LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment
|
|
|
- Alberta Park
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment Giorgio Melloni, Stefano de Pretis October 30, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction System Requirements Create a LowMACA object Find your target family of proteins or pfam you want to know more about Change default parameters Setup Align sequences Get Mutations and Map Mutations Whole setup Custom Data Statistics Plot Consensus Bar Plot LowMACA comprehensive Plot Protter plot Data driven workflow Summary Session Information
2 1 Introduction The LowMACA package is a simple suite of tools to investigate and analyse the profile of the somatic mutations provided by the cbioportal (via the cgdsr). LowMACA evaluates the functional impact of somatic mutations by statistically assessing the number of alterations that accumulates on the same residue (or residue that are conserved in Pfam domains). For example, the known driver mutations G12,G13 and Q61 in KRAS can be found on the corresponding residues of other proteins in the RAS family (PF00071) like NRAS and HRAS, but also in less frequently mutated genes like RRAS and RRAS2. The corresponding residues are identified via multiple sequence alignment. Thanks to this approach the user can identify new driver mutations that occur at low frequency at single protein level but emerge at Pfam level. In addition, the impact of known driver mutations can be transferred to other proteins that share a high degree of sequence similarity (like in the RAS family example). You can conduct an hypothesis driven exploratory analysis using our package simply providing a set of genes and/or pfam domains of your interest. The user is able to choose the kind of tumor and the type of mutations (like missense, nonsense, frameshift etc.). The data are directly downloaded from the largest cancer sequencing projects and aggregated by LowMACA to evaluate the possible functional impact of somatic mutations by spotting the most conserved variations in the cohort of cancer samples. By connecting several proteins that share sequence similarity via consensus alignment, this package is able to statistically assessing the occurrence of mutations on the same residue and ultimately see: where mutations fall and what are the involved domains what is the frequency of the aberrations and what is the more represented tumor type if and where the mutations tend to clusterize what is the degree of conservation of the mutated residues if there are new driver genes and in particular, driver mutations 2 System Requirements LowMACA relies on two external resources to work properly. Clustal Omega, our trusted aligner ( Ghostscript, a postscript interpreter needed to draw logo plots ( Clustal Omega is a fast aligner that can be downloaded from the link above. For both Unix and Windows users, remember to have "clustalo" in your PATH variable. In case you cannot set "clustalo" in the PATH, you can always set the clustalo command from inside R, after creating a LowMACA object: 2
3 #Given a LowMACA object 'lm' lm <- newlowmaca(genes=c("tp53", "TP63", "TP73")) lmparams(lm)$clustal_cmd <- "/your/path/to/clustalo" If you cannot install clustalomega, we provide a wrapper around EBI web service ( You just need to set your as explained in section setup, but you have a limit of 2000 input sequences and perl must be installed with the modules LWP and XML::Simple. Ghostscript is an interpreter of postscript language and a pdf reader that is used by the R library grimport. For Linux users, simply download the program from and compile it For MacOS users there is a dmg installer at For Windows users, download the program from and then you have 3 options: 1. Put C:/Program Files/gs/gs9.05/bin in your PATH once for all (Adjust the path to match your gs installation) 2. Run the command Sys.setenv(R_GSCMD = "C:/Program Files/gs/gs9.05/bin/gswin32c.exe" ) at every new session of R 3. Put the command showed above in your.renviron file More details can be found here: LowMACA needs an internet connection to: retrieve mutation data from cbioportal, draw the Protter-style plot ( and use the web service of clustalomega ( 3 Create a LowMACA object First of all, we have to define our target genes or pfam domains that we wish to analyse. 3.1 Find your target family of proteins or pfam you want to know more about 3
4 library(lowmaca) #User Input Genes <- c("adnp","alx1","alx4","argfx","cdx4","crx","cux1","cux2","dbx2","dlx5","dmbx1","drgx","duxa","esx1","evx2","hdx","hlx","hnf1a","hoxa1","hoxa2","hoxa3","hoxa5","hoxb1","hoxb3","hoxd3","isl1","isx","lhx8") Pfam <- "PF00046" #Construct the object lm <- newlowmaca(genes=genes, pfam=pfam) All Gene Symbols correct! str(lm, max.level=3) Formal class 'LowMACA' [package "LowMACA"] with 4 slots..@ arguments:list of 7....$ genes : chr [1:28] "ADNP" "ALX1" "ALX4" "ARGFX" $ pfam : chr "PF00046"....$ pfamallgenes:'data.frame': 249 obs. of 7 variables:....$ input :'data.frame': 28 obs. of 7 variables:....$ mode : chr "pfam"....$ params :List of 7....$ parallelize :List of 2..@ alignment: list()..@ mutations: list()..@ entropy : list() Now we have created a LowMACA object. In this case, we want to analyse the homeodomain fold pfam (PF00046), considering 28 genes that belong to this clan. If we don t specify the pfam parameter, LowMACA proceeds to analyse the entire proteins passed by the genes parameter (we map only canonical proteins, one per gene). Vice versa, if we don t specify the genes parameter, LowMACA looks for all the proteins that contain the specified pfam and analyse just the portion of the protein assigned to the domain. 3.2 Change default parameters A LowMACA object is composed by four slots. The first slot is arguments and is filled at the very creation of the object. It contains information as Uniprot name for the proteins associated to the genes, the amino acid sequences, start and end of the selected domains and the default parameters that can be change to start the analysis. 4
5 #See default parameters lmparams(lm) $mutation_type [1] "missense" $tumor_type [1] "all_tumors" $min_mutation_number [1] 1 $density_bw [1] 0 $clustal_cmd [1] "clustalo" $use_hmm [1] FALSE $datum [1] FALSE #Change some parameters #Accept sequences even with no mutations lmparams(lm)$min_mutation_number <- 0 #Changing selected tumor types #Check the available tumor types in cbioportal available_tumor_types <- showtumortype() head(available_tumor_types) Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma of the Breast "acbc" Adrenocortical Carcinoma "acc" Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma "acyc" Hypodiploid Acute Lymphoid Leukemia Infant MLL-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia "all" Ampullary Carcinoma "ampca" Bladder Cancer Bladder Cancer, Plasmacytoid Variant Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma "blca" #Select melanoma, stomach adenocarcinoma, uterine cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, #lung squamous cell carcinoma, colon rectum adenocarcinoma and breast cancer 5
6 lmparams(lm)$tumor_type <- c("skcm", "stad", "ucec", "luad", "lusc", "coadread", "brca") 4 Setup 4.1 Align sequences lm <- alignsequences(lm) Aligning sequences... This method is basically self explained. It aligns the sequences in the object. If you didn t install clustalomega yet, you can use the web service of clustalomega that we wrapped in our R package. The limit is set to 2000 sequences and it is obviously slower than a local installation. Rememeber to put your own in the mail command to activate this option since is required by the EBI server. lm <- alignsequences(lm, mail="lowmaca@gmail.com") #Access to the slot alignment myalignment <- lmalignment(lm) str(myalignment, max.level=2, vec.len=2) List of 4 $ ALIGNMENT:'data.frame': 1708 obs. of 8 variables:..$ domainid : Factor w/ 28 levels "ARGFX PF ;135",..: $ Gene_Symbol : Factor w/ 27 levels "ADNP","ALX1",..: $ Pfam : Factor w/ 1 level "PF00046": $ Entrez : Factor w/ 27 levels "1046","127343",..: $ Envelope_Start: num [1:1708] $ Envelope_End : num [1:1708] $ Align : int [1:1708] $ Ref : num [1:1708] $ SCORE :List of 2..$ DIST_MAT : num [1:28, 1:28] NA attr(*, "dimnames")=list of 2..$ SUMMARY_SCORE:'data.frame': 28 obs. of 4 variables: $ CLUSTAL :Formal class 'AAMultipleAlignment' [package "Biostrings"] with 3 slots $ df :'data.frame': 61 obs. of 2 variables:..$ consensus : Factor w/ 18 levels "A","D","E","F",..: $ conservation: num [1:61] ALIGNMENT: mapping from original position to the position in the consensus 6
7 SCORE: some score of distance between the sequences CLUSTAL: an object of class AAMultipleAlignment as provided by Biostrings R package df: Consesus sequence and conservation Trident Score at every position 4.2 Get Mutations and Map Mutations lm <- getmutations(lm) Getting mutations from cancers studies... lm <- mapmutations(lm) These commands produce a change in the slot mutation and provide the results from R cgdsr package. #Access to the slot mutations mymutations <- lmmutations(lm) str(mymutations, vec.len=3, max.level=1) List of 3 $ data :'data.frame': 1762 obs. of 8 variables: $ freq :'data.frame': 7 obs. of 29 variables: $ aligned: num [1:28, 1:61] attr(*, "dimnames")=list of 2 data: provide the mutations selected from the cbioportal divided by gene and patient/tumor type freq: a table containing the absolute number of mutated patients by gene and tumor type (this is useful to explore the mutational landscape of your genes in the different tumor types) aligned: a matrix of m rows, proteins or pfam, and n columns, consensus positions derived from the mapping of the mutations from the original positions to the new consensus If we want to check what are the most represented genes in terms of number of mutations divided by tumor type, we can simply run: mymutationfreqs <- mymutations$freq #Showing the first genes mymutationfreqs[, 1:10] StudyID Total_Sequenced_Samples ADNP ALX1 ALX4 ARGFX CDX4 CRX CUX1 CUX2 1 brca coadread
8 3 luad lusc skcm stad ucec This can be useful for a stratified analysis in the future. 4.3 Whole setup To simplify this setup process, you can use directly the command setup to launch alignsequences, getmutations and mapmutations at once #Local Installation of clustalo lm <- setup(lm) #Web Service lm <- setup(lm, mail="lowmaca@gmail.com") 4.4 Custom Data If you have your own data and you don t need to rely on the cgdsr package, you can use the getmutations or setup method with the parameter repos, like this: #Reuse the downloaded data as a toy example myowndata <- mymutations$data #How myowndata should look like for the argument repos str(mymutations$data, vec.len=1) 'data.frame': 1762 obs. of 8 variables: $ Entrez : int $ Gene_Symbol : chr "HOXA2"... $ Amino_Acid_Letter : chr "L"... $ Amino_Acid_Position: num $ Amino_Acid_Change : chr "L298M"... $ Mutation_Type : chr "Missense_Mutation"... $ Sample : chr "SA236"... $ Tumor_Type : chr "brca"... #Read the mutation data repository instead of using cgdsr package #Following the process step by step lm <- getmutations(lm, repos=myowndata) Filtering mutations from local repository... #Setup in one shot 8
9 lm <- setup(lm, repos=myowndata) Aligning sequences... Filtering mutations from local repository... 5 Statistics In this step we calculate the general statistics for the entire consensus profile lm <- entropy(lm) Making uniform model... Assigned bandwidth: 0 #Global Score myentropy <- lmentropy(lm) str(myentropy) List of 6 $ bw : num 0 $ uniform :function (nmut) $ absval : num 3.57 $ log10pval : num $ pvalue : num 7.47e-17 $ conservation_thr: num 0.1 #Per position score head(myalignment$df) consensus conservation 1 R R A R T A With the method entropy, we calculate the entropy score and a pvalue against the null hypothesis that the mutations are distributed randomly accross our consensus protein. In addition, a test is performed for every position of the consensus and the output is reported in the slot alignment. The position 4 has a conservation score of 0.88 (highly conserved) and the corrected pvalue is significant (qvalue below 0.01). There are signs of positive selection for the position 4. To retrieve the original mutations that generated that cluster, we can use the function lfm 9
10 significant_muts <- lfm(lm) #Display original mutations that formed significant clusters (column Multiple_Aln_pos) head(significant_muts) Gene_Symbol Amino_Acid_Position Amino_Acid_Change Sample 1 ALX1 184 R184M FR ALX4 218 R218Q TCGA-AA ALX4 218 R218Q coadread_dfci_2016_ ALX4 218 R218W coadread_dfci_2016_ ALX4 265 R265Q TCGA-D8-A1Y ALX4 265 R265Q coadread_dfci_2016_2944 Tumor_Type Envelope_Start Envelope_End Multiple_Aln_pos metric 1 luad e-02 2 coadread e-13 3 coadread e-13 4 coadread e-13 5 brca e-02 6 coadread e-02 Entrez Entry UNIPROT Chromosome Protein.name Q15699 ALX1_HUMAN 12q21.31 ALX homeobox protein Q9H161 ALX4_HUMAN 11p11.2 Homeobox protein aristaless-like Q9H161 ALX4_HUMAN 11p11.2 Homeobox protein aristaless-like Q9H161 ALX4_HUMAN 11p11.2 Homeobox protein aristaless-like Q9H161 ALX4_HUMAN 11p11.2 Homeobox protein aristaless-like Q9H161 ALX4_HUMAN 11p11.2 Homeobox protein aristaless-like 4 #What are the genes mutated in position 4 in the consensus? genes_mutated_in_pos4 <- significant_muts[ significant_muts$multiple_aln_pos==4, 'Gene_Symbol'] sort(table(genes_mutated_in_pos4)) genes_mutated_in_pos4 CUX1 DBX2 DLX5 EVX2 ISL1 LHX8 HDX HOXA5 ALX4 CDX4 HOXD3 DUXA HOXA1 ISX 5 18 The position 4 accounts for mutations in 13 different genes. The most represented one is ISX (ISX_HUMAN, Intestine-specific homeobox protein). 10
11 LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment 6 Plot 6.1 Consensus Bar Plot bpall(lm) Mutations by position Entropy Z Score: P Value: 7.5e ARGFX PF ;135 DUXA PF ;70 DUXA PF ;156 DRGX PF ;90 CUX2 PF ;1225 CDX4 PF ;230 CRX PF ;96 HOXA2 PF ;200 HOXA3 PF ;248 HOXB3 PF ;245 HOXB1 PF ;260 HOXA5 PF ;252 HOXD3 PF ;251 CUX1 PF ;1301 HOXA1 PF ;286 DLX5 PF ;194 ISL1 PF ;238 EVX2 PF ;245 HLX PF ;333 ALX1 PF ;189 ISX PF ;139 LHX8 PF ;282 DBX2 PF ;243 HDX PF ;496 ESX1 PF ;196 DMBX1 PF ;128 ALX4 PF ;271 ADNP PF ; This barplot shows all the mutations reported on the consensus sequence divided by protein/pfam domain 11
12 6.2 LowMACA comprehensive Plot lmplot(lm) Mutations from position 1 to 61 of the multiple alignment Log10 P Value: P Value: 7.5e 17 Bw: Mutation density Mutation # * ** Logo Conservation This four layer plot encompasses: 1 23 The bar plot visualize before position The distribution of mutations against the null hypothesis (blue line) with orange bars representing a pvalue below 0.05 for that position and a red star for qvalue below 0.05 The Trident score distribution The logo plot representing the consensus sequence 6.3 Protter plot #This plot is saved as a png image protter(lm, filename="homeobox.png") A request to the Protter server is sent and a png file is downloaded with the possible sequence structure of the protein and the significant positions colored in orange and red 12
13 7 Data driven workflow An alternative use of LowMACA consists in analysing all the Pfams and single sequences encompassed by a specific set of mutations. For example, it is possible to analyse mutations derived from a cohort of patients to see which Pfams and set of mutations are enriched, following the LowMACA statistics. The function allpfam Analysis takes as input a data.frame or the name of a file which contains the set of mutations, analyse all the Pfams that are represented and reports all the significant mutations as output. Moreover, the function allpfamanalysis analyses individually all the mutated genes and reports the significant mutations found by this analysis as part of the output. #Load Homeobox example data(lmobj) #Extract the data inside the object as a toy example mydata <- lmmutations(lmobj)$data #Run allpfamanalysis on every mutations significant_muts <- allpfamanalysis(repos=mydata) Warning in mapmutations(object): We excluded these genes (or domains) because they have less than 1 mutations NULL Warning in.clustaloalign(genesdata, clustal_cmd, clustalo_filename, mail, : There are less than 3 sequences aligned, so no distance matrix can be calculated Warning in.clustaloalign(genesdata, clustal_cmd, clustalo_filename, mail, : There are less than 3 sequences aligned, so no distance matrix can be calculated Warning in.clustaloalign(genesdata, clustal_cmd, clustalo_filename, mail, : There are less than 3 sequences aligned, so no distance matrix can be calculated Warning in mapmutations(object): We excluded these genes (or domains) because they have less than 1 mutations NULL #Show the result of alignment based analysis head(significant_muts$alignedsequence) Gene_Symbol Multiple_Aln_pos Pfam_ID binomialpvalue Amino_Acid_Position 1 ALX4 4 PF CDX4 4 PF CDX4 4 PF CDX4 4 PF
14 5 CUX1 4 PF CUX1 4 PF Amino_Acid_Change Sample Tumor_Type Envelope_Start Envelope_End 1 R218Q TCGA-AA coadread R177C TCGA-D3-A2JO-06 skcm R177C TCGA-AP-A0LM-01 ucec R177C MEL-Ma-Mel-85 skcm R1248W TCGA-ER-A skcm R1248W TCGA-BG-A18B-01 ucec metric Entrez Entry UNIPROT Chromosome e Q9H161 ALX4_HUMAN 11p e O14627 CDX4_HUMAN Xq e O14627 CDX4_HUMAN Xq e O14627 CDX4_HUMAN Xq e P39880 CUX1_HUMAN 7q e P39880 CUX1_HUMAN 7q22.1 Protein.name 1 Homeobox protein aristaless-like 4 2 Homeobox protein CDX-4 3 Homeobox protein CDX-4 4 Homeobox protein CDX-4 5 Homeobox protein cut-like 1 6 Homeobox protein cut-like 1 #Show all the genes that harbor significant mutations unique(significant_muts$alignedsequence$gene_symbol) [1] ALX4 CDX4 CUX1 DBX2 DUXA EVX2 HDX HOXA1 HOXA5 HOXD3 ISL1 ISX [13] LHX8 13 Levels: ALX4 CDX4 CUX1 DBX2 DUXA EVX2 HDX HOXA1 HOXA5 HOXD3 ISL1... LHX8 #Show the result of the Single Gene based analysis head(significant_muts$singlesequence) Gene_Symbol Amino_Acid_Position Amino_Acid_Change PF00046.DUXA.1 DUXA 103 R103Q PF00046.DUXA.2 DUXA 103 R103L PF00046.DUXA.3 DUXA 103 R103Q PF00046.DUXA.4 DUXA 17 R17H PF00046.DUXA.5 DUXA 105 R105C PF00046.DUXA.6 DUXA 105 R105H Sample Tumor_Type Envelope_Start Envelope_End PF00046.DUXA.1 TCGA-A8-A brca PF00046.DUXA.2 LUAD-S00488 luad PF00046.DUXA.3 TCGA-B5-A11E-01 ucec PF00046.DUXA.4 TCGA-D1-A0ZS-01 ucec PF00046.DUXA.5 TCGA lusc
15 PF00046.DUXA coadread Multiple_Aln_pos metric Entrez Entry UNIPROT PF00046.DUXA A6NLW8 DUXA_HUMAN PF00046.DUXA A6NLW8 DUXA_HUMAN PF00046.DUXA A6NLW8 DUXA_HUMAN PF00046.DUXA A6NLW8 DUXA_HUMAN PF00046.DUXA A6NLW8 DUXA_HUMAN PF00046.DUXA A6NLW8 DUXA_HUMAN Chromosome Protein.name PF00046.DUXA.1 19q13.43 Double homeobox protein A PF00046.DUXA.2 19q13.43 Double homeobox protein A PF00046.DUXA.3 19q13.43 Double homeobox protein A PF00046.DUXA.4 19q13.43 Double homeobox protein A PF00046.DUXA.5 19q13.43 Double homeobox protein A PF00046.DUXA.6 19q13.43 Double homeobox protein A #Show all the genes that harbor significant mutations unique(significant_muts$singlesequence$gene_symbol) [1] "DUXA" The parameter alllowmacaobjects can be used to specify the name of the file where all the Pfam analyses will be stored (by default this information is not stored, because the resulting file can be huge, according to the size of the input dataset). In this case, all the analysed Pfams are stored as LowMACA objects and they can be loaded and analysed with the usual LowMACA workflow. 8 Summary Copy and paste on your R console and perform the entire analysis by yourself. You need Ghostscript to see all the plots. library(lowmaca) Genes <- c("adnp","alx1","alx4","argfx","cdx4","crx" Pfam <- "PF00046","CUX1","CUX2","DBX2","DLX5","DMBX1","DRGX","DUXA","ESX1","EVX2","HDX","HLX","HNF1A","HOXA1","HOXA2","HOXA3","HOXA5","HOXB1","HOXB3","HOXD3","ISL1","ISX","LHX8") lm <- newlowmaca(genes=genes, pfam=pfam) lmparams(lm)$tumor_type <- c("skcm", "stad", "ucec", "luad", "lusc", "coadread", "brca") lmparams(lm)$min_mutation_number <- 0 lm <- setup(lm, mail="lowmaca@gmail.com") 15
16 lm <- entropy(lm) lfm(lm) bpall(lm) lmplot(lm) protter(lm) 16
17 9 Session Information sessioninfo() R Under development (unstable) ( r73567) Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit) Running under: Ubuntu LTS Matrix products: default BLAS: /home/biocbuild/bbs-3.7-bioc/r/lib/librblas.so LAPACK: /home/biocbuild/bbs-3.7-bioc/r/lib/librlapack.so locale: [1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C [3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=C [5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8 [7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C [9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C [11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C attached base packages: [1] stats graphics grdevices utils datasets methods base other attached packages: [1] LowMACA_ loaded via a namespace (and not attached): [1] SummarizedExperiment_1.9.0 reshape2_1.4.2 [3] lattice_ colorspace_1.3-2 [5] htmltools_0.3.6 stats4_3.5.0 [7] rtracklayer_ yaml_ [9] XML_ R.oo_ [11] BiocParallel_ BiocGenerics_ [13] RColorBrewer_1.1-2 matrixstats_ [15] GenomeInfoDbData_ plyr_1.8.4 [17] stringr_1.2.0 zlibbioc_ [19] Biostrings_ munsell_0.4.3 [21] R.methodsS3_1.7.1 htmlwidgets_0.9 [23] evaluate_ Biobase_ [25] knitr_1.17 IRanges_ [27] GenomeInfoDb_ parallel_3.5.0 [29] MotIV_ highr_0.6 [31] Rcpp_ scales_0.5.0 [33] backports_1.1.1 rgadem_ [35] BSgenome_ seqlogo_
18 [37] DelayedArray_0.5.0 S4Vectors_ [39] XVector_ cgdsr_1.2.6 [41] Rsamtools_ BiocStyle_2.7.0 [43] digest_ stringi_1.1.5 [45] GenomicRanges_ grid_3.5.0 [47] ade4_1.7-8 rprojroot_1.2 [49] tools_3.5.0 bitops_1.0-6 [51] magrittr_1.5 RCurl_ [53] Matrix_ LowMACAAnnotation_ [55] data.table_ grimport_0.9-0 [57] rmarkdown_1.6 GenomicAlignments_ [59] motifstack_ compiler_
LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment
 LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment Giorgio Melloni, Stefano de Pretis October 17, 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 System Requirements 2 3 Create a LowMACA object 3 3.1 Find
LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment Giorgio Melloni, Stefano de Pretis October 17, 2016 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 System Requirements 2 3 Create a LowMACA object 3 3.1 Find
LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment
 LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment Giorgio Melloni, Stefano de Pretis October 14, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 System Requirements 2 3 Create a LowMACA object 3 3.1 Find
LowMACA: Low frequency Mutation Analysis via Consensus Alignment Giorgio Melloni, Stefano de Pretis October 14, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 System Requirements 2 3 Create a LowMACA object 3 3.1 Find
splicer: An R package for classification of alternative splicing and prediction of coding potential from RNA-seq data
 splicer: An R package for classification of alternative splicing and prediction of coding potential from RNA-seq data Kristoffer Knudsen, Johannes Waage 5 Dec 2013 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Alternative
splicer: An R package for classification of alternative splicing and prediction of coding potential from RNA-seq data Kristoffer Knudsen, Johannes Waage 5 Dec 2013 1 Contents 1 Introduction 3 1.1 Alternative
GeneOverlap: An R package to test and visualize
 GeneOverlap: An R package to test and visualize gene overlaps Li Shen Contact: li.shen@mssm.edu or shenli.sam@gmail.com Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, New York http://shenlab-sinai.github.io/shenlab-sinai/
GeneOverlap: An R package to test and visualize gene overlaps Li Shen Contact: li.shen@mssm.edu or shenli.sam@gmail.com Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai New York, New York http://shenlab-sinai.github.io/shenlab-sinai/
MethylMix An R package for identifying DNA methylation driven genes
 MethylMix An R package for identifying DNA methylation driven genes Olivier Gevaert May 3, 2016 Stanford Center for Biomedical Informatics Department of Medicine 1265 Welch Road Stanford CA, 94305-5479
MethylMix An R package for identifying DNA methylation driven genes Olivier Gevaert May 3, 2016 Stanford Center for Biomedical Informatics Department of Medicine 1265 Welch Road Stanford CA, 94305-5479
metaseq: Meta-analysis of RNA-seq count data
 metaseq: Meta-analysis of RNA-seq count data Koki Tsuyuzaki 1, and Itoshi Nikaido 2. October 30, 2017 1 Department of Medical and Life Science, Tokyo University of Science. 2 Bioinformatics Research Unit,
metaseq: Meta-analysis of RNA-seq count data Koki Tsuyuzaki 1, and Itoshi Nikaido 2. October 30, 2017 1 Department of Medical and Life Science, Tokyo University of Science. 2 Bioinformatics Research Unit,
Using Messina. Mark Pinese. October 13, Introduction The problem Example: Designing a colon cancer screening test...
 Using Messina Mark Pinese October 13, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Using Messina to construct optimal diagnostic classifiers 1 2.1 The problem.................................................. 1 2.2
Using Messina Mark Pinese October 13, 2014 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Using Messina to construct optimal diagnostic classifiers 1 2.1 The problem.................................................. 1 2.2
AIMS: Absolute Assignment of Breast Cancer Intrinsic Molecular Subtype
 AIMS: Absolute Assignment of Breast Cancer Intrinsic Molecular Subtype Eric R. Paquet (eric.r.paquet@gmail.com), Michael T. Hallett (michael.t.hallett@mcgill.ca) 1 1 Department of Biochemistry, Breast
AIMS: Absolute Assignment of Breast Cancer Intrinsic Molecular Subtype Eric R. Paquet (eric.r.paquet@gmail.com), Michael T. Hallett (michael.t.hallett@mcgill.ca) 1 1 Department of Biochemistry, Breast
Introduction to antiprofiles
 Introduction to antiprofiles Héctor Corrada Bravo hcorrada@gmail.com Modified: March 13, 2013. Compiled: April 30, 2018 Introduction This package implements the gene expression anti-profiles method in
Introduction to antiprofiles Héctor Corrada Bravo hcorrada@gmail.com Modified: March 13, 2013. Compiled: April 30, 2018 Introduction This package implements the gene expression anti-profiles method in
Supervised analysis of MS images using Cardinal
 Supervised analsis of MS images using Cardinal Klie A. Bemis and April Harr November, 28 Contents Introduction.............................. 2 Analsis of a renal cell carcinoma (RCC) dataset.... 2 2. Pre-processing..........................
Supervised analsis of MS images using Cardinal Klie A. Bemis and April Harr November, 28 Contents Introduction.............................. 2 Analsis of a renal cell carcinoma (RCC) dataset.... 2 2. Pre-processing..........................
TCGA. The Cancer Genome Atlas
 TCGA The Cancer Genome Atlas TCGA: History and Goal History: Started in 2005 by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) with $110 Million to catalogue
TCGA The Cancer Genome Atlas TCGA: History and Goal History: Started in 2005 by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) with $110 Million to catalogue
Infer mirna-mrna interactions using paired expression data from a single sample
 Infer mirna-mrna interactions using paired expression data from a single sample Yue Li yueli@cs.toronto.edu October 0, 0 Introduction MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small ( nucleotides) RNA molecules that base-pair
Infer mirna-mrna interactions using paired expression data from a single sample Yue Li yueli@cs.toronto.edu October 0, 0 Introduction MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small ( nucleotides) RNA molecules that base-pair
September 20, 2017 SIMULATED DATA
 Tables and Figures for manuscript for Virologic Suppression and Mortality in Older HIV subjects in a Multisite Latin American and the Caribbean Cohort manuscript September 20, 2017 : RESULTS ARE NOT TO
Tables and Figures for manuscript for Virologic Suppression and Mortality in Older HIV subjects in a Multisite Latin American and the Caribbean Cohort manuscript September 20, 2017 : RESULTS ARE NOT TO
TITAN: Subclonal copy number and LOH prediction from whole genome sequencing of tumours
 TITAN: Subclonal copy number and LOH prediction from whole genome sequencing of tumours Gavin Ha October 30, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Analysis Workflow Overview 2 3 Model training and parameter
TITAN: Subclonal copy number and LOH prediction from whole genome sequencing of tumours Gavin Ha October 30, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Analysis Workflow Overview 2 3 Model training and parameter
Applying Metab. Raphael Aggio. October 30, This document describes how to use the function included in the R package Metab.
 Applying Metab Raphael Aggio October 30, 2018 Introduction This document describes how to use the function included in the R package Metab. 1 Requirements Metab requires 3 packages: xcms, svdialogs and
Applying Metab Raphael Aggio October 30, 2018 Introduction This document describes how to use the function included in the R package Metab. 1 Requirements Metab requires 3 packages: xcms, svdialogs and
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies
 OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein
 Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser
 Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
Exploring TCGA Pan-Cancer Data at the UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser Melissa S. Cline 1*, Brian Craft 1, Teresa Swatloski 1, Mary Goldman 1, Singer Ma 1, David Haussler 1, Jingchun Zhu 1 1 Center for Biomolecular
User s Manual Version 1.0
 User s Manual Version 1.0 #639 Longmian Avenue, Jiangning District, Nanjing,211198,P.R.China. http://tcoa.cpu.edu.cn/ Contact us at xiaosheng.wang@cpu.edu.cn for technical issue and questions Catalogue
User s Manual Version 1.0 #639 Longmian Avenue, Jiangning District, Nanjing,211198,P.R.China. http://tcoa.cpu.edu.cn/ Contact us at xiaosheng.wang@cpu.edu.cn for technical issue and questions Catalogue
Package msgbsr. January 17, 2019
 Type Package Package msgbsr January 17, 2019 Title msgbsr: methylation sensitive genotyping by sequencing (MS-GBS) R functions Version 1.6.1 Date 2017-04-24 Author Benjamin Mayne Maintainer Benjamin Mayne
Type Package Package msgbsr January 17, 2019 Title msgbsr: methylation sensitive genotyping by sequencing (MS-GBS) R functions Version 1.6.1 Date 2017-04-24 Author Benjamin Mayne Maintainer Benjamin Mayne
Session 4 Rebecca Poulos
 The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 28
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 28
User Guide. Association analysis. Input
 User Guide TFEA.ChIP is a tool to estimate transcription factor enrichment in a set of differentially expressed genes using data from ChIP-Seq experiments performed in different tissues and conditions.
User Guide TFEA.ChIP is a tool to estimate transcription factor enrichment in a set of differentially expressed genes using data from ChIP-Seq experiments performed in different tissues and conditions.
Module 3: Pathway and Drug Development
 Module 3: Pathway and Drug Development Table of Contents 1.1 Getting Started... 6 1.2 Identifying a Dasatinib sensitive cancer signature... 7 1.2.1 Identifying and validating a Dasatinib Signature... 7
Module 3: Pathway and Drug Development Table of Contents 1.1 Getting Started... 6 1.2 Identifying a Dasatinib sensitive cancer signature... 7 1.2.1 Identifying and validating a Dasatinib Signature... 7
Package IMAS. March 10, 2019
 Type Package Package IMAS March 10, 2019 Title Integrative analysis of Multi-omics data for Alternative Splicing Version 1.6.1 Author Seonggyun Han, Younghee Lee Maintainer Seonggyun Han
Type Package Package IMAS March 10, 2019 Title Integrative analysis of Multi-omics data for Alternative Splicing Version 1.6.1 Author Seonggyun Han, Younghee Lee Maintainer Seonggyun Han
Session 4 Rebecca Poulos
 The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) & International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC) Session 4 Rebecca Poulos Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 20
Package MSstatsTMT. February 26, Title Protein Significance Analysis in shotgun mass spectrometry-based
 Package MSstatsTMT February 26, 2019 Title Protein Significance Analysis in shotgun mass spectrometry-based proteomic experiments with tandem mass tag (TMT) labeling Version 1.1.2 Date 2019-02-25 Tools
Package MSstatsTMT February 26, 2019 Title Protein Significance Analysis in shotgun mass spectrometry-based proteomic experiments with tandem mass tag (TMT) labeling Version 1.1.2 Date 2019-02-25 Tools
User Guide. Protein Clpper. Statistical scoring of protease cleavage sites. 1. Introduction Protein Clpper Analysis Procedure...
 User Guide Protein Clpper Statistical scoring of protease cleavage sites Content 1. Introduction... 2 2. Protein Clpper Analysis Procedure... 3 3. Input and Output Files... 9 4. Contact Information...
User Guide Protein Clpper Statistical scoring of protease cleavage sites Content 1. Introduction... 2 2. Protein Clpper Analysis Procedure... 3 3. Input and Output Files... 9 4. Contact Information...
SubLasso:a feature selection and classification R package with a. fixed feature subset
 SubLasso:a feature selection and classification R package with a fixed feature subset Youxi Luo,3,*, Qinghan Meng,2,*, Ruiquan Ge,2, Guoqin Mai, Jikui Liu, Fengfeng Zhou,#. Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced
SubLasso:a feature selection and classification R package with a fixed feature subset Youxi Luo,3,*, Qinghan Meng,2,*, Ruiquan Ge,2, Guoqin Mai, Jikui Liu, Fengfeng Zhou,#. Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/283/283ra54/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Clonal status of actionable driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer evolution
www.sciencetranslationalmedicine.org/cgi/content/full/7/283/283ra54/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Clonal status of actionable driver events and the timing of mutational processes in cancer evolution
Sleep Apnea Therapy Software User Manual
 Sleep Apnea Therapy Software User Manual Page ii Notices Revised Notice Trademark Copyright 103392 Rev B Published February 8, 2013 and supersedes all previous versions. The information contained in this
Sleep Apnea Therapy Software User Manual Page ii Notices Revised Notice Trademark Copyright 103392 Rev B Published February 8, 2013 and supersedes all previous versions. The information contained in this
Nature Getetics: doi: /ng.3471
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Tables. Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Files for Zehir, Benayed et al. Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Cancer Revealed from Prospective Clinical Sequencing of 10,000 Patients Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Sample
Supplementary Files for Zehir, Benayed et al. Mutational Landscape of Metastatic Cancer Revealed from Prospective Clinical Sequencing of 10,000 Patients Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1: Sample
White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: Version: Supplemental Material
 This is a repository copy of How well can body size represent effects of the environment on demographic rates? Disentangling correlated explanatory variables. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper:
This is a repository copy of How well can body size represent effects of the environment on demographic rates? Disentangling correlated explanatory variables. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper:
USER GUIDE: NEW CIR APP. Technician User Guide
 USER GUIDE: NEW CIR APP. Technician User Guide 0 Table of Contents 1 A New CIR User Interface Why?... 3 2 How to get started?... 3 3 Navigating the new CIR app. user interface... 6 3.1 Introduction...
USER GUIDE: NEW CIR APP. Technician User Guide 0 Table of Contents 1 A New CIR User Interface Why?... 3 2 How to get started?... 3 3 Navigating the new CIR app. user interface... 6 3.1 Introduction...
SMPD 287 Spring 2015 Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development. Final Examination
 Final Examination You have a choice between A, B, or C. Please email your solutions, as a pdf attachment, by May 13, 2015. In the subject of the email, please use the following format: firstname_lastname_x
Final Examination You have a choice between A, B, or C. Please email your solutions, as a pdf attachment, by May 13, 2015. In the subject of the email, please use the following format: firstname_lastname_x
How To Use SubpathwayGMir
 How To Use SubpathwayGMir Li Feng, Chunquan Li and Xia Li May 20, 2015 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 The experimentally verified mirna-target interactions 2 3 Reconstruct KEGG metabolic pathways 2 3.1 Embed
How To Use SubpathwayGMir Li Feng, Chunquan Li and Xia Li May 20, 2015 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 The experimentally verified mirna-target interactions 2 3 Reconstruct KEGG metabolic pathways 2 3.1 Embed
A fatty liver study on Mus musculus
 Sergio Picart-Armada 1 and Alexandre Perera-Lluna 1 1 B2SLab at Polytechnic University of Catalonia sergi.picart@upc.edu alexandre.perera@upc.edu Package September 17, 2018 FELLA 1.2.0 Contents 1 Introduction..............................
Sergio Picart-Armada 1 and Alexandre Perera-Lluna 1 1 B2SLab at Polytechnic University of Catalonia sergi.picart@upc.edu alexandre.perera@upc.edu Package September 17, 2018 FELLA 1.2.0 Contents 1 Introduction..............................
A Quick-Start Guide for rseqdiff
 A Quick-Start Guide for rseqdiff Yang Shi (email: shyboy@umich.edu) and Hui Jiang (email: jianghui@umich.edu) 09/05/2013 Introduction rseqdiff is an R package that can detect differential gene and isoform
A Quick-Start Guide for rseqdiff Yang Shi (email: shyboy@umich.edu) and Hui Jiang (email: jianghui@umich.edu) 09/05/2013 Introduction rseqdiff is an R package that can detect differential gene and isoform
Expanded View Figures
 Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
Molecular Systems iology Tumor CNs reflect metabolic selection Nicholas Graham et al Expanded View Figures Human primary tumors CN CN characterization by unsupervised PC Human Signature Human Signature
The Cancer Genome Atlas & International Cancer Genome Consortium
 The Cancer Genome Atlas & International Cancer Genome Consortium Session 3 Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 31 st July 2014 1
The Cancer Genome Atlas & International Cancer Genome Consortium Session 3 Dr Jason Wong Prince of Wales Clinical School Introductory bioinformatics for human genomics workshop, UNSW 31 st July 2014 1
Supplementary Figure 1. Copy Number Alterations TP53 Mutation Type. C-class TP53 WT. TP53 mut. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.
 Supplementary Figure a Copy Number Alterations in M-class b TP53 Mutation Type Recurrent Copy Number Alterations 8 6 4 2 TP53 WT TP53 mut TP53-mutated samples (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 Missense Truncating M-class
Supplementary Figure a Copy Number Alterations in M-class b TP53 Mutation Type Recurrent Copy Number Alterations 8 6 4 2 TP53 WT TP53 mut TP53-mutated samples (%) 7 6 5 4 3 2 Missense Truncating M-class
Data mining with Ensembl Biomart. Stéphanie Le Gras
 Data mining with Ensembl Biomart Stéphanie Le Gras (slegras@igbmc.fr) Guidelines Genome data Genome browsers Getting access to genomic data: Ensembl/BioMart 2 Genome Sequencing Example: Human genome 2000:
Data mining with Ensembl Biomart Stéphanie Le Gras (slegras@igbmc.fr) Guidelines Genome data Genome browsers Getting access to genomic data: Ensembl/BioMart 2 Genome Sequencing Example: Human genome 2000:
Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes
 Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes Alexandros Manolakos, Idoia Ochoa, Kartik Venkat Supervisor: Olivier Gevaert Abstract Identification of genomic patterns in tumors is an important
Identification of Tissue Independent Cancer Driver Genes Alexandros Manolakos, Idoia Ochoa, Kartik Venkat Supervisor: Olivier Gevaert Abstract Identification of genomic patterns in tumors is an important
The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-cancer analysis Katherine A. Hoadley
 The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-cancer analysis Katherine A. Hoadley Department of Genetics Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill What is TCGA? The Cancer Genome
The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-cancer analysis Katherine A. Hoadley Department of Genetics Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill What is TCGA? The Cancer Genome
Using the DART package: Denoising Algorithm based on Relevance network Topology
 Using the DART package: Denoising Algorithm based on Relevance network Topology Katherine Lawler, Yan Jiao, Andrew E Teschendorff, Charles Shijie Zheng October 30, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Load
Using the DART package: Denoising Algorithm based on Relevance network Topology Katherine Lawler, Yan Jiao, Andrew E Teschendorff, Charles Shijie Zheng October 30, 2018 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Load
VMMC Installation Guide (Windows NT) Version 2.0
 VMMC Installation Guide (Windows NT) Version 2.0 The Shrimp Project Department of Computer Science Princeton University February 1999 About this Document Welcome to VMMC! This document describes how to
VMMC Installation Guide (Windows NT) Version 2.0 The Shrimp Project Department of Computer Science Princeton University February 1999 About this Document Welcome to VMMC! This document describes how to
Vega: Variational Segmentation for Copy Number Detection
 Vega: Variational Segmentation for Copy Number Detection Sandro Morganella Luigi Cerulo Giuseppe Viglietto Michele Ceccarelli Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Installation 1 3 Vega.RData Description 2 4 Run Vega
Vega: Variational Segmentation for Copy Number Detection Sandro Morganella Luigi Cerulo Giuseppe Viglietto Michele Ceccarelli Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Installation 1 3 Vega.RData Description 2 4 Run Vega
Sleep Apnea Therapy Software Clinician Manual
 Sleep Apnea Therapy Software Clinician Manual Page ii Sleep Apnea Therapy Software Clinician Manual Notices Revised Notice Trademark Copyright Sleep Apnea Therapy Software Clinician Manual 103391 Rev A
Sleep Apnea Therapy Software Clinician Manual Page ii Sleep Apnea Therapy Software Clinician Manual Notices Revised Notice Trademark Copyright Sleep Apnea Therapy Software Clinician Manual 103391 Rev A
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity
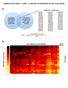 Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Supplementary Figure 1: LUMP Leukocytes unmethylabon to infer tumor purity A Consistently unmethylated sites (30%) in 21 cancer types 174,696
Lionbridge Connector for Hybris. User Guide
 Lionbridge Connector for Hybris User Guide Version 2.1.0 November 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March, 2016. Lionbridge and
Lionbridge Connector for Hybris User Guide Version 2.1.0 November 24, 2017 Copyright Copyright 2017 Lionbridge Technologies, Inc. All rights reserved. Published in the USA. March, 2016. Lionbridge and
Hour 2: lm (regression), plot (scatterplots), cooks.distance and resid (diagnostics) Stat 302, Winter 2016 SFU, Week 3, Hour 1, Page 1
 Agenda for Week 3, Hr 1 (Tuesday, Jan 19) Hour 1: - Installing R and inputting data. - Different tools for R: Notepad++ and RStudio. - Basic commands:?,??, mean(), sd(), t.test(), lm(), plot() - t.test()
Agenda for Week 3, Hr 1 (Tuesday, Jan 19) Hour 1: - Installing R and inputting data. - Different tools for R: Notepad++ and RStudio. - Basic commands:?,??, mean(), sd(), t.test(), lm(), plot() - t.test()
Journal: Nature Methods
 Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
Journal: Nature Methods Article Title: Network-based stratification of tumor mutations Corresponding Author: Trey Ideker Supplementary Item Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure
Quality assessment of TCGA Agilent gene expression data for ovary cancer
 Quality assessment of TCGA Agilent gene expression data for ovary cancer Nianxiang Zhang & Keith A. Baggerly Dept of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology MD Anderson Cancer Center Oct 1, 2010 Contents
Quality assessment of TCGA Agilent gene expression data for ovary cancer Nianxiang Zhang & Keith A. Baggerly Dept of Bioinformatics and Computational Biology MD Anderson Cancer Center Oct 1, 2010 Contents
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
A fatty liver study on Mus musculus
 Sergio Picart-Armada 1 and Alexandre Perera-Lluna 1 1 B2SLab at Polytechnic University of Catalonia sergi.picart@upc.edu alexandre.perera@upc.edu Package September 17, 2018 FELLA 1.3.1 Contents 1 Introduction..............................
Sergio Picart-Armada 1 and Alexandre Perera-Lluna 1 1 B2SLab at Polytechnic University of Catalonia sergi.picart@upc.edu alexandre.perera@upc.edu Package September 17, 2018 FELLA 1.3.1 Contents 1 Introduction..............................
Supplemental Information. Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin. Pathway across Cancer Types
 Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin Pathway across Zhongqi Ge, Jake S. Leighton, Yumeng Wang, Xinxin Peng, Zhongyuan Chen, Hu Chen, Yutong Sun,
Cell Reports, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Integrated Genomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin Pathway across Zhongqi Ge, Jake S. Leighton, Yumeng Wang, Xinxin Peng, Zhongyuan Chen, Hu Chen, Yutong Sun,
Contents. 2 Statistics Static reference method Sampling reference set Statistics Sampling Types...
 Department of Medical Protein Research, VIB, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium Department of Biochemistry, Ghent University, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium http://www.computationalproteomics.com icelogo manual Niklaas Colaert
Department of Medical Protein Research, VIB, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium Department of Biochemistry, Ghent University, B-9000 Ghent, Belgium http://www.computationalproteomics.com icelogo manual Niklaas Colaert
Diabetes Management Software V1.3 USER S MANUAL
 Diabetes Management Software V1.3 Manufacturer: BIONIME CORPORATION No. 100, Sec. 2, Daqing St., South Dist., Taichung City 40242, Taiwan http: //www.bionime.com E-mail: info@bionime.com Made in Taiwan
Diabetes Management Software V1.3 Manufacturer: BIONIME CORPORATION No. 100, Sec. 2, Daqing St., South Dist., Taichung City 40242, Taiwan http: //www.bionime.com E-mail: info@bionime.com Made in Taiwan
User Guide V: 3.0, August 2017
 User Guide V: 3.0, August 2017 a product of FAQ 3 General Information 1.1 System Overview 5 1.2 User Permissions 6 1.3 Points of Contact 7 1.4 Acronyms and Definitions 8 System Summary 2.1 System Configuration
User Guide V: 3.0, August 2017 a product of FAQ 3 General Information 1.1 System Overview 5 1.2 User Permissions 6 1.3 Points of Contact 7 1.4 Acronyms and Definitions 8 System Summary 2.1 System Configuration
Cancer Informatics Lecture
 Cancer Informatics Lecture Mayo-UIUC Computational Genomics Course June 22, 2018 Krishna Rani Kalari Ph.D. Associate Professor 2017 MFMER 3702274-1 Outline The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Genomic Data Commons
Cancer Informatics Lecture Mayo-UIUC Computational Genomics Course June 22, 2018 Krishna Rani Kalari Ph.D. Associate Professor 2017 MFMER 3702274-1 Outline The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Genomic Data Commons
Package AbsFilterGSEA
 Type Package Package AbsFilterGSEA September 21, 2017 Title Improved False Positive Control of Gene-Permuting GSEA with Absolute Filtering Version 1.5.1 Author Sora Yoon Maintainer
Type Package Package AbsFilterGSEA September 21, 2017 Title Improved False Positive Control of Gene-Permuting GSEA with Absolute Filtering Version 1.5.1 Author Sora Yoon Maintainer
TCGA-Assembler: Pipeline for TCGA Data Downloading, Assembling, and Processing. (Supplementary Methods)
 TCGA-Assembler: Pipeline for TCGA Data Downloading, Assembling, and Processing (Supplementary Methods) Yitan Zhu 1, Peng Qiu 2, Yuan Ji 1,3 * 1. Center for Biomedical Research Informatics, NorthShore University
TCGA-Assembler: Pipeline for TCGA Data Downloading, Assembling, and Processing (Supplementary Methods) Yitan Zhu 1, Peng Qiu 2, Yuan Ji 1,3 * 1. Center for Biomedical Research Informatics, NorthShore University
How To Use MiRSEA. Junwei Han. July 1, Overview 1. 2 Get the pathway-mirna correlation profile(pmset) and a weighting matrix 2
 How To Use MiRSEA Junwei Han July 1, 2015 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Get the pathway-mirna correlation profile(pmset) and a weighting matrix 2 3 Discovering the dysregulated pathways(or prior gene sets) based
How To Use MiRSEA Junwei Han July 1, 2015 Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Get the pathway-mirna correlation profile(pmset) and a weighting matrix 2 3 Discovering the dysregulated pathways(or prior gene sets) based
Nicholas Borcherding, Nicholas L. Bormann, Andrew Voigt, Weizhou Zhang 1-4
 SOFTWARE TOOL ARTICLE TRGAted: A web tool for survival analysis using protein data in the Cancer Genome Atlas. [version 1; referees: 1 approved] Nicholas Borcherding, Nicholas L. Bormann, Andrew Voigt,
SOFTWARE TOOL ARTICLE TRGAted: A web tool for survival analysis using protein data in the Cancer Genome Atlas. [version 1; referees: 1 approved] Nicholas Borcherding, Nicholas L. Bormann, Andrew Voigt,
Package xseq. R topics documented: September 11, 2015
 Package xseq September 11, 2015 Title Assessing Functional Impact on Gene Expression of Mutations in Cancer Version 0.2.1 Date 2015-08-25 Author Jiarui Ding, Sohrab Shah Maintainer Jiarui Ding
Package xseq September 11, 2015 Title Assessing Functional Impact on Gene Expression of Mutations in Cancer Version 0.2.1 Date 2015-08-25 Author Jiarui Ding, Sohrab Shah Maintainer Jiarui Ding
Integrated Analysis of Copy Number and Gene Expression
 Integrated Analysis of Copy Number and Gene Expression Nexus Copy Number provides user-friendly interface and functionalities to integrate copy number analysis with gene expression results for the purpose
Integrated Analysis of Copy Number and Gene Expression Nexus Copy Number provides user-friendly interface and functionalities to integrate copy number analysis with gene expression results for the purpose
Proteome Discoverer Version 1.3
 Xcalibur Proteome Discoverer Version 1.3 Installation Guide XCALI-97359 Revision A May 2011 2011 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. Xcalibur is a registered trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific
Xcalibur Proteome Discoverer Version 1.3 Installation Guide XCALI-97359 Revision A May 2011 2011 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. All rights reserved. Xcalibur is a registered trademark of Thermo Fisher Scientific
Benchmark Dose Modeling Cancer Models. Allen Davis, MSPH Jeff Gift, Ph.D. Jay Zhao, Ph.D. National Center for Environmental Assessment, U.S.
 Benchmark Dose Modeling Cancer Models Allen Davis, MSPH Jeff Gift, Ph.D. Jay Zhao, Ph.D. National Center for Environmental Assessment, U.S. EPA Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those
Benchmark Dose Modeling Cancer Models Allen Davis, MSPH Jeff Gift, Ph.D. Jay Zhao, Ph.D. National Center for Environmental Assessment, U.S. EPA Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those
Publishing WFS Services Tutorial
 Publishing WFS Services Tutorial Copyright 1995-2010 Esri All rights reserved. Table of Contents Tutorial: Publishing a WFS service........................... 3 Copyright 1995-2010 ESRI, Inc. All rights
Publishing WFS Services Tutorial Copyright 1995-2010 Esri All rights reserved. Table of Contents Tutorial: Publishing a WFS service........................... 3 Copyright 1995-2010 ESRI, Inc. All rights
ProScript User Guide. Pharmacy Access Medicines Manager
 User Guide Pharmacy Access Medicines Manager Version 3.0.0 Release Date 01/03/2014 Last Reviewed 11/04/2014 Author Rx Systems Service Desk (T): 01923 474 600 Service Desk (E): servicedesk@rxsystems.co.uk
User Guide Pharmacy Access Medicines Manager Version 3.0.0 Release Date 01/03/2014 Last Reviewed 11/04/2014 Author Rx Systems Service Desk (T): 01923 474 600 Service Desk (E): servicedesk@rxsystems.co.uk
Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011
 Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011 I. Purpose Drawing from the profile development of the QIBA-fMRI Technical Committee,
Incorporation of Imaging-Based Functional Assessment Procedures into the DICOM Standard Draft version 0.1 7/27/2011 I. Purpose Drawing from the profile development of the QIBA-fMRI Technical Committee,
CSDplotter user guide Klas H. Pettersen
 CSDplotter user guide Klas H. Pettersen [CSDplotter user guide] [0.1.1] [version: 23/05-2006] 1 Table of Contents Copyright...3 Feedback... 3 Overview... 3 Downloading and installation...3 Pre-processing
CSDplotter user guide Klas H. Pettersen [CSDplotter user guide] [0.1.1] [version: 23/05-2006] 1 Table of Contents Copyright...3 Feedback... 3 Overview... 3 Downloading and installation...3 Pre-processing
BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 7 Multi-Factor ANOVA
 BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 7 Multi-Factor ANOVA PART 1: Introduction to Factorial ANOVA ingle factor or One - Way Analysis of Variance can be used to test the null hypothesis that k or more treatment or group
BIOL 458 BIOMETRY Lab 7 Multi-Factor ANOVA PART 1: Introduction to Factorial ANOVA ingle factor or One - Way Analysis of Variance can be used to test the null hypothesis that k or more treatment or group
Variant Classification. Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc.
 Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
TMWSuite. DAT Interactive interface
 TMWSuite DAT Interactive interface DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface... 1 Setting up the system to use the DAT Interactive interface... 1
TMWSuite DAT Interactive interface DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface Using the DAT Interactive interface... 1 Setting up the system to use the DAT Interactive interface... 1
BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome. Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space
 Whole genome sequencing Whole exome sequencing BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space genomes Filter on MQ, distance, Cigar string Annotate
Whole genome sequencing Whole exome sequencing BWA alignment to reference transcriptome and genome Convert transcriptome mappings back to genome space genomes Filter on MQ, distance, Cigar string Annotate
Corporate Online. Using Term Deposits
 Corporate Online. Using Term Deposits About this Guide About Corporate Online Westpac Corporate Online is an internet-based electronic platform, providing a single point of entry to a suite of online transactional
Corporate Online. Using Term Deposits About this Guide About Corporate Online Westpac Corporate Online is an internet-based electronic platform, providing a single point of entry to a suite of online transactional
OneTouch Reveal Web Application. User Manual for Patients Instructions for Use
 OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Patients Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...3 Product Overview...3 Intended Use...3 System Requirements... 3 Technical Support...3
OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Patients Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...3 Product Overview...3 Intended Use...3 System Requirements... 3 Technical Support...3
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers
 Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
Machine-Learning on Prediction of Inherited Genomic Susceptibility for 20 Major Cancers Sung-Hou Kim University of California Berkeley, CA Global Bio Conference 2017 MFDS, Seoul, Korea June 28, 2017 Cancer
The LiquidAssociation Package
 The LiquidAssociation Package Yen-Yi Ho October 30, 2018 1 Introduction The LiquidAssociation package provides analytical methods to study three-way interactions. It incorporates methods to examine a particular
The LiquidAssociation Package Yen-Yi Ho October 30, 2018 1 Introduction The LiquidAssociation package provides analytical methods to study three-way interactions. It incorporates methods to examine a particular
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3967
 Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Package HAP.ROR. R topics documented: February 19, 2015
 Type Package Title Recursive Organizer (ROR) Version 1.0 Date 2013-03-23 Author Lue Ping Zhao and Xin Huang Package HAP.ROR February 19, 2015 Maintainer Xin Huang Depends R (>=
Type Package Title Recursive Organizer (ROR) Version 1.0 Date 2013-03-23 Author Lue Ping Zhao and Xin Huang Package HAP.ROR February 19, 2015 Maintainer Xin Huang Depends R (>=
Clay Tablet Connector for hybris. User Guide. Version 1.5.0
 Clay Tablet Connector for hybris User Guide Version 1.5.0 August 4, 2016 Copyright Copyright 2005-2016 Clay Tablet Technologies Inc. All rights reserved. All rights reserved. This document and its content
Clay Tablet Connector for hybris User Guide Version 1.5.0 August 4, 2016 Copyright Copyright 2005-2016 Clay Tablet Technologies Inc. All rights reserved. All rights reserved. This document and its content
Installing and Testing JMonkeyEngine (jme)
 Installing and Testing JMonkeyEngine (jme) Andrew Davison, ad@fivedots.coe.psu.ac.th July 31st 2014 This document is to help students in 242-515 Animation and Game Development (AGD) install the jmonkeyengine
Installing and Testing JMonkeyEngine (jme) Andrew Davison, ad@fivedots.coe.psu.ac.th July 31st 2014 This document is to help students in 242-515 Animation and Game Development (AGD) install the jmonkeyengine
Package inctools. January 3, 2018
 Encoding UTF-8 Type Package Title Incidence Estimation Tools Version 1.0.11 Date 2018-01-03 Package inctools January 3, 2018 Tools for estimating incidence from biomarker data in crosssectional surveys,
Encoding UTF-8 Type Package Title Incidence Estimation Tools Version 1.0.11 Date 2018-01-03 Package inctools January 3, 2018 Tools for estimating incidence from biomarker data in crosssectional surveys,
Mirsynergy: detect synergistic mirna regulatory modules by overlapping neighbourhood expansion
 Mirsynergy: detect synergistic mirna regulatory modules by overlapping neighbourhood expansion Yue Li yueli@cs.toronto.edu October 30, 2017 1 Introduction MicroRNAs (mirnas) are 22 nucleotide small noncoding
Mirsynergy: detect synergistic mirna regulatory modules by overlapping neighbourhood expansion Yue Li yueli@cs.toronto.edu October 30, 2017 1 Introduction MicroRNAs (mirnas) are 22 nucleotide small noncoding
Package biocancer. August 29, 2018
 Package biocancer August 29, 2018 Title Interactive Multi-Omics Cancers Data Visualization and Analysis Version 1.8.0 Date 2018-04-12 biocancer is a Shiny App to visualize and analyse interactively Multi-Assays
Package biocancer August 29, 2018 Title Interactive Multi-Omics Cancers Data Visualization and Analysis Version 1.8.0 Date 2018-04-12 biocancer is a Shiny App to visualize and analyse interactively Multi-Assays
Bangor University Laboratory Exercise 1, June 2008
 Laboratory Exercise, June 2008 Classroom Exercise A forest land owner measures the outside bark diameters at.30 m above ground (called diameter at breast height or dbh) and total tree height from ground
Laboratory Exercise, June 2008 Classroom Exercise A forest land owner measures the outside bark diameters at.30 m above ground (called diameter at breast height or dbh) and total tree height from ground
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.2. An example illustrating RAAF scenario 6 and related assessment elements
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.2 An example illustrating RAAF scenario 6 and related assessment elements Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read Across Assessment Framework (RAAF) The exercise Workflow
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.2 An example illustrating RAAF scenario 6 and related assessment elements Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read Across Assessment Framework (RAAF) The exercise Workflow
R documentation. of GSCA/man/GSCA-package.Rd etc. June 8, GSCA-package. LungCancer metadi... 3 plotmnw... 5 plotnw... 6 singledc...
 R topics documented: R documentation of GSCA/man/GSCA-package.Rd etc. June 8, 2009 GSCA-package....................................... 1 LungCancer3........................................ 2 metadi...........................................
R topics documented: R documentation of GSCA/man/GSCA-package.Rd etc. June 8, 2009 GSCA-package....................................... 1 LungCancer3........................................ 2 metadi...........................................
ncounter Data Analysis Guidelines for Copy Number Variation (CNV) Molecules That Count NanoString Technologies, Inc.
 ncounter Data Analysis Guidelines for Copy Number Variation (CNV) NanoString Technologies, Inc. 530 Fairview Ave N Suite 2000 Seattle, Washington 98109 www.nanostring.com Tel: 206.378.6266 888.358.6266
ncounter Data Analysis Guidelines for Copy Number Variation (CNV) NanoString Technologies, Inc. 530 Fairview Ave N Suite 2000 Seattle, Washington 98109 www.nanostring.com Tel: 206.378.6266 888.358.6266
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Medtech32 Diabetes Get Checked II Advanced Form Release Notes
 Medtech32 Diabetes Get Checked II Advanced Form Release Notes These Release Notes contain important information for all Medtech32 Users. Please ensure that they are circulated amongst all your staff. We
Medtech32 Diabetes Get Checked II Advanced Form Release Notes These Release Notes contain important information for all Medtech32 Users. Please ensure that they are circulated amongst all your staff. We
OneTouch Reveal Web Application. User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use
 OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...4 Product Overview...4 Intended Use...4 System Requirements...
OneTouch Reveal Web Application User Manual for Healthcare Professionals Instructions for Use Contents 2 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction...4 Product Overview...4 Intended Use...4 System Requirements...
IMPaLA tutorial.
 IMPaLA tutorial http://impala.molgen.mpg.de/ 1. Introduction IMPaLA is a web tool, developed for integrated pathway analysis of metabolomics data alongside gene expression or protein abundance data. It
IMPaLA tutorial http://impala.molgen.mpg.de/ 1. Introduction IMPaLA is a web tool, developed for integrated pathway analysis of metabolomics data alongside gene expression or protein abundance data. It
Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies
 Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies Dr. Maricel G. Kann Assistant Professor Dept of Biological Sciences UMBC 2 The term protein domain
Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies Dr. Maricel G. Kann Assistant Professor Dept of Biological Sciences UMBC 2 The term protein domain
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer
 Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS
 RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
# Assessment of gene expression levels between several cell group types is a common application of the unsupervised technique.
 # Aleksey Morozov # Microarray Data Analysis Using Hierarchical Clustering. # The "unsupervised learning" approach deals with data that has the features X1,X2...Xp, but does not have an associated response
# Aleksey Morozov # Microarray Data Analysis Using Hierarchical Clustering. # The "unsupervised learning" approach deals with data that has the features X1,X2...Xp, but does not have an associated response
