusion criteria Aged 18 years Signed and dated informed consent form prior to protocol-specific screening procedures Cytogenetic- or PCR-based diagnosis
Table S1. Study inclusion and exclusion criteria Inclusion criteria Aged 18 years Signed and dated informed consent form prior to protocol-specific screening procedures Cytogenetic- or PCR-based diagnosis
Methylation status of SOCS1 and SOCS3 in BCR-ABL negative and. JAK2V617F negative chronic myeloproliferative disorders.
 Methylation status of SOCS1 and SOCS3 in BCR-ABL negative and JAK2V617F negative chronic myeloproliferative disorders. To the Editor BCR-ABL negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Disorders (s) are a heterogeneous
Methylation status of SOCS1 and SOCS3 in BCR-ABL negative and JAK2V617F negative chronic myeloproliferative disorders. To the Editor BCR-ABL negative Chronic Myeloproliferative Disorders (s) are a heterogeneous
Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Benjamin Powers, MD; and Suman Kambhampati, MD The dramatic improvement in survival with tyrosine kinase inhibitors has not been demonstrated in the advanced blast
Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Benjamin Powers, MD; and Suman Kambhampati, MD The dramatic improvement in survival with tyrosine kinase inhibitors has not been demonstrated in the advanced blast
KEY WORDS Chronic myelogenous leukemia Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Relapse Imatinib mesylate Minimal residual disease
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:718-725 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1010-0007$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2004.06.033 Early Prediction of
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:718-725 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1010-0007$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2004.06.033 Early Prediction of
IN PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME positive (Ph )
 Targeted Therapies in the Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Dieter Hoelzer, Nicola Gökbuget, and Oliver G. Ottmann Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec, Novartis Pharmaceuticals
Targeted Therapies in the Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Dieter Hoelzer, Nicola Gökbuget, and Oliver G. Ottmann Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec, Novartis Pharmaceuticals
Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 03/10, 03/11, 03/12
 Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous (80130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 03/10, 03/11,
Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous (80130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 03/10, 03/11,
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
35 Current Trends in the
 35 Current Trends in the Management of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Abstract: CML is a hematopoietic stem cell disease which is characterized by the presence of Philadelphia chromosome (Ph-chromosome)
35 Current Trends in the Management of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Abstract: CML is a hematopoietic stem cell disease which is characterized by the presence of Philadelphia chromosome (Ph-chromosome)
Clinical Study Determinants of Overall and Progression-Free Survival of Nigerian Patients with Philadelphia-Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Advances in Hematology Volume 2015, Article ID 908708, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/908708 Clinical Study Determinants of Overall and Progression-Free Survival of Nigerian Patients with Philadelphia-Positive
Advances in Hematology Volume 2015, Article ID 908708, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/908708 Clinical Study Determinants of Overall and Progression-Free Survival of Nigerian Patients with Philadelphia-Positive
RCAN1,, HL60, calcineurin, NFAT
 25 6 3 RCAN1 calcineurin RCAN1 1) 2) calcineurin-nfat RCAN1 RCAN1 RCAN1 is involved in the regulation of cell functions including inhibition of calcineurin. In this study, we found that RCAN1 is extraordinarily
25 6 3 RCAN1 calcineurin RCAN1 1) 2) calcineurin-nfat RCAN1 RCAN1 RCAN1 is involved in the regulation of cell functions including inhibition of calcineurin. In this study, we found that RCAN1 is extraordinarily
Introduction to Cancer
 Introduction to Cancer Clonal Evolution Theory of Tumor Development,2,2,,2,2,,2, Numbers represent sequential mutations to cellular genes Oncogenes and Tumor Suppresser Genes On Oncogenes Tumor Suppresser
Introduction to Cancer Clonal Evolution Theory of Tumor Development,2,2,,2,2,,2, Numbers represent sequential mutations to cellular genes Oncogenes and Tumor Suppresser Genes On Oncogenes Tumor Suppresser
Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MDS/MPN) Post-HCT Data
 Instructions for Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MDS/MPN) Post-HCT Data (Form 2114) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative
Instructions for Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MDS/MPN) Post-HCT Data (Form 2114) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a slowprogressing
 At a Glance Practical Implications p e148 Author Information p e151 Full text and PDF Web exclusive Patterns of Specific Testing for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Original Research Allison
At a Glance Practical Implications p e148 Author Information p e151 Full text and PDF Web exclusive Patterns of Specific Testing for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Original Research Allison
Managing Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Concise Reference Managing Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Timothy P Hughes, David M Ross, Junia V Melo Extracted from Handbook of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Published by Springer Healthcare Ltd, 236 Gray s Inn
Concise Reference Managing Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Timothy P Hughes, David M Ross, Junia V Melo Extracted from Handbook of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Published by Springer Healthcare Ltd, 236 Gray s Inn
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 14 February 2007
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 14 February 2007 GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/120 capsules (CIP: 358 493-5) GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/180 capsules (CIP:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 14 February 2007 GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/120 capsules (CIP: 358 493-5) GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/180 capsules (CIP:
Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA
 Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Cancer Biology 2016;6(1) Imatinib Mesylate Effectiveness in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia patients in Upper Egypt. Mervat M.
 Imatinib Mesylate Effectiveness in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia patients in Upper Egypt Mervat M. Omar Department of Oncology, Assuit University Hospital, Assuit, Egypt drmervatomar@yahoo.com Abstract: Background
Imatinib Mesylate Effectiveness in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia patients in Upper Egypt Mervat M. Omar Department of Oncology, Assuit University Hospital, Assuit, Egypt drmervatomar@yahoo.com Abstract: Background
Haematology Probes for Multiple Myeloma
 Haematology Probes for Multiple Myeloma MULTIPLE MYELOMA Multiple myeloma (MM) is a plasma cell neoplasm, characterised by the accumulation of clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow and by very complex
Haematology Probes for Multiple Myeloma MULTIPLE MYELOMA Multiple myeloma (MM) is a plasma cell neoplasm, characterised by the accumulation of clonal plasma cells in the bone marrow and by very complex
Age Disparity in the Dissemination of Imatinib Mesylate (Gleevec) for Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Age Disparity in the Dissemination of Imatinib Mesylate (Gleevec) for Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Chuck Wiggins, Ph.D. Director and Principal Investigator New Mexico Tumor Registry North American
Age Disparity in the Dissemination of Imatinib Mesylate (Gleevec) for Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Chuck Wiggins, Ph.D. Director and Principal Investigator New Mexico Tumor Registry North American
Original Article. Survival of Patients with CML on Imatinib Experience with 44 Iraqi Patients
 Original Article Survival of Patients with CML on Imatinib Experience with 44 Iraqi Patients Ali M.Jawad * CABM FRCP (Edin) Batool A.G. Yassin** FICM.CM Nabeel Salman*** FRCP (Edin) Ali Al-Ameri**** CABM
Original Article Survival of Patients with CML on Imatinib Experience with 44 Iraqi Patients Ali M.Jawad * CABM FRCP (Edin) Batool A.G. Yassin** FICM.CM Nabeel Salman*** FRCP (Edin) Ali Al-Ameri**** CABM
Response to treatment with imatinib mesylate in previously treated chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients in a hospital in Brazil
 Response to treatment with imatinib mesylate in previously treated chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients in a hospital in Brazil C.A.P. Silveira 1, M.B. Daldegan 1 and I. Ferrari 2 1 Núcleo de
Response to treatment with imatinib mesylate in previously treated chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients in a hospital in Brazil C.A.P. Silveira 1, M.B. Daldegan 1 and I. Ferrari 2 1 Núcleo de
Structure and Function of Fusion Gene Products in. Childhood Acute Leukemia
 Structure and Function of Fusion Gene Products in Childhood Acute Leukemia Chromosomal Translocations Chr. 12 Chr. 21 der(12) der(21) A.T. Look, Science 278 (1997) Distribution Childhood ALL TEL-AML1 t(12;21)
Structure and Function of Fusion Gene Products in Childhood Acute Leukemia Chromosomal Translocations Chr. 12 Chr. 21 der(12) der(21) A.T. Look, Science 278 (1997) Distribution Childhood ALL TEL-AML1 t(12;21)
Tasigna. Tasigna (nilotinib) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Date: March 16, 2018 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
A novel isothermal amplification approach for rapid identification of BCR-ABL fusion genes at onset:
 A novel isothermal amplification approach for rapid identification of BCR-ABL fusion genes at onset: Josh Glason: Sales Manager, DiaSorin Australia Pty Ltd September 6, 2014 This product is not currently
A novel isothermal amplification approach for rapid identification of BCR-ABL fusion genes at onset: Josh Glason: Sales Manager, DiaSorin Australia Pty Ltd September 6, 2014 This product is not currently
Tasigna. Tasigna (nilotinib) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.77 Subject: Tasigna Page: 1of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2017 Tasigna Description Tasigna (nilotinib)
Inhibition of the Growth of Raji Cells by Precursor MicroRNA-15a
 22 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2010) 7: 22-26 DOI 10.1007/s11805-010-0022-1 Inhibition of the Growth of Raji Cells by Precursor MicroRNA-15a Dong-mei HE Qin CHEN Institute of Hematology, Medical College of
22 Clin Oncol Cancer Res (2010) 7: 22-26 DOI 10.1007/s11805-010-0022-1 Inhibition of the Growth of Raji Cells by Precursor MicroRNA-15a Dong-mei HE Qin CHEN Institute of Hematology, Medical College of
STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells
 CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Suresh Alahari Editor. MicroRNA in Cancer
 MicroRNA in Cancer Suresh Alahari Editor MicroRNA in Cancer 1 3 Editor Suresh Alahari Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center LSU Health Science center New Orleans,
MicroRNA in Cancer Suresh Alahari Editor MicroRNA in Cancer 1 3 Editor Suresh Alahari Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Stanley S. Scott Cancer Center LSU Health Science center New Orleans,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Molecular Diagnosis. Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology
 Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Objectives Describe uses of NAT in Oncology Diagnosis, Prediction, monitoring. Genetics Screening, presymptomatic testing, diagnostic testing,
Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Objectives Describe uses of NAT in Oncology Diagnosis, Prediction, monitoring. Genetics Screening, presymptomatic testing, diagnostic testing,
Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology. Molecular Diagnosis. Gain/Loss of Nucleic Acid. Objectives. MYCN and Neuroblastoma. Molecular Diagnosis
 Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Gross alterations in DNA content of tumors (ploidy) Gain/Loss of nucleic acids Markers of Clonality Oncogene/Tumor
Nucleic Acid Testing - Oncology Molecular Diagnosis Nucleic acid based testing in Oncology Gross alterations in DNA content of tumors (ploidy) Gain/Loss of nucleic acids Markers of Clonality Oncogene/Tumor
Activation of cellular proto-oncogenes to oncogenes. How was active Ras identified?
 Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
Dominant Acting Oncogenes Eugene E. Marcantonio, M.D. Ph.D. Oncogenes are altered forms of normal cellular genes called proto-oncogenes that are involved in pathways regulating cell growth, differentiation,
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019
 Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019 Disclosures Richard A. Larson, MD Research funding to the University
Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019 Disclosures Richard A. Larson, MD Research funding to the University
An Initiative to Equip Health-System Pharmacists to Select and Manage Drug Therapy for the Disease
 An Initiative to Equip Health-System Pharmacists to Select and Manage Drug Therapy for the Disease What Health-System Pharmacists Should Know About CML Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML, also known as
An Initiative to Equip Health-System Pharmacists to Select and Manage Drug Therapy for the Disease What Health-System Pharmacists Should Know About CML Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML, also known as
Protein kinase C expression is deregulated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
 Protein kinase C expression is deregulated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Kabir, Nuzhat N.; Rönnstrand, Lars; Kazi, Julhash U. Published in: Leukemia & Lymphoma DOI: 10.3109/10428194.2013.769220 2013
Protein kinase C expression is deregulated in chronic lymphocytic leukemia Kabir, Nuzhat N.; Rönnstrand, Lars; Kazi, Julhash U. Published in: Leukemia & Lymphoma DOI: 10.3109/10428194.2013.769220 2013
