Circulating micrornas in plasma of patients with gastric cancers
|
|
|
- Denis Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 British Journal of (21) 12, & 21 Research UK All rights reserved 7 92/1 $32. Circulating micrornas in plasma of s with gastric cancers M Tsujiura 1, D Ichikawa*,1, S Komatsu 1, A Shiozaki 1, H Takeshita 1, T Kosuga 1, H Konishi 1, R Morimura 1, K Deguchi 1, H Fujiwara 1, K Okamoto 1 and E Otsuji 1 1 Division of Digestive Surgery, Department of Surgery, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, 465 Kajii-cho, Kawaramachihirokoji, Kamigyo-ku, Kyoto , Japan BACKGROUND: We examined plasma microrna (mirna) concentrations from s with gastric cancers (GCs) to assess their clinical application for diagnosing and monitoring diseases. METHODS: We initially investigated the appropriateness of plasma mirna assay, and then compared plasma mirna results with the expressions in cancer tissues from eight GC s, and also compared plasma mirnas between pre- and post-operative paired samples from 1 GC s. Then, plasma mirnas (mir-17-5p, mir-21, mir-16a, mir-16b and let-7a) were analysed in 69 GC s and 3 healthy volunteers in total. RESULTS: The initial analysis showed that mirnas were stable and detectable in all plasma samples, and the plasma mirna levels reflected the tumour mirnas in most cases. The levels of these mirnas were significantly reduced in post-operative samples. In large-scale analysis, the plasma concentrations of mirnas (mir-17-5p, mir-21, mir-16a, mir-16b) were significantly higher in GC s than controls (P ¼.5,.6,.8 and o.1 respectively), whereas let-7a was lower in GC s (P ¼.2). The values of the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve were.721 for the mir-16b assay and.879 for the mir-16a/ let-7a ratio assay. CONCLUSION: Detection of circulating mirnas might provide new complementary tumour markers for GC. British Journal of (21) 12, doi:1.138/sj.bjc Published online 16 March 21 & 21 Research UK Keywords: gastric cancer; microrna; plasma; biomarker Gastric cancer (GC) is the second leading cause of cancer-related death in the world (Parkin et al, 25). Recent advances in diagnostic techniques and peri-operative management have increased the early detection of GC and decreased the mortality rate. However, s with advanced disease still frequently develop recurrent disease after extended radical resections, and consequently show extremely poor survival rates (Martin et al, 22). Thus, the primary tumours must be detected at an early stage, and recurrent disease must be diagnosed when it is still minimal or clinically occult, to improve the cure rates for s with GCs. For GC, serum tumour markers, such as carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 19-9, have been used as convenient diagnostic assays (Nakane et al, 1994; Marrelli et al, 21). These conventional serum markers, however, lack sufficient sensitivity and specificity to facilitate early detection of cancer. In addition, there are no other less invasive diagnostic tests for GC such as faecal occult blood tests for colon cancer. Recently, several studies have shown that micrornas (mirnas), which are involved in tumourigenesis and the development of various cancers, are stably detectable in plasma/ serum (Calin and Croce, 26; Chen et al, 28; Filipowicz et al, 28). Mitchell et al (28) clearly showed that circulating mirnas originate from cancer tissues, and are protected from endogenous *Correspondence: Dr D Ichikawa; ichikawa@koto.kpu-m.ac.jp Received 8 December 29; revised 4 February 21; accepted 17 February 21; published online 16 March 21 RNase activity by unknown mechanisms. They also showed the potential of using plasma/serum mirnas as a non-invasive bloodbased biomarker for the detection of prostate cancer. These findings have opened up a new and interesting field in the screening and monitoring of cancer s. In this study, we investigated the amounts of circulating mirnas in plasma samples from both pre-operative GC s and controls, and compared the relationships between the results and clinical findings to assess the diagnostic value of these biomarkers in s with GCs. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients and samples Pre-operative plasma samples were collected from 34 s with GCs, who underwent gastrectomy at Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, as well as from 15 healthy volunteers for test-scale analysis. To evaluate the appropriateness of this plasma mirna assay, we initially investigated the level of three mirnas, such as mir-21, mir-16b and let-7a, in plasma samples by real-time RT-PCR assay using the synthetic mirnas, mirvana mirna Reference Panel (Ambion, Austin, TX, USA). Thereafter, we performed two experiments to examine whether the plasma mirnas could reflect tumour dynamics. First, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tumour samples were collected from eight s with higher levels of plasma mir-16b and lower levels of plasma let-7a than healthy volunteers, and compared the mirna
2 expressions in primary lesions with those in plasma samples. Second, paired plasma samples before and 1 month after gastrectomy were collected from 1 of the test-scale s, and findings in pre- and post-operative plasma samples were compared. The initial experiments showed that plasma mirna assays were feasible and could reflect tumour dynamics, and then we performed a large-scale validation in the next step. Pre-operative plasma samples were collected from another 35 s with GCs for further large-scale analyses, as well as from another 15 healthy volunteers. Thus, between October 28 and July 29, 69 s with GC and 3 healthy volunteers were enrolled in this study. We added another two mirnas, mir-17-5p and mir-16a, as candidates for biomarkers for large-scale analyses. A peripheral blood sample was collected from s and volunteers after obtaining informed consent and agreement. Immediately after collection, the blood samples were subjected to isolation of cell-free nucleic acids using a three-spin protocol (15 r.p.m. for 3 min, 3 r.p.m. for 5 min, 45 r.p.m. for 5 min) to prevent contamination by cellular nucleic acids. Plasma samples were then stored at 81C until further processing. None of the s had received chemotherapy or radiotherapy before blood sampling. The resected GC specimens were fixed in buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin for pathological examination by standard methods. Macroscopic and microscopic classifications of tumours were based on the IGCC/TMN staging system (Sobin and Wittekind, 22). RNA extraction Total RNA was extracted from 4 ml of plasma using mirvana PARIS Kit (Ambion), and finally eluted into 1 ml of pre-heated (951C) Elution Solution according to the manufacturer s protocol. As for formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues, total RNA was extracted from four slices 15 mm thick (total 6 mm in thickness) using RecoverAll Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit (Ambion), and eluted finally into 6 ml of Elution Solution according to the manufacturer s protocol. Protocols for the detection of mirnas The amounts of mirnas were quantified in duplicate by qrt-pcr using the human TaqMan MicroRNA Assay Kits (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The reverse transcription reaction was carried out with TaqMan MicroRNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems) in 15 ml containing 5 ml of RNA extract,.15 ml of 1 mm dntps, 1 ml of Multiscribe Reverse Transcriptase (5 U ml 1 ), 1.5 ml of1reverse transcription buffer,.19 ml of RNase inhibitor (2 U ml 1 ), 1 ml of genespecific primer and 4.16 ml of nuclease-free water. For synthesis of cdna, the reaction mixtures were incubated at 161C for 3 min, at 421C for 3 min, at 851C for 5 min and then held at 41C. Then, 1.33 ml of cdna solution was amplified using 1 ml of TaqMan 2 Universal PCR Master Mix with no AmpErase UNG (Applied Biosystems), 1 ml of gene-specific primers/probe and 7.67 ml of nuclease-free water in a final volume of 2 ml. Quantitative PCR was run on a 73 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems) and the reaction mixtures were incubated at 951C for 1 min, followed by 4 cycles of 951C for 15 s and 61C for 1 min. The cycle threshold (C t ) values were calculated with the SDS 1.4 software (Applied Biosystems). The amounts of plasma mirnas were calculated on a standard curve constructed with the use of synthetic mirnas, mirvana mirna Reference Panel (Ambion). The standard reference mirnas were amplified for each reaction. However, the expression of mirnas from tissue samples was normalised using the 2 DDC t method relative to RNU6B. The DC t was calculated by subtracting the C t values of RNU6B from the C t values of the mirnas of interest. The DDC t was then calculated by subtracting DC t of the Plasma mirnas in gastric cancer s surrounding normal gastric epithelium from DC t of cancer tissues. Fold change in the gene was calculated by the equation 2-DDC t (Livak and Schmittgen, 21; Pfaffl, 21). Statistical analysis Mann Whitney test was used to compare the difference in plasma mirna concentration and mirna ratio between the cancer group and the healthy group, and Wilcoxon test was used to compare the paired plasma samples before and 1-month after gastrectomy. P-value o.5 was considered significant. Receiveroperating characteristic (ROC) curves and the area under the ROC curve (AUC) were used to assess the feasibility of using plasma mirna concentration as diagnostic tools for detecting GC. We used the Youden index for identification of the optimal cut-off point. RESULTS Evaluation of quantitative RT-PCR for measuring the mirnas in plasma sample To evaluate the appropriateness of this plasma assay, we first conducted amplification by real-time RT-PCR assay of a 1-fold serial dilution of the mirvana mirna Reference Panel. The linearity of the quantitative RT-PCR was confirmed from the concentrations of 1 to.1 fmol of each synthetic mirnas, such as mir-21, mir-16b and let-7a (R 2 ¼.999,.998 and.999 respectively) between the logarithm of the amount of input mirnas and the C t values (Figure 1). Using this assay, we found circulating mirnas (mir-21, mir-16b, and let-7a) detectable and amplified in all samples from 34 GC s and 15 healthy volunteers. The concentrations of mir-16b were significantly higher, whereas those of let-7a were significantly lower in plasma from GC s than in that from healthy controls (P ¼.2 and o.1 respectively; Figure 2B and C). However, there was no significant difference in the concentration of mir-21 between GC s and controls, although it tended to be higher in GC s (P ¼.88; Figure 2A). C t value Log concentration Δ mir-21 mir-16b let-7a Figure 1 Standard curve of mir-21, mir-16b, let-7a using synthetic mirnas. Ten-fold serial dilution of synthetic mirna was used to generate the standard curves. Linearity was confirmed within these concentrations, ranging from 1 to.1 fmol. (mir-21: y ¼ x þ (R 2 ¼.999); mir-16b: y ¼ x þ (R 2 ¼.998); let-7a: y ¼ x þ (R 2 ¼.999)) 1175 & 21 Research UK British Journal of (21) 12(7),
3 Plasma mirnas in gastric cancer s 1176 Concentrations 2.5E 1 2.E 1 1.5E 1 1.E 1 5.E 2 mir-21 1.E+ 1.E 1 1.E 2 Concentrations 8.E 1 6.E 1 4.E 1 2.E 1 mir-16b 1.E+ 1.E 1 1.E 2 (n=34) Control (n=15) 1.E 3 Control (n=34) Control (n=15) 1.E 3 Control Concentrations 1.5E E 1 1.E 1 7.5E 2 5.E 2 2.5E 2 Let-7a 1.E+ 1.E 1 1.E 2 Relationship between the mirnas in plasma and primary gastric cancer tissues There were eight s whose mir-16b concentrations exceeded the highest level of healthy volunteers, and let-7a concentrations were below the lowest value of healthy volunteers. Then we examined expressions of these mirnas in cancer tissues compared with those in adjacent normal tissues from these eight s. All the mirnas obtained from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissues were amplified, and found to be of good quality for amplification (data not shown). MiR-16b showed higher expression in primary GC tissues than normal mucosa in seven of the eight s analysed (87.5%), whereas let-7a showed lower expression in seven s (87.5%) (Table 1). Then, the concentrations of mir-21 and mir-16b were analysed in paired pre- and post-operative plasma samples from 1 GC s who underwent gastrectomy. Both mirnas were significantly reduced in post-operative samples compared with the levels in pre-operative samples (P ¼.13 and.22 respectively; Figure 3). These findings showed that primary cancer tissues and plasma samples from most s showed similar tendencies concerning the mirna levels, and indicated that the level of plasma mirnas might reflect the expression level of tumour mirnas. Large-scale validation on plasma samples In total, 69 GC s were included in this study; 38 s with TNM stage I, 13 with stage II, 14 with stage III and 4 with (n=34) Control (n=15) 1.E 3 Control Figure 2 Plasma mirnas concentration in the initial analysis. Real-time RT-PCR assay, circulating plasma mirnas (A: mir-21, B: mir-16b and C: let-7a) were detectable and amplified in all samples from 34 gastric cancer s and 15 healthy volunteers. The concentrations of mir-16b and let-7a were significantly higher and lower in plasma from gastric cancer s than in that from healthy controls (P ¼.2 and o.1 respectively). However, there was no significant difference in the concentration of mir-21 between gastric cancers s and controls although it tended to be higher in gastric cancer s (P ¼.88). The upper and lower limits of the boxes and the lines inside the boxes indicate the 75th and 25th percentiles and the median respectively. The upper and lower horizontal bars denote the 9th and 1th percentiles respectively. Table 1 Expression of mature mirnas in gastric cancer tissue vs those in normal tissue mir-16b let-7a Case Case Case Case Case Case Case Case Rate of higher expression level in gastric cancer tissue 87.5% 12.5% Rate of lower expression level in gastric cancer tissue 12.5% 87.5% stage IV. We analysed another two mirnas, mir-17-5p and mir- 16a, for large-scale validation. The plasma concentrations of mirnas, mir-17-5p, mir-21, mir-16a and mir-16b, were significantly higher in GC s than in controls (P ¼.6,.5,.8 and o.1 respectively), whereas the concentration of let-7a was significantly lower in GC s than in controls (P ¼.2; Figure 4). Analyses of the ROC curves for plasma mirnas showed that the AUC was greatest for mir-16b (AUC ¼.721; Figure 5). To investigate more sensitive plasma diagnostic biomarkers, we analysed the ratio of circulating mirna levels, dividing the plasma concentrations of mir-17-5p, mir-21, mir-16a and mir-16b by that of let-7a, and then, the ratio of British Journal of (21) 12(7), & 21 Research UK
4 1.2E 1 Plasma mirnas in gastric cancer s P=.13 P =.22 1.E mir-21 concentrations 1.E 1 8.E 2 6.E 2 4.E 2 2.E 2 mir-16b concentrations 8.E 2 6.E 2 4.E 2 2.E 2 Pre-op 1 month post-op Pre-op 1 month post-op Figure 3 Comparison of plasma mir-21 and mir-16b concentrations between pre- and post-operative samples from gastric cancer s. Expressions of both mirnas were significantly reduced in plasma samples obtained 1 month after surgical removal of the tumour. 1.E+ 1.E+ mir-17-5p concentrations 1.E 1 1.E 2 1.E 3 1.E 4 mir-16b concentrations 5.E 1 5.E 2 mir-21 concentrations 3.E 1 3.E 2 3.E 3 Let-7a concentrations 2.E 1 2.E 2 mir-16a concentrations 1.E 1 1.E 2 1.E 3 1.E 4 5.E 3 2.E 3 Figure 4 Box plots of the plasma mirna concentrations in gastric cancer s and controls. Plasma mirna concentrations were significantly higher for mir-17-5p (P ¼.5), mir-21 (P ¼.6), mir-16a (P ¼.8) and mir-16b (Po.1) in the gastric cancer s compared to those in controls, whereas let-7a was significantly lower in gastric cancer s (P ¼.2). The upper and lower limits of the boxes and the lines inside the boxes indicate the 75th and 25th percentiles and the median respectively. The upper and lower horizontal bars denote the 9th and 1th percentiles respectively. mir-16a/let-7a showed the highest AUC of.879 (Figure 6). In this model, an optimal cut-off point was indicated at.536 with a sensitivity of 85.5% and a specificity of 8.%. Other analyses of the ROC curves are shown in supplementary date (Supplementary Figures 1 and 2). DISCUSSION Numerous genetic and epigenetic alterations are known to be involved in tumourigenesis and tumour progression of various cancers. Several studies have identified tumour-specific alterations & 21 Research UK British Journal of (21) 12(7),
5 1178 Sensitivity mir-16b AUC= specificity Figure 5 Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis in the concentration of mir-16b assay for detecting gastric cancer s. Sensitivity Plasma mirnas in gastric cancer s specificity mir-16a/let-7a AUC=.879 Figure 6 Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis of the ratio of mir-16a/let-7a assay for detecting gastric cancer s. in plasma/serum nucleic acids of cancer s, and have shown the potential of plasma circulating nucleic acids to be new noninvasive biomarkers in s with various cancers (Sidransky, 1997; Anker et al, 21; Taback and Hoon, 24; Chan and Lo, 27). However, during the past decade, non-coding RNAs, so-called micrornas (mirnas), have also been shown to regulate gene expression by targeting mrnas for translational repression or cleavage. Consequently, these mirnas have recently been identified as new factors related to oncogenesis and tumour progression in various cancers (He et al, 25, 28; Lu et al, 25; Calin and Croce, 26). Mitchell et al (28) recently reported that mirnas are detectable in plasma and that circulating mirnas have the potential to be new biomarkers in s with prostate cancers. They also showed the high stability of plasma mirnas after prolonged incubation at room temperature and/or multiple freezing thawing processes. In addition to this high stability, the characteristics of mirnas such as tissue-specific mirna signatures and the availability of many copies per cell would indicate potential advantages as biomarkers compared with those of other nucleic acids, such as circulating DNA and mrna. In fact, accumulating reports also suggest the potential of mirnas in the early detection of s.8 1. with several malignancies, such as lymphoma, colorectal cancer, tongue cancer and ovarian cancer (Lawrie et al, 28; Wong et al, 28; Ng et al, 29; Resnick et al, 29). These findings prompted us to investigate the usefulness of mirnas in s with GCs. In this report, we selected four mirnas (mir-17-5p, mir-21, mir-16a and mir-16b) that have been reported to be upregulated in GC, and also selected let-7a, which has been reported to be downregulated in GC (Zhang et al, 27, 28; Chan et al, 28; Motoyama et al, 28; Guo et al, 29; Kim et al, 29). First, we confirmed a linear correlation between the logarithm of the amount of input synthetic mirna and the cycle threshold value on real-time PCR as well as the feasibility of extracting total RNA and amplifying specific mirna in plasma samples. On the basis of these results, we used the absolute concentration method for measuring plasma mirnas in this study. Some investigators have determined quantities of plasma mirnas by comparing internal control mirnas (Ng et al, 29; Resnick et al, 29). However, which mirna is suitable as an internal control for plasma assay remains controversial. Next, we investigated whether plasma mirnas could be released from the primary gastric tumours. The comparison between expressions of mirna in plasma and primary tumour tissues demonstrated that plasma and primary GC tissue samples showed similar tendencies concerning the expression of mirnas in almost all cases. Each, however, showed a different pattern of mirna levels, high plasma mir-16b with a low expression in GC tissue and low plasma let-7a with a high expression in cancer tissue. Although the reason for these discrepancies remains to be identified, one possible explanation for this finding is the heterogeneity of the primary tumours. We also measured circulating mirnas in paired plasma before and 1 month after surgical removal of the tumours, to confirm tumour release of the circulating mirnas. As a result, the concentrations of mir-21 and mir-16b were significantly reduced postoperatively in s with high pre-operative plasma mir-21 and mir-16b. The kinetics and metabolism of the plasma mirnas have not yet been clearly elucidated, however 1 month seems to be sufficient time for clearance of the circulating mirnas. Finally, we performed a large-scale study by increasing the number of plasma samples from GC s and healthy volunteers to validate the diagnostic potential of plasma mirnas. We found that the plasma concentrations of mirnas, mir-17-5p, mir-21, mir-16a and mir-16b were significantly higher in GC s than in controls, and the ROC analysis showed the greatest AUC value for mir-16b. Although, the concentration of let-7a was significantly lower in GC s than in controls, contrary to our expectation, we have also found that a certain mirna that was reported to be downregulated in primary cancer tissues showed a lower plasma expression level in oesophageal cancer s (data not shown). Because circulating mirnas are considered to have been released from cancer tissues as well as from normal tissues, the majority are expected to have originated from normal tissues. Several recent reports suggested that plasma mirnas might be protected in a complex with other molecules, such as exosomes, proteins and lipids (Valadi et al, 27; Mitchell et al, 28). The protection of mirnas might be greater in GC s than controls. An alternative hypothesis is that a lower plasma expression of certain mirnas might be due to alterations in mirna expressions in normal tissues of cancer s by unknown mechanisms. Determining the expression ratios of genes or mirnas has been reported to be a useful technique to improve diagnostic potential (Gordon et al, 22; Avissar et al, 29). Therefore, we also investigated the mirna expression ratios by dividing the plasma concentration of upregulated mirna (mir-17-5p, mir-21, mir-16a and mir-16b) by that of downregulated mirna (let-7a) toimprove the sensitivity and specificity of plasma mirna assay for use as diagnostic biomarkers. Then, the ratio of mir-16a/let-7a showed British Journal of (21) 12(7), & 21 Research UK
6 the highest AUC value of.879 in this study, and which would be satisfactory for clinical application. Plasma mirna assays have several potential clinical uses: screening s at high risk for GC and monitoring disease recurrence during the follow-up period after gastrectomy. These mirna biomarkers might also be powerful and useful for confirming the completeness of tumour resection and evaluating the efficacy of adjuvant therapies if the elimination clearance of plasma mirnas can be elucidated. Plasma mirnas in gastric cancer s In conclusion, plasma mirnas may be available as a new marker for GC. Further prospective clinical trials using a variety of plasma mirnas should be carried out to define the usefulness of the assay for each potential application. Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on British Journal of website ( REFERENCES Anker P, Lyautey J, Lederrey C, Stroun M (21) Circulating nucleic acids in plasma or serum. Clin Chim Acta 313: Avissar M, Christensen BC, Kelsey KT, Marsit CJ (29) MicroRNA expression ratio is predictive of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Res 15: Calin GA, Croce CM (26) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev 6: Chan KC, Lo YM (27) Circulating tumour-derived nucleic acids in cancer s: potential applications as tumour markers. Br J 96: Chan SH, Wu CW, Li AF, Chi CW, Lin WC (28) mir-21 microrna expression in human gastric carcinomas and its clinical association. Anticancer Res 28: Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, Wang K, Guo J, Zhang Y, Chen J, Guo X, Li Q, Li X, Wang W, Zhang Y, Wang J, Jiang X, Xiang Y, Xu C, Zheng P, Zhang J, Li R, Zhang H, Shang X, Gong T, Ning G, Wang J, Zen K, Zhang J, Zhang CY (28) Characterization of micrornas in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18: Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N (28) Mechanisms of posttranscriptional regulation by micrornas: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet 9: Gordon GJ, Jensen RV, Hsiao LL, Gullans SR, Blumenstock JE, Ramaswamy S, Richards WG, Sugarbaker DJ, Bueno R (22) Translation of microarray data into clinically relevant cancer diagnostic tests using gene expression ratios in lung cancer and mesothelioma. Res 62: Guo J, Miao Y, Xiao B, Huan R, Jiang Z, Meng D, Wang Y (29) Differential expression of microrna species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24: He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, Powers S, Cordon-Cardo C, Lowe SW, Hannon GJ, Hammond SM (25) A microrna polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature 435: He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, Jackson AL, Linsley PS, Chen C, Lowe SW, Cleary MA, Hannon GJ (28) A microrna component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature 447: Kim YK, Yu J, Han TS, Park SY, Namkoong B, Kim DH, Hur K, Yoo MW, Lee HJ, Yang HK, Kim VN (29) Functional links between clustered micrornas: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microrna clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 37: Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, Pulford K, Banham AH, Pezzella F, Boultwood J, Wainscoat JS, Hatton CS, Harris AL (28) Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated micrornas in serum of s with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 141: Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (21) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25: Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (25) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435: Marrelli D, Pinto E, De Stefano A, Farnetani M, Garosi L, Roviello F (21) Clinical utility of CEA, CA 19 9, and CA 72 4 in the follow-up of s with resectable gastric cancer. Am J Surg 181: Martin 2nd RC, Jaques DP, Brennan MF, Karpeh M (22) Extended local resection for advanced gastric cancer: increased survival versus increased morbidity. Ann Surg 236: Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova- Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (28) Circulating micrornas as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 15: Motoyama K, Inoue H, Nakamura Y, Uetake H, Sugihara K, Mori M (28) Clinical significance of high mobility group A2 in human gastric cancer and its relationship to let-7 microrna family. Clin Res 14: Nakane Y, Okamura S, Akehira K, Boku T, Okusa T, Tanaka K, Hioki K (1994) Correlation of preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen levels and prognosis of gastric cancer s. 73: Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY, Yu J, Poon TC, Ng SS, Sung JJ (29) Differential expression of micrornas in plasma of s with colorectal cancer: a potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut 58: Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (25) Global cancer statistics, 22. CA J Clin 55: Pfaffl MW (21) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29: Resnick KE, Alder H, Hagan JP, Richardson DL, Croce CM, Cohn DE (29) The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer s using a novel real-time PCR platform. Gynecol Oncol 112: Sidransky D (1997) Nucleic acid-based methods for the detection of cancer. Science 278: Sobin LH, Wittekind CH (22) TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 6th edn. John Wiley: New York Taback B, Hoon DS (24) Circulating nucleic acids in plasma and serum: past, present and future. Curr Opin Mol Ther 6: Valadi H, Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ, Lötvall JO (27) Exosome-mediated transfer of mrnas and micrornas is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol 9: Wong TS, Liu XB, Wong BY, Ng RW, Yuen AP, Wei WI (28) Mature mir- 184 as potential oncogenic microrna of squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. Clin Res 14: Zhang HH, Wang XJ, Li GX, Yang E, Yang NM (27) Detection of let-7a microrna by real-time PCR in gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 13: Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, Chen P, Chen J, Liu W, Xiao S, Lu H (28) mir-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest 88: & 21 Research UK British Journal of (21) 12(7),
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Original Article Serum expression of mirna-103, a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14212-14218 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0024943 Original Article Serum expression of mirna-103, a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(7):14212-14218 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0024943 Original Article Serum expression of mirna-103, a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Expression Analysis of mir-21 and mir-221 in Cancerous Tissues from Iranian Patients with Gastric Cancer
 Iranian Biomedical Journal 19 (4): 188-193 (October 2015) DOI: 10.7508/ibj.2015.04.001 Expression Analysis of mir-21 and mir-221 in Cancerous Tissues from Iranian Patients with Gastric Cancer Hosein Effatpanah
Iranian Biomedical Journal 19 (4): 188-193 (October 2015) DOI: 10.7508/ibj.2015.04.001 Expression Analysis of mir-21 and mir-221 in Cancerous Tissues from Iranian Patients with Gastric Cancer Hosein Effatpanah
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Original Article Prognostic value of serum mir-155 in intracerebral hemorrhage
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3845-3850 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0045182 Original Article Prognostic value of serum mir-155 in intracerebral hemorrhage Abulizi Maimaijiang 1,2, Dangmurenjiafu
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3845-3850 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0045182 Original Article Prognostic value of serum mir-155 in intracerebral hemorrhage Abulizi Maimaijiang 1,2, Dangmurenjiafu
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis
 Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Association of mir-21 with esophageal cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis S.-W. Wen 1, Y.-F. Zhang 1, Y. Li 1, Z.-X. Liu 2, H.-L. Lv 1, Z.-H. Li 1, Y.-Z. Xu 1, Y.-G. Zhu 1 and Z.-Q. Tian 1 1 Department of
Analysis of serum exosomal micrornas and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma
 Que et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:219 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of serum exosomal micrornas and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic
Que et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2013, 11:219 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of serum exosomal micrornas and clinicopathologic features of patients with pancreatic
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Original Article Serum microrna-34c acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker in breast cancer patients
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6489-6494 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0016792 Original Article Serum microrna-34c acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker in breast cancer patients Zhongcheng Gao 1,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(6):6489-6494 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0016792 Original Article Serum microrna-34c acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker in breast cancer patients Zhongcheng Gao 1,
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
Down-regulation of mir p is correlated with clinical progression and unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5914-5919 Down-regulation of mir-1236-3p is correlated with clinical progression and unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer X.-P. ZHU
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5914-5919 Down-regulation of mir-1236-3p is correlated with clinical progression and unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer X.-P. ZHU
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Original Article Downregulation of serum mir-140-5p predicts poor prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):9503-9508 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0042860 Original Article Downregulation of serum mir-140-5p predicts poor prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer Jijun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(9):9503-9508 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0042860 Original Article Downregulation of serum mir-140-5p predicts poor prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer Jijun
Clinicopathologic and prognostic relevance of mir-1256 in colorectal cancer: a preliminary clinical study
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7704-7709 Clinicopathologic and prognostic relevance of mir-1256 in colorectal cancer: a preliminary clinical study Z.-Y. LIU, L. YANG,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7704-7709 Clinicopathologic and prognostic relevance of mir-1256 in colorectal cancer: a preliminary clinical study Z.-Y. LIU, L. YANG,
Detection of let-7a MicroRNA by Real-time PCR in Colorectal Cancer: a Single-centre Experience from China
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2007; 35: 716 723 Detection of let-7a MicroRNA by Real-time PCR in Colorectal Cancer: a Single-centre Experience from China W-J FANG 1, C-Z LIN 2, H-H ZHANG
The Journal of International Medical Research 2007; 35: 716 723 Detection of let-7a MicroRNA by Real-time PCR in Colorectal Cancer: a Single-centre Experience from China W-J FANG 1, C-Z LIN 2, H-H ZHANG
Identification of plasma RGS18 and PPBP mrnas as potential biomarkers for gastric cancer using transcriptome arrays
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS Identification of plasma RGS18 and PPBP mrnas as potential biomarkers for gastric cancer using transcriptome arrays CHEN SU 1,2*, HANWEI LI 1,3*, ZHENG PENG 4*, DONG KE 5,6, HANJIANG FU
ONCOLOGY LETTERS Identification of plasma RGS18 and PPBP mrnas as potential biomarkers for gastric cancer using transcriptome arrays CHEN SU 1,2*, HANWEI LI 1,3*, ZHENG PENG 4*, DONG KE 5,6, HANJIANG FU
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array
 MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
MicroRNA Cancer qpcr Array Array Layout Pre-designed set of 95 MicroRNA detection Primers U6 snrna Normalization transcript Selection of Candidate MicroRNAs for Cancer Array Sample References of MicroRNA
Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs
 Protein Cell 15, 6(1):1 5 DOI 1.17/s13238-14-116-2 Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs Jie Xu, Xi Chen, Donghai Li, Qun Chen, Zhen Zhou, Dongxia
Protein Cell 15, 6(1):1 5 DOI 1.17/s13238-14-116-2 Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs Jie Xu, Xi Chen, Donghai Li, Qun Chen, Zhen Zhou, Dongxia
Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis
 Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis M.L. Zhi 1 *, Z.J. Liu 2 *, X.Y. Yi 1, L.J. Zhang 1 and Y.X. Bao 1 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated
Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis M.L. Zhi 1 *, Z.J. Liu 2 *, X.Y. Yi 1, L.J. Zhang 1 and Y.X. Bao 1 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological staging of the cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 1283-1287 Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 1283-1287 Expression level of microrna-195 in the serum of patients with gastric cancer and its relationship with the clinicopathological
MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction
 www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
www.muthjm.com Muthanna Medical Journal 2016; 3(1):23-33 MicroRNA-92gene expression in epithelial ovarian cancer using a novel Real-Time Polymerase change reaction Shoroq Mohammed AL-Temimi 1* Abstract
The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Gynecologic Oncology 112 (2009) 55 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Gynecologic Oncology 112 (2009) 55 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients
Original Article MicroRNA-101 is a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in breast cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3279-3285 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0022926 Original Article MicroRNA-101 is a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in breast cancer Na Wei, Qing Ni, Min
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(3):3279-3285 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0022926 Original Article MicroRNA-101 is a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in breast cancer Na Wei, Qing Ni, Min
A circulating serum mirna panel as early detection biomarkers of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4846-4851 A circulating serum mirna panel as early detection biomarkers of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia F. XIN 1, P. LIU 1, C-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4846-4851 A circulating serum mirna panel as early detection biomarkers of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia F. XIN 1, P. LIU 1, C-F.
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2103-2107 Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients J.-H. ZHANG 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2103-2107 Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LINC01133 is predictive of poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients J.-H. ZHANG 1,
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
Identification of Suitable Reference Genes for qpcr Analysis of Serum microrna in Gastric Cancer Patients
 DOI 10.1007/s10620-011-1981-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Suitable Reference Genes for qpcr Analysis of Serum microrna in Gastric Cancer Patients Jianning Song Zhigang Bai Wei Han Jun Zhang Hua
DOI 10.1007/s10620-011-1981-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Suitable Reference Genes for qpcr Analysis of Serum microrna in Gastric Cancer Patients Jianning Song Zhigang Bai Wei Han Jun Zhang Hua
Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA
 Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
Original Article Clinical significance of serum mir-21 in breast cancer compared with CA153 and CEA Jianjian Gao, Qingyun Zhang, Jianjun Xu, Lijuan Guo, Xuefeng Li Key Laboratory of Carcinogenesis and
A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
Overexpression of circulating mirna-21 and mirna-146a in plasma samples of breast cancer patients
 Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics Vol. 50, June 2013, pp. 210-214 Overexpression of circulating mirna-21 and mirna-146a in plasma samples of breast cancer patients Subramanian Kumar, Ranganathan
Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics Vol. 50, June 2013, pp. 210-214 Overexpression of circulating mirna-21 and mirna-146a in plasma samples of breast cancer patients Subramanian Kumar, Ranganathan
Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis
 Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis T.-Y. Wang 1, S.-G. Liu 2, B.-S. Zhao 2, B. Qi 2, X.-G. Qin 2 and W.-J. Yao 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis T.-Y. Wang 1, S.-G. Liu 2, B.-S. Zhao 2, B. Qi 2, X.-G. Qin 2 and W.-J. Yao 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients
 Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients
 mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
1 Introduction. Research Article
 Open Life Sci. 2017; 12: 243 247 Research Article Xiangrong Zhu*, Xiongtie Wang, Xihua Chen The diagnostic value of serum microrna-183 and TK1 as biomarkers for colorectal cancer diagnosis https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2017-0029
Open Life Sci. 2017; 12: 243 247 Research Article Xiangrong Zhu*, Xiongtie Wang, Xihua Chen The diagnostic value of serum microrna-183 and TK1 as biomarkers for colorectal cancer diagnosis https://doi.org/10.1515/biol-2017-0029
Serum mir-199a as a potential diagnostic biomarker for detection of colorectal cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8657-8663 Serum mir-199a as a potential diagnostic biomarker for detection of colorectal cancer H.-Y. TAN 1, Y.-B. ZHENG 1, J. LIU 2 1
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8657-8663 Serum mir-199a as a potential diagnostic biomarker for detection of colorectal cancer H.-Y. TAN 1, Y.-B. ZHENG 1, J. LIU 2 1
The detection rate of early gastric cancer has been increasing owing to advances in
 Focused Issue of This Month Sung Hoon Noh, MD, ph.d Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine E - mail : sunghoonn@yuhs.ac J Korean Med Assoc 2010; 53(4): 306-310 Abstract The detection
Focused Issue of This Month Sung Hoon Noh, MD, ph.d Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine E - mail : sunghoonn@yuhs.ac J Korean Med Assoc 2010; 53(4): 306-310 Abstract The detection
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Circulating Long Non-coding RNAs in Plasma of Patients with Gastric Cancer
 Circulating Long Non-coding RNAs in Plasma of Patients with Gastric Cancer TOMOHIRO ARITA*, DAISUKE ICHIKAWA, HIROTAKA KONISHI*, SHUHEI KOMATSU, ATSUSHI SHIOZAKI, KATSUTOSHI SHODA, TSUTOMU KAWAGUCHI, SHOJI
Circulating Long Non-coding RNAs in Plasma of Patients with Gastric Cancer TOMOHIRO ARITA*, DAISUKE ICHIKAWA, HIROTAKA KONISHI*, SHUHEI KOMATSU, ATSUSHI SHIOZAKI, KATSUTOSHI SHODA, TSUTOMU KAWAGUCHI, SHOJI
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization
 A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(2):2049-2053 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0014841 Original Article MicroRNA-27a acts as a novel biomarker in the diagnosis of patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology xxx (2010) xxx xxx
 Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology xxx (2010) xxx xxx Circulating micrornas: Association with disease and potential use as biomarkers Glen Reid, Michaela B. Kirschner, Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology xxx (2010) xxx xxx Circulating micrornas: Association with disease and potential use as biomarkers Glen Reid, Michaela B. Kirschner, Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 /, Vol. 7, No. 33 Circulating microrna profiles in plasma: identification of mir-224 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma independent of hepatic function Wataru Okajima 1,*, Shuhei
/, Vol. 7, No. 33 Circulating microrna profiles in plasma: identification of mir-224 as a novel diagnostic biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma independent of hepatic function Wataru Okajima 1,*, Shuhei
mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
 Molecules 2014, 19, 1568-1575; doi:10.3390/molecules19021568 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
Molecules 2014, 19, 1568-1575; doi:10.3390/molecules19021568 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Decreased mir-198 expression and its prognostic significance in human gastric cancer
 Cui et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2016) 14:33 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-0784-x RESEARCH Open Access Decreased mir-198 expression and its prognostic significance in human gastric cancer Zhigang
Cui et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2016) 14:33 DOI 10.1186/s12957-016-0784-x RESEARCH Open Access Decreased mir-198 expression and its prognostic significance in human gastric cancer Zhigang
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Serum mir-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer
 Serum mir-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer H.-P. Zhang 1 *, F.-B. Sun 2 * and S.-J. Li 2 1 Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai,
Serum mir-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer H.-P. Zhang 1 *, F.-B. Sun 2 * and S.-J. Li 2 1 Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai,
Nandi Li, 1 Xiao Bo Feng, 2,3 Qian Tan, 1 Ping Luo, 1 Wei Jing, 1 Man Zhu, 1 Chunzi Liang, 1 Jiancheng Tu, 1,3 and Yong Ning 3. 1.
 Hindawi Disease Markers Volume 217, Article ID 7439698, 8 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/217/7439698 Research Article Identification of Circulating Long Noncoding RNA Linc152 as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis
Hindawi Disease Markers Volume 217, Article ID 7439698, 8 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/217/7439698 Research Article Identification of Circulating Long Noncoding RNA Linc152 as a Novel Biomarker for Diagnosis
Expression of mir-148/152 Family as Potential Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
 e-issn 1643-375 Med Sci Monit, 215; 21: 1155-1161 DOI: 1.12659/MSM.89294 Received: 214.11.3 Accepted: 214.11.13 Published: 215.4.23 Expression of mir-148/152 Family as Potential Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell
e-issn 1643-375 Med Sci Monit, 215; 21: 1155-1161 DOI: 1.12659/MSM.89294 Received: 214.11.3 Accepted: 214.11.13 Published: 215.4.23 Expression of mir-148/152 Family as Potential Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell
A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Circulating Cell-free mrna in Plasma as a Tumor Marker for Patients with Primary and Recurrent Gastric Cancer
 Circulating Cell-free mrna in Plasma as a Tumor Marker for Patients with Primary and Recurrent Gastric Cancer NOBUYUKI TANI 1, DAISUKE ICHIKAWA 1, DAITO IKOMA 1, HARUHISA TOMITA 1, SOUJIN SAI 1, HISASHI
Circulating Cell-free mrna in Plasma as a Tumor Marker for Patients with Primary and Recurrent Gastric Cancer NOBUYUKI TANI 1, DAISUKE ICHIKAWA 1, DAITO IKOMA 1, HARUHISA TOMITA 1, SOUJIN SAI 1, HISASHI
Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association with Pathological Features
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4863609, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4863609 Review Article Long Noncoding RNA H19 in Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis of Its Association
Identification of Mouse Serum mirna Endogenous References by Global Gene Expression Profiles
 Identification of Mouse Serum mirna Endogenous References by Global Gene Expression Profiles Qing-Sheng Mi 1,2,3 *, Matthew Weiland 1,2, Rui-Qun Qi 1,2,4, Xing-Hua Gao 4, Laila M. Poisson 5, Li Zhou 1,2,3
Identification of Mouse Serum mirna Endogenous References by Global Gene Expression Profiles Qing-Sheng Mi 1,2,3 *, Matthew Weiland 1,2, Rui-Qun Qi 1,2,4, Xing-Hua Gao 4, Laila M. Poisson 5, Li Zhou 1,2,3
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
From reference genes to global mean normalization
 From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
Supplementary Figure 1: Experimental design. DISCOVERY PHASE VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) (N = 20) Healthy = 20. Healthy = 6. Endometriosis = 33
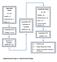 DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
Exosomal Del 1 as a potent diagnostic marker for breast cancer : A prospective cohort study
 GBCC 2017: ABS-0017 Exosomal Del 1 as a potent diagnostic marker for breast cancer : A prospective cohort study Soo Jung Lee 1, Jeeyeon Lee 2, Jin Hyang Jung 2, Ho Yong Park 2, Chan Hyeong Lee 3, Pyong
GBCC 2017: ABS-0017 Exosomal Del 1 as a potent diagnostic marker for breast cancer : A prospective cohort study Soo Jung Lee 1, Jeeyeon Lee 2, Jin Hyang Jung 2, Ho Yong Park 2, Chan Hyeong Lee 3, Pyong
Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Serum: A Fingerprint for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Clinical Chemistry 56:12 1871 1879 (2010) Cancer Diagnostics Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Serum: A Fingerprint for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Chunni Zhang, 1* Cheng Wang, 1 Xi Chen, 2 Cuihua
Clinical Chemistry 56:12 1871 1879 (2010) Cancer Diagnostics Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Serum: A Fingerprint for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Chunni Zhang, 1* Cheng Wang, 1 Xi Chen, 2 Cuihua
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population
 Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population J.J. Lu, H.Q. Zhang, P. Mai, X. Ma, X. Chen, Y.X. Yang and L.P. Zhang Gansu Provincial Hospital, Donggang
Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population J.J. Lu, H.Q. Zhang, P. Mai, X. Ma, X. Chen, Y.X. Yang and L.P. Zhang Gansu Provincial Hospital, Donggang
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits
 Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna
 Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna Carl Novina Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Qiagen Webinar 05-17-11 Outline 1. The biology
Post-transcriptional regulation of an intronic microrna Carl Novina Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Harvard Medical School Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT Qiagen Webinar 05-17-11 Outline 1. The biology
Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury. HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011
 Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011 Karol Thompson, PhD Center for Drug Evaluation & Research US Food
Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011 Karol Thompson, PhD Center for Drug Evaluation & Research US Food
Xiang Hu*, Liang Cao*, Yi Yu. Introduction
 Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Original Article Prognostic prediction in gastric cancer patients without serosal invasion: comparative study between UICC 7 th edition and JCGS 13 th edition N-classification systems Xiang Hu*, Liang
Clinicopathological Characteristics and Outcome Indicators of Stage II Gastric Cancer According to the Japanese Classification of Gastric Cancer
 Clinicopathological Characteristics and Outcome Indicators of Stage II Gastric Cancer According to the Japanese Classification of Gastric Cancer HITOSHI OJIMA 1, KEN-ICHIRO ARAKI 1, TOSHIHIDE KATO 1, KAORI
Clinicopathological Characteristics and Outcome Indicators of Stage II Gastric Cancer According to the Japanese Classification of Gastric Cancer HITOSHI OJIMA 1, KEN-ICHIRO ARAKI 1, TOSHIHIDE KATO 1, KAORI
(DNA) Real-time PCR. Exicycler 96 Rotor-Gene Q/6000 PCR
 Real-Time (DNA) Real-time Exicycler 96 Rotor-Gene Q/6000 IU Mix1 Mix2 IU/μl IU/μl IU/μl IU/μl IU/μl IPC NTC C 1 Lot# 2 Freeze & thawing 1 MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheets (TaqMan Real-time ' FAM ' BHQ1
Real-Time (DNA) Real-time Exicycler 96 Rotor-Gene Q/6000 IU Mix1 Mix2 IU/μl IU/μl IU/μl IU/μl IU/μl IPC NTC C 1 Lot# 2 Freeze & thawing 1 MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheets (TaqMan Real-time ' FAM ' BHQ1
Mir-221 in the Detection of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB) ISSN: 2455-264X, Volume 2, Issue 5 (Jul. Aug. 2016), PP 04-13 Mir-221 in the Detection of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Obaid Hayat 1,
IOSR Journal of Biotechnology and Biochemistry (IOSR-JBB) ISSN: 2455-264X, Volume 2, Issue 5 (Jul. Aug. 2016), PP 04-13 Mir-221 in the Detection of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Obaid Hayat 1,
A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer
 Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Long non-coding RNA Loc is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
Investigation of serum mir-411 as a diagnosis and prognosis biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4092-4097 Investigation of serum mir-411 as a diagnosis and prognosis biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer S.-Y. WANG 1, Y. LI 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4092-4097 Investigation of serum mir-411 as a diagnosis and prognosis biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer S.-Y. WANG 1, Y. LI 1,
Expression and significance of mir-21 in multiple myeloma patients
 Expression and significance of mir-21 in multiple myeloma patients J.H. Wang 1, W.W. Zhou 1, B.X. Liu 1, D.L. Man 1, Z.D. Yang 1, F.R. Liu 2 and H. Shang 1 1 The Laboratory Medicine of First Affiliated
Expression and significance of mir-21 in multiple myeloma patients J.H. Wang 1, W.W. Zhou 1, B.X. Liu 1, D.L. Man 1, Z.D. Yang 1, F.R. Liu 2 and H. Shang 1 1 The Laboratory Medicine of First Affiliated
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
 Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Clinical significance of serum mir-196a in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer P. Liu 1, F. Xin 1 and C.F. Ma 2 1 Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Baoding Second Central Hospital,
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population
 Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer To cite this article: J Sembiring et al 2018
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer To cite this article: J Sembiring et al 2018
Survival impact of cervical metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of hard palate
 Vol. 116 No. 1 July 2013 Survival impact of cervical metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of hard palate Quan Li, MD, a Di Wu, MD, b,c Wei-Wei Liu, MD, PhD, b,c Hao Li, MD, PhD, b,c Wei-Guo Liao, MD,
Vol. 116 No. 1 July 2013 Survival impact of cervical metastasis in squamous cell carcinoma of hard palate Quan Li, MD, a Di Wu, MD, b,c Wei-Wei Liu, MD, PhD, b,c Hao Li, MD, PhD, b,c Wei-Guo Liao, MD,
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Original Article Expression and importance of serum MicroRNAs in prostate cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):8713-8718 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022298 Original Article Expression and importance of serum MicroRNAs in prostate cancer Weidong Zhou, Denglong Wu Department of
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(5):8713-8718 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022298 Original Article Expression and importance of serum MicroRNAs in prostate cancer Weidong Zhou, Denglong Wu Department of
Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 17: 3387-3391, 2019 Clinical value of combined detection of mir 1202 and mir 195 in early diagnosis of cervical cancer XIELAN YANG 1, ZHILING YAN 1, HONGYING YANG 1, HUIJING NI 1, LEI
White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: Version: Accepted Version
 This is a repository copy of Accuracy of staging of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: should incisional biopsy be done before or after magnetic resonance imaging?. White Rose Research Online
This is a repository copy of Accuracy of staging of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: should incisional biopsy be done before or after magnetic resonance imaging?. White Rose Research Online
How to apply HCC prediction models to practice?
 How to apply HCC prediction models to practice? Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine Woo Jin Chung HCC prediction models 독특하게간세포암환자들의생존은암의진행상태뿐아니라기저간기능의중증정도에영향을받는특성이있다.
How to apply HCC prediction models to practice? Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine Woo Jin Chung HCC prediction models 독특하게간세포암환자들의생존은암의진행상태뿐아니라기저간기능의중증정도에영향을받는특성이있다.
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
