OPEN ACCESS ORIGINAL ARTICLE
|
|
|
- Oscar Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPEN ACCESS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Interobserver Variability of Gleason Score and Completeness of Histopathology Report in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma in Prostate Needle Biopsy Specimens among General Pathologists in a Multi-institutional Setting Anne Lizbeth Valdez and Jeffrey So St. Luke s Medical Center, Quezon City, Philippines ABSTRACT Introduction. Gleason score, the most widely used grading system for prostatic adenocarcinoma, is the most powerful predictor of patient s clinical outcome and is used to customize treatment strategies. It possesses an inherent degree of subjectivity, as inter-observer and intra-observer variability does exist. Moreover, there are currently no structured histopathology report guidelines for prostate needle biopsies in our setting, making relevant information overlooked by pathologists and interpretation of report between laboratories challenging. Objective. With these in mind, we sought to study the interobserver variability of Gleason score and completeness of histopathology report in prostate needle biopsy specimens. Methodology. A set of 19 prostate needle biopsy slides was sent to 18 general pathologists from different institutions in the Philippines for histopathologic analysis of Gleason scores and completeness of reporting. The interobserver agreement of each pathologist will be evaluated using Spearman s rank correlation coefficient. Results. Overall, there was moderate correlation between the interobserver s Gleason score and Gleason grade group. Low to moderate correlation was seen in primary grade while negligible correlation was seen in secondary grade. Best agreement was seen in poorly differentiated neoplasms. Undergrading was more common than overgrading. Most respondents gave an incomplete histopathology report. Conclusion. There is an overall moderate correlation between Gleason score. A non-standardized histopathology report is currently used, leaving out relevant histopathologic findings. Key words: prostate, prostate cancer, urology ISSN (Online) Printed in the Philippines. Copyright 2018 by the PJP. Received: 11 July Accepted: 2 September Published online first: 16 September Corresponding author: Anne Lizbeth B. Valdez, MD anne_lizbeth@yahoo.com ORCID: INTRODUCTION Gleason score is the most widely used grading system for prostatic adenocarcinoma. Inevitably, like all other grading systems, it is flawed by some degree of interobserver and intraobserver variability. 1 Although this grading system has undergone significant revisions for the past years, it still continues to have deficiencies that can potentially impact patient care. Gleason score is the most powerful predictor of patient s clinical outcome and is a major determinant in customizing treatment strategies that is most appropriate for a patient. It is utilized to tailor-fit post biopsy treatment, plan for the type of radiation therapy and whether to administer hormonal therapy with radiation therapy. Patients with Gleason scores of <6 may benefit from watchful waiting and surveillance as initial management. 1 The presence of high-grade Gleason pattern (Gleason pattern 4 or 5) harbors the greatest risk for metastasis and treatment failure. Thus, discordance in Gleason scoring, albeit small, will have a dramatic effect on risk stratification and clinical management.
2 Valdez et al, Interobserver Variability of Gleason Score in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Philippine Journal of Pathology 14 It has been observed that general pathologists more frequently underscore than over score, with a natural tendency to assign low Gleason pattern in such small core needle biopsies. In a study done by RV Singh et al., 2 Gleason score 7 was identified as an area of difficulty as 14 of 63 readings (22%) were underscored. The differences centered on the assessment of small areas of fused and separate glands and fused small irregular glands. This has lead to the inappropriate assignment of Gleason score 6 and probable suboptimal patient management as a consequence. In the same study, assignment of Gleason pattern 4 and 5 as distinction between few tiny poorly formed glands versus cords and nests of malignant cells were particularly challenging. As a result, sheets of cells with ill-defined lumina were inappropriately given as Gleason pattern 5 instead of pattern 4. These discrepancies suggest that misperceptions among each Gleason pattern in the scheme exist, especially for borderline cases, which exhibit features intermediate between 2 patterns. In another study by Coard, 3 the greatest discordance is seen in distinguishing Gleason score 6 from 7 in biopsy specimens with less than 30% tumor volume. This has led to the conclusion that assignment of Gleason scores in core needle samples, in contrast to TURP and radical prostatectomy specimens, poses a diagnostic dilemma as these samples contain low tumor volume. 4,5 Several data support that for needle biopsy grading, pathologist training and experience can influence the degree of interobserver agreement. 6,7 In one study, 7 41 general pathologists exhibited moderate interobserver agreement with a kappa coefficient of 0.435, while substantial interobserver agreement with a kappa coefficient of was seen among 9 of 10 urologic pathologists. Interest in urologic pathology, particularly in Gleason scoring, resulted in participation of general pathologists in educational courses and subspecialty training, which however is not readily available in our setting. Other sources of grading variation in core needle samples include difficulty in appreciation of infiltrative growth pattern, tissue sampling error and artifactual tissue distortion. A structured histopathology report for prostate needle biopsies has an essential role in conveying the result to clinicians. The report should be uniform and formatted to provide compete, clear and unambiguous data. The inclusion of tumor volume and presence of extraprostatic extension, perineural and lymphovascular invasion, prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia and intraductal carcinoma in prostate needle biopsy reports are equally essential as the Gleason score, and must be reported when present since these are associated with adverse clinical outcome. 8 Moreover, these pathologic findings are being utilized in common nomograms used to guide clinical decision making and therefore must be reported when present. In one study by Kryvenko et al., 1 analysis of needle biopsy cores showed that the number of positive cores, tumor volume and perineural invasion predicts presence of extraprostatic extension, seminal vesicle invasion and positive surgical margins in radical prostatectomy specimens. In the same study, they concluded that biopsy specimens with perineural invasion is significantly associated biochemical recurrence. With these in mind, our study intends to 1) determine the interobserver agreement of the respondent pathologists in Gleason grading of prostatic adenocarcinoma in terms of: primary grade, secondary grade, Gleason score and Gleason Grade Group; and 2) describe the completeness of reporting of histopathology results by respondent pathologists in terms of inclusion of tumor volume and mention of presence of extraprostatic extension, perineural and lymphovascular invasion, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal carcinoma. METHODOLOGY Board certified fellows or diplomates in anatomic pathology by the Philippine Society of Pathologists who acquired no formal training in uropathology and practicing as a general pathologist were recruited for this study. Information on respondents age, number of years in practice, current affiliation/s and other demographic profiles were not collected. They were invited to take part in the study via phone calls, letters and s. Our study welcomed 18 pathologists from all over the Philippines, including areas outside Metro Manila such as Ilocos Norte, Cagayan, Isabela, Zamboanga, Cebu and Davao. A set of 19 slides diagnosed by a uropathologist with prostatic adenocarcinoma at St. Luke s Medical Center Quezon City was sent to the respondent pathologists. These cases were seen by a second pathologist from the same institution who concurred with the diagnosis. The slides were selected by the original sign-out pathologist to roughly represent the spectrum of Gleason scores based on the 2015 Modified Gleason Grading System and no effort was made to select particularly difficult cases. The slides, in hematoxylin and eosin preparation, was of uniform and adequate quality and was assessed prior to shipping to ensure proper and easeful examination. Also sent along with the slides was a copy of the questionnaire and endorsement letter. The questionnaire had assigned codes (P1-P18) to maintain the respondent s anonymity while the endorsement letter contained a brief description of the study. Each slide was given a code number (1-19) to maintain patient s anonymity and to ensure that these could not be identified by the respondent pathologists. Each respondent was instructed to give a complete diagnosis as they normally would with their own cases. He/she reviewed the slides without the knowledge of the previous Gleason scores. The interobserver agreement was evaluated using Spearman s rank correlation coefficient. Agreement was calculated for primary grade, secondary grade, Gleason score and Gleason grade group (based on 2015 ISUP and 2016 WHO grading system). The completeness of reporting of each pathologist was evaluated by the mention or failure to mention of tumor volume, extraprostatic extension, perineural and lymphovascular invasion, prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia and intraductal carcinoma. Institutional Review and Ethics Research Committee approval was secured prior to the commencement of this study.
3 Valdez et al, Interobserver Variability of Gleason Score in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Philippine Journal of Pathology 15 RESULTS To assess for interobserver agreement, a mathematical consensus was first calculated (Table 1). The overall percentage of Gleason score agreement for all respondents is 43.0% (10.5% to 68.4%) (Table 2). The maximum number of readings were in the Gleason score 7 (33.9%; n=78/342) and least in Gleason score 2-4 (3.2%; n=11/342). The distribution of percentage agreement for Gleason score with consensus score was computed (Table 3). 43% Table 1. Mathematical consensus score per slide Median of primary score Median of secondary score Mathematical consensus score Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide Slide (n=147/342) of all assigned Gleason scores were in exact agreement with the consensus score. 72.8% and 83.6% of the assigned Gleason score were within ±1 and ±2 of the consensus score, respectively. Agreement was best in Gleason 9 (75%; n=25/33) and worst with Gleason 3 (0%; n=0/18) and Gleason 8 (30%; n=30/100). Overall, undergrading was seen in 30.4% while overgrading was seen in 26.9% of the readings. Most commonly undergraded is Gleason score 8 (46/100; 46%) while Gleason score 6 is most commonly overgraded (43/114; 38%). Interobserver Spearman s rank correlation coefficient for primary grade, secondary grade Gleason score and Gleason grade group were computed (Table 4). Majority had moderate to low correlation (64.7%; n=198/306) in the primary grade while majority had negligible correlation (61.4%; n=188/306) for secondary grade. Likewise, moderate correlation (35.9%; n=110/306) was seen in the majority of the Gleason scores and moderate correlation (39.2%; n=120/306) with the Gleason grade group. A total of 8 respondents (44.4%; n=8/18) mentioned at least 1 other histopathologic finding (Table 5). DISCUSSION Agreement was best seen in Gleason score 9. This is may be due to the straightforward identification of sheets, cords and solid nests of infiltrative neoplastic cells and necrosis and the large tumor volume of such poorly differentiated neoplasms. Table 2. Percent agreement with Gleason score Respondents Gleason scores Total number of readings Percent agreement with consensus Total Table 3. Distribution of percentage of agreement of Gleason scores Consensus Gleason score Number of reading with < Exact >+3 Total number of reading Total Percentage
4 Valdez et al, Interobserver Variability of Gleason Score in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Philippine Journal of Pathology 16 Table 4. Spearman s rank correlation coefficient for primary score, secondary score, Gleason score and Gleason grade group Correlation Value Primary Grade Secondary grade Gleason score Gleason grade group Number of readings % Number of readings % Number of readings % Number of readings % Very high High Moderate Low Negligible Table 5. Mention or failure to mention of other pertinent histopathologic findings* Respondent Mention of other histopathologic findings* 1 Mention 2 No mention 3 No mention 4 No mention 5 No mention 6 Mention 7 Mention 8 Mention 9 Mention 10 No mention 11 Mention 12 No mention 13 No mention 14 No mention 15 No mention 16 Mention 17 No mention 18 Mention Total 8 (n=8/18; 44.4%) * Tumor volume, extraprostatic extension, perineural and lymphovascular invasion, prostatic intra-epithelial neoplasia and/or intraductal carcinoma Predictably, underscoring is seen more often than overscoring. Literature has supported the fact that there is a natural tendency to underscore in such small specimens, most especially for low tumor volume cores and is may be due to the difficulty in appreciating the infiltrative nature of the tumor. In contrast, overscoring of consensus score 7 was seen and is may be due to the challenging distinction between subtle differences in poorly formed glands and wellformed glands and/or the loss of acinar spaces caused by compression artifact. There is moderate to low correlation between the primary grades and negligible correlation between the secondary grades. This is because of the problems faced in determining the predominant pattern present in one core. The presence of 2 distinct patterns in seemingly equal proportions and/or the discontinuous arrangement of neoplastic cells complicate the assignment of a primary grade. The most striking observation for consensus score, however, is the presence of Gleason score <6, which is traditionally not assigned to needle biopsy specimens using the upgraded Gleason grading system. This ascertains that some pathologists are indeed still using the outdated Gleason scoring system. Majority of the histopathology reports were incomplete. This indicates that a non-standardized histopathology report is still currently being used which makes interpretation of report between institutions challenging. CONCLUSION Overall, tumor heterogeneity giving rise to various patterns/mimickers and the presence of morphologically borderline tumors complicates Gleason scoring. We strongly believe that subjectivity will always be present in any grading system and that a good agreement can only achieved by understanding the definition of each pattern in the scheme, as well as the pitfalls, in the updated Gleason grading system. In addition, our study puts emphasis that a complete histopathologic report is an important contributor to the success of patient management. The need to identify relevant histopathologic findings, which are often, overlooked greatly impact patient management. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors extend their gratitude to the consultants of St. Luke s Medical Center Quezon City Institute of Pathology, all the respondent pathologists of this study for sharing their knowledge, and to the staff of the Histopathology Section of St. Luke s Medical Center Quezon City for their kind assistance during the collection of test materials. STATEMENT OF AUTHORSHIP All authors certified fulfillment of ICMJE authorship criteria. Author Disclosure The authors declared no conflict of interest. Funding Source None. REFERENCES 1. Kryvenko ON, Epstein JI. Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified Gleason grading system. Arch Patho Lab Med. 2016;140(10): PMID: Singh RV, Agashe SR, Gosavi AV, Sukhyan KR. Interobserver reproducibility of Gleason grading of prostatic adenocarcinoma among general pathologists. Indian J Cancer. 2011;48(4): PMID: Coard KC, Freeman VL. Gleason grading of prostate cancer: level of concordance between pathologists at the University Hospital of the West Indies. Am J Clin Pathol. 2004;122(3): PMID: doi.org/ /3a32-dtvm-h640-m2qa.
5 Valdez et al, Interobserver Variability of Gleason Score in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Philippine Journal of Pathology Barqawi AB, Turcanu R, Gamito EJ, et al. The value of second-opinion pathology diagnoses on prostate biopsies from patients referred for management of prostate cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2011;4(5): PMID: PMCID: PMC Majoros A, Szász AM, Nyirády, et al. The influence of expertise of the surgical pathologist to undergrading, upgrading and understaging of prostate cancer in patients undergoing subsequent radical prostatectomy. Int Urol Nephrol. 2014;46(2): PMID: Allsbrook WC Jr., Mangold KA, Johnson MH, et al. Interobserver reproducibility of Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: urologic pathologists. Hum Pathol. 2001;32(1): PMID: doi.org/ /hupa Allsbrook, WC Jr., Mangold, KA, Johnson MH, Lane RB, Lane CG, Epstein JI. Interobserver reproducibility of Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: general pathologist. Hum Pathol. 2001;32(1):81-8. PMID: Prostate cancer (core/needle biopsy) structured reporting protocol, 1st ed. NSW, Australia: RCPA, Available at: microsoft-word-v0-24-prostate-core-biospy-post-oc. html. Disclaimer: This journal is OPEN ACCESS, providing immediate access to its content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge. As a requirement for submission to the PJP, all authors have accomplished an AUTHOR FORM, which declares that the ICMJE criteria for authorship have been met by each author listed, that the article represents original material, has not been published, accepted for publication in other journals, or concurrently submitted to other journals, and that all funding and conflicts of interest have been declared. Consent forms have been secured for the publication of information about patients or cases; otherwise, authors have declared that all means have been exhausted for securing consent.
Received: 11 Feb. 2013; Accepted: 7 Jun. 2013
 ORIGINAL REPORT Inter-Observer Reproducibility before and after Web-Based Education in the Gleason Grading of the Prostate Adenocarcinoma among the Iranian Pathologists Alireza Abdollahi 1*, Sara Sheikhbahaei
ORIGINAL REPORT Inter-Observer Reproducibility before and after Web-Based Education in the Gleason Grading of the Prostate Adenocarcinoma among the Iranian Pathologists Alireza Abdollahi 1*, Sara Sheikhbahaei
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013.
 A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017
 Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
Review by urological pathologists improves the accuracy of Gleason grading by general pathologists
 Nakai et al. BMC Urology (2015) 15:70 DOI 10.1186/s12894-015-0066-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Review by urological pathologists improves the accuracy of Gleason grading by general pathologists Yasushi Nakai 1,
Nakai et al. BMC Urology (2015) 15:70 DOI 10.1186/s12894-015-0066-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Review by urological pathologists improves the accuracy of Gleason grading by general pathologists Yasushi Nakai 1,
Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology
 PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
Update on Reporting Prostate Cancer Pathology
 Update on Reporting Prostate Cancer Pathology Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON None Disclosures Learning Objectives
Update on Reporting Prostate Cancer Pathology Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON None Disclosures Learning Objectives
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
Prostate Cancer Grading, Staging and Reporting: An Update Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD
 Prostate Cancer Grading, Staging and Reporting: An Update Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD Director, Genitourinary Pathology R.J. Tomsich Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Professor of Pathology,
Prostate Cancer Grading, Staging and Reporting: An Update Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD Director, Genitourinary Pathology R.J. Tomsich Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Professor of Pathology,
S1.04 Principal clinician. G1.01 Comments. G2.01 *Specimen dimensions (prostate) S2.02 *Seminal vesicles
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Quality ID #250 (NQF 1853): Radical Prostatectomy Pathology Reporting National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #250 (NQF 1853): Radical Prostatectomy Pathology Reporting National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Quality ID #250 (NQF 1853): Radical Prostatectomy Pathology Reporting National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
The Role of the Pathologist Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer
 The Role of the Pathologist Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer Thomas M. Wheeler, M.D. W. L. Moody, Jr., Professor and Chair Department of Pathology & Immunology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
The Role of the Pathologist Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer Thomas M. Wheeler, M.D. W. L. Moody, Jr., Professor and Chair Department of Pathology & Immunology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
3/23/2017. Significant Changes in Prostate Cancer Classification, Grading, Staging and Reporting. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Staging and Reporting of Prostate Cancer: Major Changes in 8 th Edition AJCC Staging and CAP Cancer Checklists USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Staging and Reporting of Prostate Cancer: Major Changes in 8 th Edition AJCC Staging and CAP Cancer Checklists USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Correlation between Gleason Scores in Needle Biopsy and Corresponding Radical Prostatectomy Specimens: A Twelve-Year Review
 120 Review Article Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(2): 120-126 http://www.ijp.iranpath.org/ Correlation between Gleason Scores in Needle Biopsy and Corresponding Radical Prostatectomy Specimens: A Twelve-Year
120 Review Article Iran J Pathol. 2016; 11(2): 120-126 http://www.ijp.iranpath.org/ Correlation between Gleason Scores in Needle Biopsy and Corresponding Radical Prostatectomy Specimens: A Twelve-Year
Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA
 Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA Learners Objectives u Latest changes per ISUP 2014 that impact
Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA Learners Objectives u Latest changes per ISUP 2014 that impact
Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent Changes and Refinements
 USPSTF: 2012 Report on serum PSA Screening Recommendation rating of D Reduced screening, Reduced biopsies, reduced incidence Refinements currently occurring in 2017. WHY? Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent
USPSTF: 2012 Report on serum PSA Screening Recommendation rating of D Reduced screening, Reduced biopsies, reduced incidence Refinements currently occurring in 2017. WHY? Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Prediction of Prostate Cancer Recurrence using Quantitative Phase Imaging Shamira Sridharan 1, Virgilia Macias 2, Krishnarao Tangella 3, André Kajdacsy-Balla 2 and Gabriel Popescu
Supplemental Information Prediction of Prostate Cancer Recurrence using Quantitative Phase Imaging Shamira Sridharan 1, Virgilia Macias 2, Krishnarao Tangella 3, André Kajdacsy-Balla 2 and Gabriel Popescu
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 25 Nov 2018 12:22:24 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 06/07/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sun, 25 Nov 2018 12:22:24 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 06/07/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Introduction. Key Words: high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, HGPIN, radical prostatectomy, prostate biopsy, insignificant prostate cancer
 Prostate cancer after initial high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and benign prostate biopsy Premal Patel, MD, 1 Jasmir G. Nayak, MD, 1,2 Zlatica Biljetina, MD, 4 Bryan Donnelly, MD 3, Kiril
Prostate cancer after initial high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and benign prostate biopsy Premal Patel, MD, 1 Jasmir G. Nayak, MD, 1,2 Zlatica Biljetina, MD, 4 Bryan Donnelly, MD 3, Kiril
Measure #250 (NQF 1853): Radical Prostatectomy Pathology Reporting National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clincial Care
 Measure #250 (NQF 1853): Radical Prostatectomy Pathology Reporting National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clincial Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Measure #250 (NQF 1853): Radical Prostatectomy Pathology Reporting National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clincial Care 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS, REGISTRY DESCRIPTION: Percentage
In 2005, International Society of Urological Pathology
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason Score 3+4=7 Prostate Cancer With Minimal Quantity of Gleason Pattern 4 on Needle Biopsy Is Associated With Low-risk Tumor in Radical Prostatectomy Specimen Cheng Cheng Huang, MD,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason Score 3+4=7 Prostate Cancer With Minimal Quantity of Gleason Pattern 4 on Needle Biopsy Is Associated With Low-risk Tumor in Radical Prostatectomy Specimen Cheng Cheng Huang, MD,*
PSA. HMCK, p63, Racemase. HMCK, p63, Racemase
 Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Percent Gleason pattern 4 in stratifying the prognosis of patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer
 Review Article Percent Gleason pattern 4 in stratifying the prognosis of patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer Meenal Sharma 1, Hiroshi Miyamoto 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Review Article Percent Gleason pattern 4 in stratifying the prognosis of patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer Meenal Sharma 1, Hiroshi Miyamoto 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology and Laboratory
3/28/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference. Differential Diagnosis:
 GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
S1.04 PRINCIPAL CLINICIAN G1.01 COMMENTS S2.01 SPECIMEN LABELLED AS G2.01 *SPECIMEN DIMENSIONS (PROSTATE) S2.03 *SEMINAL VESICLES
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Interobserver reproducibility of modified Gleason score in radical prostatectomy specimens
 Virchows Arch (2004) 445:17 21 DOI 10.1007/s00428-004-1034-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Axel Glaessgen Hans Hamberg Carl-Gustaf Pihl Birgitta Sundelin Bo Nilsson Lars Egevad Interobserver reproducibility of modified
Virchows Arch (2004) 445:17 21 DOI 10.1007/s00428-004-1034-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Axel Glaessgen Hans Hamberg Carl-Gustaf Pihl Birgitta Sundelin Bo Nilsson Lars Egevad Interobserver reproducibility of modified
OMPRN Pathology Matters Meeting 2017
 OMPRN Pathology Matters Meeting 2017 Pathology of Aggressive Prostate Cancer Intraductal Carcinoma and Cribriform Carcinoma Dr. Michelle Downes, Staff Urologic Pathologist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre,
OMPRN Pathology Matters Meeting 2017 Pathology of Aggressive Prostate Cancer Intraductal Carcinoma and Cribriform Carcinoma Dr. Michelle Downes, Staff Urologic Pathologist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre,
Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018
 Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018 Dr. Tzahi Neuman Dep.Of Pathology Hadassah Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel, (tneuman@hadassah.org.il) Disclosure: 1 no conflicts of
Diagnostic accuracy of percutaneous renal tumor biopsy May 10 th 2018 Dr. Tzahi Neuman Dep.Of Pathology Hadassah Medical Center Jerusalem, Israel, (tneuman@hadassah.org.il) Disclosure: 1 no conflicts of
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual
ASSESSMENT OF GLEASON SYSTEM USE ON DIFFERENT TYPES OF PROSTATIC TISSUE SAMPLES
 ASSESSMENT OF GLEASON SYSTEM USE ON DIFFERENT TYPES OF PROSTATIC TISSUE SAMPLES I. E. PLEŞEA*, B. ZAHARIA*, S. D. ENACHE**, G. MITROI***, P. TOMESCU***, O. T. POP*, P. BADEA****, A. KOŻOKIĆ***** *Department
ASSESSMENT OF GLEASON SYSTEM USE ON DIFFERENT TYPES OF PROSTATIC TISSUE SAMPLES I. E. PLEŞEA*, B. ZAHARIA*, S. D. ENACHE**, G. MITROI***, P. TOMESCU***, O. T. POP*, P. BADEA****, A. KOŻOKIĆ***** *Department
Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma is a subtype of
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasialike Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Clinicopathologic Study of 28 Cases Fabio Tavora, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasialike Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Clinicopathologic Study of 28 Cases Fabio Tavora, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract:
Prostate Case Scenario 1
 Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1)
 Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Disease-specific death and metastasis do not occur in patients with Gleason score 6 at radical prostatectomy
 Disease-specific death and metastasis do not occur in patients with at radical prostatectomy Charlotte F. Kweldam, Mark F. Wildhagen*, Chris H. Bangma* and Geert J.L.H. van Leenders Departments of Pathology,
Disease-specific death and metastasis do not occur in patients with at radical prostatectomy Charlotte F. Kweldam, Mark F. Wildhagen*, Chris H. Bangma* and Geert J.L.H. van Leenders Departments of Pathology,
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition. Prostate Chapter 58. Executive Committee, AJCC. Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center
 AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition Prostate Chapter 58 Judd W Moul, MD, FACS Executive Committee, AJCC Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center Duke University Durham, North Carolina Validating science.
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition Prostate Chapter 58 Judd W Moul, MD, FACS Executive Committee, AJCC Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center Duke University Durham, North Carolina Validating science.
Since the beginning of the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) era in the. Characteristics of Insignificant Clinical T1c Prostate Tumors
 2001 Characteristics of Insignificant Clinical T1c Prostate Tumors A Contemporary Analysis Patrick J. Bastian, M.D. 1 Leslie A. Mangold, B.A., M.S. 1 Jonathan I. Epstein, M.D. 2 Alan W. Partin, M.D., Ph.D.
2001 Characteristics of Insignificant Clinical T1c Prostate Tumors A Contemporary Analysis Patrick J. Bastian, M.D. 1 Leslie A. Mangold, B.A., M.S. 1 Jonathan I. Epstein, M.D. 2 Alan W. Partin, M.D., Ph.D.
ACCME/Disclosures. Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate. Case
 Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Procedures Needle Biopsy Transurethral Prostatic Resection Suprapubic or Retropubic Enucleation (Subtotal Prostatectomy) Radical Prostatectomy
 Prostate Gland Protocol applies to invasive carcinomas of the prostate gland. Protocol web posting date: July 2006 Protocol effective date: April 2007 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Needle
Prostate Gland Protocol applies to invasive carcinomas of the prostate gland. Protocol web posting date: July 2006 Protocol effective date: April 2007 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Needle
Preoperative Gleason score, percent of positive prostate biopsies and PSA in predicting biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy
 JBUON 2013; 18(4): 954-960 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason score, percent of positive prostate and PSA in predicting biochemical
JBUON 2013; 18(4): 954-960 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason score, percent of positive prostate and PSA in predicting biochemical
Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: A clinicopathological study
 20 B. SATHESAN, S. A. S. GOONEWARDENA, H. W. D. ANURUDDHIKA AND M. V. C. DE SILVA Sri Lanka Journal of Urology, 2008, 9, 20-24 Original Article Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: A clinicopathological
20 B. SATHESAN, S. A. S. GOONEWARDENA, H. W. D. ANURUDDHIKA AND M. V. C. DE SILVA Sri Lanka Journal of Urology, 2008, 9, 20-24 Original Article Ductal adenocarcinoma of the prostate: A clinicopathological
Interpretation of Breast Pathology in the Era of Minimally Invasive Procedures
 Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An aggressive variant that is underdiagnosed and undersampled on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided needle biopsy
 Original research Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An aggressive variant that is underdiagnosed and undersampled on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided needle biopsy Previn Gulavita, MD; * Shaheed W.
Original research Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An aggressive variant that is underdiagnosed and undersampled on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided needle biopsy Previn Gulavita, MD; * Shaheed W.
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE. Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT
 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
Applying Risk Management Principles to QA in Surgical Pathology: From Principles to Practice
 Applying Risk Management Principles to QA in Surgical Pathology: From Principles to Practice Dr. Gregory Flynn CEO, Institute for Quality Management in Healthcare Managing Director, Quality Management
Applying Risk Management Principles to QA in Surgical Pathology: From Principles to Practice Dr. Gregory Flynn CEO, Institute for Quality Management in Healthcare Managing Director, Quality Management
Gleason grading and prognostic factors in carcinoma of the prostate
 & 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org in carcinoma of the prostate Peter A Humphrey Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine,
& 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org in carcinoma of the prostate Peter A Humphrey Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine,
Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland
 Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: ProstateBiopsy 4.0.3.1 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use
Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: ProstateBiopsy 4.0.3.1 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use
Supplemental Figure 1
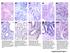 A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS.
 NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
NPQR Quality Payment Program (QPP) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: QPP 99 MEASURE TITLE: Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting pt Category (Primary Tumor) and pn Category (Regional Lymph Nodes)
Radical prostatectomy as radical cure of prostate cancer in a high risk group: A single-institution experience
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 1: 337-342, 2013 Radical prostatectomy as radical cure of prostate cancer in a high risk group: A single-institution experience NOBUKI FURUBAYASHI 1, MOTONOBU NAKAMURA 1,
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 1: 337-342, 2013 Radical prostatectomy as radical cure of prostate cancer in a high risk group: A single-institution experience NOBUKI FURUBAYASHI 1, MOTONOBU NAKAMURA 1,
According to the original drawing of D. F. Gleason,
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Grading of Invasive Cribriform Carcinoma on Prostate Needle Biopsy An Interobserver Study among Experts in Genitourinary Pathology Mathieu Latour, MD,* Mahul B. Amin, MD,y Athanase Billis
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Grading of Invasive Cribriform Carcinoma on Prostate Needle Biopsy An Interobserver Study among Experts in Genitourinary Pathology Mathieu Latour, MD,* Mahul B. Amin, MD,y Athanase Billis
Original Article. Clinicopathological Evaluation of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma: A Unicenter Study
 Original Article Clinicopathological Evaluation of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma: A Unicenter Study Clement Wilfred D 1 *, Rashmi Krishnappa 1, Sharath Soman 1, Vijaya Viswanath Mysorekar 1, Radhika Kunnavil
Original Article Clinicopathological Evaluation of Prostatic Adenocarcinoma: A Unicenter Study Clement Wilfred D 1 *, Rashmi Krishnappa 1, Sharath Soman 1, Vijaya Viswanath Mysorekar 1, Radhika Kunnavil
Prognostic value of the Gleason score in prostate cancer
 BJU International (22), 89, 538 542 Prognostic value of the Gleason score in prostate cancer L. EGEVAD, T. GRANFORS*, L. KARLBERG*, A. BERGH and P. STATTIN Department of Pathology and Cytology, Karolinska
BJU International (22), 89, 538 542 Prognostic value of the Gleason score in prostate cancer L. EGEVAD, T. GRANFORS*, L. KARLBERG*, A. BERGH and P. STATTIN Department of Pathology and Cytology, Karolinska
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
Clinicopathological Features of Prostate Ductal Carcinoma: Matching Analysis and Comparison with Prostate Acinar Carcinoma
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Oncology & Hematology http://dx.doi.org/0.3346/jkms.205.30.4.385 J Korean Med Sci 205; 30: 385-389 Clinicopathological Features of Prostate Ductal Carcinoma: Matching Analysis and Comparison
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Oncology & Hematology http://dx.doi.org/0.3346/jkms.205.30.4.385 J Korean Med Sci 205; 30: 385-389 Clinicopathological Features of Prostate Ductal Carcinoma: Matching Analysis and Comparison
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares
 Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Pancreatobiliary Frozen Section Nightmares Aatur D. Singhi, MD PhD Assistant Professor University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Department of Pathology singhiad@upmc.edu Objectives Briefly give an overview
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency
 Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Prostate cancer staging and datasets: The Nitty-Gritty. What determines our pathological reports? 06/07/2018. Dan Berney Maastricht 2018
 Prostate cancer staging and datasets: The Nitty-Gritty What determines our pathological reports? Dan Berney Maastricht 2018 Biopsy reporting. How not to do it. The TNM 8 th edition. Changes good and bad
Prostate cancer staging and datasets: The Nitty-Gritty What determines our pathological reports? Dan Berney Maastricht 2018 Biopsy reporting. How not to do it. The TNM 8 th edition. Changes good and bad
Accuracy of post-radiotherapy biopsy before salvage radical prostatectomy
 Accuracy of post-radiotherapy biopsy before salvage radical prostatectomy Joshua J. Meeks, Marc Walker*, Melanie Bernstein, Matthew Kent and James A. Eastham Urology Service, Department of Surgery and
Accuracy of post-radiotherapy biopsy before salvage radical prostatectomy Joshua J. Meeks, Marc Walker*, Melanie Bernstein, Matthew Kent and James A. Eastham Urology Service, Department of Surgery and
Study of High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia for a Period of Five Years B. Rajashekar Reddy 1, Rameswarapu Suman Babu 2 and P.
 Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 2, June-July, 2014, pp- 149-154 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00004.1 Original Research Study of High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 2, No. 2, June-July, 2014, pp- 149-154 DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2014.00004.1 Original Research Study of High Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO/SUO Guideline Very Low-/Low-Risk Disease
 Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO/SUO Guideline Very Low-/Low-Risk Disease Jeffrey A. Cadeddu, MD Professor, Department of Urology UT Southwestern Medical Center Vice-Chair, AUA/ASTRO/SUO
Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO/SUO Guideline Very Low-/Low-Risk Disease Jeffrey A. Cadeddu, MD Professor, Department of Urology UT Southwestern Medical Center Vice-Chair, AUA/ASTRO/SUO
Providing Treatment Information for Prostate Cancer Patients
 Providing Treatment Information for Prostate Cancer Patients For all patients with localized disease on biopsy For all patients with adverse pathology after prostatectomy See what better looks like Contact
Providing Treatment Information for Prostate Cancer Patients For all patients with localized disease on biopsy For all patients with adverse pathology after prostatectomy See what better looks like Contact
Division of Oncology, S Orsola-Malpighi Hospital, Bologna, Italy. Department of Surgery, Cordoba University Medical School, Cordoba, Spain
 Prostate cancer glands with cribriform architecture and with glomeruloid features should be considered as Gleason pattern 4 and not pattern 3 Daniele Minardi,1, Roberta Mazzucchelli,, Marina Scarpelli,
Prostate cancer glands with cribriform architecture and with glomeruloid features should be considered as Gleason pattern 4 and not pattern 3 Daniele Minardi,1, Roberta Mazzucchelli,, Marina Scarpelli,
2018 Surgical Pathology Update: Diagnostic Pearls for the Practicing Pathologist - Volume II
 Release Date: January 1, 15.25 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM About This CME Teaching Activity This CME Activity is designed to provide a comprehensive review of soft tissue, gastrointestinal, genitourinary,
Release Date: January 1, 15.25 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s) TM About This CME Teaching Activity This CME Activity is designed to provide a comprehensive review of soft tissue, gastrointestinal, genitourinary,
They Do Look Alike : Mimics of Prostate Cancer in Biopsy Samples
 They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY. Jonathan I. Epstein.
 1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
College of American Pathologists. Pathology Performance Measures included in CMS 2012 PQRS
 College of American Pathologists Pathology Performance Measures included in CMS 2012 PQRS Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting Measure #99 pt category (primary tumor) and pn category (regional lymph
College of American Pathologists Pathology Performance Measures included in CMS 2012 PQRS Breast Cancer Resection Pathology Reporting Measure #99 pt category (primary tumor) and pn category (regional lymph
Internationally indexed journal
 www.ijpbs.net Internationally indexed journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services (USA), Index coppernicus, Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals, Google scholar, CABI,DOAJ, PSOAR, EBSCO, Open J gate, Proquest,
www.ijpbs.net Internationally indexed journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services (USA), Index coppernicus, Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals, Google scholar, CABI,DOAJ, PSOAR, EBSCO, Open J gate, Proquest,
Pathology of the Prostate. PathoBasic Tatjana Vlajnic
 Pathology of the Prostate PathoBasic 24.01.17 Tatjana Vlajnic Overview Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Grading Special variants Mimickers of prostate adenocarcinoma Atrophy Inflammatory conditions Granulomatous
Pathology of the Prostate PathoBasic 24.01.17 Tatjana Vlajnic Overview Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Grading Special variants Mimickers of prostate adenocarcinoma Atrophy Inflammatory conditions Granulomatous
Research Article Higher Prostate Weight Is Inversely Associated with Gleason Score Upgrading in Radical Prostatectomy Specimens
 Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 710421, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/710421 Research Article Higher Prostate Weight Is Inversely Associated with Gleason Score Upgrading in Radical
Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 710421, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/710421 Research Article Higher Prostate Weight Is Inversely Associated with Gleason Score Upgrading in Radical
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Although current American Cancer Society guidelines
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
CONTEMPORARY UPDATE OF PROSTATE CANCER STAGING NOMOGRAMS (PARTIN TABLES) FOR THE NEW MILLENNIUM
 RAPID COMMUNICATION CME ARTICLE CONTEMPORARY UPDATE OF PROSTATE CANCER STAGING NOMOGRAMS (PARTIN TABLES) FOR THE NEW MILLENNIUM ALAN W. PARTIN, LESLIE A. MANGOLD, DANA M. LAMM, PATRICK C. WALSH, JONATHAN
RAPID COMMUNICATION CME ARTICLE CONTEMPORARY UPDATE OF PROSTATE CANCER STAGING NOMOGRAMS (PARTIN TABLES) FOR THE NEW MILLENNIUM ALAN W. PARTIN, LESLIE A. MANGOLD, DANA M. LAMM, PATRICK C. WALSH, JONATHAN
Outcomes Following Negative Prostate Biopsy for Patients with Persistent Disease after Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer
 Clinical Urology Post-radiotherapy Prostate Biopsy for Recurrent Disease International Braz J Urol Vol. 36 (1): 44-48, January - February, 2010 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382010000100007 Outcomes Following Negative
Clinical Urology Post-radiotherapy Prostate Biopsy for Recurrent Disease International Braz J Urol Vol. 36 (1): 44-48, January - February, 2010 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382010000100007 Outcomes Following Negative
NPQR 2018 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Measures 21_18247_LS.
 NPQR 2018 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: NPQR1 MEASURE TITLE: Notification to the Ordering Provider Requesting Myoglobin or CK-MB in the Diagnosis of Suspected
NPQR 2018 Qualified Clinical Data Registry (QCDR) Measures 21_18247_LS MEASURE ID: NPQR1 MEASURE TITLE: Notification to the Ordering Provider Requesting Myoglobin or CK-MB in the Diagnosis of Suspected
Multiparametric MR Imaging of the Prostate after Treatment of Prostate Cancer
 Multiparametric MR Imaging of the Prostate after Treatment of Prostate Cancer RadioGraphics 2018; 38:437 449 Pritesh Patel, MD Melvy S. Mathew, MD Igor Trilisky, MD Aytekin Oto, MD, MBA Jeffrey S. Klein,
Multiparametric MR Imaging of the Prostate after Treatment of Prostate Cancer RadioGraphics 2018; 38:437 449 Pritesh Patel, MD Melvy S. Mathew, MD Igor Trilisky, MD Aytekin Oto, MD, MBA Jeffrey S. Klein,
A schematic of the rectal probe in contact with the prostate is show in this diagram.
 Hello. My name is William Osai. I am a nurse practitioner in the GU Medical Oncology Department at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Today s presentation is Part 2 of the Overview
Hello. My name is William Osai. I am a nurse practitioner in the GU Medical Oncology Department at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Today s presentation is Part 2 of the Overview
MR-US Fusion Guided Biopsy: Is it fulfilling expectations?
 MR-US Fusion Guided Biopsy: Is it fulfilling expectations? Kenneth L. Gage MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Radiology 4 th Annual New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology
MR-US Fusion Guided Biopsy: Is it fulfilling expectations? Kenneth L. Gage MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Interventional Radiology 4 th Annual New Frontiers in Urologic Oncology
Recommendations for the Reporting of Prostate Carcinoma
 Recommendations for the Reporting of Prostate Carcinoma Association of Directors of Anatomic and Surgical Pathology * ADASP Reporting Guidelines It has been evident for decades that pathology reports are
Recommendations for the Reporting of Prostate Carcinoma Association of Directors of Anatomic and Surgical Pathology * ADASP Reporting Guidelines It has been evident for decades that pathology reports are
117 Applying Risk Management Principles to QA in Surgical Pathology: From Principles to Practice. Gregory Flynn MD
 117 Applying Risk Management Principles to QA in Surgical Pathology: From Principles to Practice Gregory Flynn MD 2011 Annual Meeting Las Vegas, NV AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 33 W. Monroe,
117 Applying Risk Management Principles to QA in Surgical Pathology: From Principles to Practice Gregory Flynn MD 2011 Annual Meeting Las Vegas, NV AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR CLINICAL PATHOLOGY 33 W. Monroe,
Interpretive Diagnostic Error Reduction in Surgical Pathology and Cytology
 Interpretive Diagnostic Error Reduction in Surgical Pathology and Cytology Guideline from the College of American Pathologists (CAP) Pathology and Laboratory Quality Center and the Association of Directors
Interpretive Diagnostic Error Reduction in Surgical Pathology and Cytology Guideline from the College of American Pathologists (CAP) Pathology and Laboratory Quality Center and the Association of Directors
Histological Spectrum of Prostatic Adenocarcinomas in Correlation with PSA Values
 Original Research Article Histological Spectrum of Prostatic Adenocarcinomas in Correlation with PSA Values Atchyuta. M 1,*, R. Krishna 2, P. Prema Latha 3, I. V. Renuka 4, V. Tejaswini 5, G. Vahini 6
Original Research Article Histological Spectrum of Prostatic Adenocarcinomas in Correlation with PSA Values Atchyuta. M 1,*, R. Krishna 2, P. Prema Latha 3, I. V. Renuka 4, V. Tejaswini 5, G. Vahini 6
Understanding the risk of recurrence after primary treatment for prostate cancer. Aditya Bagrodia, MD
 Understanding the risk of recurrence after primary treatment for prostate cancer Aditya Bagrodia, MD Aditya.bagrodia@utsouthwestern.edu 423-967-5848 Outline and objectives Prostate cancer demographics
Understanding the risk of recurrence after primary treatment for prostate cancer Aditya Bagrodia, MD Aditya.bagrodia@utsouthwestern.edu 423-967-5848 Outline and objectives Prostate cancer demographics
Protocol for the Examination of TURP Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Prostate 4.0.4.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of this protocol
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Prostate 4.0.4.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of this protocol
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript World J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 February 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
Hyperplastic, Premalignant and Malignant Lesions of the Prostate Gland
 Jehoram Tei Anim, md, FRCPath; Sitara Abdul Sathar, MB; Mohammed Ejaz Bhatti, MSc From the Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait. Address reprint requests and correspondence
Jehoram Tei Anim, md, FRCPath; Sitara Abdul Sathar, MB; Mohammed Ejaz Bhatti, MSc From the Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Kuwait University, Kuwait. Address reprint requests and correspondence
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Case Scenario 1. 4/19/13 Bone Scan: No scintigraphic findings to suggest skeletal metastases.
 Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
The importance of histopathologic review of biopsies in patients with prostate cancer referred to a tertiary uro - oncology center
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (x): 2018 October 10.[Ahead of print] doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2018.0099 The importance of histopathologic review of biopsies in patients with prostate cancer referred to a
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (x): 2018 October 10.[Ahead of print] doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2018.0099 The importance of histopathologic review of biopsies in patients with prostate cancer referred to a
Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified system
 2018 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/18 $32.00 S47 Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified system Jonathan I Epstein 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology, The Johns Hopkins Medical
2018 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/18 $32.00 S47 Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified system Jonathan I Epstein 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology, The Johns Hopkins Medical
Review Article Recent advances in prostate cancer pathology: Gleason grading and beyond
 Pathology International 2016; 66: 260 272 doi:10.1111/pin.12398 Review Article Recent advances in prostate cancer pathology: Gleason grading and beyond Rajal B Shah 1 and Ming Zhou 2 1 Division of Urologic
Pathology International 2016; 66: 260 272 doi:10.1111/pin.12398 Review Article Recent advances in prostate cancer pathology: Gleason grading and beyond Rajal B Shah 1 and Ming Zhou 2 1 Division of Urologic
Cleveland Clinic Laboratories. Anatomic Pathology
 Cleveland Clinic Laboratories Anatomic Pathology OUR MISSION Cleveland Clinic Laboratories contributes to excellent patient care by providing high-quality, comprehensive laboratory testing and patient-focused
Cleveland Clinic Laboratories Anatomic Pathology OUR MISSION Cleveland Clinic Laboratories contributes to excellent patient care by providing high-quality, comprehensive laboratory testing and patient-focused
Accepted Article. Received Date : 04-Dec-2015 Revised Date : 17-Mar-2016 Accepted Date : 27-Mar-2016 Article type : Original Article TITLE PAGE
 Received Date : 04-Dec-2015 Revised Date : 17-Mar-2016 Accepted Date : 27-Mar-2016 Article type : Original Article TITLE PAGE Title: Gleason Grade 4 Prostate Adenocarcinoma Patterns: An Inter-observer
Received Date : 04-Dec-2015 Revised Date : 17-Mar-2016 Accepted Date : 27-Mar-2016 Article type : Original Article TITLE PAGE Title: Gleason Grade 4 Prostate Adenocarcinoma Patterns: An Inter-observer
MEDICAL POLICY Genetic and Protein Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Risk Assessment of
 POLICY: PG0367 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 08/26/16 LAST REVIEW: 09/27/18 MEDICAL POLICY Genetic and Protein Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Risk Assessment of Prostate Cancer GUIDELINES This policy does not certify
POLICY: PG0367 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 08/26/16 LAST REVIEW: 09/27/18 MEDICAL POLICY Genetic and Protein Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Risk Assessment of Prostate Cancer GUIDELINES This policy does not certify
Are Prostate Carcinoma Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar?
 Clinical Urology Are Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (2): 165-171, March - April, 2006 Are Prostate Carcinoma Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? Athanase Billis,
Clinical Urology Are Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (2): 165-171, March - April, 2006 Are Prostate Carcinoma Clinical Stages T1c and T2 Similar? Athanase Billis,
EARLY ONLINE RELEASE
 EARLY ONLINE RELEASE Note: This article was posted on the Archives Web site as an Early Online Release. Early Online Release articles have been peer reviewed, copyedited, and reviewed by the authors. Additional
EARLY ONLINE RELEASE Note: This article was posted on the Archives Web site as an Early Online Release. Early Online Release articles have been peer reviewed, copyedited, and reviewed by the authors. Additional
Upgrading and upstaging in prostate cancer: From prostate biopsy to radical prostatectomy
 MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 2: 1145-1149 Upgrading and upstaging in prostate cancer: From prostate biopsy to radical prostatectomy CAROLINA D'ELIA, MARIA ANGELA CERRUTO, ANTONIO CIOFFI, GIOVANNI NOVELLA,
MOLECULAR AND CLINICAL ONCOLOGY 2: 1145-1149 Upgrading and upstaging in prostate cancer: From prostate biopsy to radical prostatectomy CAROLINA D'ELIA, MARIA ANGELA CERRUTO, ANTONIO CIOFFI, GIOVANNI NOVELLA,
ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS
 Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
Original Research Article Pathology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 ROLE OF PROSTATIC BASAL CELL MARKER IN DIAGNOSIS OF PROSTATIC LESIONS SUBATHRA K* Department of pathology,
PROVIDING TREATMENT INFORMATION FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS
 PROVIDING TREATMENT INFORMATION FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS For patients with localized disease on biopsy* For patients with adverse pathology after prostatectomy Contact the GenomeDx Customer Support
PROVIDING TREATMENT INFORMATION FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS For patients with localized disease on biopsy* For patients with adverse pathology after prostatectomy Contact the GenomeDx Customer Support
Exploitation of Epigenetic Changes to Distinguish Benign from Malignant Prostate Biopsies
 Exploitation of Epigenetic Changes to Distinguish Benign from Malignant Prostate Biopsies Disclosures MDxHealth Scientific Advisor 2 Case Study 54-year-old man referred for a PSA of 7 - Healthy, minimal
Exploitation of Epigenetic Changes to Distinguish Benign from Malignant Prostate Biopsies Disclosures MDxHealth Scientific Advisor 2 Case Study 54-year-old man referred for a PSA of 7 - Healthy, minimal
