American College of Radiology Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
|
|
|
- Jason Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American College of Radiology Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The American College of Radiology (ACR) received $2,043,960 in formula funds for the grant award period January 1, 2010 through December 31, Accomplishments for the reporting period are described below. Research Project 1: Project Title and Purpose Novel Methods for Cancer Clinical Trial Design and Analysis - Clinical trials provide the critical evidence necessary to advance treatment for cancer. With the ever growing number of promising interventions, there is a need for improvements in trial design in order to a) obtain answers more quickly, b) conserve and optimize resources, and c) make better choices of what treatments to pursue in further evaluation. In addition, as treatment regimens become more complex and multimodal, the ability to accurately characterize whether anticipated benefits with respect to specific disease event reduction have occurred requires extensions of standard analytic methods. To address these needs, we propose a series of methodological projects aimed at addressing current questions in clinical trial design and analysis. These projects encompass a range of needs that apply broadly to cancer clinical trials and research in general. Anticipated Duration of Project 1/1/ /31/2013 Project Overview Three specific investigations are proposed as follows: Aim 1: Development and Use of an Efficient Phase II/III Transition Design The traditional paradigm for therapy development involves a pilot safety and efficacy trial (phase II) followed by a definitive Phase III comparative trial if warranted. This development model is intensive with respect to the time and logistical overhead involved in conducting sequential studies, and too often leads to failure in Phase III despite promising Phase II data on seemingly similar targeted populations. We propose to evaluate and implement a novel Phase II/III transition design that has thus far been little used in the oncology setting. Aim 2: Alternative Metrics for Time to Event Endpoints in Phase II and III Trials Phase II trials have traditionally been formulated as one-sample designs where all patients receive the treatment of interest. While statistical power for comparison to fixed benchmark values can be adequate American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 1
2 within a feasible sample size, the design suffers from dependence on historical comparisons that may not prove reliable. An alternative is a randomized Phase II design, where either a) treatment arms are not formally compared, but rather the arm that prevails to any degree is taken as more favorable with respect to further development, or b) adequately powered comparisons for simple endpoints such as fixed-time proportions failure-free are feasible. We propose analytic development of an approach using quantile (median, etc) estimation and comparison in the randomized Phase II setting. The approach is equally applicable to Phase III trials, and may have particular advantages in the presence of non-proportionality. Aim 3: Estimating Treatment and Covariate Effects Under Competing Risks Competing risks, whereby patients are subject to multiple potential failure types, with only one of these occurring as the primary first failure, are ubiquitous in cancer. In addition to multiple cancer-specific events (i.e., local, regional, distant recurrence), patients may experience second primary cancers or deaths from other causes that preclude any cancer event. While correct estimation of eventspecific probabilities of occurrence for competing risks is straightforward, inference in the presence of competing risks remains more challenging. We propose to investigate and compare different recently developed competing risks modeling methods. Principal Investigator James J Dignam, PhD Group Statistician, Radiation Therapy Oncology Group American College of Radiology 1818 Market Street, Suite 1600 Philadelphia, PA Other Participating Researchers Ed Zhang, PhD - employed by American College of Radiology Maria Kocherginsky, PhD - employed by University of Chicago Expected Research Outcomes and Benefits Cancer clinical trials are a critical component of cancer care and as all reliable treatment options arise through this process, it is only through systemic and comprehensive evaluation in a trial setting that the risks and benefits of any option can be assessed. However, the process can be slower than desired, is always process intensive, and requires the greatly valued contribution of patient participants, who are seeking the best possible option for their personal situation while at the same time contributing to research. In addition, an increasing array of agents in which to try in some disease settings further strains the development system. A more efficient treatment evaluation strategy could improve both knowledge acquisition and patient care. Previous proposals to accelerate the development process have often been too ambitious, and remain unused. We propose three areas of research that have immediate practical implications for cancer clinical trials. The integrated Phase II/III design fits well into the current framework while at the same time offering the opportunity to improve it, and thus is more likely to become widely used. More informative and reliable endpoints for Phase II trials are needed, as typical response endpoints often fail to correlate adequately with survival and also do not fully apply to many American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 2
3 modern therapeutic agents. Analytic methods that can more directly assess risks, benefits, and effects on intended targets will increase the efficiency of trials and produce more informative reports. This investigation will provide a concrete demonstration of the worth of these innovative concepts, furthering knowledge in cancer research and treatment. Summary of Research Completed James Dignam, PhD, Radiation Therapy Oncology (RTOG) Group Statistician and Associate Professor of Biostatistics at the University of Chicago, is now the PI of this project and has replaced Meihua Wang, PhD, who is no longer employed by the ACR/RTOG. Aim 1: Development and Use of an Efficient Phase II/III Transition Design In the last progress report, we indicated that the manuscript for this project had been submitted to the journal Clinical Trials and had received a largely favorable review. We revised the manuscript and resubmitted it to Clinical Trials. After additional review, the paper was formally accepted in August 2012 and was published in December Citation: Wang M, Dignam JJ, Zhang QE, Degroot JF, Mehta MP, Hunsberger S. Integrated phase II/III clinical trials in oncology: A case study. Clin Trials. 9: , Aim 2: Alternative Metrics for Time to Event Endpoints in Phase II and III Trials Following last year s methodologic developments and simulations related to estimation of the difference in medians between two survival functions, we sought and developed clinical examples to illustrate the method. Specifically, we sought data with properties such non-proportionality and early censoring (before the median) in order to challenge the new method. To reiterate the method, complete survival times for censored observations are first imputed by drawing from the conditional distribution given survival up to the time of censoring. The difference in medians and the variance of this quantity are estimated using the formulae in Price and Bonett (2002), and Rubin s multiple imputation approach (1987) is used to obtain the total variance from which confidence intervals are derived. First, we impute survival times for each censored observation conditional on the Kaplan-Meier estimates Sj(t) in each group j = 1, 2, and then use complete data methods to construct the confidence interval for the difference in medians. Using the multiple imputation approach of Rubin (1978), each censored observation is imputed M times. Estimates from these M complete data sets are then combined to obtain a point estimate and the associated variance. We have sought data examples with specific features to evaluate the method. Two of these are presented briefly here, and two additional and most important examples are currently being analyzed, but must await publication of the primary results before these can be reported here. The first example is from NSABP R-01, a randomized trial in rectal cancer. The survival curves show reasonable proportionality that diminishes with time, and a minimal amount of censoring before the median difference, our target quantity for estimation. We focus on the subset of male patients, in whom a significant advantage for chemotherapy was noted. The median difference and associated variance were estimated by the proposed method and compared to two others American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 3
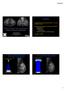
4 [Wang and Hettmansperger (shift model) 1990 and Su and Wei (purely nonparametric) 1993]. As seen in Figure 1, the proposed method has a slightly narrower confidence interval length than the Su and Wei method, but like it includes zero. The Wang and Hettmansperger method has the narrowest length and does not include zero. The second example uses a much smaller dataset from a University of Chicago clinical trial of bevacizumab in mesothelioma, where there was a large difference in outcomes based on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) status that was statistically significant according to the logrank test. Figure 2 shows the three methods applied to this dataset. Here, the proposed method has the narrowest confidence interval length. Thus, this easy to compute method performs comparably with less restrictive assumptions than Wang and Hettmansperger and similar confidence interval width to Su and Wei, and appeared to do particularly well in a small sample. The additional examples will involve much more extensive censoring before the median, one of the principal motivations for derivation of this method. We anticipate completion of these and the manuscript in Figure 1: Median difference estimates for NSABP R-01 data. Shown are estimates for the difference in median survival time by treatment arm according to the newly derived methods and two previously proposed methods. American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 4
5 Figure 2: Median difference estimates for the UC mesothelioma data. Shown are estimates for the difference in median survival time by treatment arm according to the newly derived methods and two previously proposed methods. Research Project 2: Project Title and Purpose Exploration of the RTOG Clinical Trial Database Beyond Protocol-Specified Endpoints - For over 40 years, the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) has been funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) to conduct clinical trials seeking to improve the survival and quality of life of cancer patients. Drawing upon this vast resource of demographic, treatment, outcome, and patient-reported data, the researchers will develop hypotheses and explore correlations that were not defined in the treatment protocols for patients with brain, cervix, gastrointestinal, head and neck, lung, and prostate cancer. These analyses may lead to future protocols and/or better ways to identify high-risk subgroups and screen patients for specific treatment regimens. Anticipated Duration of Project 1/1/ /31/2013 Project Overview RTOG investigators complete analyses and report on the endpoints specified in each NCIapproved protocol. Frequently these analyses raise questions or point to other potential hypotheses that were not included in the original protocol. Likewise, current literature and new research may point to areas of interest or possible correlations that were unknown during the design of the original protocol. The broad objectives of this research proposal are to (i) generate hypotheses and explore correlations that may lead to more efficient clinical trials and more patient-targeted treatments, and (ii) explore novel ways of analyzing the demographic (age, gender, race), treatment (including dose, volume, duration), outcome (survival, disease-free American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 5
6 survival, time-to-progression), and quality of life (frequency/severity of adverse events, patientreported outcomes) data in the RTOG database to potentially develop new tools for determining the best treatment regimen for each patient based upon their personal profile. Principal Investigator Kathryn A. Winter, MS RTOG Director, Statistics Radiation Therapy Oncology Group American College of Radiology 1818 Market Street, Suite 1600 Philadelphia, PA Other Participating Researchers Daniel Hunt, PhD, Jonathan Harris, MS, Jennifer Moughan, MS, Rebecca Paulus, MS, Wendy Seiferheld, MS employed by American College of Radiology Expected Research Outcomes and Benefits The identification of pre-treatment patient characteristics and demographics associated with better or worse outcome for cancer patients may allow future researchers to generate new hypotheses to address outcome disparities due to age, race, ethnic origin or gender. Exploring the radiation therapy dose volume histogram data in more detail will help with better definitions of dose constraints in future trials. In addition to aiding in the conduct of clinical trials, this type of research may help to tailor treatments to individual patients based on their demographic and/or treatment characteristics profile. Summary of Research Completed We have begun to analyze the relative contributions of pretreatment characteristics to the survival of patients treated with chemo radiation for unresectable carcinoma of the pancreas. The RTOG trials included in this analysis are: RTOG 0411, 0020, 9812, 9209, 9102, 8801, and Additional statistical analyses were performed on patients with LD-SCLC and LA-NSCLC enrolled on RTOG trials 0212 and The additional analyses were conducted to assess the impact of longitudinal decline in patient-reported quality of life (QOL) on disease relapse and overall survival following curative treatment for limited-disease small cell lung cancer (LD- SCLC) and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (LA-NSCLC). The manuscript reporting these results has been submitted to the Journal of Clinical Oncology. The manuscript reporting the results assessing the impact of PCI on self-reported cognitive functioning (SRCF), a two-item functional scale on the EORTC QLQ-C30 questionnaire, for patients following curative treatment for limited-disease small cell lung cancer (LD-SCLC) and locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (LA-NSCLC) is in press with the International Journal of Radiation Oncology Biology Physics. American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 6
7 Research Project 3: Project Title and Purpose Emerging Imaging Technology Clinical Trials in PA: Comparison of Full Field Digital Mammography with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Imaging: Comparison of Recall Rates - The purpose of this multi-center study, to be conducted as part of the American College of Radiology Imaging Network Pennsylvania, is to evaluate the digital breast tomosynthesis screening recall rates compared to routine 2D projection digital mammography. The goal is to understand if a hybrid combination of 3D tomosynthesis and low dose 2D digital mammography can significantly reduce the recall rate of women from screening mammography without a concomitant reduction of sensitivity of cancer detection. Anticipated Duration of Project 1/1/ /31/2013 Project Overview Previous C.U.R.E. funding established a network of medical centers in Pennsylvania (ACRIN PA) with the broad goal of advancing the role of imaging in the detection and/or treatment of disease by conducting early stage imaging clinical trials. This project seeks to continue the work of that network. A multi-institutional clinical trial is proposed to evaluate the impact of breast tomosynthesis on the recall rate of screening mammography. Study Hypothesis: Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) will improve the specificity of breast cancer screening as measured by a reduction in the recall rate while maintaining the sensitivity of cancer detection. This improved accuracy will be achieved by the optimization of the imaging sequence and number of views obtained at a capped radiation dose in the combined DBT and 2D screening sequence. Principal Investigator Mitchell D. Schnall, MD, PhD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Dept. of Radiology Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania 3400 Spruce St. Philadelphia, PA Other Participating Researchers Emily Conant, MD employed by University of Pennsylvania Andrew Maidment, PhD employed by University of Pennsylvania Constantine Gatsonis, PhD employed by Brown University American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 7
8 Expected Research Outcomes and Benefits Screening mammography has been extensively criticized for the high rate of false positive interpretations, a subgroup of which is the recall of patients for additional diagnostic imaging for pseudolesions or superimpositions of normal tissue, perceived on screening mammography to be potentially significant lesions that on additional imaging prove to be normal. With competing parameters of specificity and sensitivity, mammographic screening must both limit missed cancers and reduce false positive call-backs. Tomosynthesis, a new emerging technology that allows the 3D reconstruction of images, has shown early evidence suggesting that it could significantly reduce the rate of false positive recalls from screening without a loss of sensitivity or breast cancer detection. There are few published trials on breast cancer screening with tomosynthesis partly because the optimal procedural metrics for tomosynthesis have not been fully defined. Manufacturers have different platforms that offer different views, different angles, and different dose and exposure levels. The exact number of tomosynthesis views of the mediolateral-oblique (MLO) view only or both MLO and cranio-caudal (CC) tomosynthesis views varies while the screening imaging sequence with or without 2D digital mammography remains controversial. This disparity in image number and image acquisition parameters may alter the balance between specificity and sensitivity and significantly affect radiation dose. The expected outcome of this research is to show that the incorporation of tomosynthesis in the screening paradigm can reduce the number of false positive interpretations without a loss of cancer detection. This improvement in screening specificity must be gained while limiting both the number of imaging views and the radiation dose to the patient. Summary of Research Completed The study closed to accrual on January 6, 2012 with target enrollment achieved. Projected Milestone: July, 2012-June, complete participant follow-up, data cleaning, QC and analysisthe primary aim of the study, the comparison of call-back rates between full field digital mammography (FFDM) and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) showed no statistical significant difference. The study was greatly affected by the large variability of call-back rates between readers which ranged greatly from % for FFDM and from % for DBT as shown in Tables 1-3 at the end of the narrative. (Note 558 patients were accrued to the study; the target accrual was 550 cases and 501 had complete data for analysis.) The hypothesis driving the primary aim was that the addition of DBT imaging to FFDM would result in a lower call-back rate in a screening population. For 2 of the 8 readers the hypothesis held true. However, 3 readers experienced minimal change in call-back rate and 3 readers actually experienced an increase in call-back rate with the inclusion of DBT. The overall call back rate was similar between the two modalities for the group as a whole. In retrospect, a stronger design might have been achieved with fewer readers each reading more cases. As shown in tables 1 and 2, some readers read very few cases and did not read a balanced number of FFDM American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 8
9 and DBT cases. When evaluating the actual cases that were called back, there were 17 cases called back from both FFDM and DBT, 12 cases called back from FFDM only and 17 cases called back from DBT only. In the entire population accrued (including the enriched B arm), there were only 6 participants diagnosed with cancer (3 in each arm). Each cancer was detected on both FFDM and DBT imaging. A paired study design was used so that each patient underwent both routine screening digital mammogram (Standard-DM) and a low-dose, combined (DM+DBT) tomosynthesis imaging set (ACRIN Full). Cumulative mean glandular dose (MGD) was calculated in 495 women from exposure parameters of 2262 Standard-DM and 1980 low-dose DM+DBT acquisitions. Extra views in Standard-DM were obtained in some patients at the clinical discretion of reading radiologists or technicians. Sub-screening paradigms were defined based on the combination of images used to determine cumulative MGD values: Standard DM (CC+MLO), ACRIN-Limited (DM: MLO; DBT: MLO+CC), and ACRIN-Full (DM: MLO+CC; DBT: MLO+CC). The ACRIN-Limited MGD at Site A and Site B were 4.94 mgy and 5.29 mgy, respectively, while the Standard-DM MGD was 4.81 mgy and 3.52 mgy at Site A and B, respectively. (Please see Table 4 below) An additional 23.9% and 6.7% Standard-DM views were obtained at site A and B, respectively. After adjusting for extra views, the Standard-DM MGD was 3.85 mgy and 3.28 mgy at Site A and B, respectively. Our hypothesis was that it would be possible to perform the low-dose ACRIN-Limited DBT protocol at a dose comparable to the Standard DM. Comparison of MGD per breast between protocols was made by 2-sided paired Student s t-test. The ACRIN-Limited MGD did not differ significantly from Standard-DM at Site A (p=0.10) but was greater than Standard-DM at Site B (p<0.01). After adjusting for additional Standard-DM views, ACRIN-Limited dose was greater than Standard-DM at both sites (p<0.01). We attribute this difference to the fact that both sites were using very new DM technology that used doses significantly lower than the national average. The following abstract has been accepted for presentation at the American Association of Physicists in Medicine: Evaluation of Image Quality in Digital Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Phantom Observer Study from American College of Radiology Imaging Network PA 4006 Using Maximum Intensity Projection in the Evaluation of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: A Phantom Observer Study from the American College of Radiology Imaging Network PA 4006 Trial The following abstracts have been submitted to the Radiological Society of North America: ACRIN 4006: A study comparing the screening recall rates from 2D Digital American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 9
10 Mammography (DM) versus Combined low dose 2D plus Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) Effect of Reduced Radiation Dose on Breast Density Estimation in Digital Mammography: Data from the ACRIN 4006 Trial Prediction of False-Positive Recall from Screening Mammography in the ACRIN 4006 trial Using Computer-Extracted Breast Tissue Complexity Features Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Single Slice versus Slab Analysis of Objects: Phantom Observer Study from the American College of Radiology Imaging Network PA 4006 Trial ACRIN PA 4006: Comparison of Dose in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis and Standard Two-View Mammography for Prospective Breast Cancer Screening ACRIN PA 4006: Characterization of Mean Glandular Dose Adjusted to Volumetric Breast Density in a Prospective Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Screening Trial Table 1: FFDM reads and call-back by Reader (Group A only N=501*) Reader ID FFDM # Read FFDM call-back (%) Reader A 48 4 (8.3) Reader B 13 1 (7.7) Reader C 90 3 (3.3) Reader D (9.7) Reader E 42 4 (9.5) Reader F 76 4 (5.3) Reader G 42 1 (2.4) Reader H 87 2 (2.3) Total (5.8) American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 10
11 Table 2: DBT reads and call-back by Reader (Group A only) Reader ID DBT # Read DBT callback (%) Reader A 64 5 (7.8) Reader B 40 4 (10.0) Reader C (13.9) Reader D (7.0) Reader E 34 1 (2.9) Reader F 44 3 (6.8) Reader G 39 1 (2.6) Reader H 94 2 (2.1) Total (6.8) Table 3: Call-back rates per Reader by modality (Group A only) Reader FFDM Call-back(%) DBT Call-back (%) DBT vs FFDM Call-back rate Reader A Down minimally Reader B Up Reader C Up Reader D Down Reader E Down Reader F Up Reader G Up minimally Reader H Down minimally Total Up American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 11
12 Table 4: Comparison of Cumulative MGD per Breast by Protocol and Site Research Project 4: Project Title and Purpose Investigation and Analyses of Patient Co-Morbidities in a Survey of Radiation Oncology Facilities in the USA and their Association with Treatment Decisions in Radiation Oncology - The purpose of this project is to describe the distribution of co-morbidities by socio-demographic characteristics such as age, race, geographic region, insurance status and socio-economic status in patients diagnosed with cancer of the breast, cervix, stomach, lung and prostate, to investigate the association of the prevalence of co-morbidities with treatment decisions and variations in compliance with recommended disease management guidelines for such patients, and to examine the interaction of co-morbidities by site and stage of disease with gender, race, and age. Duration of Project 1/1/2010-7/2/2012 Project Overview Since 1973 the American College of Radiology (ACR) has conducted retrospective surveys of the processes of care in radiation oncology through the Quality Research in Radiation Oncology (QRRO, formerly Patterns of Care Study). Detailed information is collected from chart reviews on patient and tumor characteristics, imaging, treatment planning, surgery, radiation and systemic therapy with the purpose of measuring quality of care and comparing care actually received by patients to well-established clinical guidelines. These guidelines base treatment recommendations on tumor and patient characteristics, but provide little guidance on including patient co-morbidities in the treatment decision. Although co-morbidities are not part of the scope of the QRRO study, the current data collection American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 12
13 has included detailed data on co-morbidities for patients treated for breast, cervix, gastric and prostate cancers and non-small cell and limited stage small cell lung cancers. This project will investigate co-morbidity data in detail including interaction with other patient characteristics and association with treatment decisions. SPECIFIC AIMS 1. To describe the distribution of co-morbidities by socio-demographic characteristics such as age, race, geographic region, insurance status and socio-economic status in patients diagnosed with cancer of the breast, cervix, stomach, lung and prostate. 2. To investigate the association of the prevalence of co-morbidities with treatment decisions and variations in compliance with recommended disease management guidelines for such patients. 3. To examine the interaction of co-morbidities by site and stage of disease with gender, race, and age. Principal Investigator Jean B. Owen, PhD Senior Director American College of Radiology 1818 Market St., Suite 1600 Philadelphia, PA Other Participating Researchers Alex Ho, MS, MA, Najma Khalid, MS employed by American College of Radiology Expected Research Outcomes and Benefits This project will provide new information on the effect of co-morbidities on treatment decisions for cancer patients and the interaction of co-morbidities with other patient and tumor factors. This will help fill a knowledge gap in the application of nationally recognized treatment guidelines that currently allow vague exceptions to the established standard of care for patients who have multiple confounding medical problems. By providing analyses that help increase understanding of the impact of co-morbidities on treatment decisions, this project will help improve the standard of care for these patients. Summary of Research Completed This project ended on July 2, Although the researchers are no longer associated with the American College of Radiology, they and their collaborators have continued to draft manuscripts reporting the data analyses performed in this project for submission to peer reviewed journals. American College of Radiology 2009 Formula Grant Page 13
Outline. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation. Tomosynthesis Dataset: 2D/3D (Hologic Combo Acquisition)
 Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
Outline Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) the new standard of care Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Update and Pearls for Implementation Emily F. Conant, M.D. Professor, Chief of Breast Imaging Department
FDA Executive Summary
 Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
Meeting of the Radiological Devices Advisory Panel On October 24, 22, the panel will discuss, make recommendations, and vote on a premarket approval application supplement (P83/S) to expand the indications
Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become
 Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
Review Article Smith A, PhD email : Andrew.smith@hologic.com Since its introduction in 2000, digital mammography has become an accepted standard of care in breast cancer screening and has paved the way
American College of Radiology Annual Progress Report: 2010 Formula Grant
 American College of Radiology Annual Progress Report: 2010 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The American College of Radiology received $1,700,785 in formula
American College of Radiology Annual Progress Report: 2010 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The American College of Radiology received $1,700,785 in formula
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR)
 Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Screening with Abbreviated Breast MRI (AB-MR) Christopher Comstock, MD, FACR, FSBI Department of Radiology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center New York, NY Outline History of our approach to screening
Young Investigator Initiative for the Conduct of ACRIN Ancillary Research
 Program Purpose ACRIN is pleased to announce an opportunity for junior faculty (assistant professors and instructors within the first seven years post-fellowship or post-training) to carry out an ancillary
Program Purpose ACRIN is pleased to announce an opportunity for junior faculty (assistant professors and instructors within the first seven years post-fellowship or post-training) to carry out an ancillary
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: digital_breast_tomosynthesis 3/2011 6/2016 6/2017 11/2016 Description of Procedure or Service Conventional
Advice Statement 005/18 April 2018
 Advice Statement 005/18 April 2018 In asymptomatic women attending for breast screening, what is the clinical and cost effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) in addition to full-field digital
Advice Statement 005/18 April 2018 In asymptomatic women attending for breast screening, what is the clinical and cost effectiveness of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) in addition to full-field digital
Multicenter Trial, Phase I Assessment of 2-D FFDM Versus Combo of 2-D and 3-D Tomosynthesis in Breast Cancer Screening
 ACRIN PA 4006: Comparison of Full Field Digital Mammography with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Image Acquisition in Relation to Screening Call-Back Rate Imaging Manual Multicenter Trial, Phase I Assessment
ACRIN PA 4006: Comparison of Full Field Digital Mammography with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Image Acquisition in Relation to Screening Call-Back Rate Imaging Manual Multicenter Trial, Phase I Assessment
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? TERMS (AKA) WHAT IS TOMOSYNTHESIS? 3/3/2014. Digital breast tomosynthesis =
 #46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
#46: DIGITAL TOMOSYNTHESIS: What is the Data Really Showing? January K. Lopez, MD Hoag Breast Care Center Newport Beach, CA Disclosures: None TERMS (AKA) Digital breast tomosynthesis = DBT Tomo 3D Full
NIH NEW CLINICAL TRIAL REQUIREMENTS AND FORMS-E
 NIH NEW CLINICAL TRIAL REQUIREMENTS AND FORMS-E HOW DOES THE NIH DEFINE CLINICAL TRIAL AND HOW DO I KNOW IF MY STUDY IS ONE? 01-18-18 A clinical trial is defined by the NIH as a research study in which
NIH NEW CLINICAL TRIAL REQUIREMENTS AND FORMS-E HOW DOES THE NIH DEFINE CLINICAL TRIAL AND HOW DO I KNOW IF MY STUDY IS ONE? 01-18-18 A clinical trial is defined by the NIH as a research study in which
BreastScreen Victoria tomosynthesis screening trial, Maroondah pilot: Preliminary Outcomes
 BreastScreen Victoria tomosynthesis screening trial, Maroondah pilot: Preliminary Outcomes Dr Darren Lockie, Director and Chief Radiologist, Maroondah BreastScreen, Eastern Health Ms Michelle Clemson,
BreastScreen Victoria tomosynthesis screening trial, Maroondah pilot: Preliminary Outcomes Dr Darren Lockie, Director and Chief Radiologist, Maroondah BreastScreen, Eastern Health Ms Michelle Clemson,
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Susan Orel Roth, MD
 Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
Update of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Susan Orel Roth, MD NCI estimates that : Why DBT? Approximately 20% of breast cancers are missed at mammography screening Average recall rates approximately 10%
National Cancer Institute Clinical Trial Cooperative Groups
 National Cancer Institute Clinical Trial Cooperative Groups Perspectives from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Joyce Mull, MPM Director, Regulatory Affairs NSABP Foundation, Inc.
National Cancer Institute Clinical Trial Cooperative Groups Perspectives from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project Joyce Mull, MPM Director, Regulatory Affairs NSABP Foundation, Inc.
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose
 MicroDose Mammography Solutions Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose Several studies provide evidence that Philips MicroDose Mammography* can provide outstanding image quality at 18% to
MicroDose Mammography Solutions Proven clinical effectiveness at low radiation dose Several studies provide evidence that Philips MicroDose Mammography* can provide outstanding image quality at 18% to
TMIST A Bridge to Personalized Screening. Canadian Society of Breast Imaging April 26, 2018
 TMIST A Bridge to Personalized Screening Canadian Society of Breast Imaging April 26, 2018 Topics 1. Overview of TMIST Aims and Methods 2. Status of the Study (4/13/18) 3. How your site (in Canada) can
TMIST A Bridge to Personalized Screening Canadian Society of Breast Imaging April 26, 2018 Topics 1. Overview of TMIST Aims and Methods 2. Status of the Study (4/13/18) 3. How your site (in Canada) can
U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland Distribution Unlimited
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0236 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: EF5 PET of Tumor Hypoxia: A Predictive Imaging Biomarker of Response to Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) for Early Lung Cancer Billy
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0236 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: EF5 PET of Tumor Hypoxia: A Predictive Imaging Biomarker of Response to Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy (SABR) for Early Lung Cancer Billy
Lecture Outline Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I
 Lecture Outline Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics University of Washington Lecture 2: Statistical Classification of Scientific Questions Types of
Lecture Outline Biost 517 Applied Biostatistics I Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics University of Washington Lecture 2: Statistical Classification of Scientific Questions Types of
TMIST: Frequently Asked Questions
 TMIST: Frequently Asked Questions Key Topics for Site Investigators and Staff This document answers frequently asked questions about the Tomosynthesis Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial (TMIST/EA1151);
TMIST: Frequently Asked Questions Key Topics for Site Investigators and Staff This document answers frequently asked questions about the Tomosynthesis Mammographic Imaging Screening Trial (TMIST/EA1151);
The value of the craniocaudal mammographic view in breast cancer detection: A preliminary study
 The value of the craniocaudal mammographic view in breast cancer detection: A preliminary study P D Trieu 1, Prof. P C Brennan 1, Dr. W Lee 2, Dr. E Ryan 1, Dr. W Reed 1, Dr. M Pietrzyk 1 1. Medical Image
The value of the craniocaudal mammographic view in breast cancer detection: A preliminary study P D Trieu 1, Prof. P C Brennan 1, Dr. W Lee 2, Dr. E Ryan 1, Dr. W Reed 1, Dr. M Pietrzyk 1 1. Medical Image
Financial Disclosures
 Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Financial Disclosures 3D Mammography: The Latest Developments in the Breast Imaging Arena I have no financial disclosures Dr. Katharine Lampen-Sachar Breast and Body Radiologist Radiology Associates of
Accelerating Phase II-III Oncology Drug Development Through the Use of Adaptive Designs
 Accelerating Phase II-III Oncology Drug Development Through the Use of Adaptive Designs - Jonathan R. Smith, Ph.D. June 15th, 2004, DIA Annual Meeting, Washington Outline of Presentation Oncology Background
Accelerating Phase II-III Oncology Drug Development Through the Use of Adaptive Designs - Jonathan R. Smith, Ph.D. June 15th, 2004, DIA Annual Meeting, Washington Outline of Presentation Oncology Background
Lecture Outline. Biost 590: Statistical Consulting. Stages of Scientific Studies. Scientific Method
 Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies; Approach to Consulting Lecture Outline Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies Statistical Tasks Approach to
Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies; Approach to Consulting Lecture Outline Statistical Classification of Scientific Studies Statistical Tasks Approach to
Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography
 Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography Andrew Smith 1, Elizabeth Rafferty 2, Loren Niklason 1 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford MA, USA 2 Massachusetts
Breast tomosynthesis reduces radiologist performance variability compared to digital mammography Andrew Smith 1, Elizabeth Rafferty 2, Loren Niklason 1 1 Hologic, Inc., Bedford MA, USA 2 Massachusetts
Radiation Dosimetry in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. March, 2015 William J. O Connel, Dr. Ph, Senior Medical Physicist
 Radiation Dosimetry in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis March, 2015 William J. O Connel, Dr. Ph, Senior Medical Physicist Imagination at work. Syllabus 1. Introduction 2. Dosimetry in Mammography 3. Dosimetry
Radiation Dosimetry in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis March, 2015 William J. O Connel, Dr. Ph, Senior Medical Physicist Imagination at work. Syllabus 1. Introduction 2. Dosimetry in Mammography 3. Dosimetry
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update. Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
 Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Tomosynthesis and breast imaging update Dr Michael J Michell Consultant Radiologist King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Breast imaging new technology BREAST CANCER FLT PET shows different grades
Kish chakrabarti, Ph.D. Senior Physicist CDRH/FDA
 Facility Certification Extension Requirements, Quality Assurance and Medical Physicists role for Hologic Selenia Dimensions Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) System Kish chakrabarti, Ph.D. Senior Physicist
Facility Certification Extension Requirements, Quality Assurance and Medical Physicists role for Hologic Selenia Dimensions Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT) System Kish chakrabarti, Ph.D. Senior Physicist
2015 Patient Outcomes Report
 2015 Patient Outcomes Report Message from the Breast Leadership Team and Cancer Committee: On behalf of the Breast Leadership Team and Cancer Committee of The Hospitals, we are pleased to present to you
2015 Patient Outcomes Report Message from the Breast Leadership Team and Cancer Committee: On behalf of the Breast Leadership Team and Cancer Committee of The Hospitals, we are pleased to present to you
Demands and Perspectives of Hadron Therapy
 Demands and Perspectives of Hadron Therapy Alexander Lin, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Direction of Operations Roberts Proton Therapy Center Disclosures Teva Pharmaceuticals: Advisory
Demands and Perspectives of Hadron Therapy Alexander Lin, M.D. Assistant Professor University of Pennsylvania Direction of Operations Roberts Proton Therapy Center Disclosures Teva Pharmaceuticals: Advisory
8/3/2016. DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis. Tomosynthesis Pedigree
 DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
DBT Physics Basic to Advanced: Primer On Tomosynthesis Andrew D. A. Maidment, Ph.D. University of Pennsylvania Department of Radiology Acknowledgements of Support Research support from the Komen Foundation,
Mammography limitations. Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study
 Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
Clinical performance of digital breast tomosynthesis compared to digital mammography: blinded multi-reader study G. Gennaro (1), A. Toledano (2), E. Baldan (1), E. Bezzon (1), C. di Maggio (1), M. La Grassa
Critical reading of diagnostic imaging studies. Lecture Goals. Constantine Gatsonis, PhD. Brown University
 Critical reading of diagnostic imaging studies Constantine Gatsonis Center for Statistical Sciences Brown University Annual Meeting Lecture Goals 1. Review diagnostic imaging evaluation goals and endpoints.
Critical reading of diagnostic imaging studies Constantine Gatsonis Center for Statistical Sciences Brown University Annual Meeting Lecture Goals 1. Review diagnostic imaging evaluation goals and endpoints.
Volume 14 - Issue 3, Matrix
 Volume 14 - Issue 3, 2014 - Matrix Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Author ECRI ECRI Institute 29 Broadwater Road Suite 104 Welwyn Garden City AL7 3BQ United Kingdom
Volume 14 - Issue 3, 2014 - Matrix Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Screening and Diagnosis of Breast Cancer Author ECRI ECRI Institute 29 Broadwater Road Suite 104 Welwyn Garden City AL7 3BQ United Kingdom
Investigator Initiated Study Proposal Form
 Please submit completed form to IISReview@KCI1.com Date Submitted Name & Title Institution Address Phone Number Email Address Principal Investigator / Institution YES NO Multi Center Study Acelity Product(s)
Please submit completed form to IISReview@KCI1.com Date Submitted Name & Title Institution Address Phone Number Email Address Principal Investigator / Institution YES NO Multi Center Study Acelity Product(s)
Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
 Implementing a National Cancer Clinical Trials System for the 21 st Century, Workshop #2 Session #5: Accelerating Innovation Through Effective Partnerships Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
Implementing a National Cancer Clinical Trials System for the 21 st Century, Workshop #2 Session #5: Accelerating Innovation Through Effective Partnerships Accelerating Innovation in Statistical Design
1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background & Clinical Effectiveness Gillian Ells & Malcolm Oswald 24/11/2016
 Lead team presentation Nivolumab for treating recurrent or metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck after platinum-based chemotherapy [ID971] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background
Lead team presentation Nivolumab for treating recurrent or metastatic squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck after platinum-based chemotherapy [ID971] 1 st Appraisal Committee meeting Background
Title: Breast Screen Reader Assessment Strategy (BREAST): UK Collaboration
 Susan Williams CoRIPS Research Grant 147 5000 awarded Title: Breast Screen Reader Assessment Strategy (BREAST): UK Collaboration Principle Aim The principal aim of the study is to evaluate the performance
Susan Williams CoRIPS Research Grant 147 5000 awarded Title: Breast Screen Reader Assessment Strategy (BREAST): UK Collaboration Principle Aim The principal aim of the study is to evaluate the performance
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The NSABP Foundation
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 June 30, 2013 Formula Grant Overview The NSABP Foundation
Hepatitis B Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant
 Hepatitis B Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Hepatitis B Foundation received $654 in formula funds for the
Hepatitis B Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2011 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Hepatitis B Foundation received $654 in formula funds for the
2018 PUBLIC REPORTING OF OUTCOMES
 2018 PUBLIC REPORTING OF OUTCOMES The Cancer Committee at Western Maryland Health System s Schwab Family Cancer Center reports annually on program and patient outcomes in compliance with the accreditation
2018 PUBLIC REPORTING OF OUTCOMES The Cancer Committee at Western Maryland Health System s Schwab Family Cancer Center reports annually on program and patient outcomes in compliance with the accreditation
Sample Size Considerations. Todd Alonzo, PhD
 Sample Size Considerations Todd Alonzo, PhD 1 Thanks to Nancy Obuchowski for the original version of this presentation. 2 Why do Sample Size Calculations? 1. To minimize the risk of making the wrong conclusion
Sample Size Considerations Todd Alonzo, PhD 1 Thanks to Nancy Obuchowski for the original version of this presentation. 2 Why do Sample Size Calculations? 1. To minimize the risk of making the wrong conclusion
Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination?
 Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination? Poster No.: B-0926 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. Elizalde, P. Garcia Barquin, M.
Additional US or DBT after digital mammography: which one is the best combination? Poster No.: B-0926 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper A. Elizalde, P. Garcia Barquin, M.
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY
 EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
EARLY DETECTION: MAMMOGRAPHY AND SONOGRAPHY Elizabeth A. Rafferty, M.D. Avon Comprehensive Breast Center Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Breast Cancer Screening Early detection of
WHAT TO EXPECT. Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam. The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years
 WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
WHAT TO EXPECT Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY Exam The most exciting advancement in mammography in over 30 years 91% of patients agree the quality of care provided by the facility was better with a Genius 3D MAMMOGRAPHY
Instructions for Completing the UVMCC Clinical Research Protocol Submission Form UVMCC CLINICAL RESEARCH PROTOCOL SUBMISSION FORM
 Instructions for Completing the UVMCC Clinical Research Protocol Submission Form SUBMITTING THE APPLICATION 1. The PI must complete this application. National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) Protocols only
Instructions for Completing the UVMCC Clinical Research Protocol Submission Form SUBMITTING THE APPLICATION 1. The PI must complete this application. National Clinical Trials Network (NCTN) Protocols only
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography
 Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Challenges to Delivery of High Quality Mammography Overview of Current Challenges Barbara Monsees, Washington University Geographic Access, Equity and Impact on Quality Tracy Onega, Dartmouth Medical School
Research Questions and Survey Development
 Research Questions and Survey Development R. Eric Heidel, PhD Associate Professor of Biostatistics Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Graduate School of Medicine Research Questions 1 Research
Research Questions and Survey Development R. Eric Heidel, PhD Associate Professor of Biostatistics Department of Surgery University of Tennessee Graduate School of Medicine Research Questions 1 Research
Experience with Tomosynthesis (3-D) Mammography in a Mobile Setting and Current Controversies
 Experience with Tomosynthesis (3-D) Mammography in a Mobile Setting and Current Controversies Jennifer Lance, MHSA, MS Jerry McLarty, PhD LSU Feist-Weiller Cancer Center Shreveport LA Sept 15, 2008 A brief
Experience with Tomosynthesis (3-D) Mammography in a Mobile Setting and Current Controversies Jennifer Lance, MHSA, MS Jerry McLarty, PhD LSU Feist-Weiller Cancer Center Shreveport LA Sept 15, 2008 A brief
SKCC Protocol Review Committee New Study Application
 Instructions: Submit the following documents to prc@jefferson.edu - Completed New Study Application (aka MCSF) - Protocol - Protocol Facilitation Committee Approval (if applicable) - MDG Priority Score
Instructions: Submit the following documents to prc@jefferson.edu - Completed New Study Application (aka MCSF) - Protocol - Protocol Facilitation Committee Approval (if applicable) - MDG Priority Score
TITLE: A Phase II Trial of Androgen Suppression and Radiation Therapy with Samarium-1 53 in Localized, High-Risk, Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0769 TITLE: A Phase II Trial of Androgen Suppression and Radiation Therapy with Samarium-1 53 in Localized, High-Risk, Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Richard K. Valicenti,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0769 TITLE: A Phase II Trial of Androgen Suppression and Radiation Therapy with Samarium-1 53 in Localized, High-Risk, Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Richard K. Valicenti,
TITLE: Outcomes of Screening Mammography in Elderly Women
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-00-1-0193 TITLE: Outcomes of Screening Mammography in Elderly Women PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Philip W. Chu Rebecca Smith-Bindman, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California,
AD Award Number: DAMD17-00-1-0193 TITLE: Outcomes of Screening Mammography in Elderly Women PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Philip W. Chu Rebecca Smith-Bindman, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of California,
RECENT TRENDS. The Impact of the NCI and NIBIB
 The Impact of the NCI and NIBIB James Deye, Ph.D. Program Director on Medical Physics RECENT TRENDS doubling of the NIH budget over last 5 years; appointment of new heads of NIH and NCI; creation of NIBIB;
The Impact of the NCI and NIBIB James Deye, Ph.D. Program Director on Medical Physics RECENT TRENDS doubling of the NIH budget over last 5 years; appointment of new heads of NIH and NCI; creation of NIBIB;
Comparison Study: Impact of Thin Protective Coverlets on Positioning and Tissue Acquisition in Breast Imaging
 Comparison Study: Impact of Thin Protective Coverlets on Positioning and Tissue Acquisition in Breast Imaging Author: Steve K. Wagner Co-Author: Alex Merkulov, MD OBJECTIVE To determine whether the use
Comparison Study: Impact of Thin Protective Coverlets on Positioning and Tissue Acquisition in Breast Imaging Author: Steve K. Wagner Co-Author: Alex Merkulov, MD OBJECTIVE To determine whether the use
Mammographic Breast Density Classification by a Deep Learning Approach
 Mammographic Breast Density Classification by a Deep Learning Approach Aly Mohamed, PhD Robert Nishikawa, PhD Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD David Gur, ScD Shandong Wu, PhD Department of Radiology, University
Mammographic Breast Density Classification by a Deep Learning Approach Aly Mohamed, PhD Robert Nishikawa, PhD Wendie A. Berg, MD, PhD David Gur, ScD Shandong Wu, PhD Department of Radiology, University
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Community Benefit Strategic Implementation Plan. Better together.
 Community Benefit Strategic Implementation Plan 2016 2019 Better together. Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Priority 1: Community Health Infrastructure... 5 Objective 1.1: Focus resources strategically
Community Benefit Strategic Implementation Plan 2016 2019 Better together. Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Priority 1: Community Health Infrastructure... 5 Objective 1.1: Focus resources strategically
Statistics and Epidemiology Practice Questions
 1. Which of the following is not considered a measure of central tendency? a. Median b. Range c. Mode d. Average 2. Given the following set of values, what is the median? 4 5 9 3 8 3 7 1 5 3 a. 3 b. 5
1. Which of the following is not considered a measure of central tendency? a. Median b. Range c. Mode d. Average 2. Given the following set of values, what is the median? 4 5 9 3 8 3 7 1 5 3 a. 3 b. 5
Fundamental Clinical Trial Design
 Design, Monitoring, and Analysis of Clinical Trials Session 1 Overview and Introduction Overview Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics, University of Washington February 17-19, 2003
Design, Monitoring, and Analysis of Clinical Trials Session 1 Overview and Introduction Overview Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics, University of Washington February 17-19, 2003
The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000
 WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
WOMEN S HEALTH BREAST SOLUTIONS HEALTH The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 5000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Single Technology Appraisal (STA)
 Single Technology Appraisal (STA) Tisagenlecleucel-T for previously treated B-cell acute lymphoblastic Response to consultee and commentator comments on the draft remit and draft scope (pre-referral) Please
Single Technology Appraisal (STA) Tisagenlecleucel-T for previously treated B-cell acute lymphoblastic Response to consultee and commentator comments on the draft remit and draft scope (pre-referral) Please
TOMOSYNTHESIS. Daniela Bernardi. U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy
 TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
TOMOSYNTHESIS Daniela Bernardi U.O. Senologia Clinica e Screening mammografico APSS Trento, Italy BACKGROUND early detection through screening MAMMOGRAPHY is associated with reduced breast cancer morbidity
Expanding the Toolkit: The Potential for Bayesian Methods in Education Research (Symposium)
 Expanding the Toolkit: The Potential for Bayesian Methods in Education Research (Symposium) Symposium Abstract, SREE 2017 Spring Conference Organizer: Alexandra Resch, aresch@mathematica-mpr.com Symposium
Expanding the Toolkit: The Potential for Bayesian Methods in Education Research (Symposium) Symposium Abstract, SREE 2017 Spring Conference Organizer: Alexandra Resch, aresch@mathematica-mpr.com Symposium
DRAFT (Final) Concept Paper On choosing appropriate estimands and defining sensitivity analyses in confirmatory clinical trials
 DRAFT (Final) Concept Paper On choosing appropriate estimands and defining sensitivity analyses in confirmatory clinical trials EFSPI Comments Page General Priority (H/M/L) Comment The concept to develop
DRAFT (Final) Concept Paper On choosing appropriate estimands and defining sensitivity analyses in confirmatory clinical trials EFSPI Comments Page General Priority (H/M/L) Comment The concept to develop
Community Comprehensive Cancer Program at Swedish Covenant Hospital 2009 Annual Report reflecting 2008 statistical data
 Community Comprehensive Cancer Program at Swedish Covenant Hospital 2009 Annual Report reflecting 2008 statistical data Chairman s Message K. Joseph Philip, MD Section head, Medical Oncology/Hematology
Community Comprehensive Cancer Program at Swedish Covenant Hospital 2009 Annual Report reflecting 2008 statistical data Chairman s Message K. Joseph Philip, MD Section head, Medical Oncology/Hematology
Innovations in decreasing recall rates for screening mammography
 Tomosynthesis & Screening Moderators: Dr. Stephen A. Feig, Dr. Linda J. Warren Saturday, April 9, 1:30-2:30 p.m. Room: Brazos Innovations in decreasing recall rates for screening mammography CLINICAL RELEVANCE:
Tomosynthesis & Screening Moderators: Dr. Stephen A. Feig, Dr. Linda J. Warren Saturday, April 9, 1:30-2:30 p.m. Room: Brazos Innovations in decreasing recall rates for screening mammography CLINICAL RELEVANCE:
Objectives. Explanation of Radiation Dose Terminology 10/9/2018. What are these lines?
 Oh no, it s not!!! with Breast Tomosynthesis It s not what you may be thinking, so I ll tell you! IT IS A VIETNAMESE PUMPKIN! Oh yes, it is! Objectives Explain radiation dose terminology Recognize 2D and
Oh no, it s not!!! with Breast Tomosynthesis It s not what you may be thinking, so I ll tell you! IT IS A VIETNAMESE PUMPKIN! Oh yes, it is! Objectives Explain radiation dose terminology Recognize 2D and
Title: Meta-analysis of Individual patient Data (IPD) of Patients with INH (mono or poly-drug) Resistant Tuberculosis.
 Title: Meta-analysis of Individual patient Data (IPD) of Patients with INH (mono or poly-drug) Resistant Tuberculosis. Principal Investigator: Dick Menzies, MD Evidence base for treatment of INH resistant
Title: Meta-analysis of Individual patient Data (IPD) of Patients with INH (mono or poly-drug) Resistant Tuberculosis. Principal Investigator: Dick Menzies, MD Evidence base for treatment of INH resistant
FDA SUMMARY OF SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS DATA (SSED) CLINICAL SECTION CHECKLIST OFFICE OF DEVICE EVALUATION
 FDA SUMMARY OF SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS DATA (SSED) CLINICAL SECTION CHECKLIST OFFICE OF DEVICE EVALUATION Note to FDA PMA Reviewers: The Summary of Safety and Effectiveness (SSED) is a document mandated
FDA SUMMARY OF SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS DATA (SSED) CLINICAL SECTION CHECKLIST OFFICE OF DEVICE EVALUATION Note to FDA PMA Reviewers: The Summary of Safety and Effectiveness (SSED) is a document mandated
Bringing Together Clinical, Economic and Patient Reported Outcomes Data Future Of Real World Evidence. March IIeX Health, Philadelphia, PA
 Bringing Together Clinical, Economic and Patient Reported Outcomes Data Future Of Real World Evidence March 27 2018 IIeX Health, Philadelphia, PA Overview Current Landscape Data Sources to generate Real
Bringing Together Clinical, Economic and Patient Reported Outcomes Data Future Of Real World Evidence March 27 2018 IIeX Health, Philadelphia, PA Overview Current Landscape Data Sources to generate Real
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue. Public Meeting December 13, 2013
 Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Supplemental Screening for Women with Dense Breast Tissue Public Meeting December 13, 2013 Agenda Meeting Convened 10am-10:15am Presentation of the Evidence and Voting Questions, Q&A 10:15am 11:15am Discussion
Comparison of Futility Monitoring Methods Using RTOG Clinical Trials. Q. Ed Zhang, PhD
 Comparison of Futility Monitoring Methods Using RTOG Clinical Trials Q. Ed Zhang, PhD 1 Futility Monitoring Definition: Monitoring for early determination that trial results will not be in favor of H 1
Comparison of Futility Monitoring Methods Using RTOG Clinical Trials Q. Ed Zhang, PhD 1 Futility Monitoring Definition: Monitoring for early determination that trial results will not be in favor of H 1
AVEO and Astellas Announce Positive Findings from TIVO-1 Superiority Study of Tivozanib in First-Line Advanced RCC
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE AVEO and Astellas Announce Positive Findings from TIVO-1 Superiority Study of Tivozanib in First-Line Advanced RCC - Tivozanib is the First Agent to Demonstrate Greater than One Year
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE AVEO and Astellas Announce Positive Findings from TIVO-1 Superiority Study of Tivozanib in First-Line Advanced RCC - Tivozanib is the First Agent to Demonstrate Greater than One Year
The document history table was updated to include Amendment 6.
 For Protocol Amendment #6 to: RTOG 0913, Phase I/II Trial of Concurrent RAD001 (Everolimus) With Temozolomide/Radiation Followed by Adjuvant RAD001/Temozolomide in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma NCI Protocol
For Protocol Amendment #6 to: RTOG 0913, Phase I/II Trial of Concurrent RAD001 (Everolimus) With Temozolomide/Radiation Followed by Adjuvant RAD001/Temozolomide in Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma NCI Protocol
TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE?
 X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
X-Ray Associates of New Mexico, P.C. TOMOSYNTHESIS: WORTH ALL THE HYPE? MICHAEL N. LINVER, MD, FACR MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE NOT SO GOOD MAMMOGRAPHY: THE GOOD, THE PRETTY GOOD, & THE
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS. The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here. Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000
 WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
WOMEN S HEALTH SOLUTIONS The power and promise of breast tomosynthesis is here Selenia Dimensions system with Acquisition Workstation 8000 3D mammography: A new dimension in early breast cancer detection
CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN GERIATRICS *)
 3CC9a CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN GERIATRICS *) Guideline Title Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products in Geriatrics*) Legislative basis Directive 75/318/EEC, as amended Date
3CC9a CLINICAL INVESTIGATION OF MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN GERIATRICS *) Guideline Title Clinical Investigation of Medicinal Products in Geriatrics*) Legislative basis Directive 75/318/EEC, as amended Date
John T. Mather Memorial Hospital and St. Charles Hospital Community Health Needs Assessment: Cancer Executive Summary
 John T. Mather Memorial Hospital and St. Charles Hospital 2015 Community Health Needs Assessment: Cancer Executive Summary Purpose The purpose of the Mather-St. Charles Cancer Program 2015 Community Health
John T. Mather Memorial Hospital and St. Charles Hospital 2015 Community Health Needs Assessment: Cancer Executive Summary Purpose The purpose of the Mather-St. Charles Cancer Program 2015 Community Health
Women s Imaging Original Research
 Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Women s Imaging Original Research Brandt et al. DBT for Screening Recalls Without Calcifications Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: Kathleen R. Brandt 1 Daniel A. Craig 1 Tanya L. Hoskins 2 Tara
Checklist for Prevalence Studies. The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tools for use in JBI Systematic Reviews
 The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tools for use in JBI Systematic Reviews Checklist for Prevalence Studies http://joannabriggs.org/research/critical-appraisal-tools.html www.joannabriggs.org
The Joanna Briggs Institute Critical Appraisal tools for use in JBI Systematic Reviews Checklist for Prevalence Studies http://joannabriggs.org/research/critical-appraisal-tools.html www.joannabriggs.org
Breast health and screening
 Breast health and screening Dr Kathy Wong MBBS (HK), FRCR (UK), FHKCR FHKAM (Radiology) Clinical Radiologist Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Kwong Wah Hospital Questions regarding
Breast health and screening Dr Kathy Wong MBBS (HK), FRCR (UK), FHKCR FHKAM (Radiology) Clinical Radiologist Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Kwong Wah Hospital Questions regarding
Propensity Score Matching with Limited Overlap. Abstract
 Propensity Score Matching with Limited Overlap Onur Baser Thomson-Medstat Abstract In this article, we have demostrated the application of two newly proposed estimators which accounts for lack of overlap
Propensity Score Matching with Limited Overlap Onur Baser Thomson-Medstat Abstract In this article, we have demostrated the application of two newly proposed estimators which accounts for lack of overlap
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.05.012 06/28/2013 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST 06/28/2013 Section: Radiology Place(s) of Service:
Biost 590: Statistical Consulting
 Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Questions October 3, 2008 Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics, University of Washington 2000, Scott S. Emerson,
Biost 590: Statistical Consulting Statistical Classification of Scientific Questions October 3, 2008 Scott S. Emerson, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Biostatistics, University of Washington 2000, Scott S. Emerson,
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients
 Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Policy Library Clinical Advantages of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in Symptomatic Patients Version: 1 Approved by: Faculty of Clinical Radiology Council Date of approval: Click and type: day month and
Lung cancer is the most common cause of cancer death in
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of a Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Clinic on the Timeliness of Care Richard F. Riedel, MD,* Xiaofei Wang, PhD, Meg McCormack, PA-C,* Eric Toloza, MD, Gustavo S. Montana, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of a Multidisciplinary Thoracic Oncology Clinic on the Timeliness of Care Richard F. Riedel, MD,* Xiaofei Wang, PhD, Meg McCormack, PA-C,* Eric Toloza, MD, Gustavo S. Montana, MD,
Chapter 18 Section 2. EXPIRED - Department Of Defense (DoD) Cancer Prevention And Treatment Clinical Trials Demonstration
 s And Pilot Projects Chapter 18 Section 2 EXPIRED - Department Of Defense (DoD) Cancer Prevention And Treatment Clinical Trials 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this demonstration is to improve TRICARE-eligible
s And Pilot Projects Chapter 18 Section 2 EXPIRED - Department Of Defense (DoD) Cancer Prevention And Treatment Clinical Trials 1.0 PURPOSE The purpose of this demonstration is to improve TRICARE-eligible
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine
 International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
International Master Programm Biomedical Engineering Digital Breast Tomosynthesis from a first idea to clinical routine Historical background 2D imaging of 3D objects has important limitations Jörg Barkhausen
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Rollman BL, Herbeck Belnap B, Abebe KZ, et al. Effectiveness of online collaborative care for treating mood and anxiety disorders in primary care: a randomized clinical trial.
Supplementary Online Content Rollman BL, Herbeck Belnap B, Abebe KZ, et al. Effectiveness of online collaborative care for treating mood and anxiety disorders in primary care: a randomized clinical trial.
The following page contains the final YODA Project review approving this proposal.
 The YODA Project Research Proposal Review The following page contains the final YODA Project review approving this proposal. The Yale University Open Data Access (YODA) Project Yale University Center for
The YODA Project Research Proposal Review The following page contains the final YODA Project review approving this proposal. The Yale University Open Data Access (YODA) Project Yale University Center for
Statistical Considerations in Study Development: How to write good objectives!
 Statistical Considerations in Study Development: How to write good objectives! Emily Van Meter, PhD Assistant Professor, Division of Cancer Biostatistics University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center UK
Statistical Considerations in Study Development: How to write good objectives! Emily Van Meter, PhD Assistant Professor, Division of Cancer Biostatistics University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center UK
Statistical Considerations for Novel Trial Designs: Biomarkers, Umbrellas and Baskets
 Statistical Considerations for Novel Trial Designs: Biomarkers, Umbrellas and Baskets Bibhas Chakraborty, PhD Centre for Quantitative Medicine, Duke-NUS March 29, 2015 Personalized or Precision Medicine
Statistical Considerations for Novel Trial Designs: Biomarkers, Umbrellas and Baskets Bibhas Chakraborty, PhD Centre for Quantitative Medicine, Duke-NUS March 29, 2015 Personalized or Precision Medicine
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Page 1 of 31 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Professional Institutional Original Effective
BIOSTATISTICAL METHODS AND RESEARCH DESIGNS. Xihong Lin Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
 BIOSTATISTICAL METHODS AND RESEARCH DESIGNS Xihong Lin Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA Keywords: Case-control study, Cohort study, Cross-Sectional Study, Generalized
BIOSTATISTICAL METHODS AND RESEARCH DESIGNS Xihong Lin Department of Biostatistics, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA Keywords: Case-control study, Cohort study, Cross-Sectional Study, Generalized
PATIENTS REPORTED OUTCOMES IN ONCOLOGY PATIENT- CENTERED DRUG DEVELOPMENT: OPPORTUNITIES & CHALLENGES
 PATIENTS REPORTED OUTCOMES IN ONCOLOGY PATIENT- CENTERED DRUG DEVELOPMENT: OPPORTUNITIES & CHALLENGES 10th Alpine Conference Innsbruck, Austria, 27 February 2018 1 Disclaimer The views and opinions expressed
PATIENTS REPORTED OUTCOMES IN ONCOLOGY PATIENT- CENTERED DRUG DEVELOPMENT: OPPORTUNITIES & CHALLENGES 10th Alpine Conference Innsbruck, Austria, 27 February 2018 1 Disclaimer The views and opinions expressed
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations
 Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
Breast density: imaging, risks and recommendations Maureen Baxter, MD Radiologist Director of Ruth J. Spear Breast Center Providence St. Vincent Medical Center Alison Conlin, MD/MPH Medical Oncologist
Patient Dosimetry in Mammography and Tomosynthesis:
 2013 ICTP/IAEA Training Course on Radiation Protection of Patients Trieste Patient Dosimetry in Mammography and Tomosynthesis: What to measure, why and how John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FSBI, FACR Professor
2013 ICTP/IAEA Training Course on Radiation Protection of Patients Trieste Patient Dosimetry in Mammography and Tomosynthesis: What to measure, why and how John M. Boone, Ph.D., FAAPM, FSBI, FACR Professor
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound
 Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
Current Status of Supplementary Screening With Breast Ultrasound Stephen A. Feig, M.D., FACR Fong and Jean Tsai Professor of Women s Imaging Department of Radiologic Sciences University of California,
EUROPA DONNA Advocates Guide to the ECIBC European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer
 EUROPA DONNA Advocates Guide to the ECIBC European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer Part 1 About EUROPA DONNA EUROPA DONNA The European Breast Cancer Coalition is an independent non-profit organisation
EUROPA DONNA Advocates Guide to the ECIBC European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer Part 1 About EUROPA DONNA EUROPA DONNA The European Breast Cancer Coalition is an independent non-profit organisation
Mammography. What is Mammography?
 Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
Scan for mobile link. Mammography Mammography is a specific type of breast imaging that uses low-dose x-rays to detect cancer early before women experience symptoms when it is most treatable. Tell your
