Diagnostic value of autofluorescence imaging combined with narrow band imaging in intraepithelial neoplasia of Barrett s esophagus
|
|
|
- Elijah Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JBUON 2015; 20(2): ISSN: , online ISSN: ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic value of autofluorescence imaging combined with narrow band imaging in intraepithelial neoplasia of Barrett s esophagus Nu-Yun Jin1, Kai Wang1, Shuang-Qin Wei1, Yu-Qin Li1, Hong-Wei Wang1, Lei-Ming Xu2, Jian- Ping Shi1 1Department of Digestion, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Fudan University Pudong Medical Center, Shanghai , China; 2Department of Digestive Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment, Xinhua Hospital affiliated to Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai , China Summary Purpose: To evaluate the diagnostic values of Auto Fluorescence Imaging (AFI) combined with Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) in the diagnosis of the intraepithelial neoplasia of Barrett s esophagus (BE). Methods: Seventy four suspicious BE intraepithelial lesions were assessed in 50 patients by AFI, who were further subjected to NBI mode to observe the changes of gastric mucosal capillaries and gastric pits. The corresponding lesions were biopsied for pathological examination. Results: Among the 74 AFI-diagnosed cases of suspicious lesions, 44 (59.5%) were high-grade intraepithelial neoplasias (BE HGIN), while the remaining 30 cases (40.5%) were false-positive. The NBI-diagnostic results of these 44 BE HGIN lesions were as follows: 39 cases were confirmed and 5 were suspicious; among the 30 false-positive BE HGIN cases, NBI gave 7 false-positive cases. The false-positive rates decreased from 40.5% of AFI to 9.5% (7/74) of NBI- AFI (p<0.05). The positive predictive value of AFI in BE HGIN was 59.5% (44/74), while that of AFI-NBI combination was 84.8% (39/46; p<0.05). Conclusions: The AFI-NBI combination technology could significantly improve (p<0.05) the detection rate of BE HGIN. Key words: auto fluorescence imaging, Barrett s esophagus, high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia, narrow band imaging Introduction In Barrett s esophagus (BE) the normal columnar epithelium is gradually replaced by squamous epithelium in the lower segment of esophagus [1], and this could be accompanied with or without intestinal metaplasia. If BE is accompanied with dysplasia, the risk of developing esophageal adenocarcinoma could be high, thus this condition is regarded as a precancerous lesion [2,3]. Conventional electronic endoscopy mainly relies on naked-eye observations under white light, and can find lesions with significant changes in shape or color (e.g. protruded lumps, depressed ulcer, etc.), while it is difficult to diagnose tiny and flat early cancerization and dysplasia. In recent years, with the applications of new optical technologies in the field of endoscopy, the targets of endoscopic observation have been gradually refined. The electronic-staining endoscope includes the AFI and NBI, which could not only overcome the time-consuming problem of conventional staining endoscopy, but also avoid the potential risks of chemical dyeing [4], and could help dis- Correspondence to: Jian-Ping Shi, MD. Department of Digestion, Shanghai Pudong Hospital, Fudan University Pudong Medical Center, No Gongwei Road Pudong New District, Shanghai , China. Tel: , Fax: , jianpingshicn@163.com Received: 29/08/2014; Accepted: 27/09/2014
2 400 Autofluorescene with narrow band imaging in Barrett s esophagus tinguish the normal gastrointestinal mucosa from the lesion tissues, thus improving the detection rate of intraepithelial neoplasia and early cancer [5-8], thus helping a lot to get a successful optical biopsy [9]. In this study, the diagnostic value of AFI-NBI combination in BE intraepithelial neoplasia was investigated, and the results are reported below. Methods Patients Fifty pathologically-confirmed BE patients from the Department of Digestion, Shanghai Pudong Hospital and the Affiliated Xinhua Hospital of Shanghai Jiatong University, from July 2012 to December 2013 were enrolled in this study. The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) Patients with gastroscopic biopsy for suspicious BE and being followed-up thereafter; 2) positive pathological confirmation, while conventional endoscopy was negative or suspicious; 3) patients subjected to endoscopic BE treatment (argon plasma coagulation) and followed up. These 50 patients were subjected to AFI, and the 74 BE lesions found to be suspicious for intraepithelial neoplasia were subjected to further AFI- NBI combined examination with Olympus GIF FQ260Z electronic endoscope (Olympus EVIS LUCERA CV- 260SL and CLV-260SL, Japan). Of these 50 patients, 22 were males and 28 females, aged years (mean 41-42). This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki and after approval from the Ethics Committee of Shanghai Pudong Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Device and specific operation This study used the electronic endoscope Olympus GIF FQ260Z, which could smoothly switch the 3 modes (WLI, AFI and ME -NBI) of detection simply through a button on the handle. The AFI system uses blue light at a wavelength of nm, as well as green and red light at a wavelength of nm and nm as the excitation source, and a filter, which allows the light to pass only within a wavelength range of nm, was installed in front of the charge-coupled device (CCD) fluorescence endoscope, thus the blue light is cutoff and blocked. The CCD collects the generated autofluorescence and reflects the green and red light to construct the fluorescence images. NBI imaging system uses the narrow band interference blue/ green filter, which produces a 30 nm narrow band bluegreen light, with the center wavelength as 415 nm and 540 nm as the light source for the lighting. It can clearly show the submucosal microvascular morphology. The endoscopic observation was performed by one endoscopic doctor. After the patient was positioned under the scope, the endoscope passed through the esophagus and stomach, and entered the descending duodenum, followed by slowly moving back for observation. The profiles of gastroesophageal junction and squamocolumnar junction were carefully examined. Conventional white light imaging (WLI) was firstly performed. The suspicious lesions were rinsed with saline, and then the AFI was conducted to observe the color changes of suspicious lesions. The observation plane depth was adjusted to make the image clear. The AFI images were acquired and stored for the fluorescence diagnosis of suspicious lesions. Then, NBI with zooming function was performed to observe the shape and structure of gastric mucosal microvessels and pits. The mainly blue narrow band light could clearly show the mucosal surface and shapes of mucosal glandular opening. Furthermore, the optical property of haemoglobin could absorb the blue light strongly [10]. The diagnosis was made according to the form and structure changes of the gastric pit and mucosal capillaries. The diagnosis of BE intraepithelial neoplasia was divided as highly suspicious, suspicious and negative. After rinsing the coloring agent, biopsy of the mucosa in the examined sites was performed in NBI amplification mode, and then the histopathological examination was carried out by the same pathologist who was blinded to the results of endoscopic diagnosis. Classification of gastric pits According to the classification criteria of Sakaki et al. [11], the gastric pits were divided into the following 6 basic types: A type: dot-like; B type: short rod-like, the pits are deep, might have branches and bending, although significantly less than C type; C type: the pits are prolonged, tortuous, with significantly increased bending and branches, which might be connected to each other and dendritic; D type: plaque-like, grid-like, with cobblestone-like changes; E type: the pits appear as villous-like and finger-like protrusions, and intestinal villi-like changes; F type: disordered or no structure [12]. Observation indicators The esophageal mucosal pathological changes were graded as inflammation, intestinal metaplasia, low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (LGIN) and highgrade intraepithelial neoplasia (HGIN). Lesions with overlap of histopathologic diagnosis were incorporated into high-grade pathological change. According to the results of pathological diagnosis, the positive predictive value (PPV) and false-positive rate of AFI and AFI- NBI for BE HGIN were determined. Statistics Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 13.0 statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, III, USA). Comparisons were carried out using Student s t-test and chi-square test. Two groups of independent sam- JBUON 2015; 20(2): 400
3 Autofluorescene with narrow band imaging in Barrett s esophagus 401 Table 1. Diagnosis of 74 AFI-suspicious BE HGIN cases by AFI-NBI Pathology Total cases Highly suspicious Suspicious HGIN positive 44 (100) 39 (52.7) 5 (6.76) 0 Negative HGIN negative 30 (100) 7 (9.46) 0 23 (31.08) BE: Barett s esophagus, HGIN: high grade intraepithelial neoplasia Table 2. Diagnosis of 74 BE-suspicious HGIN lesions by NBI Pathology Cases Highly suspicious Suspicious Negative Inflammation (9.46) Intestinal metaplasia 18 4 (5.45) 0 14 (18.91) LGIN 5 3 (4.05) 0 2 (2.70) HGIN (52.7) 5 (6.76) 0 BE: Barett s esophagus, LGIN: low grade intraepithelial neoplasia, HGIN: high grade intraepithelial neoplasia ples were analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank sum test, and multiple groups of samples were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis test. P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Results General information According to the inclusion criteria, 74 lesions found in 50 patients were observed with AFI and magnifying endoscopy (ME) -NBI mode, and 44 BE HGIN cases were confirmed by pathological examination, while 30 cases were characterized as false positive. The false positive lesions included 7 cases of inflammation, 18 cases of intestinal metaplasia, and 5 cases of low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (LGIN). The NBI diagnosis for the 44 BE HGIN cases was: 39 cases were positive, and 5 cases were suspicious; among the 30 false-positive BE HGIN cases, 7 cases were proved to be false positive by NBI (Tables 1 and 2). Positive predictive value and false positive rate of AFI in the BE HGIN diagnosis Among the 74 AFI-diagnosed suspicious lesions, 44 were diagnosed as BE HGIN, while 30 lesions were false positive. The false positive rate of AFI in BE HGIN was 40.5% (30/74), and the positive predictive value was 59.5% (44/74; p<0.05). Positive predictive value and false positive rate of AFI-NBI in the BE HGIN diagnosis The diagnosis of AFI-NBI in these 44 BE HGIN lesions was that 39 cases were positive and 5 were suspicious. Among the 30 false positive BE HGIN lesions, the false positive diagnosis by NBI was 7 cases. The positive predictive value of AFI-NBI was 84.8% (39/46), which was much higher than that of AFI alone in BE HGIN (59.5%) (p<0.05). The 24 AFI-suspected BE HGIN lesions clearly exhibited capillary structures and regular gastric pits structures in NBI, which indicated they were not BE HGIN changes (Figure 1). Therefore, the false positive rate dropped from 40.5% (30/74) to 14.9% (7/74) (p<0.05). AFI-NBI diagnosed 7 cases as false positive, among which 3 cases were LGIN, and 4 cases were intestinal metaplasia. Fluorescence endoscopy Under AFI mode, the normal gastric mucosa showed green fluorescence, while mucosa with erosion, inflammation and benign ulcer was light purple, the one with bleeding dots was dark red, that with malignant lesions was dark red or deep red, the white fur that covered the ulcer surface was still white, with clear distinction from the surrounding normal mucosa. The mucosal blood vessels also exhibited vascular network with clear boundaries in the AFI mode (Figure 1). AFI-NBI combination diagnosis The AFI-NBI combination could diagnose HGIN much more accurately. Under white light, some lesions only showed anabrotic and rough surface and it was difficult to determine whether they were benign or malignant. In the AFI mode, the lesions showed abnormal red changes that could improve the detection rate of biopsy. In the NBI mode, the lesions outlines were clearly visi- JBUON 2015; 20(2): 401
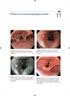
4 402 Autofluorescene with narrow band imaging in Barrett s esophagus Figure 1. Images of suspicious BE HGIN under WLI, AFI, NBI and ME -NBI. A: No obvious suspicious lesions under WLI; B: AFI shows existence of suspicious HGIN; C, D: NBI exhibits regular shapes of mucosal vessels and gastric pits in which pathology confirmed that there were no BE HGIN. For abbreviations see text. Figure 2. Images of suspicious BE HGIN under AFI, NBI and ME-NBI. A: AFI shows existence of suspicious BE HGIN; B, C: NBI exhibits disordered mucosal vessels and irregular gastric pits shapes in which pathology confirmed the existence of BE HGIN. For abbreviations see text. ble, with depression on the surface, irregular gastric pit structures were obvious when amplified, the microvascular network was disordered, thus the total picture was highly suspected of being BE HGIN (Figure 2). The relative pathological examination confirmed the existence of BE HGIN, thus it could be said that the AFI-NBI combination could improve the detection rate of BE HGIN and the diagnostic accuracy of benign and malignant lesions. Relationship of gastric pits basic forms and histology The 18 cases with intestinal metaplasia appeared mainly as C, D and E type under the endoscope, among which 66.7% were of the D-type; 5 cases of LGIN showed mild depression, bumps or flat lesions, associated with disordered or disappeared gastric pits, among which 80% were of E-type. The important feature of BE HGIN was the pleomorphism of gastric pits, mainly as F-type, and the shapes of small pits were various, irregular and dendritic (Table 3). Discussion When WLI reveals that the lesions display roughness of gastric mucosa, erosion, plaques, abnormal color, slight ample or depression, the AFI mode should be performed for the observation. When the excitated light shines the submucosa, the generated strong fluorescence would become reduced and weakened after meeting the abnormal lesions (e.g. abnormal aggregation or mucosal thickening of superficial vessels), so these subtle changes would be converted into color information, making such subtle differences more sharp between normal mucosa and lesions [13,14]. After recording the diagnostic results of fluorescence endoscopy, the diagnostic procedure was switched JBUON 2015; 20(2): 402
5 Autofluorescene with narrow band imaging in Barrett s esophagus 403 Table 3. Relationship of gastric pit basic forms and histology Group Cases N A B C D E Gastritis 7 5 (6.8) 2 (2.7) Intestinal metaplasia (6.8) 12 (16.2) 1 (1.4) 0 F LGIN (1.4) 4 (5.4) 1 (1.4) HGIN (6.8) 12 (16.2) 27 (36.5) A type: dot-like; B type: short red-like, the pits are deep, might have branches and bending, although significantly less than C type; C type: the pits are prolonged, tortuous, with significantly increased bending and branches which might be connected to each other and dendritic; D type: plaque-like, grid-like, with cobblestone-like changes; E type: pits appear as villous-like and finger-like protrusions, and intestinal villi-like changes; F type: disordered or no structure to ME-NBI mode because this modality could significantly improve the contrast of intrapapillary capillary loop and subcutaneous capillaries, and focus mainly on the microglandular and fine capillary morphologies on the gastric mucosal surface, thus it could guide more precisely to getting biopsy [15], as well as to improve the positive rate of the lesions [15]. In recent years, an increasing number of authors have studied the value of fluorescence endoscopy in the BE diagnosis. Kara et al. [16] applied fluorescence endoscopy and conventional endoscopy to inspect 60 BE patients, and detected 20 cases of early cancer or severe dysplasia, among which 6 cases were detected by fluorescence endoscopy alone, and 14 cases were found with obvious abnormalities by conventional endoscopy and fluorescence endoscopy. This study found that the positive predictive value of AFI-NBI combination was 84.8% (39/46), much higher than that of AFI alone (59.5%) in the diagnosis of BE HGIN. In parallel, the false positive rate decreased from 40.5 to 14.9%, similar to another Kara s et al. study [17], which combined AFI and NBI to find the BE dysplasia and early cancerous lesions. Among the 19 false positive lesions, 14 exhibited basically normal mucosal pit patterns under NBI, so the false positive rate was decreased from 40 to 10%. This was similar to the Curvers et al. study [18]. The diagnostic value of AFI-NBI combination in precancerous lesions and early gastric cancer was higher compared to simple fluorescence endoscopy, because the current fluorescence endoscope still lacks considerable sensitivity in autofluorescence generated by the tissues, and the image quality still needs to be improved. Furthermore, it is often affected by some confounding factors, such as mucosal thickening edema etc [19]. Our study found that, under the AFI mode, the normal mucosa was green, while the inflammation, erosion, depression and ulcers exhibited purple or dark red changes. Yet, during the research, some parts were found as suspicious red lesions, which exhibited no obvious changes of gastric pits and microvessels under the NBI mode, a finding consistent with the Singh et al. study [20]. NBI could increase the sensitivity and specificity, while a meta analysis came to the conclusion that NBI could accurately diagnose BE accompanied with atypical hyperplasia [21]. And this might be related to: (1) the necrotic tissues, mucus and bile attached to the stomach, thus interfering with the autofluorescence information; and (2) possible shaded areas caused by geometric factors when constructing the autofluorescence images. These shaded areas might be likely to be misdiagnosed as abnormal mucosa. A study reported that because of the difference between the molecular structures of normal tissues and tumor tissues, the characteristics of their fluorescence spectrum were easy to be distinguished, so the combination of fluorescence endoscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy could significantly improve the diagnostic reliability and sensitivity of fluorescence endoscopy [18]. The autofluorescence characteristics represented the biochemical structure of tissues, and the changes of tissues biochemical structure was the main cause of the changes of the autofluorescence features. The characteristics of the emission spectrum of tumor tissues and normal tissues could thus be exploited to distinguish the malignant tumors. This study found that the AFI-NBI combination technology could identify BE HGIN, thus improving the diagnostic reliability and sensitivity over AFI. By observing the morphological changes of gastric pits and microvessels, ME-NBI could better distinguish the small lesions [18]. This research studied 5 cases of LGIN, which all appeared as mild depressions, bumps or flat lesions, accompanied with disordered or disappeared gastric pits structures, and 80% of them were of E type. The main characteristic of BE HGIN was the pleomorphism of gastric pits, exhibited as F type, JBUON 2015; 20(2): 403
6 404 Autofluorescene with narrow band imaging in Barrett s esophagus along with the irregular and dendritic shapes. In summary, the advantages of AFI-NBI combination-guided biopsy were as follows: the combination could reduce the numbers of biopsies. The objectivity was good and not restricted by the doctor s experience. The sensitivity and specificity in BE HGIN diagnosis were high, thus increasing significantly the positive rate of biopsies. In addition, this most relevant information was obtained from a small-sample clinical study. The reliability and clinical value of this technology still needs further large-scale randomized controlled studies for verification of the present results. Acknowledgements This study was supported by the hospital s dominant academic project of 3rd- 985 projects, Fudan University Special Foundation of Science and Technology Development of Health and Family Planning Commission, Shanghai Pudong New-District, Number: PW2013A-16. References 1. Spechler SJ. Barrett s esophagus. N Engl J Med 2002;346; Bhat S, Coleman HG, Yousef F et al. Risk of malignant progression in Barrett s esophagus patients: results from a large population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst 2011;103: Hvid-Jensen F, Pedersen L, Drewes AM, Sørensen HT, Funch-Jensen P. Incidence of adenocarcinoma among patients with Barrett s esophagus. N Engl J Med 2011;365: Olliver JR, Wild CP, Sahay P, Dexter S, Hardie LJ. Chromoendoscopy with methylene blue and associated DNA damage in Barrett s esophagus. Lancet 2003;362: Aihara H, Saito S, Inomata H et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of neoplastic colorectal lesions using real-time numerical color analysis during autofluorescence endoscopy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;25: Kara MA, Peters FP, Fockens P, ten Kate FJ, Bergman JJ. Endoscopic video-autofluorescence imaging followed by narrow band imaging for detecting early neoplasia in Barrett s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2006; Nakaniwa N, Namihisa A, Ogihara T et al. Newly developed auto fluorescence imaging videoscope system for the detection of colonic neoplasms. Digest Endosc 2005;17: Inomata H, Tamai N, Aihara H et al. Efficacy of a novel auto-fluorescence imaging system with computer-assisted color analysis for assessment of colorectal lesions. World J Gastroenterol 2013;19: East JE, Tan EK, Bergman JJ, Saunders BP, Tekkis PP. Meta-analysis: narrow band imaging for lesion characterization in the colon, esophagus, duodenal ampulla and lung. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2008;28: Song LM, Adler DG, Conway JD et al. Narrow band imaging. Gastrointest En- imaging and multiband dosc 2008;67: Sakaki N, Iida Y, Okazaki Y, Kawamura S, Takemoto T. Magnifying endoscopic observation of the gastric mucosa, particularly in patients with atrophic gastritis. Endoscopy 1978;10: Sunjin K, Haruma K, Ito N et al. Magnifying video endoscopy is useful to diagnose histological gastritis-applicable to the estimation of Hp eradication. Gastrointest Endosc 2001;53: Ang TL1, Fock KM, Teo EK et al. The diagnostic utility of narrow band imaging magnifying endoscopy in clinical practice in a population with intermediate gastric cancer risk. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;24: Boerwinkel DF1, Shariff MK, di Pietro M et al. Fluorescence imaging for the detection of early neoplasia in Barrett s esophagus: old looks or new vision? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;26: Sharma P, Bansal A, Mathur S et al. The utility of a novel narrow band imaging endoscopy system in patients with Barrett s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2006;64: Kara MA, Peters FP, ten Kate FJ, Van Deventer SJ, Fockens P, Bergman JJ. Endoscopic video autofluorescence imaging may improve the detection of early neoplasia in patients with Barrett s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2005;61: Kara MA, Bergman JJ. Autofluorescence imaging and narrow-band imaging for the detection of early neoplasia in patients with Barrett s esophagus. Endoscopy 2006;38: Curvers WL, Singh R, Song LM et al. Endoscopic trimodal imaging for detection of early neoplasia in Barrett s oesophagus: a multi-centre feasibility study using high resolution endoscopy, autofluorescence imaging and narrow band imaging incorporated in one endoscopy system. Gut 2008;57: JBUON 2015; 20(2): 404
7 Autofluorescene with narrow band imaging in Barrett s esophagus Uedo N, Iishi H, Tatsuta M et al. A novel videoendoscopy system by using autofluorescence and reflectance imaging for diagnosis of esophagogastric cancer. Gastrointest Endosc 2005;62: Singh R, Karageorgiou H, Owen V et al. Comparison of high-resolution magnification narrow-band imaging and white-light endoscopy in the prediction of histology in Barrett s oesophagus. Scand J Gastroenterol 2009;44: Song J, Zhang J, Wang J et al. Meta-analysis of the effects of endoscopy with narrow band imaging in detecting dysplasia in Barrett s esophagus. Dis Esophagus Apr 24. doi: /dote (Epub ahead of print). JBUON 2015; 20(2): 405
Advances in Endoscopic Imaging
 Advances in Endoscopic Imaging SGNA meeting February 20, 2010 Amar R. Deshpande, MD Asst Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Objectives To recognize
Advances in Endoscopic Imaging SGNA meeting February 20, 2010 Amar R. Deshpande, MD Asst Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Objectives To recognize
Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Fujiya M, Saitoh Y, Watari J, Moriichi K, Kohgo Y.
 Digestive Endoscopy (2007) 19(s1):S145-S149. Auto-Fluorescence Imaging is useful to assess the activity of ulcerative colitis Fujiya M, Saitoh Y, Watari J, Moriichi K, Kohgo Y. Auto-Fluorescence Imaging
Digestive Endoscopy (2007) 19(s1):S145-S149. Auto-Fluorescence Imaging is useful to assess the activity of ulcerative colitis Fujiya M, Saitoh Y, Watari J, Moriichi K, Kohgo Y. Auto-Fluorescence Imaging
Comparison of the Diagnostic Usefulness of Conventional Magnification and Near-focus Methods with Narrow-band Imaging for Gastric Epithelial Tumors
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1738-3331, http://dx.doi.org/10.7704/kjhugr.2015.15.1.39 The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research, 2015;15(1):39-43 Comparison of the Diagnostic Usefulness
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1738-3331, http://dx.doi.org/10.7704/kjhugr.2015.15.1.39 The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research, 2015;15(1):39-43 Comparison of the Diagnostic Usefulness
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
 Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Advanced endoscopic imaging of esophageal neoplasia; old looks and new visions Boerwinkel, David
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Advanced endoscopic imaging of esophageal neoplasia; old looks and new visions Boerwinkel, David Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Boerwinkel,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Advanced endoscopic imaging of esophageal neoplasia; old looks and new visions Boerwinkel, David Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Boerwinkel,
Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia
 Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Gastrointestinal Imaging
 Endoscopic Imaging of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kerry B Dunbar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Abstract
Endoscopic Imaging of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kerry B Dunbar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Abstract
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Novel endoscopic observation in Barrett s oesophagus using high resolution magnification endoscopy and narrow band imaging
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Novel endoscopic observation in Barrett s oesophagus using high resolution magnification endoscopy and narrow band imaging G. K. ANAGNOSTOPOULOS*, K. YAO*, P. KAYE,
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Novel endoscopic observation in Barrett s oesophagus using high resolution magnification endoscopy and narrow band imaging G. K. ANAGNOSTOPOULOS*, K. YAO*, P. KAYE,
Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection: A single-center retrospective study
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
Application of magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesion
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Application of magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesion Jing Zhang 1,2, Shi-Bin Guo 1 and Zhi-Jun Duan 1* Abstract
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Application of magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesion Jing Zhang 1,2, Shi-Bin Guo 1 and Zhi-Jun Duan 1* Abstract
University Mainz. Early Gastric Cancer. Ralf Kiesslich. Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany. Early Gastric Cancer 15.6.
 Ralf Kiesslich Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany DIAGNOSIS Unmask lesions - Chromoendoscopy -NBI Red flag technology - Autofluorescence Surface and detail analysis - Magnifying endoscopy - High
Ralf Kiesslich Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany DIAGNOSIS Unmask lesions - Chromoendoscopy -NBI Red flag technology - Autofluorescence Surface and detail analysis - Magnifying endoscopy - High
Vital staining and Barrett s esophagus
 Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Current Management of Low-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett Esophagus
 Current Management of Low-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett Esophagus Gary W. Falk, MD, MS Dr Falk is a professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School
Current Management of Low-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett Esophagus Gary W. Falk, MD, MS Dr Falk is a professor of medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD?
 How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R
 170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze
 Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze John R. Saltzman MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Disclosures No relevant disclosures
Ablation for Barrett s Esophagus: Burn or Freeze John R. Saltzman MD Director of Endoscopy Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Disclosures No relevant disclosures
REPORT. McMahon Publishing Group. PENTAX Medical i-scan Technology for Improved Endoscopic Evaluations
 Brought to You by MAY 2014 PENTAX Medical i-scan Technology for Improved Endoscopic Evaluations Endoscopy plays a vital role in the diagnosis and clinical management of diseases of the gastrointestinal
Brought to You by MAY 2014 PENTAX Medical i-scan Technology for Improved Endoscopic Evaluations Endoscopy plays a vital role in the diagnosis and clinical management of diseases of the gastrointestinal
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
Investigation of mucosal pattern of gastric antrum using magnifying narrow-band imaging in patients with chronic atrophic fundic gastritis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (017) 0, 0-08 Investigation of mucosal pattern of gastric antrum using magnifying narrow-band imaging in patients with chronic atrophic fundic gastritis Yasushi
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Gastroenterology (017) 0, 0-08 Investigation of mucosal pattern of gastric antrum using magnifying narrow-band imaging in patients with chronic atrophic fundic gastritis Yasushi
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행
 Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy
 Dig Dis Sci (2010) 55:3442 3448 DOI 10.1007/s10620-010-1189-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy Lisette
Dig Dis Sci (2010) 55:3442 3448 DOI 10.1007/s10620-010-1189-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy Lisette
Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis
 Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis Bret A. Lashner, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director,
Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis Bret A. Lashner, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director,
American Journal of Gastroenterology. Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma
 Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma Journal: Manuscript ID: AJG-13-1412.R1 Manuscript Type: Letter to the Editor Keywords: Barrett-s esophagus, Esophagus, Endoscopy
Volumetric Laser Endomicroscopy Detects Subsquamous Barrett s Adenocarcinoma Journal: Manuscript ID: AJG-13-1412.R1 Manuscript Type: Letter to the Editor Keywords: Barrett-s esophagus, Esophagus, Endoscopy
Dysplasia 4/19/2017. How do I practice Chromoendoscopy for Surveillance of Colitis? SCENIC: Polypoid Dysplasia in UC. Background
 SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology
 Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Definition of GERD American College of Gastroenterology GERD is defined as chronic symptoms or mucosal damage produced by the abnormal reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus DeVault et al. Am J
Marginal turbid band and light blue crest, signs observed in magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy, are indicative of gastric intestinal metaplasia
 An et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:169 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Marginal turbid band and light blue crest, signs observed in magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy, are indicative of gastric
An et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:169 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Marginal turbid band and light blue crest, signs observed in magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy, are indicative of gastric
Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of oesophageal cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (9): 4121-4125 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of o. Jie Gao #, Ailan Xian #, Tingfeng
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (9): 4121-4125 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of o. Jie Gao #, Ailan Xian #, Tingfeng
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions
 Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
The Paris classification of colonic lesions
 The Paris classification of colonic lesions Training to improve the interobserver agreement among international experts Sascha van Doorn, MD, PhD-student in CRC-reserach group of Evelien Dekker Introduction
The Paris classification of colonic lesions Training to improve the interobserver agreement among international experts Sascha van Doorn, MD, PhD-student in CRC-reserach group of Evelien Dekker Introduction
Identification of gastric atrophic changes: from histopathology to endoscopy
 Evidence in perspective 533 Identification of gastric atrophic changes: from histopathology to endoscopy Authors Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1,2, Ernst J. Kuipers 3 Institutions Bibliography DOI http://dx.doi.org/
Evidence in perspective 533 Identification of gastric atrophic changes: from histopathology to endoscopy Authors Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1,2, Ernst J. Kuipers 3 Institutions Bibliography DOI http://dx.doi.org/
Barrett Esophagus - RadioFrequency Ablation (BE-RFA) - Project manual + FAQ
 Barrett Esophagus - RadioFrequency Ablation (BE-RFA) - Project manual + FAQ Table of contents 1 General project information...3 1.1 Inclusion criteria...3 1.2 Registration time points...3 1.3 Project variable
Barrett Esophagus - RadioFrequency Ablation (BE-RFA) - Project manual + FAQ Table of contents 1 General project information...3 1.1 Inclusion criteria...3 1.2 Registration time points...3 1.3 Project variable
Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma is rising in the ENDOSCOPY CORNER
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:843 847 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Acetic Acid Spray Is an Effective Tool for the Endoscopic Detection of Neoplasia in Patients With Barrett s Esophagus GAIUS LONGCROFT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:843 847 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Acetic Acid Spray Is an Effective Tool for the Endoscopic Detection of Neoplasia in Patients With Barrett s Esophagus GAIUS LONGCROFT
Newly developed magnifying endoscopic classification of the Japan Esophageal Society to identify superficial Barrett s esophagus related neoplasms
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0623-y SPECIAL ARTICLE Newly developed magnifying endoscopic classification of the Japan Esophageal Society to identify superficial Barrett s esophagus related neoplasms
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0623-y SPECIAL ARTICLE Newly developed magnifying endoscopic classification of the Japan Esophageal Society to identify superficial Barrett s esophagus related neoplasms
The Usefulness Of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy For The Real Time Characterization Of Colonic Lesions
 Acta Medica Marisiensis 2016;62(2):182-186 DOI: 10.1515/amma-2016-0004 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Usefulness Of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy For The Real Time Characterization Of Colonic Lesions Boeriu Alina
Acta Medica Marisiensis 2016;62(2):182-186 DOI: 10.1515/amma-2016-0004 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Usefulness Of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy For The Real Time Characterization Of Colonic Lesions Boeriu Alina
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
153 esophagus. We also aim to evaluate this technology for the early detection of precancerous changes in the specialized columnar epithelium of Barrr
 152 Department of Endoscopy Hisao Tajiri, Professor Hiroshi Arakawa, Assistant Professor Hiroo Imazu, Assistant Professor Keiichi Ikeda, Assistant Professor Kazuki Sumiyama, Assistant Professor Tomohiro
152 Department of Endoscopy Hisao Tajiri, Professor Hiroshi Arakawa, Assistant Professor Hiroo Imazu, Assistant Professor Keiichi Ikeda, Assistant Professor Kazuki Sumiyama, Assistant Professor Tomohiro
Barrett s Esophagus. Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book
 Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book 540 Oakmead Parkway, Sunnyvale, CA 94085 What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a change that occurs within the cellular lining
Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book 540 Oakmead Parkway, Sunnyvale, CA 94085 What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a change that occurs within the cellular lining
The white globe appearance (WGA): a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying. endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-
 E120 The white globe appearance (WGA): a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-NBI) Authors Hisashi Doyama 1, Naohiro Yoshida
E120 The white globe appearance (WGA): a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-NBI) Authors Hisashi Doyama 1, Naohiro Yoshida
Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of the Colon
 clinical imaging Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of the Colon Dan Ionut Gheonea, Adrian Saftoiu, Tudorel Ciurea, Carmen Popescu, Claudia Valentina Georgescu, Anca Malos Research Center of Gastroenterology
clinical imaging Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of the Colon Dan Ionut Gheonea, Adrian Saftoiu, Tudorel Ciurea, Carmen Popescu, Claudia Valentina Georgescu, Anca Malos Research Center of Gastroenterology
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH
 HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDY OF ENDOSCOPIC BIOPSIES OF STOMACH Pages with reference to book, From 177 To 179 Javed Iqbal Kazi, Syed Mahmood Alam ( Departments of Pathology, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Your Chance to Improve Patient Outcome. Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) The New Standard for Diagnostics and Treatment
 Your Chance to Improve Patient Outcome 17999 Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) The New Standard for Diagnostics and Treatment 1 Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) The New Standard for Diagnostics and Treatment Better Patient
Your Chance to Improve Patient Outcome 17999 Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) The New Standard for Diagnostics and Treatment 1 Narrow Band Imaging (NBI) The New Standard for Diagnostics and Treatment Better Patient
The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
 Real-Time Increased Detection of Neoplastic Tissue in Barrett s Esophagus with Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy: Final Results of an International Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Controlled
Real-Time Increased Detection of Neoplastic Tissue in Barrett s Esophagus with Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy: Final Results of an International Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Controlled
In 1998, the American College of Gastroenterology issued ALIMENTARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1232 1236 ALIMENTARY TRACT Effects of Dropping the Requirement for Goblet Cells From the Diagnosis of Barrett s Esophagus MARIA WESTERHOFF,* LINDSEY HOVAN,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2012;10:1232 1236 ALIMENTARY TRACT Effects of Dropping the Requirement for Goblet Cells From the Diagnosis of Barrett s Esophagus MARIA WESTERHOFF,* LINDSEY HOVAN,
Learning Objectives:
 Crescent City GI Update 2018 Ochsner Clinic, NOLA Optimizing Endoscopic Evaluation of Barrett s Esophagus What Should I Do in My Practice? Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of
Crescent City GI Update 2018 Ochsner Clinic, NOLA Optimizing Endoscopic Evaluation of Barrett s Esophagus What Should I Do in My Practice? Gregory G. Ginsberg, M.D. Professor of Medicine University of
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy. Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital
 Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration
 Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Histopathology: gastritis and peptic ulceration These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual
Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery
 Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery Norman Barrett (1950) described the esophagus as: that part of the foregut, distal to the cricopharyngeal sphincter, which is lined
Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery Norman Barrett (1950) described the esophagus as: that part of the foregut, distal to the cricopharyngeal sphincter, which is lined
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics
 Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Pharynx and esophagus atlas
 163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
Introduction. Original articles. Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra Huertas, 2 Rosario Albis, 3 Diego Aponte, 4 Luis Carlos Sabbagh. 5
 Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment Barrett s esophagus
 E318 Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment esophagus Authors Institution Arvind J. Trindade, Benley J. George, Joshua Berkowitz,
E318 Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment esophagus Authors Institution Arvind J. Trindade, Benley J. George, Joshua Berkowitz,
EMR, ESD and Beyond. Peter Draganov MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida
 EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy
 Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy Policy Number: 2.01.84 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy Policy Number: 2.01.84 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
In Vivo Colorectal Polyp Analysis Archived Medical Policy
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy
 Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Tools of the Gastroenterologist: Introduction to GI Endoscopy Objectives Endoscopy Upper endoscopy Colonoscopy Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) Endoscopic
Comprehensive Investigation of Areae Gastricae Pattern in Gastric Corpus using
 1 Comprehensive Investigation of Areae Gastricae Pattern in Gastric Corpus using Magnifying Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy in Patients with Chronic Atrophic Fundic Gastritis Running head: Magnifying NBI
1 Comprehensive Investigation of Areae Gastricae Pattern in Gastric Corpus using Magnifying Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy in Patients with Chronic Atrophic Fundic Gastritis Running head: Magnifying NBI
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Endoscopic atrophic classification before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
 E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: chromoendoscopy_as_an_adjunct_to_colonoscopy 7/2012 11/2017
Corporate Medical Policy Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: chromoendoscopy_as_an_adjunct_to_colonoscopy 7/2012 11/2017
How to remove BE cancer: EMR or ESD? Expected outcome
 How to remove BE cancer: EMR or ESD? Expected outcome Presented by Horst Neuhaus Institution Dpt. of Gastroenterology Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf, Germany Indications for endoscopic resection
How to remove BE cancer: EMR or ESD? Expected outcome Presented by Horst Neuhaus Institution Dpt. of Gastroenterology Evangelisches Krankenhaus Düsseldorf, Germany Indications for endoscopic resection
Magnification endoscopy, high resolution endoscopy, and chromoscopy; towards a better optical diagnosis
 iv7 PAPER Magnification endoscopy, high resolution endoscopy, and chromoscopy; towards a better optical diagnosis M J Bruno... In the past few years, optical magnification endoscopy and chromoscopy have
iv7 PAPER Magnification endoscopy, high resolution endoscopy, and chromoscopy; towards a better optical diagnosis M J Bruno... In the past few years, optical magnification endoscopy and chromoscopy have
A multicenter validation of an endoscopic classification with narrow band imaging for gastric precancerous and cancerous lesions
 236 A multicenter validation of an endoscopic classification with narrow band imaging for gastric precancerous and cancerous lesions Authors P. Pimentel-Nunes 1,2, *, M. Dinis-Ribeiro 1,3, *, J. B. Soares
236 A multicenter validation of an endoscopic classification with narrow band imaging for gastric precancerous and cancerous lesions Authors P. Pimentel-Nunes 1,2, *, M. Dinis-Ribeiro 1,3, *, J. B. Soares
BENEFIT APPLICATION BLUE CARD/NATIONAL ACCOUNT ISSUES
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.84 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.87 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy 6.01.32 Virtual Colonoscopy/Computed
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.84 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.87 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy 6.01.32 Virtual Colonoscopy/Computed
MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S RELATED NEOPLASIA IN 2018
 MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S RELATED NEOPLASIA IN 2018 Sachin Wani Medical Director Esophageal and Gastric Center Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus DISCLOSURES
MANAGEMENT OF BARRETT S RELATED NEOPLASIA IN 2018 Sachin Wani Medical Director Esophageal and Gastric Center Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus DISCLOSURES
비확대협대역대장내시경을이용한대장용종의감별진단
 Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 63 No. 5, 276-282 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.63.5.276 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 비확대협대역대장내시경을이용한대장용종의감별진단 김봉진, 박무인, 박선자, 문 고신대학교의과대학내과학교실 원, 박은택,
Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 63 No. 5, 276-282 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.63.5.276 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 비확대협대역대장내시경을이용한대장용종의감별진단 김봉진, 박무인, 박선자, 문 고신대학교의과대학내과학교실 원, 박은택,
Barrett esophagus. Bible class Inselspital
 Barrett esophagus Bible class Inselspital 2015.08.10 Guidelines Definition? BSG: ACG: Definition? BSG: ACG: What are the arguments for and against IM as prerequisite for the Dg? What are the arguments
Barrett esophagus Bible class Inselspital 2015.08.10 Guidelines Definition? BSG: ACG: Definition? BSG: ACG: What are the arguments for and against IM as prerequisite for the Dg? What are the arguments
Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy
 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Policy Number: 2.01.87 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2013 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for
Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Policy Number: 2.01.87 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2013 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for
Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD?
 Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD? Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina 1 Outline What are the risks of progression
Barrett s Esophagus: What to Do for No Dysplasia, LGD, and HGD? Nicholas Shaheen, MD, MPH Center for Esophageal Diseases and Swallowing University of North Carolina 1 Outline What are the risks of progression
Evaluating Treatments of Barrett s Esophagus That Shows High-Grade Dysplasia
 ...PRESENTATIONS... Evaluating Treatments of Barrett s Esophagus That Shows High-Grade Dysplasia Based on a presentation by Bergein F. Overholt, MD Presentation Summary Thermal ablation and surgery are
...PRESENTATIONS... Evaluating Treatments of Barrett s Esophagus That Shows High-Grade Dysplasia Based on a presentation by Bergein F. Overholt, MD Presentation Summary Thermal ablation and surgery are
Relative risk of dysplasia for patients with intestinal metaplasia in the distal oesophagus and in the gastric cardia
 Gut 2000;46:9 13 9 PAPERS Division of Gastroenterology, University of Kansas, VA Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri, USA P Sharma A P Weston Department of Pathology, VA Medical Center, Kansas M Topalovski
Gut 2000;46:9 13 9 PAPERS Division of Gastroenterology, University of Kansas, VA Medical Center, Kansas City, Missouri, USA P Sharma A P Weston Department of Pathology, VA Medical Center, Kansas M Topalovski
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Barrett s esophagus. Barrett s neoplasia treatment trends
 Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Options for endoscopic treatment of Barrett s esophagus Patrick S. Yachimski, MD MPH Director of Pancreatobiliary Endoscopy Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition
Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 Morphologic Criteria of Invasive Colonic Adenocarcinoma on Biopsy Specimens C Rose, H Wu Citation C Rose, H Wu.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric carcinoma using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging
 E832 THIEME Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging Authors Masashi Kawamura 1, Hiroshi Naganuma 2, Rie Shibuya 2, Tatsuya Kikuchi 1, Yoshitaka
E832 THIEME Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging Authors Masashi Kawamura 1, Hiroshi Naganuma 2, Rie Shibuya 2, Tatsuya Kikuchi 1, Yoshitaka
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1261 1267 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT In Vivo Histopathology for Detection of Gastrointestinal Neoplasia With a Portable, Confocal Miniprobe: An Examiner
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1261 1267 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT In Vivo Histopathology for Detection of Gastrointestinal Neoplasia With a Portable, Confocal Miniprobe: An Examiner
History. Prevalence at Endoscopy. Prevalence and Reflux Sx. Prevalence at Endoscopy. Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management
 Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management History Norman Barrett (1950) Chronic Peptic Ulcer of the Oesophagus and Oesophagitis Allison and Johnstone (1953) The Oesophagus Lined with Gastric Mucous
Barrett s Esophagus: Controversy and Management History Norman Barrett (1950) Chronic Peptic Ulcer of the Oesophagus and Oesophagitis Allison and Johnstone (1953) The Oesophagus Lined with Gastric Mucous
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts..
 COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts.. Detection: I see an abnormality (usually a polyp) Characterization: Is this abnormality neoplastic? (for example: an adenoma) Treatment: it is neoplastic. Can I treat
COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts.. Detection: I see an abnormality (usually a polyp) Characterization: Is this abnormality neoplastic? (for example: an adenoma) Treatment: it is neoplastic. Can I treat
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Effect of Route of Preoperative Biopsy on Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Patients with Early Gastric Cancer
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.20.8917 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of Route of Preoperative Biopsy on Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Patients with Early Gastric Cancer Hui Jiang 1, Hui-Ming
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.20.8917 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effect of Route of Preoperative Biopsy on Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Patients with Early Gastric Cancer Hui Jiang 1, Hui-Ming
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Management of Barrett s: From Imaging to Resection
 Management of Barrett s: From Imaging to Resection Michael Wallace, MD, MPH, FACG Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Goals of Endoscopic Evaluation in Barrett s Detect Barrett s and dysplasia Reduce/eliminate
Management of Barrett s: From Imaging to Resection Michael Wallace, MD, MPH, FACG Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Florida Goals of Endoscopic Evaluation in Barrett s Detect Barrett s and dysplasia Reduce/eliminate
Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined With Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus With Early Neoplasia
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:23 29 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined With Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus With Early Neoplasia ROOS E. POUW,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:23 29 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Efficacy of Radiofrequency Ablation Combined With Endoscopic Resection for Barrett s Esophagus With Early Neoplasia ROOS E. POUW,*
Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Gastric Cancer
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
Current Management: Role of Radiofrequency Ablation
 Esophageal Adenocarcinoma And Barrett s Esophagus: Current Management: Role of Radiofrequency Ablation Ketan Kulkarni, MD Regional Gastroenterology Associates of Lancaster INTRODUCTION The prognosis of
Esophageal Adenocarcinoma And Barrett s Esophagus: Current Management: Role of Radiofrequency Ablation Ketan Kulkarni, MD Regional Gastroenterology Associates of Lancaster INTRODUCTION The prognosis of
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy
 Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Surveying the Colon; Polyps and Advances in Polypectomy Educational Objectives Identify classifications of polyps Describe several types of polyps Verbalize rationale for polypectomy Identify risk factors
Present Day Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 Slide 1 Present Day Management of Barrett s Esophagus Kinnari R. Kher, M.D. Slide 2 Goals Risk factors for development of Barrett s esophagus Risks for progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Current
Slide 1 Present Day Management of Barrett s Esophagus Kinnari R. Kher, M.D. Slide 2 Goals Risk factors for development of Barrett s esophagus Risks for progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Current
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Barrett s Esophagus Consequence of chronic GERD Mean
Endoscopic Management of Barrett s Esophagus Sammy Ho, MD Director of Pancreaticobiliary Services and Endoscopic Ultrasound Montefiore Medical Center Barrett s Esophagus Consequence of chronic GERD Mean
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Linked color imaging improves detection of minimal change esophagitis in non-erosive reflux esophagitis patients
 Linked color imaging improves detection of minimal change esophagitis in non-erosive reflux esophagitis patients Authors Pei Deng *,MinMin *, Tenghui Dong, Yiliang Bi, Airong Tang, Yan Liu Institution
Linked color imaging improves detection of minimal change esophagitis in non-erosive reflux esophagitis patients Authors Pei Deng *,MinMin *, Tenghui Dong, Yiliang Bi, Airong Tang, Yan Liu Institution
Circular stripes were more common in Barrett s esophagus after acetic acid staining
 Sun et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:17 DOI 10.1186/s12876-018-0745-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Circular stripes were more common in Barrett s esophagus after acetic acid staining Yating Sun 1,
Sun et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2018) 18:17 DOI 10.1186/s12876-018-0745-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Circular stripes were more common in Barrett s esophagus after acetic acid staining Yating Sun 1,
Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy
 Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT.
 PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
PATHOLOGY OF NON NEOPLASTIC LESIONS OF THE UPPER GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. OESOPHAGEAL LESIONS OESOPHAGITIS AND OTHER NON NEOPLASTIC DISORDERS Corrosive Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD), Pills, Acid intake,
