Review Qing Ji1,2, Yun-quan Luo3, Wen-hai Wang4, Xuan Liu2, Qi Li2, Shi-bing Su1 ABSTRACT Keywords: Citation: Received accepted Correspondence:
|
|
|
- Whitney Poole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal homepage: Available also online at Copyright 2015, Journal of Integrative Medicine Editorial Offi ce. E-edition published by Elsevier (Singapore) Pte Ltd. All rights reserved. Review Qing Ji 1,2, Yun-quan Luo 3, Wen-hai Wang 4, Xuan Liu 2, Qi Li 2, Shi-bing Su 1 1. Research Center for Traditional Chinese Medicine Complexity System, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai , China 2. Department of Medical Oncology, Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai , China 3. Department of Liver and Gallbladder Surgery, Shuguang Hospital, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai , China 4. Department of Medical Oncology, Seventh People s Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai , China ABSTRACT Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) syndrome, also known as TCM ZHENG or TCM pattern, is an integral and essential part of TCM theory that helps to guide the design of individualized treatments. A TCM syndrome, in essence, is a characteristic profi le of all clinical manifestations in one patient that can be readily identifi ed by a TCM practitioner. In this article, the authors reviewed the presentations of TCM syndromes in seven common malignancies (liver, lung, gastric, breast, colorectal, pancreatic and esophageal cancers), the objectivity and the standardization of TCM syndrome differentiation, the evaluation of TCM syndrome modeling in cancer research, and syndrome differentiation-guided TCM treatment of cancers. A better understanding of TCM syndrome theory, as well as its potential biological basis, may contribute greatly to the clinical TCM diagnosis and the treatment of cancer. Keywords: traditional Chinese medicine; TCM syndrome differentiation; biological basis; TCM treatment; cancer; review Citation: Ji Q, Luo YQ, Wang WH, Liu X, Li Q, Su SB. Research advances in traditional Chinese medicine syndromes in cancer patients. J Integr Med September; Epub ahead of print. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has the concept of syndromes, known as ZHENG in Chinese, an integral and essential part of TCM theory [1]. A TCM syndrome is a profile of signs and symptoms that are clinical ph enotypes reflecting the essence of pathological changes at certain stages of a disease. TCM syndromes can be useful for identifying patterns in the human body, and helping to guide TCM treatments [2]. TC M theory of tumor pathogenesis describes the invasion of pathogenic evils, such as qi stagnation, blood stasis and phlegm stagnation, over time [3]. These are specifically classified as ca ncer toxins [4]. Cancer toxins must exist before the formation of malignant tumors, which grow in the target organs ( the soil ); the stasis, phlegm and other pathological factors are the fertilizers that feed the tumors. Therefore, stasis, phlegm and other pathological patterns produce cancer toxins in the target organ, take root, grow and metastasize to other sites. The TCM concept of qi is akin to the human body s vital energy. It helps to maintain blood circulation, warm the body, and fight ag ainst diseases. Vital qi is the body s defense and repair system, while evil qi incites pathogenic Received March 27, 2015; accepted May 4, Correspondence: Shi-bing Su, PhD, Professor; shibingsu07@163.com. Qi Li, MD, PhD, Professor; Lzwf@hotmail.com Journal of Integrative Medicine Epub ahead of print
2 factors. The interplay between vital qi and evil qi determines how diseases such as cancer develop in the body [5]. An evil qi, i.e., cancer toxin, can accumulate in the body, and if it overcomes the vital qi, cancer can befall. At the early stage of cancer, both the evil qi and the vital qi are strong, so the patient may have an excessive syndrome. Once cancer toxins impair the vital qi, excess and deficiency syndromes may co-exist. During the development of cancer, the cancer toxins often deplete the vital qi, accelerating cancer progression and metastasis. Deficiency syndrome in the progression of cancer is an extremely important clinical phenotype and cause of pathology, especially in the advanced stages [6]. Strengthening the vital qi and eliminating the evil qi are general T CM principles in the treatment of disease, including cancer. An effective TCM treatment must begin with a correct syndrome differentiation. One type of cancer may exhibit different TCM syndromes, while different cancers may have an identical syndrome. Therefore, the classical TCM therapeutic principle, same disease treated by different therapies or different diseases treated by same therapy, is usually adopted in cancer treatments. Patients who have undergone tumor resection, postoperative chemotherapy, radiotherapy or immunotherapy, or have not tolerated the above therapies, can be treated by TCM based on syndrome differentiation [7]. In this study, the authors reviewed the recent advances in research on TCM syndromes in cancer patients, including presentation of TCM syndromes, objectivity and standardization of TCM syndrome differentiation, biological basis of TCM syndromes, and TCM syndrome differentiation-based TCM treatment of cancer. First of all, we systematically analyzed the clinical presentations of TCM syndromes in patients of seven types of cancer: liver, lung, gastric, pancreatic, breast, colorectal and esophageal cancers. Results are listed in Table General presentations of TCM syndromes in cancers According to TCM theory, liver cancer develops by the following process: depressed emotions, heat toxin, stagnation, improper diet and other internal injuries give rise to the disharmony of liver and spleen, and further aggravate the phlegm and blood stasis, which gradually accumulate and form a blockage in the flank [15]. After analyzing TCM syndrome types of patients with primary liver cancer (PLC), Liu et al [8] found that the most common syndrome types were qi stagnation and blood stasis, liver stagnation and spleen deficiency, yin deficiency of liver-kidney, liver stagnation and qi stagnation, qi deficiency of spleenstomach, dampness-heat of liver-gallbladder, internal accumulation of dampness-heat, as well as deficiency of qi and yin. In non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to the reports by Yuan et al [9] in 2011, qi deficiency, blood stasis, yin deficiency, phlegm-dampness dominated in TCM syndromes of the 120 patients with advanced NSCLC. In gastric cancer, a summary of TCM syndromes in 767 patients were ranked as follows: liver-stomach disharmony, exuberance of stomach heat, deficiency-cold of spleen-stomach, internal retention of blood and toxin stagnation, stagnation of phlegm-dampness and qi deficiency [10]. In esophageal cancer, the main TCM syndromes were qi deficiency and yang declination, yin deficiency, phlegm-dampness and blood stasis [11]. In pancreatic cancer, 47 late-stage patients mainly suffered from 4 syndromes: qi stagnation and blood stasis, spleen deficiency and qi stagnation, deficiency of qi and yin, and qi deficiency and blood stasis [12]. In breast cancer, 95 patients were categorized into qi deficiency (n = 37), blood deficiency (n = 26), yin deficiency (n = 40), and yang deficiency (n = 28); taking all the accompanying syndromes into account, there were a total of 131 TCM syndromes. As a whole, the patients with qi deficiency syndrome had a lower quality of life [13]. In colorectal cancer [14], the most common syndromes arranged in descending order were blood deficiency, qi and yin deficiency, phlegm-dampness, and relative equilibrium of yin-yang (not meeting with the syndrome diagnostic criteria). Within TCM theory, yin and yang are complementary but opposite parts of a dynamic system that interact within a greater whole. Generally speaking, yang embodies characteristics such as moving, ascending, brightness, progressing, hyperactivity, and is often attributable for functional diseases of the body; while yin embodies characteristics such as stillness, descending, darkness, degeneration, hypo-activity, and is more involved in organic diseases. 2.2 Different TCM syndromes, same cancers; same TCM syndromes, different cancers Analysis of Table 1 shows that deficiency syndromes account for 27.89% of liver cancer, 67.54% of lung cancer, 18.64% of gastric cancer, 44.44% of esophageal cancer, 38.31% of pancreatic cancer, 80.15% of breast cancer, and 61.90% of colorectal cancer. This demonstrates that the deficiency syndrome exists in nearly all the cancer patients. Particularly, qi deficiency is the main deficiency syndrome in liver, lung, esophageal, breast and colorectal cancers, and yin deficiency is commonly seen in liver, esophageal, breast and colorectal cancers. However, blood deficiency is only seen in colorectal cancer and breast cancer (Table 1). In addition, blood stasis is another syndrome existing in and different cancers including liver, esophageal, pancreatic and breast cancers, ranking first in liver,esophageal and pancreatic cancers. Otherwise, blood stasis is seldom seen in other cancers. Qi stagnation and blood sta- Epub ahead of print Journal of Integrative Medicine
3 General distributions of TCM syndromes in cancers TCM syndromes in cancers Case number Proportion (%) Reference Liver cancer [8] Qi stagnation and blood stasis Liver stagnation and spleen deficiency Yin deficiency of liver-kidney Liver stagnation and qi stagnation Qi deficiency of spleen-stomach Dampness-heat of liver-gallbladder Internal accumulation of dampness-heat Deficiency of qi and yin Others Lung cancer 120 [9] Qi deficiency Others Gastric cancer 767 [10] Liver-stomach disharmony Exuberance of stomach heat Deficiency-cold of spleen-stomach Internal retention of blood and toxin stagnation Stagnation of phlegm-dampness Qi deficiency Esophageal cancer 63 [11] Qi deficiency and yang declination Yin deficiency Phlegm-dampness Blood stasis Pancreatic cancer 47 [12] Qi stagnation and blood stasis Spleen deficiency and qi stagnation Deficiency of qi and yin Qi deficiency and blood stasis Internal accumulation of dampness-heat Qi stagnation and damp obstruction Spleen deficiency and damp obstruction Yin deficiency Phlegm obstruction and blood stasis Breast cancer 131 [13] Qi deficiency Blood deficiency Yin deficiency Yang deficiency Colorectal cancer 210 [14] Blood deficiency Qi and yin deficiency Phlegm-dampness Others TCM: traditional Chinese medicine. Journal of Integrative Medicine Epub ahead of print
4 sis were found as accompanying syndromes in liver and pancreatic cancers, and were both the primary syndromes (Table 1). Our analysis of the clinical TCM syndromes in seven cancer types showed that each cancer has different sets of TCM syndromes. For example, in liver cancer [15], qi stagnation and blood stasis, liver stagnation and spleen deficiency, yin deficiency of liver-kidney, liver stagnation and qi stagnation, and qi deficiency of spleen-stomach were identified. Moreover, in PLC patients treated by transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE), eight TCM single syndromes occurred in the 106 patients before the treatment, and those eight syndromes occurred in 456 cases after TACE. The number of qi stagnation syndrome cases decreased, while that of excess-heat syndrome, qi deficiency syndrome, blood deficiency syndrome, and yang deficiency syndrome cases increased after TACE [16]. 2.3 Dynamic changes of TCM syndromes in liver and colorectal cancers In the progression of cancer, TCM syndromes also change from early stage to late stage. TCM syndrome analysis for patients with PLC showed that, comparing early to advanced stages, the occurrence rate and severity of the vital qi deficiency increased. This demonstrates that weaker vital qi from deficiency increases the ability of the evil qi pathogenic factors to do harm, which results in heightened seriousness of the illness [17]. Elsewhere, TCM syndrome changes help to explain the progression of colorectal cancer: the early stages show excessive syndromes, including qi stagnation and blood stasis, and damp-heat and toxin accumulation; in the intermediate stage, evil qi becomes stronger and vital qi is deficient, and both excessive and deficiency syndromes such as phlegm-dampness and qi and yin deficiency are present; and the advanced stage presents predominantly deficiency syndromes, including vital qi deficiency, blood deficiency, and qi and yin deficiency [18]. 3.1 TCM syndrome differentiation in cancer General understanding of TCM syndrome differentiation Syndrome differentiation is an important tool that TCM practitioners use to accurately understand and treat diseases, including cancer. Different syndromes can exist for one kind of cancer, and all the diagnostic methods of TCM may be used for identifying the syndromes Clinical TCM syndrome measurement and information collection The four main diagnostic methods in TCM are inspection, auscultation and olfaction, inquiry, and palpation. These are used with a questionnaire for TCM syndrome measurement and information collection. Cheng et al [19] established a questionnaire comprised of three parts: patient s demographics, patients perception of bowel function, and the TCM syndrome patterns, which is diagnosed by a registered Chinese medicine practitioner who collects data with the four classic diagnostic methods, completes the table included in the questionnaire, and makes the patient s TCM diagnosis. Traditional diagnoses are mainly dependent upon the TCM practitioner s experience. In recent years, clinicians and researchers have worked on improving the four traditional diagnostic methods. Objective measures seek to quantify what were traditionally qualitative measures. These objective measures include computer-assisted quantitative approach for lip and tongue images; TCM pulse detectors that take place of pulse diagnosis based solely on the clinician s tactile sense; and digitalization and quantification of techniques of auxiliary diagnosis based on the combination of the four TCM diagnostic methods [20 25]. Specifically, Liu et al [26] established the fuzzy mathematical model for syndrome differentiation of gastric cancer. Li et al [27] set up a quantitative model for evaluating the degree of the TCM basic syndromes often encountered in PLC patients. Hou et al [28] proposed a quantified diagnostic standard for colon cancer of spleen qi deficiency syndrome Data analysis and mining for TCM syndrome differentiation TCM syndromes are not merely an assembly of various disease symptoms, but also an organization of interrelated clinical manifestations defined by TCM theory. The symptoms and signs in TCM syndrome measurement can be analyzed by statistical tools for their use in TCM syndrome differentiation. Recent research has presented clinical information dimensionality reduction and data mining for TCM syndrome differentiation. Data mining for TCM syndrome differentiation in cancer has been carried out using logistic regression in gastric cancer [29]. Liu et al [26] developed a method for establishing the fuzzy mathematical model for syndrome differentiation of gastric cancer based on the analysis of 769 cases, and found that the actual coincidence rate in TCM syndromes of disharmony between liver and stomach was 65.00%; in yin deficiency due to gastric heat was 72.22%; in deficiencycold of spleen and stomach was 70.00%; in blood stasistoxin was 57.14%; in phlegm-dampness was 53.33%; and in exhaustion of both qi and blood was 72.22%. The overall coincidence rate was 65.71%, which offers a solution for objective research of TCM syndrome differentiation. This analysis model offers a good solution for objective research of syndrome differentiation in diagnosing cancers. Li et al [27] established a quantitative model for evaluating the degree of the TCM basic syndromes often encountered Epub ahead of print Journal of Integrative Medicine
5 in patients with PLC, and the verification on 459 times/cases of PLC showed that the coincidence rate between the outcomes derived from specialists and those from the additive model was 84.53%, and with those from the additive-multificative model was 62.75%; the difference between the above two showed statistical significance. This principle model is suitable for quantitative evaluation for the degrees of TCM basic syndromes in patients with PLC. Hou et al [28] set up a quantified diagnostic standard for colon cancer of spleen qi deficiency syndrome, including weakness, fatigue, loose stool and poor appetite. The data analyzed by this method were in accordance with clinical characteristics of colon cancer and TCM syndrome. However, to apply this method to the actual patients, validation in large-sample clinical trials is needed. 3.2 Biological basis of TCM syndrome differentiation in cancer Physiological and pathological features Many physiological and pathological features are associated with the TCM syndromes in cancers, such as tongue images [30,31], fungal pneumonia [32], glucose metabolic rate [33], trace elements [34,35], and function of autonomic nervous system [36,37]. With regard to tongue images, Su et al [30] revealed a significant statistical difference between different syndrome groups of lung cancer on tongue color, coating color, and thickness of tongue coating. Deng et al [31] found that the proportion of normal tongue manifestation was higher in healthy adults (38.89%) than that in patients with PLC (2.32%), which provided supportive evidence for the use of tongue inspection in syndrome differentiation. For the trace elements, previous research results demonstrated that the levels of serum selenium (Se) reflected the change between the pathogenic factors and body resistance in lung cancer, suggesting that some Chinese medicinal herbs rich in Se should be selected to treat lung cancer so as to improve the therapeutic effect [34]. Other authors found that the Cu/Zn ratio can reflect the change of body resistance and pathogenic factors, suggesting that the ratio of Cu/Zn may be used as the criteria of TCM syndrome differentiation in lung cancer [35] Tumor markers in clinical application In Western medicine, many tumor markers are used as indicators for diagnosis and prognosis of cancers. Hence, the correlations between tumor markers and TCM syndromes were investigated. Yan et al [38] showed that the levels of a variety of tumor markers including CA19-9, CEA and CA242 were elevated in all 30 patients with lung cancer. The levels of tumor markers in patients with excessive syndromes, such as qi stagnation and blood stasis, phlegm turbidity and lung obstruction, and excessive heat and toxin, all increased significantly, and were higher than those of deficiency syndromes such as qi and yin deficiency. These results show that CA19-9, CEA and CA242 may be related to the excessive pathogens in lung cancer, which supports the basic TCM therapeutic principles of clear the excessive pathogens when treating cancer. Yu et al [39] demonstrated higher levels of CEA, CA19-9, CA125, AFP and CA153 in 200 colorectal cancer patients who had different TCM syndromes. CEA levels were the highest in patients with the syndrome of internal accumulation of blood-toxin. The levels of CA19-9, CA125 and CA153 in patients with yin deficiency of liver-kidney syndrome were higher than those in patients with other syndromes. These results implied that, tumor markers can define TCM syndrome differentiation and guide the alternative TCM treatments in colorectal cancer Gene expression and gene polymorphism Cancer is known to be influenced by changes to genes that control the body s phenotypes [40]. Gene polymorphisms and expressions are correlated tightly with tumorigenesis and the progression of cancer. The correlation between TCM syndromes and gene expression and polymorphism has been studied. Wang et al [41] found that heat shock 70 kd protein (HSP70) and P53 positive ratio and HSP70 expression levels in patients with malignant tumor with TCM heat syndrome were higher than those in patients with nonheat syndrome. Chen et al [42] demonstrated that high vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression levels positively correlated with gastric cancer metastasis with liver-stomach disharmony syndrome and phlegm-stasis-poison stagnant syndrome. Luo et al [43] showed that the serum levels of VEGF, endostatin, soluble intercellular adhesive molecule-1 and CD44 can serve as the microcosmic basis for qi-deficiency and blood stasis syndrome differentiation. Pan et al [44] revealed the characteristics of gene expression (33 up-regulated coincident genes and 26 down-regulated coincident genes) in adrenal glands of H22 tumor mice correlated with typical syndromes and the different liver cancer stages. All these results demonstrated that the altered gene expressions significantly affect the patients TCM syndromes. Gene polymorphism was shown to be another important factor affecting the TCM syndromes in various cancer patients. Cui et al [45] found that the frequencies of crosscomplementing 1 (ERCC1) C19007T genotype and allele in different TCM syndrome types of colorectal cancer patients had statistical difference. Moreover, statistical difference existed between dampness-heat accumulation syndrome and yang deficiency of spleen-kidney syndrome as well as yin deficiency of liver-kidney syndrome, and between qi stagnation with blood stasis syndrome and yang deficiency of spleen-kidney syndrome as well as yin deficiency of liver-kidney syndrome. Zhang et al [46] Journal of Integrative Medicine Epub ahead of print
6 showed significant difference in E-cadherin (CDH1) gene (rs13689) genotype distributions between several pairs of TCM syndromes of gastric cancer, and the formation of the syndrome was related to EGF, TGFA (rs ), and EGFR (rs884225) gene polymorphisms. This tight connection of the gene polymorphism and TCM syndromes will provide benefits for syndrome differentiation and TCM treatment. 3.3 TCM syndrome identification following systemomics approach Systems biology ( -omics ) technologies including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabonomics are rapidly growing large-scale detection technologies [47]. With features such as non-destructiveness, integrity, multi-target, high-throughput, and digitalization, it may be feasible to use system-omics to investigate TCM syndromes, which will be characterized by multi-factors, multi-phenotypes, and dynamic-status approaches [48]. Gao et al [49] showed in pancreatic cancer that, certain mirnas mir-17, mir-21 and mir-181b were found to be specifically expressed in TCM dampness-heat syndrome, and mir-196a in spleen deficiency syndrome. These studies indicated that mirnas may play important roles in different syndromes, and can be potential molecular markers for the diagnosis of TCM syndromes in cancer. Liu et al [50] screened serum tumor biomarkers by surfaceenhanced laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF-MS) to establish a subset which could be used for the prediction of qi deficiency syndrome and phlegm and blood stasis syndrome in NSCLC patients. Fifteen serum proteins were selected as significant biomarkers, and the predictive model can be used to discriminate among Chinese medicine diagnostic models of disease. Yang et al [51] studied the different expression levels of serum proteins in patients with PLC, and showed that different peaks of serum proteins occurred in different TCM syndromes of PLC in the perioperative period of interventional treatment. Additionally, compared with the healthy control group, the expression of serum proteins was significantly down-regulated in liver depression syndrome, damp-heat syndrome, and yin deficiency syndrome, while being up-regulated in spleen deficiency syndrome and in blood stasis syndrome. Compared with that in the preintervention patients, the expression of serum proteins was down-regulated in Gan depression syndrome, Pi deficiency syndrome, damp-heat syndrome and blood stasis syndrome, while being up-regulated in yin deficiency syndrome [52]. 3.4 Molecular mechanisms of TCM syndromes in cancer TCM syndrome is a phenotype, underlined by the multi-level, complicated interaction of biological molecules, their functions and/or signal pathways in the live body, suggesting an imbalance in the biological molecular network at the systematic level. The biological molecular multiple factor interaction-biological network-multiple function network warrants a new research direction for TCM syndromes of cancer, TCM syndrome-oriented effects of Chinese herbal medicines or formulas, and ultimately a better understanding of the molecular mechanisms of cancer. In an mirna array anal ysis by Chen et al [53], hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) had gene ontology terms that were more stringently associated with liver-kidney yin deficiency syndrome (LKYDS) and deregulated the core cellular functions. Compared with Kyoto Encyclopedia of G enes and Genomes pathway, liver-gallbladder dampness heat syndrome was only related to small-cell lung cancer, liver depression and spleen deficiency syndrome (LDSDS) mainly associated with cell cycle, focal adhesion, endocytosis and cancer pathways, and LKYDS associated with apoptosis, chronic/acute myeloid leukemia and many cancer related pathways. Compared with BIOCARTA pathway, LKYDS was mainly associated with transcriptional regulation and map kinase pathways, while LDSDS more likely related to cell cycle, cyclins, and cell cycle regulation. By analysis of gene-chip, Pan et al [54,55] found that compared to normal mice, in H22 tumor mice, ERK signal pathway was activated most in yang deficiency syndrome, p38 and ERK5 signal pathway was activated most in toxin syndrome, and JNK signal pathway was inhibited most in yang deficiency syndrome. In addition, gene products of Smad signal pathway in adrenal gland were activated most in mice bearing H22 liver cancer with different TCM syndromes. For example, TGF-Br1, Bmp3 and Smad8 decreased in evil-toxin exuberance syndrome, but increased in yang qi deficiency syndrome; TGF-Br2 and Bmp5 increased in evil-toxin exuberance syndrome and qi deficiency syndrome, but decreased in qi and yin-yang deficiency syndrome. 3.5 Animal models of TCM syndromes in cancer Appropriate animal models can help in our understanding of the onset and development of TCM syndromes and the TCM syndrome-based treatment in the progression of cancer. Dai et al [56] established subcutaneous tumor models of pancreatic cancer syndromes of damp-heat and spleen deficiency, and found that the tumor growth of dampheat syndrome was slower than that of the control nonsyndrome group. They found that the levels of CCR5 protein increased in damp-heat syndrome and spleen deficiency syndrome. Additionally, were pound in dampheat syndrome the lowest levels of CCL5 and CCL4 expression. All the results suggested that different TCM syndromes may influence the tumor growth in pancreatic cancer via regulating the expression of CCR5/CCL5/CCL4. Chen et al [57] established a xenograft tumor mouse model with blood stasis syndrome, and found that mice with the blood stasis syndrome developed less metastasis than their counterparts without blood stasis. Yin et al [58] established Epub ahead of print Journal of Integrative Medicine
7 a pancreatic cancer xenograft mouse model with dampheat syndrome, and found that damp-heat syndrome mice exhibited altered cancer-associated myofibroblast proliferative activities and tumor-associated macrophage infiltration. In our previous study [59], we established 4T1 mouse breast cancer with liver fire invading stomach syndrome model (4T1 LFISS mice), and there were the features of LFISS including irritability, loss of appetite, yellow urine, and hot tails and/or claws in the 4T1 LFISS mice. In summary, good animal models will provide effective tools for understanding the TCM syndromes in cancers and guide the syndrome differentiation-based TCM treatment. 4.1 The same cancer with different treatments If two people with the same type of cancer present with different TCM syndromes, they should be treated with different therapeutic approaches. For example, liver cancer could manifest as spleen deficiency and qi stagnation, and thus be treated by spleen-strengthening and qi-regulating principles [60], or it can manifest as blood stasis syndrome, in which case the treatment would focus on removing blood stasis [61]. Previous study of treating PLC indicated that the most frequently used herbs were for strengthening the spleen, which helped promote appetite, remove toxic materials, inhibit tumor growth and activate blood circulation [62]. As for lung cancer, Chen et al [63] treated patients of different TCM syndrome types with different oral Chinese herbal medicines. For example, spleen deficiency and phlegm-dampness syndrome was treated with Liujunzi decoction for strengthening the spleen, removing dampness, regulating qi, and removing phlegm; yin deficiency inner heat syndrome was treated with Baihegujin decoction for clearing lung-heat and nourishing lung-yin; qi and yin deficiency syndrome was treated with Shengmai powder and Shashen-Maidong decoction for qi nourishing and yin; yin and yang deficiency syndrome was treated with Shashen-Maidong decoction and Zanyudan for warming yang and nourishing yin; qi stagnation and blood stasis syndrome was treated with Fuyuan Huoxue decoction for regulating qi and removing blood-stasis. In addition, intravenous injection of Kanglaite is frequently used as a basic TCM treatment choice for lung cancer [64]. As for colorectal cancer, the same treatment strategy is also applied. For instance, patients with spleen qi deficiency syndrome were treated with Sijunzi decoction for strengthening spleen and nourishing qi; kidney yang deficiency syndrome was treated with Erxian decoction for invigorating kidney yang; kidney yin deficiency syndrome was treated with Liuwei Dihuang decoction for nourishing kidney yin; dampness stagnation syndrome was treated with Erchen decoction for awaking spleen and removing dampness; blood stasis syndrome was treated with Xuefu Zhuyu decoction for removing stasis; intestinal damp-heat syndrome was treated with Siteng decoction for clearing intestine and removing dampness [65]. 4.2 Different cancers with the same treatment If presenting the same TCM syndromes, different cancers can be treated with the same medicine. One example is Aidi injection, which is used to treat several types of cancer with qi deficiency, such as small-cell lung cancer, colorectal cancer, gastrointestinal cancer and liver cancer. Aidi injection is generally combined with chemotherapy [66]. More than 140 clinical studies between the years of 2001 and 2009 tested the Aidi recipe, which consists of the four herbs Radix Astragali (Huangqi), Radix Ginseng (Rensheng), Acanthopanacis Senticosi (Ciwujia), and Mylabris (Banmao). Among them, Ginseng mainly strengthens vital qi, while Astragali and Mylabris have anti-cancer and detoxification effects. Shenling Baizhu powder, a broadly used anti-cancer TCM medicine in the treatment of various malignant tumors, has spleen-strengthening and qi-nourishing effects. Clinical studies showed that Shenling Baizhu powder improves the deficiency of spleen and stomach qi syndrome of colorectal cancer with liver metastases, lung cancer, ovarian cancer with peritoneal metastases, or breast cancer with lung and bone metastases [67]. In TCM practice, Chinese herbal medicines are prescribed according to a syndrome, and that syndrome guides the treatment. However, some important issues still need to be addressed. First of all, as syndrome differentiation is usually based upon the treating physician s intuition and personal experience, the results may be different between different physicians or clinics. The differentiation process lacks reproducibility, and no standard diagnostic criteria have been published. It remains one of the main obstacles to the wide application of TCM in the clinical and research settings. Therefore, a large, multi-center, high-throughput data collection and analysis platform of TCM syndromes in clinical cancer research is direly needed. Secondly, in this review, we emphasized the importance of TCM syndromes since they help guide the design of individual patients treatment regimen, and the reported studies we referred to may be helpful for the clinical diagnosis and treatment in TCM syndromes of cancer. However, it bears mentioning that so far syndrome differentiation-based TCM treatments have not produced consistent satisfactory therapeutic effects in cancer treatment. Recently, there has been increasing interest in the potential clinical use of the theory analogous TCM syndrome type existing in Journal of Integrative Medicine Epub ahead of print
8 the same disease [68], which means that the patients who suffer from the same disease may manifest a common basic syndrome type, in spite of slight differences in other accompanying minor syndromes. Therefore, a strategy combining TCM syndrome differentiation and d isease diagnosis is considered as the most promising approach for future cancer treatment. While many studies have attempted to elucidate the molecular basis of the cancer-associated TCM syndromes, the available data are subject to several limitations when guiding the clinical cancer treatment. First, TCM is focused on alleviating a particular disease or a symptom, while the TCM syndrome is based on systemic and holistic concepts. Thus, a systems biology approach may be the optimal way to investigate the clinical use and therapeutic efficacy of TCM syndrome. Second, at present, TCM is practiced with respect to the rules of treating the same diseases with different methods and treating different diseases with the same methods. The same molecular mechanisms underlying the same TCM syndromes in different cancers have been elucidated by many researchers. So cancer- or diagnosis-specific molecular mechanisms, which may share a TCM syndrome, might prove particularly important in designing effective individualized TCM treatment regimens. Third, a comprehensive profile of TCM syndrome-specific molecules has not been identified, and the correlation between TCM syndromes and biological molecules has to be firmly established. And last, we should acknowledge that TCM syndromes are now considered as multisystem and multiorgan functional impairment as well as a phenotype. With more and more modern technologies being applied in TCM syndrome research, we are getting closer to obtaining a clear understanding of the exact molecular basis and mechanisms of TCM syndromes in cancers. This study was supported by Key Program of National Science Foundation of China (No ), 085 First-Class Discipline Construction Innovation Science and Technology Support Project of Shanghai University of TCM (No. 085ZY1206), E-institutes of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. E03008), and National Natural Science F oundation of China (No , , , and ). The authors declare that they have no competing interests. 1 Su SB, Lu A, Li S, Jia W. Evidence-based ZHENG: a traditional Chinese medicine syndrome. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012: Chen Z, Wang P. Clinical distribution and molecular basis of traditional Chinese medicine ZHENG in cancer. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012: Ling CQ. My view on tr aditional Chinese medicine etiology and pathogenesis of cancer. Zhong Yi Za Zhi. 2009; 50(10): Chinese. 4 Ling CQ. Cancerous tox in is the key pathogenic factor of malignant tumor. J Chin Integr Med. 2008; 6(2): Chinese 5 Yue XQ. Towards better understanding the definition of cancerous toxin. J Chin Integr Med. 2010; 8(9): Chinese 6 Wang XM, Zhang Q. Discussion on oc currence and development of tumor based on cancerous toxin. Zhonghua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi. 2011; 26(7): Chinese with abstract in English. 7 Ling CQ. Problems in cancer treatment and major research of integrative medicine. J Chin Integr Med. 2003; 1(3): Chinese 8 Liu YJ, Fang ZQ, Di RH, Xu LY. Statistical analysis of clinically reported syndromes differentiation of 2492 PHC cases. Zhongguo Zhong Yi Ji Chu Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2001; 7(6): Chinese 9 Yuan L, Zhang PT, Yang ZY. Study on Qi deficiency syndrome distribution and quality of life in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2011; 31(7): Chinese 10 Sun DZ, Liu L, Jiao JP, Wei PK, Jiang LD, Xu L. Syndrome characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine: summary of a clinical survey in 767 patients with gastric cancer. J Chin Integr Med. 2010; 8(4): Yang ZJ, Zhang Y, Guo ZQ. Preliminary study on relationship between syndrome differentiation of esophageal cancer and changes of exfoliated cells of tongue coating. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1995; 15(5): Chinese 12 Liang F, Sun J, Li Q, Li CH, Fan ZZ. Analysis of clinical syndromes in 47 patients with pancreatic cancer at late stage. J Tradit Chin Med. 2011; 31(3): Chien TJ, Song YL, Lin CP, Hsu CH. The correlation of traditiona l Chinese medicine deficiency syndromes, cancer related fatigue, and quality of life in breast cancer patients. J Tradit Complement Med. 2012; 2(3): Guo Y, Zou Y, Xu YF, Wang H, Li Y, Qian LY, Yang WH. Study on Chinese medicine synd rome of colorectal carcinoma in perioperative period. Chin J Integr Med. 2015; 21(3): Cheng RF, Wu ZL. Discussion of the pathogenesis theory of primary liver cancer: deficiency, depression, phlegm, blood stasis, toxin. Shandong Zhong Yi Za Zhi. 2014; 33(10): Chinese 16 Zhang YH, Qin X, Xu J. Analysis of Chinese medical syn drome features of patients with primary liver cancer before and after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012; 32(9): Chinese 17 Fang ZQ, Li YJ, Tang CL, Ma J, Guan DY, Chen DS. Analysis on characteristics of s yndromes in 2060 cases of primary hepatic cancer. Zhong Yi Za Zhi. 2004; 45(1): Chinese 18 Zhang YM. Bo Liansong s experience in treat ing large Epub ahead of print Journal of Integrative Medicine
9 intestine cancer by supporting healthy qi and eliminating pathogenic facors. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi. 2005; 39(9): 28. Chinese. 19 Cheng CW, Kwok AO, Bian ZX, Tse DM. The quintessence of traditional Chinese medicine: syndrome and its distribution among advanced cancer patients with constipation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012: Li F, Zhao C, Xia Z, Wang Y, Zhou X, Li GZ. Computer-assisted lip diagnosis on traditional Chinese medicine using multi-class support vector machines. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012; 12: Yue XQ, Liu Q. Analysis of studies on pattern recognition of tongue image in traditional Chinese medicine by computer technology. J Chin Integr Med. 2004; 2(5): Chinese 22 Pang B, Zhang D, Li N, Wang K. Computerized tongue diagnosis based on Bayesian networks. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2004; 51(10): Hu JQ, Zhao T, Xu GC, Wu L, Kou QA, Zhuang H, Li ZH, Su ML, Zhang GF. Assessment on the accuracy of four t ypes of pulse by SM-1A TCM pulse detector. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shi Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua. 2011; 13(1): Chinese 24 Niu X, Yang XZ, Zhu QW, Li HY, Ma LX, Niu TL, Guo Z, Dong XY. Realization of the digitalization and quantification of key techniques of auxiliary diagnosis based on the four TCM diagnostic methods used in combination. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shi Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua. 2011; 13(1): Chinese 25 Wang YQ, Yan HX, Guo R, Li FF, Xia CM, Yan JJ, Xu ZX, Liu GP, Xu J. Study on intelligent syndrome differentiation in traditional Chinese medicine based on multiple information fusion methods. Int J Data Min Bioinform. 2011; 5(4): Liu L, Xu L, Sun DZ, Wei PK. Establishment of a fuzzy mathematical model for syndrome differentiation of gastric cancer. J Chin Integr Med. 2008; 6(11): Chinese 27 Li DT, Ling CQ, Zhu DZ. Study on the quantitative evaluation on the degree of TCM basic syndromes often encountered in patients with primary liver cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2007; 27(7): Chinese 28 Hou FG, Cen Y, Guan J, Zhu LY, Yin XL. Quantified diagnostic standard for large intestinal cancer of spleen qi deficiency syndrome. J Chin Integr Med. 2009; 7(9): Chinese 29 Luo HG, Han Z, Li JX, Ma R, Yuan Q, Song XJ, Huang XM. Study on syndrome law of gastric precance rous lesion in traditional Chinese medicine. Zhonghua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi. 2007; 22(6): Chinese. 30 Su W, Xu ZY, Wang ZQ, Xu JT. Objectified study on tongue images of patients with lung cancer of different syndromes. Chin J Integr Med. 2011; 17(4): Deng WZ, Yue XQ, Liu Q, Gao JD, Ren RZ, Ling CQ. Comparative study on normal tongue manifestation in patients with primary liver cancer and healthy adults. J Chin Integr Med. 2006; 4(1): Chinese 32 Hu KW, Wang F, Cao Y, He XL, Zuo MH, Chen WQ. Risk factors of traditional Chinese medical syndromes in moderate and advanced lung cancer patients with concurrent fungal pneumonia. J Chin Integr Med. 2004; 2(5): Chinese 33 He SL, Dong JC, Guan YH. Study on glucose metabolic rate in non-small cell lung cancer patients with blood stasis syndrome and non-blood stasis syndrome. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2004; 24(1): Chinese with abstract in English. 34 Mi YY, Hu YJ, Zhou MZ. Study of relationship between level of serum selenium and syndrome differentiation and typing of traditional Chinese medicine in lung cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1995; 15(11): Chinese 35 Mi YY, Zhou MZ. Probe into internal relation between classification of the differentiation-syndrome in traditional Chinese medicine and serum copper and zinc in lung cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 1992; 12(3): Chinese 36 Lin SC, Huang ML, Liu SJ, Huang YF, Chiang SC, Chen MF. Severity of Yin deficiency syndrome and autonomic nervous system function in cancer patients. J Altern Complement Med. 2009; 15(1): Lin SC, Chen MF. Increased yin-deficient symptoms and aggravated autonomic nervous system function in patients with metastatic cancer. J Altern Complement Med. 2010; 16(10): Yan XS, Li HM, Peng YQ. The relevant research on neoplastic marker of lun g cancer and TCM differentiation of syndromes. Hubei Zhong Yi Za Zhi. 2007; 29(9): Chinese. 39 Yu LJ, Chen Q, Mo CW, Wang J. Study on the correlation between TCM syndrome differen tiation and tumor markers in colorectal cancer. Yi Xue Qian Yan. 2013; (18): Chinese. 40 Lech A, Daneva T, Pashova S, Gagov H, Crayton R, Kukwa W, Czarnecka AM, Szczylik C. Ovarian cancer as a genetic disease. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013; 18: Wang HQ, Zhang Z, Zhao YP, Li J, Chen K. Expression of HSP70 and P53 in malignant tumor tissues and its relationship to heat syndrome of TCM. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2004; 24(10): Chinese 42 Chen W, Ouyang XN, Lin QC. Study on the relationship between vascular endothelial growth factor and syndrome type of traditional Chinese medicine in patients with gastric carcinoma. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2007; 27(2): Chinese 43 Luo XQ, Xu YM, Tang Y. Pathological basis of qi-deficiency and blood stasis syndrome in patients with non-small cell lung cancer viewing from tumor metastasis related factors. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2009; 29(10): Chinese 44 Pan ZQ, Fang ZQ, Lu WL, Liang C, Wu ZH, Liu XM, Hou L, Zhang H, Zhuo SY, Liao MJ, Gao BF. Differentially expressed genes in adrenal gland of H22 liver cancer mice with different syndromes and in different stages. J Chin Integr Med. 2008; 6(8): Chinese 45 Cui TJ, Chen YQ, Dai YM. Study of the correlation between the colorectal cancer Chinese medicine syndrome types and (excision repair cross-complementing 1, ERCC1) gene polymorphisms. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012; 32(5): Chinese 46 Zhang J, Zhan Z, Wu J, Zhang C, Yang Y, Tong S, Wang R, Yang X, Dong W. Association among lifestyle, clinical examination, polymorphisms in CDH1 gene and traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation of gastric cancer. J Tradit Chin Med. 2013; 33(5): Hood L, Heath JR, Phelps ME, Lin B. System biology and new technologies enable predictive and preventative medicine. Science. 2004; 306(5696): Journal of Integrative Medicine Epub ahead of print
10 48 Dai J, Sun S, Cao H, Zheng N, Wang W, Gou X, Su S, Zhang Y. Applications of new technologies and new methods in ZHENG differentiation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012; 2012: Gao S, Chen LY, Wang P, Liu LM, Chen Z. MicroRNA expression in salivary supernatant of patients with pancreatic cancer and its relationship with ZHENG. Biomed Res Int. 2014; 2014: Liu Z, Yu Z, Ouyang X, Du J, Lan X, Zhao M. Applied research on serum protein fingerprints for prediction of Qi deficiency syndrome and phlegm and blood stasis in patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. J Tradit Chin Med. 2012; 32(3): Yang SF, Qiu SP, Liu QH. Observation of serum protein fingerprinting in primary liver cancer patients of different Chinese medical syndromes before and after interventional treatment. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013; 33(10): Chinese 52 Yang SF. Differentially expressed proteins in serum among different Chinese medical syndrome types of primary liver cancer in the perioperative period of interventional treatment. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2013; 33(3): Chinese 53 Chen QL, Lu YY, Zhang GB, Song YN, Zhou QM, Zhang H, Zhang W, Tang XS, Su SB. Characteristic analysis from excessive to deficient syndromes in hepatocarcinoma underlying mirna array data. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013: Pan ZQ, Fang ZQ, Lu WL, Liang C, Wu ZH, Liu XM, Gao BF. Differe ntially expressed genes of MAPK signal pathway in different symptoms and signs about H22 tumour mice on base of adrenal gland gene-chip. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Gan Bing Za Zhi. 2009; 19(1): Chinese with abstract in English. 55 Pan ZQ, Fang ZQ, Lu WL, Liang C, Wu ZH, Liu XM, Gao BF. Gene expression of Smad signal pathway in adrenal gland in H22 tumor-bearing mice with different syndromes. Beijing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao. 2009; 32(5): Chinese 56 Dai HY, Wang P, Feng LY, Liu LM, Meng ZQ, Zhu XY, Wang K, Hua YQ, Mao YX, Chen LY, Chen Z. The molecular mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine ZHENG syndromes on pancreatic tumor growth. Integr Cancer Ther. 2010; 9(3): Chen Z, Liu LM, He YB. Characteri stics of W256 tumor growth and liver metastasis in rats with blood stasis syndrome. Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan. 2003; 21(6): Chinese. 58 Yin JH, Shi WD, Zhu XY, Chen Z, Liu LM. Qingyihuaji formula inhibits progress of liver metastases from advanced pancreatic cancer xenograft by targeting to decrease expression of Cyr61 and VEGF. Integr Cancer Ther. 2012; 11(1): Du J, Sun Y, Wang XF, Lu YY, Zhou QM, Su SB. Establishment of an experimental breast cancer ZHENG model and curative effect evaluation of Zuo-Jin Wan. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013: Yang XB, Long SQ, Wu WY, Deng H, Pan ZQ, He WF, Zhou YS, Liao GY. Treating primary liver cancer patients by Pi-strengthening and Qi-regulating method: univariate and multivariate analyses of their prognoses. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2014; 34(2): Chinese 61 Chen XZ, Tian HQ, Huang XQ, Liang GW, Huang ZQ. Effect of Gan ji formula on blood stasis in patients with advanced liver cancer. Shaanxi Zhong Yi. 2005; 26(9): Chinese. 62 Wang P, Huang WX, Liu LM. Overview of cl inical and experimental study on Spleen-nourishing and Qi-regulating therapy for liver cancer. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi. 2005; 39(5): Chinese 63 Chen XP, Zhang YP, Zhu XR. Clinical study on effects of Tiepi fengdou granule/capsule combined with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in treating lung cancer with Qi-yin asthenia syndrome. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2006; 26(5): Chinese 64 Qin ZF, Wei PK, Li J. Effect of kanglaite injection combined with Chinese drug therapy according to syndrome differentiation on quality of life and immune function in patients with advanced lung cancer. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2002; 22(8): Chinese 65 Tao L, Zhu YJ, Lu XM, Gu Y, Zhao AG, Zheng J, Fu CG, Yang JK. Clinical study on survival benefit for elderly patients with resected stage II or III colorectal cancer based on traditional Chinese medicine syndrome differentiation and treatment. J Chin Integr Med. 2010; 8(12): Chinese 66 Lang WJ. Analysis of the c linical application of Aidi injection in treating cancer. Zhongguo Shi Yong Yi Yao. 2011; 6(32): Chinese. 67 Xue Q, Zhao JF. The clinical application of Shenling Baizhu decoction in the treatment of malignant tumor. Neimenggu Zhong Yi Yao. 2014; 33(1): Chinese. 68 Wang P, Chen Z. Traditional Chinese medicine ZHENG and Omics convergence: a systems approach to post-genomics medicine in a global world. OMICS. 2013; 17(9): Journal of Integrative Medicine (JIM) is an international, peer-reviewed, PubMed-indexed journal, publishing papers on all aspects of integrative medicine, such as acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine, Ayurvedic medicine, herbal medicine, homeopathy, nutrition, chiropractic, mind-body medicine, Taichi, Qigong, meditation, and any other modalities of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM). Article types include reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analyses, randomized controlled and pragmatic trials, translational and patient-centered effectiveness outcome studies, case series and reports, clinical trial protocols, preclinical and basic science studies, papers on methodology and CAM history or education, editorials, global views, commentaries, short communications, book reviews, conference proceedings, and letters to the editor. For information on manuscript preparation and submission, please visit JIM website. Send your postal address by to jcim@163.com, we will send you a complimentary print issue upon receipt. Epub ahead of print Journal of Integrative Medicine
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts
 Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
Liu Jing and Liu Jing Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Discussions of Six Divisions or Six Confirmations Diagnosis System in Classical TCM Texts Liu Jing Bian Zheng system had developed about 1800 years
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE II
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
COURSE DESCRIPTION The second of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. Categories covered in Formulae II include the Tonify Qi and Blood, Regulate Qi, Invigorate the Blood, Stop Bleeding, Stabilize
Single Herbs III / Quiz I
 Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz I 1. What herb is good to generate fluids? A. Ren Shen C. Xi Yang Shen B. Tai Zi Shen D. All the Shens 2. What herb is best for Qi collapse? A. Huang Qi C. Dang Shen B. Ren Shen
Root & Branch Bulk Formula List
 An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
An asterisk * indicates the inclusion of 1 or more granule versions of an herb because of limited availability on the American herbal market. These products are usually animal in nature like E Jiao, Shui
Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding
 Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
Acupuncture Heals Erectile Dysfunction Finding Published by HealthCMI on 02 May 2018. erectile dysfunction. Acupuncture and herbs are effective for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In research conducted
24 h. P > h. R doi /j. issn
 38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
38 4 2015 4 Vol. 38 No. 4 Apr. 2015 Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine 271 2 ~ 3 * 1 2 2 2 2 2 1# 1 201203 2 2 ~ 3 55 2 18 37 24 2 0 8 16 24 24 h 2 P > 0. 05 P < 0. 05 P < 0.
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10. Function in Formula. Disperse stagnation
 Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
Course: Formulas 1 Date: December 2, 2009 Class #: 10 Xi Jiao Di Huang Tang : o Clear Heat toxins o o Disperse stagnation : o Heat in the blood Xi jiao Sheng di Shao yao Mu dan pi Clear Heart heat Nourish
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 )
 4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
4-1 Dyspnea (Chuan, 喘 ) Concept Breathing with difficulty (open wide mouth, raise shoulders) Etiology and pathogenesis Climatic factors Phlegm fluid Emotion Chronic diseases Exertion Over sex Diagnosis
Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine
 Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine World Century Compendium to TCM Volume 1 Volume 2 Volume 3 Volume 4 Volume 5 Volume 6 Volume 7 Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine by Hong-zhou Wu,
Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine World Century Compendium to TCM Volume 1 Volume 2 Volume 3 Volume 4 Volume 5 Volume 6 Volume 7 Fundamentals of Traditional Chinese Medicine by Hong-zhou Wu,
Objective research on tongue manifestation of patients with eczema
 Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S143 S149 DOI 10.3233/THC-171316 IOS Press S143 Objective research on tongue manifestation of patients with eczema Zhifeng Yu, Haifang Zhang, Linjie Fu and Xiaozuo
Technology and Health Care 25 (2017) S143 S149 DOI 10.3233/THC-171316 IOS Press S143 Objective research on tongue manifestation of patients with eczema Zhifeng Yu, Haifang Zhang, Linjie Fu and Xiaozuo
Our ongoing interest in spirit
 Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
Soothing the Troubled Spirit with Blue Poppy Originals Formulas with Honora Lee Wolfe Our ongoing interest in spirit Western practitioners of Chinese medicine have always had more interest in diseases
ratio in patients treated by sorafenib alone decreased after treatment (P<0.05), while CD 8
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4625-4629 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015836 Original Article Effect of sorafenib combined with CIK cell treatment on immunity and adverse events in patients with late-stage
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4625-4629 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015836 Original Article Effect of sorafenib combined with CIK cell treatment on immunity and adverse events in patients with late-stage
Integrative network analysis: Bridging the gap between Western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine
 Hong Kong Baptist University HKBU Institutional Repository HKBU Staff Publication 2015 Integrative network analysis: Bridging the gap between Western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine Bing He Hong
Hong Kong Baptist University HKBU Institutional Repository HKBU Staff Publication 2015 Integrative network analysis: Bridging the gap between Western medicine and traditional Chinese medicine Bing He Hong
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
Single Herbs III / Quiz II
 Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
Single Herbs III / Quiz II 1. What herb can nourish St Yin and brightens the eyes? A. Mai Dong C. Sha Shen B. Shi Hu D. Tian Dong 2. What herb can be used for an exterior invasion with Yin Xu? A. Sha Shen
Construction of the Vesselcollateral. Guidance for Prevention and Treatment of Vasculopathy. Section 1. China. Clinical Trials.
 Section 1 05 Clinical Trials Construction of the Vesselcollateral Theory and its Guidance for Prevention and Treatment of Vasculopathy China Yiling Wu The Integration of Traditional and Western Medical
Section 1 05 Clinical Trials Construction of the Vesselcollateral Theory and its Guidance for Prevention and Treatment of Vasculopathy China Yiling Wu The Integration of Traditional and Western Medical
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease
 Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
Acupuncture and Herbs Eliminate Meniere s Disease Published by HealthCMi on June 2018 Acupuncture has been proven clinically effective for the treatment of Meniere s disease, a disorder characterized by
EMPEROR'S COLLEGE MTOM COURSE SYLLABUS HERB FORMULAE I
 COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
COURSE DESCRIPTION The first of three courses in the Herb Formulae series. These courses can be taken in any order. The Herb Formulae series analyzes the functions, ingredients, and properties of approximately
Single Herbs II / Quiz II
 1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
1. What herb is good to treat cholesterol? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Gu Ya 2. What herb can inhibit lactation? A. Shan Zha C. Shen Qu B. Mai Ya D. Lai Fu Zi 3. What herb can dissolve stones?
The association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene C677T polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in Chinese population
 Tumor Biol. (2015) 36:9153 9158 DOI 10.1007/s13277-015-3321-6 EDITORIAL The association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene C677T polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in Chinese population
Tumor Biol. (2015) 36:9153 9158 DOI 10.1007/s13277-015-3321-6 EDITORIAL The association between methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene C677T polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in Chinese population
Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population
 Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population J.J. Lu, H.Q. Zhang, P. Mai, X. Ma, X. Chen, Y.X. Yang and L.P. Zhang Gansu Provincial Hospital, Donggang
Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population J.J. Lu, H.Q. Zhang, P. Mai, X. Ma, X. Chen, Y.X. Yang and L.P. Zhang Gansu Provincial Hospital, Donggang
Seasonal and geographical dispersal regularity of airborne pollens in China LI Quan-sheng, JIANG Sheng-xue, LI Xin-ze, ZHU Xiao-ming, WEI Qing-yu *
 Med J Chin PLA, Vol. 42, No. 11, November 1, 2017 951 [] [ ] [ ] R562.25[ ] A[] 0177-7402(2017)11-0951-05 [DOI] 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2017.11.03 Seasonal and geographical dispersal regularity of airborne
Med J Chin PLA, Vol. 42, No. 11, November 1, 2017 951 [] [ ] [ ] R562.25[ ] A[] 0177-7402(2017)11-0951-05 [DOI] 10.11855/j.issn.0577-7402.2017.11.03 Seasonal and geographical dispersal regularity of airborne
Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma
 Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma WEEK TWO: Class 2 Goals: Students will learn traditional treatment methods - sweating, vomiting, draining downward, harmonizing, warming,
Course: Formulas 1 Date: September 30, 2009 Class #: 2 Prof: Dr. Ma WEEK TWO: Class 2 Goals: Students will learn traditional treatment methods - sweating, vomiting, draining downward, harmonizing, warming,
Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment
 Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment Published by HealthCMi on 29 May 2018 Researchers find acupuncture combined with herbal medicine effective for the treatment of chronic pelvic inflammatory
Acupuncture And Herbs Proven Effective For PID Treatment Published by HealthCMi on 29 May 2018 Researchers find acupuncture combined with herbal medicine effective for the treatment of chronic pelvic inflammatory
Medicated diet. Tonify the Qi
 Medicated diet Tonify the Qi 1. Ren shen ginseng root Properties: sweet, slightly bitter, slightly warm Channels entered: LU, SP a. Strongly tonifies the basal qi, Tonifies the lung and spleen qi. a. Benefits
Medicated diet Tonify the Qi 1. Ren shen ginseng root Properties: sweet, slightly bitter, slightly warm Channels entered: LU, SP a. Strongly tonifies the basal qi, Tonifies the lung and spleen qi. a. Benefits
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS
 Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
Acupuncture Outmatches Drug For IBS Published by HealthCMi on December 2017 Acupuncture and Chinese herbal medicine are found effective for the alleviation of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). Two independent
Xiao-Ling Chi, Mei-Jie Shi, Huan-Ming Xiao, Yu-Bao Xie, and Gao-Shu Cai. Correspondence should be addressed to Xiao-Ling Chi;
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 3743427, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3743427 Research Article The Score Model Containing Chinese Medicine Syndrome
Research Article Clinical and Epidemiological Investigation of TCM Syndromes of Patients with Coronary Heart Disease in China
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 714517, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/714517 Research Article Clinical and Epidemiological Investigation of TCM Syndromes of Patients
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 714517, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/714517 Research Article Clinical and Epidemiological Investigation of TCM Syndromes of Patients
Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities
 Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities D F E G ctions: Warms the channels, disperses cold, nourishes the xue, and unblocks the xue vessels. hief Deputy (a) Dang Gui (b) Gui Zhi (c)
Dang Gui Si Ni Tang Tangkuei Decoction for Frigid Extremities D F E G ctions: Warms the channels, disperses cold, nourishes the xue, and unblocks the xue vessels. hief Deputy (a) Dang Gui (b) Gui Zhi (c)
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma
 Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Genetic variability of genes involved in DNA repair influence treatment outcome in osteosarcoma M.J. Wang, Y. Zhu, X.J. Guo and Z.Z. Tian Department of Orthopaedics, Xinxiang Central Hospital, Xinxiang,
Integr Med Int 2016;3: DOI: / Received: May 27, 2016 Accepted: August 15, 2016 Published online: October 14, 2016
 Received: May 27, 2016 Accepted: August 15, 2016 Published online: October 14, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
Received: May 27, 2016 Accepted: August 15, 2016 Published online: October 14, 2016 2016 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel This article is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into
 Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
Section 1 Used for exterior conditions such as common colds, fevers, and flu s. Many of these formulas induce sweating. This category can be subdivided into formulas the release cold or heat. Traditionally
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic
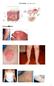 1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
1 Eczema (Shi Zhen, 湿疹 ) Eczema/ 湿疹 pic 1 [Introduction] dermal inflammation: polymorphous serious itching symmetrical chronic / recurrence effusing tendency delayed allergic reaction int factors ext factors
Prostate Disease A Pass By TANG QIAN LI ZHU BIAN
 Prostate Disease A Pass By TANG QIAN LI ZHU BIAN Oxytocin and the Human Prostate in Health and - and PSA is then able to pass into the proliferation within the normal prostate. 4.4. Oxytocin and prostate
Prostate Disease A Pass By TANG QIAN LI ZHU BIAN Oxytocin and the Human Prostate in Health and - and PSA is then able to pass into the proliferation within the normal prostate. 4.4. Oxytocin and prostate
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang. Shi Jue Ming ** Properties: Salty, mild cold LV. Actions: Suppress LV yang, clear eye heat
 C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
C 22. Calming LV, tranquilizing internal wind (13) LV yang Shi Jue Ming ** Zhen Zhu Mu * (Long Gu -)*** Mu Li *** Dai Zhe Shi ** Bai Ji Li/Ci Ji Li Wind/spasm Gou Teng ** Tian Ma *** Di Long ** Quan Xie
Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee
 1. Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee 2. Two Cases of Thoracic Diseases with Effective Clinical Results 3. Dr. Pu-Tao Chang on Health Preservation Ginseng (Ren Shen) 4. Pharmacodynamics
1. Case Study for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee 2. Two Cases of Thoracic Diseases with Effective Clinical Results 3. Dr. Pu-Tao Chang on Health Preservation Ginseng (Ren Shen) 4. Pharmacodynamics
Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18538-18542 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012561 Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):18538-18542 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012561 Original Article Relation between qualitative and quantitative 3-dimensional ultrasound and ki-67 expression in breast
In the October, 2009 issue of ACUPUNCTURE TODAY, I wrote on how to use pulse
 The Herbalist s Corner Acupuncture Today, April, 2010 TREATING COMPLEX MULTI-LAYERED CASES Part 2: Treatment Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. In the October, 2009 issue of ACUPUNCTURE TODAY, I wrote on how
The Herbalist s Corner Acupuncture Today, April, 2010 TREATING COMPLEX MULTI-LAYERED CASES Part 2: Treatment Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, L.Ac. In the October, 2009 issue of ACUPUNCTURE TODAY, I wrote on how
GYNECOLOGY & TCM. On line course provided by. Taught by Clara Cohen
 GYNECOLOGY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen 1 GYNECOLOGY & TCM INTRODUCTION WOMEN S PHYSIOLOGY MENSTRUATION CONCEPTION PREGNANCY MENOPAUSE CAUSES OF IMBALANCE PREVENTION 2 Physiology
GYNECOLOGY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen 1 GYNECOLOGY & TCM INTRODUCTION WOMEN S PHYSIOLOGY MENSTRUATION CONCEPTION PREGNANCY MENOPAUSE CAUSES OF IMBALANCE PREVENTION 2 Physiology
The Herbalist s Corner
 Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
Acupuncture Today, July 2008 The Herbalist s Corner Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD. L.Ac. MANAGING A PATIENT WITH MULTIPLE COMPLAINTS A situation common to American herbalist/acupuncturists is the arrival of a
DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING
 DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING HISTORICAL CONTEXT Mai Jing (Pulse Treatise) By Wang Shu He (180-270 CE) Discusses static pulses and pulses that occupy more than one position Li Shi Zhen (1518-1593) Pulse Diagnosis
DIRECTIONAL PULSE READING HISTORICAL CONTEXT Mai Jing (Pulse Treatise) By Wang Shu He (180-270 CE) Discusses static pulses and pulses that occupy more than one position Li Shi Zhen (1518-1593) Pulse Diagnosis
Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū
 Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū Shùn Qì Yī Rì Fēn Wéi Sì Shí The Human Healthy Energy in the Day and Night Corresponds with the Energies of the Four Seasons Paragraph 1 The initiation of the various
Summary of Chapter 44 of the Líng Shū Shùn Qì Yī Rì Fēn Wéi Sì Shí The Human Healthy Energy in the Day and Night Corresponds with the Energies of the Four Seasons Paragraph 1 The initiation of the various
TCM Ideology and Methodology
 Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, June 2011; 31(2): 147-151 147 TCM Ideology and Methodology The TCM Pattern of the Six-Zang and Six-Fu Organs Can Be Simplified into the Pattern of Five-Zang and
Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, June 2011; 31(2): 147-151 147 TCM Ideology and Methodology The TCM Pattern of the Six-Zang and Six-Fu Organs Can Be Simplified into the Pattern of Five-Zang and
Symptom clustering in chronic gastritis based on spectral clustering
 Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 04 August 5; 4(4): 50450 info@journaltcm.com ISSN 0559 04 JTCM. All rights reserved. INFORMATION STUDY TOPIC Symptom clustering in chronic
Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 04 August 5; 4(4): 50450 info@journaltcm.com ISSN 0559 04 JTCM. All rights reserved. INFORMATION STUDY TOPIC Symptom clustering in chronic
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
FOUNDATIONS, ACUPUNCTURE, CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE, BIO-MEDICINE. Stage Four Review
 ICAOM LEARNING PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION FOUNDATIONS, ACUPUNCTURE, CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE, BIO-MEDICINE Review and know the following: Stage Four Review 1. Familiar with the disease or symptom of the following
ICAOM LEARNING PROFICIENCY EXAMINATION FOUNDATIONS, ACUPUNCTURE, CHINESE HERBAL MEDICINE, BIO-MEDICINE Review and know the following: Stage Four Review 1. Familiar with the disease or symptom of the following
Acupuncture and herbal treatment for breast cancer after mastectomy
 Acupuncture and herbal treatment for breast cancer after mastectomy Dijana Arsova 1, Biljana Lazarova 1, Jihe Zhu 1, Blagica Arsovska 1, 2, Kristina Kozovska 1 1 Faculty of Medical Sciences, University
Acupuncture and herbal treatment for breast cancer after mastectomy Dijana Arsova 1, Biljana Lazarova 1, Jihe Zhu 1, Blagica Arsovska 1, 2, Kristina Kozovska 1 1 Faculty of Medical Sciences, University
How Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine Can Help You Build a Resilient Body ALYSSA JOHNSON, L. AC, MA. OM
 How Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine Can Help You Build a Resilient Body ALYSSA JOHNSON, L. AC, MA. OM What is Oriental Medicine? or Traditional Chinese Medicine Oriental Medicine (OM) =Traditional Chinese
How Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine Can Help You Build a Resilient Body ALYSSA JOHNSON, L. AC, MA. OM What is Oriental Medicine? or Traditional Chinese Medicine Oriental Medicine (OM) =Traditional Chinese
Chapter 14 Warming interior
 Chapter 14 Warming interior [7. Herbs That Warm the Interior, 9] Fu Zi 附子 Gan Jiang 乾薑 Rou Gui 肉桂 Wu Zhu Yu 吳茱萸 Xiao Hui Xiang 小茴香 9 herbs Ding Xiang 丁香 Gao Liang Jiang 高良薑 Hua Jiao 花椒 Hu Jiao 胡椒 : Pungent,
Chapter 14 Warming interior [7. Herbs That Warm the Interior, 9] Fu Zi 附子 Gan Jiang 乾薑 Rou Gui 肉桂 Wu Zhu Yu 吳茱萸 Xiao Hui Xiang 小茴香 9 herbs Ding Xiang 丁香 Gao Liang Jiang 高良薑 Hua Jiao 花椒 Hu Jiao 胡椒 : Pungent,
Five Virtues Center for Acupuncture
 Five Virtues Center for Acupuncture Case Study: Headaches and Amenorrhea By Ross Rosen and Jennifer Sobonski History: Patient is a 15- year- old girl who was referred with headaches and amenorrhea. Her
Five Virtues Center for Acupuncture Case Study: Headaches and Amenorrhea By Ross Rosen and Jennifer Sobonski History: Patient is a 15- year- old girl who was referred with headaches and amenorrhea. Her
Original Article Association of osteopontin polymorphism with cancer risk: a meta-analysis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):20911-20917 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015120 Original Article Association of osteopontin polymorphism with cancer risk: a meta-analysis Gang Yang 1, Xiaoxing Peng
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(11):20911-20917 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0015120 Original Article Association of osteopontin polymorphism with cancer risk: a meta-analysis Gang Yang 1, Xiaoxing Peng
Analysis on Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome elements and relevant factors for senile diabetes
 Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 203 August 5; 33(4): 473478 info@journaltcm.com ISSN 02552922 203 JTCM. All rights reserved. CLINICAL STUDY TOPIC Analysis on Traditional
Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 203 August 5; 33(4): 473478 info@journaltcm.com ISSN 02552922 203 JTCM. All rights reserved. CLINICAL STUDY TOPIC Analysis on Traditional
Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population
 Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population L.Q. Yang 1, Y. Zhang 2 and H.F. Sun 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology, The Second Affiliated
Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population L.Q. Yang 1, Y. Zhang 2 and H.F. Sun 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology, The Second Affiliated
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Acupuncture Boosts Breast Milk Production
 Acupuncture Boosts Breast Milk Production Published by HealthCMi on July 2017 Acupuncture restores normal breast milk production to lactating mothers with low milk secretion levels. Research conducted
Acupuncture Boosts Breast Milk Production Published by HealthCMi on July 2017 Acupuncture restores normal breast milk production to lactating mothers with low milk secretion levels. Research conducted
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Abbreviated Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates
Original Article Influence of retinal photocoagulation applied to severe diabetic retinopathy on the life quality of patients
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4630-4634 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016207 Original Article Influence of retinal photocoagulation applied to severe diabetic retinopathy on the life quality of patients
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4630-4634 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016207 Original Article Influence of retinal photocoagulation applied to severe diabetic retinopathy on the life quality of patients
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in 2010
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in 2010 Kuang-Rong Wei 1, Rong-Shou Zheng 2, Si-Wei Zhang 2, Zhi-Heng Liang 1, Zhi-Xiong Ou 1 and Wan-Qing
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Nasopharyngeal carcinoma incidence and mortality in China in 2010 Kuang-Rong Wei 1, Rong-Shou Zheng 2, Si-Wei Zhang 2, Zhi-Heng Liang 1, Zhi-Xiong Ou 1 and Wan-Qing
Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology
 Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
Preliminary Agenda. 9:55-10:20 How to overcome TKI resistance? James Chih-Hsin Yang 10:20-10:40 Discussion All 10:40-10:55 Coffee break
 Preliminary Agenda November 7, 2018 14:00-17:00 Registration and check in Satellite Symposia with Dinner 17:00-18:30 Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd 17:00-18:30 Satellite Symposia with Dinner 17:00-18:30
Preliminary Agenda November 7, 2018 14:00-17:00 Registration and check in Satellite Symposia with Dinner 17:00-18:30 Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co., Ltd 17:00-18:30 Satellite Symposia with Dinner 17:00-18:30
Research Article Traditional Chinese Medicine Zheng in the Era of Evidence-Based Medicine: A Literature Analysis
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 409568, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/409568 Research Article Traditional Chinese Medicine Zheng in the Era of Evidence-Based Medicine:
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 409568, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/409568 Research Article Traditional Chinese Medicine Zheng in the Era of Evidence-Based Medicine:
Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong
 Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(6):1384-1388 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0048028 Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong Jie Jin 1*, Xiao-yan
Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(6):1384-1388 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0048028 Original Article Application of AFP whole blood one-step rapid detection kit in screening for HCC in Qidong Jie Jin 1*, Xiao-yan
Original Article Pre-miR-149 rs polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk and AKT1/cyclinD1 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13628-13633 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012040 Original Article Pre-miR-149 rs71428439 polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk and AKT1/cyclinD1 signaling
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):13628-13633 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0012040 Original Article Pre-miR-149 rs71428439 polymorphism is associated with increased cancer risk and AKT1/cyclinD1 signaling
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Analyses on Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Huai an Area, China, 2010
 Open Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2014, 4, 504-512 Published Online June 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojpm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojpm.2014.46059 Analyses on Cancer Incidence and
Open Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2014, 4, 504-512 Published Online June 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojpm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojpm.2014.46059 Analyses on Cancer Incidence and
Acupuncture Immune System Discovery
 Acupuncture Immune System Discovery Published by HealthCMi on November 2017 Researchers conclude that acupuncture benefits the immune system. In a controlled laboratory experiment, Hubei University of
Acupuncture Immune System Discovery Published by HealthCMi on November 2017 Researchers conclude that acupuncture benefits the immune system. In a controlled laboratory experiment, Hubei University of
Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
The progressing research of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of. insomnia. Liu Jing1 a
 4th International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2017) The progressing research of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of insomnia Liu Jing1 a 1 Shandong University
4th International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2017) The progressing research of traditional Chinese medicine treatment of insomnia Liu Jing1 a 1 Shandong University
Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: April 28, 2009 Class #: 3 Chapter 12 C Herbs that Tonify Yang. Chapter 12 C Herbs that Tonify Yang
 Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: April 28, 2009 Class #: 3 Chapter 12 C Herbs that Tonify Yang Chapter 12 C Herbs that Tonify Yang Know the Yang xu symptoms for the organs which can be involved. Kidney,
Course: Chinese Herbology 3 Date: April 28, 2009 Class #: 3 Chapter 12 C Herbs that Tonify Yang Chapter 12 C Herbs that Tonify Yang Know the Yang xu symptoms for the organs which can be involved. Kidney,
Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences
 Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences By Dr. Yin Hongchun Email: h.yin1@btopenworld.com Tel: 02086722088 Main point of diagnosis (1)
Acupuncture for the syndrome of prolapsed lumbar Intervertebral disc --Case studies and clinical experiences By Dr. Yin Hongchun Email: h.yin1@btopenworld.com Tel: 02086722088 Main point of diagnosis (1)
HISTORICAL BASIS OF CHINESE MEDICINE. Linda Boggie, DVM Okkenbroek, The Netherlands
 HISTORICAL BASIS OF CHINESE MEDICINE Linda Boggie, DVM Okkenbroek, The Netherlands Chinese Medical Theory Based on observation of phenomena and integrated with Chinese philosophy Chinese philosophy has
HISTORICAL BASIS OF CHINESE MEDICINE Linda Boggie, DVM Okkenbroek, The Netherlands Chinese Medical Theory Based on observation of phenomena and integrated with Chinese philosophy Chinese philosophy has
Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population
 Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population H.B. Gui 1, X.G. Du 2, Z.H. Fu 3 and X.M. Chen 1 1 Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated
Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population H.B. Gui 1, X.G. Du 2, Z.H. Fu 3 and X.M. Chen 1 1 Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline
 The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who
The Foundations of Oriental Medicine Expanded Content Outline (Effective as of February 1, 2014) Note to Candidate: This document serves as a guide to assist in examination preparation for candidates who
The evidence system of traditional Chinese medicine based on the Grades of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation framework
 Viewpoint Page 1 of 5 The evidence system of traditional Chinese medicine based on the Grades of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation framework Hao Chen 1, Yan Wang 2, Wen-Bo Jiang 1,3,
Viewpoint Page 1 of 5 The evidence system of traditional Chinese medicine based on the Grades of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation framework Hao Chen 1, Yan Wang 2, Wen-Bo Jiang 1,3,
A 4-year study of Red Yeast Rice extract known as Xuezhikang which lowers cholesterol... Monday, July 27, 2009
 A 4-year study of Red Yeast Rice extract known as Xuezhikang which lowers cholesterol... 1 At a dose of 600 mg twice a day... 2 Reduced coronary events by 37%... 3 Reduced death from coronary heart disease
A 4-year study of Red Yeast Rice extract known as Xuezhikang which lowers cholesterol... 1 At a dose of 600 mg twice a day... 2 Reduced coronary events by 37%... 3 Reduced death from coronary heart disease
Chronic Fatigue Recovery With Acupuncture
 Chronic Fatigue Recovery With Acupuncture Published by HealthCMi on August 2017 Shenzhen Hospital of Chinese Medicine researchers determined that acupuncture is safe and effective for the alleviation of
Chronic Fatigue Recovery With Acupuncture Published by HealthCMi on August 2017 Shenzhen Hospital of Chinese Medicine researchers determined that acupuncture is safe and effective for the alleviation of
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD. Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China. Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine
 GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
Case-control study on the associations between lifestyle-behavioral risk factors and phlegm-wetness constitution
 Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 204 June 5; 34(3): 286-292 info@journaltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 204 JTCM. All rights reserved. CLINICAL STUDY TOPIC Case-control study on the
Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 204 June 5; 34(3): 286-292 info@journaltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 204 JTCM. All rights reserved. CLINICAL STUDY TOPIC Case-control study on the
Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs
 Course: Chinese Herbology 1 Date: October 28, 2008 Class #: 6 Clear Heat/Cool Blood Herbs Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs Introduction Used for Ying and Xue stages, the 2 deepest of the four levels of
Course: Chinese Herbology 1 Date: October 28, 2008 Class #: 6 Clear Heat/Cool Blood Herbs Clear Heat and Cool Blood Herbs Introduction Used for Ying and Xue stages, the 2 deepest of the four levels of
IMPROVED OUTCOMES WHEN COMBINING TCM WITH WESTERN INTERVENTIONS FOR CANCER
 IMPROVED OUTCOMES WHEN COMBINING TCM WITH WESTERN INTERVENTIONS FOR CANCER by Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, Lac Acupuncture Today, September, 2005 Patients undergoing treatment for cancer is becoming more commonplace
IMPROVED OUTCOMES WHEN COMBINING TCM WITH WESTERN INTERVENTIONS FOR CANCER by Jake Paul Fratkin, OMD, Lac Acupuncture Today, September, 2005 Patients undergoing treatment for cancer is becoming more commonplace
Screening of Monacolin K-high-yielding Monascus strain by combinative mutation treatment
 264507~5162007 Mycosystema 1 550002 2 100039 3 550002 4 550000 Monascus purpureus 45s 1.0 Monacolin K Monascus purpureus ZT32 5 Monacolin K 219.9µg/mL 2 Monacolin K 8.33mg/g 3.3 Q939.5 A 1672-6472200704-0507-0516
264507~5162007 Mycosystema 1 550002 2 100039 3 550002 4 550000 Monascus purpureus 45s 1.0 Monacolin K Monascus purpureus ZT32 5 Monacolin K 219.9µg/mL 2 Monacolin K 8.33mg/g 3.3 Q939.5 A 1672-6472200704-0507-0516
Acupuncture Found Effective For IBS-D
 Acupuncture Found Effective For IBS-D Published by HealthCMI on 26 February 2018. Investigators find acupuncture effective for the treatment of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). In a controlled study, Yiwu
Acupuncture Found Effective For IBS-D Published by HealthCMI on 26 February 2018. Investigators find acupuncture effective for the treatment of IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). In a controlled study, Yiwu
This Sense, other Interventions that Focus on the Strengthening of. the Co-Parenting Relationship are Recommended
 ISSN: 2576-4772 This Sense, other Interventions that Focus on the Strengthening of the Co-Parenting Relationship are Recommended Liping Ma, Haiyong Chen, YanboZhang and WeiMeng* Hong Kong Branch of zhu
ISSN: 2576-4772 This Sense, other Interventions that Focus on the Strengthening of the Co-Parenting Relationship are Recommended Liping Ma, Haiyong Chen, YanboZhang and WeiMeng* Hong Kong Branch of zhu
CORRELATION BETWEEN SURVIVIN OVEREXPRESSION AND CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF INVASIVE CERVICAL CANCER: A META-ANALYSIS
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 1091 CORRELATION BETWEEN SURVIVIN OVEREXPRESSION AND CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF INVASIVE CERVICAL CANCER: A META-ANALYSIS HUI-RONG LI 1, JI-LI BAI 2*, RUI XU 2,
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 1091 CORRELATION BETWEEN SURVIVIN OVEREXPRESSION AND CLINICO-PATHOLOGICAL FEATURES OF INVASIVE CERVICAL CANCER: A META-ANALYSIS HUI-RONG LI 1, JI-LI BAI 2*, RUI XU 2,
Contents. Basic Theory of Acupuncture. (Page 1) Acupuncture Points. (Page 31) Side Effects of Acupuncture. (Page 51)
 VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
VII Contents Basic Theory of Acupuncture (Page 1) Scientific Aspects of Acupuncture..................... 2 Indication and Direction of Action of Acupuncture.................................... 12 Relative
HCV / HIV Co i n f ec t i o n
 c h a p t e r HCV / HIV Co i n f ec t i o n Misha Cohen, OMD, LAc 20 S E C T I O N 3 Alternative Eastern Treatment Options Traditional Chinese Medicine for HCV/HIV Coinfection Many people with the hepatitis
c h a p t e r HCV / HIV Co i n f ec t i o n Misha Cohen, OMD, LAc 20 S E C T I O N 3 Alternative Eastern Treatment Options Traditional Chinese Medicine for HCV/HIV Coinfection Many people with the hepatitis
This article is downloaded from.
 This article is downloaded from http://researchoutput.csu.edu.au It is the paper published as: Author: G.-Y. Li, J.-Z. Liu, S.-G. Chen, C.-B. Wang, B. Zhang and L. Wang Title: Effect of a seashell protein
This article is downloaded from http://researchoutput.csu.edu.au It is the paper published as: Author: G.-Y. Li, J.-Z. Liu, S.-G. Chen, C.-B. Wang, B. Zhang and L. Wang Title: Effect of a seashell protein
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Original Article Vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphisms and lung cancer risk
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):6406-6411 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003921 Original Article Vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphisms and lung cancer risk Junli Fan 1, Weiguo Zhang 1, Caipeng
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(4):6406-6411 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003921 Original Article Vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphisms and lung cancer risk Junli Fan 1, Weiguo Zhang 1, Caipeng
Relationship Between GSTT1 Gene Polymorphism and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients from China
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Relationship Between GSTT1 Gene Polymorphism and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients from China Jie Chen, Liang Ma, Ning-Fu Peng, Shi-Jun Wang, Le-Qun Li* Abstract Objective: The results
RESEARCH ARTICLE Relationship Between GSTT1 Gene Polymorphism and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients from China Jie Chen, Liang Ma, Ning-Fu Peng, Shi-Jun Wang, Le-Qun Li* Abstract Objective: The results
Literature-based analysis on relationship of symptoms, drugs and therapies in treatment of intestinal diseases
 Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 0 February ; (): 6- info@journaltcm.com ISSN 05-9 0 JTCM. All rights reserved. LITERATURE STUDY TOPIC Literature-based analysis on relationship
Online Submissions: http://www.journaltcm.com J Tradit Chin Med 0 February ; (): 6- info@journaltcm.com ISSN 05-9 0 JTCM. All rights reserved. LITERATURE STUDY TOPIC Literature-based analysis on relationship
The Big Picture. The Good & The Bad 9/13/2012
 ChiroCredit.com Presents: AcuPractice Seminars 211: Spleen / Stomach Spleen AKA: Pi Wife of the Stomach The Minister Of Agriculture The Official In Charge of T & T Stomach AKA: Wei Husband of the Spleen
ChiroCredit.com Presents: AcuPractice Seminars 211: Spleen / Stomach Spleen AKA: Pi Wife of the Stomach The Minister Of Agriculture The Official In Charge of T & T Stomach AKA: Wei Husband of the Spleen
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Research Article Bin Huang1, Zhang-ling Zhou1, Li-li Wang1, Cong Zuo2, Yan Lu3, Yong Chen3 OBJECTIVE METHODS RESULTS CONCLUSION KEYWORDS
 Journal Homepage: www.jcimjournal.com/jim www.elsevier.com/locate/issn/20954964 Available also online at www.sciencedirect.com. Copyright 2014, Editorial office. E-edition published by Elsevier (Singapore)
Journal Homepage: www.jcimjournal.com/jim www.elsevier.com/locate/issn/20954964 Available also online at www.sciencedirect.com. Copyright 2014, Editorial office. E-edition published by Elsevier (Singapore)
Colon cancer. Stages of cancer. TCM Anti-Cancer Centre Zhao Cheng R.TCMP, R.Ac., Ph.D.
 Colon cancer TCM Anti-Cancer Centre Zhao Cheng R.TCMP, R.Ac., Ph.D. Stages of cancer The staging of a carcinoma has to do with the size of the tumor, and the degree to which it has penetrated. When the
Colon cancer TCM Anti-Cancer Centre Zhao Cheng R.TCMP, R.Ac., Ph.D. Stages of cancer The staging of a carcinoma has to do with the size of the tumor, and the degree to which it has penetrated. When the
Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer
 Feng et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:737 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer Fan Feng 1, Yangzi
Feng et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:737 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer Fan Feng 1, Yangzi
