Oligoelements Se, Zn, Mn Plus Lachesis Muta as Radioprotectors of Normal Tissues and Radiosensitizers of Malignant Cells
|
|
|
- Lilian McBride
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oligoelements Se, Zn, Mn Plus Lachesis Muta as Radioprotectors of Normal Tissues and Radiosensitizers of Malignant Cells E.J. Crescenti (1), E.S. Rivera (2), M. Croci (1), V. Medina (2), G. Cricco (2), N. Mohamad (2), G. Martín (2), M. Núñez (2), R. M. Bergoc (2) (1) Immunooncology Institute, 3 Cordoba Av., 1187 Buenos Aires, ARGENTINA. (2) Radioisotopes Laboratory, School of Pharmacy and Biochemistry, Buenos Aires University, 956 Junin St., 1113 Buenos Aires, ARGENTINA. rmbergoc@arnet.com.ar / rmbergoc@ffyb.uba.ar Abstract. The in vitro effect of on radiosensitivity of different human cell lines and the in vivo tolerance to high doses of ionizing radiation induced by the combination of Se, Zn and Mn plus Lachesis muta () was evaluated. Sprague-Dawley rats received whole-body irradiation with a single dose (2 to 15 Gy) employing a 137 Cs source of 189 TBq (7.7 Gy/min). A half of rats received daily sc starting 1 days before irradiation. These animals receiving 8, 1, and 12 Gy showed significantly higher survival versus controls (p<.1,.3 and.83, respectively). 3 LD 5 value for treated rats was 9.6 Gy vs. 5.8 Gy for controls (p<.1). The protective effect of was also in vivo evaluated on small intestine and bone marrow of nude mice irradiated with a single whole-body dose of 1 Gy. Mice were sacrificed 5 days after irradiation. Mice receiving sc daily starting 9 days before irradiation, showed better villous and crypts conservation, lack of oedema and vascular damage in comparison to controls. Bone marrows of treated animals showed grade I-II aplasia instead of grade III aplasia in control ones. For in vitro studies, MDA-231 cells (human breast carcinoma) and HBL- (normal mammary epithelium) were irradiated with -1 Gy employing the same source. Cell cultures were treated with for 24 hs previous and up to 24 hs post-irradiation. Number of colonies over 5 cells where counted after 1 days. Cell surviving curves indicated that produced a significant decrease (p<.1) in survival of transformed cells while no difference was observed in normal HBL-. These results demonstrated a protective effect on normal tissues exerted by for in vivo high doses of ionizing irradiation and a significant increase in radiosensitivity on the transformed MDA-231 cells but not in normal HBL- cells. 1. Introduction. Ionizing radiation, alone or in combination with other therapies, is one of the most used anticancer treatments. It is well know that hematopoyetic toxicity and immune suppression are one of the major problems after irradiation of patients [1]. Injury resulting from the irradiation of biological tissue by ionizing radiation is a consequence of the transfer of radiation energy to critical macromolecules. The initial chemical injury can occur directly by the absorption of radiation or indirectly through the action of free radicals [2]. On the tissue, since water is so abundant, the contribution of free radicals to radiation damage is quite important [2, 3, 4]. Early investigations demonstrate that one of the most important modifiers of radiation damage in biological systems is the oxygen [4]; the oxygen enhances the indirect effect of radiation damage and prevents the repair of damaged molecules by fixing the radiation lesions [2, 3, 4]. More recent experiments indicate that reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in the action of ionizing radiation [5]. Superoxide dismutases (SODs) and gluthatione peroxidase (GPx), are free radical scavenging enzymes that defend cells from oxidant stress. The superoxide (SO 2 ) and the hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) generated post-irradiation are detoxified by GPxs and SODs. MnSOD (mitochondrial) and CuZnSOD (cytoplasmatic), were reported to be involved in protecting cell against radiation injury [6]. The radioprotective agents appear related to free radicals in competition with oxygen or with increased repair of radiation injury. On the contrary, radiosensitizers are chemical agents that have the capacity to increase the lethal effects of radiation. The development of drugs that radiosensitize the malignant cell and radioprotect the normal tissues, is yet a challenge for oncologists and radiobiologists. In previous studies we demonstrated the protective effect of the combination of Selenium (Se), Zinc (Zn), Manganese (Mn) plus Lachesis muta () against carcinogenic drugs and high doses of chemotherapy [7, 8]. This treatment is also applied to
2 human patients with colon cancer with liver metastases [9], with breast cancer [1], or with pancreatic carcinoma [11], producing in all cases a significant increase in survival rates. In the present study we evaluated in vivo the tolerance induced by to high doses of ionizing radiation and the in vitro effect of on radiosensitivity of malignant and normal human cell lines. 2. Materials and Methods Source. In all studies, a 137 Cs source of 189 TBq (7.7 Gy/min) calibrated by Argentine National Commission of Atomic Energy with a TLD 7 dosimeter and validated by Argentine Nuclear Regulatory Authority was employed treatment. In all studies the medication employed () was a combination of the oligoelements Zn, Se, and Mn (4µg/ml each) plus Lachesis muta (4ng/ml) In vivo studies Rats. Ninety-six male Sprague-Dawley rats received whole-body irradiation with a single dose ranging from 2 to 15 Gray. The half of animals (48, divided in 8 rats per group) received daily.5 ml of via sc ( group) starting 1 days before irradiation; the treatment continued for 7 days; the other 48 rats were injected daily with placebo. Each group received a single dose of 2, 5, 8, 1, 12 or 15 Gy, respectively. Parameters recorded on these studies were: Survival, 3 DL 5 value, Observation of collateral macroscopic effect and body weight determination, Histopathology of organs as liver, spleen, kidney, lung, heart Nude mice. To evaluate the possible protective capability of, nude mice were utilized. The nude mice were employed in order to carry further experiments with transplanted human tumours in these mice. Twenty mice were randomly separated in two groups and small intestine and bone marrow were processed post-irradiation to evaluate the histopathological changes. Group 1,, irradiated receiving sc daily placebo, and Group 2, irradiated receiving.2 ml sc daily treatment starting 9 days before irradiation. All mice received a single whole-body dose of 1 Gy and were sacrificed 5 days after irradiation. Parameters analyzed in these studies were: Number of intestinal crypt, Villous edema, Ulceration, Vascular damage, Bone marrow aplasia. The small-intestine specimens were pinned flat on corkboard and immediately fixed. Haematoxylin- Eosin (H.E.) stained sections were examined for mucosae highness and crypt number per circumference evaluation. Histological and cytological condition of intestinal villi was carefully
3 evaluated. Nuclear changes (anisocariosis, macronuclei, picnosis), anisocytosis, cell ballooning, interstitial edema, mucosae exulceration and vascular damage signs were registered and compared in both groups In vitro studies Cell survival fraction. MDA-231 cells (human breast carcinoma) and HBL- (normal mammary epithelium) were cultured in RPMI 164 medium (Gibco BRL, Grand Island Biological Co, NY) supplemented with 1% of calf serum (Gibco BRL), glutamine,3 g/l (Sigma Co, Saint Louis, USA) and gentamicine,4 mg/l. To carry on radiosensitivity studies 33 cells were seeded in plastic flasks and after 24 hrs were irradiated with doses ranging from to 1 Gy. Eight days post irradiation the clonogenic proliferation was evaluated by counting the colonies containing 5 cells or more. Colonies were fixed with 1 % buffered saline-formaline solution and stained with Toluidine Blue (T.B.). For cell treatment,.2 ml of per ml of culture medium was added to flasks immediately after plating and continued up to 24 hrs post irradiation. The parameters analyzed were: Survival curve, and Radiosensivity parameters (alpha, beta, alpha/beta, survival fraction at 2 Gy and Doses that reduce survival fraction at.1. Survival curves were graphed and adjusted to the Linear-quadratic mathematical model [3] employing the GraphPrism program. 3. Results and Discussion In vivo results Rats Survival. The results obtained indicate that animals receiving 8, 1, and 12 Gy (figure 1a, 1b and 1c, respectively) presented significantly higher survival versus controls (p<.1,.3 and.83, respectively, longrank test). Global survival of treated rats, also showed a significantly higher value vs (p<.5, logrank test) (figure1d) Determination of 3 DL 5 value. 3 LD 5 value for treated rats was 9.6 Gy vs. 5.8 Gy for control (p<.1, two way ANOVA). These values clearly indicate a protective action of in treated animals (figure 2) Collateral effects and Body weight determination. No collateral effect was seen in rats treated with and irradiated with 2 or 5 Gy. The figure 3 clearly illustrate that rats receiving and irradiated with 2 Gy show a recovery of body weight significantly higher than control (p<.1, two way ANOVA test).
4 Survival(%) 8 Gy 4 a Days post-irradiation Survival(%) 1 Gy 4 b Days Days after post-irradiation Survival(%) 4 12 Gy c Days post-irradiation Survival(%) 4 GLOBAL SURVIVAL d Days post-irradiation FIG 1. Survival of rats ( treated vs ) whole body irradiated with different Dose. Dead rats (%) 1 4 = 5.8 Gy = 9.6 Gy Whole Body Dose FIG 2. 3 LD 5 value of vs. rats.
5 1.25 Relative Body Weight Days post-irradiation FIG 3. Relative Body weight of rats treated vs., irradiated with 2 Gy Histopathology of organs. Anatomopathological alterations involving bone marrow, kidney and liver were found. Histopathological studies indicated that % of the rats presented severe spleen atrophy specially of lymphoid related structures but also the sinusoidal sectors were affected. All the animals presented severe bone marrow aplasia usually grade III in the control groups, instead the treated animal showed mainly Grade II or Grade I-II bone marrow aplasia. Acute renal tubular necrosis was seen in some cases and cellular hepatic lesions were also evident Nude mice. Organic manifestations of the radiation damage were scarce; only an important loss of lymphoid tissue of the spleen, ballooning and macronuclei in hepatocytes and slight irritative tubular renal lesions were seen. Some degree of vascular damage may surely be present but the short time between irradiation and the termination of the experiment may be responsible of the scarce histological findings in the studied organs. The intestinal mucosae of mice of group 1, (irradiated with 1 Gy) showed severe degenerative changes characterized by decreased villous height, reduction of crypt number, villous edema, ulceration, vascular damage, anisocariosis and cytoplasmic alterations. In contrast, the mucosae of animals of group 2, irradiated with 1 Gy and receiving daily, showed higher number of crypts, better villous conservation, lack of edema and of vascular damage and showed less nuclear and cytoplasmic alterations (Table I).
6 Table 1. Comparative histopathological changes observed in control and treated mice. Autopsy results Small bowel mucosal trophism Average N of crypts/,5 cm Mucosal exulceration Nuclear and cytoplasmic changes Villous edema Vascular damage Marked atrophy 75 Severe Anisocariosis, anisocitosis Present Present Moderate atrophy 137 Mild Mild anisocariosis (conservation of Panneth cells) Absent Absent The markedly alteration on intestinal mucosae of nude mice irradiated with 1 Gy can be seen. On the contrary, mice receiving treatment show conservation of the normal number of crypts and intestinal villi (figure 4). A B C D FIG 4. A) Normal looking intestinal mucosae of control non irradiated nude mice (H.E. X). B) Markedly altered intestinal mucosae of 1 Gy irradiated nude mice, reduced number of crypts, disorganization of the remaining villi, edema and loss of entire sectors of columnar epithelium can be seen (H.E. X). C) 1 Gy irradiated pretreated nude mice showing conservation of crypts and villi. Only slight edema and scarce epithelium loss can be seen. (H.E. X). D) 1 Gy irradiated pretreated mice showing some grade of anisocitosis and anisocariosis of the mucosal cells (HE X).
7 A B C D FIG 5. A) Normal bone marrow of a non-irradiated nude mice (H.E. X). B) Grade III (total) medullar aplasia in a 1 Gy irradiated nude mice (H.E. X). C) Bone marrow of a 1 Gy irradiated pretreated nude mice showing partial conservation of medullar cell lines and also partial hemorrhagic replacement of the lost elements; grade I-II aplasia (H.E. X). D) Bone marrow of a 1 Gy irradiated pretreated nude mice with partial conservation of granulocitic, megacariocitic and eritroblastic cell lines (H.E. 4X). Also, important differences were observed on bone marrow of mice versus ones (figure 5) In vitro results Cell survival fraction Survival curves obtained with the human cell lines indicate that MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma cells are moderately radiosensitive according to the calculated parameters (Table II). The treatment with O- LM significantly increased cell radiosensitivity decreasing the survival fraction at 2 Gy from.25±.7 in controls to.14±.3 in treated cells (p<.1 ANOVA). On the contrary in the HBL- normal cells the treatment with did not modified the calculated parameters and the survival fraction, in coincidence with the results obtained in vivo that showed a protective effect of in normal tissue (figure 6).
8 MDA-MB-231 HBL- Survival fraction Survival fraction Dose (Gy) Dose (Gy) FIG 6. Survival curves obtained with the human cell lines MDA-MB-231 and HBL-, treated and non-treated with Radiobiological parameters Table II. Radiobiological Parameters Cell line α (Gy -1 ) β (Gy -2 ) α/β (Gy) SF 2Gy SF 2Gy () Dose,1 (Gy) MDA-MB ±.8.± ±.7.14±.3 a 5.2±.8 HBL-.5±.1.16± ±.11.53±.1 5.±.1 Table II. MDA-231 and HBL- cells irradiated with 1 Gy. a p<.1 irradiated and treated with O- LM vs. irradiated control. 4. Conclusions. The present studies demonstrated a protective effect on normal tissues exerted by for in vivo high doses of ionizing radiation. In addition, produced a significant increase in radiosensitivity only on the transformed MDA-MB-231 cells but not on normal HBL- cells. Experiments carried out in our laboratory clearly show that the treatment with modulates MnSOD activity as well as superoxide and hydrogen peroxide intracellular levels. This effect may represent the basis of the mechanism responsible for the selective protection against ionizing radiation. The ability of radioprotectores to produce their effect is a result of their capacity to inhibit indirect damage, to repair direct or indirect effects when occur, and to facilitate the recovery of damaged cells or depleted cell population. In that sense it was evident the protective effect of treatment on
9 normal medullar cell in both rats and mice. In histopathological studies a lower grade of medullar aplasia was observed in treated animals; in the intestinal mucosae of treated mice the loss of crypts and normal intestinal villi was markedly lower than in control animals. These findings prove the protective effect on two highly radiosensitive normal tissues. Based on these results we propose that may be considered a potentially clinical useful radioprotectant with the possibility of applying this protective treatment to human patients undergoing radiotherapy. 5. References. 1. Betzen, S. M., Overgaard, J. Clinical manifestations of normal tissue damage, in Basic Clinical Radiobiology, edited by G.Gordon Steel, London, Boston, Sydney, Auckland, (1995). 2. Dendy, P. P., Heaton, B. Physics for Radiologists, Blackwell, Oxford, (1988). 3. Tubiana M., Dutreix, J., Wambersei, A. Introduction to radiobiology. Taylor & Francis. London, New York, Philadelphia, (199) 4. Steel, J. J. Basic Clinical Radiobiology for radiation oncologists. Arnold. New York, (1995). 5. Holahan, E. V. Factors that affect cellular radiosensitivity, in Military Radiobiology, edited by J. J. Conklin, Academic Press Inc., New York, (1987). 6. Sun, J., Chen, Y., Li, M., Ge, Z. Role of antioxidant enzymes on ionizing radiation resistance. Free Radic. Biol. Med., 24: , (1998). 7. Crescenti, E., Croci, M., Bergoc, R., Rivera, E. Enhanced tolerance to high doses of Ionizing radiation or chemotherapy by oligoelements plus phospholipase A2, in Proceedings of the 17 th International Cancer Congress UICC, Rio de Janeiro, 1998, edited by Moraes,M, Brentani, R., Bevilaqua, R. (Monduzzi Editore, Bologna, 1998), p Crescenti, E. J., Croci, M., Rivera, E., Bergoc, R. M. Enhanced tolerance to high cytostatic doses by means of oligoelements Mn, Se, and Zn plus Lachesis muta venom. J Trace Elem in Exp Med, 16:39-53 (3). 9. Crescenti, E., Croci, M., Cantarella, J., Crescenti, E. A2 phospholipase and trace elements (Zn, Se, and Mn) applied to the treatment of 291 patients with liver metastases of colon adenocarcinoma, 21 cases of them with no other therapy. First International Meeteng on Advanced of Cancer Management, Vienna, Austria, vol 1, (1987), pg Crescenti, E., Croci, M., Pereyra, G., Cantarella, J. A2 phospholipase and oligoelements Zn, Se, and Mn in breast cancer treatment: 186 cases, 7 year s follow-up, in Proceedings of the 17 th International Cancer Congress UICC, Rio de Janeiro, 1998, edited by Moraes,M, Brentani, R., Bevilaqua, R. (Monduzzi Editore, Bologna, 1998), p Crescenti, E., Alegre, E., Croci, M. Novel treatment for advanced pancreatic cancer: 73 patientes, 1 years follow-up. Int. J. Cancer, S13:245,(2).
Radiosensitivity of Human Melanoma Cell Lines
 Radiosensitivity of Human Melanoma Cell Lines R. M. Bergoc (1), V. Medina (1), G. Cricco (1), N. Mohamad (1), G. Martín (1), M. Núñez (1), M. Croci (2), E.J. Crescenti (2), E.S. Rivera (1). (1) Radioisotopes
Radiosensitivity of Human Melanoma Cell Lines R. M. Bergoc (1), V. Medina (1), G. Cricco (1), N. Mohamad (1), G. Martín (1), M. Núñez (1), M. Croci (2), E.J. Crescenti (2), E.S. Rivera (1). (1) Radioisotopes
Radioprotection of Sensitive Rat Tissues by Oligoelements Se, Zn, Mn Plus Lachesis Muta Venom
 J. Radiat. Res., 52, 557 567 (2011) Regular Paper Radioprotection of Sensitive Rat Tissues by Oligoelements Se, Zn, Mn Plus Lachesis Muta Venom Ernesto JV CRESCENTI 1, Vanina A MEDINA 2, Máximo CROCI 1,
J. Radiat. Res., 52, 557 567 (2011) Regular Paper Radioprotection of Sensitive Rat Tissues by Oligoelements Se, Zn, Mn Plus Lachesis Muta Venom Ernesto JV CRESCENTI 1, Vanina A MEDINA 2, Máximo CROCI 1,
Histamine Protects Bone Marrow against Cellullar Damage induced by Ionizing Radiation
 Histamine Protects Bone Marrow against Cellullar Damage induced by Ionizing Radiation Vanina Medina *1,3, Maximo Croci 2, Ernesto Crescenti 2, Lorena Sambuco 1, Noelia Massari 1, Graciela Cricco 1, Gabriela
Histamine Protects Bone Marrow against Cellullar Damage induced by Ionizing Radiation Vanina Medina *1,3, Maximo Croci 2, Ernesto Crescenti 2, Lorena Sambuco 1, Noelia Massari 1, Graciela Cricco 1, Gabriela
KEYWORDS: Ionizing radiation, Irradiation, Immunity, Lymphocyte, Cytokine
 Deleterious effect on immunity produced by ionizing radiation; protective effect of a novel therapeutic formulation composed by Zn, Se and Mn plus Lachesis Muta venom (O-LM) E. J. Crescenti 1, G. Cremaschi
Deleterious effect on immunity produced by ionizing radiation; protective effect of a novel therapeutic formulation composed by Zn, Se and Mn plus Lachesis Muta venom (O-LM) E. J. Crescenti 1, G. Cremaschi
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall
 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 1 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 2 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 3 UNC-Duke Biology Course for Residents Fall 2018 4 UNC-Duke
Non-classical radiobiology relevant to high-doses per fraction
 Non-classical radiobiology relevant to high-doses per fraction Michael Joiner Wayne State University Radiation Oncology Detroit, Michigan joinerm@wayne.edu Why reconsider high dose fractions? Because we
Non-classical radiobiology relevant to high-doses per fraction Michael Joiner Wayne State University Radiation Oncology Detroit, Michigan joinerm@wayne.edu Why reconsider high dose fractions? Because we
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview. Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga
 Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
Therapeutic ratio - An Overview Past Present Future Prof Ramesh S Bilimaga Radiation Oncology Discipline of human medicine concerned with the generation, conservation and dissemination of knowledge concerning
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS
 10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
10-2 densely ionizing radiation CHAPTER TWO MECHANISMS OF RADIATION EFFECTS 2.0 INTRODUCTION Cell survival curves describe the relationship between the fractional survival, S, of a population of radiated
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs. Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica
 Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
Radiobiology of fractionated treatments: the classical approach and the 4 Rs Vischioni Barbara MD, PhD Centro Nazionale Adroterapia Oncologica Radiobiology It is fundamental in radiation oncology Radiobiology
María José Mesa López
 María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
María José Mesa López q Radiobiology. q Ionizing Radiations. q Mutations. q Stochastic Effects Vs Deterministic Effects. q Cellular Radiosensitivity. q Bibliography. Science which combines the basic principles
Radiobiology of high dose per fraction
 Radiobiology of high dose per fraction Michael Joiner Wayne State University Radiation Oncology Detroit, Michigan joinerm@wayne.edu AAPM 2014 Historically Research focused on clinically relevant doses
Radiobiology of high dose per fraction Michael Joiner Wayne State University Radiation Oncology Detroit, Michigan joinerm@wayne.edu AAPM 2014 Historically Research focused on clinically relevant doses
Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
Radiation and Radioisotope Applications EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031 Biological Effects of Radiation Lecture 09 Rafael Macian 23.11.06 EPFL Doctoral Course PY-031: Radioisotope and Radiation Applications
Ionizing Radiation. Nuclear Medicine
 Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
Ionizing Radiation Nuclear Medicine Somatic Deterministic Effect Erythema Somatic Stochastic Effect Leukemia Genetic Effects DNA BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF IONIZING RADIATION ON TISSUES, ORGANS AND SYSTEMS
PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY
 PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY Ravi Pachigolla, MD Faculty Advisor: Anna Pou, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2000 HISTORY
PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION ONCOLOGY Ravi Pachigolla, MD Faculty Advisor: Anna Pou, MD The University of Texas Medical Branch Department of Otolaryngology Grand Rounds Presentation January 5, 2000 HISTORY
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE
 COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
COMPARISON OF RADIOBIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF CARBON IONS TO PROTONS ON A RESISTANT HUMAN MELANOMA CELL LINE I. Petrovi a, A. Risti -Fira a, L. Kori anac a, J. Požega a, F. Di Rosa b, P. Cirrone b and G. Cuttone
Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration between LNS INFN and Vinca Institute of Nuclear Sciences
 ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
ENSAR2 Midterm Meeting of Networking Activity 5: MediNet March 12 th 14 th, 218 Vinča Institute of Nuclear sciences, University of Belgrade Hadrons on Malignant Cells: Recent Activities within Collaboration
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[rivera, Elena Susana] On: 29 November 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 787665161] Publisher: Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered
This article was downloaded by:[rivera, Elena Susana] On: 29 November 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 787665161] Publisher: Informa Healthcare Informa Ltd Registered in England and Wales Registered
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof. Dr. Dürdane Kolankaya**
 The possible protective effects of some flavonoids that found honey by experimental ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced nitrosative damage in kidney of male rats Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof.
The possible protective effects of some flavonoids that found honey by experimental ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) induced nitrosative damage in kidney of male rats Assoc. Prof. Dr. Aslı Korkmaz* and Prof.
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation.
 Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
Radiation Therapy Use of radiation to kill diseased cells. Cancer is the disease that is almost always treated when using radiation. One person in three will develop some form of cancer in their lifetime.
Radiation Damage Comparison between Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy (IMRT) and Field-in-field (FIF) Technique In Breast Cancer Treatments
 Radiation Damage Comparison between Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy () and Field-in-field (FIF) Technique In Breast Cancer Treatments Huisi Ai 1 and Hualin Zhang 2 1. Department of Radiation Oncology,
Radiation Damage Comparison between Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy () and Field-in-field (FIF) Technique In Breast Cancer Treatments Huisi Ai 1 and Hualin Zhang 2 1. Department of Radiation Oncology,
Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit
 Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2525 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H₂O₂ in a variety
Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2525 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H₂O₂ in a variety
Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter
 Ohio UNIVERSITY Fall 2018 Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter Alan Watts Radiation Safety Officer In This Issue: Instruction Concerning Risks From Occupational Radiation Exposure... pg.1-5 = Required = Optional
Ohio UNIVERSITY Fall 2018 Lab & Rad Safety Newsletter Alan Watts Radiation Safety Officer In This Issue: Instruction Concerning Risks From Occupational Radiation Exposure... pg.1-5 = Required = Optional
Antioxidant Products
 Antioxidant Products Introduction Introduction Antioxidant Total Antioxidant Status (TAS) Ransel Ransod Glutathione Reductase Antioxidants help defend living organisms against free radical attack. Many
Antioxidant Products Introduction Introduction Antioxidant Total Antioxidant Status (TAS) Ransel Ransod Glutathione Reductase Antioxidants help defend living organisms against free radical attack. Many
HDF Case Whipple s disease
 HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
HDF Case 952556 Whipple s disease 63 yo female complaining of a diarrhea for 2 months, weigth loss (12 Kg in 3 months), and joint pains. Duodenal biopsy performed. Scanning view, enlarged intestinal villi,
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA
 LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
LET, RBE and Damage to DNA Linear Energy Transfer (LET) When is stopping power not equal to LET? Stopping power (-de/dx) gives the energy lost by a charged particle in a medium. LET gives the energy absorbed
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage
 Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK
 Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Norges teknisk-naturvitenskaplige universitet Institutt for fysikk EKSAMENSOPPGÅVER med løysingsforslag Examination papers with solution proposals TFY4315 STRÅLINGSBIOFYSIKK Biophysics of Ionizing Radiation
Chemical Modification of Radiation Response
 Chemical Modification of Radiation Response Oxygen Oxygen best known and most general radiosensitizer The slopes of survival curves for cells exposed to sparsely ionizing radiation in hypoxia and in well
Chemical Modification of Radiation Response Oxygen Oxygen best known and most general radiosensitizer The slopes of survival curves for cells exposed to sparsely ionizing radiation in hypoxia and in well
CONTENTS NOTE TO THE READER...1 LIST OF PARTICIPANTS...3
 CONTENTS NOTE TO THE READER...1 LIST OF PARTICIPANTS...3 PREAMBLE...9 Background...9 Objective and Scope...9 Selection of Topics for Monographs...10 Data for Monographs...11 The Working Group...11 Working
CONTENTS NOTE TO THE READER...1 LIST OF PARTICIPANTS...3 PREAMBLE...9 Background...9 Objective and Scope...9 Selection of Topics for Monographs...10 Data for Monographs...11 The Working Group...11 Working
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (CLINICAL ONCOLOGY) PART I EXAMINATION - AUGUST Time : p.m p.m.
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (CLINICAL ONCOLOGY) PART I EXAMINATION - AUGUST 2015 Date :- 24 th August 2015 PAPER I Time :- 2.00 p.m. - 4.15 p.m. If the examiners cannot
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO MP (CLINICAL ONCOLOGY) PART I EXAMINATION - AUGUST 2015 Date :- 24 th August 2015 PAPER I Time :- 2.00 p.m. - 4.15 p.m. If the examiners cannot
By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1)
 BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF TURMERIC ON BREAST CANCER OF RATS By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1) 1) Biochemistry Div. Chemistry Dep. Faculty
BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF TURMERIC ON BREAST CANCER OF RATS By Soha Mohamed Hamdy (1),Abdelkarim Mohamed Abdellatif (2) and Rania Mortada Mahmuod (1) 1) Biochemistry Div. Chemistry Dep. Faculty
Chapter 7. What is Radiation Biology? Ionizing Radiation. Energy Transfer Determinants 09/21/2014
 Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
Chapter 7 Molecular & Cellular Radiation Biology What is Radiation Biology? A branch of biology concerned with how ionizing radiation effects living systems. Biological damage that occurs from different
ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko ; IIZUKA, Hajime
 Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
Journal of Dermatology (2011) 38(5):515-517. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor-producing squamous cell carcinoma of the skin ITO, Yasuhiro ; FUJII, Mizue ; SHIBUYA, Takashi ; UEHARA, Jiro ; SATO, Katsuhiko
INFLUENCE OF MELATONIN ON ARSENIC MEDIATED PANCREATIC DAMAGE IN SWISS ALBINO MICE
 INFLUENCE OF MELATONIN ON ARSENIC MEDIATED PANCREATIC DAMAGE IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DIMPLE DAMORE Bhavan s Sheth R.A.College of Science, Gujarat University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India INTRODUCTION Arsenic
INFLUENCE OF MELATONIN ON ARSENIC MEDIATED PANCREATIC DAMAGE IN SWISS ALBINO MICE DIMPLE DAMORE Bhavan s Sheth R.A.College of Science, Gujarat University, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India INTRODUCTION Arsenic
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2009)
 PROTECTIVE ROLE OF ALOE VERA AGAINST RADIATION AND CADMIUM INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE LIVER OF SWISS ALBINO MICE R.K.Purohit, Seema Tak, Aruna Chakrawarti and K.M.Bhartiya Radiation Biology
PROTECTIVE ROLE OF ALOE VERA AGAINST RADIATION AND CADMIUM INDUCED HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN THE LIVER OF SWISS ALBINO MICE R.K.Purohit, Seema Tak, Aruna Chakrawarti and K.M.Bhartiya Radiation Biology
Radiobiology and bioeffect-models CRISTER CEBERG
 Radiobiology and bioeffect-models CRISTER CEBERG Radiobiology» Molecular and cellular level» Stochastic effects Hereditary effects Cancer» Deterministic effects» Effects on embryo and fetus Radiobiology»
Radiobiology and bioeffect-models CRISTER CEBERG Radiobiology» Molecular and cellular level» Stochastic effects Hereditary effects Cancer» Deterministic effects» Effects on embryo and fetus Radiobiology»
Current Thinking on the Early Effects from Uniform and Non-Uniform Radiation
 Current Thinking on the Early Effects from Uniform and Non-Uniform Radiation Jacqueline Williams, PhD, FASTRO University of Rochester Medical College Casualties from radiation: 1896- Medical errors/overexposures
Current Thinking on the Early Effects from Uniform and Non-Uniform Radiation Jacqueline Williams, PhD, FASTRO University of Rochester Medical College Casualties from radiation: 1896- Medical errors/overexposures
SPECIFIC AIMS PROGRAM IMAGING. V year (1st semester) Scientific Field DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING AND RADIOTHERAPY TUTOR ECTS
 V year (1st semester) Scientific Field DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING AND RADIOTHERAPY TUTOR ECTS SANTONI R. COORDINATOR MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Santoni Riccardo 1 MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Manenti Guglielmo 1 MED/36
V year (1st semester) Scientific Field DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING AND RADIOTHERAPY TUTOR ECTS SANTONI R. COORDINATOR MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Santoni Riccardo 1 MED/36 Diagnostic Imaging Manenti Guglielmo 1 MED/36
Serum Superoxide dismutase activity in thalassemia patients and healthy subjects with new method
 The 5 th International & 10 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Serum Superoxide dismutase activity in thalassemia patients and healthy subjects with new method Elham Ghahramanlu,
The 5 th International & 10 th National Congress on Quality Improvement in Clinical Laboratories Serum Superoxide dismutase activity in thalassemia patients and healthy subjects with new method Elham Ghahramanlu,
Oxidative stress and antioxidative status in patients with alcoholic liver disease
 Biomedical Research 2012; 23 (1): 105-108 Oxidative stress and antioxidative status in patients with alcoholic liver disease Ashok Shinde 1, Jayshree Ganu 2, Pankaja Naik 3, Annasaheb Sawant 4 1 Department
Biomedical Research 2012; 23 (1): 105-108 Oxidative stress and antioxidative status in patients with alcoholic liver disease Ashok Shinde 1, Jayshree Ganu 2, Pankaja Naik 3, Annasaheb Sawant 4 1 Department
BIOASTIN Bioastin is product that contains 4 mg astaxantin and 50 i.e. vitamin E (α-tocopherol) per tabl.. Carotenoids are family of around 700 substa
 INTRODUCTION In 1956 Rebecca Gerchman and Daniel Gilbert detected toxic effect of superoxid on aerobs. Till today there are identificated many free radicals. Their toxic effect is registrated in more than
INTRODUCTION In 1956 Rebecca Gerchman and Daniel Gilbert detected toxic effect of superoxid on aerobs. Till today there are identificated many free radicals. Their toxic effect is registrated in more than
Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit
 Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2552 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H2O2 in
Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2552 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H2O2 in
COX-2 inhibitor and irradiation. Saitama Cancer Center Kunihiko Kobayashi MD, PhD
 COX-2 inhibitor and irradiation Saitama Cancer Center Kunihiko Kobayashi MD, PhD Synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid by cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes JNCI 95:1440, 2003 Difference between
COX-2 inhibitor and irradiation Saitama Cancer Center Kunihiko Kobayashi MD, PhD Synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid by cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes JNCI 95:1440, 2003 Difference between
HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c
 Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
Research Article HEPATIC CELL INJURY BY ETHINYL OESTRADIOL ESTROGEN Pandey Govind a*, Pandey S.P. b and Madhuri S. c a* Ex-Professor & Head of Pharmacology (Pharmacy), presently Officer-In-Charge of Rinder
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Therapeutic Medical Physics. Stephen J. Amadon Jr., Ph.D., DABR
 Therapeutic Medical Physics Stephen J. Amadon Jr., Ph.D., DABR Outline 1. Why physicists are needed in medicine 2. Branches of medical physics 3. Physics in Radiation Oncology 4. Treatment types and Treatment
Therapeutic Medical Physics Stephen J. Amadon Jr., Ph.D., DABR Outline 1. Why physicists are needed in medicine 2. Branches of medical physics 3. Physics in Radiation Oncology 4. Treatment types and Treatment
Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis
 Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology
 Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology This set of 88 slides is based on Chapter 14 authored by N. Suntharalingam, E.B. Podgorsak, J.H. Hendry of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics:
Chapter 14 Basic Radiobiology This set of 88 slides is based on Chapter 14 authored by N. Suntharalingam, E.B. Podgorsak, J.H. Hendry of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics:
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded
 BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
BY Dr. Hany M. Abo-Haded Pediatric Cardiology Unit, Mansoura Universty Children Hospital, Mansoura, Egypt Co-authors: Dina S El-Agamy and Mohamed A Elkablawy Background Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline
Radiation biology. Dr. István Voszka. Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology. Grotthus (1815) - Draper (1845)
 Radiation biology Dr. István Voszka Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen Antoine Henri Becquerel 1845-1923 1852-1908 1895 x-radiation 1896 - radioactivity Grotthus (1815)
Radiation biology Dr. István Voszka Department of Biophysics and Radiation Biology Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen Antoine Henri Becquerel 1845-1923 1852-1908 1895 x-radiation 1896 - radioactivity Grotthus (1815)
A Summary of the studies conducted with CV247
 A Summary of the studies conducted with CV247 Introduction Several epidemiological studies have shown that people deficient in trace elements such as selenium, copper, manganese, and vitamins, mainly C,D
A Summary of the studies conducted with CV247 Introduction Several epidemiological studies have shown that people deficient in trace elements such as selenium, copper, manganese, and vitamins, mainly C,D
Targeted Chemoprevention of Progressive Marrow Failure in Patients with Fanconi Anemia using Quercetin, a Pilot study
 Targeted Chemoprevention of Progressive Marrow Failure in Patients with Fanconi Anemia using Quercetin, a Pilot study Parinda Mehta, M.D. Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Immune Deficiency Cincinnati
Targeted Chemoprevention of Progressive Marrow Failure in Patients with Fanconi Anemia using Quercetin, a Pilot study Parinda Mehta, M.D. Division of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Immune Deficiency Cincinnati
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
Ozone in Complementary Medicine Possible Mechanism of Ozone in Rheumatic and Inflammatory Diseases
 Ozone in Complementary Medicine Possible Mechanism of Ozone in Rheumatic and Inflammatory Diseases 10.11.2004 OZONOSAN 1 Mechanism of Action in Rheumatic Pain Syndroms Acute stage: Activation of cell metabolism,
Ozone in Complementary Medicine Possible Mechanism of Ozone in Rheumatic and Inflammatory Diseases 10.11.2004 OZONOSAN 1 Mechanism of Action in Rheumatic Pain Syndroms Acute stage: Activation of cell metabolism,
PROSPECTS FOR RADIOPROTECTION
 Chapter 11 PROSPECTS FOR RADIOPROTECTION LEO I. GIAMBARRESI, Ph.D.* AND RICHARD I. WALKER, Ph.D.** INTRODUCTION RADIATION INJURY Ionizing Radiation Biological Damage PROTECTION AGAINST RADIATION INJURY
Chapter 11 PROSPECTS FOR RADIOPROTECTION LEO I. GIAMBARRESI, Ph.D.* AND RICHARD I. WALKER, Ph.D.** INTRODUCTION RADIATION INJURY Ionizing Radiation Biological Damage PROTECTION AGAINST RADIATION INJURY
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3
 Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
Molecular Radiobiology Module 4 Part #3 Bushong - Chapter 31 10-526-197 - Rhodes Interaction & damage is a matter of chance Energy deposited rapidly 10-17 seconds Interactions are non-selective in tissue
7/16/2009. An overview of classical radiobiology. Radiobiology and the cell kill paradigm. 1. Repair: Radiation cell killing. Radiation cell killing
 tcp 0.8 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 55 65 75 group 4 7/16/2009 An overview of classical radiobiology 5 or 6 R s of radiobiology and their impacts on treatments R Impact/exploitable effect 35 45 55 1. Repair Fractionation
tcp 0.8 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 55 65 75 group 4 7/16/2009 An overview of classical radiobiology 5 or 6 R s of radiobiology and their impacts on treatments R Impact/exploitable effect 35 45 55 1. Repair Fractionation
Clinical Applications of Brachytherapy Radiobiology. Radiobiology is Essential
 Clinical Applications of Brachytherapy Radiobiology Dr Alexandra Stewart University of Surrey St Luke s Cancer Centre Guildford, England Radiobiology is Essential Knowledge of radiobiological principles
Clinical Applications of Brachytherapy Radiobiology Dr Alexandra Stewart University of Surrey St Luke s Cancer Centre Guildford, England Radiobiology is Essential Knowledge of radiobiological principles
Research Article A Mathematical Model of Tumor Volume Changes during Radiotherapy
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 203, Article ID 8070, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/203/8070 Research Article A Mathematical Model of Tumor Volume Changes during Radiotherapy Ping Wang and Yuanming
The Scientific World Journal Volume 203, Article ID 8070, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/0.55/203/8070 Research Article A Mathematical Model of Tumor Volume Changes during Radiotherapy Ping Wang and Yuanming
ABSTRACT OF Ph.D. THESIS IN VIVO DETECTION OF LIGHT STRESS INDUCED REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES IN PLANTS. Ph.D. Thesis. Csengele Barta
 ABSTRACT OF Ph.D. THESIS IN VIVO DETECTION OF LIGHT STRESS INDUCED REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES IN PLANTS Ph.D. Thesis Csengele Barta Supervisor: Dr. Éva Hideg Biological Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy
ABSTRACT OF Ph.D. THESIS IN VIVO DETECTION OF LIGHT STRESS INDUCED REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES IN PLANTS Ph.D. Thesis Csengele Barta Supervisor: Dr. Éva Hideg Biological Research Centre of the Hungarian Academy
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Clinical Studies supporting the use of Antioxidants during Chemotherapy and Radiation
 Clinical Studies supporting the use of Antioxidants during Chemotherapy and Radiation Poly-MVA ORAC Analysis As you are reading the 5 Clinical Studies below, pay close attention to the list of Antioxidants
Clinical Studies supporting the use of Antioxidants during Chemotherapy and Radiation Poly-MVA ORAC Analysis As you are reading the 5 Clinical Studies below, pay close attention to the list of Antioxidants
In-situ and invasive carcinoma of the colon in patients with ulcerative colitis
 Gut, 1972, 13, 566-570 In-situ and invasive carcinoma of the colon in patients with ulcerative colitis D. J. EVANS AND D. J. POLLOCK From the Departments of Pathology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School
Gut, 1972, 13, 566-570 In-situ and invasive carcinoma of the colon in patients with ulcerative colitis D. J. EVANS AND D. J. POLLOCK From the Departments of Pathology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School
Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine
 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine 0 \ Second Edition BARRY HALLIWELL Professor of Medical Biochemistry, University of London King's College and JOHN M.C. GUTTERIDGE Senior Scientist, National Institute
Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine 0 \ Second Edition BARRY HALLIWELL Professor of Medical Biochemistry, University of London King's College and JOHN M.C. GUTTERIDGE Senior Scientist, National Institute
Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment
 Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment The reactive oxygen species (ROS) are group of very unstable compounds that
Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment The reactive oxygen species (ROS) are group of very unstable compounds that
Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy
 Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Why do patients take herbs and nutritional supplements?
 Why do patients take herbs and nutritional supplements? Dissatisfaction with conventional medicine > Relieve cancer-related symptoms > Treat adverse effects of anticancer drugs > Treat cancer > Promote
Why do patients take herbs and nutritional supplements? Dissatisfaction with conventional medicine > Relieve cancer-related symptoms > Treat adverse effects of anticancer drugs > Treat cancer > Promote
Joint ICTP-IAEA Advanced School on Internal Dosimetry. Trieste, April 2010
 Joint ICTP-IAEA Advanced School on Internal Dosimetry Trieste, 12-16 April 2010 Dosimetry in PRRT: what for Dosimetry has the purpose to address %&!"# '!&!"#!(%)* $ *!$+ Most Used Radiopeptides for PRRT
Joint ICTP-IAEA Advanced School on Internal Dosimetry Trieste, 12-16 April 2010 Dosimetry in PRRT: what for Dosimetry has the purpose to address %&!"# '!&!"#!(%)* $ *!$+ Most Used Radiopeptides for PRRT
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden
 Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence
 Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Supplemental Table 1. Primers used for RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory cytokines Gene Primer Sequence IL-1α Forward primer 5 -CAAGATGGCCAAAGTTCGTGAC-3' Reverse primer 5 -GTCTCATGAAGTGAGCCATAGC-3 IL-1β
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
ICRP = International Commission on. recommendations and guidance on. Functioning since 1928.
 ICRP = International Commission on Radiological Protection; An advisory body providing recommendations and guidance on radiation protection; Functioning since 1928. While the use of ionising radiation
ICRP = International Commission on Radiological Protection; An advisory body providing recommendations and guidance on radiation protection; Functioning since 1928. While the use of ionising radiation
Three-dimensional structure of the human small intestinal mucosa in health and disease
 Gut, 1969, 10, 6-12 Three-dimensional structure of the human small intestinal mucosa in health and disease C. A. LOEHRY AND B. CREAMER From the Gastrointestinal Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London
Gut, 1969, 10, 6-12 Three-dimensional structure of the human small intestinal mucosa in health and disease C. A. LOEHRY AND B. CREAMER From the Gastrointestinal Laboratory, St Thomas' Hospital, London
Radioactivity. Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation
 Radioactivity Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation Studies of impact of ionizing radiation on the human body - Hiroshima - US-Japanese teams medical tests, autopsies, human organ analysis, on-site
Radioactivity Lecture 8 Biological Effects of Radiation Studies of impact of ionizing radiation on the human body - Hiroshima - US-Japanese teams medical tests, autopsies, human organ analysis, on-site
Glycinates Animal Nutrition G-ENL/MT, G-ENL/MP
 Glycinates Animal Nutrition G-ENL/MT, G-ENL/MP Lampertheim, 02.12.2013 1 Introduction 2 Product offer 3 Value 4 Product portfolio 5 Dosage recommendation 6 Backup: - Animal trial data - Packaging and Labelling
Glycinates Animal Nutrition G-ENL/MT, G-ENL/MP Lampertheim, 02.12.2013 1 Introduction 2 Product offer 3 Value 4 Product portfolio 5 Dosage recommendation 6 Backup: - Animal trial data - Packaging and Labelling
VITAMINS, MINERALS AND THE GUT
 VITAMINS, MINERALS AND THE GUT Nutrients Looking at individual nutrients that are involved with gut health can be misleading This is not about taking individual nutrients It supports more a whole food
VITAMINS, MINERALS AND THE GUT Nutrients Looking at individual nutrients that are involved with gut health can be misleading This is not about taking individual nutrients It supports more a whole food
Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for breast cancer: Updated evidence
 2 rd Bangladesh Breast Cancer Conference, Dhaka, December 2017 Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for breast cancer: Updated evidence Tabassum Wadasadawala Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology Tata Memorial
2 rd Bangladesh Breast Cancer Conference, Dhaka, December 2017 Hypofractionated Radiotherapy for breast cancer: Updated evidence Tabassum Wadasadawala Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology Tata Memorial
A263 A352 A204. Pan CK. pstat STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3. Columns Columns 1-6 Positive control. Omentum. Rectosigmoid A195.
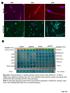 pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
pstat3 75 Pan CK A A263 A352 A24 B Columns 1-6 Positive control A195 A22 A24 A183 Rectal Nodule STAT3 pstat3 STAT3 pstat3 Columns 7-12 Omentum Rectosigmoid Left Ovary Right Ovary Omentum Uterus Uterus
Effects of Ionizing Radiation on Normal and Tumor-Associated Lymphatic Vessels
 Effects of Ionizing Radiation on Normal and Tumor-Associated Lymphatic Vessels By Jennifer D. Lobo Submitted to the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering In partial fulfillment of the requirements
Effects of Ionizing Radiation on Normal and Tumor-Associated Lymphatic Vessels By Jennifer D. Lobo Submitted to the Department of Nuclear Science and Engineering In partial fulfillment of the requirements
Lankenau Institute for Medical Research Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Lankenau Institute for Medical Research nnual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Lankenau Institute for Medical Research received
Lankenau Institute for Medical Research nnual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Lankenau Institute for Medical Research received
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation
 Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350.
 Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
Biological Effects of Radiation KJ350 deborah.oughton@nmbu.no 2111 2005 Radiation Biology Interaction of radiation with biological material Doses (Gy, Sv) and effects Scientific Controversy Radiation Protection
1/31/2014. Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public
 Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Radiation Biology and Risk to the Public Dr. David C. Medich University of Massachusetts Lowell Lowell MA 01854 Introduction Definition: Radiation Biology is the field of science that studies the biological
Principles of chemotherapy
 Principles of chemotherapy Chemotherapy first coined by Paul Ehrlich Aim to selectively destroy cancer cells whilst relatively sparing tumours cells Growth characteristics of cancer cells allows for selective
Principles of chemotherapy Chemotherapy first coined by Paul Ehrlich Aim to selectively destroy cancer cells whilst relatively sparing tumours cells Growth characteristics of cancer cells allows for selective
Cell survival following high dose rate flattening filter free (FFF) and conventional dose rate irradiation
 Cell survival following high dose rate flattening filter free (FFF) and conventional dose rate irradiation Peter Sminia p.sminia@vumc.nl Λαβορατοριυµβεσπρεκινγ 8 νοϖεµβερ 2005 Progress in Radiotherapy:
Cell survival following high dose rate flattening filter free (FFF) and conventional dose rate irradiation Peter Sminia p.sminia@vumc.nl Λαβορατοριυµβεσπρεκινγ 8 νοϖεµβερ 2005 Progress in Radiotherapy:
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
Chapter-IV. Geraniol attenuates phorbol ester-induced inflammatory responses in mouse skin: possible role of p38 MAP Kinase and NF-kB
 attenuates phorbol ester-induced inflammatory responses in mouse skin: possible role of p38 MAP Kinase and NF-kB Introduction Dietary natural products have shown protection against various degenerative
attenuates phorbol ester-induced inflammatory responses in mouse skin: possible role of p38 MAP Kinase and NF-kB Introduction Dietary natural products have shown protection against various degenerative
Side effects of radiotherapy.
 Side effects of radiotherapy. Paweł Potocki, MD Jagiellonian University Medical College Kraków University Hospital Departament of Clinical Oncology ppotocki@su.krakow.pl Basics Techniques: Radiation type:
Side effects of radiotherapy. Paweł Potocki, MD Jagiellonian University Medical College Kraków University Hospital Departament of Clinical Oncology ppotocki@su.krakow.pl Basics Techniques: Radiation type:
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy
 Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
Radiobiology of radionuclide therapy Prof Sarah Baatout Sarah.Baatout@sckcen.be Head of the Radiobiology Unit, SCK CEN Faculty of Biosciences Engineering, Universiteit Gent, Belgium Faculté des Sciences,
Radiation induced bystander effects adaptive responses and low dose risk
 Radiation induced bystander effects adaptive responses and low dose risk Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour Medical Physics and Applied Radiation Sciences McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario Canada
Radiation induced bystander effects adaptive responses and low dose risk Carmel Mothersill and Colin Seymour Medical Physics and Applied Radiation Sciences McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario Canada
Chapter 10. Summary, conclusions and future perspectives
 Chapter 10 Summary, conclusions and future perspectives 10.1 SUMMARY In this thesis, a new tumor imaging tracer in nuclear medicine is studied. This 123 tracer, L-3-[ I]Iodo-alpha-methyl-tyrosine (IMT),
Chapter 10 Summary, conclusions and future perspectives 10.1 SUMMARY In this thesis, a new tumor imaging tracer in nuclear medicine is studied. This 123 tracer, L-3-[ I]Iodo-alpha-methyl-tyrosine (IMT),
Stanford University Stanford, California Approved for Public Release; Distribution Unlimited
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0160 TITLE: Selenium is a Chemotherapeutic Agent for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Susan J. Knox, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Stanford
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0160 TITLE: Selenium is a Chemotherapeutic Agent for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Susan J. Knox, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Stanford
American Nuclear Society Annual Meeting Chicago, June 24-28, 2012 President s Special Session
 American Nuclear Society Annual Meeting Chicago, June 24-28, 2012 President s Special Session LOW-LEVEL LEVEL RADIATION AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR FUKUSHIMA RECOVERY Radiation Oncology Kiyohiko Sakamoto
American Nuclear Society Annual Meeting Chicago, June 24-28, 2012 President s Special Session LOW-LEVEL LEVEL RADIATION AND ITS IMPLICATIONS FOR FUKUSHIMA RECOVERY Radiation Oncology Kiyohiko Sakamoto
Aging and nutrition 03/11/2012. Why do people age? Oxidative stress and damage
 Aging and nutrition % of elderly people in Canadian population is increasing more than for other age groups within the elderly age group there is great variability in terms health, metabolism, physical
Aging and nutrition % of elderly people in Canadian population is increasing more than for other age groups within the elderly age group there is great variability in terms health, metabolism, physical
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model
 Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
Health Physics and the Linear No-Threshold Model Understanding Radiation and Its Effects John Baunach Vanderbilt University Nashville, TN What is health physics? Outline What organizational bodies govern
RADIATION HAZARDS AND SAFETY
 RADIATION HAZARDS AND SAFETY Dr. S. P. Tyagi All types of radiation produce changes in the living tissues. The resultant cellular injury causes physiological and pathological changes leading to Radiation
RADIATION HAZARDS AND SAFETY Dr. S. P. Tyagi All types of radiation produce changes in the living tissues. The resultant cellular injury causes physiological and pathological changes leading to Radiation
