Prostate Cancer Grading, Staging and Reporting: An Update Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD
|
|
|
- Laurence Parsons
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Prostate Cancer Grading, Staging and Reporting: An Update Cristina Magi-Galluzzi, MD, PhD Director, Genitourinary Pathology R.J. Tomsich Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Professor of Pathology, Lerner College of Medicine Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
2 Objectives Discuss relevant modifications of Gleason grading system Update on staging of radical prostatectomy (RP) specimens Review essential reporting parameters for cancer-bearing prostate needle biopsies (PBx)
3 Evolution of Gleason grading Based on Minneapolis VA data accumulated in Architecture evaluated at low-medium magnification Combined 1 st and 2 nd most common pattern to arrive at a Gleason score (GS) 2-10 Gleason Era RP More advanced clinical disease Fewer RPs, which were not entirely processed PBx/TUR No PSA screening Prostatic tissue from TUR specimens Needle biopsy (few thick cores) Modern Era RP Increased volume of cases GS included in predictive models Grading of multiple nodules Tertiary pattern PBx Systematic sampling Thin needle PBx Grading multiple cores from different sites New entities, recently described
4 Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma Original Gleason scheme 1967 ISUP modified 2005 ISUP modified 2015
5 Gleason Score 2-4 Diagnosis of GS 2-4 PCA should NOT be made on needle Bx Poor reproducibility even among experts Poor correlation with RP grade GS 2-4 PCA may misguide clinicians/patients into believing that tumor is indolent Most cases diagnosed as GS 2-4 in the past represented adenosis JI Epstein AJSP 2000; JI Epstein et al. AJSP, 2005
6 Evolution of original Gleason patterns 1 and 2 - Circumscribed nodule of uniform, single, separate, closely packed glands - Most cases diagnosed as GS 2-4 in the past represented adenosis
7 Evolution of Gleason pattern ISUP modified 2014 ISUP modified Epstein et al. AJSP 29, 2005 Epstein et al. AJSP 40, 2016 Small well-formed glands Small cribriform lesions: exclude HGPIN with IHC Medium to large sized cribriform glands eliminated Small well-formed glands Branched glands are allowed Small cribriform glands All cribriform glands should be graded as pattern 4 - ISUP, prostate cancer grading, Chicago, % consensus
8 2014 ISUP modified Gleason system pattern 3 Well-formed individual glands, discrete unit Variation is size and shape (microcystic and pseudohyperplastic) Branching glands are allowed in pattern 3
9 Evolution of Gleason pattern ISUP modified Epstein et al. AJSP 29, ISUP modified Epstein et al. AJSP 40, 2016 Large cribriform glands Ill-defined glands with poorly-formed lumens Fused microacinar glands Hypernephroma-like tumors All cribriform, fused, poorly formed and glomeruloid glands Hypernephromatoid term should not be used
10 2014 ISUP modified Gleason system pattern 4 Small cribriform Fused Poorly formed Glomeruloid
11 2014 ISUP modified Gleason system pattern 4 Large cribriform Fused microacinar
12 Gleason pattern 4: poorly formed glands
13 Gleason pattern 4: glomeruloid and cribriform glands
14 Evolution of Gleason pattern ISUP modified Epstein et al. AJSP 40, 2016 single cells Small solid cylinders Solid medium to large nests with rosette-like spaces Unequivocal comedonecrosis, even if focal Single cells solid sheets
15 2015 ISUP modified Gleason system pattern 5
16 Pitfalls Fused glands (modified Gleason pattern 4): May be under-graded when present in small foci On the other hand, careful evaluation of multiple tissue levels may be necessary to determine whether few glands are truly fused or simply tangentially cut Ill-defined glands: Ill-defined glands with poorly formed glandular lumina should be graded as pattern 4 Caution should be applied in distinguishing them from very small well-formed glands (modified Gleason pattern 3)
17 GS 3+3=6 vs. GS 3+4=7
18 GS 3+3=6 vs. GS 3+4=7
19 GS 3+3=6 vs. GS 3+4=7
20 2014 ISUP Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading: Recommendations For a diagnosis of Gleason pattern 4, it needs to be seen at x10 lens magnification - Vote: 78% yes Occasional/seemingly poorly formed or fused glands between well-formed glands is insufficient for a diagnosis of pattern 4 - Vote: 85% yes In cases with borderline morphology between Gleason pattern 3 and pattern 4 and crush artifacts, the lower grade should be favored - Vote: 98% yes
21 Gleason grading of prostate cancer variants Ductal GP4 (GP5 if necrosis present) Sarcomatoid GP5 (glandular component graded separately) Mucinous grading based on its underlying growth pattern extract mucin and grade architecture Signet ring cells GP5 Atrophic GP3 Foamy gland GP3 or 4 (depending on architecture) Pseudohyperplastic GP3 Small cell/ne not graded Squamous not graded Basaloid not graded Intraductal carcinoma not graded (ISUP 2014, WHO 2016)
22 Impact of modified Gleason grading system GS6 is lowest score on PBx (confusing for patients and clinicians) Current GS6 has little propensity to recur or metastasize Several morphologies previously considered pattern 3 are currently assigned a Gleason pattern 4 - GS6 tumors have decreased - GS7 tumors have increased Inter-observer reproducibility and PBx PR concordance have improved GS7 includes patients with different prognosis: - 3+4=7 have better prognosis than 4+3=7
23 New 5-Grade Group system (ISUP & WHO) S Grade group 1 GS 6 Only individual discrete well-formed glands Grade group 2 GS 3+4=7 Predominantly well-formed glands with lesser component of poorly-formed/fused/cribriform glands Grade group 3 GS 4+3=7 Predominantly poorly-formed/fused/cribriform glands with a lesser component of well-formed glands Grade group 4 GS 4+4=8 GS 3+5=8 GS 5+3=8 Only poorly-formed/fused/cribriform glands Predominantly well-formed glands with a lesser component lacking glands Predominantly lacking glands or with a lesser component of well-formed glands Grade group 5 GS 9/10 Lacks gland formation (or with necrosis) with or w/o poorly-formed/fused/cribriform glands Pierorazio et al. BJU Int 2013; Epstein JI et al. AJSP 2016
24 Recurrence-free progression after RP stratified by Bx grade Grade group 1 Grade group 2 Grade group 3 Grade group 4 Grade group 5 Epstein JI et al. Eur Urol 2016
25 RFP following RP stratified by RP grade Grade group 1 Grade group 2 Grade group 3 Grade group 4 Grade group 5
26 Hazard ratio for biochemical recurrence Bx GS HR for BCR* RP GS HR for BCR* Grade group 1 GS 6 Reference GS 6 Reference Grade group 2 GS 3+4=7 2.5 GS 3+4=7 1.9 Grade group 3 GS 4+3=7 5.7 GS 4+3=7 5.1 Grade group 4 GS 4+4=8 9.1 GS 4+4=8 8.0 Grade group 5 GS GS Low risk GS 6 Reference GS 6 Reference Intermediate GS7 3.4 GS 3+4=7 2.7 High risk GS GS 4+3=7 8.5 * Multivariate hazard ratio (HR) for biochemical recurrence (BCR) Epstein JI et al. Eur Urol 2016
27 Independent surgical validation of the new prostate cancer grade-grouping system 3,694 men treated with RP; median follow-up 52.7 months Spratt et al. BJUI 2016
28 Independent validation of the prognostic capacity of PCA grade grouping system for radiation treated patients 847 men treated with definitive external beam radiation at a single center median follow-up 88 months 5-grade group system improved prognostic discrimination for brfs, DMFS, PCSS compared to three-tiered system (GS 6, 7, 8-10) Figure 2 Spratt et al. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 2016
29 Validation of a contemporary PCA grading system using PCA death as outcome 988 men with PCA on PBx were treated conservatively; grade was assigned to each core as well as an overall grade; max. FU 232 mos. Worst Grade Group Overall Grade Group Berney et al. British Journal of Cancer 2016
30 Take home points Diagnosis of GS 2-4 should NOT be made on PBx GS 6 (Grade Group 1) is the lowest grade possible Small well-formed glands should be graded as pattern 3 All cribriform glands should be graded as pattern 4 Glomeruloid, fused and poorly-formed glands should be graded as pattern 4 In cases with borderline morphology between Gleason pattern 3 and pattern 4, the lower grade should be favored New prostate cancer Grade Group system reflects more accurately the prognosis of each group
31 Update on Staging
32 Handling and reporting of RP specimens Handling of RP specimens (Samaratunga et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) - prostate weight without seminal vesicles should be obtained - prostate should be measured in three dimensions - surface of gland should be inked with at least two colors - apex and base regions should be sampled by cone method/sagittal sectioning T2 substaging and PCa volume (van der Kwast et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) - pt2 substages of PCa in RP specimens is optional - some quantitative measure of tumor volume should be obtained - dominant/index tumor likely represents the tumor with highest grade and/or stage
33 Handling and reporting of RP specimens Extraprostatic extension (EPE), lymphovascular invasion (LVI) and locally advanced disease (Magi-Galluzzi et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) - EPE is defined as presence of PCa beyond confines of prostate gland - In posterior, posterolateral, and lateral regions of prostate, PCa admixed with periprostatic adipose tissue is most easily recognized manifestation of EPE - Presence of PCa in skeletal muscle does not constitute EPE - When EPE is identified, location and extent should be documented
34 EPE - Tumor admixed with periprostatic adipose tissue
35 EPE - Tumor at level of or beyond periprostatic adipose tissue
36 EPE - Tumor within loose connective tissue or perineural spaces
37 EPE -Tumor nodule bulging beyond normal prostate contour
38 EPE -Tumor extend beyond contour of normal prostate (apex)
39 Handling and reporting of RP specimens Microscopic bladder neck involvement (Magi-Galluzzi et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) Presence of neoplastic cells within smooth muscle bundles of bladder neck in absence of benign glandular tissue Should be staged as pt3a, not pt4
40 Handling and reporting of RP specimens Lymphovascular invasion (LVI) (Magi-Galluzzi et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) - Unequivocal presence of tumor cells within endothelial-lined spaces with no underlying muscular walls - Documentation of presence of LVI in RP is critical
41 Handling and reporting of RP specimens Seminal vesicles (SVI) involvement (Berney et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) - Tumor invades muscular wall of extraprostatic seminal vesicle - Equivalent to pt3b
42 Handling and reporting of RP specimens Surgical margin involvement (Tan et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) - Tumor (extraprostatic or intraprostatic) that extends to inked surface (surgical tissue plane) of prostate gland - Important to document location and extent of positive margins (linear length)
43 Handling and reporting of RP specimens Lymph nodes (LN) involvement (Berney et al. Mod Pathol 24, 2011) - LN metastasis is important for adequate staging of PCa in RP - Size/diameter of largest metastatic focus appears to be one of most significant predictors of cancer specific survival
44 Reporting minor high-grade pattern (tertiary pattern) on RP specimens If tertiary pattern 5 is >5% on RP, it is assigned as secondary pattern, rather than tertiary pattern: Gleason pattern 4 (60%) + pattern 3 (30%) + pattern 5 (10%) = Gleason score 4+5=9 If tertiary pattern 5 is 5% on RP, it is assigned as tertiary pattern: Gleason pattern 4 (70%) + pattern 3 (25%) + pattern 5 (5%) = Gleason score 4+3=7 with tertiary pattern 5 Tertiary pattern does not impact Grade Groups If only two patterns are present (98% pattern 4 and 2% pattern 5), both are included in final GS
45 Update on Reporting
46 Essential reporting parameters for cancerbearing prostate needle biopsies (PBx) Histologic type (acinar vs. nonacinar and other tumor types) - Ductal adenocarcinoma - Small cell carcinoma - Sarcomatoid carcinoma - Intraductal carcinoma Gleason grade and score Location of positive cores (based on biopsy site) Tumor quantification: - # and % of positive biopsy cores - Linear % or length (mm) of core involved by PCa - Total % or length of carcinoma in all biopsy cores Other (reported only if present) - Perineural invasion (PNI) - Extraprostatic extension (EPE) - Seminal vesicle invasion (SVI)
47 Reporting Limited Secondary Patterns of Lower and Higher Grade and Tertiary Pattern on PBx In a setting of high-grade PCa, ignore lower patterns if <5% High-grade tumor in ANY quantity on PBx (at low to medium magnification) should be included within GS In a setting of three patterns, most common (primary pattern) is added to highest pattern 4 3 <5% Previous GS 4+3= Modified GS 4+4=8 4 pattern 3 5 Previous GS 3+3=6 (tertiary 4/5) ---- Modified GS 3+4=7 or 3+5=8 <5% pattern 3 pattern 4 5 Previous GS 3+4=7 with tertiary Modified GS 3+5=8
48 Reporting % pattern 4 in Bx and RP specimens in which GS7 is highest grade 2014 consensus conference recommended reporting % pattern 4 in GS7 tumors (particularly 3+4), since it may have implications for management (active surveillance, radiation therapy) 3+4=7 PCA with minimal pattern 4 (<5%) on PBx is associated with low-risk tumor on RP (Huang et al. AJSP 2014, Kir at al. Ann Diagn Pathol 2016) Since cribriform morphology is associated with worse prognosis, cribriform glands may be incorporated in into grading practice in the future Large cribriform pattern 4 and IDC-P are significant prognostic factors in determining outcome (Trudel D et al. Eur J Cancer. 2014, Flood et al. Virchows Arch 2016) JI Epstein et al. AJSP 2017
49 Reporting GS7 PCA on Needle Biopsy Prostate, left base, biopsy (A) - Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Gleason score 3+4=7 (Grade Group 2), involving 10% of one of two cores and measuring 1 mm. Gleason pattern 4 represents approximately 5% of the tumor Cribriform pattern 4 is not identified Prostate left mid, biopsy (B) - Benign prostatic tissue. Prostate, left apex, biopsy (C) - Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Gleason score 3+4=7 (Grade Group 2), involving 20% of one of two cores and measuring 2 mm. Gleason pattern 4 represents approximately 10% of the tumor Cribriform pattern 4 is identified
50 Tumor quantification in PBx Fraction of positive cores (# of biopsy cores involved by PCa out of total number of cores) Linear extent (% or mm) of cancer length in each core Total % or length of cancer in all biopsy cores Greatest % or length of cancer involvement Amount of cancer in single core with largest amount of tumor ^ fragmentation may preclude accurate assessment From Montironi el al. Eur Urol 2012
51 Measuring discontinuous foci of PCA on PBx Discontinuous involvement by multiple PCA foci separated by benign tissue No consensus on quantification method: a. Adding foci and ignoring benign intervening prostatic tissue (additive quantification) b. Assessing discontinuous foci as a single focus (linear quantification, end-to-end measurement) Both methods showed excellent correlation with % of tumor at RP; linear quantification improved prediction of PCA extent Discontinuous tumor on PBx often (78%) results from a single tumor focus b a Schultz et al. AJSP 2013; Arias-Stella et al AJSP 2015
52 Perineural invasion (PNI) on PBx Present in 11-37% of PCA on PBx It has been advocated as a marker of EPE; its independent value as a predictor of stage has not been established Despite variable findings, PNI is reported by a large majority of pathologists; it should be reported if identified (CAP protocol)
53 EPE on needle core biopsy
54 Seminal vesicles (SV) invasion on PBx SV Bx in PCa staging is controversial, but may alter treatment decisions Intermediate- and highrisk patients who elect RT may undergo SV Bx (~ 10% are +) Patients with SV invasion can be managed by a combined approach of seed implantation + EBRT Stone et al. Brachytherapy 2012
55 Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P) Distinct entity in 2016 WHO Malignant secretory cells that grow within and expand prostatic ducts/acini Associated with adverse prognostic features at RP: - High GS, large tumor, EPE, SVI, + margins Independent predictor of outcome - poor response to ADT and neoadjuvant chemo - associated with early recurrence after XRT
56 Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P) 17% of RP cases 2.8% of PBx with high-grade invasive PCA (mean GS 8) % of PBx without invasive PCA p63/erg
57 IDC-P on PBx: reporting recommendations IDC-P + invasive PCA Gleason pattern 4 or 5: - Reporting IDC-P provides prognostic information IDC-P + invasive PCA Gleason pattern 3: - Grade PCA and document presence of IDC-P - Recommend re-biopsy within 3 months or definitive therapy Isolated IDC-P: - Grading is NOT recommended - Report with a comment (clinical significance) - Recommend re-biopsy within 3 months or definitive therapy (depending on extension)
58 Take home message Pathologist s role is not limited to accurate PCA diagnosis, but includes reporting essential elements useful to estimate its malignant potential Pathological parameters need to be: - Accurate - Reproducible - Consistently reported to improve and individualize patient s treatment
59 Thank you!
3/23/2017. Significant Changes in Prostate Cancer Classification, Grading, Staging and Reporting. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Staging and Reporting of Prostate Cancer: Major Changes in 8 th Edition AJCC Staging and CAP Cancer Checklists USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Staging and Reporting of Prostate Cancer: Major Changes in 8 th Edition AJCC Staging and CAP Cancer Checklists USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017
 Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
S1.04 Principal clinician. G1.01 Comments. G2.01 *Specimen dimensions (prostate) S2.02 *Seminal vesicles
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Sex Male
Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology
 PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology and prognosis including variant pathology No Conflict of Interest Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona F.Algaba Section of Pathology PROSTATE CANCER Diagnosis, pathology
Update on Reporting Prostate Cancer Pathology
 Update on Reporting Prostate Cancer Pathology Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON None Disclosures Learning Objectives
Update on Reporting Prostate Cancer Pathology Dr. Andrew J. Evans MD, PhD, FACP, FRCPC Consultant in Genitourinary Pathology University Health Network, Toronto, ON None Disclosures Learning Objectives
Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent Changes and Refinements
 USPSTF: 2012 Report on serum PSA Screening Recommendation rating of D Reduced screening, Reduced biopsies, reduced incidence Refinements currently occurring in 2017. WHY? Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent
USPSTF: 2012 Report on serum PSA Screening Recommendation rating of D Reduced screening, Reduced biopsies, reduced incidence Refinements currently occurring in 2017. WHY? Grading Prostate Cancer: Recent
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE. Jonathan I. Epstein
 INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
INTRADUCTAL LESIONS OF THE PROSTATE Jonathan I. Epstein Topics Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) Intraductal adenocarcinoma (IDC-P) Intraductal urothelial carcinoma Ductal adenocarcinoma High Prostatic
ACCME/Disclosures. Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate. Case
 Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
Cribriform Lesions of the Prostate Ming Zhou, MD, PhD Departments of Pathology and Urology New York University Langone Medical Center New York, NY Ming.Zhou@NYUMC.ORG ACCME/Disclosures The USCAP requires
S1.04 PRINCIPAL CLINICIAN G1.01 COMMENTS S2.01 SPECIMEN LABELLED AS G2.01 *SPECIMEN DIMENSIONS (PROSTATE) S2.03 *SEMINAL VESICLES
 Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Prostate Cancer Histopathology Reporting Proforma (Radical Prostatectomy) Includes the International Collaboration on Cancer reporting dataset denoted by * Family name Given name(s) Date of birth Indigenous
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1)
 Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Prostate Pathology: Prostate Carcinoma, variants and Gleason Grading (Part 1) Jae Y. Ro, MD, PhD June 7, 2012 Ten Leading Cancer Types for the Estimated New Cancer Cases and Deaths By Sex, United States,
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 Includes ptnm requirements from the 8 th Edition, AJCC Staging Manual
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE. Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT
 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE Peter A. Humphrey, MD, PhD Yale University School of Medicine New Haven, CT 2016 WHO CLASSIFICATION OF TUMOURS OF THE PROSTATE AUTHORS : PROSTATE CHAPTER
Prostate cancer staging and datasets: The Nitty-Gritty. What determines our pathological reports? 06/07/2018. Dan Berney Maastricht 2018
 Prostate cancer staging and datasets: The Nitty-Gritty What determines our pathological reports? Dan Berney Maastricht 2018 Biopsy reporting. How not to do it. The TNM 8 th edition. Changes good and bad
Prostate cancer staging and datasets: The Nitty-Gritty What determines our pathological reports? Dan Berney Maastricht 2018 Biopsy reporting. How not to do it. The TNM 8 th edition. Changes good and bad
Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA
 Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA Learners Objectives u Latest changes per ISUP 2014 that impact
Gleason Scoring System 2017 JASREMAN DHILLON, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMIC PATHOLOGY, MOFFITT CANCER CENTER, TAMPA, FLORIDA Learners Objectives u Latest changes per ISUP 2014 that impact
PSA. HMCK, p63, Racemase. HMCK, p63, Racemase
 Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Case 1 67 year old male presented with gross hematuria H/o acute prostatitis & BPH Urethroscopy: small, polypoid growth with a broad base emanating from the left side of the verumontanum Serum PSA :7 ng/ml
Percent Gleason pattern 4 in stratifying the prognosis of patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer
 Review Article Percent Gleason pattern 4 in stratifying the prognosis of patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer Meenal Sharma 1, Hiroshi Miyamoto 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Review Article Percent Gleason pattern 4 in stratifying the prognosis of patients with intermediate-risk prostate cancer Meenal Sharma 1, Hiroshi Miyamoto 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
Procedures Needle Biopsy Transurethral Prostatic Resection Suprapubic or Retropubic Enucleation (Subtotal Prostatectomy) Radical Prostatectomy
 Prostate Gland Protocol applies to invasive carcinomas of the prostate gland. Protocol web posting date: July 2006 Protocol effective date: April 2007 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Needle
Prostate Gland Protocol applies to invasive carcinomas of the prostate gland. Protocol web posting date: July 2006 Protocol effective date: April 2007 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition Procedures Needle
In 2005, International Society of Urological Pathology
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason Score 3+4=7 Prostate Cancer With Minimal Quantity of Gleason Pattern 4 on Needle Biopsy Is Associated With Low-risk Tumor in Radical Prostatectomy Specimen Cheng Cheng Huang, MD,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gleason Score 3+4=7 Prostate Cancer With Minimal Quantity of Gleason Pattern 4 on Needle Biopsy Is Associated With Low-risk Tumor in Radical Prostatectomy Specimen Cheng Cheng Huang, MD,*
OMPRN Pathology Matters Meeting 2017
 OMPRN Pathology Matters Meeting 2017 Pathology of Aggressive Prostate Cancer Intraductal Carcinoma and Cribriform Carcinoma Dr. Michelle Downes, Staff Urologic Pathologist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre,
OMPRN Pathology Matters Meeting 2017 Pathology of Aggressive Prostate Cancer Intraductal Carcinoma and Cribriform Carcinoma Dr. Michelle Downes, Staff Urologic Pathologist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre,
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland
 Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: ProstateBiopsy 4.0.3.1 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use
Protocol for the Examination of Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: ProstateBiopsy 4.0.3.1 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use
They Do Look Alike : Mimics of Prostate Cancer in Biopsy Samples
 They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
They Do Look Alike : in Biopsy Samples Gladell P. Paner, MD Departments of Pathology and Surgery (Urology) University of Chicago, IL USA Gladell.paner@uchospitals.edu Benign in Needle Biopsy 1. Benign
Recommendations for the Reporting of Prostate Carcinoma
 Recommendations for the Reporting of Prostate Carcinoma Association of Directors of Anatomic and Surgical Pathology * ADASP Reporting Guidelines It has been evident for decades that pathology reports are
Recommendations for the Reporting of Prostate Carcinoma Association of Directors of Anatomic and Surgical Pathology * ADASP Reporting Guidelines It has been evident for decades that pathology reports are
Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified system
 2018 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/18 $32.00 S47 Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified system Jonathan I Epstein 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology, The Johns Hopkins Medical
2018 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/18 $32.00 S47 Prostate cancer grading: a decade after the 2005 modified system Jonathan I Epstein 1,2,3 1 Department of Pathology, The Johns Hopkins Medical
Protocol for the Examination of TURP Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Prostate 4.0.4.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of this protocol
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: Prostate 4.0.4.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 Accreditation Requirements The use of this protocol
Case Discussions: Prostate Cancer
 Case Discussions: Prostate Cancer Andrew J. Stephenson, MD FRCSC FACS Chief, Urologic Oncology Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic Elevated PSA 1 54 yo, healthy male, family Hx of
Case Discussions: Prostate Cancer Andrew J. Stephenson, MD FRCSC FACS Chief, Urologic Oncology Glickman Urological and Kidney Institute Cleveland Clinic Elevated PSA 1 54 yo, healthy male, family Hx of
3/28/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference. Differential Diagnosis:
 GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
GU Evening Subspecialty Case Conference Rajal B. Shah, M.D. VP, Medical Director, Urologic Pathology Miraca Life Sciences, Irving, Texas Clinical Associate Professor of Pathology Baylor College of Medicine,
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013.
 A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
A re-audit of Prostate biopsies from January to December 2010 and 2013. Dr. M S Siddiqui Consultant Histopathologist University Hospital of North Tees Stockton on Tees. Objectives To assess and compare
Review Article Recent advances in prostate cancer pathology: Gleason grading and beyond
 Pathology International 2016; 66: 260 272 doi:10.1111/pin.12398 Review Article Recent advances in prostate cancer pathology: Gleason grading and beyond Rajal B Shah 1 and Ming Zhou 2 1 Division of Urologic
Pathology International 2016; 66: 260 272 doi:10.1111/pin.12398 Review Article Recent advances in prostate cancer pathology: Gleason grading and beyond Rajal B Shah 1 and Ming Zhou 2 1 Division of Urologic
Introduction. Key Words: high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, HGPIN, radical prostatectomy, prostate biopsy, insignificant prostate cancer
 Prostate cancer after initial high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and benign prostate biopsy Premal Patel, MD, 1 Jasmir G. Nayak, MD, 1,2 Zlatica Biljetina, MD, 4 Bryan Donnelly, MD 3, Kiril
Prostate cancer after initial high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and benign prostate biopsy Premal Patel, MD, 1 Jasmir G. Nayak, MD, 1,2 Zlatica Biljetina, MD, 4 Bryan Donnelly, MD 3, Kiril
TOPICS FOR DISCUSSION
 INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF UROLOGIC PATHOLOGY PATHOLOGIC STAGING OF SELECT UROLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Mahul B. Amin, MD Professor and Chairman Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los
INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF UROLOGIC PATHOLOGY PATHOLOGIC STAGING OF SELECT UROLOGIC MALIGNANCIES Mahul B. Amin, MD Professor and Chairman Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los
Radical prostatectomy is the most widely used treatment. Partial Sampling of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of Positive Margins and Extraprostatic Extension Viacheslav Iremashvili, MD, PhD,* Soum D. Lokeshwar,* Mark S. Soloway, MD,* Lise tpelaez,md,w Saleem A. Umar, MD,w Murugesan
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of Positive Margins and Extraprostatic Extension Viacheslav Iremashvili, MD, PhD,* Soum D. Lokeshwar,* Mark S. Soloway, MD,* Lise tpelaez,md,w Saleem A. Umar, MD,w Murugesan
A schematic of the rectal probe in contact with the prostate is show in this diagram.
 Hello. My name is William Osai. I am a nurse practitioner in the GU Medical Oncology Department at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Today s presentation is Part 2 of the Overview
Hello. My name is William Osai. I am a nurse practitioner in the GU Medical Oncology Department at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. Today s presentation is Part 2 of the Overview
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Prediction of Prostate Cancer Recurrence using Quantitative Phase Imaging Shamira Sridharan 1, Virgilia Macias 2, Krishnarao Tangella 3, André Kajdacsy-Balla 2 and Gabriel Popescu
Supplemental Information Prediction of Prostate Cancer Recurrence using Quantitative Phase Imaging Shamira Sridharan 1, Virgilia Macias 2, Krishnarao Tangella 3, André Kajdacsy-Balla 2 and Gabriel Popescu
Protocol for the Examination of Radical Prostatectomy Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland
 Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: ProstateRadicalProstatectomy 4.0.4.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 CAP Laboratory Accreditation
Protocol for the Examination of Specimens From Patients With Carcinoma of the Prostate Gland Version: ProstateRadicalProstatectomy 4.0.4.0 Protocol Posting Date: February 2019 CAP Laboratory Accreditation
ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY. Jonathan I. Epstein.
 1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
Case Scenario 1. 4/19/13 Bone Scan: No scintigraphic findings to suggest skeletal metastases.
 Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Case Scenario 1 3/8/13 H&P 68 YR W/M presents w/elevated PSA. Patient is a non-smoker, current alcohol use. Physical Exam: On digital rectal exam the sphincter tone is normal and there is a 1 cm nodule
Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma
 http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
Disease-specific death and metastasis do not occur in patients with Gleason score 6 at radical prostatectomy
 Disease-specific death and metastasis do not occur in patients with at radical prostatectomy Charlotte F. Kweldam, Mark F. Wildhagen*, Chris H. Bangma* and Geert J.L.H. van Leenders Departments of Pathology,
Disease-specific death and metastasis do not occur in patients with at radical prostatectomy Charlotte F. Kweldam, Mark F. Wildhagen*, Chris H. Bangma* and Geert J.L.H. van Leenders Departments of Pathology,
5/21/2018. Difficulty in Underdiagnosing Prostate Cancer. Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Evaluation of Prostate Cancer and Atypical on Needle Biopsy
 Evaluation of Prostate Cancer and Atypical on Needle Biopsy Jonathan I. Epstein Difficulty in Underdiagnosing Prostate Cancer Limited tissue on needle biopsy (1 cm. x
Evaluation of Prostate Cancer and Atypical on Needle Biopsy Jonathan I. Epstein Difficulty in Underdiagnosing Prostate Cancer Limited tissue on needle biopsy (1 cm. x
Supplemental Figure 1
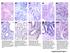 A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
A1 A A5 A7 A9 A A4 A6 A8 A10 A1/A Gleason Score +=6 A/A4 Gleason Score +=6 Small glands with well defined Prominent feature of size variation lumen of various size infiltrating in to and distinct lumina
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues
 A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
Accuracy of post-radiotherapy biopsy before salvage radical prostatectomy
 Accuracy of post-radiotherapy biopsy before salvage radical prostatectomy Joshua J. Meeks, Marc Walker*, Melanie Bernstein, Matthew Kent and James A. Eastham Urology Service, Department of Surgery and
Accuracy of post-radiotherapy biopsy before salvage radical prostatectomy Joshua J. Meeks, Marc Walker*, Melanie Bernstein, Matthew Kent and James A. Eastham Urology Service, Department of Surgery and
Prostate Cancer: 2010 Guidelines Update
 Prostate Cancer: 2010 Guidelines Update James L. Mohler, MD Chair, NCCN Prostate Cancer Panel Associate Director for Translational Research, Professor and Chair, Department of Urology, Roswell Park Cancer
Prostate Cancer: 2010 Guidelines Update James L. Mohler, MD Chair, NCCN Prostate Cancer Panel Associate Director for Translational Research, Professor and Chair, Department of Urology, Roswell Park Cancer
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency
 Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Updates in Urologic Pathology WHO Made Those Changes?! Peyman Tavassoli Pathology Department BC Cancer Agency World Health Organization Available in Feb 2016 Frame work for reporting Major contributing
Disclosures. Outline. What IS tumor budding?? Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How. I have nothing to disclose
 Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Tumor Budding in Colorectal Carcinoma: What, Why, and How Disclosures I have nothing to disclose Soo-Jin Cho, MD, PhD Assistant Professor UCSF Dept of Pathology Current Issues in Anatomic Pathology 2017
Pathology of the Prostate. PathoBasic Tatjana Vlajnic
 Pathology of the Prostate PathoBasic 24.01.17 Tatjana Vlajnic Overview Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Grading Special variants Mimickers of prostate adenocarcinoma Atrophy Inflammatory conditions Granulomatous
Pathology of the Prostate PathoBasic 24.01.17 Tatjana Vlajnic Overview Adenocarcinoma of the prostate Grading Special variants Mimickers of prostate adenocarcinoma Atrophy Inflammatory conditions Granulomatous
The Role of the Pathologist Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer
 The Role of the Pathologist Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer Thomas M. Wheeler, M.D. W. L. Moody, Jr., Professor and Chair Department of Pathology & Immunology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
The Role of the Pathologist Active Surveillance for Prostate Cancer Thomas M. Wheeler, M.D. W. L. Moody, Jr., Professor and Chair Department of Pathology & Immunology Baylor College of Medicine Houston,
Update on staging colorectal carcinoma, the 8 th edition AJCC. General overview of staging. When is staging required? 11/1/2017
 Update on staging colorectal carcinoma, the 8 th edition AJCC Dale C. Snover, MD November 3, 2017 General overview of staging Reason for uniform staging Requirements to use AJCC manual and/or CAP protocols
Update on staging colorectal carcinoma, the 8 th edition AJCC Dale C. Snover, MD November 3, 2017 General overview of staging Reason for uniform staging Requirements to use AJCC manual and/or CAP protocols
When PSA fails. Urology Grand Rounds Alexandra Perks. Rising PSA after Radical Prostatectomy
 When PSA fails Urology Grand Rounds Alexandra Perks Rising PSA after Radical Prostatectomy Issues Natural History Local vs Metastatic Treatment options 1 10 000 men / year in Canada 4000 RRP 15-year PSA
When PSA fails Urology Grand Rounds Alexandra Perks Rising PSA after Radical Prostatectomy Issues Natural History Local vs Metastatic Treatment options 1 10 000 men / year in Canada 4000 RRP 15-year PSA
Outline (1) Outline (2) Concepts in Prostate Pathology. Peculiarities of Prostate Cancer. Peculiarities of Prostate Cancer
 Concepts in Prostate Pathology Murali Varma Cardiff, UK wptmv@cf.ac.uk Sarajevo Nov 2013 Outline (1) Peculiarities of prostate cancer Peculiarities of prostate needle biopsy Needle bx vs. TURP Prostate
Concepts in Prostate Pathology Murali Varma Cardiff, UK wptmv@cf.ac.uk Sarajevo Nov 2013 Outline (1) Peculiarities of prostate cancer Peculiarities of prostate needle biopsy Needle bx vs. TURP Prostate
Definition of Synoptic Reporting
 Definition of Synoptic Reporting The CAP has developed this list of specific features that define synoptic reporting formatting: 1. All required cancer data from an applicable cancer protocol that are
Definition of Synoptic Reporting The CAP has developed this list of specific features that define synoptic reporting formatting: 1. All required cancer data from an applicable cancer protocol that are
Staging Challenges in Lower GI Cancers. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. AJCC 8 th edition and CAP protocol updates
 Staging Challenges in Lower GI Cancers Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco March 05, 2017 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Staging Challenges in Lower GI Cancers Sanjay Kakar, MD University of California, San Francisco March 05, 2017 Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Handling and Staging Radical Prostatectomy Specimens: Recommendations from the 2009 ISUP Consensus Conference
 Handling and Staging Radical Prostatectomy Specimens: Recommendations from the 2009 ISUP Consensus Conference Lars Egevad Dept of oncology-pathology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden The clinical
Handling and Staging Radical Prostatectomy Specimens: Recommendations from the 2009 ISUP Consensus Conference Lars Egevad Dept of oncology-pathology, Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden The clinical
Evaluation of prognostic factors after radical prostatectomy in pt3b prostate cancer patients in Japanese population
 Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2015, 45(8) 780 784 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv077 Advance Access Publication Date: 15 May 2015 Original Article Original Article Evaluation of prognostic factors after
Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2015, 45(8) 780 784 doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv077 Advance Access Publication Date: 15 May 2015 Original Article Original Article Evaluation of prognostic factors after
Division of Oncology, S Orsola-Malpighi Hospital, Bologna, Italy. Department of Surgery, Cordoba University Medical School, Cordoba, Spain
 Prostate cancer glands with cribriform architecture and with glomeruloid features should be considered as Gleason pattern 4 and not pattern 3 Daniele Minardi,1, Roberta Mazzucchelli,, Marina Scarpelli,
Prostate cancer glands with cribriform architecture and with glomeruloid features should be considered as Gleason pattern 4 and not pattern 3 Daniele Minardi,1, Roberta Mazzucchelli,, Marina Scarpelli,
5/21/2018. Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma. Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology. Jonathan I.
 Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Common Differential Diagnoses in Urological Pathology Jonathan I. Epstein Prostate Adenocarcinoma vs. Urothelial Carcinoma 1 2 NKX3.1 NKX3.1 3 4 5 6 Proposed ISUP Recommendations Option to use PSA as a
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
PROGNOSTIC ROLE OF NEW CONTEMPORARY GRADING SYSTEM IN PROSTATE CANCER
 ejpmr, 2016,3(9), 243-250. Lakkarasu et al. SJIF Impact Factor 3.628 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF European PHARMACEUTICAL Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical Research AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN
ejpmr, 2016,3(9), 243-250. Lakkarasu et al. SJIF Impact Factor 3.628 Research Article EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF European PHARMACEUTICAL Journal of Pharmaceutical and Medical Research AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN
Session Number: 1020 Session: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix: Diagnostic Pitfalls and New Prognostic Implications. Andres A. Roma, MD Cleveland Clinic
 Session Number: 1020 Session: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix: Diagnostic Pitfalls and New Prognostic Implications Andres A. Roma, MD Cleveland Clinic No Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have not had
Session Number: 1020 Session: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix: Diagnostic Pitfalls and New Prognostic Implications Andres A. Roma, MD Cleveland Clinic No Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have not had
Prostate Case Scenario 1
 Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Prostate Case Scenario 1 H&P 5/12/16: A 57-year-old Hispanic male presents with frequency of micturition, urinary urgency, and hesitancy associated with a weak stream. Over the past several weeks, he has
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Gleason grading and prognostic factors in carcinoma of the prostate
 & 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org in carcinoma of the prostate Peter A Humphrey Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine,
& 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $25.00 www.modernpathology.org in carcinoma of the prostate Peter A Humphrey Department of Pathology and Immunology, Washington University School of Medicine,
Case Scenario 1: Breast
 Case Scenario 1: Breast A 63 year old white female presents with a large mass in her left breast. 4/15/13 Mammogram/US: 1. Left breast mammographic and sonographic at 3:00 measuring 7.1 cm highly suggestive
Case Scenario 1: Breast A 63 year old white female presents with a large mass in her left breast. 4/15/13 Mammogram/US: 1. Left breast mammographic and sonographic at 3:00 measuring 7.1 cm highly suggestive
Providing Treatment Information for Prostate Cancer Patients
 Providing Treatment Information for Prostate Cancer Patients For all patients with localized disease on biopsy For all patients with adverse pathology after prostatectomy See what better looks like Contact
Providing Treatment Information for Prostate Cancer Patients For all patients with localized disease on biopsy For all patients with adverse pathology after prostatectomy See what better looks like Contact
Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An aggressive variant that is underdiagnosed and undersampled on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided needle biopsy
 Original research Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An aggressive variant that is underdiagnosed and undersampled on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided needle biopsy Previn Gulavita, MD; * Shaheed W.
Original research Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma: An aggressive variant that is underdiagnosed and undersampled on transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided needle biopsy Previn Gulavita, MD; * Shaheed W.
SEER Summary Stage Still Here!
 SEER Summary Stage Still Here! CCRA NORTHERN REGION STAGING SYMPOSIUM SEPTEMBER 20, 2017 SEER Summary Stage Timeframe: includes all information available through completion of surgery(ies) in the first
SEER Summary Stage Still Here! CCRA NORTHERN REGION STAGING SYMPOSIUM SEPTEMBER 20, 2017 SEER Summary Stage Timeframe: includes all information available through completion of surgery(ies) in the first
Update on 2015 WHO Classification of Lung Adenocarcinoma 1/3/ Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. All rights reserved.
 1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
1 Our speaker for this program is Dr. Anja Roden, an associate professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology at Mayo Clinic as well as consultant in the Anatomic Pathology Laboratory and co-director of
Large blocks in prostate and bladder pathology
 Large blocks in prostate and bladder pathology Farkas Sükösd Department of Pathology, University of Szeged The history of the large block technique in radical prostatectomy and cystectomy The first large
Large blocks in prostate and bladder pathology Farkas Sükösd Department of Pathology, University of Szeged The history of the large block technique in radical prostatectomy and cystectomy The first large
Standards and Datasets for Reporting Cancers. Dataset for histopathology reports for prostatic carcinoma (2 nd edition) October 2009
 Standards and Datasets for Reporting Cancers Dataset for histopathology reports for prostatic carcinoma (2 nd edition) October 2009 Unique document number Document name G084 Dataset for histopathology
Standards and Datasets for Reporting Cancers Dataset for histopathology reports for prostatic carcinoma (2 nd edition) October 2009 Unique document number Document name G084 Dataset for histopathology
VULVAR CARCINOMA. Page 1 of 5
 VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
VULVAR CARCINOMA EXAMPLE OF A VULVAR CARCINOMA USING PROPOSED TEMPLATE Case: Invasive squamous cell carcinoma arising in D-VIN Tumor in left labia major Left partial vaginectomy and sentinel lymph node
PROSTATE CANCER (RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY) STRUCTURED REPORTING PROTOCOL (3rd Edition 2018)
 PROSTATE CANCER (RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY) STRUCTURED REPORTING PROTOCOL (3rd Edition 2018) Incorporating the: International Collaboration on Cancer Reporting (ICCR) Prostate Cancer - Radical Prostatectomy
PROSTATE CANCER (RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY) STRUCTURED REPORTING PROTOCOL (3rd Edition 2018) Incorporating the: International Collaboration on Cancer Reporting (ICCR) Prostate Cancer - Radical Prostatectomy
Although current American Cancer Society guidelines
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffuse Adenosis of the Peripheral Zone in Prostate Needle Biopsy and Prostatectomy Specimens Tamara L. Lotan, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract: We have observed a group of
IRANIAN MEDICINE. Original Article
 Arch Iran Med. vember 2018;21(11):518-523 http www.aimjournal.ir Original Article ARCHIVES OF IRANIAN MEDICINE Open Access Correlation of Prognostic Gleason Grade Grouping and Histopathological Parameters:
Arch Iran Med. vember 2018;21(11):518-523 http www.aimjournal.ir Original Article ARCHIVES OF IRANIAN MEDICINE Open Access Correlation of Prognostic Gleason Grade Grouping and Histopathological Parameters:
Prognostic value of the Gleason score in prostate cancer
 BJU International (22), 89, 538 542 Prognostic value of the Gleason score in prostate cancer L. EGEVAD, T. GRANFORS*, L. KARLBERG*, A. BERGH and P. STATTIN Department of Pathology and Cytology, Karolinska
BJU International (22), 89, 538 542 Prognostic value of the Gleason score in prostate cancer L. EGEVAD, T. GRANFORS*, L. KARLBERG*, A. BERGH and P. STATTIN Department of Pathology and Cytology, Karolinska
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Evaluation of the 7th American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM Staging System for Prostate Cancer in Point of Classification of Bladder Neck Invasion
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2013;43(2)184 188 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys196 Advance Access Publication 5 December 2012 Evaluation of the 7th American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM Staging System for Prostate Cancer in
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2013;43(2)184 188 doi:10.1093/jjco/hys196 Advance Access Publication 5 December 2012 Evaluation of the 7th American Joint Committee on Cancer TNM Staging System for Prostate Cancer in
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Q&A. Overview. Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate. Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate 5/5/2011. NAACCR Webinar Series 1
 Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series May 5, 2011 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel Overview NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series 1
Collecting Cancer Data: Prostate NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series May 5, 2011 Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel Overview NAACCR 2010-2011 Webinar Series 1
Short ( 1 mm) positive surgical margin and risk of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy
 Short ( 1 mm) positive surgical margin and risk of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy Sergey Shikanov, Pablo Marchetti, Vikas Desai, Aria Razmaria, Tatjana Antic, Hikmat Al-Ahmadie*, Gregory
Short ( 1 mm) positive surgical margin and risk of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy Sergey Shikanov, Pablo Marchetti, Vikas Desai, Aria Razmaria, Tatjana Antic, Hikmat Al-Ahmadie*, Gregory
Prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma is a subtype of
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasialike Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Clinicopathologic Study of 28 Cases Fabio Tavora, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasialike Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Clinicopathologic Study of 28 Cases Fabio Tavora, MD* and Jonathan I. Epstein, MD*w z Abstract:
Lymphadenectomy in RCC: Yes, No, Clinical Trial?
 Lymphadenectomy in RCC: Yes, No, Clinical Trial? Viraj Master MD PhD FACS Professor Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs and Quality Director of Clinical Research Unit Department of Urology Emory University
Lymphadenectomy in RCC: Yes, No, Clinical Trial? Viraj Master MD PhD FACS Professor Associate Chair for Clinical Affairs and Quality Director of Clinical Research Unit Department of Urology Emory University
PROSTATE CANCER (CORE/NEEDLE BIOPSY) STRUCTURED REPORTING PROTOCOL (2nd Edition 2018)
 PROSTATE CANCER (CORE/NEEDLE BIOPSY) STRUCTURED REPORTING PROTOCOL (2nd Edition 2018) Incorporating the: International Collaboration on Cancer Reporting (ICCR) Prostate Cancer Core Needle Biopsy Specimen
PROSTATE CANCER (CORE/NEEDLE BIOPSY) STRUCTURED REPORTING PROTOCOL (2nd Edition 2018) Incorporating the: International Collaboration on Cancer Reporting (ICCR) Prostate Cancer Core Needle Biopsy Specimen
Understanding the risk of recurrence after primary treatment for prostate cancer. Aditya Bagrodia, MD
 Understanding the risk of recurrence after primary treatment for prostate cancer Aditya Bagrodia, MD Aditya.bagrodia@utsouthwestern.edu 423-967-5848 Outline and objectives Prostate cancer demographics
Understanding the risk of recurrence after primary treatment for prostate cancer Aditya Bagrodia, MD Aditya.bagrodia@utsouthwestern.edu 423-967-5848 Outline and objectives Prostate cancer demographics
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017
 Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Prostate MRI: Who needs it?
 Prostate MRI: Who needs it? Fergus Coakley MD, Professor of Radiology and Urology, Vice Chair for Clinical Services, Chief of Abdominal Imaging, UCSF Abdominal Imaging Magnetic Resonance Science Center
Prostate MRI: Who needs it? Fergus Coakley MD, Professor of Radiology and Urology, Vice Chair for Clinical Services, Chief of Abdominal Imaging, UCSF Abdominal Imaging Magnetic Resonance Science Center
PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA
 PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA 1 A good H & E helps! ADENOCARCINOMA DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Relatively uniform proliferation
PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA AND IMPORTANT MIMICKERS PROSTATIC ADENOCARCINOMA: DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA 1 A good H & E helps! ADENOCARCINOMA DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Relatively uniform proliferation
OPEN ACCESS ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 OPEN ACCESS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Interobserver Variability of Gleason Score and Completeness of Histopathology Report in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma in Prostate Needle Biopsy Specimens among General Pathologists
OPEN ACCESS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Interobserver Variability of Gleason Score and Completeness of Histopathology Report in Prostatic Adenocarcinoma in Prostate Needle Biopsy Specimens among General Pathologists
Disclosures. The Importance of Pathology? Pathologic, Morphologic and Clinical Features. Pathologic Reproducibility
 The Importance of Pathology? Seth P. Lerner, MD, FACS Beth and Dave Swalm Chair in Urologic Oncology Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Support for research Disclosures Photocure, Imalux,
The Importance of Pathology? Seth P. Lerner, MD, FACS Beth and Dave Swalm Chair in Urologic Oncology Scott Department of Urology Baylor College of Medicine Support for research Disclosures Photocure, Imalux,
6/5/2010. Renal vein invasion & Capsule Penetration (T3a) Adrenal Gland involvement (T4 vs. M1) Beyond Gerota s Fascia? (?T4).
 GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition. Prostate Chapter 58. Executive Committee, AJCC. Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center
 AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition Prostate Chapter 58 Judd W Moul, MD, FACS Executive Committee, AJCC Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center Duke University Durham, North Carolina Validating science.
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th Edition Prostate Chapter 58 Judd W Moul, MD, FACS Executive Committee, AJCC Professor and Director, Duke Prostate Center Duke University Durham, North Carolina Validating science.
Ground Glass Opacities
 Ground Glass Opacities A pathologist s perspective Marie-Christine Aubry, M.D. Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic Objectives Discuss the proposed new pathologic classification of adenocarcinoma with historical
Ground Glass Opacities A pathologist s perspective Marie-Christine Aubry, M.D. Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic Objectives Discuss the proposed new pathologic classification of adenocarcinoma with historical
BIOCHEMICAL RECURRENCE POST RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY
 BIOCHEMICAL RECURRENCE POST RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY AZHAN BIN YUSOFF AZHAN BIN YUSOFF 2013 SCENARIO A 66 year old man underwent Robotic Radical Prostatectomy for a T1c Gleason 4+4, PSA 15 ng/ml prostate
BIOCHEMICAL RECURRENCE POST RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY AZHAN BIN YUSOFF AZHAN BIN YUSOFF 2013 SCENARIO A 66 year old man underwent Robotic Radical Prostatectomy for a T1c Gleason 4+4, PSA 15 ng/ml prostate
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 369 373 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial Original Gleason System Versus 2005 ISUP Modified Gleason System: The Importance
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 58 (2010) 369 373 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Editorial Original Gleason System Versus 2005 ISUP Modified Gleason System: The Importance
BLADDER CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY
 BLADDER CANCER WHAT IS NEW AND CLINICALLY RELEVANT Canadian Geese - Geist Reservoir (my backyard), Indianapolis, USA BLADDER CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY Urinary bladder 17,960 2% Urinary bladder 4,390 1.6% Siegel
BLADDER CANCER WHAT IS NEW AND CLINICALLY RELEVANT Canadian Geese - Geist Reservoir (my backyard), Indianapolis, USA BLADDER CANCER EPIDEMIOLOGY Urinary bladder 17,960 2% Urinary bladder 4,390 1.6% Siegel
