Breast Tomosynthesis
|
|
|
- Harry Brandon Jackson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for Routine Clinical Use
2 Breast Tomosynthesis Considerations for routine clinical use Andrew Smith, Ph.D., Vice President - Imaging Sciences, Hologic This white paper serves to summarize the state of the art in the clinical use and performance of tomosynthesis. Clinical Trial Results Hologic conducted a large clinical trial, and two reader studies, in support of their submission to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to achieve approval for sale in the United States. The reader studies results are summarized briefly below and are in the FDA s Summary of Safety and Effectiveness 1 following approval of Hologic s tomosynthesis product. Full details of the clinical trial and results are currently being submitted for publication. The product was approved by the FDA for use in the same clinical indications as 2D mammography, and can be used for both screening and diagnosis of breast cancer. The purpose of the clinical trial was to compare the performance of 2D plus 3D imaging (also known as combo imaging) to that of 2D imaging alone. The trial revealed that adding tomosynthesis to the 2D reading significantly improved accuracy as demonstrated by an improved area under the Receiver Operating Characteristics (ROC) curve and a reduced non-cancer recall rate, for 2D plus 3D imaging compared to 2D alone. Results from this trial were first presented by Rafferty at the RSNA. 2 Images were acquired from 5 clinical centers in the U.S. under an IRB-approved protocol and informed patient consent. All subjects had bilateral 2-view mammograms (MLO and CC) in both 2D and 3D imaging modes. Two reader studies were conducted using images from this set. In the two reader studies conducted, the performance of 2D plus 3D was shown to be significantly superior to the performance of 2D alone. The fact that the ROC curve of 2D plus 3D is higher than the 2D curve illustrates that 2D plus 3D can offer either improved cancer detection rate, or superior recall rate, or both, compared to 2D alone. These are certainly very positive results, and are much stronger than the ACRIN DMIST study s results which compared the performance of digital to film mammography, and found no average difference in performance between those two technologies 3. The area under the ROC curves for both studies were significantly higher for 2D plus 3D compared to 2D alone, and are consistent with the results of an independent third study from the University of Pittsburgh which found a 7% improvement in the ROC curve area for 2D plus 3D compared to 2D alone. 4 Sensitivity of Tomosynthesis In Hologic s clinical studies reviewed by the FDA advisory panel radiologists reading in combo-mode (2D +3D breast tomosynthesis) compared to 2D mammography alone demonstrated improved sensitivity [the proportion of mammograms with cancer which were correctly diagnosed]. The sensitivity gain from using tomosynthesis in screening can be estimated from ROC curves, although the exact improvement in cancer detection will not be known until the technology is more widely implemented in routine screening practices. Figure 1 shows hypothetical examples of ROC curves from 2D and 2D plus 3D imaging. The diagonal arrow shows how one can improve both cancer detection and reduce recall rates using a technology that has a higher ROC curve. Because of the demonstrated improvement in ROC area using 2D plus 3D imaging, the expected sensitivity gain will be considerable, and will vary by site based on individual radiologist s thresholds on detection and recall rate. Cancer Detection 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Recall Rate 2D plus 3D Figure 1 The use of 2D plus 3D imaging offers the possibility to both improve cancer detection and decrease recall rates. 2D
3 Recall Rate Reduction In three Selenia Dimensions 3D Breast Tomosynthesis studies reviewed by the FDA advisory panel, the radiologists reduced their recall rates using combo-mode (2D + 3D breast tomosynthesis) compared with 2D mammography alone The recall rate from the use of tomosynthesis in screening was studied in Hologic s FDA study. A reduction of recall rate was reported for 2D plus 3D compared to 2D alone. Several studies have shown the potential to reduce the recall rate in screening. For example, the results from Gur suggest that the use of tomosynthesis during baseline screening mammography may reduce the recall rate by 28%. 5 Rafferty in her 2007 RSNA presentation estimated the recall rate reduction to be over 40%. 1 Single View Tomosynthesis Based on Hologic s clinical studies, two-view tomosynthesis (CC and MLO) was superior to one-view tomosynthesis (MLO) in combo-mode (2D + 3D breast tomosynthesis) imaging. The reader studies above used 2-view mammography in both 2D and 3D imaging. One of the reader studies also investigated a 3 rd arm: single-view tomosynthesis (3D-MLO) imaging in combination with 2-view (CC and MLO) 2D mammography. The performance of two-view mammography plus 3D-MLO showed that the 3D-MLO-only arm performed better than 2D but not as well as two-view 2D plus 3D. These results are consistent with several other studies, illustrating that MLO-only breast tomosynthesis is likely to be inferior to twoview tomosynthesis. Summary of Clinical Trial Results The Hologic reader studies showed the following conclusions regarding the the use of 2D plus 3D imaging compared to 2D alone: 2D plus 3D is superior to 2D The screening recall rate of 2D plus 3D is lower than that of 2D The sensitivity of 2D plus 3D is higher than 2D Performance using both 3D CC and MLO views was greater than 3D MLO alone Why do 2D plus 3D rather than 3D alone? There are several reasons why acquiring both the 2D and 3D images together are useful, especially in screening. It is well known that comparison of current images with prior images is standard mammography practice and critical to perceive subtle changes which may be associated with a cancer. Obtaining a 2D exam along with the 3D exam allows direct comparison of current 2D images with prior 2D images. The 2D exam is also useful for the rapid detection of calcifications and perception of their distribution. Segmental and clustered calcifications are more easily and quickly appreciated with 2D because they can traverse multiple slices in 3D. The 3D portion of the 2D plus 3D exam is also critical in optimizing performance. The 3D image reduces structure overlap, minimizing recalls for overlapped structures and better demonstrates masses and architectural distortions. Thus we see that 2D and 3D are complementary and acquired together offers an advantage in clinical use. There may be methods to eliminate the need to separately acquire the 2D exam, through mathematical algorithms that generate a synthesized 2D image reconstructed from the 3D dataset. This approach is discussed in the following section of this paper. In conclusion, the 2D exam as part of a 2D plus 3D exam is valuable because: The 2D image is useful for comparison to priors The 2D image allows for quick reading of microcalcifications INCREASED CANCER DETECTION: The 3D tomosynthesis reconstructed slice reveals a definitive spiculated mass that perhaps is only faintly revealed on 2D imaging (Invasive Ductal Carcinoma). Synthesized 2D We have seen how 2D plus 3D imaging is superior to 2D alone. The question has been asked - Can a synthesized 2D image be created from a 3D data set for use in a tomosynthesis-only acquisition mode for screening? One value of such a synthesized 2D image would be reduced patient dose approximately half the dose of a 2D plus 3D exam, and approximately the same as a 2D exam alone. The algorithms to create such a synthesized image that approximate the necessary components of the true 2D, involve smart summing of the individual slices that make up the 3D exam. In clinical use, the synthesized 2D image will be reviewed together with the 3D image set.
4 There are technical challenges to creating a synthesized 2D image that is close in quality to that from a true 2D image, however much progress has been made recently in this area. Gur has studied the performance of an early version of synthesized 2D in a pilot study. 6 He concluded that a minor improvement in the quality of a synthesized 2D image could lead to an acceptable diagnostic quality and eliminate the need for acquiring both a 2D and 3D dataset during tomosynthesisbased screening. This is certainly promising and offers the possibility of providing the improved performance gain of twoview breast tomosynthesis without increasing the dose beyond normal 2D mammography levels. Hologic has also conducted a study to investigate the performance of synthesized 2D images. In this study, the performance of 3D (with synthesized 2D) was compared to 2D alone. As seen in the ROC performance of 3D was superior to 2D, and this was accomplished without requiring the dose of a separate 2D exposure. The ROC curves from this study are shown in Figure 2, and 3D with synthesized 2D shows improved ROC performance relative to 2D alone. Cancer Detection 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 3D 2D in recall rate compared to single-view mammography; the paper by Wald estimates the sensitivity gain is 24% and recall rate reduction is 15%. 7 It is not unreasonable to ask if a similar effect is observed in the clinical implementation of tomosynthesis. Perhaps, not surprisingly, the use of single view tomosynthesis is associated with poorer performance compared to tomosynthesis using two views. This phenomenon is no different with one-view vs. twoview tomosynthesis. There is mounting evidence that two-view tomosynthesis has increased sensitivity relative to one-view tomosynthesis. This has been illustrated in the Hologic clinical data, where the clinical performance of two-view 2D combined with a single MLO 3D view, as measured using ROC curve analysis, was inferior to the performance of two-view 2D combined with two-view 3D imaging Other data is consistent with this finding. Rafferty found that 12% of lesions were better seen on 3D MLO, 15% better seen on 3D CC and 9% of lesions were visible only on CC. 8 Similar results were reported by Baker, who found 8% of lesions were visible only on the CC tomosynthesis view and 1.4% only on the MLO. 9 These results are also consistent with evaluations where studies comparing ROC performance of two 3D views demonstrate superior performance over two-view digital mammography (Michell), but studies comparing one 3D view to two-view digital mammography have poorer performance and do not show superiority (Gennaro, Wallis). 10,11,12 20% 10% 0% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% Recall Rate Figure 2 ROC curves comparing 2D to 3D imaging One-view Versus Two-View Tomosynthesis Should one perform one- or two-view tomosynthesis imaging? Single view tomosynthesis (either CC or MLO) is a lower-dose procedure compared to two-view tomosynthesis, but it has been demonstrated to have poorer clinical performance. The relative performance of one-view versus two-view 2D mammography is well understood. Screening using two views offers an increase in cancer detection and a reduction TWO VIEW TOMOSYNTHESIS OPTIMIZES CHANCE FOR CANCER DETECTION: The lesion can be seen in the tomosynthesis CC view but is not apparent in any of the tomosynthesis MLO slices, of which the central slice is shown. Two-view tomosynthesis improves performance over single view tomosynthesis.
5 In addition to the likely loss of sensitivity that occurs if only one 3D view is taken, there are some clinical challenges that arise with single view tomosynthesis imaging. Neither the CC nor the MLO views capture all the breast tissue, so both views in some form are needed. Mixing up the technologies such as 3D MLO and 2D CC might address the tissue coverage but creates its own set of issues. It might be difficult, for example, to correlate a suspicious lesion seen in 2D CC with the same lesion in the 3D MLO, or vice versa. An even more challenging situation is when the exam consists of solely a 3D MLO. It could be difficult to see asymmetries with only one view, and comparison to 2D prior images would also be challenging. The best clinical performance will likely be seen in protocols that acquire both a CC and an MLO 3D image set. Performing two views uses more radiation dose than one view and having two views may increase the reading time; however, these doses are well within the federally established limits and are commonly accepted in conventional mammography, where two-view mammography is performed so as to optimize the mammogram for cancer detection, with tolerable recall rates such as was found by Wald et al, Performing two-view tomosynthesis is associated with higher sensitivity along with reduction in recall rates, as compared to single view tomosynthesis where sensitivity will suffer. Given that there is an established dose limit for mammographic imaging in the U.S., it would seem reasonable to maximize the use of the dose budget. An alternative approach to acquiring two tomosynthesis views, given a fixed radiation dose budget, would be to acquire only one tomosynthesis view, but double the dose for that view. This certainly would lower noise and may result in a superior image due to the increased photon statistics, however, based on the above results, it is better for a fixed 2x dose budget to split the dose into two views. The Gennaro (2009) study confirmed that the use of single-view 3D at 2x dose achieved inferior performance, compared to digital mammography, than did Michell (2010) who used two 3D views at approximately 1x 11, 10 dose each. How well does tomosynthesis image calcifications and masses and distortions? The clinical trial data presented as part of Hologic s FDA submission has been analyzed by separating the image sets into cases that separately contained calcifications, or noncalcifications. Rafferty found that 2D plus 3D offered a very significant increase in performance relative to 2D imaging for cases involving masses and distortions. For the imaging of cases involving microcalcifications, there was a small improvement in the ROC performance with the addition of 3D, but that was not a significant improvement. Importantly, the use of 3D was not associated with a poorer microcalcification ROC performance compared to 2D alone. Other studies have looked at calcifications and their visibility with tomosynthesis. Early investigations found that digital mammography was often superior to tomosynthesis for calcification visualization 13, however these early systems had long scan times (10-18 seconds) which can lead to patient motion. Scan times have been reduced significantly in some systems, and many papers give a positive outlook. For example, Kopans found that the characterization of calcifications in tomosynthesis was equal or superior to their characterization in conventional digital mammography in 92% of cases. 14 If one acquires 2D plus 3D exam then one is assured that calcifications are always optimal in at least one image set. ADDED VALUE FOR CALCIFICATIONS: The 2D mammogram shows right medial microcalcifications. The 3D tomosynthesis reconstructed slice illustrates the associated architectural distortion only revealed on the CC tomosynthesis image and not on the mammogram. (Ductal Carcinoma in-situ/high Grade). What is the performance of tomosynthesis in fatty and dense breasts? Tomosynthesis has been shown to improve the performance of mammography in both fatty and dense breasts. Researchers have performed an analysis on cases following their grouping into fatty breast and dense breast sub-groups. For this
6 analysis, fatty breasts were defined as BI-RADS density 1 and 2 and dense breasts were defined as BI-RADS density 3 and 4. In a study by Rafferty, she found that 2D plus 3D was significantly better than 2D alone in ROC performance for both fatty and dense breasts. 15 The gain in area under the ROC curve was 2-3 times higher in dense breasts than it was in fatty breasts, with a gain in both breast density types. She also reported large recall rate reductions in both fatty and dense breast types. In a separate study, Rafferty studied the performance of tomosynthesis in women with dense breasts and found an increase in the recall for cancer cases and a reduction in the recall rate for non-cancer cases. 16 These results are not unexpected. Fatty breasts may have sufficient parenchyma that tomosynthesis would be expected to offer some advantages, and the larger improvement in performance in denser breasts using tomosynthesis illustrates that tomosynthesis is doing what is expected from the physics principles reducing superimposed parenchyma. calcifications. We thus expect that the gain in sensitivity using tomosynthesis can be attributable to invasive cancers. A cancer found on the 3D image and not seen in the 2D image during routine screening would not have been found until a successive screening round had the 3D exam not been performed. GREATER PERCEPTION OF EXTENT OF DISEASE: In addition to the subtle area of architectural distortion, best defined on the tomosynthesis reconstructed slice (top arrow), a second spiculated mass was also revealed (bottom arrow) 21mm posterior to the primary (Both areas: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma). VALUE IN FATTY BREASTS: While the 2D mammogram reveals the 12:00 mass, tomosynthesis more accurately characterizes this mass as spiculated (Invasive Ductal Carcinoma). Is tomosynthesis finding invasive cancers or just more DCIS? It is expected that the additional cancers found by tomosynthesis will be found to be an increase in mass lesions, and not calcification-only cancers. The reasoning for this is seen in the much greater improvement in the ROC curve performance for non-calcifications than for cases involving Tomosynthesis Computer-Aided Detection (CAD) Just as in conventional 2D digital mammography, CAD may help find suspicious objects in a 3D dataset. However, there are differences in the use for CAD in tomosynthesis. Conventional 2D CAD helps find both masses and microcalcifications. In tomosynthesis, there may be less of a need for a mass-detection algorithm, because often the masses and distortions are found very quickly and easily by the human observer. The situation is different in the case of microcalcifications. It can be time consuming to have to carefully search a large number of slices looking for subtle microcalcifications. An efficient and sensitive calcification CAD algorithm could help speed up the search by, for example, identifying suspicious calcification clusters on a scout image, and rapidly navigating to the appropriate slices of interest without the need to scan
7 through the 3D dataset. Figure 3 shows an example of a CAD algorithm marking potentially suspicious microcalcifications on a single slice from a 3D study. Figure 3 CAD marks identify areas of interest on a single 3D slice Patient Dose and Risk/Benefit The dose of both a 2D and a 3D exam are very small. Even taken together, as a combo acquisition, they are below the U.S. FDA/MQSA-determined safe level, and are not far from where mammography was historically 17. We have seen how the clinical protocol of CC and MLO 2D plus CC and MLO 3D gives the best clinical accuracy for screening; however, there are many methods of performing the 2D and the 3D exam, and the patient dose will vary depending upon how many exposures are made, i.e. what combinations of CC and MLO and 2D and 3D images are taken, such as is the case in a diagnostic workup. Effective Dose (msv) D Hologic System 2D Plus 3D Tomosynthesis Average Annual Background US Figure 4 Dose levels of 2D and 3D exams compared to natural background radiation Average Annual Background Colorado The doses of a 2D and a 3D exam can be compared to the levels of background radiation that everyone receives from natural sources such as cosmic rays and the soil. These exposure levels are shown in Figure 4. A 2D, 3D, or combined 2D plus 3D study all have effective dose levels that are fractions of typical doses that people are annually exposed to in the U.S., Europe, and elsewhere in the world. There are normal variations in these levels, and higher altitude cities have higher background radiation levels that can give an occupant more radiation than on average, as seen in the background radiation in Colorado compared to the average in the U.S. Breast cancer mortality rates are lower in Colorado than on average in the U.S., which is an indication that radiation at these levels should not be a concern. 18 Indeed, the Health Physics Society issued a position statement on the very topic, stating that Estimation of health risk associated with radiation doses that are of similar magnitude as those received from natural sources should be strictly qualitative and encompass a range of hypothetical health outcomes, including the possibility of no adverse health effects at such low levels. 19 It is important to keep a perspective on the actual risks from the very low radiation doses delivered by modern mammography and tomosynthesis systems. Doses at current levels are low and risks are hypothetical. 20 The benefits of screening mammography and early detection of cancer, on the contrary, are not hypothetical they are proven. And tomosynthesis will be an improvement over conventional mammography, in improving sensitivity, and avoiding unnecessary workup of women without disease. Tomosynthesis In the Evaluation of the Symptomatic Patient The use of tomosynthesis in diagnostic assessment offers the opportunity for both improved performance and a reduction in the number of x-ray images and dose and time. Zuley found comparable sensitivity and specificity in the use of two-view 3D imaging in place of the additional diagnostic 2D views typically taken. 21 Because the number of diagnostic views in the evaluation of masses or focal asymmetries can average three or more, there is a clear opportunity to reduce radiation exposure through the use of 3D in diagnostic evaluations. 22 Other researchers such as Svahn have also shown that the combined diagnostic performance of digital mammography and tomosynthesis is superior to either digital mammography or tomosynthesis alone. 23
8 Several studies have shown that tomosynthesis is superior to 2D mammography in predicting tumor size, demonstrating margins, extents of lesions, and in staging. Michell showed that tomosynthesis is superior to 2D mammography in predicting the histological tumor size, because tomosynthesis demonstrates the margins and extents of the mammographic lesions more clearly, and concluded that this is critical information for prospective treatment planning by the multi-disciplinary team. 24 Fornvik found breast tomosynthesis superior to digital mammography in the assessment of breast tumor size and stage. 25 Meacock found that 3D was more accurate than 2D in tumor size measurement. 26 Tagliafico found that tomosynthesis could replace spot compression views, lowering both radiation dose and the potential to reduce biopsies on non-malignant lesions. 27 Tomosynthesis Reading Time Reading tomosynthesis images involves the evaluation of more images than a 2D image, because one must view each slice from a 3D stack with an average of 50 or more slices. Typical slice thicknesses in tomosynthesis range from 0.5 to 1.0 mm thick, with more slices to review as the slice thickness is made thinner. Nonetheless, reading times for tomosynthesis are not unreasonable. 28 The increase in the number of images reflects the increase in the information available to the radiologist, and is justified by the superior clinical performance. Tomosynthesis Compared to Ultrasound No studies have been published directly comparing the performance of tomosynthesis compared to ultrasound in a screening usage. Nonetheless, several observations may be made about this. Tomosynthesis, like ultrasound, has a superior performance in dense breasts relative to mammography. However, unlike ultrasound, where the recall rate of 2D and ultrasound was 4 times that of 2D alone as was seen in the ACRIN 6666 trial, tomosynthesis improves sensitivity without increasing the recall rate. 29 Contrast Enhanced Breast Imaging Contrast enhanced breast imaging is a procedure that images the distribution of an iodinated contrast agent using either 2D or 3D x-ray imaging technologies. This technology is in its early evaluation stage, but may offer some advantages relative to contrast breast MRI in terms of reduced cost and access for patients currently contraindicated for MRI. Contrast enhanced breast imaging combines functional information from the distribution of the contrast agent and morphological information from the x-ray images. Hologic is investigating this technology using a dual modality system, capable of imaging the functional 2D contrast uptake and the morphological 3D image in rapid sequence, and combining these two image sets into a single fused study. It is thought that the 3D tomosynthesis image can give additional morphological information not found in either a 2D or 3D contrast image or a standard 2D image. REDUCED NEED FOR WORK-UP: Tomosynthesis demonstrates a definitive architectural distortion only subtly appreciated on the 2D mammogram, replacing the need for diagnostic work-up that may not fully or accurately resolve the 2D imaging dilemma. Implementation of Tomosynthesis In Clinical Practice Which patients should receive tomosynthesis imaging? How should one incorporate it into one s practice? This section will contain some examples from users that have adopted tomosynthesis.
9 Should I use tomosynthesis for screening or diagnostic imaging? Tomosynthesis has shown value in a diagnostic evaluation of a symptomatic breast. It also can be used in screening to improve sensitivity and reduce recalls. Therefore, either or both indications are acceptable uses of tomosynthesis. Diagnostic procedures often take longer than screening examinations. With a limited number of tomosynthesis systems, more women per day can be accommodated in machines dedicated to screening use, so this might be a consideration for a clinic that cannot convert all systems to tomosynthesis. Should I use tomosynthesis only on women with dense breasts? Tomosynthesis showed value in both fatty and dense breasts, but had a greater impact on improving performance for women with dense breasts. Therefore, if a practice does not have enough systems to screen all women, it is reasonable to triage them and reserve tomosynthesis for the harder cases with denser breasts. However, as tomosynthesis offers a benefit in both fatty and dense breasts, the goal for screening should be to screen 100% of women with tomosynthesis. How should I select which patients get tomosynthesis? Tomosynthesis benefits all women, irrespective of breast type, and will find cancers not found using 2D mammography. Nonetheless, as discussed above, one could choose to image only women with dense breasts, creating a possible scheduling challenge. And remember, tomosynthesis does offer an advantage for women with fatty breasts, and these women would not have access to this technology in this model. Some clinics offer tomosynthesis using the next available free system model, where if the room with the tomosynthesis system is free, the next patient will be scanned on this system, regardless of their breast density. Some clinics also offer full access to a tomosynthesis system for any woman who requests the procedure. There can be special after-hours or otherwise scheduled blocks to give access to the system. Both these methods solve the dilemma of giving unequal care in a predefined and ecumenical way. Different Implementation Scenarios We have discussed a variety of different implementation scenarios. All of these are reasonable. Example 1: Complete conversion of the clinic to tomosynthesis. All screening and diagnostic patients get the procedure. Example 2: Partial conversion to tomosynthesis. Use for diagnostic patients only. Example 3: Partial conversion to tomosynthesis. Use for some screening patients, selected populations subgroups such as women with dense breasts. Example 4: Partial conversion to tomosynthesis. Use for some screening patients, as the tomosynthesis system(s) are free and available. Handling Priors Current mammography practice involves the comparison of current images to priors. The acquisition of a 2D plus 3D image exam gives the radiologist access to a 2D current for comparison to 2D priors. This 2D plus 3D image procedure also offers some advantages in the scenarios mentioned above where a patient this year might get a tomosynthesis study and in the next year receive only a 2D study because of scheduling constraints or equipment access. In such a situation, the radiologist reading the study in the following year would have access to the 2D exams from previous 2D plus 3D mode studies. These types of scenarios are illustrated in Figure 5, and represent a hypothetical clinic that switches, in the current year, some but not all of their screening systems to tomosynthesis. In the prior year(s) the woman had 2D mammograms. In the current year she receives a combo image exam. The radiologist can diagnose from the 2D and 3D dataset, and uses the current year s 2D to compare to prior years 2D images. Come next year, she might get a 2D exam or a 2D plus 3D exam, depending upon which system she is imaged on. If she gets a 2D plus 3D exam in the next year, the radiologist has both 2D and 3D currents and priors. If she gets a 2D exam in the next year, the radiologist has the next year s 2D, and can compare that to the current year 2D prior, and also the current year 3D prior if desired. Figure 5 Different scenarios when the imaging modality changes year to year
10 Radiologist Training Hologic learned from the tomosynthesis clinical trials the importance of proper training on how to interpret tomosynthesis images. To that end, Hologic has set up training classes around the world, taught by radiologists experienced in tomosynthesis, to aid in the education in tomosynthesis interpretation. These classes cover the appearance in tomosynthesis of different density parenchymal patterns, benign, and malignant lesions, and review clinical cases. Selfassessment practice cases are reviewed and discussed to give radiologists chances to test their learning. The following is a link to Hologic s tomosynthesis training page for radiologists: For radiologists in the U.S., the following is a link to the U.S. FDA s website that covers the requirements for facilities and personnel using breast tomosynthesis: MammographyQualityStandardsActandProgram/ FacilityCertificationandInspection/ucm htm In the U.S., radiologists are required to have 8 hours of instruction prior to reading tomosynthesis clinically. Example of 2D mammogram and a 2D image synthesized from a 3D dataset. While still being improved, the quality of a synthesized 2D image is very good and offers the potential for dose savings when using tomosynthesis. Archiving and Display Tomosynthesis display and storage is covered by a DICOM standard. 30 Nonetheless, at this time not all PACS vendors support either the storage or display of these images. Hologic has developed, as an interim solution, a storage method whereby the tomosynthesis images are stored in a secondary capture format, which allows the storage in PACS, but for display one must use a Hologic SecurView diagnostic workstation. It is expected that PACS companies will rapidly implement and support the viewing of tomosynthesis images, now that the systems are in widespread use in Europe and the U.S. following the FDA approval for Hologic s tomosynthesis system. In planning a site, careful consideration must be given to the size of the images. The images from a 3D study can be 5 times larger than the corresponding size of a 2D digital mammography dataset. Network speeds and PACS storage must be adequate for the increase data flow. These larger datasets are a natural result of tomosynthesis offering more information than digital mammograms. Conclusions Tomosynthesis is an exciting new technology that will likely revolutionize mammography, and will offer benefits to all women. It offers the potential for improvements in both screening and diagnostic evaluations. The improvements in clinical performance, compared to 2D, are significant. Glossary 2D 3D BI-RADS CAD Combo mode Forced BI-RADS IRB MQSA Recall rate ROC Sensitivity Synthesized 2D Specificity Tomosynthesis Two-dimensional imaging. The same thing as conventional digital mammography. Three-dimensional imaging. The same thing as tomosynthesis. Breast imaging, reporting and diagnosis system Computer Aided Detection A procedure whereby a 3D and a 2D image are acquired in rapid sequence in a single breast compression. A rating method where only scores from 1 to 5 are allowed Institutional review board Mammography Quality Systems Act The percentage of women recalled from screening for further assessment. In mammography screening, the majority of recalled cases are false positives. Receiver Operating Characteristics The measure of how many cancers are detected A method of creating an enhanced 2D image from a reconstruction of a 3D dataset The measure of how many non-cancers are correctly identified A form of three-dimensional imaging involving limited angle tomography acquisition and reconstruction
11 REDUCED RECALL RATES: The 2D mammogram reveals a spiculated mass laterally in the right CC view. 3D tomosynthesis slices at 23, 33, and 43 mm above the breast platform show that this 2D finding was superimposed structures, resolved through the use of 3D imaging. CONTRAST IMAGING: This study of 2D and 3D iodine contrast mammography was acquired under a single compression. The proven cancer in the lateral subareolar breast (horizontal arrow) is not visible on the unenhanced 2D mammogram (except for the clips placed at biopsy) but is easily seen on the 2D and 3D dual energy contrast images. Contrast imaging led to the detection of an additional enhancing cancer in the far medial breast (downward arrow). The 3D image shows the irregular shape of that lesion, greatly increasing its likelihood of malignancy.
12 References Rafferty E, Niklason L, Halpern E, et al. Assessing radiologist performance using combined full-field digital mammography and breast tomosynthesis versus full-field digital mammography alone: results of a multi-center multi-reader trial. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Pisano ED, Gatsonis C, Hendrick E, et al. Diagnostic performance of digital versus film mammography for breast-cancer screening. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: Gur D, Bandos AI, Rockette HE, et al. Is an ROC-type response truly always better than a binary response in observer performance studies? Acad Radiol. (17)5: , Gur D, Sumkin J, Zuley R et al. Recall rate reduction with tomosynthesis during baseline examinations- preliminary assessment from a prospective screening trial. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Gur D, Zuley ML, Lu A et al. A two-fold dose reduction in breast screening with tomosynthesis (DBT) through the use of reconstructed 2D images from the DBT dataset? Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Wald NJ, Murphy P, Major P, et al. UKCCCR multicentre randomized controlled trial of one and two view mammography in breast cancer screening. BMJ 311: , Rafferty E, Niklason L, Jameson-Meehan L. Breast tomosynthesis: one view or two? Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Baker JA, Lo JY. Breast Tomosynthesis: state-of-the-art and review of the literature. Academic Radiology 18: (2011). 10 Michell MJ, Iqbal A, Wasan R, et al. Phase I trial to determine the performance of digital breast tomosynthesis versus two dimension digital and film-screen mammography. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Gennaro G, Toledano A, di Maggio C, et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis versus digital mammography: a clinical performance study. Eur Radiol. 20: (2009). 12 Wallis MG, Moa E, Zanca F et al. Comparing diagnostic accuracy of full field digital mammography and photon counting tomosynthesis: a multireader, multicentre observer study. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Poplack SP, Tosteson TD, Kogel CA, et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis: initial experience in 98 women with abnormal digital screening mammography. Am J Roentgenol. 189: (2007). 14 Kopans D, Moore R. Calcifications in digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT). Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Raffery EA, Niklason L, Smith A. Comparison of FFDM with breast tomosynthesis to FFDM alone: performance in fatty and dense breasts. Tomosynthesis Imaging Symposium, Duke University, Rafferty EA, Niklason L. FFDM versus FFDM with tomosynthesis for women with radiographically dense breasts: an enriched retrospective reader study. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, See, for example, Updated trends in mammography dose and image quality. MammographyQualityStandardsActandProgram/FacilityScorecard/ ucm htm Health Physics Society Position Statement- Radiation Risk in Perspective Feig SA, Hendrick RE. J Natl Cancer Inst Mongr. 22: , Zuley M, Sumkin J, Ganott M, et al. Digital breast tomosynthesis vs supplemental diagnostic mammography images for the evaluation of non-calcified breast lesions. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Harvey JA, Nicholson BT, Cohen MA. Finding early invasive breast cancers: a practical approach. Radiology, July 2008; 248: Svahn T, Andersson I, Chakraborty D, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of dual-view digital mammography, single-view breast tomosynthesis and a dual-view combination of breast tomosynthesis and digital mammography in a free-response observer performance study. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 139(1-3): (2010). 24 Michell M, Iqbal A, Wasan R et al. A comparison of the accuracy of digital breast tomosynthesis with tow dimension digital mammography in measurement of breast tumour size. FFDM versus FFDM with tomosynthesis for women with radiographically dense breasts: an enriched retrospective reader study. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Fornvik, D, Zackrisson S, Ljungberg O, et al. Breast Tomosynthesis: Accuracy of tumor measurement compared with digital mammography and ultrasonography. Acta Radiol 3; , Meacock, LM et al. The accuracy of breast cancer size measurement: Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) vs 2D digital mammography (DM). European College of Radiology annual meeting, Vienna, Austria, Tagliafico A, Astengo D, Cavagnetto F et al. One-to-one comparison between digital spot compression view and digital breast tomosynthesis. Eur Radiol Oct 11 [Epub ahead of print]. 28 Skaane P, Gullien R, Eben EB et al. Reading time of FFDM and tomosynthesis in a population-based screening program. Radiological Society of North America annual meeting. Chicago, IL, Berg WA, Blume JD, Cormack JB, et al. Combined screening with ultrasound and mammography vs mammography alone in women at elevated risk of breast cancer. JAMA May 14;299(18): , ftp://medical.nema.org/medical/dicom/final/sup125_ft.pdf
13 United States/ Latin America 35 Crosby Drive Bedford, MA USA Hologic UK Limited Unit 2, Link 10, Napier Way, Crawley, West Sussex, RH10 9RA United Kingdom Hologic Asia Pacific 7th Floor, Biotech Centre 2 No. 11 Science Park West Avenue Hong Kong Science Park Shatin, New Territories Hong Kong Hologic Belgium Everest (Cross Point) Leuvensesteenweg 250A 1800 Vilvoorde Belgium Hologic Australia Hologic (Australia) Pty Ltd Suite 402, Level 4 2 Lyon Park Road Macquarie Park NSW 2113 Australia Hologic China Hologic Healthcome Room 1606, Building A, Feng Lan Guo Ji Center 32 Xi Zhi Men Bei Da Jie Haidian District, Beijing, (100082) China
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis
 Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Breast Tomosynthesis The Use of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Clinical Setting 2 What s Inside Introduction... 1 Initial Hologic Clinical Trial Purpose and Methodology... 1 Clinical Trial Results... 2 Improved
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in the Diagnostic Environment: A Subjective Side-by-Side Review
 Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Women s Imaging Original Research Hakim et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Women s Imaging Original Research Christiane M. Hakim 1 Denise M. Chough 1 Marie A. Ganott 1 Jules H. Sumkin 1 Margarita L. Zuley
Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer
 What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
What to Expect Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer Every woman over 40 should be examined for breast cancer once a year. American Cancer Society What to
A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography, full-field digital mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis
 Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
Clinical Radiology xxx (2012) 1e6 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Clinical Radiology journal homepage: www.clinicalradiologyonline.net A comparison of the accuracy of film-screen mammography,
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Susan Orel Roth, MD
 Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
WHAT TO EXPECT. Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC. The Women's Health Company
 WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
WHAT TO EXPECT Breast Tomosynthesis An additional screening tool in the fight against breast cancer HOLOGIC The Women's Health Company ...,. Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE?
 X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
3D Mammography. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
What to Expect 3D Mammography The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense against breast
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Fundamentals of Breast Tomosynthesis
 Fundamentals of Breast Tomosynthesis Improving the Performance of Mammography Andrew Smith, Ph.D. This white paper is one in a series of research overviws on advanced technologies in women s healthcare.
Fundamentals of Breast Tomosynthesis Improving the Performance of Mammography Andrew Smith, Ph.D. This white paper is one in a series of research overviws on advanced technologies in women s healthcare.
FDA Executive Summary
 Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
the one name in cancer care.
 the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
the one name in cancer care. Landmark study evaluating close to half a million mammography exams published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) 1 Hologic 3D Mammography Significantly
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography
 BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
BI-RADS classification in breast tomosynthesis. Our experience in breast cancer cases categorized as BI-RADS 0 in digital mammography Poster No.: C-0562 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors:
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana, Inc.(collectively referred to as the Company ), unless otherwise provided
Detection and Classification of Calcifications on Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and 2D Digital Mammography: A Comparison
 Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
Women s Imaging Original Research Spangler et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Versus 2D Digital Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: M. Lee Spangler 1 Margarita L. Zuley 2 Jules H.
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? TERMS (AKA) WHAT IS TOMOSYNTHESIS? 3/3/2014. Digital breast tomosynthesis =
 #46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update. Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS. The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000
 WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000
 WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D Mammography Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D Mammography Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years Screening for breast cancer Doctors and scientists agree that early detection is the best defense
What s New in Breast Imaging. Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia
 What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
What s New in Breast Imaging Jennifer A. Harvey, M.D., FACR Professor of Radiology University of Virginia Disclosure Hologic, Inc. Shareholder and research agreement. Volpara Solutions, Ltd. Shareholder
Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography
 Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography Andrew Smith 1, Elizabeth Rafferty 2, Loren Niklason 1 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford MA, USA 2 Massachusetts
Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography Andrew Smith 1, Elizabeth Rafferty 2, Loren Niklason 1 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford MA, USA 2 Massachusetts
B R E A S T I M A G I N G S O L U T I O N S. Selenia Dimensions A Revolution in Breast Imaging
 B R E A S T I M A G I N G S O L U T I O N S Selenia Dimensions A Revolution in Breast Imaging The promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Hologic has been at the forefront of the industry s transformation
B R E A S T I M A G I N G S O L U T I O N S Selenia Dimensions A Revolution in Breast Imaging The promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Hologic has been at the forefront of the industry s transformation
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis
 Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Correlation between lesion type and the additional value of digital breast tomosynthesis Poster No.: C-1604 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Van Ongeval, L. Cockmartin, A. Van Steen,
Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer 3/10/16
 Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer Policy Number: MCP-270 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 3/10/16 Review Date: 6/22/17, 3/8/18 MCPC Approval Date: 3/8/18 DISCLAIMER
Subject: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) for Breast Cancer Policy Number: MCP-270 Revision Date(s): Original Effective Date: 3/10/16 Review Date: 6/22/17, 3/8/18 MCPC Approval Date: 3/8/18 DISCLAIMER
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese
 Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Dansk Radiologisk Selskab 9.årsmøde Odense 3.januar, 214 Fremtidens rolle for tomosyntese Professor dr. med. Per Skaane Oslo University Hospital Ullevaal Breast Imaging Center Oslo / Norway PERSKA@ous-hf.no
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine
 International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research David Gur 1 Andriy I. Bandos 2 Howard E. Rockette 2 Margarita L. Zuley 3 Jules H. Sumkin 3 Denise M. Chough 3 Christiane M. Hakim 3 Gur
Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research David Gur 1 Andriy I. Bandos 2 Howard E. Rockette 2 Margarita L. Zuley 3 Jules H. Sumkin 3 Denise M. Chough 3 Christiane M. Hakim 3 Gur
Comparison of one-view digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and two-view full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Comparison of one-view digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and two-view full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-2258 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Saguatti, P. Mainoldi,
Comparison of one-view digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) and two-view full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-2258 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Saguatti, P. Mainoldi,
Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography
 2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
2015 ARRS Breast Symposium Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography John Lewin, M.D. Diversified Radiology of Colorado CEDM - Outline History Technique Literature Review / Cases Clinical Status Inexpensive,
Breast Tomosynthesis. What is breast tomosynthesis?
 Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
Scan for mobile link. Breast Tomosynthesis Breast tomosynthesis is an advanced form of mammography, a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early when it is most treatable.
MRI of the Breast Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scintimammography/Breast-Specific Gamma Imaging/Molecular Breast Imaging
 6.01.53 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Section Radiology Subsection Effective Date September 30, 2014 Original Policy Date June 28, 2013 Next Review Date September 2015 Description Digital breast tomosynthesis
6.01.53 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Section Radiology Subsection Effective Date September 30, 2014 Original Policy Date June 28, 2013 Next Review Date September 2015 Description Digital breast tomosynthesis
Dense Breasts, Get Educated
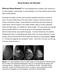 Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Dense Breasts, Get Educated What are Dense Breasts? The normal appearances to breasts, both visually and on mammography, varies greatly. On mammography, one of the important ways breasts differ is breast
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Waldherr et al. One-View Breast Tomosynthesis Versus Two-View Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Christian Waldherr 1 Peter Cerny 1 Hans J. Altermatt 2 Gilles
Women s Imaging Original Research Waldherr et al. One-View Breast Tomosynthesis Versus Two-View Mammography Women s Imaging Original Research Christian Waldherr 1 Peter Cerny 1 Hans J. Altermatt 2 Gilles
Mammography. What is Mammography? What are some common uses of the procedure?
 Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
Mammography What is Mammography? Mammography is a specific type of imaging that uses a low-dose x-ray system to examine breasts. A mammography exam, called a mammogram, is used to aid in the early detection
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection
 White Paper Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection WHITE PAPER 2 3 Abstract PowerLook Tomo Detection, a concurrent computer-aided detection (CAD)
White Paper Improving Reading Time of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Concurrent Computer Aided Detection WHITE PAPER 2 3 Abstract PowerLook Tomo Detection, a concurrent computer-aided detection (CAD)
Mammography limitations. Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study
 Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
 Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
TOMOSYNTHESIS. Daniela Bernardi. U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy
 TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
Corporate Medical Policy. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT)
 Corporate Medical Policy Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Description of Procedure or Service DBT is a three-dimensional (3D) breast imaging technology that uses a rotating X-ray source to acquire multiple
Corporate Medical Policy Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Description of Procedure or Service DBT is a three-dimensional (3D) breast imaging technology that uses a rotating X-ray source to acquire multiple
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM)
 Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Assessment of extent of disease: digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) versus full-field digital mammography (FFDM) Poster No.: C-1237 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: N. Seo 1, H. H. Kim
Superior Performance. Lower Dose.* 1,2. World s first and only. 3D breast biopsy. Breast Biopsy Guidance System. Affirm
 World s first and only 3D breast biopsy Superior Performance. Lower Dose.* 1,2 TM Affirm Breast Biopsy Guidance System For Stereotactic and Tomosynthesis Interventional Procedures Breast and Skeletal Health
World s first and only 3D breast biopsy Superior Performance. Lower Dose.* 1,2 TM Affirm Breast Biopsy Guidance System For Stereotactic and Tomosynthesis Interventional Procedures Breast and Skeletal Health
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
A Breast Surgeon s Use of Three Dimensional Specimen Tomosynthesis
 A Breast Surgeon s Use of Three Dimensional Specimen Tomosynthesis Cary S. Kaufman MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery A Breast Surgeon s Use of Three Dimensional Specimen Tomosynthesis Cary
A Breast Surgeon s Use of Three Dimensional Specimen Tomosynthesis Cary S. Kaufman MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery A Breast Surgeon s Use of Three Dimensional Specimen Tomosynthesis Cary
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients
 Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS
 ABBY DUROJAYE,M.D CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS BOTH HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO BE EFFECTIVE TOOLS EARLY DETECTION OF BREAST
ABBY DUROJAYE,M.D CURRENTLY FDA APPROVED ARE FULL FIELD DIGITAL MAMMOGRAPHY SYSTEMS AND FILM SCREEN STILL BEING USED AT SOME INSTITUTIONS BOTH HAVE BEEN SHOWN TO BE EFFECTIVE TOOLS EARLY DETECTION OF BREAST
Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, Inc. Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis A WHITEPAPER INTRODUCTION Numerous published studies have shown
Konica Minolta Healthcare Americas, Inc. Exa Mammo A Solution that Overcomes the Challenges of Implementing Digital Breast Tomosynthesis A WHITEPAPER INTRODUCTION Numerous published studies have shown
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts. Reagan Leverett, MD, MS
 Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
Supplemental Screening for Dense Breasts Reagan Leverett, MD, MS Outline Anatomy and Density Risk of dense breasts Theory of Supplemental Screening Options for supplemental screening Tomosynthesis Ultrasound
Research Article The Adjunctive Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Diagnosis of Breast Cancer
 BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 597253, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/597253 Research Article The Adjunctive Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Tsung-Lung
BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 597253, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/597253 Research Article The Adjunctive Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Tsung-Lung
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium. Sat Nov 12 th 2016
 Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Epworth Healthcare Benign Breast Disease Symposium Breast cancer is common Sat Nov 12 th 2016 Benign breast disease is commoner, and anxiety about breast disease commoner still Breast Care Campaign UK
Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) Updates
 Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) Updates Georgeta Mihai, PhD, DABR Medical Physicist, BIDMC, Boston Assistant Professor, Harvard Medical School, Boston Disclosures None Acknowledgments: Da
Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) Updates Georgeta Mihai, PhD, DABR Medical Physicist, BIDMC, Boston Assistant Professor, Harvard Medical School, Boston Disclosures None Acknowledgments: Da
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography
 Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Illuminating Breast Cancer Detection SenoBright HD TM gehealthcare.com/senobright Mammography is the most reliable imaging technique for breasts, but limitations
Contrast-Enhanced Breast Tomosynthesis: Combining the Best of Both Worlds for Better Breast-Cancer Diagnosis
 Contrast-Enhanced Breast Tomosynthesis: Combining the Best of Both Worlds for Better Breast-Cancer Diagnosis T Wu (twu2@partners.org), E Rafferty, R Moore, D Kopans, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston,
Contrast-Enhanced Breast Tomosynthesis: Combining the Best of Both Worlds for Better Breast-Cancer Diagnosis T Wu (twu2@partners.org), E Rafferty, R Moore, D Kopans, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston,
Multicenter Trial, Phase I Assessment of 2-D FFDM Versus Combo of 2-D and 3-D Tomosynthesis in Breast Cancer Screening
 ACRIN PA 4006: Comparison of Full Field Digital Mammography with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Image Acquisition in Relation to Screening Call-Back Rate Imaging Manual Multicenter Trial, Phase I Assessment
ACRIN PA 4006: Comparison of Full Field Digital Mammography with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Image Acquisition in Relation to Screening Call-Back Rate Imaging Manual Multicenter Trial, Phase I Assessment
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening?
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Ready for Routine Screening? Sophia Zackrisson MD, PhD, Assoc Prof of Radiology Skåne University Healthcare, Lund University, Sweden 1 Mammography screening 20% reduced breast
arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018 arxiv: v2 [cs.cv] 8 Mar 2018](/thumbs/87/97094636.jpg) Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network Timothy de Moor a, Alejandro Rodriguez-Ruiz a, Albert Gubern Mérida a, Ritse Mann a, and
Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network Timothy de Moor a, Alejandro Rodriguez-Ruiz a, Albert Gubern Mérida a, Ritse Mann a, and
Volume 14 - Issue 3, Matrix
 Volume 14 - Issue 3, 2014 - Matrix Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Author ECRI ECRI Institute 29 Broadwater Road Suite 104 Welwyn Garden City AL7 3BQ United Kingdom
Volume 14 - Issue 3, 2014 - Matrix Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Author ECRI ECRI Institute 29 Broadwater Road Suite 104 Welwyn Garden City AL7 3BQ United Kingdom
9/3/2015. New Mammographic Modality Training. Mammographer. Qualified Radiologic Technologist. Tomosynthesis Training
 FDA Required Breast Tomosynthesis Training New Mammographic Modality Training On any new mammography technology, such as breast tomosynthesis, the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) (http:fda.gov/radiation-emitting
FDA Required Breast Tomosynthesis Training New Mammographic Modality Training On any new mammography technology, such as breast tomosynthesis, the Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA) (http:fda.gov/radiation-emitting
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Updates in Mammography. Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre
 Updates in Mammography Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre Updates in Mammography Breast Imaging Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical
Updates in Mammography Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University Malaya Medical Centre Updates in Mammography Breast Imaging Dr. Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical
The Radiology Aspects
 REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
REQUIREMENTS FOR INTERNATIONAL ACCREDITATION OF BREAST CENTERS/UNITS The Radiology Aspects Miri Sklair-Levy, Israel RADIOLOGY GUIDELINES FOR QUALITY ASSURANCE IN BREAST CANCER SCREENING AND DIAGNOSIS Radiologists
Mammography is a most effective imaging modality in early breast cancer detection. The radiographs are searched for signs of abnormality by expert
 Abstract Methodologies for early detection of breast cancer still remain an open problem in the Research community. Breast cancer continues to be a significant problem in the contemporary world. Nearly
Abstract Methodologies for early detection of breast cancer still remain an open problem in the Research community. Breast cancer continues to be a significant problem in the contemporary world. Nearly
Hacia la imagenología tomográfica de mama
 Hacia la imagenología tomográfica de mama Futuro y presente Ioannis Sechopoulos, Ph.D., DABR Advanced X ray Tomographic Imaging (AXTI) Lab Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Radboud University
Hacia la imagenología tomográfica de mama Futuro y presente Ioannis Sechopoulos, Ph.D., DABR Advanced X ray Tomographic Imaging (AXTI) Lab Department of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Radboud University
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- AIDED DETECTION (CAD) POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Technology Assessment
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: MAMMOGRAPHY: COMPUTER- PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including
The role of digital breast tomosynthesis in the breast assessment clinic: a review
 REVIEW ARTICLE The role of digital breast tomosynthesis in the breast assessment clinic: a review Suneeta Mall, BE, 1 Sarah Lewis, PhD, 1 Patrick Brennan, PhD, 1 Jennie Noakes, BMed(Newcastle), FRANZCR,
REVIEW ARTICLE The role of digital breast tomosynthesis in the breast assessment clinic: a review Suneeta Mall, BE, 1 Sarah Lewis, PhD, 1 Patrick Brennan, PhD, 1 Jennie Noakes, BMed(Newcastle), FRANZCR,
Breast positioning system for full field digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis system
 Breast positioning system for full field digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis system Mari Varjonen* a, Martti Pamilo b, Pirjo Hokka b, Riina Hokkanen a, Pekka Strömmer a a Planmed Oy Asentajankatu
Breast positioning system for full field digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis system Mari Varjonen* a, Martti Pamilo b, Pirjo Hokka b, Riina Hokkanen a, Pekka Strömmer a a Planmed Oy Asentajankatu
Opportunities and Innovations in Digital Mammography John M. Sandrik, Ph.D. GE Healthcare Milwaukee, WI
 Opportunities and Innovations in Digital Mammography John M. Sandrik, Ph.D. GE Healthcare Milwaukee, WI john.sandrik@med.ge.com with many thanks to Vince Polkus, Advanced Applications Product Mgr. 1 Content
Opportunities and Innovations in Digital Mammography John M. Sandrik, Ph.D. GE Healthcare Milwaukee, WI john.sandrik@med.ge.com with many thanks to Vince Polkus, Advanced Applications Product Mgr. 1 Content
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Comparison of Tomosynthesis Plus Digital Mammography and Digital Mammography Alone for Breast Cancer Screening 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Clinical Policy: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Reference Number: CP.MP.90
 Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.90 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 12/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Clinical Policy: Reference Number: CP.MP.90 Effective Date: 01/18 Last Review Date: 12/17 Coding Implications Revision Log See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS. See what others miss.
 HMH 3D Mammography BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS See what others miss. 2 BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY exams are clinically proven to detect 41% More invasive breast cancer, while simultaneously
HMH 3D Mammography BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS See what others miss. 2 BREAST HEALTH SOLUTIONS Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY exams are clinically proven to detect 41% More invasive breast cancer, while simultaneously
Jing Zhang, PhD, Lars J. Grimm, MD, MHS, Joseph Y. Lo, PhD, Karen S. Johnson, MD,
 This manuscript has been accepted for publication in Journal of the American College of Radiology. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published
This manuscript has been accepted for publication in Journal of the American College of Radiology. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR)
 Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Look differently. Invenia ABUS. Automated Breast Ultrasound
 Look differently. Invenia ABUS Automated Breast Ultrasound InveniaTM ABUS from GE Healthcare offers a view beyond mammography, with breast screening technology that looks differently. 40 % The unseen risk.
Look differently. Invenia ABUS Automated Breast Ultrasound InveniaTM ABUS from GE Healthcare offers a view beyond mammography, with breast screening technology that looks differently. 40 % The unseen risk.
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Breast cancer screening: Does tomosynthesis augment mammography?
 REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
REVIEW TRACI A. TAKAHASHI, MD, MPH Director, Seattle VA Women Veterans Clinic at VA Puget Sound Health Care System, Seattle, WA; Associate Professor of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle CHRISTOPH
Disclosures. Breast Cancer. Breast Imaging Modalities. Breast Cancer Screening. Breast Cancer 6/4/2014
 : Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
: Information for the Primary Care Physician Disclosures No financial relationships with commercial entities producing health care products/services. Roxsann Roberts, MD Section Chief, MRI Erlanger/EmCare
Implementation of Breast Tomosynthesis in a Routine Screening Practice: An Observational Study
 Women s Imaging Original Research Rose et al. Tomosynthesis in Routine Screening Women s Imaging Original Research Stephen L. Rose 1 Andra L. Tidwell Louis J. Bujnoch Anne C. Kushwaha Amy S. Nordmann Russell
Women s Imaging Original Research Rose et al. Tomosynthesis in Routine Screening Women s Imaging Original Research Stephen L. Rose 1 Andra L. Tidwell Louis J. Bujnoch Anne C. Kushwaha Amy S. Nordmann Russell
Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose
 MicroDose Mammography Solutions Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose Several studies provide evidence that Philips MicroDose Mammography* can provide outstanding image quality at 18% to
MicroDose Mammography Solutions Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose Several studies provide evidence that Philips MicroDose Mammography* can provide outstanding image quality at 18% to
Contrast enhanced spectral mammography: A literature review
 Contrast enhanced spectral mammography: A literature review Poster No.: R-0172 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. Buzynski, D. Taylor; Perth/AU Breast, Digital
Contrast enhanced spectral mammography: A literature review Poster No.: R-0172 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. Buzynski, D. Taylor; Perth/AU Breast, Digital
Better detection. Clinically superior. Low dose The Selenia Dimensions 3D Mammography System
 Better detection. Clinically superior. Low dose. 1-13 The Selenia Dimensions 3D Mammography System Revolutionary Technology 1, 5-9 Simply a better mammogram. The Genius 3D Mammography exam from the Selenia
Better detection. Clinically superior. Low dose. 1-13 The Selenia Dimensions 3D Mammography System Revolutionary Technology 1, 5-9 Simply a better mammogram. The Genius 3D Mammography exam from the Selenia
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning. Dr. med. M. Golatta
 The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
The value of the craniocaudal mammographic view in breast cancer detection: A preliminary study
 The value of the craniocaudal mammographic view in breast cancer detection: A preliminary study P D Trieu 1, Prof. P C Brennan 1, Dr. W Lee 2, Dr. E Ryan 1, Dr. W Reed 1, Dr. M Pietrzyk 1 1. Medical Image
The value of the craniocaudal mammographic view in breast cancer detection: A preliminary study P D Trieu 1, Prof. P C Brennan 1, Dr. W Lee 2, Dr. E Ryan 1, Dr. W Reed 1, Dr. M Pietrzyk 1 1. Medical Image
Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion: Original Research n Breast Imaging
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Original Article Comparative study on diagnosis efficacy of digital breast tomosynthesis and color Doppler ultrasound for breast lesions
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(4):3455-3461 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0066311 Original Article Comparative study on diagnosis efficacy of digital breast tomosynthesis and color Doppler ultrasound
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(4):3455-3461 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0066311 Original Article Comparative study on diagnosis efficacy of digital breast tomosynthesis and color Doppler ultrasound
