Signaling pathway switch in breast cancer
|
|
|
- Jemima Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guille et al. Cancer Cell International 2013, 13:66 HYPOTHESIS Open Access Signaling pathway switch in breast cancer Arnaud Guille, Max Chaffanet and Daniel Birnbaum * Abstract Next generation sequencing studies have drawn the general landscape of breast cancers and identified hundreds of new, actual therapeutic targets. Two major signaling pathways seem to be altered in a vast proportion of breast cancers. The PI3 kinase/akt pathway is activated and the JUN/MAPK pathway is repressed. Via the regulation of the cell cycle this metabolic switch impacts on the balance between self-renewal, proliferation and differentiation of the tumor-initiating cells Keywords: Next generation sequencing, Breast cancer, Signaling pathways, Cell cycle, Kinases Background Recent results from next generation sequencing (NGS) studies have established the repertoire of driver gene mutations and copy number alterations (CNA) in breast cancer [1-4]. Nearly 900 cancers representative of all major expression subtypes (basal, luminal A and B, ERBB2 and normal-like) have been studied. Many recurrent mutations have been uncovered. Mutations in TP53, PIK3CA, GATA3 and PTEN genes are among the most frequent. These studies have forever changed our understanding of mammary oncogenesis. Hypothesis Many studies will extend these pioneering ones but it is already possible to speculate further on the NGS data. Data analysis revealed that some alterations (CNA and/ or mutations) never occur in the same tumor, i.e. are mutually exclusive [1-4]. Two main signaling pathways seem to be targeted, the PI3K/AKT pathway and the JUN/ MAPK pathway [1-4]. Alterations in components of the PI3K/AKT pathway (PIK3CA, PIK3R1, AKTs, PTEN, INPP4B ) are mutually exclusive but strikingly, amplification and upregulation of genes encoding receptor-type tyrosine kinases (RTKs) (IGF1R, EGFR, ERBB2) are also (globally) mutually exclusive with alterations of the PI3K/ AKT pathway. This suggests that the primary role of RTK amplification or mutation is to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway. Thus, in the normal mammary epithelium these * Correspondence: daniel.birnbaum@inserm.fr Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Marseille, Oncologie Moléculaire, Equipe labellisée Ligue Contre le Cancer, UMR1068 Inserm, CNRS UMR7258, Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Aix-Marseille Université, 27 bd. Leï Roure, BP 30059, Marseille 13273, France RTKs are repressed or expressed at a low level and their signaling is primarily oriented toward the JUN/MAPK pathway, whereas when upregulated in tumor cells they stimulate the PI3K/AKT pathway. To obtain this dosage effect could be the reason for the amplification of ERBB2 and FGFR1 genes, although there could be other reasons [5]. It is known that the PI3K/AKT pathway is activated in tumors with mutated EGFR or overexpression of ERBB2 and determines the response to ERBB targeted inhibitors [6]. Within the JUN/MAPK pathway alterations of the components are also mutually exclusive [1]. Components of the JUN/MAPK pathway are inactivated by deletions and mutations, such as MAP2K4 and MAP3K1, orbyamplifications, such as PAK1. Most importantly, alterations leading to the activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway and those leading to the inactivation of the JUN/MAPK pathway are mutually exclusive [1]. Finally, not only mutations and genomic rearrangements affect genes encoding components of the two pathways but opposite modifications in expression patterns of these genes could also participate to their switch in breast cancer. Our hypothesis is that one important consequence of mutations, CNA and modifications of expression is to shift cell signaling in the targeted mammary epithelial cell from an active JUN/MAPK pathway inactive PI3K/AKT pathway state to an active PI3K/AKT pathway inactive JUN/MAPK pathway state. Testing the hypothesis In the diagram shown in Figure 1 we have represented 19 KEGG metabolic and signaling pathways and cell processes altered by mutations in their components in 2013 Guille et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
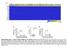
2 Guille et al. Cancer Cell International 2013, 13:66 Page 2 of 5 Figure 1 Altered KEGG pathways in breast cancers. In the bar-plot depicting the proportion of cancer samples with altered pathways (19 pathways are listed in the x-axis) the y-axis represents the percentage of samples altered in a given pathway stratified by subtype (red for basal, purple for ERBB2, blue for luminal A, cyan for luminal B, and green for normal-like). The analysis was done in 602 samples from different studies in which the molecular subtype (using PAM50) was available (466 from ref. 1, 98 from ref. 2, 38 from ref. 3). the 602 breast cancer samples of the NGS studies for which the molecular subtype had been assigned [1-4]. All pathways and processes are altered, although to different extents. Many potential therapeutical targets can be found in these pathways. Two main signaling pathways are targeted (Figure 2), the JUN/MAPK pathway and the PI3K/AKT pathway [1-4]. Mutations in PTEN, amplifications and mutations in PIK3CA and AKT genes, the MAGI3-AKT3 gene fusion [3], activate the PI3K/AKT pathway whereas mutations in MAP3K1, MAP3K13 and MAP2K4 inactivate the JUN/MAPK pathway. The PI3K/AKT and JUN/MAPK pathways are intimately related and intricate. For example, AKT activation inhibits MAP2K4. This interaction and the mirror effect of the alterations on the two signaling pathways suggest that the PI3K/AKT pathway stimulates the growth of tumor cells whereas the JUN/MAPK pathway has an opposite effect and that the two pathways are the two sides of the same coin. The downstream effects of the activated PI3K/AKT and inhibited JUN/MAPK pathways are multiple, but at least two could be of primary importance for the behavior of the tumor-initiating cell that fuels the tumor growth. A first major effect could be on the cell cycle. During the G1 phase of the cell cycle, a checkpoint before entering S phase, also called the restriction (R) point, has been defined as an important cell cycle stage controling various cell fates [8] (Figure 3). The G1 phase of the cell cycle has been thus divided into an early, signaling factor-dependent subphase, controled by D cyclins and a late, factor-independent subphase, controled by E cyclins and a fully inactivated (hyperphosphorylated) RB protein. The JUN/MAPK signaling pathway plays a role in the early G1 subphase, where the cell may be induced into quiescence, senescence or committed to differentiation, depending on the presence of external factors [9]. When entering the late G1 subphase, quiescence, cell death or differentiation are no longer options and the cell
3 Guille et al. Cancer Cell International 2013, 13:66 Page 3 of 5 Figure 2 Subnetwork representation of protein interactions based on 78 mutated genes in 602 breast cancers [1-3]. Gene networks were inferred using the Reactome FI Cytoscape Plugin [7]. A total of 182 genes with more than 7 mutations in 602 breast cancer samples were used. Among them, 78 (43%) were mapped in the subnetwork and subsequently clustered into 12 modules, six of which were greater than 4. Finally, modules functions were assessed with pathway enrichment analysis (FDR < 0.05). Three main pathways can be recognized: the P53 pathway and DNA repair (14 genes/18%) in blue, the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (13 genes/18%) in pink and the MAPK pathway (8 genes/10%) in green. progresses to S phase and then to either symetric (proliferation) or asymetric (self-renewal) division. At the level of the tumor-initiating cell, the PI3K/AKT pathway could stimulate self-renewal and/or proliferation and the JUN/MAPK pathway cell differentiation or cell cycle arrest. A compromised JUN/MAPK pathway and constitutively activated PI3K/AKT pathway could force the cell to go through the R point and progress to S-phase. In this scheme, amplification of cyclin D1 appears as a particularity; however, it occurs mainly in luminal tumors, which are the most differentiated and less proliferative of all breast tumors. Combined cyclin D1 amplification (or a mutation with similar effect) and PI3K/ AKT pathway would give luminal tumors their particular phenotype. In addition to the signaling pathways, the P53 protein acts as an important checkpoint on the way to the late G1 subphase. Inactivation of P53 (by way of mutations or deletions of the TP53 gene, or another mechanism such as the amplification of the MDM2 gene) is a prominent feature of all subtypes of breast cancer. However, it is more frequent in aggressive breast cancers, especially the basal cases, where alterations of the PI3K/AKT and JUN/MAPK pathways are less predominant. Basal breast cancers display a rearranged genome. P53 inactivation, which has consequences on thestabilityofthegenomebeyondthosethatcouldresult from an activation of signaling pathways, could be the major cause of the basal phenotype. A second major effect of PI3K/AKT pathway activation and JUN/MAPK inhibition is on the metabolism of the tumor-initiating cells. The latter are particularly resistant to oxidative processes and ROS production. The PI3K/AKT pathway, beside its role on cell growth and survival, regulates a number of metabolic processes including cell glucose uptake and neoglucogenesis in relation with nutrient availability and redox and energy conditions. It plays an important role in the glycolytic phenotype of tumors [10]. Forkhead transcription
4 Guille et al. Cancer Cell International 2013, 13:66 Page 4 of 5 Figure 3 Hypothetical representation of opposite downstream effects of two signaling pathways on the G1 phase of the cell cycle in a breast tumor-initiating cell. During the early G1 subphase the cell integrates signals that may lead it to several fates (differentiation, apoptosis, senescence, quiescence, pause for DNA repair, progression to S phase) [8]. Inhibition of the JUN/MAPK pathway shortens the early G1 subphase rendering the cell independent of differentiation and apoptotic factors. In the same time, activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway induces the cell to progress to late G1 subphase beyond the restriction (R) point; the cell may then undergo symmetric (proliferation) or asymmetric (self-renewal) division. In green: proteins with repressive effect, in red: proteins with activating effect. factors FOXO are downstream of the PI3K/AKT and JUN/MAPK cascades. FOXOs play a major role in the regulation of both the cell cycle and metabolism [11]. They prevent stem cells to accumulate ROS and allow DNA repair or quiescence. FOXOs are activated by the JUN kinase signaling pathway in the presence of oxidative stress. Conversely, activation of the PI3K/AKT and inhibition of JUN/MAPK pathways overrules the tumor suppressive effect of FOXOs and allows G1 progression. With respect to cell cycle and cell fate decisions FOXO transcription factors could thus represent important integrators of the two signaling pathways that are predominantly altered in breast cancer. They are therefore important targets in mammary oncogenesis. FOXO genes have not been found among the most frequently altered genes in breast cancer in NGS studies [1-4]; they are probably not directly targeted (yet, we have recently found rare mutations and deletions of the FOXO3 gene; Cornen et al., submitted). FOXOs functions may also be modified but maintained to ensure some degree of metabolic regulation in the tumorinitiating cells. FOXOs and P53 act on the same cellular processes and transcription programs, and are intimately cross-regulated [11]. Implications of the hypothesis The NGS studies have drawn the general landscape of breast cancers and identified hundreds of new, actual targets. Although the role of many of them needs clarification, especially regarding the transcription factors (e.g. GATA3, RUNX, NCORs ), two major signaling pathways seem to be altered. This is good news since strategies to counter the consequences of pathway alterations are known and could be improved. Inhibiting the PI3K/ AKT pathway appears as a paramount strategy to stop tumor growth [12]. If it fails one could adopt a strategy that takes into account both the PI3K/AKT and JUN/ MAPK pathways but because they are truly interrelated this may not be helpful. Targeting additional alterations or pathways (including synthetic lethal ones) [13] outside the PI3K/AKT and JUN/MAPK pathways could be more successful. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions The hypothesis came to view during discussions between the three authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
5 Guille et al. Cancer Cell International 2013, 13:66 Page 5 of 5 Acknowledgements Studies on breast cancer in our laboratory are supported by Inserm, Institut Paoli-Calmettes, Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (Label DB) and Institut National du Cancer (ACI2007, AO2008, IVOIRES, and INCa-DGOS-Inserm 6038) Received: 14 May 2013 Accepted: 20 June 2013 Published: 27 June 2013 References 1. The Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490: Shah P, Roth A, Goya R, Oloumi A, Ha G, Zhao Y, et al: The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature 2012, 486: Banerji S, Cibulskis K, Rangel-Escareno K, Brown KK, Carter SL, Frederick AM, et al: Sequence analysis of mutations and translocations across breast cancer subtypes. Nature 2012, 486: Ellis MJ, Ding L, Shen D, Luo J, Suman VJ, Wallis JW, et al: Whole-genome analysis informs breast cancer response to aromatase inhibition. Nature 2012, 486: Birnbaum D, Sircoulomb F, Imbert J: A reason why the ERBB2 gene is amplified and not mutated in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int 2009, 9:5. 6. Hynes N, MacDonald G: ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr Op Cell Biol 2009, 21: Wu G, Feng X, Lincoln Stein L: A human functional protein interaction network and its application to cancer data analysis. Genome Biol 2010, 11:R Oxford KW, Scadden DT: Deconstructing stem cell self-renewal: genetic insights into cell-cycle regulation. Nat Rev Genet 2008, 9: Burdon T, Smith A, Savatier P: Signalling, cell cycle and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Trends Cell Biol 2002, 12: Cairns RA, Harris IS, Mak TW: Regulation of cancer metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 2011, 11: Eijkelenboom A, Burgering BMT: FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2013, 14: Grunt TW, Mariani GL: Novel approaches for molecular targeted therapy of breast cancer: interfering with PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13: Eisinger F, Sobol H, Birnbaum D: Hypothesis: more mutations to cure cancer? Oncol Rep 1999, 6: doi: / Cite this article as: Guille et al.: Signaling pathway switch in breast cancer. Cancer Cell International :66. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San
 Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Osamu Tetsu, MD, PhD Associate Professor Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery School of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco Lung Cancer Classification Pathological Classification
Multiplexed Cancer Pathway Analysis
 NanoString Technologies, Inc. Multiplexed Cancer Pathway Analysis for Gene Expression Lucas Dennis, Patrick Danaher, Rich Boykin, Joseph Beechem NanoString Technologies, Inc., Seattle WA 98109 v1.0 MARCH
NanoString Technologies, Inc. Multiplexed Cancer Pathway Analysis for Gene Expression Lucas Dennis, Patrick Danaher, Rich Boykin, Joseph Beechem NanoString Technologies, Inc., Seattle WA 98109 v1.0 MARCH
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Characterisation of structural variation in breast. cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on. the Illumina Genome Analyser
 Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Characterisation of structural variation in breast cancer genomes using paired-end sequencing on the Illumina Genome Analyser Phil Stephens Cancer Genome Project Why is it important to study cancer? Why
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis
 Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
Cell cycle, signaling to cell cycle, and molecular basis of oncogenesis MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. CELL CYCLE - SUMMARY Basic terminology: Cyclins conserved proteins with homologous regions; their cellular
609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits)
 Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Master of Chemical and Life Sciences Program College of Computer, Mathematical, and Natural Sciences 609G: Concepts of Cancer Genetics and Treatments (3 credits) Text books: Principles of Cancer Genetics,
Genomic tests to personalize therapy of metastatic breast cancers. Fabrice ANDRE Gustave Roussy Villejuif, France
 Genomic tests to personalize therapy of metastatic breast cancers Fabrice ANDRE Gustave Roussy Villejuif, France Future application of genomics: Understand the biology at the individual scale Patients
Genomic tests to personalize therapy of metastatic breast cancers Fabrice ANDRE Gustave Roussy Villejuif, France Future application of genomics: Understand the biology at the individual scale Patients
The mutations that drive cancer. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer.
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer. Copy number patterns established from plasma samples of male individuals without cancer
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Plasma-Seq conducted with blood from male individuals without cancer. Copy number patterns established from plasma samples of male individuals without cancer
Contents. Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX
 Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer
 Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer No disclosures Objectives Understand how FISH and NGS provide complementary data for the evaluation of lung cancer Recognize the challenges of performing testing
Disclosures Genomic testing in lung cancer No disclosures Objectives Understand how FISH and NGS provide complementary data for the evaluation of lung cancer Recognize the challenges of performing testing
EXAMPLE. - Potentially responsive to PI3K/mTOR and MEK combination therapy or mtor/mek and PKC combination therapy. ratio (%)
 Dr Kate Goodhealth Goodhealth Medical Clinic 123 Address Road SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Melanie Citizen Referring Doctor Your ref Address Dr John Medico 123 Main Street, SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Phone 02 9999 9999
Dr Kate Goodhealth Goodhealth Medical Clinic 123 Address Road SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Melanie Citizen Referring Doctor Your ref Address Dr John Medico 123 Main Street, SUBURBTOWN NSW 2000 Phone 02 9999 9999
Clinical Oncology - Science in focus - Editorial. Understanding oestrogen receptor function in breast cancer, and its interaction with the
 Clinical Oncology - Science in focus - Editorial TITLE: Understanding oestrogen receptor function in breast cancer, and its interaction with the progesterone receptor. New preclinical findings and their
Clinical Oncology - Science in focus - Editorial TITLE: Understanding oestrogen receptor function in breast cancer, and its interaction with the progesterone receptor. New preclinical findings and their
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
Supplement 8: Candidate age-related genes and pathways
 Supplement 8: Candidate age-related genes and pathways Function Untreated cohort (cohort 1) Treated cohort (cohort 2) Genes Gene sets Effect of age Effect of age FDR of 2 nd Effect of age adjusted Effect
Supplement 8: Candidate age-related genes and pathways Function Untreated cohort (cohort 1) Treated cohort (cohort 2) Genes Gene sets Effect of age Effect of age FDR of 2 nd Effect of age adjusted Effect
S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A. b Normal Generalized Fraction 0.075
 Aiello & Alter (216) PLoS One vol. 11 no. 1 e164546 S1 Appendix A-1 S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A a Tumor Generalized Fraction b Normal Generalized Fraction.25.5.75.25.5.75 1 53 4 59 2 58 8 57 3 48
Aiello & Alter (216) PLoS One vol. 11 no. 1 e164546 S1 Appendix A-1 S1 Appendix: Figs A G and Table A a Tumor Generalized Fraction b Normal Generalized Fraction.25.5.75.25.5.75 1 53 4 59 2 58 8 57 3 48
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies
 OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
Early cell death (FGF) B No RunX transcription factor produced Yes No differentiation
 Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS
 MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
MOLECULAR BASIS OF ONCOGENESIS MUDr. Jiří Vachtenheim, CSc. 1 Cell processes which result also in cell cycle effects. Differentiation. Differentiated cells are usually in the G0 phase of the cell cycle.
Clinical Grade Genomic Profiling: The Time Has Come
 Clinical Grade Genomic Profiling: The Time Has Come Gary Palmer, MD, JD, MBA, MPH Senior Vice President, Medical Affairs Foundation Medicine, Inc. Oct. 22, 2013 1 Why We Are Here A Shared Vision At Foundation
Clinical Grade Genomic Profiling: The Time Has Come Gary Palmer, MD, JD, MBA, MPH Senior Vice President, Medical Affairs Foundation Medicine, Inc. Oct. 22, 2013 1 Why We Are Here A Shared Vision At Foundation
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma. Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute
 Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
Whole Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of Anaplastic Meningioma Patrick Tarpey Cancer Genome Project Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute Outline Anaplastic meningioma compared to other cancers Whole genomes
Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical Informatics (CoSBBI) Outline. Molecular Biology of Cancer AND. Goals/Expectations. David Boone 7/1/2015
 Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Goals/Expectations Computer Science, Biology, and Biomedical (CoSBBI) We want to excite you about the world of computer science, biology, and biomedical informatics. Experience what it is like to be a
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Tratamiento neoadyuvante: Enfermedad residual como marcador de resistencia Carlos L. Arteaga, MD Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Vanderbilt
 Tratamiento neoadyuvante: Enfermedad residual como marcador de resistencia Carlos L. Arteaga, MD Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Vanderbilt University Neoadjuvant (preoperative) therapy Surgery Systemic
Tratamiento neoadyuvante: Enfermedad residual como marcador de resistencia Carlos L. Arteaga, MD Vanderbilt-Ingram Cancer Center Vanderbilt University Neoadjuvant (preoperative) therapy Surgery Systemic
Expanded View Figures
 Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Results and Discussion of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. Activation
 Results and Discussion of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation To demonstrate the contribution which RCytoscape s molecular maps can make to biological understanding via exploratory data analysis, we here
Results and Discussion of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation To demonstrate the contribution which RCytoscape s molecular maps can make to biological understanding via exploratory data analysis, we here
AperTO - Archivio Istituzionale Open Access dell'università di Torino
 AperTO - Archivio Istituzionale Open Access dell'università di Torino From the nucleus to the mitochondria and backthe odyssey of a multitask STAT3 This is the author's manuscript Original Citation: From
AperTO - Archivio Istituzionale Open Access dell'università di Torino From the nucleus to the mitochondria and backthe odyssey of a multitask STAT3 This is the author's manuscript Original Citation: From
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis
 Kajbaf and Lalau BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2013, 14:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis Farshad
Kajbaf and Lalau BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2013, 14:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis Farshad
Liposarcoma*Genome*Project*
 LiposarcomaGenomeProject July2015! Submittedby: JohnMullen,MD EdwinChoy,MD,PhD GregoryCote,MD,PhD G.PeturNielsen,MD BradBernstein,MD,PhD Liposarcoma Background Liposarcoma is the most common soft tissue
LiposarcomaGenomeProject July2015! Submittedby: JohnMullen,MD EdwinChoy,MD,PhD GregoryCote,MD,PhD G.PeturNielsen,MD BradBernstein,MD,PhD Liposarcoma Background Liposarcoma is the most common soft tissue
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
Mechanisms of hormone drug resistance
 Mechanisms of hormone drug resistance Ljiljana Stamatović Institute for Oncology and Radiology of Serbia Tenth UMOS Conference, Belgrade, 16-17 th May 2015. Hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (HR+
Mechanisms of hormone drug resistance Ljiljana Stamatović Institute for Oncology and Radiology of Serbia Tenth UMOS Conference, Belgrade, 16-17 th May 2015. Hormone receptor-positive breast cancer (HR+
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 Douglas et al. BMC Cancer 2012, 12:425 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma Sarah Douglas 1, Steven E Schild 2 and Dirk
Douglas et al. BMC Cancer 2012, 12:425 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma Sarah Douglas 1, Steven E Schild 2 and Dirk
La via del segnale PI3K/AKT/mTOR Inibitori di mtor nel carcinoma mammario
 La via del segnale PI3K/AKT/mTOR Inibitori di mtor nel carcinoma mammario Alessandra Modena U.O.C. Oncologia Medica Direttore: Dott.ssa Stefania Gori Ospedale Sacro Cuore - Don Calabria 29 novembre 2016
La via del segnale PI3K/AKT/mTOR Inibitori di mtor nel carcinoma mammario Alessandra Modena U.O.C. Oncologia Medica Direttore: Dott.ssa Stefania Gori Ospedale Sacro Cuore - Don Calabria 29 novembre 2016
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Intergenic Fusions in Advanced HR+ Breast Cancer
 Intergenic Fusions in Advanced HR+ Breast Cancer Leif W. Ellisen, MD, PhD Program Director, Breast Medical Oncology Disclosures: Lief W. Ellisen, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Intergenic Fusions in Advanced HR+ Breast Cancer Leif W. Ellisen, MD, PhD Program Director, Breast Medical Oncology Disclosures: Lief W. Ellisen, MD, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer
 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer Robert A. Weinberg 1 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer 2 Review (V1) - Number of somatic mutations in human cancers Top: children vs. adults Numbers in parentheses
Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer Robert A. Weinberg 1 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer 2 Review (V1) - Number of somatic mutations in human cancers Top: children vs. adults Numbers in parentheses
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
7/6/2015. Cancer Related Deaths: United States. Management of NSCLC TODAY. Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview
 Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
The PI3K/AKT axis. Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia. Introduction
 The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
The PI3K/AKT axis Dr. Lucio Crinò Medical Oncology Division Azienda Ospedaliera-Perugia Introduction Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway are a family of lipid kinases discovered in 1980s. They have
The clonal and mutational spectrum of marker negative breast cancers (TNBC)
 The clonal and mutational spectrum of marker negative breast cancers (TNBC) Samuel AJR Aparicio BM BCh PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair, UBC Canada Research Chair, Molecular Oncology BC Cancer
The clonal and mutational spectrum of marker negative breast cancers (TNBC) Samuel AJR Aparicio BM BCh PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair, UBC Canada Research Chair, Molecular Oncology BC Cancer
BIO360 Quiz #1. September 14, Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points)
 Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Lecture 8 Neoplasia II Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Understand the definition of neoplasia. List the classification of neoplasia. Describe the general characters of benign tumors. Understand the nomenclature
Looking Beyond the Standard-of- Care : The Clinical Trial Option
 1 Looking Beyond the Standard-of- Care : The Clinical Trial Option Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H., F.A.C.S. Medical Director, Comprehensive Breast Program UF Health Cancer Center at Orlando Health Professor
1 Looking Beyond the Standard-of- Care : The Clinical Trial Option Terry Mamounas, M.D., M.P.H., F.A.C.S. Medical Director, Comprehensive Breast Program UF Health Cancer Center at Orlando Health Professor
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
Clinical audit for occupational therapy intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder: sampling steps and sample size calculation
 DOI 10.1186/s13104-015-1247-0 CORRESPONDENCE Open Access Clinical audit for occupational therapy intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder: sampling steps and sample size calculation Scott
DOI 10.1186/s13104-015-1247-0 CORRESPONDENCE Open Access Clinical audit for occupational therapy intervention for children with autism spectrum disorder: sampling steps and sample size calculation Scott
Multimedia Appendix 6 Educational Materials Table of Contents. Intervention Educational Materials Audio Script (version 1)
 Multimedia Appendix 6 Educational Materials Table of Contents Intervention Educational Materials... 1 Audio Script (version 1)... 1 Text (version 1)... 5 Slides (version 1)... 17 Audio Script (version
Multimedia Appendix 6 Educational Materials Table of Contents Intervention Educational Materials... 1 Audio Script (version 1)... 1 Text (version 1)... 5 Slides (version 1)... 17 Audio Script (version
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Genomic analysis of childhood High grade glial (HGG) brain tumors
 Genomic analysis of childhood High grade glial (HGG) brain tumors Linda D Cooley Children s Mercy, Kansas City The Children s Mercy Hospital, 2017 Genomic analysis of childhood High grade glial (HGG) brain
Genomic analysis of childhood High grade glial (HGG) brain tumors Linda D Cooley Children s Mercy, Kansas City The Children s Mercy Hospital, 2017 Genomic analysis of childhood High grade glial (HGG) brain
Breast Cancer Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms and Pathways in Hormone Receptor Positive Disease
 Breast Cancer Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms and Pathways in Hormone Receptor Positive Disease 1 Nearly Two-Thirds of Metastatic Breast Cancers Express Hormone Receptors Breast cancer tumors are often classified
Breast Cancer Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms and Pathways in Hormone Receptor Positive Disease 1 Nearly Two-Thirds of Metastatic Breast Cancers Express Hormone Receptors Breast cancer tumors are often classified
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
IPA Advanced Training Course
 IPA Advanced Training Course October 2013 Academia sinica Gene (Kuan Wen Chen) IPA Certified Analyst Agenda I. Data Upload and How to Run a Core Analysis II. Functional Interpretation in IPA Hands-on Exercises
IPA Advanced Training Course October 2013 Academia sinica Gene (Kuan Wen Chen) IPA Certified Analyst Agenda I. Data Upload and How to Run a Core Analysis II. Functional Interpretation in IPA Hands-on Exercises
Mechanism for targeting CDK4, BTK and PI3K in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Selina Chen-Kiang, Ph.D. Weill Cornell Medicine
 Mechanism for targeting CDK4, BTK and PI3K in Mantle Cell Lymphoma Selina Chen-Kiang, Ph.D. Weill Cornell Medicine Goal To develop mechanism-based therapy in mantle cell lymphoma Effective, tolerable,
Mechanism for targeting CDK4, BTK and PI3K in Mantle Cell Lymphoma Selina Chen-Kiang, Ph.D. Weill Cornell Medicine Goal To develop mechanism-based therapy in mantle cell lymphoma Effective, tolerable,
Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer
 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer Robert A. Weinberg 1 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer 2 Review (V1) - Number of somatic mutations in human cancers Top: children vs. adults Numbers in parentheses
Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer Robert A. Weinberg 1 Review (V1) - The Hallmarks of Cancer 2 Review (V1) - Number of somatic mutations in human cancers Top: children vs. adults Numbers in parentheses
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Treatment Landscape in R/R DLBCL Novel Targets and Strategies. Wyndham H. Wilson, M.D., Ph.D. Senior Investigator
 Treatment Landscape in R/R DLBCL Novel Targets and Strategies Wyndham H. Wilson, M.D., Ph.D. Senior Investigator Gene-expression profiling of DLBCL subtypes Roschewski, M. et al. (2013) Nat. Rev. Clin.
Treatment Landscape in R/R DLBCL Novel Targets and Strategies Wyndham H. Wilson, M.D., Ph.D. Senior Investigator Gene-expression profiling of DLBCL subtypes Roschewski, M. et al. (2013) Nat. Rev. Clin.
Pancreatic intraepithelial
 Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) Markéta Hermanová St. Anne s University Hospital Brno Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University Precursor lesions of invasive pancreatic cancer Pancreatic intraepithelial
Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PanIN) Markéta Hermanová St. Anne s University Hospital Brno Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University Precursor lesions of invasive pancreatic cancer Pancreatic intraepithelial
Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Glioblastoma Multiforme: Finding Ways Forward
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
Transcript Details This is a transcript of a continuing medical education (CME) activity accessible on the ReachMD network. Additional media formats for the activity and full activity details (including
From pathology research to stratified medicine trials
 From pathology research to stratified medicine trials Dr. John Bartlett Program Director Transformative Pathology C CCTG Breast Group Steering Committee ASCO-CAP HER2 Panel As is your Pathology, so is
From pathology research to stratified medicine trials Dr. John Bartlett Program Director Transformative Pathology C CCTG Breast Group Steering Committee ASCO-CAP HER2 Panel As is your Pathology, so is
Simultaneous Identification of Multiple Driver Pathways in Cancer
 Simultaneous Identification of Multiple Driver Pathways in Cancer Mark D. M. Leiserson 1, Dima Blokh 2, Roded Sharan 2., Benjamin J. Raphael 1. * 1 Department of Computer Science and Center for Computational
Simultaneous Identification of Multiple Driver Pathways in Cancer Mark D. M. Leiserson 1, Dima Blokh 2, Roded Sharan 2., Benjamin J. Raphael 1. * 1 Department of Computer Science and Center for Computational
CDx in oncology Prof. Christophe Le Tourneau, MD, PhD FEAM Geneva September 27, 2018
 CDx in oncology Prof. Christophe Le Tourneau, MD, PhD Institut Curie Paris & Saint-Cloud France Head, Department of Drug Development and Innovation (D 3 i) INSERM U900 Research unit Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines
CDx in oncology Prof. Christophe Le Tourneau, MD, PhD Institut Curie Paris & Saint-Cloud France Head, Department of Drug Development and Innovation (D 3 i) INSERM U900 Research unit Versailles Saint-Quentin-en-Yvelines
Introduction to Cancer Bioinformatics and cancer biology. Anthony Gitter Cancer Bioinformatics (BMI 826/CS 838) January 20, 2015
 Introduction to Cancer Bioinformatics and cancer biology Anthony Gitter Cancer Bioinformatics (BMI 826/CS 838) January 20, 2015 Why cancer bioinformatics? Devastating disease, no cure on the horizon Major
Introduction to Cancer Bioinformatics and cancer biology Anthony Gitter Cancer Bioinformatics (BMI 826/CS 838) January 20, 2015 Why cancer bioinformatics? Devastating disease, no cure on the horizon Major
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database
 Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Genomic landscape of breast cancer
 Genomic landscape of breast cancer Aleix Prat MD PhD Head of the Translational Genomics Group Attending Physician at the Breast Cancer Unit VHIO, Barcelona, Spain Major research advance for breast cancer
Genomic landscape of breast cancer Aleix Prat MD PhD Head of the Translational Genomics Group Attending Physician at the Breast Cancer Unit VHIO, Barcelona, Spain Major research advance for breast cancer
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Emerging" hallmarks of cancer, a. Reprogramming of energy metabolism b. Evasion of the immune system, Enabling characteristics, a.
 HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
HALLMARKS OF CANCER - Together dictate the malignant phenotype. 1. Self-sufficiency in growth signals 2. Insensitivity to growth inhibitory signals 3. Evasion of cell death 4. Limitless replicative potential
Akt targeting as a strategy to boost chemotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer through metabolism suppression.
 Akt targeting as a strategy to boost chemotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer through metabolism suppression. Marion Le Grand 1,2, Raphael Berges 1, Eddy Pasquier 1,3, Marie-Pierre Montero 1,
Akt targeting as a strategy to boost chemotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer through metabolism suppression. Marion Le Grand 1,2, Raphael Berges 1, Eddy Pasquier 1,3, Marie-Pierre Montero 1,
Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers
 Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers from genomics to clinical application Aldo Scarpa ARC-NET Applied Research on Cancer Department of Pathology and Diagnostics
Next generation histopathological diagnosis for precision medicine in solid cancers from genomics to clinical application Aldo Scarpa ARC-NET Applied Research on Cancer Department of Pathology and Diagnostics
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
FOR REVIEW. BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission. Manuscript Draft. Manuscript Number: BMB
 BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
BMB Reports - Manuscript Submission Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: BMB-18-095 Title: Insulin Receptor Substrate 2:A Bridge between Hippo and AKT Pathways Article Type: Perspective (Invited Only) Keywords:
Supplementary Figure 1. Copy Number Alterations TP53 Mutation Type. C-class TP53 WT. TP53 mut. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.
 Supplementary Figure a Copy Number Alterations in M-class b TP53 Mutation Type Recurrent Copy Number Alterations 8 6 4 2 TP53 WT TP53 mut TP53-mutated samples (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 Missense Truncating M-class
Supplementary Figure a Copy Number Alterations in M-class b TP53 Mutation Type Recurrent Copy Number Alterations 8 6 4 2 TP53 WT TP53 mut TP53-mutated samples (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 Missense Truncating M-class
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
 Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
Molecular Cell Biology. Prof. D. Karunagaran. Department of Biotechnology. Indian Institute of Technology Madras
 Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Molecular Cell Biology Prof. D. Karunagaran Department of Biotechnology Indian Institute of Technology Madras Module 9 Molecular Basis of Cancer, Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes Lecture 2 Genes Associated
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy
 Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
Changing demographics of smoking and its effects during therapy Egbert F. Smit MD PhD. Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, Vrije Universiteit Medical Centre, Amsterdam, The Netherlands Smoking prevalence adults
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
AP VP DLP H&E. p-akt DLP
 A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
A B AP VP DLP H&E AP AP VP DLP p-akt wild-type prostate PTEN-null prostate Supplementary Fig. 1. Targeted deletion of PTEN in prostate epithelium resulted in HG-PIN in all three lobes. (A) The anatomy
GENERAL SUMMARY Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro
 Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro-gestational hormone, essential for establishment and maintenance of
Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro-gestational hormone, essential for establishment and maintenance of
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK
 TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
TARGETS OF CYCLIN D1-CDK FIRST TARGET OF THE COMPLEX CYCLIN D-KINASI: prb, IS THE PRODUCT OF THE GENE CONFERRING SUSCEPTIBILITY TO RETINOBLASTOMA - ABSENT OR MUTATED IN SEVERAL HUMAN CANCERS - TRANSCRIPTIONL
Cancer. Death Rates for the Main Causes of Death in the U.S. Leading Sites of New Cases & Deaths (2015 estimates in the U.S.)
 11/25/17 Learning Goals for This Lecture Cancer - To recognize that cancer largely is a preventable disease. - To recognize that cancer is a disease of our own genes. Weimin Zhong, Ph.D. weimin.zhong@yale.edu
11/25/17 Learning Goals for This Lecture Cancer - To recognize that cancer largely is a preventable disease. - To recognize that cancer is a disease of our own genes. Weimin Zhong, Ph.D. weimin.zhong@yale.edu
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Fig. 1: Quality assessment of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE)-derived DNA and nuclei. (a) Multiplex PCR analysis of unrepaired and repaired bulk FFPE gdna from
1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples. Major Principles:
 Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Carcinogenesis 1. Basic principles 2. 6 hallmark features 3. Abnormal cell proliferation: mechanisms 4. Carcinogens: examples Carcinogenesis Major Principles: 1. Nonlethal genetic damage is central to
Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada?
 Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada? Alberto Ocana Albacete University Hospital Salamanca May 19th, 2016 WHAT IS PERSONALIZED MEDICINE? Molecular
Identificación de vulnerabilidades en tumores sólidos: aportes hacia una medicina personalizada? Alberto Ocana Albacete University Hospital Salamanca May 19th, 2016 WHAT IS PERSONALIZED MEDICINE? Molecular
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Genomic instability. Amin Mahpour
 Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
Genomic instability Amin Mahpour 1 Some questions to ponder What is Genomic instability? What factors contribute to the genomic integrity? How we identify these aberrations? 2 PART I: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC)
 PERSPECTIVE 1 LARGE SCALE DATASET EXAMPLES MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) BC Cancer Agency, Vancouver Samuel Aparicio, PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair
PERSPECTIVE 1 LARGE SCALE DATASET EXAMPLES MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) BC Cancer Agency, Vancouver Samuel Aparicio, PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Mutational signatures in BCC compared to melanoma.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational signatures in BCC compared to melanoma. (a) The effect of transcription-coupled repair as a function of gene expression in BCC. Tumor type specific gene expression levels
Supplementary Figure 1 Mutational signatures in BCC compared to melanoma. (a) The effect of transcription-coupled repair as a function of gene expression in BCC. Tumor type specific gene expression levels
Relationship between incident types and impact on patients in drug name errors: a correlational study
 Tsuji et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2015) 1:11 DOI 10.1186/s40780-015-0011-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between incident types and impact on patients in drug
Tsuji et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2015) 1:11 DOI 10.1186/s40780-015-0011-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between incident types and impact on patients in drug
