Identification of new mirna biomarkers associated with HER2-positive breast cancers
|
|
|
- Sandra Johnson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2015, Vol.2, No.11 Identification of new mirna biomarkers associated with HER2-positive breast cancers Hossam Tashkandi 1,2, Nirav Shah 1,2, Yogin Patel 1,2 and Hexin Chen 1,2 1 Department of Biological Science, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, U.S.A 2 Center for Colon Cancer Research, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, U.S.A Correspondence to: Hexin Chen, hchen@biol.sc.edu Keywords: microrna, mirna, biomarker, breast cancer, HER2 Received: July 30, 2015 Accepted: November 25, 2015 Published: December 02, 2015 This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. ABSTRACT Research Paper Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is overexpressed/amplified in ~30% breast cancers which are associated with poor prognosis. micrornas are small non-coding RNA which play an important role in many physiological conditions including cancer. Here we screened and identified many mirnas which are dysregulated by HER2 overexpression. In line with our quantitative PCR analysis data, in silico analysis of microrna expression profiles of 1302 breast tumors revealed that mir-146a-5p is up-regulated and mir-181d and mir-195-5p are down-regulated in HER2-positive tumors. Furthermore, the expression levels of these micrornas can significantly predict patient survival and thus potentially serve as new prognostic markers for HER2-positive breast cancer. INTRODUCTION Breast cancer is a heterogeneous disease, comprising of multiple entities associated with distinctive histological and biological features. Based upon microarray gene expression profiles, breast cancers can be classified into biologically and clinically meaningful subgroups: luminal A, luminal B, basal-like, normal-like, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) positive tumors [1]. Luminal A and luminal B breast tumors are estrogen receptor positive (ER+). Among all types of breast cancers, luminal A has the best prognosis for the patient along with the normal-like tumors. Basal-like tumors, that are negative for ER, progesterone receptor (PR) and HER2, are found in 10%-15% of all patients and showed the worst prognosis among all subtypes of breast cancers [2]. HER2 is over-expressed/amplified in approximately 20-30% breast cancers, and this type of breast cancer is known as HER2-positive breast cancer [3]. Major HER2-downstream signaling cascades include phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT and Ras/ MAPK kinase pathway which are known to regulate cell proliferation and survival [4, 5]. Overexpression of HER2 is associated with relatively poor prognosis and predictive for response to trastuzumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets HER2. However, the average response rate for trastuzumab treatment was approximately 35% with response rate varying from 12-68% [6], necessitating the identification of more biomarkers for selection of treatments and prediction of clinical outcomes. MicroRNAs (mirna) are small non-coding RNA that negatively regulate protein-coding messenger RNAs (mrna) at the post transcriptional level. Dysregulation of mirnas have been found to be associated with many human diseases including cancer [7]. mirnas can be oncogenic mirna or tumor suppressor mirna depending on their target genes. In addition, mirnas have also been proposed to be used as biomarkers for cancers, for example, mir-146a-5p as a biomarker for colorectal tumor localization [8, 9]. However, mirnas involvement in the HER2 pathway have not studied extensively, and their role in HER2 signaling remains elusive. We propose that the HER2 overexpression will lead to differential regulation of a number of mirnas which are important in HER2 mediated tumorigenesis. RESULTS Identification of differentially expressed micrornas in HER2-overexpressing cells using q-rt-pcr analysis For screening purposes, immortalized human breast epithelial cells called MCF10A-Vector and its HER2 positive counterpart were used. To confirm whether HER2 transformed cells do produce HER2 receptor, a 924
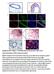
2 western blot was performed for evidence ( Figure 1a). The MCF10A-HER2 indeed have a higher expression of the phosphorylated HER2 (p-her2), which signifies the activation of the HER2 receptor in the cells. The activation of HER2 triggers the activation of the downstream signaling pathways. This downstream pathway activation is affirmed by the increased phosphorylation of STAT3 (p-stat3 Y705 and S727), AKT (p-akt) and ERK (p-erk1/2), which are well-known downstream targets of the HER2 signaling pathway [10]. Real-time RT-PCR analysis were performed to screen for mirnas that are differentially regulated by HER2. Three hundred and three cancer-related mirna were selected for this screening. Considering that some primers may not work at this PCR condition, the melting curve analysis for each pair of primer was performed and the qpcr products were run on agarose gel to determine if the product of each mirna primer is correct ( Figure 1c). For the qpcr products which didn t show single band and correct sizes or have low abundance (> 35 PCR cycles in both cells) were eliminated for further study. Using two fold change as the cutoff, we further narrowed down the list to fifty mirnas that are differentially expressed in MCF10A-HER2 cells compared to MCF10A-Vector cells ( Figure 1b). Among these differentially expressed mirnas, mir-146a-5p, mir-195-5p, and mir-181d are potentially involved in breast cancer development based on previous research and therefore they were selected for further statistical analysis. In silico analysis of mirnas expression in breast cancer Recently, Devinge et al. have reported the mirna expression profile of 1302 breast cancer samples by microarray analysis [11]. We first analyzed the expression statuses of the three selected mirnas in the five subtypes of breast cancers. Both mirnas mir-195-5p and 181d are down-regulated in HER2-positive breast epithelial cells compared to control cells ( Figure 1b). Consistently, the expression levels of these two micrornas are significantly lower in the HER2-positve subtype compared to luminal subtypes of breast cancers ( Figure 2a and 2c). However, mir-146a-5p is up-regulated in HER2-positive breast cancer. Indeed, we found that the expression level of mir-146a-5p is higher in HER2-positive and basal subtypes compared to both luminal and normal-like subtypes of breast cancer ( Figure 2e). Given that the expression status of these selected mirnas tend to be associated with the aggressive subtypes of breast cancer, we performed the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis to further evaluate their clinical relevance. As predicted, low expression of mir-195-5p and 181d shows an association Figure 1: Identification of differentially expressed mirnas in HER2-overexpressed breast epithelial cells. MCF10A- Vector and MCF10A-HER2 were used to screen for differentially regulated mirnas. a) Western blot analysis of HER2-downstream signaling pathways in MCF10A-Vector and MCF10A-HER2 cells. b) Differentially expressed mirnas in HER2-overexpressed cells. Over 300 mirnas were screened using qpcr analysis. The differentially expressed mirnas were selected with the 2-fold change cutoff. c) Agarose gel picture depicting the expression of representative qpcr products from the mirna screening. 925
3 with poor patient survival ( Figure 2b and 2d) whereas high expression of mir-146a-5p shows an association with poor patient survival ( Figure 2f). DISCUSSION Deregulated expression of mirnas can promote tumorigenesis and contribute to a variety of cancer related phenotypes such as uncontrolled cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis. HER2-overexpressing breast cancers are generally associated with aggressive phenotypes and poor prognosis. Despite of extensive research on HER2 positive breast cancer, the involvement of mirnas in HER2 signaling pathway is not well understood [12-15]. We screened and identified many mirnas which were differentially expressed in HER2- overexpressing breast cells compared to control cells. Furthermore, we evaluated their clinical relevance in breast cancer samples. Three mirnas mir-146a-5p, mir-95-5p and mir-181d show their expected expression profile in HER2-positive breast cancers when compared with other subtypes of breast cancers. Interestingly, the role of mir-146a in breast tumorigenesis remains controversial. Several studies indicated that mir-146a can function as oncomir while few have demonstrated it as tumor suppressor mirna in breast cancer. As an oncomir, mir-146a could bind to the 3 - untranslated regions (UTRs) of BRCA1 and BRCA2 Figure 2: Expression and prognostic values of mir-181d, mir-195-5p and mir-146a-5p in clinical breast cancer samples. (a, c, e) Relative expression levels of mir-181d, mir-195-5p and mir-146a-5p in breast cancer subtypes. (b, d, f) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis based on the mir-181, mir-195-5p and mir-146a-5p expression levels. The microarray data was extracted from previous publication [11].The mean value of mirna expression levels was used the cutoff to stratify patient into two groups. *p value < 0.05; **p value <
4 messenger RNAs (mrnas) and potentially modulate their mrna expression [16, 17]. On the contrary, it has been reported that mir146a negatively regulates NFκB signaling [18, 19]. Overexpression of mir-146a/b results in downregulation of IRAK1 and TRAF6 and subsequently inhibits NF-κB activation, leading to tumor suppression in breast cancer cells [18]. mir-146a has been shown to inhibit both migration, invasion, and metastasis by reducing EGFR expression [20]. It will be interesting to examine the function of mir-146a in the HER2-positive breast cancer. mir-195-5p has been found to be down-regulated [21] and also been suggested as a possible diagnostic target for breast cancer [22]. Overexpression of mir-195-5p inhibited cell proliferation, reduced cell colony formation, suppressed cell migration and caused an accumulation of cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle by directly targeting cyclin E1 (CCNE1)[22]. In support of the hypothesis that mir-195-5p acts as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer, we found that mir-195-5p expression is downregulated in aggressive subtypes of breast cancers, especially in HER2- positive and basal types of breast cancers. Unlike the previous two mirnas, mir-181d has not been extensively studied. The amount of information and connection between mir-181d and cancer is scarce and it is even more in HER2 positive breast cancers. However, it has been observed that the mir-181 family (mir-181a, mir-181b, mir-181c, and mir-181d), more precisely mir-181c, is activated by HER2 expression [13]. Even though mir-181c is possibly co-expressed or repressed with mir-181d, there has not been many research done regarding this co-expression or repression. Given that mir-181d is down-regulated with the overexpression of HER2 in both cell lines and clinical samples, mir-181d may be classified as a tumor suppressor mirna and may target an oncogene. In summary, we presented a strategy to effectively identify novel and clinically relevant microrna biomarkers by combining a high-throughput screening approach with in silico data-mining analysis. Further research is warranted to explore their functions in breast tumorigenesis and develop them as novel therapeutic targets. MATERIALS AND METHODS Cell culture MCF10A-Vector and MCF10A-HER2 cells were provided through the courtesy of Emily Wang at the Institute of City of Hope. Culturing MCF10A cells require DMEM/F12 medium from Corning cellgro. In a 500ml bottle, 25ml of 5% horse serum from Sigma Life Science is added to the medium along with 100μl of 500μg/ml of cholera toxin for a final concentration of 100ηg/ml. In addition, 1ml of 5mg/ml insulin for a final concentration of 10μg/ml, 63μl of 4mg/ml of hydrocortisone for a final concentration of 0.5μg/ml, and 50μl of 200μg/ml of EGF for a final concentration of 20ηg/ml are added. When detaching cells from cell culture plate, 0.25% of Trypsin acquired from Sigma Life Science. Western blot analysis Protein extraction was achieved using standard protocol [23, 24]. The protein concentration is then quantified and normalized to ensure equal loading into polyacrylamide gels. 8% polyacrylamide gels were used to separate the proteins. Antibodies used were acquired from Cell Signaling Technology. Real-time RT-PCR analysis of mirna expression RNA extraction from this point was done using TRIzol protocol [25]. RNA was first poly-adenylated using E.coli poly(a) polymerase from New England Biolabs. Poly-adenylated RNA was then used for reverse transcription and the reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). For the quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qpcr), 2μl of cdna was mixed with 10μl of RT² SYBR Green ROX qpcr Mastermix from Qiagen, 6μl of RNase-free water, 1μl of a universal reverse primer (5 GCG AGC ACA GAA TTA ATA CGA C3 ) and a forward primer specific to the mirna. The reaction is run in an Applied Biosystem qpcr machine with the following parameters: Stage 1: 3 minutes hot start at 95 C. Stage 2: 15 seconds denaturing step at 95 C followed by 30 seconds annealing step at 60 C and finally the extension step is held for 35 seconds at 70 C. This stage is repeated for 45 cycles. In silico analysis of mirnas expression in breast cancer The clinical effect of the gene expression profiles of microrna was evaluated using a published data set of breast cancer patients [11]. The mean expression value was used as the cutoff to classify mirna expression as high or low. Recurrence-free survival was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and compared with log-rank tests. The statistical analysis was conducted with R and GraphPad software packages (GraphPad, CA, USA). The p-values were calculated using the logrank test, and differences were considered statistically significant at p <
5 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by the NIH grant (5R01 CA ) and the USC ASPIRE-1 grant to HC. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest. REFERENCES 1. Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000; 406(6797): Perou CM. Molecular stratification of triple-negative breast cancers. Oncologist. 2011; 16 Suppl 1: Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Thorsen T, Quist H, Matese JC, Brown PO, Botstein D, Eystein Lonning P, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2001; 98(19): Feldman AM, Koch WJ and Force TL. Developing strategies to link basic cardiovascular sciences with clinical drug development: another opportunity for translational sciences. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutics. 2007; 81(6): Merkhofer EC, Cogswell P and Baldwin AS. Her2 activates NF-kappaB and induces invasion through the canonical pathway involving IKKalpha. Oncogene. 2010; 29(8): Murphy CG and Modi S. HER2 breast cancer therapies: a review. Biologics. 2009; 3: Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009; 136(2): Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A, Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M, Menard S, Palazzo JP, Rosenberg A, Musiani P, Volinia S, Nenci I, et al. MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2005; 65(16): Omrane I, Kourda N, Stambouli N, Privat M, Medimegh I, Arfaoui A, Uhrhammer N, Bougatef K, Baroudi O, Bouzaienne H, Marrakchi R, Bignon YJ and Benammar- Elgaaied A. MicroRNAs 146a and 147b Biomarkers for Colorectal Tumor s Localization. BioMed research international. 2014; 2014: Rubin I and Yarden Y. The basic biology of HER2. Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology / ESMO. 2001; 12 Suppl 1:S Dvinge H, Git A, Graf S, Salmon-Divon M, Curtis C, Sottoriva A, Zhao Y, Hirst M, Armisen J, Miska EA, Chin SF, Provenzano E, Turashvili G, Green A, Ellis I, Aparicio S, et al. The shaping and functional consequences of the microrna landscape in breast cancer. Nature. 2013; 497(7449): Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, Sensinger K, Wong L, Scott GK, Fedele V, Ginzinger D, Getts R and Haqq C. Optimized high-throughput microrna expression profiling provides novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer biopsies. Molecular cancer. 2006; 5: Lowery AJ, Miller N, Devaney A, McNeill RE, Davoren PA, Lemetre C, Benes V, Schmidt S, Blake J, Ball G and Kerin MJ. MicroRNA signatures predict oestrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and HER2/neu receptor status in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2009; 11(3):R Lee Y, Ahn C, Han J, Choi H, Kim J, Yim J, Lee J, Provost P, Radmark O, Kim S and Kim VN. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microrna processing. Nature. 2003; 425(6956): Bailey ST, Westerling T and Brown M. Loss of estrogenregulated microrna expression increases HER2 signaling and is prognostic of poor outcome in luminal breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015; 75(2): Shen J, Ambrosone CB, DiCioccio RA, Odunsi K, Lele SB and Zhao H. A functional polymorphism in the mir-146a gene and age of familial breast/ovarian cancer diagnosis. Carcinogenesis. 2008; 29(10): Tanic M, Zajac M, Gomez-Lopez G, Benitez J and Martinez-Delgado B. Integration of BRCA1-mediated mirna and mrna profiles reveals microrna regulation of TRAF2 and NFkappaB pathway. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 134(1): Bhaumik D, Scott GK, Schokrpur S, Patil CK, Campisi J and Benz CC. Expression of microrna-146 suppresses NF-kappaB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2008; 27(42): Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and Baltimore D. NFkappaB-dependent induction of microrna mir-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006; 103(33): Chen G, Umelo IA, Lv S, Teugels E, Fostier K, Kronenberger P, Dewaele A, Sadones J, Geers C and De Greve J. mir-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8(3):e Ouyang M, Li Y, Ye S, Ma J, Lu L, Lv W, Chang G, Li X, Li Q, Wang S and Wang W. MicroRNA Profiling Implies New Markers of Chemoresistance of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE. 2014; 9(5):e Luo Q, Wei C, Li X, Li J, Chen L, Huang Y, Song H, Li D and Fang L. MicroRNA-195-5p is a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for breast cancer. Oncology reports. 2014; 31(3):
6 23. Chen H, Zhang H, Lee J, Liang X, Wu X, Zhu T, Lo P, Zhang X and Sukumar S. HOXA5 acts directly downstream of RARβ and contributes to retinoic acid-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition. Cancer Research. 2007; In press. 24. Chen H, Zhang H, Lee J, Liang X, Wu X, Zhu T, Lo PK, Zhang X and Sukumar S. HOXA5 acts directly downstream of retinoic acid receptor beta and contributes to retinoic acid-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition. Cancer Res. 2007; 67(17): Lo PK, Kanojia D, Liu X, Singh UP, Berger FG, Wang Q and Chen H. CD49f and CD61 identify Her2/neu-induced mammary tumor-initiating cells that are potentially derived from luminal progenitors and maintained by the integrin- TGFbeta signaling. Oncogene. 2012; 31(21):
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array
 MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis
 Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA
 Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Keratin 19 expression correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Keratin 19 expression correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer Kabir, Nuzhat N.; Rönnstrand, Lars; Uddin, Kazi Published in: Molecular Biology Reports DOI: 10.1007/s11033-014-3684-6 Published: 2014-01-01
Keratin 19 expression correlates with poor prognosis in breast cancer Kabir, Nuzhat N.; Rönnstrand, Lars; Uddin, Kazi Published in: Molecular Biology Reports DOI: 10.1007/s11033-014-3684-6 Published: 2014-01-01
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Title: Dysregulated mir-183 Inhibits Migration in Breast Cancer
 Author's response to reviews Title: Dysregulated mir-183 Inhibits Migration in Breast Cancer Authors: Aoife J Lowery (aoife.lowery@gmail.com) Nicola Miller (nicola.miller@nuigalway.ie) Roisin M Dwyer (roisin.dwyer@nuigalway.ie)
Author's response to reviews Title: Dysregulated mir-183 Inhibits Migration in Breast Cancer Authors: Aoife J Lowery (aoife.lowery@gmail.com) Nicola Miller (nicola.miller@nuigalway.ie) Roisin M Dwyer (roisin.dwyer@nuigalway.ie)
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Significance of E-cadherin expression in triple-negative breast cancer
 British Journal of Cancer (21) 13, 249 255 & 21 Cancer Research UK All rights reserved 7 92/1 www.bjcancer.com Significance of E-cadherin expression in triple-negative breast cancer S Kashiwagi 1, M Yashiro*,1,2,
British Journal of Cancer (21) 13, 249 255 & 21 Cancer Research UK All rights reserved 7 92/1 www.bjcancer.com Significance of E-cadherin expression in triple-negative breast cancer S Kashiwagi 1, M Yashiro*,1,2,
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets
 2010 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets Lee H. Chen Bioinformatics and Biostatistics
2010 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine Workshops Comparison of Triple Negative Breast Cancer between Asian and Western Data Sets Lee H. Chen Bioinformatics and Biostatistics
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression
 Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Claudin-4 Expression in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation with Androgen Receptors and Ki-67 Expression Mona A. Abd-Elazeem, Marwa A. Abd- Elazeem Pathology department, Faculty of Medicine, Tanta
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis
 Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
Clinical pathological and epidemiological study of triple negative breast cancer
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajay A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 217 Jun;5(6):2657-2661 www.msjonline.org pissn 232-71 eissn 232-12 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/232-12.ijrms2172465
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ajay A et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 217 Jun;5(6):2657-2661 www.msjonline.org pissn 232-71 eissn 232-12 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/1.1823/232-12.ijrms2172465
Low Expression of Circulating MicroRNA-34c is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
 Original Article Yonsei Med J 2017 Jul;58(4):697-702 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Low Expression of Circulating MicroRNA-34c is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Zhihao
Original Article Yonsei Med J 2017 Jul;58(4):697-702 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Low Expression of Circulating MicroRNA-34c is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Zhihao
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients
 mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
95% CI: , P=0.037).
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS
 GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS Dra. Margarita Sánchez-Beato Lymphoma Group Molecular Pathology Programme CNIO Agilent Microarray and Sequencing Roadshow,
GENE EXPRESSION AND microrna PROFILING IN LYMPHOMAS. AN INTEGRATIVE GENOMICS ANALYSIS Dra. Margarita Sánchez-Beato Lymphoma Group Molecular Pathology Programme CNIO Agilent Microarray and Sequencing Roadshow,
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis
 Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Original Article MicroRNA-21 and microrna-146a identification in stool and its clinical significance in colorectal neoplasms
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):16441-16449 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021973 Original Article MicroRNA-21 and microrna-146a identification in stool and its clinical significance in colorectal neoplasms
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):16441-16449 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021973 Original Article MicroRNA-21 and microrna-146a identification in stool and its clinical significance in colorectal neoplasms
Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Pathway. R. Armijo, D. Dinh, S. Hindi, S. Jehle, J. Jones & L. Lawson
 Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Pathway R. Armijo, D. Dinh, S. Hindi, S. Jehle, J. Jones & L. Lawson Overview of the EGF Pathway AK LECTURES. EGF Signal Transduction Pathway. Accessed October 10, 2018.
Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Pathway R. Armijo, D. Dinh, S. Hindi, S. Jehle, J. Jones & L. Lawson Overview of the EGF Pathway AK LECTURES. EGF Signal Transduction Pathway. Accessed October 10, 2018.
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples
 Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Table S2. Expression of PRMT7 in clinical breast carcinoma samples (All data were obtained from cancer microarray database Oncomine.) Analysis type* Analysis Class(number sampels) 1 2 3 4 Correlation (up/down)#
Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy
 Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Outline Predictive Assays in Radiation Therapy Radiation Biology Introduction Early predictive assays Recent trends in predictive assays Examples for specific tumors Summary Lecture 4-23-2014 Introduction
Microarrays in primary breast cancer lessons from chemotherapy studies
 Endocrine-Related Cancer (2001) 8 259 263 Microarrays in primary breast cancer lessons from chemotherapy studies P E Lønning, T Sørlie 1,2, C M Perou 2, P O Brown 3, D Botstein 2 and A-L Børresen-Dale
Endocrine-Related Cancer (2001) 8 259 263 Microarrays in primary breast cancer lessons from chemotherapy studies P E Lønning, T Sørlie 1,2, C M Perou 2, P O Brown 3, D Botstein 2 and A-L Børresen-Dale
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours
 Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Immunohistochemical classification of breast tumours Workshop in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry September 19 th - 21 th 2018 Anne-Vibeke Lænkholm Department of Surgical Pathology, Zealand University Hospital,
Circulating mir-195 as a Therapeutic Biomarker in Turkish Breast Cancer Patients
 APJCP.2016.17.9.4241 Importance of Circulating mir-195 as a Therapeutic Marker in Breast Cancer RESEARCH ARTICLE Circulating mir-195 as a Therapeutic Biomarker in Turkish Breast Cancer Patients Gulsah
APJCP.2016.17.9.4241 Importance of Circulating mir-195 as a Therapeutic Marker in Breast Cancer RESEARCH ARTICLE Circulating mir-195 as a Therapeutic Biomarker in Turkish Breast Cancer Patients Gulsah
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience
 Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Breast cancer in elderly patients (70 years and older): The University of Tennessee Medical Center at Knoxville 10 year experience Curzon M, Curzon C, Heidel RE, Desai P, McLoughlin J, Panella T, Bell
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population
 Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Heather M. Gage, MD, Avanti Rangnekar, Robert E. Heidel, PhD, Timothy Panella, MD, John Bell, MD, and Amila Orucevic, MD, PhD
 HER2 POSITIVE BREAST CARCINOMA IN THE PRE AND POST ADJUVANT ANTI-HER-2 THERAPY ERA: A SINGLE ACADEMIC INSTITUTION EXPERIENCE IN THE SETTING OUTSIDE OF CLINICAL TRIALS Heather M. Gage, MD, Avanti Rangnekar,
HER2 POSITIVE BREAST CARCINOMA IN THE PRE AND POST ADJUVANT ANTI-HER-2 THERAPY ERA: A SINGLE ACADEMIC INSTITUTION EXPERIENCE IN THE SETTING OUTSIDE OF CLINICAL TRIALS Heather M. Gage, MD, Avanti Rangnekar,
Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association with Pathological Features
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
 Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Molecular Characterization of Breast Cancer: The Clinical Significance
 Molecular Characterization of : The Clinical Significance Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville
Molecular Characterization of : The Clinical Significance Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine-Jacksonville
Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients
 Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological staging of the cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 1283-1287 Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 1283-1287 Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Cancer Problems in Indonesia
 mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0387 TITLE: MiR-146-SIAH2-AR Signaling in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Goberdhan Dimri, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: George Washington University,
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Response to Paclitaxel in Node-positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 J Korean Surg Soc 2010;79:173-179 DOI: 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.3.173 원 저 Response to Paclitaxel in Node-positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine,
J Korean Surg Soc 2010;79:173-179 DOI: 10.4174/jkss.2010.79.3.173 원 저 Response to Paclitaxel in Node-positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer Department of Surgery, Kosin University College of Medicine,
MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction
 www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the. mutated sequence.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Edith Peterson Mitchell, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine and Medical Oncology Program Leader, Gastrointestinal Oncology Department
Understanding and Optimizing Treatment of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Edith Peterson Mitchell, MD, FACP Clinical Professor of Medicine and Medical Oncology Program Leader, Gastrointestinal Oncology Department
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Triple Negative Breast Cancer
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Prof. Dr. Pornchai O-charoenrat Division of Head-Neck & Breast Surgery Department of Surgery Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Breast Cancer Classification Traditional
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Increased mir-146a in gastric cancer directly targets SMAD4 and is involved in modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 27: 559-566, 2012 Increased mir-146a in gastric cancer directly targets SMAD4 and is involved in modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis BIN XIAO 1 *, EN-DONG ZHU 1 *, NA LI 1, DONG-SHUI
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 27: 559-566, 2012 Increased mir-146a in gastric cancer directly targets SMAD4 and is involved in modulating cell proliferation and apoptosis BIN XIAO 1 *, EN-DONG ZHU 1 *, NA LI 1, DONG-SHUI
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College of Medicine Houston, TX 77030
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0428 TITLE: MicroRNA and Breast Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Konstantin Galaktionov, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College of Medicine Houston, TX 77030
AD Award Number: W81XWH-05-1-0428 TITLE: MicroRNA and Breast Cancer Progression PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Konstantin Galaktionov, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Baylor College of Medicine Houston, TX 77030
Question 1 A. ER-, PR-, HER+ B. ER+, PR+, HER2- C. ER-, PR+, HER2- D. ER-, PR-, HER2- E. ER-, PR+, HER2+
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Question 1 The tumor depicted on the next slide
Triple Negative Breast Cancer Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA Question 1 The tumor depicted on the next slide
Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients
 BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
BIOSCIENCES BIOTECHNOLOGY RESEARCH ASIA, December 2015. Vol. 12(3), 2221-2225 Evaluation the Correlation between Ki67 and 5 Years Disease Free Survival of Breast Cancer Patients S.M. Hosseini¹, H. Shahbaziyan
Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed.
 Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
Supplementary Note The potential association and implications of HBV integration at known and putative cancer genes of TERT, MLL4, CCNE1, SENP5, and ROCK1 on tumor development were discussed. Human telomerase
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
MicroRNAs: the primary cause or a determinant of progression in leukemia?
 MicroRNAs: the primary cause or a determinant of progression in leukemia? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
MicroRNAs: the primary cause or a determinant of progression in leukemia? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning
 Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
Identifying Relevant micrornas in Bladder Cancer using Multi-Task Learning Adriana Birlutiu (1),(2), Paul Bulzu (1), Irina Iereminciuc (1), and Alexandru Floares (1) (1) SAIA & OncoPredict, Cluj-Napoca,
Comparing Subtypes of Breast Cancer Using a Message-Passing Network
 Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Comparing Subtypes of Breast Cancer Using a Message-assing Network Kamrine oels Outline Breast cancer and its molecular subtypes assing Attributes between Networks for Data
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Comparing Subtypes of Breast Cancer Using a Message-assing Network Kamrine oels Outline Breast cancer and its molecular subtypes assing Attributes between Networks for Data
Expression and clinicopathological significance of mir 193a 3p and its potential target astrocyte elevated gene 1 in non small lung cancer tissues
 DOI 10.1186/s12935-015-0227-8 PRIMARY RESEARCH Open Access Expression and clinicopathological significance of mir 193a 3p and its potential target astrocyte elevated gene 1 in non small lung cancer tissues
DOI 10.1186/s12935-015-0227-8 PRIMARY RESEARCH Open Access Expression and clinicopathological significance of mir 193a 3p and its potential target astrocyte elevated gene 1 in non small lung cancer tissues
Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
mir-206 Expression Is Down-regulated in Estrogen Receptor A Positive Human Breast Cancer
 Priority Report mir-206 Expression Is Down-regulated in Estrogen Receptor A Positive Human Breast Cancer Naoto Kondo, Tatsuya Toyama, Hiroshi Sugiura, Yoshitaka Fujii, and Hiroko Yamashita Oncology, Immunology,
Priority Report mir-206 Expression Is Down-regulated in Estrogen Receptor A Positive Human Breast Cancer Naoto Kondo, Tatsuya Toyama, Hiroshi Sugiura, Yoshitaka Fujii, and Hiroko Yamashita Oncology, Immunology,
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna
 Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna Carl Novina Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Qiagen Webinar 05-17-11 Outline 1. The biology
Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna Carl Novina Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Qiagen Webinar 05-17-11 Outline 1. The biology
Guangfa Xiao, Huihuan Tang, Wei Wei, Jian Li, Liandong Ji, and Jie Ge. 1. Introduction
 Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 364549, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/364549 Research Article Aberrant Expression of MicroRNA-15a and MicroRNA-16 Synergistically Associates
Gastroenterology Research and Practice, Article ID 364549, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/364549 Research Article Aberrant Expression of MicroRNA-15a and MicroRNA-16 Synergistically Associates
FISH mcgh Karyotyping ISH RT-PCR. Expression arrays RNA. Tissue microarrays Protein arrays MS. Protein IHC
 Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
Classification of Breast Cancer in the Molecular Era Susan J. Done University Health Network, Toronto Why classify? Prognosis Prediction of response to therapy Pathogenesis Invasive breast cancer can have
SALL1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by regulating cancer cell senescence and metastasis through the NuRD complex
 Ma et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:78 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0824-y RESEARCH SALL1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by regulating cancer cell senescence and metastasis through
Ma et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:78 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0824-y RESEARCH SALL1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by regulating cancer cell senescence and metastasis through
Breast cancer Molecular subtypes and their clinicopathological characteristics amongst patients at the Aga Khan University hospital (Nairobi)
 The ANNALS of AFRICAN SURGERY www.sskenya.org Breast cancer Molecular subtypes and their clinicopathological characteristics amongst patients at the Aga Khan University hospital (Nairobi) Gakinya S.M.
The ANNALS of AFRICAN SURGERY www.sskenya.org Breast cancer Molecular subtypes and their clinicopathological characteristics amongst patients at the Aga Khan University hospital (Nairobi) Gakinya S.M.
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
