Identification of Mouse Serum mirna Endogenous References by Global Gene Expression Profiles
|
|
|
- Jewel Dalton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Identification of Mouse Serum mirna Endogenous References by Global Gene Expression Profiles Qing-Sheng Mi 1,2,3 *, Matthew Weiland 1,2, Rui-Qun Qi 1,2,4, Xing-Hua Gao 4, Laila M. Poisson 5, Li Zhou 1,2,3 * 1 Henry Ford Immunology Program, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, Michigan, United States of America, 2 Department of Dermatology, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, Michigan, United States of America, 3 Department of Internal Medicine, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, Michigan, United States of America, 4 Department of Dermatology, No 1 Hospital, China Medical University, Shenyang, China, 5 Department of Public Health Sciences, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit, Michigan, United States of America Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are recently discovered small non-coding RNAs and can serve as serum biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognoses. Lack of reliable serum mirna endogenous references for normalization in mirna gene expression makes single mirna assays inaccurate. Using TaqManH real-time PCR mirna arrays with a global gene expression normalization strategy, we have analyzed serum mirna expression profiles of 20 female mice of NOD/ShiLtJ (n = 8), NOR/LtJ (n = 6), and C57BL/6J (n = 6) at different ages and disease conditions. We identified five mirnas, mir-146a, mir-16, mir-195, mir-30e and mir-744, to be stably expressed in all strains, which could serve as mouse serum mirna endogenous references for single assay experiments. Citation: Mi Q-S, Weiland M, Qi R-Q, Gao X-H, Poisson LM, et al. (2012) Identification of Mouse Serum mirna Endogenous References by Global Gene Expression Profiles. PLoS ONE 7(2): e doi: /journal.pone Editor: Judith Homberg, Radboud University, Netherlands Received August 22, 2011; Accepted January 5, 2012; Published February 10, 2012 Copyright: ß 2012 Mi et al. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited. Funding: This work was supported in part by a grant from Henry Ford Health System Start-up Grant for the Immunology Program (T71016 and T71017), Henry Ford Stubnitz Grant (J80005), Melanoma Research Alliance, and Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Teams in Universities, Ministry of Education, China (IRT0760), and the Shahani Foundation. No additional external funding received for this study. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist. * qmi1@hfhs.org (QSM); lzhou1@hfhs.org (LZ) Introduction MicroRNAs (mirnas) are a recently discovered class of nt single stranded non-coding RNAs, which are widely expressed in plants, animals, and humans, and function through translational repression of specific target mrnas. As regulators of gene expression, mirnas act in a complementary fashion by partially binding to the 39 untranslated region of target mrnas [1]. Repression of protein translation follows the pairing of mirnas to target sequences. The unique mechanism of gene regulation make mirnas an important regulator of a diverse set of physiological processes [2,3], including immune cell development [3,4,5]. mirnas have been found to be dysregulated in multiple disease states, most notably in cancer where expression of mirnas appear to be tissue-specific [6,7]. Circulating nucleic acids were first described by Mandel and Metais in 1948, when nucleic acids were measured in human plasma [8]. The potential use of circulating nucleic acids extended to disease diagnosis much later, when increased levels of serum DNA distinguished cancer patients from healthy controls [9]. In addition, the possibility of nucleic acids as evaluators of therapeutic effectiveness was also reported, levels of serum DNA in cancer patients decreased when treatment was effective [10,11]. Recent studies have demonstrated that serum and plasma also contain a large amount of stable mirnas and have potential to serve as biomarkers for changes in physiological and pathological conditions, such as pregnancy, cancer, and other diseases [12,13,14,15,16]. Circulating mirnas show remarkable stability and demonstrate consistent expression profiles between healthy controls and patients [12,13,15,16]. The extraction and quantification of serum mirnas is a challenging task, however mirna detection is much easier than the detection of some current protein biomarkers. Although most studies have focused on using circulating mirnas as biomarkers in human, circulating mirnas in rodent models are able to distinguish healthy animals from diseased animals as well [14,17,18,19]. The exciting research of circulating mirna biomarkers has a great potential; however, the issue currently at the forefront of serum mirna research is proper normalization of mirna gene expression with invariant housekeeping genes. Normalization of circulating mirna remains a significant hurdle that must be addressed in order to facilitate biomarker discovery and fully validate single mirna quantitative real-time PCR (qrt-pcr) assays. It is important to ensure that gene expression differences are a direct result of the diseases under study and not due to other sources of variation [20]. Uncontrolled variation can be limited through normalization. Equal amounts of total RNA are commonly used as the initial normalizer when conducting qrt- PCR experiments. However, the total amount of mirna extracted from even the same quantities of serum or plasma from different samples is generally not equal. Research has been done to discover normalizers of mirna expression in tissue samples, which addresses the variation of RNA loading amounts between samples. For example Peltier and Latham reported expression of tissue mir-191 and mir-103 to be more consistent than commonly used small RNAs and even total RNA [20]. Even though mirna normalizers may be present in tissue, endogenous references specific to circulating mirnas have not been identified. PLoS ONE 1 February 2012 Volume 7 Issue 2 e31278
2 In this report, we have evaluated the serum mirna profiles of 20 individual mice from different strains using a TaqManH Array MicroRNA real-time PCR strategy in order to identify the mirnas with the most stable expression in the serum of mouse. These samples represent multiple strains of mice at different ages as well as different conditions, including autoimmune diabetes. Microarray analysis of 277 mirnas, using global normalization and subsequent data filters, identified five mirnas as circulating mirna endogenous references. Methods Mouse Female NOD/ShiLtJ (NOD n = 8, stock# ), NOR/LtJ (NOR n = 6, stock# ), and C57BL/6J (B6 n = 6, stock# ) (Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, Maine) mice were used for all experiments. NOD mice spontaneously develop T-cell mediated insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus staring at weeks old, while NOR mice only develop pancreatic insulitis without diabetes development. All animal studies have been approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC). Serum Collection Mouse blood was collected following euthanization via heart puncture. Blood was allowed to clot for at least 1 hour, centrifuged for 10 minutes63,000 rpm, and supernatant (serum) was removed. Centrifugation was repeated for 10 minutes62,500 rpm and the resulting serum layer was used for RNA isolation or stored at 280uC until further use. For NOD mice, serum was collected at 3 4 weeks, 7 8 weeks, weeks (non-diabetic), and after developing diabetes. For NOR and B6 mice, serum were collected at 3 4 weeks, 7 8 weeks, and weeks. Each time point from each mouse strain was duplicated. RNA Extraction and TaqManH Low-Density Array mirna qrt-pcr RNA was isolated from serum samples by using a combination of TrizolH LS (Invitrogen TM, Carlsbad, CA) and the mirvana TM mirna Isolation kit (AmbionH, Austin, TX) or the QiagenH mirneasyh Mini kit (Qiagen Inc.H, Germantown, MD) with some modifications. Each sample was measured by a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific). The RNA (about 50 ng) was reverse transcribed using the TaqManH MiRNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), and the TaqManH MiRNA Multiplex RT Assays, Rodent pool A (v2.0) (Applied Biosystems). 3 ml of RNA was added to each reaction and RT-PCR was carried out on the ABI Veriti TM Thermal cycler (Applied Biosystems). 2.5 ml of the product from each reverse transcription reaction was preamplified per the manufacturer s protocol with the Megaplex TM PreAmp Primers (106), Rodent pool A (v2.0), and TaqManH PreAmp Master Mix (26) using the ABI Veriti TM (Applied Biosystems). Following preamplification the mirna expression was profiled with TaqManH Rodent MicroRNA array card A v2.0, performed on a 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems), using the manufacturer s recommended protocol. Global Normalization and Statistical Analysis Raw cycle threshold (C T ) values were calculated using SDS 2.3 and RQ manager 1.2 software (Applied Biosystems) applying automatic baselines and threshold settings. The C T values were imported into StatMinerH 4.2 (IntegromicsH Inc., Philadelphia, PA) for global normalization of each sample. The mirnas that were detected in all 20 samples were selected for the reference set in global normalization [21]. Within each sample, the global normalization process subtracts the mean C T value of the reference set from the C T value of each mirna from the same sample. The resulting value is the DC T. Endogenous controls must be consistently expressed, thus only the mirnas that were expressed in all samples were considered to be candidates and subjected to further data analysis. These DC T values were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) using mouse strain as the predictor and the Least-significant difference method for pair-wise comparisons using SPSS (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). The mirnas with ANOVA p-values greater than 0.3, demonstrating no significant difference between strains, were retained as endogenous reference candidates. Endogenous references should have a small variation among all samples. Therefore the standard deviation (SD) across all samples was calculated using SPSS mirnas with an SD less than 1 were selected. Finally, in order to increase the strictness of our criteria the pair-wise DDC T of the candidate mirnas were analyzed to determine the difference in mean DC T values within the 3 strains. Candidate mirnas had DDC T values less than 0.5. Consequently genes with an ANOVA p.0.3, an SD,1, and all pair-wise DDC T,0.5 were selected as endogenous reference genes. Results Identification of serum mirna endogenous references Our data is based on 20 serum mirna expression profiles from B6, autoimmune-prone NOD, and NOR mouse strains, across different ages, and with diabetes and pancreatic inflammation. A total of 277 mirnas were expressed between all serum samples in the TaqManH Array MicroRNA Rodent A card, which contains 335 potential target mirnas. The DC T values for each mirna were calculated using the global normalization option of the StatMinerH software. The global normalization method is convenient for high-throughput mirna assays where quantities of initial loading amounts of RNA are difficult to accurately quantify. Of the 277 individually expressed mirnas, 72 displayed consistent expression across all 20 samples (Table S1). Using these 72 mirnas as the global normalization reference set in StatminerH, a heat map of all expression values (2DC T ) was generated (Figure 1). In order to be considered as potential endogenous references, only those mirnas that had an ANOVA p.0.3 for the comparison of the B6, NOD, and NOR (n = 20) mouse strains were selected. This 3-group comparison provided 21 mirnas with ANOVA p.0.3. The same criterion was applied to the pair-wise comparison of the 21 genes which produced 10 mirnas with least-significant difference p.0.3. These 10 mirnas passed our initial criteria of p.0.3 and were considered further (Table 1). The second criterion necessary for endogenous reference consideration were mirnas with a SD,1. This is similar to the criterion used to determine normalizers for mirna expression in various tissues [22,23]. As a result the SD values of the 10 candidate genes were calculated, and five mirnas passed our criteria of a p.0.3, and an SD,1. Finally, the five mirnas also met the criterion of all pair-wise DDC T,0.5 (Table 1). As shown in Figure 2, these five serum mirnas, mir-146a, mir-16, mir-195, mir-30e, and mir-744 were stably expressed in mouse regardless of strain, age, and disease condition. Furthermore, mir- 146a and mir-16 are highly expressed in serum, while mir-30e, mir-195, and mir-744 have relatively lower expression. PLoS ONE 2 February 2012 Volume 7 Issue 2 e31278
3 Figure 1. Global expression of serum mirnas in different mouse strains. Serum RNA was isolated from different aged (w = weeks) mouse strains (n = 20), with each time point duplicated. The globally normalized DC T values are represented in the heat map with mirna species ordered by hierarchical clustering. mirna expression was analyzed by TaqManH mirna arrays and normalized by StatMinerH global normalization. doi: /journal.pone g001 U6 is not stably expressed in mouse serum MammU6 (U6) RNA is commonly used as a normalizer for mirna expression in tissues and cells [20,24]. Recently, the use of this RNA has been extended to normalization of circulating mirna biomarkers [25,26,27]. As shown in Figure 3, U6 is expressed in all 20 samples, however, failed to meet our criteria as an endogenous reference. Based on the global normalization, U6 displays an ANOVA p-value of and an SD of 2.4, with at least a 4 fold difference in the expression between NOD vs. both B6 and NOR. Thus, U6 may not serve as a serum normalizer for mirnas. Discussion In the current study, we have defined five serum mirnas as endogenous references. To our knowledge this is the first study of serum endogenous references for mouse mirnas. Normalization techniques for circulating mirnas have yet to be perfected. Some of the normalizing methods for serum or plasma mirna reported are adopted from tissue studies, including the use of U6, which has stirred concern in recent studies. snorna and RNU6B (U6) have been described as instable in serum and therefore cannot be used for normalization [28]. U6 and 5S were reportedly degraded in some serum samples [15]. As reported in our current study, our data further confirmed that U6 is not a good candidate for an endogenous reference for serum mirna expression. Additionally, mirna mir-191 and mir-103 have been reported as internal controls for tissue mirna expression [20]. Serum mir-191 is expressed in all samples, however there is a significant difference (p = 0.001) between all samples (data not shown here). Therefore, mir-191 fails to meet our endogenous control criteria and was not considered further as a serum mirna internal reference. Similarly, serum mir-103 does not have the stability as reported in tissue samples, being only expressed in 5 of our 20 samples (data not shown here), and does not meet our endogenous control requirements either. Thus, tissue mirna internal controls may not be suitable for serum internal references. The total mirnas present in serum and plasma are very low, and efficient reproducible recovery of this RNA is a challenging task. Furthermore, the yield of RNA from small volume serum or plasma samples has, in our hand and others, been below the limit of accurate quantitation by OD measurement. Considerable sample-to-sample (strain to strain in mouse) variability in both protein and lipid content of plasma and serum samples, which could potentially affect efficiency of RNA extraction and introduce inhibitors of PCR reactions, will further add to the variation of RNA extraction and efficiency of PCR reactions. In order to adjust for those variations, C. elegans synthetic mirnas spiked in at the onset of the RNA isolation process has been adopted by many researchers to provide an internal reference for normalization of technical variations between samples [13]. However, variation of the amount of mirnas present in a given individual serum or PLoS ONE 3 February 2012 Volume 7 Issue 2 e31278
4 Table 1. Mouse endogenous control selection process. Candidate mirna ANOVA Pair-wise p.0.3 LSD p.0.3 SD,1 DDCt,0.5 mir pass pass mir-30e pass pass mir-146a pass pass mir pass pass mir pass pass mir-29a pass mir-200c pass mir-let 7g pass mir pass mir-2965p pass mir-133b fail mir-199a3p fail mir-5325p fail mir-146b fail mir fail mir-1395p fail mir-200b fail mir fail mir fail mir fail mir-92a fail From 335 potential target mirnas, 277 total mirnas were expressed over all samples, and 72 mirnas were expressed in all 20 samples. These 72 mirnas were candidate endogenous controls, following a series of statistical analyses only five genes (mir-146a, mir-16, mir-195, mir-30e, and mir-744) passed the criteria of ANOVA p.0.3, SD,1, and pair-wise DDC T,0.5. doi: /journal.pone t001 plasma sample, which could be genetically controlled or introduced by many factors, cannot be normalized by this strategy. Invariant serum housekeeping mirnas are urgently needed for circulating mirna studies [29]. Without an acceptable standard for normalization, circulating mirna biomarkers are limited in claims of diagnostic discovery and evaluation because they cannot be evaluated individually. It is expected, theoretically, that a true endogenous reference would be stably expressed, where expressions are not affected by the difference of strains, age, and conditions, including diseases. The five genes we identified here are an important discovery and may serve as good normalizers for circulating mirnas for several reasons. First, 20 mirna microarrays have been completed which are a large number of arrays from a variety of mouse strains and ages. Second, in addition to a low SD, a criterion successfully used to identify tissue endogenous references [22,23], the additional criteria, ANOVA p.0.3 and pair-wise DDC T,0.5, have also been employed in our strategy in order to strengthen our endogenous reference selection. Finally, the fact that consistent expression of five genes in circulating mirna expression profiles exists from multiple mouse strains, at different ages, and with different disease models provides strong evidence that mir-146a, mir-16, mir-195, mir-30e, and mir-744 are useful as circulating mirna endogenous references. Using a selection of these candidates, we have successfully validated some serum biomarkers for diabetes in NOD mice as well as metastatic lung melanoma in the mouse model by single qrt-pcr reactions following global normalization of array data (our unpublished data). When choosing a qrt-pcr serum endogenous reference, we recommend careful consideration of endogenous mirna controls based on RNA loading amounts and mirna expression abundances. As shown in Figure 2, mir-146a and mir-16 are highly expressed in serum, while mir-30e, mir-195, and mir-744 have lower expression levels. For instance, if an experiment is working with lower abundance of mirna, it may be worthwhile to select those controls with lower expression in order to properly validate the mirna of interest. In addition, mir-146a has been implicated in immune cell regulation, cancer, b-cell failure, and potentially type 2 diabetes [29,30,31,32]. Therefore, more precautions should be taken for the use of mir-146a as an endogenous reference in certain disease models. We preformed normalization of single qrt-pcr targets from the related mouse disease model using mir-146a, mir-16, and mir-195. Cross normalization of these references to each other revealed that mir- 16 and mir-195 are extremely stable endogenous references in this particular mouse model (our unpublished data). We recommend that suitable endogenous controls should be selected in light of the study design and research conditions, and that the use of 2 3 endogenous references together may additionally reduce bias and variation [20,30,31]. Choosing more than one reference mirna will reduce the possibility that any endogenous references may be regulated by specific conditions, in which these references should not serve as endogenous references. Small fold change differences of potential biomarkers may not be identified with our reference genes, however we are confident that based on the stability of the mirnas presented here the biomarkers Figure 2. Five serum mirnas as endogenous references stably expressed across different mouse strains. 2DC T values of mir-146a, mir-16, mir-195, mir-30e, and mir-744 show stability across all samples (w = weeks). The 2DC T average of all five mirnas is also displayed. Each gene is expressed across all samples, has an ANOVA p.0.3, an SD,1 and all pair-wise DDC T,0.5. doi: /journal.pone g002 PLoS ONE 4 February 2012 Volume 7 Issue 2 e31278
5 Figure 3. MammU6 is differentially expressed in the different mouse strains. Bar plots of the average MammU6 expression for each mouse strain are given with standard error bars. An ANOVA comparison detects a significant difference in the means, p-value of 0.049, an LSD p- value of (B6 vs. NOD), and common SD of 2.4. doi: /journal.pone g003 identified with these reference genes is better than currently accepted serum mirna references. Currently, there are no reliable human serum internal references reported. It is unclear whether the identified five mirnas here are also stably expressed in human serum samples. Notably, these five mirnas, mir-16, mir-744, mir-195, mir- 146a, and mir-30e share a 100% identity between human and mouse [32,33,34,35]. Interestingly, two recently published papers reporting on serum mirna biomarkers for specific diseases have used mir-16 as an internal control to normalize qrt-pcr data [16,36]. However, a large number of human samples are needed to further validate this endogenous reference. In conclusion, using a TaqManH real-time PCR mirna array and global gene expression normalization strategy, we have analyzed 20 individual serum mirna expression profiles from multiple animal strains across different ages as well as different References 1. Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: Chen CZ, Lodish HF (2005) MicroRNAs as regulators of mammalian hematopoiesis. Semin Immunol 17: Zhou L, Seo KH, Wong HK, Mi QS (2009) MicroRNAs and immune regulatory T cells. Int Immunopharmacol 9: Zhou L, Seo KH, He HZ, Pacholczyk R, Meng DM, et al. (2009) Tie2creinduced inactivation of the mirna-processing enzyme Dicer disrupts invariant NKT cell development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: Cobb BS, Hertweck A, Smith J, O Connor E, Graf D, et al. (2006) A role for Dicer in immune regulation. J Exp Med 203: Calin GA, Croce CM (2006) MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer 6: Esquela-Kerscher A, Slack FJ (2006) Oncomirs - micrornas with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6: Mandel P, Metais P (1948) Les acides necleiques du plasma sanguin chez l Homme. C R Acad Sci Paris 142: Stroun M, Anker P, Maurice P, Lyautey J, Lederrey C, et al. (1989) Neoplastic characteristics of the DNA found in the plasma of cancer patients. Oncology 46: Leon SA, Shapiro B, Sklaroff DM, Yaros MJ (1977) Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy. Cancer Res 37: Tong YK, Lo YM (2006) Diagnostic developments involving cell-free (circulating) nucleic acids. Clin Chim Acta 363: Gilad S, Meiri E, Yogev Y, Benjamin S, Lebanony D, et al. (2008) Serum micrornas are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One 3: e Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, et al. (2008) Circulating micrornas as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: Wang K, Zhang S, Marzolf B, Troisch P, Brightman A, et al. (2009) Circulating micrornas, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106: conditions. We have found five mirnas, mir-146a, mir-16, mir-195, mir-30e, and mir-744 to be stably expressed in all tested strains across different ages and conditions. Thus, these mirnas may be used as mouse serum mirna endogenous references necessary for single assay studies. The discovery of consistent expression of these specific serum mirnas will promote the generation of more accurate mirna expression profiles and more accurate interpretation of qrt-pcr data. Although we are convinced that these five mirnas are the best circulating endogenous references reported so far, the question why these mirnas are stable in mouse serum remains to be answered. Further investigation into the function of these specific serum mirnas, the validation of their expression stability in different disease conditions, and their expression stability in human samples are needed. Supporting Information Table S1 Results of TaqManH Low-Density Array mirna qrt-pcr expression levels of B6, NOD, and NOR female mice. C T values of mirna expressed in all samples. These mirnas were considered as candidates for circulating endogenous control candidates. mirna names and identification numbers are from the TaqManH Rodent Micro- RNA qrt-pcr array card A v2.0. (DOC) Acknowledgments We thank Min Liu for her efforts in maintaining our mouse colony and assistance with serum collection, and all members of our laboratory for their advice and encouragement. Author Contributions Conceived and designed the experiments: QSM LZ MW RQ XG. Performed the experiments: MW RQ QSM LZ. Analyzed the data: MW RQ LP QSM LZ. Wrote the paper: MW QSM LZ XG. 15. Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, Cai X, Yin Y, et al. (2008) Characterization of micrornas in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res 18: Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, Pushkaran B, Liggins AP, et al. (2008) Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated micrornas in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol 141: Ji X, Takahashi R, Hiura Y, Hirokawa G, Fukushima Y, et al. (2009) Plasma mir-208 as a biomarker of myocardial injury. Clin Chem 55: Laterza OF, Lim L, Garrett-Engele PW, Vlasakova K, Muniappa N, et al. (2009) Plasma MicroRNAs as sensitive and specific biomarkers of tissue injury. Clin Chem 55: D Alessandra Y, Devanna P, Limana F, Straino S, Di Carlo A, et al. (2010) Circulating micrornas are new and sensitive biomarkers of myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J 31: Peltier HJ, Latham GJ (2008) Normalization of microrna expression levels in quantitative RT-PCR assays: identification of suitable reference RNA targets in normal and cancerous human solid tissues. RNA 14: Cui W, Ma J, Wang Y, Biswal S (2011) Plasma mirna as biomarkers for assessment of total-body radiation exposure dosimetry. PLoS One 6: e de Kok JB, Roelofs RW, Giesendorf BA, Pennings JL, Waas ET, et al. (2005) Normalization of gene expression measurements in tumor tissues: comparison of 13 endogenous control genes. Lab Invest 85: Lossos IS, Czerwinski DK, Wechser MA, Levy R (2003) Optimization of quantitative real-time RT-PCR parameters for the study of lymphoid malignancies. Leukemia 17: Shell S, Park SM, Radjabi AR, Schickel R, Kistner EO, et al. (2007) Let-7 expression defines two differentiation stages of cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: Ng EK, Chong WW, Jin H, Lam EK, Shin VY, et al. (2009) Differential expression of micrornas in plasma of patients with colorectal cancer: a potential marker for colorectal cancer screening. Gut 58: PLoS ONE 5 February 2012 Volume 7 Issue 2 e31278
6 26. Vasilescu C, Rossi S, Shimizu M, Tudor S, Veronese A, et al. (2009) MicroRNA fingerprints identify mir-150 as a plasma prognostic marker in patients with sepsis. PLoS One 4: e Tsujiura M, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, Shiozaki A, Takeshita H, et al. (2010) Circulating micrornas in plasma of patients with gastric cancers. Br J Cancer 102: Wittmann J, Jack HM (2010) Serum micrornas as powerful cancer biomarkers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1806: Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, Tewari M (2010) Analysis of circulating microrna biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-pcr (qrt-pcr). Methods 50: Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-pcr data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64: Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, et al. (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3: RESEARCH Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S (2011) mirbase: integrating microrna annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 39: D Griffiths-Jones S, Saini HK, van Dongen S, Enright AJ (2008) mirbase: tools for microrna genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 36: D Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ (2006) mirbase: microrna sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34: D Griffiths-Jones S (2004) The microrna Registry. Nucleic Acids Res 32: D Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, Peng Z, Sheng W, et al. (2010) Plasma micrornas are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 127: PLoS ONE 6 February 2012 Volume 7 Issue 2 e31278
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization
 A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
Identification of Suitable Reference Genes for qpcr Analysis of Serum microrna in Gastric Cancer Patients
 DOI 10.1007/s10620-011-1981-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Suitable Reference Genes for qpcr Analysis of Serum microrna in Gastric Cancer Patients Jianning Song Zhigang Bai Wei Han Jun Zhang Hua
DOI 10.1007/s10620-011-1981-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Identification of Suitable Reference Genes for qpcr Analysis of Serum microrna in Gastric Cancer Patients Jianning Song Zhigang Bai Wei Han Jun Zhang Hua
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo. Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale
 Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
From reference genes to global mean normalization
 From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Supplementary webappendix
 Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Kratz JR, He J, Van Den Eeden SK, et
Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis
 Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis M.L. Zhi 1 *, Z.J. Liu 2 *, X.Y. Yi 1, L.J. Zhang 1 and Y.X. Bao 1 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated
Diagnostic performance of microrna-29a for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis M.L. Zhi 1 *, Z.J. Liu 2 *, X.Y. Yi 1, L.J. Zhang 1 and Y.X. Bao 1 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Affiliated
Research Article Base Composition Characteristics of Mammalian mirnas
 Journal of Nucleic Acids Volume 2013, Article ID 951570, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/951570 Research Article Base Composition Characteristics of Mammalian mirnas Bin Wang Department of Chemistry,
Journal of Nucleic Acids Volume 2013, Article ID 951570, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/951570 Research Article Base Composition Characteristics of Mammalian mirnas Bin Wang Department of Chemistry,
encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most /BSR BIOSCIENCE REPORTS
 Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control
 microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
microrna analysis for the detection of autologous blood transfusion in doping control Application note Doping Control Authors Francesco Donati*, Fiorella Boccia, Xavier de la Torre, Alessandra Stampella,
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology xxx (2010) xxx xxx
 Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology xxx (2010) xxx xxx Circulating micrornas: Association with disease and potential use as biomarkers Glen Reid, Michaela B. Kirschner, Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases
Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology xxx (2010) xxx xxx Circulating micrornas: Association with disease and potential use as biomarkers Glen Reid, Michaela B. Kirschner, Nico van Zandwijk Asbestos Diseases
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury. HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011
 Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011 Karol Thompson, PhD Center for Drug Evaluation & Research US Food
Assaying micrornas in biofluids for detection of drug induced cardiac injury HESI Annual Meeting State of the Science Session June 8, 2011 Karol Thompson, PhD Center for Drug Evaluation & Research US Food
Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD! Assistant Member! Department of Thoracic Surgery! Roswell Park Cancer Institute!
 Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Thoracic Surgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute MicroRNA biology, techniques and applications History Biogenesis Nomenclature Tissue specificity Mechanisms
Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Thoracic Surgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute MicroRNA biology, techniques and applications History Biogenesis Nomenclature Tissue specificity Mechanisms
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer
 Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury
 Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury Susumu Hachisuka 1, Naosuke Kamei, MD, PhD 2, Satoshi Ujigo 3, Shigeru Miyaki 3, Mitsuo Ochi 3. 1 Hiroshima
Circulating Microrna Expression As A Biomarker For Early Diagnosis Of Severity In Spinal Cord Injury Susumu Hachisuka 1, Naosuke Kamei, MD, PhD 2, Satoshi Ujigo 3, Shigeru Miyaki 3, Mitsuo Ochi 3. 1 Hiroshima
Serum MicroRNA Expression Profile Distinguishes Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus 16 Infections in Patients with Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease
 Serum MicroRNA Expression Profile Distinguishes Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus 16 Infections in Patients with Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease Lunbiao Cui 1,2., Yuhua Qi 1., Haijing Li 2, Yiyue Ge 1, Kangchen
Serum MicroRNA Expression Profile Distinguishes Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus 16 Infections in Patients with Hand-Foot-and-Mouth Disease Lunbiao Cui 1,2., Yuhua Qi 1., Haijing Li 2, Yiyue Ge 1, Kangchen
Supplementary Figure 1: Experimental design. DISCOVERY PHASE VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) (N = 20) Healthy = 20. Healthy = 6. Endometriosis = 33
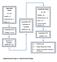 DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
Cellecta Overview. Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA
 Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Identification of Potential Reference mirna for qrt-pcr Studies in Cancers Using mirna-seq Data
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 12 (2017) pp. 1327-1333 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.150
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 6 Number 12 (2017) pp. 1327-1333 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.612.150
Morphogens: What are they and why should we care?
 Morphogens: What are they and why should we care? Historic, Theoretical Mechanism of Action Nucleoprotein: the specific trophic cellular material extracted from the cell nucleus. DNA and RNA which regulates
Morphogens: What are they and why should we care? Historic, Theoretical Mechanism of Action Nucleoprotein: the specific trophic cellular material extracted from the cell nucleus. DNA and RNA which regulates
Clinical Study MicroRNA Expression Profile in CAD Patients and the Impact of ACEI/ARB
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Cardiology Research and Practice Volume 20, Article ID 53295, 5 pages doi:0.406/20/53295 Clinical Study MicroRNA Expression Profile in CAD Patients and the Impact of ACEI/ARB
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Cardiology Research and Practice Volume 20, Article ID 53295, 5 pages doi:0.406/20/53295 Clinical Study MicroRNA Expression Profile in CAD Patients and the Impact of ACEI/ARB
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing
 Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing RNA-seq Course November 8th 2017 Marc Friedländer ComputaAonal RNA Biology Group SciLifeLab / Stockholm University Special thanks to Jakub Westholm for
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing RNA-seq Course November 8th 2017 Marc Friedländer ComputaAonal RNA Biology Group SciLifeLab / Stockholm University Special thanks to Jakub Westholm for
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Plasma mirna-134 is a diagnostic biomarker for acute pulmonary embolism in middle and high altitude areas.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (12): 5494-5498 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Plasma mirna-134 is a diagnostic biomarker for acute pulmonary embolism in middle and high altitude areas. Yaping Wang 1#,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (12): 5494-5498 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Plasma mirna-134 is a diagnostic biomarker for acute pulmonary embolism in middle and high altitude areas. Yaping Wang 1#,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers
 Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Detection of let-7a MicroRNA by Real-time PCR in Colorectal Cancer: a Single-centre Experience from China
 The Journal of International Medical Research 2007; 35: 716 723 Detection of let-7a MicroRNA by Real-time PCR in Colorectal Cancer: a Single-centre Experience from China W-J FANG 1, C-Z LIN 2, H-H ZHANG
The Journal of International Medical Research 2007; 35: 716 723 Detection of let-7a MicroRNA by Real-time PCR in Colorectal Cancer: a Single-centre Experience from China W-J FANG 1, C-Z LIN 2, H-H ZHANG
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Marta Puerto Plasencia. microrna sponges
 Marta Puerto Plasencia microrna sponges Introduction microrna CircularRNA Publications Conclusions The most well-studied regions in the human genome belong to proteincoding genes. Coding exons are 1.5%
Marta Puerto Plasencia microrna sponges Introduction microrna CircularRNA Publications Conclusions The most well-studied regions in the human genome belong to proteincoding genes. Coding exons are 1.5%
micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD
 micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD mentors: Dr. Yael Nevo-Caspi & Prof. Gidi Paret Or Bercovich Liat Mor What will we talk about Congenital heart defects (CHD) Scientific
micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD mentors: Dr. Yael Nevo-Caspi & Prof. Gidi Paret Or Bercovich Liat Mor What will we talk about Congenital heart defects (CHD) Scientific
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success
 micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
medoct group, Medical University Vienna, Jack Ballantyne, PhD National Center for Forensic Science, Orlando, FL USA
 medoct group, Medical University Vienna, Jack Ballantyne, PhD National Center for Forensic Science, Orlando, FL USA Association of Forensic DNA Analysts and Administrators San Antonio, TX June 2012 Perceived
medoct group, Medical University Vienna, Jack Ballantyne, PhD National Center for Forensic Science, Orlando, FL USA Association of Forensic DNA Analysts and Administrators San Antonio, TX June 2012 Perceived
A Blood-Based Biomarker for screening for Colorectal Cancer
 WEO CRC SC Meeting Hong Kong, 25 Sep, 2017 A Blood-Based Biomarker for screening for Colorectal Cancer K.G. YEOH MBBS, MMed, FRCP (London), FRCP (Glasg), FAMS Dean, School of Medicine, National University
WEO CRC SC Meeting Hong Kong, 25 Sep, 2017 A Blood-Based Biomarker for screening for Colorectal Cancer K.G. YEOH MBBS, MMed, FRCP (London), FRCP (Glasg), FAMS Dean, School of Medicine, National University
95% CI: , P=0.037).
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Bi 8 Lecture 17. interference. Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016
 Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Bi 8 Lecture 17 REGulation by RNA interference Ellen Rothenberg 1 March 2016 Protein is not the only regulatory molecule affecting gene expression: RNA itself can be negative regulator RNA does not need
Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(6) Hypothesis Deciphering the Role of micrornas in BRD4-NUT Fusion Gene Induced NUT Midline Carcinoma Ekta Pathak 1, Bhavya 1, Divya Mishra 1, Neelam Atri 1, 2, Rajeev
Circulating Nucleic Acids in Plasma and Serum: An Overview
 Circulating Nucleic Acids in Plasma and Serum: An Overview Y. M. DENNIS LO Department of Chemical Pathology and Institute of Molecular Oncology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital,
Circulating Nucleic Acids in Plasma and Serum: An Overview Y. M. DENNIS LO Department of Chemical Pathology and Institute of Molecular Oncology, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Prince of Wales Hospital,
Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping
 Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping Melanie Rae Simpson PhD candidate Department of Public Health and General Practice Norwegian University of
Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping Melanie Rae Simpson PhD candidate Department of Public Health and General Practice Norwegian University of
Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
The mirna Revolution. mirna Profiling in serum & plasma: On the road to biomarker development
 Isolation Quantification Functionalization The mirna Revolution mirna Profiling in serum & plasma: On the road to biomarker development Eric Lader, PhD Senior Director, R&D eric.lader@qiagen.com - 1 -
Isolation Quantification Functionalization The mirna Revolution mirna Profiling in serum & plasma: On the road to biomarker development Eric Lader, PhD Senior Director, R&D eric.lader@qiagen.com - 1 -
mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
 Molecules 2014, 19, 1568-1575; doi:10.3390/molecules19021568 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
Molecules 2014, 19, 1568-1575; doi:10.3390/molecules19021568 Article OPEN ACCESS molecules ISSN 1420-3049 www.mdpi.com/journal/molecules mirna in Plasma Exosome is Stable under Different Storage Conditions
CRS4 Seminar series. Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4. Biomedicine. Bioinformatics. Paolo Uva July 11, 2012
 CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
CRS4 Seminar series Inferring the functional role of micrornas from gene expression data CRS4 Biomedicine Bioinformatics Paolo Uva July 11, 2012 Partners Pharmaceutical company Fondazione San Raffaele,
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research
 MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in skin research Eniko Sonkoly, Andor Pivarcsi KI, Department of Medicine, Unit of Dermatology and Venerology What are micrornas? Small, ~21-mer RNAs 1993: The first mirna discovered,
AmoyDx TM BRAF V600E Mutation Detection Kit
 AmoyDx TM BRAF V600E Mutation Detection Kit Detection of V600E mutation in the BRAF oncogene Instructions For Use Instructions Version: B3.1 Date of Revision: April 2012 Store at -20±2 o C 1/5 Background
AmoyDx TM BRAF V600E Mutation Detection Kit Detection of V600E mutation in the BRAF oncogene Instructions For Use Instructions Version: B3.1 Date of Revision: April 2012 Store at -20±2 o C 1/5 Background
STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells
 CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
CAMDA 2009 October 5, 2009 STAT1 regulates microrna transcription in interferon γ stimulated HeLa cells Guohua Wang 1, Yadong Wang 1, Denan Zhang 1, Mingxiang Teng 1,2, Lang Li 2, and Yunlong Liu 2 Harbin
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis
 Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Reduced mirna-218 expression in pancreatic cancer patients as a predictor of poor prognosis B.-S. Li, H. Liu and W.-L. Yang Department of Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Surgery, The Third Xiangya Hospital
Chapter 18. mirna Expression Profiling: From Reference Genes to Global Mean Normalization
 Chapter 18 mirna Expression Profiling: From Reference Genes to Global Mean Normalization Barbara D haene, Pieter Mestdagh, Jan Hellemans, and Jo Vandesompele Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are an important
Chapter 18 mirna Expression Profiling: From Reference Genes to Global Mean Normalization Barbara D haene, Pieter Mestdagh, Jan Hellemans, and Jo Vandesompele Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are an important
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients
 mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
mir-125a-5p expression is associated with the age of breast cancer patients H. He 1 *, F. Xu 2 *, W. Huang 1, S.Y. Luo 1, Y.T. Lin 1, G.H. Zhang 1, Q. Du 1 and R.H. Duan 1 1 The State Key Laboratory of
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant
 National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) Foundation Annual Progress Report: 2009 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The National Surgical
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
RNA-seq Introduction
 RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients
 Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles
 On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
Cancer Problems in Indonesia
 mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
mirna and Cancer : mirna as a Key Regulator in Cancer Sofia Mubarika 2 nd Symposium Biomolecular Update in Cancer PERABOI Padang 18 Mei 2013 Cancer Problems in Indonesia 1. Chemoresistency / recurrency
Lombardi Cancer Center Georgetown University Washington, DC
 Lombardi Cancer Center Georgetown University Washington, DC Lombardi Cancer Center Georgetown University Washington, DC microrna and other nucleic acids analysis in liquid biopsies Anton Wellstein World
Lombardi Cancer Center Georgetown University Washington, DC Lombardi Cancer Center Georgetown University Washington, DC microrna and other nucleic acids analysis in liquid biopsies Anton Wellstein World
Title: Dysregulated mir-183 Inhibits Migration in Breast Cancer
 Author's response to reviews Title: Dysregulated mir-183 Inhibits Migration in Breast Cancer Authors: Aoife J Lowery (aoife.lowery@gmail.com) Nicola Miller (nicola.miller@nuigalway.ie) Roisin M Dwyer (roisin.dwyer@nuigalway.ie)
Author's response to reviews Title: Dysregulated mir-183 Inhibits Migration in Breast Cancer Authors: Aoife J Lowery (aoife.lowery@gmail.com) Nicola Miller (nicola.miller@nuigalway.ie) Roisin M Dwyer (roisin.dwyer@nuigalway.ie)
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Circulating micrornas in plasma of patients with gastric cancers
 British Journal of (21) 12, 1174 1179 & 21 Research UK All rights reserved 7 92/1 $32. www.bjcancer.com Circulating micrornas in plasma of s with gastric cancers M Tsujiura 1, D Ichikawa*,1, S Komatsu
British Journal of (21) 12, 1174 1179 & 21 Research UK All rights reserved 7 92/1 $32. www.bjcancer.com Circulating micrornas in plasma of s with gastric cancers M Tsujiura 1, D Ichikawa*,1, S Komatsu
Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs
 Protein Cell 15, 6(1):1 5 DOI 1.17/s13238-14-116-2 Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs Jie Xu, Xi Chen, Donghai Li, Qun Chen, Zhen Zhou, Dongxia
Protein Cell 15, 6(1):1 5 DOI 1.17/s13238-14-116-2 Small RNA existed in commercial reverse transcriptase: primary evidence of functional small RNAs Jie Xu, Xi Chen, Donghai Li, Qun Chen, Zhen Zhou, Dongxia
Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational Methods
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 5 May 2013 PP.70-74 Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 2 Issue 5 May 2013 PP.70-74 Identification of mirnas in Eucalyptus globulus Plant by Computational
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities
 Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
Supplementary information for: Human micrornas co-silence in well-separated groups and have different essentialities Gábor Boross,2, Katalin Orosz,2 and Illés J. Farkas 2, Department of Biological Physics,
Milk micro-rna information and lactation
 Christophe Lefèvre, BioDeakin,. Deakin University, Geelong VIC Australia Milk micro-rna information and lactation New Signals in milk? - Markers of milk and lactation status? - Signal infant development?
Christophe Lefèvre, BioDeakin,. Deakin University, Geelong VIC Australia Milk micro-rna information and lactation New Signals in milk? - Markers of milk and lactation status? - Signal infant development?
Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Serum: A Fingerprint for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Clinical Chemistry 56:12 1871 1879 (2010) Cancer Diagnostics Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Serum: A Fingerprint for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Chunni Zhang, 1* Cheng Wang, 1 Xi Chen, 2 Cuihua
Clinical Chemistry 56:12 1871 1879 (2010) Cancer Diagnostics Expression Profile of MicroRNAs in Serum: A Fingerprint for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Chunni Zhang, 1* Cheng Wang, 1 Xi Chen, 2 Cuihua
Analyses on Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Huai an Area, China, 2010
 Open Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2014, 4, 504-512 Published Online June 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojpm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojpm.2014.46059 Analyses on Cancer Incidence and
Open Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2014, 4, 504-512 Published Online June 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojpm http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojpm.2014.46059 Analyses on Cancer Incidence and
The Role of micrornas in Pain. Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan
 The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
The Role of micrornas in Pain Phd Work of: Rehman Qureshi Advisor: Ahmet Sacan 1 Motivation for molecular analysis of Pain Chronic pain one of the most common causes for seeking medical treatment Approximate
Research Article Malignancy Associated MicroRNA Expression Changes in Canine Mammary Cancer of Different Malignancies
 ISRN Veterinary Science, Article ID 148597, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/148597 Research Article Malignancy Associated MicroRNA Expression Changes in Canine Mammary Cancer of Different Malignancies
ISRN Veterinary Science, Article ID 148597, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/148597 Research Article Malignancy Associated MicroRNA Expression Changes in Canine Mammary Cancer of Different Malignancies
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr)
 Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Single Cell Quantitative Polymer Chain Reaction (sc-qpcr) Analyzing gene expression profiles from a bulk population of cells provides an average profile which may obscure important biological differences
Strathprints Institutional Repository
 Strathprints Institutional Repository Tate, Rothwelle and Rotondo, Dino and Davidson, Jillian (2015) Regulation of lipid metabolism by micrornas. Current Opinion in Lipidology, 26 (3). pp. 243-244. ISSN
Strathprints Institutional Repository Tate, Rothwelle and Rotondo, Dino and Davidson, Jillian (2015) Regulation of lipid metabolism by micrornas. Current Opinion in Lipidology, 26 (3). pp. 243-244. ISSN
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing. Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven
 Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
Deploying the full transcriptome using RNA sequencing Jo Vandesompele, CSO and co-founder The Non-Coding Genome May 12, 2016, Leuven Roadmap Biogazelle the power of RNA reasons to study non-coding RNA
A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8281-8287 A meta-analysis of the effect of microrna-34a on the progression and prognosis of gastric cancer Z. LI 1, Z.-M. LIU 2, B.-H.
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis
 Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Author's response to reviews Title:Identification of a novel microrna signature associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) patient prognosis Authors: Mei-Yin Zhang (zhangmy@sysucc.org.cn) Shu-Hong
Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Benchmarking the Multiplex Circulating and Cellular mirna Assays using Abcam s Firefly particle technology
 Benchmarking the Multiplex Circulating and Cellular mirna Assays using Abcam s Firefly particle technology Technical note Abstract The full utility of mirna profiling has yet to be realized largely due
Benchmarking the Multiplex Circulating and Cellular mirna Assays using Abcam s Firefly particle technology Technical note Abstract The full utility of mirna profiling has yet to be realized largely due
The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients using a novel real-time PCR platform
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Gynecologic Oncology 112 (2009) 55 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Gynecologic Oncology 112 (2009) 55 59 www.elsevier.com/locate/ygyno The detection of differentially expressed micrornas from the serum of ovarian cancer patients
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Chapter 7 Conclusions
 VII-1 Chapter 7 Conclusions VII-2 The development of cell-based therapies ranging from well-established practices such as bone marrow transplant to next-generation strategies such as adoptive T-cell therapy
VII-1 Chapter 7 Conclusions VII-2 The development of cell-based therapies ranging from well-established practices such as bone marrow transplant to next-generation strategies such as adoptive T-cell therapy
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer
 The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis
 Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis T.-Y. Wang 1, S.-G. Liu 2, B.-S. Zhao 2, B. Qi 2, X.-G. Qin 2 and W.-J. Yao 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
Implications of microrna-197 downregulated expression in esophageal cancer with poor prognosis T.-Y. Wang 1, S.-G. Liu 2, B.-S. Zhao 2, B. Qi 2, X.-G. Qin 2 and W.-J. Yao 2 1 Department of Biochemistry
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
