Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
|
|
|
- Cornelia Wells
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
2 Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different, specialized functions? How have new genes evolved? Prokaryote vs. eukaryote genome Prokaryotes o small size of genome o circular molecule of naked DNA o most of DNA codes for protein or RNA small amount of non-coding DNA regulatory sequences promoters, operators Eukaryotes o Much greater size of genome o DNA packaged in chromatin fibers Regulates access to DNA by RNA polymerase o Cell specialization Need to turn on & off large numbers of genes o Most of DNA does not code for protein or RNA 97% in humans = junk DNA 1
3 Points of control The control of gene expression can occur at any step in the pathway from gene to functional protein o unpacking DNA o transcription o mrna processing o mrna degradation o translation o protein processing o protein degradation Gene Expression Specialization o Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genes. Development o Some gene expression must be controlled on a long-term basis for cellular differentiation & specialization during development. Responding to organism s needs o Cells of multicellular organisms must continually turn certain genes on & off in response to signals from their external & internal environment. DNA Packing Current model for stages of DNA coiling & folding Culminating in condensed metaphase chromosome Nucleosomes: Beads on a string 1st level of DNA packing o histone proteins have high proportion of positively charged amino acids (arginine & lysine) bind tightly to negatively charged DNA 2
4 DNA Packing & Methylation Chromatin modifications affect the availability of genes for transcription o packing DNA into compact form serves to regulate transcription heterochromatin is compact & not transcribed less compacted euchromatin may be transcribed o DNA methylation inactivates genes = off attachment of methyl groups ( CH3) to DNA bases (cytosine) after DNA is synthesized nearly permanent suppression of genes ex. the inactivated mammalian X chromosome Histone Acetylation Histone acetylation activates genes = on o Attachment of acetyl groups ( COCH3) to certain amino acids of histone proteins. When histones are acetylated they change shape & grip DNA less tightly = unwinding DNA. Transcription proteins have easier access to genes. Chromatin structure Chromatin structure is part of gene regulation o Heterochromatin highly compact not transcribed found in regions of few genes o Euchromatin true chromatin transcribed found in regions of many genes Heterochromatin Highly compact Not transcribed (inactive genes) o increased methylation of histones & cytosines o decreased acetylation of histones Found in regions of few genes o centromeres o telomeres o other junk DNA Euchromatin Loosely packed in loops of 30nm fibers o near nuclear pores Transcribed active genes o decreased methylation of histones & cytosines o increased acetylation of histones Found in regions of many genes 3
5 Transcription Initiation Transcription factors o Control proteins which interact with DNA & with each other o Initiation complex only when complete complex has assembled can RNA polymerase move along DNA template to make mrna Model for Enhancer Action Enhancer DNA sequences o distant control sequences Activator proteins o bind to enhancer sequence & stimulates gene transcription. Silencer proteins o bind to enhancer sequence & block gene transcription. Post Transcriptional Control Alternative RNA splicing Variable processing of exons creates a family of proteins Regulation of mrna Degradation Life span of mrna determines pattern of protein synthesis. mrna can last from hours to weeks. 4
6 Control of Translation Block initiation stage o regulatory proteins attach to 5 end of mrna prevent attachment of ribosomal subunits & initiator trna block translation of mrna to protein Protein Processing & Degradation Protein processing o Folding, cleaving, adding sugar groups, targeting for transport Protein degradation o Ubiquitin tagging & proteosome degradation Cancers = Cell Cycle Genes Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle o Proto-oncogenes Normal cellular genes code for proteins that stimulate normal cell growth & division. o Oncogenes Mutations that alter proto-oncogenes cause them to become cancer-causing genes. 5
7 Cancers = Cell Cycle Genes Proto-oncogenes & Oncogenes Genetic changes that can turn proto-oncogenes into oncogenes o Removing repression of genes Cancers = Failures of Regulation Cancer cells have escaped cell cycle controls. o Do not respond normally to the body s control mechanisms. Divide excessively & invade other tissues. If unchecked, they can kill the organism. Multi-step model for cancer Multiple mutations underlie the development of cancer o Several changes must occur at DNA level for cell to become fully cancerous. Including at least 1 active oncogene & mutation or loss of several tumor-suppressor genes. Telomerase is often activated. 1
8 Effects of Signal Pathways p53 gene Guardian of the Genome o The anti-cancer gene o After DNA damage is detected, p53 initiates: DNA repair growth arrest apoptosis Almost all cancers have mutations in p53. 2
9 Repetitive DNA Repetitive DNA & other noncoding sequences account for most of eukaryotic DNA. Genetic disorders of repeats Fragile X syndrome most common form of inherited mental retardation defect in X chromosome o mutation of FMR1 gene causing many repeats of CGG triplet in promoter region 200+ copies normal = 6-40 CGG repeats o FMR1 gene not expressed & protein (FMRP) not produced function of FMR1 protein unknown binds RNA Fragile X Syndrome The more triplet repeats there are on the X chromosome, the more severely affected the individual will be. Mutation causes increased number of repeats (expansion) with each generation. 3
10 Huntington s Disease Rare autosomal dominant degenerative neurological disease. o 1st described in 1872 by Dr. Huntington o Most common in white Europeans o 1st symptoms at age Death comes ~12 years after onset Mutation on chromosome 4 o CAG repeats copies normal = CAG repeats CAG codes for glutamine amino acid Abnormal (Huntington) protein produced. o Chain of charged glutamines in protein. o Bonds tightly to brain protein, HAP-1. Families of Genes Human globin gene family. o Evolved from duplication of common ancestral globin gene. o Different versions are expressed at different times in development allowing hemoglobin to function throughout life of developing animal. 4
11 Interspersed Repetitive DNA Repetitive DNA is spread throughout genome. o Interspersed repetitive DNA make up 25-40% of mammalian genome. o In humans, at least 5% of genome is made of a family of similar sequences called, Alu elements. 300 bases long Alu is an example of a "jumping gene" a transposon DNA sequence that "reproduces" by copying itself & inserting into new chromosome locations. Transposons Insertion of transposon sequence in new position in genome Insertion sequences cause mutations when they happen to land within the coding sequence of a gene or within a DNA region that regulates gene expression Barbara McClintock o Discovered 1st transposons in Zea mays (corn) in Retrotransposons Transposons actually make up over 50% of the corn (maize) genome & 10% of the human genome. Most of these transposons are retrotransposons, transposable elements that move within a genome by means of RNA intermediate, transcript of the retrotransposon DNA. 5
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
You may need to shop for a new brain after this chapter
 You may need to shop for a new brain after this chapter Introduction Gene expression in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes. First, the eukaryotic genome is much larger. Second, different eukaryotic cells in multicellular
You may need to shop for a new brain after this chapter Introduction Gene expression in eukaryotes vs. prokaryotes. First, the eukaryotic genome is much larger. Second, different eukaryotic cells in multicellular
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Chapter 19 Eukaryotic Genomes
 Chapter 19 Eukaryotic Genomes Lecture Outline Overview: How Eukaryotic Genomes Work and Evolve Two features of eukaryotic genomes present a major information-processing challenge. First, the typical multicellular
Chapter 19 Eukaryotic Genomes Lecture Outline Overview: How Eukaryotic Genomes Work and Evolve Two features of eukaryotic genomes present a major information-processing challenge. First, the typical multicellular
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
I. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genome
 CHAPTER 18 GENOME ORGANIZATION AND EXPRESSION IN EUKARYOTES OUTLINE I. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genome II. III. IV. The structural organization of chromatin
CHAPTER 18 GENOME ORGANIZATION AND EXPRESSION IN EUKARYOTES OUTLINE I. Each cell of a multicellular eukaryote expresses only a small fraction of its genome II. III. IV. The structural organization of chromatin
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes
 Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes biologiemoleculara.usmf.md pass.: bmgu e.usmf.md 1 DNA in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria biologiemoleculara.usmf.md e.usmf.md pass.: bmgu
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions
 Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
Genetics and Genomics in Medicine Chapter 6 Questions Multiple Choice Questions Question 6.1 With respect to the interconversion between open and condensed chromatin shown below: Which of the directions
9/3/2009 DNA i DNA n euk euk yotes Organizatio Organ izatio n of o f gen ge e n tic Locati t on: In n ucleu e s material mater in e ial
 DNA in eukaryotes Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria DNA in eukaryotes Nuclear DNA: Long, linear molecules; Chromatin chromosomes; 10% of DNA in genes,
DNA in eukaryotes Organization of genetic material in eukaryotes Location: In nucleus In mitochondria DNA in eukaryotes Nuclear DNA: Long, linear molecules; Chromatin chromosomes; 10% of DNA in genes,
Eukaryotic transcription (III)
 Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Gene Regulation - 4. One view of the Lactose Operon
 Gene Regulation - 1 Regulating Genes We have been discussing the structure of DNA and that the information stored in DNA is used to direct protein synthesis. We've studied how RNA molecules are used to
Gene Regulation - 1 Regulating Genes We have been discussing the structure of DNA and that the information stored in DNA is used to direct protein synthesis. We've studied how RNA molecules are used to
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Mary
'''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
 '''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Anggraini'Barlian,' Iriawa-' Tjandra'Anggraeni' SITH4ITB' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
'''''''''''''''''Fundamental'Biology' BI'1101' ' an'interdisciplinary'approach'to'introductory'biology' Anggraini'Barlian,' Iriawa-' Tjandra'Anggraeni' SITH4ITB' Five'Levels'of'Organiza-on' Molecular'
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Connecting
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
Cell Growth and Division
 Cell Growth and Division CHAPTER 10 EQ Why do cells grow and divide? DID YOU KNOW THAT The adult human body produces roughly 2 TRILLION cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can
Cell Growth and Division CHAPTER 10 EQ Why do cells grow and divide? DID YOU KNOW THAT The adult human body produces roughly 2 TRILLION cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can
Gene Regulation Part 2
 Michael Cummings Chapter 9 Gene Regulation Part 2 David Reisman University of South Carolina Other topics in Chp 9 Part 2 Protein folding diseases Most diseases are caused by mutations in the DNA that
Michael Cummings Chapter 9 Gene Regulation Part 2 David Reisman University of South Carolina Other topics in Chp 9 Part 2 Protein folding diseases Most diseases are caused by mutations in the DNA that
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
 RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
TRANSLATION: 3 Stages to translation, can you guess what they are?
 TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
Chapter 11 Gene Expression
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
How Cells Divide. Chapter 10
 How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis.
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division The Links in Life s Chain: Genetics and Cell Division 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics 9.2 An Introduction to Cell Division 9.3
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 9: The Links in Life s Chain Genetics and Cell Division The Links in Life s Chain: Genetics and Cell Division 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics 9.2 An Introduction to Cell Division 9.3
Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience. Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1
 Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1 Nature versus Nurture Despite the belief that the Nature vs. Nurture
Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1 Nature versus Nurture Despite the belief that the Nature vs. Nurture
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
Chapter 8 DNA Replication, Binary Fission, and Mitosis
 Chapter 8 DNA Replication, Binary Fission, and Mitosis World s tallest man Frederic J. Brown/AFP/Getty Images Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without
Chapter 8 DNA Replication, Binary Fission, and Mitosis World s tallest man Frederic J. Brown/AFP/Getty Images Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction or distribution without
DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis.
 Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Section 3: DNA codes for RNA, which guides protein synthesis. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Vocabulary Review synthesis New RNA messenger RNA ribosomal RNA transfer RNA transcription
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Protein Synthesis
 Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
Protein Synthesis 10.6-10.16 Objectives - To explain the central dogma - To understand the steps of transcription and translation in order to explain how our genes create proteins necessary for survival.
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
5.1. KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 68 Reinforcement Unit 2 Resource Book
 5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
5.1 THE CELL CYCLE KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. Cells have a regular pattern of growth, DNA duplication, and division that is called the cell cycle.
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Gene Regulation. Bacteria. Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
Chapter 18: Regulation of Gene Expression A Biology 2013 1 Gene Regulation rokaryotes and eukaryotes alter their gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled
 Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction Well-preserved
Chapter 11 How Genes Are Controlled PowerPoint Lectures Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections, Eighth Edition REECE TAYLOR SIMON DICKEY HOGAN Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko Introduction Well-preserved
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs
 p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
p53 cooperates with DNA methylation and a suicidal interferon response to maintain epigenetic silencing of repeats and noncoding RNAs 2013, Katerina I. Leonova et al. Kolmogorov Mikhail Noncoding DNA Mammalian
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
Regulation of Gene Expression
 18 Regulation of Gene Expression KEY CONCEPTS Figure 18.1 What regulates the precise pattern of gene expression in the developing wing of a fly embryo? 18.1 Bacteria often respond to environmental change
18 Regulation of Gene Expression KEY CONCEPTS Figure 18.1 What regulates the precise pattern of gene expression in the developing wing of a fly embryo? 18.1 Bacteria often respond to environmental change
HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED. Patterns of Gene Expression in Differentiated Cells
 HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 5 HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 6 Every somatic cell in an organism contains identical genetic instructions. They all share the same genome. So what makes cells different
HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 5 HOW AND WHY GENES ARE REGULATED 6 Every somatic cell in an organism contains identical genetic instructions. They all share the same genome. So what makes cells different
7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions
 Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Name Section 7.012 Problem Set 6 Solutions Question 1 The viral family Orthomyxoviridae contains the influenza A, B and C viruses. These viruses have a (-)ss RNA genome surrounded by a capsid composed
Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother
 Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Almost every cell in the human body has an identical set of 46 chromosomes, produced through the process of mitosis.
 M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
M I T O S I S Mitosis Mitosis is the type of cell division that occurs for growth (adding new cells) and repair (replacing old or damaged cells). It results in two daughter cells that have identical chromosomes
General Biology 1004 Chapter 11 Lecture Handout, Summer 2005 Dr. Frisby
 Slide 1 CHAPTER 11 Gene Regulation PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
Slide 1 CHAPTER 11 Gene Regulation PowerPoint Lecture Slides for Essential Biology, Second Edition & Essential Biology with Physiology Presentation prepared by Chris C. Romero Neil Campbell, Jane Reece,
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP
 Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability
 Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Cell Division. Chromosome structure. Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division
 Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Chromosome structure Made of chromatin (mix of DNA and protein) Only visible during cell division Chromosome structure The DNA in a cell is packed into an elaborate, multilevel system of coiling and folding.
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction
 Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
Unit 5 Part B Cell Growth, Division and Reproduction Cell Size Are whale cells the same size as sea stars cells? Yes! Cell Size Limitations Cells that are too big will have difficulty diffusing materials
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER. Cellular Reproduction II
 CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
CELL CYCLE REGULATION AND CANCER Cellular Reproduction II THE CELL CYCLE Interphase G1- gap phase 1- cell grows and develops S- DNA synthesis phase- cell replicates each chromosome G2- gap phase 2- cell
Eukaryotic Genetics. Expression & Regulation
 Eukaryotic Genetics Expression & Regulation Molecular Basis of Inheritance I.Main Idea: Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription. Regulating Gene Expression A cell s genome
Eukaryotic Genetics Expression & Regulation Molecular Basis of Inheritance I.Main Idea: Bacteria often respond to environmental change by regulating transcription. Regulating Gene Expression A cell s genome
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Differential Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental conditions In multicellular eukaryotes,
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Differential Expression of Genes Prokaryotes and eukaryotes precisely regulate gene expression in response to environmental conditions In multicellular eukaryotes,
Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer
 CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
Fragile X Syndrome. Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype
 Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Week 1 - Introduction
 Genetics Summary 1 Week 1 - Introduction - Polygenic > traits with multiple genes - Gregor Mendel > predictable offspring (didn t work with polygenic) - Friedrich Miescher > discovered DNA in 1869-2 sister
Genetics Summary 1 Week 1 - Introduction - Polygenic > traits with multiple genes - Gregor Mendel > predictable offspring (didn t work with polygenic) - Friedrich Miescher > discovered DNA in 1869-2 sister
TRANSCRIPTION. DNA à mrna
 TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
TRANSCRIPTION DNA à mrna Central Dogma Animation DNA: The Secret of Life (from PBS) http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=41_ne5ms2ls&list=pl2b2bd56e908da696&index=3 Transcription http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
Focus on the Concepts
 Focus on the Concepts ~is chapter describes how genes are controlled and how this relates to differentiation, development, cloning, signal transduction, and what can happen when cells escape their normal
Focus on the Concepts ~is chapter describes how genes are controlled and how this relates to differentiation, development, cloning, signal transduction, and what can happen when cells escape their normal
Gene Expression DNA RNA. Protein. Metabolites, stress, environment
 Gene Expression DNA RNA Protein Metabolites, stress, environment 1 EPIGENETICS The study of alterations in gene function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence. Epigenetic gene regulatory
Gene Expression DNA RNA Protein Metabolites, stress, environment 1 EPIGENETICS The study of alterations in gene function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence. Epigenetic gene regulatory
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Campbell Biology 10. A Global Approach. Chapter 18 Control of Gene Expression
 Lecture on General Biology 2 Campbell Biology 10 A Global Approach th edition Chapter 18 Control of Gene Expression Chul-Su Yang, Ph.D., chulsuyang@hanyang.ac.kr Infection Biology Lab., Dept. of Molecular
Lecture on General Biology 2 Campbell Biology 10 A Global Approach th edition Chapter 18 Control of Gene Expression Chul-Su Yang, Ph.D., chulsuyang@hanyang.ac.kr Infection Biology Lab., Dept. of Molecular
Biol115 The Thread of Life"
 Biol115 The Thread of Life" Lecture 9" Gene expression and the Central Dogma"... once (sequential) information has passed into protein it cannot get out again. " ~Francis Crick, 1958! Principles of Biology
Biol115 The Thread of Life" Lecture 9" Gene expression and the Central Dogma"... once (sequential) information has passed into protein it cannot get out again. " ~Francis Crick, 1958! Principles of Biology
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Histones modifications and variants
 Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Let s quickly return to that siliconbased life form, since
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Spring 2011 Section A Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 Let s quickly return to that siliconbased life form, since
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D. Steve Thompson:
 BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 The cell cycle and mitosis Now that we ve seen how DNA
BIOL 1030 Introduction to Biology: Organismal Biology. Fall 2009 Sections B & D Steve Thompson: stthompson@valdosta.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net 1 The cell cycle and mitosis Now that we ve seen how DNA
Regulation of Gene Expression
 Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Epigenetics. Lyle Armstrong. UJ Taylor & Francis Group. f'ci Garland Science NEW YORK AND LONDON
 ... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections & Steve Thompson:
 SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections 20585 & 20586 Steve Thompson: steven.thompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 We ll start with the exam review. A few people did well,
SGCEP BIOL 1010K Introduction to Biology I Spring 2012 Sections 20585 & 20586 Steve Thompson: steven.thompson@sgc.edu http://www.bioinfo4u.net/ 1 We ll start with the exam review. A few people did well,
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes
 Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
Part II The Cell Cell Division, Chapter 2 Outline of class notes 1 Cellular Division Overview Types of Cell Division Chromosomal Number The Cell Cycle Mitoses Cancer Cells In Vitro Fertilization Infertility
BIOLOGY. Regulation of Gene Expression CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Differential Expression of Genes
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 18 Regulation of Gene Expression Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Differential Expression of Genes
Regulation of Gene Expression
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Transcription of DNA 1 3.4 A 2 Expression of Genetic information DNA Double stranded In the nucleus Transcription mrna Single stranded Translation In the cytoplasm
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Chapter 8. Human Chromosomes. Humans, like all other species, store their genetic information in cells as large DNA molecules called
 Chapter 8 Human Chromosomes Figure 8-1 Human metaphase chromosome spread. To make these figures white blood cells in metaphase are dropped onto a slide. The cells burst open and the chromosomes can then
Chapter 8 Human Chromosomes Figure 8-1 Human metaphase chromosome spread. To make these figures white blood cells in metaphase are dropped onto a slide. The cells burst open and the chromosomes can then
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function. The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Chromosome loci. Organization of the Chromatin. Nucleotide Structure
 Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Chapter 4 Genetics and Cellular Function The Nucleic Acids (medical history) Nucleus and nucleic acids Protein synthesis and secretion DNA replication and the cell cycle Chromosomes and heredity Organization
Cell Cycle Notes chromatin, somatic cells gametes mitosis sister chromatids, centromere cytokinesis binary fission,
 Cell Cycle Notes 1. Importance of Cell Division a. For single celled organisms, cell division increases the number of individuals. b. In a multicellular organism, cell division functions to repair and
Cell Cycle Notes 1. Importance of Cell Division a. For single celled organisms, cell division increases the number of individuals. b. In a multicellular organism, cell division functions to repair and
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
MMB (MGPG) Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics. A.Turco
 MMB (MGPG) 2017 Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics A.Turco NON TRADITIONAL INHERITANCE EXCEPTIONS TO MENDELISM - Genetic linkage (2 loci close to each other) - Complex or Multifactorial Disease (MFD)
MMB (MGPG) 2017 Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics A.Turco NON TRADITIONAL INHERITANCE EXCEPTIONS TO MENDELISM - Genetic linkage (2 loci close to each other) - Complex or Multifactorial Disease (MFD)
Cell Cycle. Trends in Cell Biology
 Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Keywords: Daughter Cells Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Chromosomes Chromatin Homologous Chromosomes Diploid
 Name: CP Biology Unit 6: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 6.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Name: CP Biology Unit 6: Cell Growth and Development Students will be able to: 6.1 Understand and explain the different aspects of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Explain how cell size is related to cell division
Chapter 12. living /non-living? growth repair renew. Reproduction. Reproduction. living /non-living. fertilized egg (zygote) next chapter
 Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division.
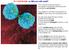 10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division. This relates to cell theory because this is HOW all cells come
10 1 Cell Growth Why are cells small? This colorized scanning electron micrograph is showing a white blood cell undergoing cell division. This relates to cell theory because this is HOW all cells come
