Application of magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesion
|
|
|
- Ira Conrad Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Application of magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesion Jing Zhang 1,2, Shi-Bin Guo 1 and Zhi-Jun Duan 1* Abstract Background: Gastric carcinoma is the second commonest cause of cancer deaths worldwide. Early detection and diagnosis of gastric cancer in the stomach is important for improving the prognosis of gastric cancer. This retrospective study was designed to investigate the value of magnifying narrow-band imaging (NBI) in the diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early gastric cancer. Methods: This study included 122 patients who were diagnosed with early gastric cancer or precancerous gastric lesions by endoscopy. The patients underwent an examination with conventional endoscopy, magnifying NBI, and magnifying chromoendoscopy. Images resolution was evaluated, and the morphology, pit patterns and blood capillary forms of lesions were analyzed. The presence of gastric carcinoma and high grade intraepithelial neoplasia in the biopsy samples was considered as a positive pathological result, which is used to assess accuracy of endoscopic diagnosis. Results: For image resolution, magnifying NBI and magnifying chromoendoscopy were significantly superior to magnifying conventional endoscopy in morphology, pit pattern and blood capillary form (P < 0.01), and magnifying NBI was significantly superior to magnifying chromoendoscopy in blood capillary form (P < 0.01). IV, V 1, and VI type of gastric pit pattern were detected in 14 cases, 43 cases, and 17 cases in patients with high grade intraepithelial neoplasia, respectively. V 1 and VI type of gastric pit pattern were detected in 9 cases and 39 cases in patients with early gastric cancer, respectively. The presence of irregular minute vessels and variation in the caliber of vessels was found in 109 cases. The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, false positive rate and false negative rate for diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions were 68.9%, 95.1%, 63.1%, 24.5%, and 32.4% for conventional endoscopy, 93.6%, 92.7%, 94.5%, 5.7%, and 6.9% for magnifying NBI, and 91.3%, 88.6%, 93.2%, 13.2%, and 21.48% for magnifying chromoendoscopy, respectively. Conclusions: This study demonstrates that magnifying NBI is superior to conventional endoscopy in the diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions, and can be used for screening early malignancies of the stomach. Background Gastric carcinoma is one of the most common malignant tumors, and is the second commonest cause of cancer deaths worldwide [1]. About new gastric cancer cases are diagnosed every year on a global scale. There is a considerable geographical variation in the incidence of this cancer [2]. It is reported that incidence * Correspondence: cathydoctor@yahoo.com 1 Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian , Liaoning Province, China Full list of author information is available at the end of the article rates are high in eastern Asia, and low in Europe, North America and Africa [1]. Chinese have high gastric cancer rates with about 30% new cases diagnosed each year, which are only less than those found in Korea and Japan [3]. The prognosis of gastric carcinoma is closely related to the stage of disease at the time of diagnosis. The survival rate is greater than 90% in 5 years [4] for early gastric cancer, but the prognosis is very poor for advanced gastric cancer. Therefore, early diagnosis of gastric cancer is very important for an excellent prognosis. However, since most patients with early gastric 2011 Zhang et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
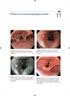
2 Page 2 of 7 carcinoma do not have specific symptoms, it is difficult to distinguish early gastric carcinoma from benign peptic ulcer or gastritis, and only about 10-20% of gastric cancers are diagnosed as early cancers in many countries [3]. With the development of technology, some endoscopic imaging modalities, such as magnifying narrow-band imaging (NBI) endoscopy, have been used recently for the diagnosis of early gastric cancer. Although many studies have reported that this endoscopic imaging modality can increase the rate of diagnosis of early cancers and precancerous lesions by enhancing visualization [5,6], there are few studies about comparison between NBI and conventional endoscopy. This retrospective study was designed to compare the accuracy and sensitivity of magnifying NBI endoscopy with conventional endoscopy and chromoendoscopy for diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early gastric cancer. Methods Patients This retrospective study was performed in the Department of Gastroenterology, Dalian Central hospital. During January 2008 to January 2011, a total of patients underwent endoscopic examination, and 526 lesions were detected. Among them, 122 patients were diagnosed as early gastric cancer or precancerous gastric lesions by the pathologic results, and were enrolled in this retrospective study. The ages of the122 patients (83 males and 39 females) ranged from 16 to 94 years with a mean age of 63.5 ± 14.1 years. Early gastric cancer was defined as cancer confined to the mucosa or submucosa regardless of lymph node metastasis. In our study, precancerous lesions referred to high grade intraepithelial neoplasia, which included intraepithelial carcinoma and severe dysplasia according to the Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasms [7]. All the lesions were confirmed by pathologic diagnosis of endoscopic resection or post-surgery tissue. Exclusion criteria were pre-existing or advanced gastric cancer, recent upper gastrointestinal bleeding or coagulation disorders, and severe comorbidities that may affect tolerance to upper endoscopy. The presenting manifestations were abdominal pain in 88 cases (72.1%), distension in 52 cases (42.6%), heartburn in 60 cases (49.2%), belching in 28 cases (23.0%), acid regurgitation in 32 cases (26.2%), and nausea in 29 cases (23.8%). Procedures The patients were first given careful observation in order to identify any abnormalities of the surface or the color with conventional endoscopy. After detecting lesions, magnifying chromoendoscopy and NBI magnifying endoscopy examination were followed on the same day or on another day. The morphology, pit pattern and blood capillary form of lesions were observed and recorded to determine that the lesion was malignant or benign (Figure 1). Then, biopsies were taken and studied by the same expert pathologist. The image quality was scored by two other endoscopists during the examination. Pathological diagnosis was regarded as the gold standard, and was used to assess accuracy of endoscopic diagnosis. Once lesions were diagnosed as gastric cancer or precancerous lesions, patients were underwent endoscopic resection or surgery. This study was approved by the Medical Science s ethics committee of Dalian Central hospital, patients were informed of the possible risks and benefits of participation in the study, and written informed consent was obtained from all the patients or their relatives before their examination. Instruments The NBI main unit was an Olympus CV-260SL and the endoscope was an Olympus GIF-H260Z (80 ) (Olympus Corporation, Japan); 1.2% iodine was used for staining (Micro-Tech, Nanjing, CO., LTD). Image evaluation The image quality was scored as follow: 1 point: obscure; 2 points: clouding; 3 points: more clear; and 4 points: clear [8]. Statistical analysis Data analysis was performed using SPSS 10.0 software (Chicago, IL, USA). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Wilcoxon statistical methods were used to determine statistical significance. All measurements in this study were expressed as mean ± SD. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results A total of 122 cases were diagnosed as early gastric cancer or precancerous lesions by pathologic diagnosis of endoscopic resection or post-surgery tissue. The lesions were located in gastric antrum in 67 cases (54.9%), gastric angle in 29 cases (23.8%), gastric body in 22 cases (18.0%), and cardia and gastric fundus in 4 cases (3.3%). The image quality of 3 modes was compared concerning the morphology, pit pattern and blood capillary form of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesions. We found that magnifying NBI and magnifying chromoendoscopy were significantly superior to magnifying conventional endoscopy in respect of morphology, pit pattern and blood capillary form (P < 0.01), and magnifying NBI is significantly superior to magnifying chromoendoscopy in respect of blood capillary form (P < 0.01). There is no significant difference between magnifying NBI and
3 Page 3 of 7 Figure 1 Demonstration of gastric precancerous lesion with conventional endoscopy(a) and iodine staining pattern (B); Pit pattern of this precancerous lesion with magnifying chromoendoscopy (C) and Blood capillary form with magnifying NBI (D). magnifying chromoendoscopy with regard to morphology and pit pattern (P > 0.05) (Table 1, Figure 2). The gastric pit pattern is classified into six types according to Sakaki [9]. In our studies, a total of 122 patients with early gastric cancer or precancerous gastric lesions were diagnosed, including 74 cases of high grade intraepithelial neoplasia and 48 cases of early gastric cancer. In patients with high grade intraepithelial neoplasia, IV type of gastric pit pattern was detected in 14 cases, V 1 type of gastric pit pattern was detected in 43 cases, and VI type of gastric pit pattern was detected in 17 cases; while in patients with early gastric cancer, V 1 type of gastric pit pattern was detected in 9 cases, and VI type of gastric pit pattern was detected in 39 cases. Table 1 Comparison of image quality among three endoscopic modalities item mode Score of image quality total score conventional endoscopy morphology magnifying NBI magnifying chromoendoscopy conventional endoscopy pit pattern magnifying NBI magnifying chromoendoscopy conventional endoscopy blood capillary form magnifying NBI magnifying chromoendoscopy
4 Page 4 of 7 Figure 2 Comparition of image quality about morphology, pit pattern and blood capillary form among conventional endoscopy, magnifying NBI and magnifying chromoendoscopy. A represent conventional endoscopy; B represent NBI; C represent chromoendoscopy. We also observed blood capillary form of gastric lesions. The disappearance of the normal mucosa capillary network or the presence of microvessels with irregular size, shape and distribution were found in 109 cases. The accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, false positive rate and false negative rate of conventional endoscopic diagnosis for early gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions were 68.9%, 95.1%, 63.1%, 24.5% and 32.4%, respectively, while the corresponding values of magnifying NBI were 93.6%, 92.7%, 94.5%, 5.7% and 6.9%, respectively, and the corresponding values of magnifying chromoendoscopy were 91.3%, 88.6%, 93.2%, 13.2% and 21.48%, respectively. Compared with conventional endoscopic, magnifying NBI was superior in the diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions. However, there was no diagnostic difference between magnifying NBI and magnifying chromoendoscopy. Discussion Gastric cancer is one of the main causes of cancer death in China. Most of these patients have poor prognosis because of late presentation and diagnosis. The best tactics for dealing with gastric cancer is prevention, early detection and early treatment. It is generally believed that gastric cancer is a multi-step progression from chronic gastritis to gastric atrophy, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia and cancer. Early gastric cancer is defined as a cancer confined to the mucosa or submucosa regardless of lymph node metastasis [10]. If gastric cancer can be detected in early stage, the prognosis for gastric cancer is excellent, the survival rate is greater than 90% in 5 years, and curative endoscopic resection may be possible in some cases with early gastric cancers and precancerous gastric lesions, without the need for surgery. Therefore, it is necessary to mass screen for symptomatic groups in high-incidence areas, and endoscopy has been considered as one of the most useful tool for detecting early gastric cancer. However, at present, only about 4-10% of patients with gastric cancer are diagnosed as early cancer in China, and the missed diagnosis of gastric cancer on endoscopy is a common occurrence. It is reported that the false-negative rates are high up to 5-19% [11,12]. There may be two reasons for this situation. One reason is that the symptoms of early gastric cancer are not specific to distinguish from those of gastritis and benign peptic ulcer disease. In our group, about 90% of patients with early gastric carcinoma have heartburn, abdominal pain and discomfort in the upper
5 Page 5 of 7 abdomen. The other reason is that some of the lesions are so subtle that they are overlooked by inexperienced endoscopist. Without being aware of early gastric cancer, they pay much attention to the detection of gross lesions, rather than tiny changes in color, vascularity or texture, which are distinctive characteristics of early gastric cancer. There has been great advancement about the technology of endoscopic imaging in recent years, and these new technologies have improved the sensitivity in identifying early gastric cancer. Magnifying endoscope (GIF-Q240Z) used in our study can provide magnified images up to x80. This new magnifying endoscope can detect minute changes of gastric mucosal surface, such as the color of lesions (same color as surrounding tissues, red or pale), the surface of lesions (flat, elevated or depressed), the presence of granules or nodules, with or without ulcer and fold change. Irregular and destruction of the minute surface pattern and color change of mucosal surface were all considered as characteristics of precancerous gastric lesion or early gastric cancer [13-15]. Dye spray chromoendoscopy can enhance the recognition of minute structural alteration caused by neoplastic changes, which is difficult to be perceived by conventional endoscopy. Magnifying chromoendoscopy is also useful in observing the surface mucosal pattern and capillary structure. By analyzing the surface structure pattern, histological changes of carcinoma, dysplasia, adenoma and hyperplasia might be suspected. Since histopathological examination of biopsy material is very important for the final diagnosis, accurate biopsy contributes to acquire the correct diagnosis of the lesion. Magnifying chromoendoscopy can improve the diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesions in the stomach by facilitating the identification and biopsy of abnormal areas. It is difficult in some cases to identify the margins of the lesions by conventional endoscopy, especially those of superficial or flat-type lesions. Magnifying chromoendoscopy has an advantage in coping with this difficulty [13,16]. Narrow-band imaging (NBI) is a new kind of endoscopic technology designed to enhance the contrast of the mucous membrane without staining. NBI uses special narrow-band filters which filter broad-band spectrum to leave a narrow-band spectrum for the diagnosis of digestive tract disease [17-19]. NBI endoscopy significantly improves diagnostic accuracy in two ways. First, because the shorter wavelength light left by the special narrow-band filter can not penetrate deeply into the mucosa, NBI improves visibility of mucosal pit pattern. Second, since the specific wavelength 415 nm left by special narrow-band filter corresponds to the peak absorption spectrum for hemoglobin [20], magnifying the image with NBI can give important information about microvascular pattern [21]. In our study, we find that the image quality of magnifying NBI is superior not only to magnifying conventional endoscopy in respect of morphology, pit pattern and blood capillary form of abnormal areas, but also to magnifying chromoendoscopy concerning blood capillary form. However, in our study, the image quality was scored during the examination, and the scoring system itself has subjective nature, so it would be better to score the image quality in a blinded fashion by more investigators. We also find that the diagnotic accuracy of early gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions by magnifying NBI is significantly higher than that of conventional endoscopy. Moreover, NBI has all the functions that conventional endoscopy has, and the NBI and conventional endoscopy pattern can be easily switched just by pushing one button [22,23]. Both NBI and chromoendoscopy can show the enhanced mucosal pattern and the microvascular structureofthemucosabytheamplificatoryfunction[13], and mucosal pattern and microvascular structure have been regarded as distinctive characteristics of early gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions. It has been known that angiogenesis is an important factor in gastrointestinal carcinogenesis [24], suggesting that the vascular pattern of gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesion is differ from that of normal mucosa [25]. Therefore, observation of vascular pattern contributes to diagnosis of such lesions [26]. Nakayoshi [5] et al observed the microvascular networks of 165 patients with early gastric carcinoma with magnifying NBI, and found that 66.1% of differentiated adenocarcinoma had fine microvascular networks, and 85.7% of undifferentiated adenocarcinoma had corkscrew microvascular networks. Liu [27] et al also drawn the conclusion that vascular architecture was helpful in the identification of early gastric cancer. They studied the microvascular architecture with confocal endomicroscopy, and demonstrated that differentiated gastric cancerous mucosa showed hypervascularity and various caliber microvessels with irregular shapes, and undifferentiated gastric cancer showed hypovascularity and irregular short branched vessels. In our study, we found abnormal capillary patterns in 109 cases including disappearance of the normal mucosa capillary network, tortuous microvessels with irregular length and irregular arrangement, and variation in the caliber of vessels or even dilated microvessels with tortile tips. However, at present, as a new technology, there is no unified standard for diagnosis of early gastric carcinoma by using microvascular architecture. Many studies have shown that gastric mucosa patterns of gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions are characteristic. Tanaka et al classified pit patterns of gastric mucosa into five types, and pointed out that
6 Page 6 of 7 differentiated tubular adenocarcinomas mainly showed the type IV, and poorly differentiated tubular adenocarcinomas mainly showed type V [17]. Yoshida et al distinguished gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions from controls by analyzing the surface structure pattern [28]. In our study, V 1 and VI type of gastric pit pattern are the most common mucosa pattern of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesions. Therefore determination of pit pattern as well as microvascular architecture is very important for detecting early gastric cancer and precancerous lesion [29]. Conclusions Magnifying NBI endoscopy has advantages in the detection of some lesions with minute changes of gastric mucosa pattern and capillary form, and facilitates the diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous gastric lesions by identification and biopsy of the lesions. Clearly, it can be used for the screening of early malignancies of the stomach. However, since the present study is uncontrolled, and the number of cases is not big enough, a further prospective, blinded study with a sufficient number of patients who have or have no gastric carcinoma is needed to assess the value of magnifying narrow-band imaging in the diagnosis of precancerous lesions and early gastric cancer in clinical practice. Author details 1 Department of Gastroenterology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian , Liaoning Province, China. 2 This auther is currently working in Dalian Centric Hospital, Dalian , Liaoning Province, China. Authors contributions JZ and ZJD designed the experiment, JZ and SBG performed the experiments, analyzed the data, SBG and JZ wrote the manuscript, ZJD revised it. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Received: 29 August 2011 Accepted: 14 December 2011 Published: 14 December 2011 References 1. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P: Global cancer statistics, CA Cancer J Clin 2005, 55: Sung J: Early gastric cancer: diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006, 18: Tan YK, Fielding JW: Early diagnosis of early gastric cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006, 18: Onodera H, Tokunaga A, Yoshiyuki T, Kiyama T, Kato S, Matsukura N, Masuda G, Tajiri T: Surgical outcome of 483 patients with early gastric cancer: prognosis, postoperative morbidity and mortality, and gastric remnant cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2004, 51: Nakayoshi T, Tajiri H, Matsuda K, Kaise M, Ikegami M, Sasaki H: Magnifying endoscopy combined with narrow band imaging system for early gastric cancer: correlation of vascular pattern with histopathology (including video). Endoscopy 2004, 36: Dinis-Ribeiro M: Chromoendoscopy for early diagnosis of gastric cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2006, 18: The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, Gastrointest Endosc 2003, 58:S3-S Hamamoto Y, Endo T, Nosho K, Arimura Y, Sato M, Imai K: Usefulness of narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of Barrett s esophagus. J Gastroenterol 2004, 39: Sakaki N, Iida Y, Okazaki Y, Kawamura S, Takemoto T: Magnifying endoscopic observation of the gastric mucosa, particularly in patients with atrophic gastritis. Endoscopy 1978, 10: Katai H, Sano T: Early gastric cancer; concepts, diagnosis, and management. Int J Clin Oncol 2005, 10: Voutilainen ME, Juhola MT: Evaluation of the diagnostic accuracy of gastroscopy to detect gastric tumours: clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with gastric cancer missed on endoscopy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005, 17: Hosokawa O, Tsuda S, Kidani E, Watanabe K, Tanigawa Y, Shirasaki S, Hayashi H, Hinoshita T: Diagnosis of gastric cancer up to three years after negative upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Endoscopy 1998, 30: Otsuka Y, Niwa Y, Ohmiya N, Ando N, Ohashi A, Hirooka Y, Goto H: Usefulness of magnifying endoscopy in the diagnosis of early gastric cancer. Endoscopy 2004, 36: Kawamura M, Abe S, Oikawa K, Terai S, Saito M, Shibuya D, Kato K, Inomata Y, Ohara S, Shimosegawa T: Magnifying endoscopic findings of the surface structure of non-cancerous mucosa surrounding differentiated and undifferentiated gastric carcinoma. Dig Endosc 2011, 23: Yao K, Anagnostopoulos GK, Ragunath K: Magnifying endoscopy for diagnosing and delineating early gastric cancer. Endoscopy 2009, 41: Tanaka K, Toyoda H, Kadowaki S, Kosaka R, Shiraishi T, Imoto I, Shiku H, Adachi Y: Features of early gastric cancer and gastric adenoma by enhanced-magnification endoscopy. J Gastroenterol 2006, 41: Sharma P, Wani S, Bansal A, Hall S, Puli S, Mathur S, Rastogi A: A feasibility trial of narrow band imaging endoscopy in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology 2007, 133: Curvers W, Baak L, Kiesslich R, Van Oijen A, Rabenstein T, Ragunath K, Rey JF, Scholten P, Seitz U, Ten Kate F, Fockens P, Bergman J: Chromoendoscopy and narrow-band imaging compared with highresolution magnification endoscopy in Barrett s esophagus. Gastroenterology 2008, 134: Miehlke S, Morgner A, Aust D, Madisch A, Vieth M, Baretton G: Combined use of narrow-band imaging magnification endoscopy and miniprobe confocal laser microscopy in neoplastic Barrett s esophagus. Endoscopy 2007, 39:E Nass JP, Connolly SE: Current status of chromoendoscopy and narrow band imaging in colonoscopy. Clin Colon Rectal Surg 2010, 23: Gono K, Obi T, Yamaguchi M, Ohyama N, Machida H, Sano Y, Yoshida S, Hamamoto Y, Endo T: Appearance of enhanced tissue features in narrow-band endoscopic imaging. J Biomed Opt 2004, 9: Kara MA, Peters FP, Fockens P, ten Kate FJ, Bergman JJ: Endoscopic videoautofluorescence imaging followed by narrow band imaging for detecting early neoplasia in Barrett s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2006, 64: Sharma P, Bansal A, Mathur S, Wani S, Cherian R, McGregor D, Higbee A, Hall S, Weston A: The utility of a novel narrow band imaging endoscopy system in patients with Barrett s esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc 2006, 64: Folkman J, Klagsbrun M: Angiogenic factors. Science 1987, 235: Lambert R, Kuznetsov K, Rey JF: Narrow-band imaging in digestive endoscopy. ScientificWorldJournal 2007, 7: Rey JF, Kuznetsov K, Lambert R: Narrow band imaging: a wide field of possibilities. Saudi J Gastroenterol 2007, 13: Liu H, Li YQ, Yu T, Zhao YA, Zhang JP, Zhang JN, Guo YT, Xie XJ, Zhang TG, Desmond PV: Confocal endomicroscopy for in vivo detection of microvascular architecture in normal and malignant lesions of upper gastrointestinal tract. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2008, 23: Yoshida T, Kawachi H, Sasajima K, Shiokawa A, Kudo SE: The clinical meaning of a nonstructural pattern in early gastric cancer on magnifying endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2005, 62:48-54.
7 Page 7 of Mine T: The role of magnifying endoscopy in the diagnosis of early gastric carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 2006, 41: Pre-publication history The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: /prepub doi: / x Cite this article as: Zhang et al.: Application of magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy for diagnosis of early gastric cancer and precancerous lesion. BMC Gastroenterology :135. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract
 Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Magnifying Endoscopy and Chromoendoscopy of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Alina M.Boeriu 1, Daniela E.Dobru 1, Simona Mocan 2 1) Department of Gastroenterology, University of Medicine and Pharmacy;
Comparison of the Diagnostic Usefulness of Conventional Magnification and Near-focus Methods with Narrow-band Imaging for Gastric Epithelial Tumors
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1738-3331, http://dx.doi.org/10.7704/kjhugr.2015.15.1.39 The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research, 2015;15(1):39-43 Comparison of the Diagnostic Usefulness
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1738-3331, http://dx.doi.org/10.7704/kjhugr.2015.15.1.39 The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research, 2015;15(1):39-43 Comparison of the Diagnostic Usefulness
Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric carcinoma using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging
 E832 THIEME Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging Authors Masashi Kawamura 1, Hiroshi Naganuma 2, Rie Shibuya 2, Tatsuya Kikuchi 1, Yoshitaka
E832 THIEME Analysis of microvascular density in early gastric using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging Authors Masashi Kawamura 1, Hiroshi Naganuma 2, Rie Shibuya 2, Tatsuya Kikuchi 1, Yoshitaka
Novel endoscopic observation in Barrett s oesophagus using high resolution magnification endoscopy and narrow band imaging
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Novel endoscopic observation in Barrett s oesophagus using high resolution magnification endoscopy and narrow band imaging G. K. ANAGNOSTOPOULOS*, K. YAO*, P. KAYE,
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Novel endoscopic observation in Barrett s oesophagus using high resolution magnification endoscopy and narrow band imaging G. K. ANAGNOSTOPOULOS*, K. YAO*, P. KAYE,
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia
 Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Chromoendoscopy and Endomicroscopy for detecting colonic dysplasia Ralf Kiesslich I. Medical Department Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany Cumulative cancer risk in ulcerative colitis 0.5-1.0%
Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy
 Dig Dis Sci (2010) 55:3442 3448 DOI 10.1007/s10620-010-1189-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy Lisette
Dig Dis Sci (2010) 55:3442 3448 DOI 10.1007/s10620-010-1189-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Narrow Band Imaging for the Detection of Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Dysplasia During Surveillance Endoscopy Lisette
Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong
 Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Application of Chromoendoscopy, NBI and AFI in Esophagus why, who, and how? Philip Chiu Associate Professor Department of Surgery, Prince of Wales Hospital The Chinese University of Hong Kong Cancer of
Diagnostic value of autofluorescence imaging combined with narrow band imaging in intraepithelial neoplasia of Barrett s esophagus
 JBUON 2015; 20(2): 399-405 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic value of autofluorescence imaging combined with narrow band
JBUON 2015; 20(2): 399-405 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic value of autofluorescence imaging combined with narrow band
Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer
 He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection: A single-center retrospective study
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 679-685 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic analysis of gastric mucosal dysplasia after endoscopic resection:
Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic Patterns and Histopathological Severity of
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 808505, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/808505 Research Article Correlation between Gastric Mucosal Morphologic
University Mainz. Early Gastric Cancer. Ralf Kiesslich. Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany. Early Gastric Cancer 15.6.
 Ralf Kiesslich Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany DIAGNOSIS Unmask lesions - Chromoendoscopy -NBI Red flag technology - Autofluorescence Surface and detail analysis - Magnifying endoscopy - High
Ralf Kiesslich Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany DIAGNOSIS Unmask lesions - Chromoendoscopy -NBI Red flag technology - Autofluorescence Surface and detail analysis - Magnifying endoscopy - High
Advances in Endoscopic Imaging
 Advances in Endoscopic Imaging SGNA meeting February 20, 2010 Amar R. Deshpande, MD Asst Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Objectives To recognize
Advances in Endoscopic Imaging SGNA meeting February 20, 2010 Amar R. Deshpande, MD Asst Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Objectives To recognize
Helicobacter pylori Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2016.17.4.2099 RESEARCH ARTICLE Improved Detection of Helicobacter pylori Infection and Premalignant Gastric Mucosa Using Conventional White Light Source Gastroscopy
The Usefulness Of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy For The Real Time Characterization Of Colonic Lesions
 Acta Medica Marisiensis 2016;62(2):182-186 DOI: 10.1515/amma-2016-0004 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Usefulness Of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy For The Real Time Characterization Of Colonic Lesions Boeriu Alina
Acta Medica Marisiensis 2016;62(2):182-186 DOI: 10.1515/amma-2016-0004 RESEARCH ARTICLE The Usefulness Of Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy For The Real Time Characterization Of Colonic Lesions Boeriu Alina
Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 297 306, September 2017 Original Image Analysis of Magnifying Endoscopy for Differentiation between Early Gastric Cancers and Gastric Erosions Shotaro HANAMURA, Kuniyo GOMI,
Endoscopic Corner CASE 1. Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R
 170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
170 Endoscopic Corner Kimtrakool S Aniwan S Linlawan S Muangpaisarn P Sallapant S Rerknimitr R CASE 1 A 54-year-old woman underwent a colorectal cancer screening. Her fecal immunochemical test was positive.
비확대협대역대장내시경을이용한대장용종의감별진단
 Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 63 No. 5, 276-282 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.63.5.276 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 비확대협대역대장내시경을이용한대장용종의감별진단 김봉진, 박무인, 박선자, 문 고신대학교의과대학내과학교실 원, 박은택,
Korean J Gastroenterol Vol. 63 No. 5, 276-282 http://dx.doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.63.5.276 pissn 1598-9992 eissn 2233-6869 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 비확대협대역대장내시경을이용한대장용종의감별진단 김봉진, 박무인, 박선자, 문 고신대학교의과대학내과학교실 원, 박은택,
Newly developed magnifying endoscopic classification of the Japan Esophageal Society to identify superficial Barrett s esophagus related neoplasms
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0623-y SPECIAL ARTICLE Newly developed magnifying endoscopic classification of the Japan Esophageal Society to identify superficial Barrett s esophagus related neoplasms
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-018-0623-y SPECIAL ARTICLE Newly developed magnifying endoscopic classification of the Japan Esophageal Society to identify superficial Barrett s esophagus related neoplasms
Identification of gastric atrophic changes: from histopathology to endoscopy
 Evidence in perspective 533 Identification of gastric atrophic changes: from histopathology to endoscopy Authors Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1,2, Ernst J. Kuipers 3 Institutions Bibliography DOI http://dx.doi.org/
Evidence in perspective 533 Identification of gastric atrophic changes: from histopathology to endoscopy Authors Mário Dinis-Ribeiro 1,2, Ernst J. Kuipers 3 Institutions Bibliography DOI http://dx.doi.org/
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions
 Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
Diagnostic accuracy of pit pattern and vascular pattern in colorectal lesions Digestive Disease Center, Showa University Northern Yokohama Hospital Department of Pathology Yoshiki Wada, Shin-ei Kudo, Hiroshi
The white globe appearance (WGA): a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying. endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-
 E120 The white globe appearance (WGA): a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-NBI) Authors Hisashi Doyama 1, Naohiro Yoshida
E120 The white globe appearance (WGA): a novel marker for a correct diagnosis of early gastric cancer by magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging (M-NBI) Authors Hisashi Doyama 1, Naohiro Yoshida
Gastrointestinal Imaging
 Endoscopic Imaging of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kerry B Dunbar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Abstract
Endoscopic Imaging of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Kerry B Dunbar, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Abstract
Probe-based confocal endomicroscopy is accurate for differentiating gastric lesions in patients in a Western center
 Original Article Probe-based confocal endomicroscopy is accurate for differentiating gastric lesions in patients in a Western center Adriana Vaz Safatle-Ribeiro, Elisa Ryoka Baba, Rodrigo Corsato Scomparin,
Original Article Probe-based confocal endomicroscopy is accurate for differentiating gastric lesions in patients in a Western center Adriana Vaz Safatle-Ribeiro, Elisa Ryoka Baba, Rodrigo Corsato Scomparin,
Frozen Section Biopsy to Evaluation of Obscure Lateral Resection Margins during Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Gastric Cancer
 J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(3):155-161 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.3.155 Original Article Frozen Section Biopsy to Evaluation of Obscure Lateral Resection Margins during Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal
J Gastric Cancer 2011;11(3):155-161 http://dx.doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2011.11.3.155 Original Article Frozen Section Biopsy to Evaluation of Obscure Lateral Resection Margins during Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.5.2765 RESEARCH ARTICLE Correlation between Magnifying Narrow-band Imaging Endoscopy Results and Organoid Differentiation Indicated by Cancer Cell Differentiation
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.5.2765 RESEARCH ARTICLE Correlation between Magnifying Narrow-band Imaging Endoscopy Results and Organoid Differentiation Indicated by Cancer Cell Differentiation
Gastric Polyps. Bible class
 Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Gastric Polyps Bible class 29.08.2018 Starting my training in gastroenterology, some decades ago, my first chief always told me that colonoscopy may seem technically more challenging but gastroscopy has
Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis
 Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis Bret A. Lashner, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director,
Chromoendoscopy or Narrow Band Imaging with Targeted biopsies Should be the Cancer Surveillance Endoscopy Procedure of Choice in Ulcerative Colitis Bret A. Lashner, M.D. Professor of Medicine Director,
Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy
 Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
Volume 2012, Article ID 368160, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/368160 Case Report Features of the Atrophic Corpus Mucosa in Three Cases of Autoimmune Gastritis Revealed by Magnifying Endoscopy Kazuyoshi Yagi,
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
Review Article Current Clinical Applications of Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging in the Stomach
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2012, Article ID 271914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/271914 Review Article Current Clinical Applications of Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging in the
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy Volume 2012, Article ID 271914, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/271914 Review Article Current Clinical Applications of Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging in the
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus
 Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Histopathology of Endoscopic Resection Specimens from Barrett's Esophagus Br J Surg 38 oct. 1950 Definition of Barrett's esophagus A change in the esophageal epithelium of any length that can be recognized
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행
 Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Paris classification (2003) 삼성의료원내과이준행 JGCA classification - Japanese Gastric Cancer Association - Type 0 superficial polypoid, flat/depressed, or excavated tumors Type 1 polypoid carcinomas, usually attached
Management of pt1 polyps. Maria Pellise
 Management of pt1 polyps Maria Pellise Early colorectal cancer Malignant polyp Screening programmes SM Invasive adenocar cinoma Advances in diagnostic & therapeutic endoscopy pt1 polyps 0.75 5.6% of large-bowel
Management of pt1 polyps Maria Pellise Early colorectal cancer Malignant polyp Screening programmes SM Invasive adenocar cinoma Advances in diagnostic & therapeutic endoscopy pt1 polyps 0.75 5.6% of large-bowel
Endoscopic atrophic classification before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia
 E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
E311 before and after H. pylori eradication is closely associated with histological atrophy and intestinal metaplasia Authors Institution Masaaki Kodama, Tadayoshi Okimoto, Ryo Ogawa, Kazuhiro Mizukami,
Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of the Colon
 clinical imaging Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of the Colon Dan Ionut Gheonea, Adrian Saftoiu, Tudorel Ciurea, Carmen Popescu, Claudia Valentina Georgescu, Anca Malos Research Center of Gastroenterology
clinical imaging Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of the Colon Dan Ionut Gheonea, Adrian Saftoiu, Tudorel Ciurea, Carmen Popescu, Claudia Valentina Georgescu, Anca Malos Research Center of Gastroenterology
Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of oesophageal cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (9): 4121-4125 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of o. Jie Gao #, Ailan Xian #, Tingfeng
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (9): 4121-4125 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Clinical studies of indicative biopsies in opportunistic screening in high risk population of o. Jie Gao #, Ailan Xian #, Tingfeng
Page 1. Is the Risk This High? Dysplasia in the IBD Patient. Dysplasia in the Non IBD Patient. Increased Risk of CRC in Ulcerative Colitis
 Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
Diagnosis of gastric intraepithelial neoplasia by narrowband imaging and confocal laser endomicroscopy
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4771 World J Gastroenterol 2012 September 14; 18(34): 4771-4780 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2012
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v18.i34.4771 World J Gastroenterol 2012 September 14; 18(34): 4771-4780 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online) 2012
malignant polyp Daily Challenges in Digestive Endoscopy for Endoscopists and Endoscopy Nurses BSGIE Annual Meeting 18/09/2014 Mechelen
 Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Plan Incidental finding of a malignant polyp 1. What is a polyp malignant? 2. Role of the pathologist and the endoscopist 3. Quantitative and qualitative risk assessment 4. How to decide what to do? Hubert
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD
 Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection ESD Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated
Marginal turbid band and light blue crest, signs observed in magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy, are indicative of gastric intestinal metaplasia
 An et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:169 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Marginal turbid band and light blue crest, signs observed in magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy, are indicative of gastric
An et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2012, 12:169 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Marginal turbid band and light blue crest, signs observed in magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy, are indicative of gastric
REPORT. McMahon Publishing Group. PENTAX Medical i-scan Technology for Improved Endoscopic Evaluations
 Brought to You by MAY 2014 PENTAX Medical i-scan Technology for Improved Endoscopic Evaluations Endoscopy plays a vital role in the diagnosis and clinical management of diseases of the gastrointestinal
Brought to You by MAY 2014 PENTAX Medical i-scan Technology for Improved Endoscopic Evaluations Endoscopy plays a vital role in the diagnosis and clinical management of diseases of the gastrointestinal
Can magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging be useful for low grade adenomas in preoperative biopsy specimens?
 Gastric Cancer (2012) 15:170 178 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0093-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Can magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging be useful for low grade adenomas in preoperative biopsy specimens? Kazuhiro
Gastric Cancer (2012) 15:170 178 DOI 10.1007/s10120-011-0093-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Can magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging be useful for low grade adenomas in preoperative biopsy specimens? Kazuhiro
Optical biopsy of early gastroesophageal cancer by catheter-based reflectance-type laser-scanning confocal microscopy
 Optical biopsy of early gastroesophageal cancer by catheter-based reflectance-type laser-scanning confocal microscopy Madoka Nakao, M.D. 1, Shigeto Yoshida, M.D. 2, Shinji Tanaka, M.D. 2, Yoshito Takemura,
Optical biopsy of early gastroesophageal cancer by catheter-based reflectance-type laser-scanning confocal microscopy Madoka Nakao, M.D. 1, Shigeto Yoshida, M.D. 2, Shinji Tanaka, M.D. 2, Yoshito Takemura,
153 esophagus. We also aim to evaluate this technology for the early detection of precancerous changes in the specialized columnar epithelium of Barrr
 152 Department of Endoscopy Hisao Tajiri, Professor Hiroshi Arakawa, Assistant Professor Hiroo Imazu, Assistant Professor Keiichi Ikeda, Assistant Professor Kazuki Sumiyama, Assistant Professor Tomohiro
152 Department of Endoscopy Hisao Tajiri, Professor Hiroshi Arakawa, Assistant Professor Hiroo Imazu, Assistant Professor Keiichi Ikeda, Assistant Professor Kazuki Sumiyama, Assistant Professor Tomohiro
EMR, ESD and Beyond. Peter Draganov MD. Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida
 EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
EMR, ESD and Beyond Peter Draganov MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Florida Gastrointestinal Cancer Lesion that Can be Treated by Endoscopy
Clinical Study Status of the Gastric Mucosa with Endoscopically Diagnosed Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
 Diagnostic and erapeutic Endoscopy, Article ID 429761, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/429761 Clinical Study Status of the Gastric Mucosa with Endoscopically Diagnosed Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
Diagnostic and erapeutic Endoscopy, Article ID 429761, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/429761 Clinical Study Status of the Gastric Mucosa with Endoscopically Diagnosed Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks
 Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Barrett s Esophagus: Old Dog, New Tricks Stuart Jon Spechler, M.D. Chief, Division of Gastroenterology, VA North Texas Healthcare System; Co-Director, Esophageal Diseases Center, Professor of Medicine,
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: chromoendoscopy_as_an_adjunct_to_colonoscopy 7/2012 11/2017
Corporate Medical Policy Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: chromoendoscopy_as_an_adjunct_to_colonoscopy 7/2012 11/2017
ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology
 ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology Jun Haeng Lee, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Biopsy: M/D adenocarcinoma ESD: SRC >>
ESD for EGC with undifferentiated histology Jun Haeng Lee, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Biopsy: M/D adenocarcinoma ESD: SRC >>
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics
 Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
Colon Polyps: Detection, Inspection and Characteristics Stephen Kim, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine Interventional Endoscopy Services UCLA Division of Digestive Diseases September 29, 2018 1 Disclosures
A multicenter validation of an endoscopic classification with narrow band imaging for gastric precancerous and cancerous lesions
 236 A multicenter validation of an endoscopic classification with narrow band imaging for gastric precancerous and cancerous lesions Authors P. Pimentel-Nunes 1,2, *, M. Dinis-Ribeiro 1,3, *, J. B. Soares
236 A multicenter validation of an endoscopic classification with narrow band imaging for gastric precancerous and cancerous lesions Authors P. Pimentel-Nunes 1,2, *, M. Dinis-Ribeiro 1,3, *, J. B. Soares
Highest power magnification with narrowband imaging is useful for improving diagnostic performance for endoscopic delineation of early gastric cancers
 Uchita et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2015) 15:155 DOI 10.1186/s12876-015-0385-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Highest power magnification with narrowband imaging is useful for improving diagnostic performance
Uchita et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2015) 15:155 DOI 10.1186/s12876-015-0385-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Highest power magnification with narrowband imaging is useful for improving diagnostic performance
Development of a new contrast endoscopic method With Techno Color blue P
 Bulletin of the Osaka Medical College 53 1 45-55, 2007 45 Original Article Development of a new contrast endoscopic method With Toshihisa TAKEUCHI, Eiji UMEGAKI, Satoshi TOKIOKA, Nozomi TAKEUCHI, Minekazu
Bulletin of the Osaka Medical College 53 1 45-55, 2007 45 Original Article Development of a new contrast endoscopic method With Toshihisa TAKEUCHI, Eiji UMEGAKI, Satoshi TOKIOKA, Nozomi TAKEUCHI, Minekazu
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD?
 How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
How to characterize dysplastic lesions in IBD? Name: Institution: Helmut Neumann, MD, PhD, FASGE University Medical Center Mainz What do we know? Patients with IBD carry an increased risk of developing
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy
 Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy Policy Number: 2.01.84 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Chromoendoscopy as an Adjunct to Colonoscopy Policy Number: 2.01.84 Last Review: 1/2018 Origination: 7/2017 Next Review: 7/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide
Vital staining and Barrett s esophagus
 Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Marcia Irene Canto, MD, MHS Baltimore, Maryland Vital staining or chromoendoscopy refers to staining of endoscopic tissue or topical application of chemical stains or pigments to alter tissue appearances
Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy
 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Policy Number: 2.01.87 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2013 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for
Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy Policy Number: 2.01.87 Last Review: 3/2018 Origination: 3/2013 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue KC) will not provide coverage for
Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor
 Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor Authors Kensuke Yokoyama 1,JunUshio 1,NorikatsuNumao 1, Kiichi Tamada 1, Noriyoshi Fukushima 2, Alan
Esophageal seeding after endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of a mediastinal tumor Authors Kensuke Yokoyama 1,JunUshio 1,NorikatsuNumao 1, Kiichi Tamada 1, Noriyoshi Fukushima 2, Alan
BENEFIT APPLICATION BLUE CARD/NATIONAL ACCOUNT ISSUES
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.84 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.87 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy 6.01.32 Virtual Colonoscopy/Computed
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.01.84 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 11/15/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 2.01.87 Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy 6.01.32 Virtual Colonoscopy/Computed
Disclosures. Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Early Gastric Cancer: Screening, Surveillance, and Endoscopic Therapy. ASGE Guidelines.
 Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Early Gastric Cancer: Screening, Surveillance, and Endoscopic Therapy Consultant for: Olympus Medtronic US Endoscopy Disclosures Joo Ha Hwang, MD, PhD Associate Professor
Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia and Early Gastric Cancer: Screening, Surveillance, and Endoscopic Therapy Consultant for: Olympus Medtronic US Endoscopy Disclosures Joo Ha Hwang, MD, PhD Associate Professor
Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1984;86;1437-42 ALIMENTARY TRACT Fundic Gland Polyposis in Patients Without Familial Adenomatosis Coli: Its Incidence and Clinical Features MITSUO IIDA, TSUNEYOSHI YAO, HIDENOBU WATANABE,
Correlation between microvascular characteristics and the expression of MVD, IGF-1 and STAT3 in the development of colonic polyps carcinogenesis
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 13: 49-54, 2017 Correlation between microvascular characteristics and the expression of MVD, IGF-1 and STAT3 in the development of colonic polyps carcinogenesis HONG
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 13: 49-54, 2017 Correlation between microvascular characteristics and the expression of MVD, IGF-1 and STAT3 in the development of colonic polyps carcinogenesis HONG
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Atrophic gastritis in patients with Dyspepsia
 ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
ADVANCES IN BIORESEARCH Adv. Biores., Vol 8 [3] May 2017: 137-141 2017 Society of Education, India Print ISSN 0976-4585; Online ISSN 2277-1573 Journal s URL:http://www.soeagra.com/abr.html CODEN: ABRDC3
Early and long term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in a large patient series
 594 Early and long term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in a large patient series KEN OHNITA 1, HAJIME ISOMOTO 1, SABURO SHIKUWA 2, HIROYUKI YAJIMA 1, HITOMI MINAMI
594 Early and long term outcomes of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in a large patient series KEN OHNITA 1, HAJIME ISOMOTO 1, SABURO SHIKUWA 2, HIROYUKI YAJIMA 1, HITOMI MINAMI
The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
 Real-Time Increased Detection of Neoplastic Tissue in Barrett s Esophagus with Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy: Final Results of an International Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Controlled
Real-Time Increased Detection of Neoplastic Tissue in Barrett s Esophagus with Probe-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy: Final Results of an International Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized, Controlled
Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging of Early Gastric Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology and Mucin Phenotype
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 4, July 2016, pp. 532-541 ORiginal Article Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging of Early Gastric Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology and Mucin Phenotype Kyung-Sun
Gut and Liver, Vol. 10, No. 4, July 2016, pp. 532-541 ORiginal Article Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging of Early Gastric Cancer: Correlation with Histopathology and Mucin Phenotype Kyung-Sun
Dysplasia 4/19/2017. How do I practice Chromoendoscopy for Surveillance of Colitis? SCENIC: Polypoid Dysplasia in UC. Background
 SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
SCENIC: Polypoid in UC Definition How do I practice for Surveillance of Colitis? Themos Dassopoulos, M.D. Director, BSW Center for IBD Themistocles.Dassopoulos@BSWHealth.org Tel: 469-800-7189 Cell: 314-686-2623
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus
 New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
New Developments in the Endoscopic Diagnosis and Management of Barrett s Esophagus Prateek Sharma, MD Key Clinical Management Points: Endoscopic recognition of a columnar lined distal esophagus is crucial
INTRODUCTION. Key Words: Gastroesophageal reflux; Agreement; Experience. ORiginal Article
 Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 154-159 ORiginal Article Endoscopic Experience Improves Interobserver Agreement in the Grading of Esophagitis by Los Angeles Classification: Conventional Endoscopy
Gut and Liver, Vol. 8, No. 2, March 2014, pp. 154-159 ORiginal Article Endoscopic Experience Improves Interobserver Agreement in the Grading of Esophagitis by Los Angeles Classification: Conventional Endoscopy
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 744-749 Interobserver Variability and Accuracy of High-Definition Endoscopic Diagnosis for Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia among
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gastroenterology & Hepatology J Korean Med Sci 2013; 28: 744-749 Interobserver Variability and Accuracy of High-Definition Endoscopic Diagnosis for Gastric Intestinal Metaplasia among
Multi-disciplinary team for early gastric cancer diagnosis improves the detection rate of early gastric cancer
 Di et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2017) 17:147 DOI 10.1186/s12876-017-0711-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Multi-disciplinary team for early gastric cancer diagnosis improves the detection rate of early gastric cancer
Di et al. BMC Gastroenterology (2017) 17:147 DOI 10.1186/s12876-017-0711-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Multi-disciplinary team for early gastric cancer diagnosis improves the detection rate of early gastric cancer
COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts..
 COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts.. Detection: I see an abnormality (usually a polyp) Characterization: Is this abnormality neoplastic? (for example: an adenoma) Treatment: it is neoplastic. Can I treat
COLON: Innovations 3 steps, 3 parts.. Detection: I see an abnormality (usually a polyp) Characterization: Is this abnormality neoplastic? (for example: an adenoma) Treatment: it is neoplastic. Can I treat
Barrett s Esophagus. Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI
 Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Barrett s Esophagus Abdul Sami Khan, M.D. Gastroenterologist Aurora Healthcare Burlington, Elkhorn, Lake Geneva, WI A 58 year-old, obese white man has had heartburn for more than 20 years. He read a magazine
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Barrett s Esophagus. Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book
 Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book 540 Oakmead Parkway, Sunnyvale, CA 94085 What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a change that occurs within the cellular lining
Radiofrequency Ablation with the HALO Technology A Reference Book 540 Oakmead Parkway, Sunnyvale, CA 94085 What is Barrett s esophagus? Barrett s esophagus is a change that occurs within the cellular lining
Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment Barrett s esophagus
 E318 Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment esophagus Authors Institution Arvind J. Trindade, Benley J. George, Joshua Berkowitz,
E318 Volumetric laser endomicroscopy can target neoplasia not detected by conventional endoscopic measures in long segment esophagus Authors Institution Arvind J. Trindade, Benley J. George, Joshua Berkowitz,
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy. Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital
 Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Emerging Interventions in Endoscopy Margaret Vance Nurse Consultant in Gastroenterology St Mark s Hospital Colon Cancer Colon cancer is common. 1 in 20 people in the UK will develop the disease 19 000
Gastroenterology Tutorial
 Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Gastroenterology Tutorial Gastritis Poorly defined term that refers to inflammation of the stomach. Infection with H. pylori is the most common cause of gastritis. Most patients remain asymptomatic Some
Technical and Endoscopic Factors in. in CDH1 Mutation Carriers
 Technical and Endoscopic Factors in Gastric Cancer Surveillance in CDH Mutation Carriers Carol A. Burke,3,5, Michael Cruise 2,5, Lisa LaGuardia 3,5, Margaret O Malley 3,5, Matthew Kalady 3,5, James Church
Technical and Endoscopic Factors in Gastric Cancer Surveillance in CDH Mutation Carriers Carol A. Burke,3,5, Michael Cruise 2,5, Lisa LaGuardia 3,5, Margaret O Malley 3,5, Matthew Kalady 3,5, James Church
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Quality ID #249 (NQF 1854): Barrett s Esophagus National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: CLAIMS ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process DESCRIPTION: Percentage
Risk factors for non-curative resection of early gastric neoplasms with endoscopic submucosal dissection: Analysis of 1,123 lesions
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 9: 1209-1214, 2015 Risk factors for non-curative resection of early gastric neoplasms with endoscopic submucosal dissection: Analysis of 1,123 lesions TATSUYA TOYOKAWA
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 9: 1209-1214, 2015 Risk factors for non-curative resection of early gastric neoplasms with endoscopic submucosal dissection: Analysis of 1,123 lesions TATSUYA TOYOKAWA
Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection for Early Gastric Cancer
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2015;48:251-255 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.3.251 Open Access Delayed Perforation Occurring after Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
The incidence of esophageal adenocarcinoma is rising in the ENDOSCOPY CORNER
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:843 847 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Acetic Acid Spray Is an Effective Tool for the Endoscopic Detection of Neoplasia in Patients With Barrett s Esophagus GAIUS LONGCROFT
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2010;8:843 847 ENDOSCOPY CORNER Acetic Acid Spray Is an Effective Tool for the Endoscopic Detection of Neoplasia in Patients With Barrett s Esophagus GAIUS LONGCROFT
Pharynx and esophagus atlas
 163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
163 Pharynx and esophagus atlas 11 Figure 11.1 High resolution white light image of normal vocal cords (NYU School of Medicine). Figure 11.2 Small nodule on arytenoid and cyst on vocal cord (Erasmus University
Introduction. Original articles. Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra Huertas, 2 Rosario Albis, 3 Diego Aponte, 4 Luis Carlos Sabbagh. 5
 Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Original articles Correlation of endoscopic and histological findings in diagnosis of gastrointestinal metaplasia in patients referred to the Clinica Colombia for upper endoscopies Nicolás Rocha, 1 Sandra
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2006, 47(3):
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 26, 7(3):239 23 ORIGINAL PAPER Predictive parameters for advanced neoplastic adenomas and colorectal cancer in patients with colonic polyps a study in a tertiary
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 26, 7(3):239 23 ORIGINAL PAPER Predictive parameters for advanced neoplastic adenomas and colorectal cancer in patients with colonic polyps a study in a tertiary
Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal Neoplasms: A Single Center Clinical Experience in China
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clin Endosc 2015;48:405-410 http://dx.doi.org/10.5946/ce.2015.48.5.405 Print ISSN 2234-2400 On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Factors for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection in Early Colorectal
ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1261 1267 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT In Vivo Histopathology for Detection of Gastrointestinal Neoplasia With a Portable, Confocal Miniprobe: An Examiner
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1261 1267 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ALIMENTARY TRACT In Vivo Histopathology for Detection of Gastrointestinal Neoplasia With a Portable, Confocal Miniprobe: An Examiner
Gastric Extremely Well-Diferentiated Intestinal-Type Adenocarcinoma: A Challenging Lesion to Achieve Complete Endoscopic Resection
 Gastric Extremely Well-Diferentiated Intestinal-Type Adenocarcinoma: A Challenging Lesion to Achieve Complete Endoscopic Resection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Gastric Extremely Well-Diferentiated Intestinal-Type Adenocarcinoma: A Challenging Lesion to Achieve Complete Endoscopic Resection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Mucosal Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma With Intramural Gastric Metastasis Invading Liver and Pancreas: A Case Report
 Int Surg 2014;99:458 462 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00069.1 Case Report Mucosal Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma With Intramural Gastric Metastasis Invading Liver and Pancreas: A Case Report Nobuhiro
Int Surg 2014;99:458 462 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00069.1 Case Report Mucosal Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma With Intramural Gastric Metastasis Invading Liver and Pancreas: A Case Report Nobuhiro
ASGE and AGA Issue Consensus Statement on Surveillance and Management of Dysplasia in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 ASGE and AGA Issue Consensus Statement on Surveillance and Management of Dysplasia in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease DOWNERS GROVE, Ill., (March 5, 2015) The American Society for Gastrointestinal
ASGE and AGA Issue Consensus Statement on Surveillance and Management of Dysplasia in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease DOWNERS GROVE, Ill., (March 5, 2015) The American Society for Gastrointestinal
Introduction. Keywords Gastric cancer Endoscopic resection Helicobacter pylori Endoscopic gastrointestinal surgery
 Gastric Cancer (2018) 21:988 997 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-018-0819-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic accuracy of demarcation using magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging for Helicobacter pylori
Gastric Cancer (2018) 21:988 997 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-018-0819-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic accuracy of demarcation using magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging for Helicobacter pylori
Case Report Intramucosal Signet Ring Cell Gastric Cancer Diagnosed 15 Months after the Initial Endoscopic Examination
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 479625, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/479625 Case Report Intramucosal Signet Ring Cell Gastric Cancer Diagnosed
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 479625, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/479625 Case Report Intramucosal Signet Ring Cell Gastric Cancer Diagnosed
Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery
 Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery Norman Barrett (1950) described the esophagus as: that part of the foregut, distal to the cricopharyngeal sphincter, which is lined
Joel A. Ricci, MD SUNY Downstate Medical Center Department of Surgery Norman Barrett (1950) described the esophagus as: that part of the foregut, distal to the cricopharyngeal sphincter, which is lined
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath
 Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Gastrointestinal pathology 2018 lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad FRCPath Eosinophilic esophagitis Incidence of eosinophilic gastritis is increasing. Symptoms: food impaction and dysphagia. Histology: infiltration
Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Endoscopic management of Barrett s esophagus with dysplasia Phoa, Nadine Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Phoa, K. Y. N. (2014). Endoscopic
