This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
|
|
|
- Adelia Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered by the Free Radical and Radiation Biology Program B-180 Med Labs The University of Iowa Iowa City, IA Spring 2001 Term Instructors: GARRY R. BUETTNER, Ph.D. LARRY W. OBERLEY, Ph.D. with guest lectures from: Drs. Freya Q. Schafer, Douglas R. Spitz, and Frederick E. Domann The Fine Print: Because this is a paper written by a beginning student as an assignment, there are no guarantees that everything is absolutely correct and accurate. In view of the possibility of human error or changes in our knowledge due to continued research, neither the author nor The University of Iowa nor any other party who has been involved in the preparation or publication of this work warrants that the information contained herein is in every respect accurate or complete, and they are not responsible for any errors or omissions or for the results obtained from the use of such information. Readers are encouraged to confirm the information contained herein with other sources. All material contained in this paper is copyright of the author, or the owner of the source that the material was taken from. This work is not intended as a threat to the ownership of said copyrights.
2 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 1 Ultraviolet Radiation and Skin Carcinogenesis by Jun Luo B-180 Medical Laboratories Free Radical and Radiation Biology Program The University of Iowa Iowa City, IA For 77:222, Spring April, 2001 BCC: basal cell carcinoma Cdk: cyclin-dependent kinase NMSC: non-melanoma skin cancer 1 O 2 : singlet oxygen ROS: reactive oxygen species UV: ultraviolet
3 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 2 Table of Content Pages Abstract 2 Introduction 3 Skin cancer epidemiology and UV carcinigenesis 3 Molecular biology and UV carcinogenesis 4 UV-induced Immunosuppression and skin cancer 6 UV-induced reactive oxygen species and skin cancer 6 Summary 8 References 9 Abstract Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is the main cause of skin cancer. Sun exposure in children increases the risk of skin cancer development in their later life. The identification of UV specific mutations in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in skin cancers provides confirmation at the molecular level of the importance of UV mutagenesis in skin carcinogenesis. Ultraviolet-induced skin immune supression may contribute to the carcinogenic effects of UV radiation. Ultravioletinduced reactive oxygen species can cause permanent genetic changes in photooncogenes and
4 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 3 tumor suppressor genes. This paper will review the recent developments in the understanding of the epidemiology, immunology, molecular and free radical biology of skin carcinogenesis. Introduction Ultraviolet (UV) radiation comprises a broad band of energy extending from 200 nm to the 400 nm range [1]. The UV part of the solar electromagnetic spectrum can be subdivided into three regions: UVC ( nm), UVB ( nm) and UVA ( nm). UVC radiation, although widely used in in vitro studies of the effects of UV radiation, is not relevant to human skin cancer as it is efficiently attenuated by the earth s atmosphere. UVB radiation is the main waveband responsible for sunburn, skin aging and skin cancer induction. UVA differs from UVB in a number of ways. UVA is the main component of terrestrial sunlight and accounts for more than 90% of the spectral energy in sunlight. UVA is carcinogenic and less biologically active than UVB. Both UVA and UVB are largely contributed to the increasing skin cancer [1]. Skin cancer epidemiology and UV carcinigenesis The incidence of skin cancer increased dramatically over the last years [2]. The evidence implicating sun exposure as the main cause of skin cancer is overwhelming. Studies of skin cancer incidence and mortality rates in people who have emigrated from areas of low to high ambient sun exposure suggest that sun exposure in childhood is especially important and the sharp change in relative risk for arrival in Australia before and after the age of 10 years suggests that the effects of UV radiation on the skin may be qualitatively different in early life [2]. The American service personnel who had brief periods of high intensity sun exposure in early life had
5 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 4 a increased incidence of skin cancer [3]. These findings imply that UV radiation can produce an irreversible change in melanocytes and kerotinocytes many years before the development of skin cancer. Also, the differences in body site distribution of skin cancer suggest that intermittent sun exposure is even more important than cumulative sun exposure as a risk factor [3]. Molecular biology and UV carcinogenesis Exposure to both UVB and UVA can cause genetic changes in many biological systems [4]. Although UVB is a much more efficient mutagen than UVA, there is evidence that UVA alone can induce mutations. For UVB the action spectra for DNA damage closely coincides with the absorption spectra of DNA and exposure produces pyrimidine photoproducts. Misrepair of these photoproducts is associated with a high frequency of C to T transitions at dypyrimidine sites which is a signature of UVB-induced DNA damage [5]. For VUA the spectra for DNA damage diverges from that for DNA absorption. Pyrimidine photoproducts are rare and do not correlate with mutation rates. The types of DNA damage associated with exposure to UVA are DNA strand breaks, and DNA to protein crosslinks [4]. The mutation at GC base pairs induced by UVA suggest that oxidative DNA damage is important. Critical target genes implicated in skin cancer development can be broadly divided into two types: oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes [6]. C to T type mutations at dypyrimidine dimer sites have been identified in oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes in both melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), providing evidence at the molecular level of the importance of
6 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 5 UVB as a mutagen. UV specific mutations in members of the Ras oncogen family have been reported in melanoma and NMSC [7]. C to T transitions at dypyrimidine sites in the p53 tumor suppressor are a common finding in human NMSC [8]. p53 mutations have also been detected in actinic keratosis and Bowen s disease of the skin which are though to be precancerous precursors of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) [9]. Also, Jonason etal found p53 mutant cells in normal sun exposed skin [10]. These findings indicate that p53 gene is an important target for UV induced mutations in keratinocytes in human skin. UV specific mutations in melanoma have been identified in the p16 tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 9p in some melanoma cell lines [11]. Petrocelli etal repoeted that UVB radiation induces p21 and mediates G1 and S phase checkpoints [12]. They found that UVB radiation caused a rise in p53 protein levels, in association with induction of p21 and cyclin G expression. UVB treatment of asynchronous neonatal rat keratinocytes led to a marked inhibition of replicative DNA synthesis and prolonged G1 and S phase arrests, persisting to 18-24h, with recovery of cycling by 36h post-uvb. G1 arrest was accompanied by inhibition of cyclin D-, E- and A-associated kinases. The association of cyclin E with Cdk2 was moderately reduced. An incremental binding of p21 with Cdk4 paralleled the inhibition of cyclin D1/Cdk4 kinase and similar rise in Cdk2 binding to p21 was associated with inhibition of cyclin E and cyclin A dependent kinases. Furthermore, a rise in measurable p21-cdk2 inhibitory activity paralleled the loss of G1 cyclin-dependent kinase activity, supporting the important role for p21 in the UVB-induced checkpoints [12]. Further evidence for the importance of UV-induced mutations in skin cancer development have emerged from studies of the patched tumor suppressor gene in basal cell carcinoma
7 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 6 (BCC). The patched gene, which is the human homolog of a gene originally identified in Drosophila, is mutated in patients with the naevoid BCC syndrome [13]. This syndrome is an autosomal dominant familial cancer syndrome which predisposes affected individuals to the development of multiple BCCs of skin. Mutation analysis of sporadic BCCs has shown that 50% of patched mutations in sporadic BCCs on sunexposed sites are UV specific [14]. UV-induced Immunosuppression and skin cancer In addition to the direct effects of UV radiation on keratinocytes and melanocytes there has been considerable speculation about the importance of alterations in skin immune function following UV radiation exposure in skin carcinogenesis [15]. The importance of the immune system in human skin carcinogenesis is dramatically illustrated by the marked increase in skin cancer incidence, particularly cutaneous SCCs in immunosuppressed organ transplant recipients. In mice, exposure to low dose UV radiation prevents rejection of highly immunogenic tumor cell lines. Also, UV radiation exposure decreases the ability to mount a delayed type hypersensitivity response when the initial immunization occurs on exposed skin. In humans this effect is seen with doses of UVB which produce little or no reddening of the skin [16]. These findings and the importance of pharmacological inhibition of the immune system as a risk factor for skin cancer indicate that UV-induced immunological injury is likely to contribute to the carcinogenic effects of UV radiation. UV-induced reactive oxygen species and skin cancer Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been shown to be involved in all three stages of carcinogenesis ( initiation, promotion and progression), and are produced by both UVA and
8 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 7 UVB component of sunlight [17]. Besides direct absorption of UVB-photons by DNA and subsequent structural changes, generation of ROS following UVA and UVB radiation requires the absorption of photons by endogenous photosensitizer molecules. The absorption of UVphotons by a sensitizer results in its electronically excited state. The excited sensitizer subsequently reacts with another substrate (type I reaction) or with oxygen (type II reaction). The resulting products of type I reactions are radicals or radical ions, where type II reactions produce ROS including superoxide anion (O - 2 ), and singlet oxygen ( 1 O 2 ). Superoxide dismutases can convert O - 2 to hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ). Hydrogen peroxide is able to cross all membranes easily. However, both O - 2 and H 2 O 2 can not react directly with DNA [18]. Therefore, both O - 2 and H 2 O 2 are thought to participate in the generation of more dangerous species such as hydroxyl radical (HO ). This can happen in vitro and in vivo by two mechanisms. Superoxide can reduce Fe(III) or Cu(II) and the subsequent Fe(II) or Cu(I) can reduce H 2 O 2 finally resulting in the generation of the HO via the Fenton reaction [19]. In vivo, O - 2 enhances a release of Fe(II) from [4Fe-4S] clusters of dehydratases and the released Fe(II) subsequently reduces H 2 O 2 to OH - and HO. In addition, O - 2 is able to release Fe(II) from ferritin. This release could also be mediated by UVB-generated O - 2. Using electron spin resonance techniques, HO has been detected in skin upon UV-irradiation [20]. Increased ROS upon UV radiation cause extensive damage to DNA (e.g. in tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes), proteins and lipids. Furthermore, ROS activate signal transduction pathways and modulate stress genes that regulate effector genes related to growth, cellular senescence and transformation of cells to a malignant matastatic phenotype [21]. DNA oxidation by 1 O 2 has been shown to give rise to G T transversions. Interestingly, G T
9 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 8 transversions are frequently observed in the hotspot codon 12 of Ha-ras and Ki-ras in nonmelanoma skin cancer [22]. These mutations could be generated by misreplication of 8- hydroxy-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo G) lesions induced by ROS. 8-oxo G is the major mutagenic oxidative DNA lesion and most likely involved in the formation of both spontaneous cancers and neoplasias induced by a number of prooxidant agents. In addition, G A transversions in the p53 tumor suppressor gene of non-melanoma skin cancer may also be due to 8-oxo G induced by ROS. In the multistep carcinogenesis, the second wild-type allele of a mutated tumor suppressor gene or a protooncogene is often inactivated, resulting in the loss of the compensatory effect of the wild-type allele and thus to the fully malignant phenotype. Summary The evidence implicating UV radiation as the most important skin carcinogen comes from the diverse aspects including clinical medicine, epidemiology, immunology, molecular and free radical biology. The key aspect over the next few years will be to determine the critical molecular changes in keratinocytes and melanocytes that underlie skin cancer development after UV radiation exposure.
10 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis 9 References 1. Speight EL, Dahl MG, Farr PM, etal. (1994) Actinic keratosis induced by use of sunbed. Br Med J. 308: Kricher A, Armstrong BK, English DR, etal. (1991) Pigmentary and cutaneous risk factors for non-melanocytic skin cancer - a case control study. Int J Cancer. 48: Ramani ML, Bennett RG. (1993) High prevalence of skin cancer in world war II serviceman stationed in the pacific theater. J Am Acad Dermatol. 28: Peak MJ, Peak JG. (1989) Solar-ultraviolet-induced damage to DNA. Photodermatol. 6: Mitchell DL, Jen L, Cleaver JE. (1992) Sequence specificity of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in DNA treated with solar (ultraviolet B) radiation. Nucl Acids Res. 20: Quinn AG. (1996) Molecular genetics of human non-melanoma skin cancer. Cancer Surv. 26: Bos JL. (1989) Ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 49: Dumaz N, Stary A, Soussi T, etal. (1994) Can we predict solar ultraviolet radiation as the causal event in human tumours by analysing the mutation spectra of p53 gene? Mutat Res. 307: Campbell C, Quinn AG, Ro YS, etal. (1993) p53 mutations are common and early events that precede tumor invasion in squamous cell neoplasia of the skin. J Invest Dermatol. 100: Jonason AS, Kunala S, Price GJ, etal. (1996) Frequent clones of p53-mutated keratinocytes in normal human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93: Kamb A, Gruis NA, Weaver Feldhaus J, etal. (1994) A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types. Sciences. 264: Petrocelli T, Poon R, Drucker DJ, etal. (1996) UVB radiation induces p21 and mediates G1 and S phase checkpoints. Oncogene.12: Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulos PG, etal. (1996) Mutations of the human homolog of drosophila patched in the neroid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell. 85:
11 J. Luo UV radiation and skin cacinogenesis Gailani MR, Stahle Backdahl M, Leffell DJ, etal. (1996) The role of the human homologue of drosophila patched in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Nat Gent. 14: Noonan FP, De Fabo EC, Kripke ML. (1981) Suppression of contact hypersensitivity by UV radiation and its relationship to UV-induced supression of yumor immunity. Photochem Photobiol. 34: Cooper KD, Oberhelman L, hamilton TA, etal. (1992) UV exposure reduces immunization rates and promotes tolerance to epicutaneous antigens in humans: relationship to dose, CD1a-DR + epidermal macrophage induction, and langerhans cell depletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89: Masini V, Noel-hudson MS, Wepiene J. (1994) Free radical damage by UV or hypoxanthine-xanthine oxidase in cultured human skin fibroblasts: protective effect of two human plasma fractions. Toxicol. 8: Halliwell B, Aruoma OI. (1991) DNA damage by oxygen-derived species: Its mechanism and measurement in mammalian systems. FEBS Lett. 281: Darr D, Fridovich I. (1994) Free radicals in cutaneous biology. J Invest Dermatol. 102: Jurkiewicz BA, Buettner GR. (1994) Ultraviolet-light-induced free radical formation in skin: an electron paramagnetic resonance study. Photochem Photobiol. 59: Cerutti RA. (1985) Prooxidant states and tumor promotion. Sciences. 227:
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
Work Place Carcinogens Solar Radiation and Skin Cancer. November 2013 Dr Mark Foley
 Work Place Carcinogens Solar Radiation and Skin Cancer November 2013 Dr Mark Foley Overview Work place carcinogens and skin cancer Who is a risk? Screening and Self skin exam Common skin cancers Many work
Work Place Carcinogens Solar Radiation and Skin Cancer November 2013 Dr Mark Foley Overview Work place carcinogens and skin cancer Who is a risk? Screening and Self skin exam Common skin cancers Many work
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Defining how BRAF and NRAS mutations cooperate with UVA and UVB light to initiate melanoma.
 Defining how BRAF and NRAS mutations cooperate with UVA and UVB light to initiate melanoma. Abstract Melanoma is the malignant transformation of pigment-producing melanocytes in the body. The majority
Defining how BRAF and NRAS mutations cooperate with UVA and UVB light to initiate melanoma. Abstract Melanoma is the malignant transformation of pigment-producing melanocytes in the body. The majority
UV and Children s Skin
 UV and Children s Skin Beate Volkmer and Rüdiger Greinert Division of Molecular Cellbiology Center of Dermatology, Elbeklinikum Buxtehude Germany Epidemiological studies indicate that sunburns in childhood
UV and Children s Skin Beate Volkmer and Rüdiger Greinert Division of Molecular Cellbiology Center of Dermatology, Elbeklinikum Buxtehude Germany Epidemiological studies indicate that sunburns in childhood
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA)
 Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on the Use of Sunbeds Introduction A sunbed, also known as a tanning bed or sun tanning bed, is a device that emits ultraviolet radiation (typically
Cancer Association of South Africa (CANSA) Fact Sheet on the Use of Sunbeds Introduction A sunbed, also known as a tanning bed or sun tanning bed, is a device that emits ultraviolet radiation (typically
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
House Health Care Committee
 March 11, 2015 House Health Care Committee From: Dr. Sancy Leachman, Chair, Department of Dermatology, OHSU RE: Support for HB 3041 Dear Members of the House Health Care Committee: The purpose of my testimony
March 11, 2015 House Health Care Committee From: Dr. Sancy Leachman, Chair, Department of Dermatology, OHSU RE: Support for HB 3041 Dear Members of the House Health Care Committee: The purpose of my testimony
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
Sunscreens and cutaneous neoplasia:
 Sunscreens and cutaneous neoplasia: Overview and update from the literature Catherine Olsen, Louise Wilson, Neela Biswas, Juhi Loyalka, David Whiteman Cancer Control Group QIMR Berghofer Medical Research
Sunscreens and cutaneous neoplasia: Overview and update from the literature Catherine Olsen, Louise Wilson, Neela Biswas, Juhi Loyalka, David Whiteman Cancer Control Group QIMR Berghofer Medical Research
UVB Induced Mutation of p53 in Non Melanoma Skin Cancer Raizy Berger
 UVB Induced Mutation of p53 in Non Melanoma Skin Cancer graduated June 2018 with a B.S. degree in Biology and is currently attending the Physician Assistant Program at Touro College Manhattan. Abstract
UVB Induced Mutation of p53 in Non Melanoma Skin Cancer graduated June 2018 with a B.S. degree in Biology and is currently attending the Physician Assistant Program at Touro College Manhattan. Abstract
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
The European Commission's non-food Scientific Committees DG SANTE Country Knowledge and Scientific Committee Unit
 The European Commission's non-food Scientific Committees DG SANTE Country Knowledge and Scientific Committee Unit SCENIHR Opinion: Biological effects of UV radiation relevant to health with particular
The European Commission's non-food Scientific Committees DG SANTE Country Knowledge and Scientific Committee Unit SCENIHR Opinion: Biological effects of UV radiation relevant to health with particular
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS. (Start your clickers)
 MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS (Start your clickers) How do mutations arise? And how do they affect a cell and its organism? Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA But
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS (Start your clickers) How do mutations arise? And how do they affect a cell and its organism? Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA But
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
 MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
Early Embryonic Development
 Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
Early Embryonic Development Maternal effect gene products set the stage by controlling the expression of the first embryonic genes. 1. Transcription factors 2. Receptors 3. Regulatory proteins Maternal
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
Carcinogenesis. pathophysiology of altered cellular growth. Prof. Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv
 Carcinogenesis pathophysiology of altered cellular growth. Prof. Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv 1 Neoplasia - definition Neoplasia ("new growth ) is the
Carcinogenesis pathophysiology of altered cellular growth. Prof. Blagoi Marinov, MD, PhD Pathophysiology Department Medical University of Plovdiv 1 Neoplasia - definition Neoplasia ("new growth ) is the
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
Quantitative assessment of human exposure UVA radiation
 Environmental Exposure and Health 329 Quantitative assessment of human exposure UVA radiation M. G. Kimlin 1, A. V. Parisi 2, J. M. Macaranas 1 & D. J. Turnbull 1,2 1 Centre for Health Research, School
Environmental Exposure and Health 329 Quantitative assessment of human exposure UVA radiation M. G. Kimlin 1, A. V. Parisi 2, J. M. Macaranas 1 & D. J. Turnbull 1,2 1 Centre for Health Research, School
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
SUN, SAVVY AND SKIN : A REVIEW OF SKIN CANCER IN SOUTH AFRICA AND BEYOND
 SUN, SAVVY AND SKIN : A REVIEW OF SKIN CANCER IN SOUTH AFRICA AND BEYOND Dr Lester M. Davids Redox Laboratory, Dept of Human Biology University of Cape Town Crafting a Road Map for Research on Sun Exposure
SUN, SAVVY AND SKIN : A REVIEW OF SKIN CANCER IN SOUTH AFRICA AND BEYOND Dr Lester M. Davids Redox Laboratory, Dept of Human Biology University of Cape Town Crafting a Road Map for Research on Sun Exposure
nuclear science and technology
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
EUROPEAN COMMISSION nuclear science and technology Radiation-specific DNA non-double strand break lesions: repair mechanisms and biological effects (Non-DSB Lesions) Contract N o FIGH-CT2002-00207 Final
Functional Limitations
 Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
Regulation of the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Functional Limitations Various factors determine whether and when a cell divides. Two functional limitations for cell size limit growth or influence
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB. Friday, February 13, :30 am 11:00 am
 MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
MECHANISMS OF HUMAN DISEASE: LABORATORY SESSION PATHOLOGY OF THE SKIN LAB Friday, February 13, 2009 9:30 am 11:00 am FACULTY COPY GOALS: Describe the basic clinical and morphologic features of various
HEALTH EFFECTS Biology Dr. Rüdiger Greinert Head of Dept. Mol. Cellbiology Skin Cancer Center Buxtehude/Elbeclinics Buxtehude
 Scientific Committee on Health, Environmental and Emerging Risks (SCHEER) Opinion on Biological effects of ultraviolet radiation relevant to health with particular reference to sunbeds for cosmetic purposes
Scientific Committee on Health, Environmental and Emerging Risks (SCHEER) Opinion on Biological effects of ultraviolet radiation relevant to health with particular reference to sunbeds for cosmetic purposes
Skin Cancer and Vitamin D
 Skin Cancer and Vitamin D British Society for Dermatological Surgery Undergraduate Essay Prize 2013 Verity Williams Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Queen Mary, University of London
Skin Cancer and Vitamin D British Society for Dermatological Surgery Undergraduate Essay Prize 2013 Verity Williams Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry Queen Mary, University of London
HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.161 Molecular Biology and Genetics in Modern Medicine Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Carcinogenic potential of solar radiation and artificial sources of UV radiation
 Carcinogenic potential of solar radiation and artificial sources of UV radiation 1 Introduction Exposure of the eyes and skin to ultraviolet radiation may lead to both acute and long-term damage. Where
Carcinogenic potential of solar radiation and artificial sources of UV radiation 1 Introduction Exposure of the eyes and skin to ultraviolet radiation may lead to both acute and long-term damage. Where
Men and Women Are Not Just From Different Planets: The Role of Sex- Based Differences in the Prevention of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer DISSERTATION
 Men and Women Are Not Just From Different Planets: The Role of Sex- Based Differences in the Prevention of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
Men and Women Are Not Just From Different Planets: The Role of Sex- Based Differences in the Prevention of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer DISSERTATION Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
Sun Safety and Skin Cancer Prevention. Maryland Skin Cancer Prevention Program
 Sun Safety and Skin Cancer Prevention Maryland Skin Cancer Prevention Program Do You Know the Facts About Skin Cancer? Skin cancer is the most common cancer but also the most preventable Childhood sunburn
Sun Safety and Skin Cancer Prevention Maryland Skin Cancer Prevention Program Do You Know the Facts About Skin Cancer? Skin cancer is the most common cancer but also the most preventable Childhood sunburn
UV Index 3 as a cut-off
 Relative Response (Wn) UV Index - History The UV index was first introduced in Canada in 1992 in response to growing concerns about the potential increase of ultraviolet radiation due to ozone depletion(fioletov
Relative Response (Wn) UV Index - History The UV index was first introduced in Canada in 1992 in response to growing concerns about the potential increase of ultraviolet radiation due to ozone depletion(fioletov
Sunlight-Induced Immunosuppression in Humans Is Initially Because of UVB, Then UVA, Followed by Interactive Effects
 Sunlight-Induced Immunosuppression in Humans Is Initially Because of UVB, Then UVA, Followed by Interactive Effects Terence S. C. Poon, Ross St. C. Barnetson, and Gary M. Halliday Discipline of Medicine
Sunlight-Induced Immunosuppression in Humans Is Initially Because of UVB, Then UVA, Followed by Interactive Effects Terence S. C. Poon, Ross St. C. Barnetson, and Gary M. Halliday Discipline of Medicine
The Global Solar UV Index and Health Effects of UV Exposure
 German Meteorological Service, Human Biometeorology, Stefan-Meier-Str. 4, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany The Global Solar UV Index and Health Effects of UV Exposure Introduction Everyone is exposed to Ultraviolet
German Meteorological Service, Human Biometeorology, Stefan-Meier-Str. 4, D-79104 Freiburg, Germany The Global Solar UV Index and Health Effects of UV Exposure Introduction Everyone is exposed to Ultraviolet
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline. University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology
 Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
Neoplasia Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea School of Medicine & Health Sciences Division of Pathology General Considerations Overview: Neoplasia uncontrolled,
THE CANCER/MITOSIS CONNECTION
 THE CANCER/MITOSIS CONNECTION All cells have a controlled rate of division that is appropriate for their role in the body. Rates of Division ex. The cells of the skin reproduces perfectly so that it does
THE CANCER/MITOSIS CONNECTION All cells have a controlled rate of division that is appropriate for their role in the body. Rates of Division ex. The cells of the skin reproduces perfectly so that it does
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
AN ACTIVE SHELTER AGAINST POLLUTION V.16
 AN ACTIVE SHELTER AGAINST POLLUTION V.16 THE SKIN IS CONSTANTLY EXPOSED The skin is an interface and thus is constantly exposed to environmental agents: Sun radiation Smoke Air pollution Free radicals
AN ACTIVE SHELTER AGAINST POLLUTION V.16 THE SKIN IS CONSTANTLY EXPOSED The skin is an interface and thus is constantly exposed to environmental agents: Sun radiation Smoke Air pollution Free radicals
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
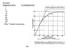 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
An analysis of cumulative lifetime. solar ultraviolet radiation exposure and the benefits of daily sun protection
 Dermatologic Therapy, Vol. 17, 2004, 57 62 Printed in the United States All rights reserved Copyright Blackwell Publishing, Inc., 2004 DERMATOLOGIC THERAPY ISSN 1396-0296 An analysis of cumulative lifetime
Dermatologic Therapy, Vol. 17, 2004, 57 62 Printed in the United States All rights reserved Copyright Blackwell Publishing, Inc., 2004 DERMATOLOGIC THERAPY ISSN 1396-0296 An analysis of cumulative lifetime
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
Photoprotection Beyond UV Spectrum
 Photoprotection Beyond UV Spectrum Henry W. Lim, MD Chair Emeritus, Department of Dermatology Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan Disclosure Investigator:
Photoprotection Beyond UV Spectrum Henry W. Lim, MD Chair Emeritus, Department of Dermatology Senior Vice President for Academic Affairs Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan Disclosure Investigator:
Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit
 Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2525 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H₂O₂ in a variety
Human Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2525 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H₂O₂ in a variety
Research Paper Outline
 Anika De Vore P.1 9/23/11 Research Paper Outline I. Introduction: Ultraviolet Radiation Main Ideas: Description & Origins of Term Ultraviolet Classification Sources of UV Blocking UV Variability of UV
Anika De Vore P.1 9/23/11 Research Paper Outline I. Introduction: Ultraviolet Radiation Main Ideas: Description & Origins of Term Ultraviolet Classification Sources of UV Blocking UV Variability of UV
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture:
 Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Skin Malignancies Non - Melanoma & Melanoma Marilyn Ng, MD Dept. of Surgery M&M Conference Downstate Medical Center July 19, 2012
 Skin Malignancies Non - Melanoma & Melanoma Marilyn Ng, MD Dept. of Surgery M&M Conference Downstate Medical Center July 19, 2012 Case Presentation 57 yo man with 3 month hx of a nonhealing < 1 cm right
Skin Malignancies Non - Melanoma & Melanoma Marilyn Ng, MD Dept. of Surgery M&M Conference Downstate Medical Center July 19, 2012 Case Presentation 57 yo man with 3 month hx of a nonhealing < 1 cm right
Cancer genetics
 Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
Cancer genetics General information about tumorogenesis. Cancer induced by viruses. The role of somatic mutations in cancer production. Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressor Genes (TSG). Hereditary cancer. 1
NEOPLASIA. 3. Which of the following tumour is benign a. Chondrosarcoma b. Osteochondroma c. Chondroblastoma d. Ewing s tumour e.
 NEOPLASIA 1. malignant neoplasms a. are independent of hormonal influence b. are always composed of homogenous cell lines c. arise from differentiated cells by a process of anaplasia d. display abnormal
NEOPLASIA 1. malignant neoplasms a. are independent of hormonal influence b. are always composed of homogenous cell lines c. arise from differentiated cells by a process of anaplasia d. display abnormal
Biochemistry 201: DNA repair January 24, 26, 2000 Gilbert Chu
 1) Why study DNA repair? Biochemistry 201: DNA repair January 24, 26, 2000 Gilbert Chu The genome is assaulted by a myriad of different agents that cause DNA damage. Sources of damage can be both exogenous
1) Why study DNA repair? Biochemistry 201: DNA repair January 24, 26, 2000 Gilbert Chu The genome is assaulted by a myriad of different agents that cause DNA damage. Sources of damage can be both exogenous
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit
 Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2552 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H2O2 in
Mouse Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Fluorescent Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2552 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hydrogen Peroxide Fluorescent Detection Kit is designed to quantitatively measure H2O2 in
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Bone, soft tissue and skin tumors. By: Shefaa qa qa
 Bone, soft tissue and skin tumors By: Shefaa qa qa Bone tumors Most bone neoplasms develop during the first several decades of life and have a propensity for the long bones of the extremities. The occurrence
Bone, soft tissue and skin tumors By: Shefaa qa qa Bone tumors Most bone neoplasms develop during the first several decades of life and have a propensity for the long bones of the extremities. The occurrence
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Skin Care in Renal Transplant Patients
 Skin Care in Renal Transplant Patients Introduction Skin Care in Renal Transplant Patients Skin care is very important for everyone, but particularly for renal patients who have received transplants. Because
Skin Care in Renal Transplant Patients Introduction Skin Care in Renal Transplant Patients Skin care is very important for everyone, but particularly for renal patients who have received transplants. Because
Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment
 Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment The reactive oxygen species (ROS) are group of very unstable compounds that
Sensitivity of mammalian cells to higher concentrations of reactive oxygen species induced by radiation or chemical treatment The reactive oxygen species (ROS) are group of very unstable compounds that
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 202-BZG-05 03
 DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 202-BZG-05 03 TEST 1 11 MARCH 2010 INSTRUCTOR: I. DIONNE PRINT YOUR NAME: Answers INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions in the space provided.
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II 202-BZG-05 03 TEST 1 11 MARCH 2010 INSTRUCTOR: I. DIONNE PRINT YOUR NAME: Answers INSTRUCTIONS: Answer all questions in the space provided.
Chapter 16 Mutations. Practice Questions:
 Biology 234 J. G. Doheny Chapter 16 Mutations Practice Questions: Answer the following questions with one or two sentences. 1. List the name of one test that can be used to identify mutagens. 2. What is
Biology 234 J. G. Doheny Chapter 16 Mutations Practice Questions: Answer the following questions with one or two sentences. 1. List the name of one test that can be used to identify mutagens. 2. What is
WHY IS NEW ZEALAND S MELANOMA PROBLEM SO BAD?
 WHY IS NEW ZEALAND S MELANOMA PROBLEM SO BAD? Gerald Smith Industrial Research Limited PO Box 31-310, Lower Hutt The annual incidence of melanoma amongst the non-maori population in New Zealand has doubled
WHY IS NEW ZEALAND S MELANOMA PROBLEM SO BAD? Gerald Smith Industrial Research Limited PO Box 31-310, Lower Hutt The annual incidence of melanoma amongst the non-maori population in New Zealand has doubled
Lecture: Variability. Different types of variability in Biology and Medicine. Cytological essentials of heritable diseases. Plan of the lecture
 Lecture: Variability. Different types of variability in Biology and Medicine. Cytological essentials of heritable diseases Plan of the lecture 1. Notion of variability. Different types of variability.
Lecture: Variability. Different types of variability in Biology and Medicine. Cytological essentials of heritable diseases Plan of the lecture 1. Notion of variability. Different types of variability.
The effect of UVA irradiation on the DNA damage response in a human keratinocyte cell line
 The effect of UVA irradiation on the DNA damage response in a human keratinocyte cell line Matthew Eastham Division of Biomedical and Life Sciences Faculty of Health and Medicine Lancaster University Thesis
The effect of UVA irradiation on the DNA damage response in a human keratinocyte cell line Matthew Eastham Division of Biomedical and Life Sciences Faculty of Health and Medicine Lancaster University Thesis
I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee
 I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee Some thoughts Is this skin cancer? How common is this? How likely is this in this patient? What happens next if it s something
I have a skin lump doc! What s next? 12 th August 2017 Dr. Sue-Ann Ho Ju Ee Some thoughts Is this skin cancer? How common is this? How likely is this in this patient? What happens next if it s something
Chapter 9. Cells Grow and Reproduce
 Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
Chapter 9 Cells Grow and Reproduce DNA Replication DNA polymerase Addition of a nucleotide to the 3 end of a growing strand Use dntps as substrate Release of pyrophosphate Initiation of Replication Replication
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY CLINICAL, HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE EPITHELIAL PRECANCEROUS LESIONS PRECURSORS OF
Breakup Of The Ward Ice Shelf Antarctica 2004
 Breakup Of The Ward Ice Shelf Antarctica 2004 http://sedac.ciesin.org/ozone/docs/uvd-home.html Medical Ecology Of Stratospheric Ozone Depletion: Impacts on the Human Condition Photo Aging UVB Solar Radiation
Breakup Of The Ward Ice Shelf Antarctica 2004 http://sedac.ciesin.org/ozone/docs/uvd-home.html Medical Ecology Of Stratospheric Ozone Depletion: Impacts on the Human Condition Photo Aging UVB Solar Radiation
Radiation Oncology. Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology
 Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
Radiation Oncology Initial Certification Qualifying (Computer-based) Examination: Study Guide for Radiation and Cancer Biology This exam tests your knowledge of the principles of cancer and radiation biology
In vitro studies to assess the potential of Quercetin as a topical. sunscreen; photooxidative properties, photostability and inhibition of UV
 In vitro studies to assess the potential of Quercetin as a topical sunscreen; photooxidative properties, photostability and inhibition of UV radiation-mediated skin damage A Thesis Submitted to the College
In vitro studies to assess the potential of Quercetin as a topical sunscreen; photooxidative properties, photostability and inhibition of UV radiation-mediated skin damage A Thesis Submitted to the College
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Mastomys coucha: A natural animal model for papillomavirus-induced skin carcinogenesis
 Mastomys coucha: A natural animal model for papillomavirus-induced skin carcinogenesis Kai Schaefer, Julia Nafz, Myriam Ibberson and Frank Rösl Angewandte Tumorvirologie, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum,
Mastomys coucha: A natural animal model for papillomavirus-induced skin carcinogenesis Kai Schaefer, Julia Nafz, Myriam Ibberson and Frank Rösl Angewandte Tumorvirologie, Deutsches Krebsforschungszentrum,
Field vs Lesional Therapies for AKs 3/2/2019, 9:00-12 AM
 Dilemmas and Challenges in Skin Cancer Therapies and Management Field vs Lesional Therapies for AKs 3/2/2019, 9:00-12 AM Roger I. Ceilley, M.D. Clinical Professor of Dermatology The University of Iowa
Dilemmas and Challenges in Skin Cancer Therapies and Management Field vs Lesional Therapies for AKs 3/2/2019, 9:00-12 AM Roger I. Ceilley, M.D. Clinical Professor of Dermatology The University of Iowa
( 2smooth muscle actin, 2SM actin)
 UV2C 234, 1999 4, 51 (2), 234 239 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 (, 510315) (220 W, 220 V, 50 Hz) UV2C (254 nm), 10 cm (smooth muscle cells, SM2 Cs),, ; / ; DNA UV2C SMCs SMCs : ; ; ; : Q2233 (smooth muscle
UV2C 234, 1999 4, 51 (2), 234 239 Acta Physiologica Sinica 3 (, 510315) (220 W, 220 V, 50 Hz) UV2C (254 nm), 10 cm (smooth muscle cells, SM2 Cs),, ; / ; DNA UV2C SMCs SMCs : ; ; ; : Q2233 (smooth muscle
