Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
|
|
|
- Jerome French
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided in the applicable contract. Medical technology is constantly evolving, and we reserve the right to review and update Medical Policy periodically. Services Are Considered Investigational Coverage is not available for investigational medical treatments or procedures, drugs, devices or biological products. Based on review of available data, the Company considers digital breast tomosynthesis in the screening or diagnosis of breast cancer to be investigational.* Background/Overview Digital breast tomosynthesis uses modified digital mammography equipment to obtain additional radiographic data that are used to reconstruct cross-sectional slices of breast tissue. Tomosynthesis may improve the accuracy of digital mammography by reducing problems caused by overlapping tissue. Tomosynthesis typically involves additional imaging time and radiation exposure, although a recently improved modification may change this. Conventional mammography produces two-dimensional (2D) images of the breast. Overlapping tissue on a 2D image can mask suspicious lesions or make benign tissue appear suspicious, particularly in women with dense breast tissue. As a result, women may be recalled for additional mammographic spot views. Inaccurate results may lead to unnecessary biopsies and emotional stress, or to a potential delay in diagnosis. The spot views are often used to evaluate microcalcifications, opacities or architectural distortions or to distinguish masses from overlapping tissue, as well as to view possible findings close to the chest wall or in the retro-areolar area behind the nipple. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) reports that approximately 20% of cancers are missed at mammography screening. Average recall rates are approximately 10%, with an average cancer detection rate of 4.7 per 1,000 screening mammography examinations. The Mammography Quality Standards Act audit guidelines anticipate 2-10 cancers detected per 1,000 screening mammograms. Interval cancers, which are detected between screenings, tend to have poorer prognoses. Digital breast tomosynthesis was developed to improve the accuracy of mammography by capturing threedimensional (3D) images of the breast, further clarifying areas of overlapping tissue. Developers proposed that its use would result in increased sensitivity and specificity, as well as fewer recalls due to inconclusive results. Digital breast tomosynthesis produces a 3D image by taking multiple low-dose images per view along an arc over the breast. During breast tomosynthesis, the compressed breast remains stationary while the x-ray tube moves approximately 1 degree for each image in a degree arc, acquiring images. These images are projected as cross-sectional slices of the breast, with each slice typically 1-mm thick. Adding breast tomosynthesis takes about 10 seconds per view. In one study in a research setting, the mean time to interpret the results was 1.22 (standard deviation [SD] = 1.15) minutes for digital mammography and 2.39 (SD = 1.65) for combined digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis. Page 1 of 9
2 With conventional 2D mammography, breast compression helps decrease tissue overlap and improve visibility. By reducing problems with overlapping tissue, compression with breast tomosynthesis may be reduced by up to 50%. This change could result in improved patient satisfaction. A machine equipped with breast tomosynthesis can perform 2D digital mammography, 3D digital mammography, or a combination of both 2D and 3D mammography during a single compression. The radiation exposure from tomosynthesis is roughly equivalent to a mammogram. Therefore, adding tomosynthesis to mammography doubles the radiation dose, although it still is below the maximum allowable dose established in the U.S. Mammography Quality Standards Act. Studies typically compare one- or more commonly, two-view breast tomosynthesis alone or combined with standard 2D mammography to standard 2D mammography alone. The assessment focuses on two-view tomosynthesis. According to the FDA Radiological Devices Panel, which reviewed this new modality: 2D [full-field digital mammography] plus a single [digital breast tomosynthesis] view (3D MLO) could be another exam option, but the full 2-view [digital breast tomosynthesis] protocol (MLO [mediolateral oblique view] and CC [cranio-caudal view]) would be recommended. In May 2013, the FDA approved new tomosynthesis software that will permit creation of a 2D image (called C view) from the tomosynthesis images. As a result, the 2D mammography may become unnecessary, thereby lowering the radiation dose. In other words, only the tomosynthesis procedure will be needed and both 2D and 3D images will be created from them. It is too early to gauge how traditional mammography plus tomosynthesis compares to the C view plus 3D images. The study submitted to the FDA was a noninferiority trial that compared the combined C view and 3D reconstruction to digital tomosynthesis alone, so it does not provide information on the comparison of greater interest. FDA or Other Governmental Regulatory Approval U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) The Selenia Dimensions 3D System manufactured by Hologic, Inc. achieved FDA approval on February 11, 2011 through the premarket application (PMA) approval process. It is currently the only tomosynthesis system with FDA approval on the market. This system is a software and hardware upgrade of the Selenia Dimensions 2D full-field digital mammography system, which the FDA approved in Facilities using a digital breast tomosynthesis system must apply to the FDA for a certificate extension covering the use of the breast tomosynthesis portion of the unit. The Mammography Quality Standards Act requires the interpreting physicians, radiologic technologists, and medical physicists to complete 8 hours of digital breast tomosynthesis training and mandates a detailed mammography equipment evaluation prior to use. In May 2013, the FDA also approved Hologic's C-View 2D imaging software. This software is used to create 2D images from the tomosynthesis results, rather than performing a separate mammogram. Several other manufacturers are working toward FDA approval of their digital breast tomosynthesis systems. GE Healthcare is seeking FDA PMA for breast tomosynthesis, specifically as an add-on option for the Senographe Essential mammography device. The FDA has agreed to a modular PMA submission, which means that GE Healthcare will submit the request in different sections. The first of 4 sections was submitted in November Three completed trials sponsored by GE are listed at online site Page 2 of 9
3 clinicaltrials.gov. They focus on the use of breast tomosynthesis in routine screening (NCT ), in women undergoing diagnostic mammography (NCT ), and in women referred for breast biopsy (NCT ). The results do not appear to have been published to date. Rationale/Source The primary outcomes to be examined include the number of cancers detected and the number of unnecessary recalls and biopsies. Improvement in sensitivity and specificity of testing is an intermediate outcome that will impact the ultimate health outcomes, but is not by itself sufficient to establish that outcomes are improved. If the sensitivity of breast cancer detection is improved by tomosynthesis, then the number of cases detected will increase. If the specificity of cancer detection is improved, then the number of recalls and biopsies for patients without cancer will decreased. If tomosynthesis is performed during screening, the number of unnecessary recalls may decline, with the attendant anxiety and inconvenience for the patient. If tomosynthesis is performed as part of the diagnostic workup, after a woman is recalled for questionable findings during screening, then a lower false-positive rate could prevent unnecessary biopsies. Screening: Four studies addressed the use of mammography with or without digital breast tomosynthesis for screening. The strongest evidence for using mammography and breast tomosynthesis for screening women for breast cancer comes from the interim results of a large trial in Norway. The sample consisted of 12,621 women with 121 screening-detected cancers who underwent routine screening. The cancer detection rate was 6.1 per 1000 screenings for mammography alone and 8.0 per 1000 screenings for mammography plus digital breast tomosynthesis. After adjusting for reader differences, the ratio of cancer detection rates for mammography versus mammography plus breast tomosynthesis was 1.27 (98.5% confidence interval [CI]: 1.06 to 1.53; p = 0.001). The authors note that they did not ascertain any improvement in detecting ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) by adding breast tomosynthesis; the additional cancers detected were largely invasive. The false-positive rate was 61.1 per 1,000 screenings for mammography alone and 53.1 per 1,000 screenings for mammography plus breast tomosynthesis. A reduction in the false-positive rate would decrease the number of women recalled after screening for additional imaging or biopsy. In Norway, as in much of Europe, women are screened every other year, and 2 readers independently interpret the images, which differs from usual practice in the U.S. After adjusting for differences across readers, the ratio of false-positive rates for mammography alone versus mammography plus breast tomosynthesis was 0.85 (98.5% CI: 0.76 to 0.96; p < 0.001). The authors note that for this interim analysis, only limited data were available about interval cancers so they could not estimate conventional absolute sensitivity and specificity. Additional information will be available when the trial is completed. The second study examined comparative cancer detection for traditional mammography with or without breast tomosynthesis in a general Italian, asymptomatic screening population of 7,292 women. The reference standard was pathology for women undergoing biopsies; women with negative results on both mammography and breast tomosynthesis were not followed up, so neither the sensitivity nor specificity could be calculated. Mammography plus breast tomosynthesis revealed all 59 cancers, while 20 of them were missed by traditional mammography (p < ). The incremental cancer detection of using both modalities was 2.7 cancers per 1,000 screens (95% CI: 1.7 to 4.2). There were 395 false-positive results: 181 were false positive using either mammography or both imaging modalities together; an additional 141 Page 3 of 9
4 occurred using mammography only and 73 occurred using mammography and breast tomosynthesis combined (p < ). In preplanned analyses, the researcher found that the combined results of mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis yielded more cancers in both age groups (< 60 versus > 60 years) and breast density categories (1, least dense, and 2 versus 3 and 4, most dense). Another study compared the results of mammography alone versus breast tomosynthesis plus mammography among 997 subjects with mixed indications: 780 were women undergoing routine screening, and 217 were women scheduled for biopsy. Two retrospective reader studies were conducted. Some of these results were included in the submission to the FDA for premarketing application approval of Hologic, Inc. s Selenia Dimensions tomosynthesis system. Readers were trained in interpreting tomosynthesis images, and the training was augmented between the first and second reader studies to emphasize how to read certain lesions that were often misinterpreted in the first reader study. In both reader studies, the area under the ROC curve for mammography plus breast tomosynthesis was greater than for mammography alone; the difference for the second study was 6.8% (95% CI: 4.1% to 9.5%, p < 0.001). For noncancer cases, adding breast tomosynthesis to mammography changed the mean recall rate across readers for study 2 from 48.8% (95% CI: 28.2% to 69.1%; SD = 12.3%) to 30.1% (95% CI: 19.8% to 41.3%; SD = 7.6%) for the combined modalities. Almost all of the improvement among readers was attributable to noncalcification cases, including masses, asymmetries, and architectural distortions. All of these studies had a medium risk of bias using the QUADAS-2 (Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies; available online at: tool, except for the fourth screening study, which had a high risk of bias. One of the 3 related articles on this study reported that the recall rate among noncancer cases was 0.42 (95% CI: 0.38 to 0.45) for digital mammography alone and 0.28 (95% CI: 0.25 to 0.31) for digital mammography plus breast tomosynthesis (p < ). The analogous rates for cancer cases were 0.88 (95% CI: 0.84 to 0.91) for digital mammography alone and 0.93 (95% CI: 0.90 to 0.96) for digital mammography plus breast tomosynthesis. The sensitivity of digital mammography alone was 60% and increased to 72% when breast tomosynthesis was added (p = 0.034, but the authors note the small number of positive findings). These articles did not describe the sample, the time between digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis, or how the reference standard was verified. These studies provide some evidence that adding breast tomosynthesis to mammography may increase the accuracy (and possibly the sensitivity) of screening while reducing the number of women who are recalled unnecessarily. Two of the studies took place in a routine screening environment and did not have adequate follow-up of women with negative screening results; the larger study provided interim results. The other two studies were retrospective reviews of cases; the sample for one had a mixed indications, while it is unclear for the other study. Diagnosis: Six studies address the use of breast tomosynthesis in the diagnostic setting, i.e., if there are suspicious findings on screening mammography or if the woman is symptomatic. The studies vary considerably in the types of suspicious mammographic findings (e.g., calcifications versus noncalcifications); the patient population; and the comparators to breast tomosynthesis, e.g., two-view mammography, mammographic spot views, ultrasound. One study had a medium risk of bias; the remainder, a high risk of bias using the QUADAS-2 tool. Page 4 of 9
5 In a study of 158 women consecutively recalled after screening mammography, breast tomosynthesis was evaluated as a possible triage tool to reduce the number of false-positive results. The results of the diagnostic assessment (including ultrasound and needle biopsy where performed) were used as the reference standard. Breast tomosynthesis eliminated 102 of the 158 recalls, all of which were unnecessary (i.e., false-positive results on mammography). No cancers were missed on breast tomosynthesis. The performance of breast tomosynthesis did not vary by breast density or age group, but the reduction in recalls was greater for asymmetric densities and distortions, and nodular opacities with regular margins. The authors note that the decline in recall rates following the use of breast tomosynthesis was higher in this study than in blinded comparisons of digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis. Another study compared the performance of mammographic spot views versus tomosynthesis among 52 consecutive recalled women with a BI-RADS rating on initial screening of 0 (which means Need Additional Imaging Evaluation and/or Prior Mammograms for Comparison ). Women with calcifications were excluded. The study was designed as a noninferiority analysis for areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, sensitivity, and specificity, with a noninferiority margin of delta = 0.05, so that if breast tomosynthesis were noninferior to mammographic spot views, breast tomosynthesis could be performed right after screening mammography to avoid a recall. The sensitivity and specificity were extremely high for both modalities, and there was no statistically significant difference between them. A third study compared diagnostic mammography to breast tomosynthesis among women with abnormalities on screening mammography with no calcifications in a simulated clinical setting. The breast tomosynthesis rating was based on both readers ratings and their confidence that no additional studies were needed, as well as ultrasound results in some cases. The reference standard was either the results of the entire clinical workup, including biopsy if performed, or follow-up for women not undergoing biopsy (86.1% of entire sample).there was not a statistically significant difference between diagnostic mammography and breast tomosynthesis in sensitivity or specificity. Two of the these 3studies found no difference in sensitivity and specificity between breast tomosynthesis and a clinical workup that consisted of diagnostic mammographic images or a more comprehensive diagnostic work-up. The third study examined the use of breast tomosynthesis to triage women recalled after screening and substantially reduced the recall rate. Another study evaluated 738 women with 759 lesions recalled after screening with film mammography. In this unblinded study, the incremental value of breast tomosynthesis added to film and digital mammography was assessed. The reference standard consisted of pathology results or follow-up for 18 to 36 months. Adding breast tomosynthesis to film and digital mammography results increased the area under the ROC curve from ( ) to ( ) (p = 0.001). The complete sensitivity (counting ratings of 3-5 as positive) increased from 39.7% for digital mammography to 58.3% when breast tomosynthesis was added; no CIs or p values were reported. The specificity increased from 51% to 74.2% when breast tomosynthesis was added to digital mammography. The difference in areas under the ROC curve after the addition of breast tomosynthesis was statistically significant for soft-tissue lesions, but not for microcalcifications. Page 5 of 9
6 One study compared diagnostic mammography images to dual-view breast tomosynthesis in 217 lesions (72 [33%] malignant) among 182 women. In this retrospective study, women who had undergone diagnostic mammography and breast tomosynthesis were included. The sample included women with clinical symptoms such as a palpable lump, or findings on mammograms, ultrasound, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Women with only calcifications were excluded. The area under the ROC curve for diagnostic mammography was 0.83 (95% CI: 0.77 to 0.83; range across readers = ), while for tomosynthesis, it was 0.87 (95% CI: 0.82 to 0.92; range across readers = ; p < 0.001).. The authors of the Norse trial also wrote another article on their initial experience with digital breast tomosynthesis in a clinical setting. This mixed set of articles provides evidence of either a similar diagnostic performance between breast tomosynthesis and other approaches or an advantage for breast tomosynthesis. The mixed patient populations, differences in references standard, use of different imaging tests to compare to breast tomosynthesis, and variations in follow-up make it difficult to draw a conclusion from these studies. Conclusions Screening: The Norse and Italian screening studies published in 2013 provide the strongest evidence available to date on the use of mammography plus digital breast tomosynthesis versus mammography alone for screening women for breast cancer. This evidence suggests that the use of the mammography plus breast tomosynthesis may modestly increase the number of cancers detected, while having a large impact on decreasing the number of women who undergo unnecessary recalls or biopsies. For example, the interim results of the Norway screening trial reported that the ratio of cancer detection rates per 1,000 screens for mammography versus mammography plus breast tomosynthesis was 1.27 (98.5% CI: 1.06 to 1.53; p = 0.001). The ratio of false-positive rates for mammography alone versus mammography plus breast tomosynthesis was 0.85 (98.5% CI: 0.76 to 0.96; p < 0.001). Even if adding breast tomosynthesis simply maintained the same sensitivity as for mammography, a decline in the false-positive rate would reduce the substantial number of unnecessary diagnostic work-ups in the U.S. and spare women the psychological stress these engender. Completion of the Norse trial and additional studies are needed to confirm these findings, as well as studies that indicate whether the use of breast tomosynthesis should be targeted at certain subgroups, e.g., by age and breast density. The configuration of mammography and breast tomosynthesis used in these studies roughly doubled the radiation dose of mammography alone, but the exposure was still lower than the guideline established in the Mammography Standards and Quality Act. On May 20, 2013, the FDA approved new tomosynthesis software from Hologic that would create a 2d image from the tomosynthesis images and obviate the need for a separate mammogram. This approach would reduce the radiation dose of the combination, but studies are needed to compare its performance to traditional mammography plus breast tomosynthesis, since the study submitted to the FDA only compared C view and 3D tomosynthesis to tomosynthesis alone. Diagnosis: The potential of digital breast tomosynthesis, as an addition to diagnostic mammography (such as spot views), is primarily to reduce the number of women who are biopsied by screening out some Page 6 of 9
7 fraction of women with false-positive results. The body of evidence on the use of breast tomosynthesis to evaluate women who are recalled for a diagnostic work-up after a suspicious finding on screening mammography is weaker than that on adding breast tomosynthesis to mammography for screening. Confounding this analysis is the fact that diagnostic mammography is not the only imaging modality used during the diagnostic work-up. Ultrasound is also commonly used and less often, MRI. As a result, the study designs are more complicated in terms of how they incorporate ultrasound into the comparison between diagnostic mammography and breast tomosynthesis. A different research design would be needed to assess the incremental value of tomosysnthesis compared to the set of diagnostic tests currently used. In addition, some of the studies focused on one type of finding, e.g., masses versus calcification. They do not provide data on the accuracy of breast tomosynthesis for the full range of findings. Ongoing Research Digital breast tomosynthesis continues to be an active field of investigation. According to online site clinicaltrials.gov ( as of May 18, 2013, there were 15 trials on breast tomosynthesis enrolling subjects and 7 that were active but not recruiting. All but 2 of the studies had sample sizes larger than 100, and 6 studies were larger than 1,000 e.g., studies had estimated sample sizes of 10,000 (NCT ); 15,000 (NCT ); and 25,000 (the study whose interim analysis is reported by Skaane et al; NCT ). A study comparing screening recall rates for digital mammography versus breast tomosynthesis is being conducted by the American College of Radiology Imaging Network (ACRIN) and has a sample size of 550 (NCT ). One large study with target enrollment of 12,000 was suspended due to funding unavailability (NCT ). Several studies have also been conducted using different breast tomosynthesis equipment, including one using the Siemens Inspiration system (NCT ) and 3 completed studies sponsored by GE Healthcare that have not yet been published (NCT NCT , NCT NCT , NCT ). References 1. Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, Medical Policy Reference Manual,, , 7: Tagliafico A, Astengo D, Cavagnetto F et al. One-to-one comparison between digital spot compression view and digital breast tomosynthesis. Eur Radiol 2012; 22(3): National Cancer Institute (NCI). Factsheet: Mammograms Available online at: 4. Rosenberg RD, Yankaskas BC, Abraham LA et al. Performance benchmarks for screening mammography. Radiology 2006; 241(1): Brandt KR, Craig DA, Hoskins TL et al. Can digital breast tomosynthesis replace conventional diagnostic mammography views for screening recalls without calcifications? A comparison study in a simulated clinical setting. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013; 200(2): Shen Y, Yang Y, Inoue LY et al. Role of detection method in predicting breast cancer survival: analysis of randomized screening trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 2005; 97(16): Smith A. Fundamentals of breast tomosynthesis [WP-00007]. Bedford, MA: Hologic, Inc.; 2008:8. 8. Alakhras M, Bourne R, Rickard M et al. Digital tomosynthesis: A new future for breast imaging? Clin Radiol Gur D, Abrams GS, Chough DM et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis: observer performance study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009; 193(2): U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Summary of Safety and Effectiveness Data (SSED) Available online at: Page 7 of 9
8 11. Hologic I. Press release: Hologic Receives FDA Approval for a New Low-dose 3D Mammography (Breast Tomosynthesis) Solution for Breast Cancer Screening. Bedford, MA Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Technology Evaluation Center (TEC). Use of with Mammography for Breast Cancer Screening or Diagnosis. TEC Assessments 2013; Volume 28, Tab TBA. 13. Skaane P, Bandos AI, Gullien R et al. Comparison of Digital Mammography Alone and Digital Mammography Plus Tomosynthesis in a Population-based Screening Program. Radiology 2013; 267(1): Ciatto S, Houssami N, Bernardi D et al. Integration of 3D digital mammography with tomosynthesis for population breast-cancer screening (STORM): a prospective comparison study. Lancet Oncol 2013; 14(7): Rafferty EA, Park JM, Philpotts LE et al. Assessing radiologist performance using combined digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis compared with digital mammography alone: results of a multicenter, multireader trial. Radiology 2013; 266(1): Good WF, Abrams GS, Catullo VJ et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis: a pilot observer study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008; 190(4): Gur D, Bandos AI, Rockette HE et al. Localized detection and classification of abnormalities on FFDM and tomosynthesis examinations rated under an FROC paradigm. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2011; 196(3): Bernardi D, Ciatto S, Pellegrini M et al. Prospective study of breast tomosynthesis as a triage to assessment in screening. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2012; 133(1): Michell MJ, Iqbal A, Wasan RK et al. A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography, full-field digital mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis. Clin Radiol 2012; 67(10): Zuley ML, Bandos AI, Ganott MA et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis versus supplemental diagnostic mammographic views for evaluation of noncalcified breast lesions. Radiology 2013; 266(1): Skaane P, Gullien R, Bjorndal H et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT): initial experience in a clinical setting. Acta Radiol 2012; 53(5): Coding The five character codes included in the Blue Cross Blue Shield of Louisiana Medical Policy Coverage Guidelines are obtained from Current Procedural Terminology (CPT ), copyright 2013 by the American Medical Association (AMA). CPT is developed by the AMA as a listing of descriptive terms and five character identifying codes and modifiers for reporting medical services and procedures performed by physician. The responsibility for the content of Blue Cross Blue Shield of Louisiana Medical Policy Coverage Guidelines is with Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and no endorsement by the AMA is intended or should be implied. The AMA disclaims responsibility for any consequences or liability attributable or related to any use, nonuse or interpretation of information contained in Blue Cross Blue Shield of Louisiana Medical Policy Coverage Guidelines. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the AMA, are not part of CPT, and the AMA is not recommending their use. The AMA does not directly or indirectly practice medicine or dispense medical services. The AMA assumes no liability for data contained or not contained herein. Any use of CPT outside of Blue Cross Blue Shield of Louisiana Medical Policy Coverage Guidelines should refer to the most current Current Procedural Terminology which contains the complete and most current listing of CPT codes and descriptive terms. Applicable FARS/DFARS apply. CPT is a registered trademark of the American Medical Association. Codes used to identify services associated with this policy may include (but may not be limited to) the following: Code Type Code CPT 76499, 77055, 77056, HCPCS G0202, G0204, G0206 ICD-9 Diagnosis thru 174.9, thru 175.9, , 233.0, , V10.3, V16.3, V84.01 ICD-9 Procedure No codes Page 8 of 9
9 Policy History 04/07/2011 Medical Policy Committee review 04/13/2011 Medical Policy Implementation Committee approval. New policy. 04/12/2012 Medical Policy Committee review 04/25/2012 Medical Policy Implementation Committee approval. No change to policy coverage. 05/02/2013 Medical Policy Committee review 05/22/2013 Medical Policy Implementation Committee approval. No change to policy coverage. 05/01/2014 Medical Policy Committee review 05/21/2014 Medical Policy Implementation Committee approval. Coverage eligibility unchanged. 07/25/2014 Coding update: codes G0202, G0204, G0206 included for this policy due to coding guidelines. Next Scheduled Review Date: 05/2015 *Investigational A medical treatment, procedure, drug, device, or biological product is Investigational if the effectiveness has not been clearly tested and it has not been incorporated into standard medical practice. Any determination we make that a medical treatment, procedure, drug, device, or biological product is Investigational will be based on a consideration of the following: A. whether the medical treatment, procedure, drug, device, or biological product can be lawfully marketed without approval of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and whether such approval has been granted at the time the medical treatment, procedure, drug, device, or biological product is sought to be furnished; or B. whether the medical treatment, procedure, drug, device, or biological product requires further studies or clinical trials to determine its maximum tolerated dose, toxicity, safety, effectiveness, or effectiveness as compared with the standard means of treatment or diagnosis, must improve health outcomes, according to the consensus of opinion among experts as shown by reliable evidence, including: 1. Consultation with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association technology assessment program (TEC) or other nonaffiliated technology evaluation center(s); 2. credible scientific evidence published in peer-reviewed medical literature generally recognized by the relevant medical community; or 3. reference to federal regulations. Indicated trademarks are the registered trademarks of their respective owners. NOTICE: Medical Policies are scientific based opinions, provided solely for coverage and informational purposes. Medical Policies should not be construed to suggest that the Company recommends, advocates, requires, encourages, or discourages any particular treatment, procedure, or service, or any particular course of treatment, procedure, or service. Page 9 of 9
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
MRI of the Breast Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scintimammography/Breast-Specific Gamma Imaging/Molecular Breast Imaging
 6.01.53 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Section Radiology Subsection Effective Date September 30, 2014 Original Policy Date June 28, 2013 Next Review Date September 2015 Description Digital breast tomosynthesis
6.01.53 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Section Radiology Subsection Effective Date September 30, 2014 Original Policy Date June 28, 2013 Next Review Date September 2015 Description Digital breast tomosynthesis
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Cryosurgical Ablation of Breast Fibroadenomas
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
vedolizumab (Entyvio )
 vedolizumab (Entyvio ) Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ),
vedolizumab (Entyvio ) Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ),
denosumab (Prolia ) Policy # Original Effective Date: 07/21/2011 Current Effective Date: 04/19/2017
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Based on review of available data, the Company may consider the use of denosumab (Prolia) for the
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Analysis of Human DNA in Stool Samples as a Technique for Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Analysis of Human DNA in Stool Samples as a Technique for Colorectal Cancer Screening Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Analysis of Human DNA in Stool Samples as a Technique for Colorectal Cancer Screening Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Implantable Hormone Pellets
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
burosumab (Crysvita )
 burosumab (Crysvita ) Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ),
burosumab (Crysvita ) Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ),
sebelipase alfa (Kanuma )
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography, full-field digital mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis
 Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Vertebral Axial Decompression
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Corporate Medical Policy. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT)
 Corporate Medical Policy Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Description of Procedure or Service DBT is a three-dimensional (3D) breast imaging technology that uses a rotating X-ray source to acquire multiple
Corporate Medical Policy Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Description of Procedure or Service DBT is a three-dimensional (3D) breast imaging technology that uses a rotating X-ray source to acquire multiple
and will be denied as not medically necessary** if not met. This criterion only applies to the initial
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Monitoring of Regional Cerebral Blood Flow Using an Implanted Cerebral Thermal Perfusion Probe Archived Medical Policy
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
2017 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Susan Orel Roth, MD
 Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer 3/10/16
 Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer Policy Number: MCP-270 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 3/10/16 Review Date: 6/22/17, 3/8/18 MCPC Approval Date: 3/8/18 DISCLAIMER
Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer Policy Number: MCP-270 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 3/10/16 Review Date: 6/22/17, 3/8/18 MCPC Approval Date: 3/8/18 DISCLAIMER
FDA Executive Summary
 Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? TERMS (AKA) WHAT IS TOMOSYNTHESIS? 3/3/2014. Digital breast tomosynthesis =
 #46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
Partial Coherence Interferometry as a Technique to Measure the Axial Length of the Eye Archived Medical Policy
 Partial Coherence Interferometry as a Technique to Measure the Axial Length of the Eye Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Partial Coherence Interferometry as a Technique to Measure the Axial Length of the Eye Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
2018 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE?
 X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast cancer screening: Does tomosynthesis augment mammography?
 REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
End-Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Lymphedema
 End-Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
End-Diastolic Pneumatic Compression Boot as a Treatment of Peripheral Vascular Disease or Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Prostate Cancer
 Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Prostate Cancer Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana,
Saturation Biopsy for Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Prostate Cancer Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana,
ustekinumab (Stelara )
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS
 ABBY DUROJAYE,M.D CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS BOTH HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO BE EFFECTIVE TOOLS EARLY DETECTION OF BREAST
ABBY DUROJAYE,M.D CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS BOTH HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO BE EFFECTIVE TOOLS EARLY DETECTION OF BREAST
2017 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Urinary Metabolite Tests for Adherence to Direct-Acting Antiviral Medications for Hepatitis C Archived Medical Policy
 Urinary Metabolite Tests for Adherence to Direct-Acting Antiviral Medications for Hepatitis C Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Urinary Metabolite Tests for Adherence to Direct-Acting Antiviral Medications for Hepatitis C Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS. The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000
 WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000
 WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
Percutaneous Discectomy
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D Mammography Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
Peripheral Subcutaneous Field Stimulation
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in the Diagnostic Environment: A Subjective Side-by-Side Review
 Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Zurampic, Duzallo (lesinurad Products)
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Ustekinumab (Stelara )
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
What s New in Breast Imaging. Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia
 What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
3D Mammography. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
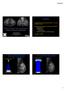 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Nutrient/Nutritional Panel Testing
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Note: Repository Corticotropin Injection (ACTH Gel, H.P. Acthar Gel) is addressed in medical policy
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
 Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Volume 14 - Issue 3, Matrix
 Volume 14 - Issue 3, 2014 - Matrix Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Author ECRI ECRI Institute 29 Broadwater Road Suite 104 Welwyn Garden City AL7 3BQ United Kingdom
Volume 14 - Issue 3, 2014 - Matrix Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Author ECRI ECRI Institute 29 Broadwater Road Suite 104 Welwyn Garden City AL7 3BQ United Kingdom
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography
 BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer
 What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update. Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
WHAT TO EXPECT. Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC. The Women's Health Company
 WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine
 International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis
 Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Detection and Classification of Calcifications on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and 2D Digital Mammography: A Comparison
 Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for Routine Clinical Use Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for routine clinical use Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President - Imaging Sciences, Hologic This white paper
Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for Routine Clinical Use Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for routine clinical use Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President - Imaging Sciences, Hologic This white paper
Mammography. What is Mammography? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
the one name in cancer care.
 the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients
 Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Implantable Hormone Pellets
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
2015 Reimbursement Information for Mammography, CAD and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis 1
 GE Healthcare 2015 Reimbursement Information for Mammography, CAD and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis 1 April, 2015 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This advisory addresses Medicare coding, coverage and
GE Healthcare 2015 Reimbursement Information for Mammography, CAD and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis 1 April, 2015 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This advisory addresses Medicare coding, coverage and
Vertebroplasty/Kyphoplasty
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese
 Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose
 MicroDose Mammography Solutions Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose Several studies provide evidence that Philips MicroDose Mammography* can provide outstanding image quality at 18% to
MicroDose Mammography Solutions Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose Several studies provide evidence that Philips MicroDose Mammography* can provide outstanding image quality at 18% to
certolizumab pegol (Cimzia )
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening?
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
DESCRIPTION: Percentage of final reports for screening mammograms that are classified as probably benign
 Quality ID #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL
Quality ID #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL
Sensipar (cinacalcet)
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Breast Tomosynthesis. What is breast tomosynthesis?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
TOMOSYNTHESIS. Daniela Bernardi. U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy
 TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
Jing Zhang, PhD, Lars J. Grimm, MD, MHS, Joseph Y. Lo, PhD, Karen S. Johnson, MD,
 This manuscript has been accepted for publication in Journal of the American College of Radiology. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published
This manuscript has been accepted for publication in Journal of the American College of Radiology. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Greenberg et al. Breast Cancer Screening Using 3D DBT Versus 2D DM Women s Imaging Original Research Julianne S. Greenberg 1 Marcia C. Javitt 2 Jason Katzen 1 Sara Michael
Women s Imaging Original Research Greenberg et al. Breast Cancer Screening Using 3D DBT Versus 2D DM Women s Imaging Original Research Julianne S. Greenberg 1 Marcia C. Javitt 2 Jason Katzen 1 Sara Michael
The Radiology Aspects
 REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research David Gur 1 Andriy I. Bandos 2 Howard E. Rockette 2 Margarita L. Zuley 3 Jules H. Sumkin 3 Denise M. Chough 3 Christiane M. Hakim 3 Gur
Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research David Gur 1 Andriy I. Bandos 2 Howard E. Rockette 2 Margarita L. Zuley 3 Jules H. Sumkin 3 Denise M. Chough 3 Christiane M. Hakim 3 Gur
Clinical Policy: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Reference Number: CP.MP.90
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.90 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 12/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.90 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 12/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Analysis of Human DNA in Stool Samples as a Technique for Colorectal Cancer Screening
 Analysis of Human DNA in Stool Samples as a Technique for Colorectal Cancer Screening Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Analysis of Human DNA in Stool Samples as a Technique for Colorectal Cancer Screening Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Laboratory Tests for Heart Transplant Rejection
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Medical Policy Coverage Guidelines
 Medical Policy Coverage Guidelines Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc. (collectively referred to as "BCBSLA") have developed these medical policies to serve
Medical Policy Coverage Guidelines Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc. (collectively referred to as "BCBSLA") have developed these medical policies to serve
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- AIDED DETECTION (CAD) POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
2017 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Recall and Cancer Detection Rates for Screening Mammography: Finding the Sweet Spot
 Women s Imaging Original Research Grabler et al. Optimal Recall and Cancer Detection Rates for Screening Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Paula Grabler 1 Dominique Sighoko 2 Lilian Wang 3
Women s Imaging Original Research Grabler et al. Optimal Recall and Cancer Detection Rates for Screening Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Paula Grabler 1 Dominique Sighoko 2 Lilian Wang 3
dichlorphenamide (Keveyis )
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography
 Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Tumor-Treatment Fields Therapy for Glioblastoma
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
DESCRIPTION: Percentage of final reports for screening mammograms that are classified as probably benign
 Measure #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F
Measure #146 (NQF 0508): Radiology: Inappropriate Use of Probably Benign Assessment Category in Screening Mammograms National Quality Strategy Domain: Efficiency and Cost Reduction 2016 PQRS OPTIONS F
Advice Statement 005/18 April 2018
 Advice Statement 005/18 April 2018 In asymptomatic women attending for breast screening, what is the clinical and cost effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) in addition to full-field digital
Advice Statement 005/18 April 2018 In asymptomatic women attending for breast screening, what is the clinical and cost effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) in addition to full-field digital
Transvaginal and Transurethral Radiofrequency Tissue Remodeling for Urinary Stress Incontinence
 Transvaginal and Transurethral Radiofrequency Tissue Remodeling for Urinary Stress Incontinence Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Transvaginal and Transurethral Radiofrequency Tissue Remodeling for Urinary Stress Incontinence Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary,
Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination?
 Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination? Poster No.: B-0926 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. Elizalde, P. Garcia Barquin, M.
Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination? Poster No.: B-0926 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. Elizalde, P. Garcia Barquin, M.
2018 Reimbursement Information for Mammography, CAD and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis 1
 GE Healthcare 2018 Reimbursement Information for Mammography, CAD and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis 1 May 2018 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This advisory addresses Medicare coding, coverage and payment
GE Healthcare 2018 Reimbursement Information for Mammography, CAD and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis 1 May 2018 www.gehealthcare.com/reimbursement This advisory addresses Medicare coding, coverage and payment
