MATERIALS AND METHODS
|
|
|
- Norah O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cornea Inhibits Inflammatory Lymphangiogenesis in Early and Middle Stages Don Yuen, 1 Bronek Pytowski, 2 and Lu Chen 1 PURPOSE. Lymphangiogenesis (LG) accompanies many corneal diseases after inflammatory, infectious, or chemical insults and is a primary mediator of transplant rejection. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether there is a time window for therapeutic intervention of corneal LG and whether a combined blockade of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 effectively suppresses early-, middle-, or late-stage LG. METHODS. Corneal inflammatory neovascularization was induced by a standard suture placement model in mice. Neutralizing antibodies against VEGFR-3 and/or VEGFR-2 were administrated systemically with the treatment started at postoperative day 0, day 7, or day 14. Whole mount corneas were sampled for immunofluorescence microscopic studies using LYVE-1 (a lymphatic marker) antibodies. Digital images were analyzed by software. RESULTS. Both VEGFR-3 and VEGFR-2 were involved in corneal suture-induced inflammatory LG. Their combined blockade led to a significant inhibition of both early- and middle-stage LG while demonstrating no effect on late-stage LG. CONCLUSIONS. Corneal inflammatory LG has a discrete time window for intervention therapy. Although it is important to start the treatment as soon as possible, interventions initiated in the middle of the LG process are still effective. These novel findings will shed some light on our understanding of inflammatory LG and the development of new therapeutic protocols for LG-related diseases at different stages. (Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52: ) DOI: /iovs From the 1 Center of Eye Disease and Development, Program in Vision Science, and School of Optometry, University of California, Berkeley, California; and 2 ImClone Systems, Eli Lilly and Company, New York, New York. Supported in part by research grants from the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Defense, and the University of California at Berkeley (LC). Submitted for publication August 13, 2010; revised December 2, 2010; accepted December 17, Disclosure: D. Yuen, None; B. Pytowski, ImClone Systems (E); L. Chen, None Corresponding author: Lu Chen, 689 Minor Hall, Center of Eye Disease and Development, Program in Vision Science, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720; chenlu@berkeley.edu. Lymphatic research has experienced exponential growth in recent years largely because of the advancement of technologies and the discoveries of several lymphatic endothelial specific molecules, including lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronic acid receptor-1 (LYVE-1), Prox-1, and VEGFR-3. The lymphatic network penetrates most tissues in the body, and its dysfunction has been found in a broad spectrum of disorders, such as cancer metastasis, inflammation, transplant rejection, obesity, and hypertension. 1 6 To date, there is still little effective treatment for lymphatic diseases; it is, therefore, a field with an urgent demand for new therapeutic protocols. Given its accessible location and transparent nature, the cornea provides an optimal site for lymphatic research. Although the normal cornea does not have lymphatic vessels, lymphangiogenesis (LG; the development of new lymphatic vessels) can be induced in this tissue after inflammatory, traumatic, chemical, or infectious damage. 7 9 LG also constitutes the afferent arm of the immune reflex arc of corneal transplantation immunity, 7,9,10 and, most recently, it has been demonstrated that LG is a primary mediator of corneal transplant rejection. 11 The VEGF family is the backbone of a complex network controlling blood and lymphatic vessel processes. A number of previous studies have shown that VEGFR-3 mediates LG in the cornea and other tissues, and its inhibition suppresses transplant rejection, tumor growth, and metastasis The specific role of VEGFR-2 in LG, however, has been much less studied. It is known that this factor is critically involved in hemangiogenesis (HG; the development of new blood vessels) and that its inhibition suppresses HG and tumor growth Most recently, it has been indicated that VEGFR-2 also plays a role in corneal LG, 12,22,23 though the underlying mechanisms still remain largely unknown. Although results from previous corneal studies on LG are promising, there is still a large knowledge gap when translating these results to clinic settings. For example, almost all the previous studies focused on how to prevent LG by testing an intervention started right before, or on the same day as, a pathologic stimulation, which happens only infrequently in patients. Indeed, many patients who need LG treatment miss their first chance to receive emergent care, possibly because of difficult living conditions, transportation problems, or insufficient knowledge about the disease process itself. Indeed, LG is a progressive event that can occur insidiously at its early phases. In this study, we first demonstrate that VEGFR-2 is involved in suture-induced inflammatory LG but to a lesser extent than VEGFR-3. More important, we reveal that there is a discrete time window for therapeutic intervention of corneal inflammatory LG. We show that a combined blockade of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 suppresses both early- and middle-stage LG while demonstrating no effect on late-stage LG. Close correlation between the timing and outcomes of the treatment is also defined. It is hoped that our results will provide a useful guide for understanding of the LG processes and the development of novel therapeutic protocols for LG-related diseases at various stages. MATERIALS AND METHODS Animals Six- to 8-week-old male BALB/c mice (Taconic Farms, Germantown, NY) were used for these experiments. All mice were treated in accordance with the ARVO Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research, and all protocols were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the University of California at Berkeley. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, April 2011, Vol. 52, No. 5 Copyright 2011 The Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, Inc. 2593
2 2594 Yuen et al. IOVS, April 2011, Vol. 52, No. 5 Mice were anesthetized using a mixture of ketamine, xylazine, and acepromazine (50 mg, 10 mg, and 1 mg/kg body weight, respectively) for each surgical procedure. Corneal Inflammatory Neovascularization and Pharmaceutical Interventions The standard suture placement model was used to induce inflammatory LG and HG, as described previously Briefly, three 11 0 nylon sutures (AROSurgical, Newport Beach, CA) were placed into the stroma of the central corneas without penetrating to the anterior chamber. Mice were randomized to receive systemic administration of neutralizing antibodies of VEGFR-2 (800 g; DC101) and/or VEGFR-3 (700 g; mf4 31C1; kindly provided by ImClone Systems Incorporated, Eli Lilly and Company, New York, NY), or their isotype controls twice a week for 2 weeks, as illustrated in Figure 1. The experiments were repeated at least twice with a total of 10 mice in each group of the study. Immunofluorescence Microscopic Assay The experiments were performed according to the standard protocol. 24,26 28 Briefly, freshly excised corneas were fixed in acetone for immunofluorescent staining. Nonspecific staining was blocked with donkey serum (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories Inc., West Grove, PA). The samples were stained with purified rabbit anti-mouse LYVE-1 (Abcam, Cambridge, MA) overnight, visualized by a Cy3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit secondary antibody (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories Inc.). Samples were then covered with mounting medium (Vectashield; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and were examined with an epifluorescence microscope (AxioImager M1; Carl Zeiss AG, Göttingen, Germany), and digital images were taken (Axio- Vision version 4.8; Carl Zeiss AG). Vascular Quantification LG was graded using ImageJ software (developed by Wayne Rasband, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD; available at info.nih.gov/ij/index.html), as described previously. 26,28 Basically, the LG area was normalized to the total corneal area to obtain a percentage coverage score for each sample. The LG area refers to the fraction of the corneal area in which vessels were present, and the total corneal area was measured by outlining the innermost vessels of the limbal arcade. Additionally, corneal HG was examined by a slit lamp with an integrated digital camera system (SL-D4 and DC-3; Topcon Medical Systems, Tokyo, Japan) and was graded according to the standard protocol, as described previously. 27,29 Briefly, quantification was based on two primary parameters. One was the circumferential extent of 12 areas around the clock. A score of 1 was given to each area if the vessels were present in the sector. The other was the centripetal growth of the longest vascular frond in each area. A grade between 0 (no growth) and 2 (at suture site) was given to each area. Scores for each area were then summed to derive the final index (range, 0 24). Statistical Analysis Data are expressed as the mean SEM. The statistical significance of the difference between each group (n 10) was evaluated using the Mann-Whitney U test, and the comparison between groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA test statistical analysis software (Prism; GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA). P 0.05 was considered significant. RESULTS Both VEGFR-3 and VEGFR-2 Are Involved in Corneal Inflammatory LG We first set out to study whether VEGFR-2 is involved in suture-induced inflammatory LG in the cornea using VEGFR-3 as a reference control. To approach this, mice after suture placement (day 0) were randomized to receive systemic administration of VEGFR-2 or VEGFR-3 neutralizing antibodies or their isotype control antibodies twice a week for 2 weeks. Corneas were sampled by the end of the treatment for immunofluorescence microscopic assays. As shown in Figure 2, our results showed that single blockade of VEGFR-3 or VEGFR-2 suppressed LG in terms of the invasion area, indicating that both factors are involved in the process. Nevertheless, the effect of the VEGFR-2 blockade was less significant than that of the VEGFR-3 blockade. Suppresses Early-Stage LG We next investigated the effect of the combined blockade of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 on early-stage LG. To approach this, the experiments were preformed as described except that combined antibodies of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3, or their isotype control antibodies, were administered to the mice. As shown in Figures 3A and 3B (left panels), this combined blockade led to a significant reduction of corneal LG when the treatment started on day 0 of the suture placement. Suppresses Middle-Stage LG We next examined whether the combined blockade was also effective in inhibiting middle-stage LG, which mimics a patient s condition when the chance for emergent care has been missed and the cornea is already invaded by some vessels. To study this, the combined antibodies or their isotype controls were administered systemically twice a week for 2 weeks with the treatment started on day 7 after suture placement. At this time with the suture placement model, the cornea was already occupied by a certain degree of LG. 30 As shown in Figures 3A FIGURE 1. Schematic illustration of the experimental procedures. Briefly, three sutures were placed in the cornea, and mice were randomized to receive systemic administrations of the VEGFR-2 and/or VEGFR-3 neutralizing antibodies or their isotype controls twice a week for 2 weeks. For early, middle, and late intervention strategies, the treatment was started at postoperative day 0, 7, or 14, respectively. Corneas were sampled by the end of the treatment for immunofluorescence microscopic assays.
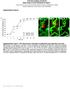
3 IOVS, April 2011, Vol. 52, No. 5 Critical Time Window for Intervening Lymphangiogenesis 2595 FIGURE 4. Effect of timing on treatment outcomes of LG. Summarized data from a series of studies showing a correlation between the timing and outcomes of treatment. Treatment efficacy decreased as the delay time increased. ***P n.s., not significant. Yields No Effect on Late-Stage LG FIGURE 2. VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 are both involved in corneal inflammatory LG. (A) Representative immunofluorescence micrographs showing that VEGFR-2 or VEGFR-3 single blockade significantly inhibited corneal LG. Treatment started at day 0 of the suture placement (early intervention). Scale bars, 100 m. (B) Summarized data from repetitive experiments showing the blockade of VEGFR-3 led to a more significant suppression of corneal LG than that of VEGFR-2. ***P and 3B (middle panels), surprisingly, it was found that the combined strategy was also effective in suppressing middlestage LG, though to a slightly less extent. To further investigate whether the combined blockade of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 can interfere with late-stage LG, we performed another experiment and started the treatment on day 14 after suture placement. Results from this study showed that this significant delay in treatment abolished the inhibitory effect of the intervention, as shown in Figures 3A and 3B (right panels). Taken together, our data from all three stage studies have revealed that timing is a crucial factor in determining the treatment outcome of corneal LG. This trend of decreased treatment efficacy with increased time delay is presented in Figure 4. FIGURE 3. Effect of combined treatment on early-, middle-, and late-stage LG. (A) Representative immunofluorescence micrographs demonstrating VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 combined blockade significantly inhibited both earlyand middle-stage but not late-stage LG. Scale bars, 100 m. (B) Summarized data from repetitive experiments. ***P 0.001; *P n.s., not significant. FIGURE 5. Effect of combined treatment on early-, middle-, and latestage HG. (A) Representative slit-lamp micrographs at the end of the study demonstrating VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 combined blockade only inhibited early HG. Scale bars, 200 m. (B) Summarized data from repetitive experiments. ***P n.s., not significant.
4 2596 Yuen et al. IOVS, April 2011, Vol. 52, No. 5 Suppresses Only Early-Stage HG Finally, we investigated whether corneal HG, a process also induced by inflammation, is affected by the combined treatment and how it differs from LG. As demonstrated in Figure 5, it was revealed that, in contrast to LG, HG responded to the combined intervention only at its early stage. No significant difference was observed for middle- or late-stage HG between the treatment and control groups. DISCUSSION In this study, we provide the first evidence showing that corneal inflammatory LG has a discrete time window for intervention therapy. At least two important conclusions can be drawn from our data: combined blockade of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 is effective in suppressing corneal LG at its early and middle stages; though it is important to initiate treatment as soon as possible, any interventions falling within the therapeutic time window should still be effective. However, a significant time delay will result in a loss of treatment efficacy. VEGFR-2 is an emerging factor for LG research. 12,22,23 Our data derived from the suture placement model are consistent with recent findings showing that corneal LG induced by VEGF-C or VEGF-D pellets is regulated by VEGFR-2. 12,22 Given that the doses of the growth factors used in the micropocket assays are much higher than physiological levels, results from the present study should more closely mimic patients conditions and thus provide additional data supporting VEGFR-2 interference as an adjunctive treatment for LG. Additionally, because the VEGFR-2 pathway also plays a major role in HG, 12,18 21 a process accompanies LG and contributes to tissue injury after myriad corneal insults, combined blockade of VEGFR-2 and another key lymphatic receptor, such as VEGFR-3, will maximize the treatment effect when significant inhibition on both processes is pursued. Moreover, this study also provides a new guideline for modulating corneal LG. Because LG is a progressive process, it is imperative to determine appropriate strategies for intervention therapy. Our finding that the combined blockade strategy is almost equally effective in suppressing early- and middlestage LG bears broad implications. Most important, it will help to define a suitable population for treatment, which is larger than previously assumed. As indicated by this study, this population should include patients not only immediately after corneal damage but also those who have missed the chance for emergent care and are still in the middle of LG processes. Although it is yet to be determined how the combined treatment suppresses middle-stage LG, it is plausible to hypothesize that the outcome is a net effect of a prevention of LG progression, a disturbance of LG maturation or induction of LG regression, or both. Further analysis of this exciting finding may, therefore, yield crucial insight into the mechanisms of various aspects of LG. Last, LG is a primary mediator of corneal transplant rejection. In the high-risk setting in which grafting is performed in the inflamed and lymphatic-rich beds, the rejection rate can be as high as 90%. 7,9,10 At this stage, there is little effective treatment. Unfortunately, many patients who are in need of corneal transplantation fall into this category. Our study indicates that we may be able to modify or normalize the high-risk grafting beds, particularly when they are still at the early or middle stages of LG, by the combination strategy to improve the survival rate of high-risk transplants; this warrants further investigation. Acknowledgments The authors thank Jeffrey LeDue and Steven Ruzin (University of California at Berkeley) for their excellent technical assistance with the immunofluorescence microscopic studies. References 1. Tammela T, Alitalo K. Lymphangiogenesis: molecular mechanisms and future promise. Cell. 2010;140: Cueni LN, Detmar M. The lymphatic system in health and disease. Lymphat Res Biol. 2008;6: Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV. Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature. 2005;438: Brown P. Lymphatic system: unlocking the drains. Nature. 2005; 436: Jackson DG. Biology of the lymphatic marker LYVE-1 and applications in research into lymphatic trafficking and lymphangiogenesis. APMIS. 2004;112: Witte MH, Bernas MJ, Martin CP, Witte CL. Lymphangiogenesis and lymphangiodysplasia: from molecular to clinical lymphology. Microsc Res Tech. 2001;55: Chen L. Ocular lymphatics: state-of-the-art review. Lymphology. 2009;42: Wuest TR, Carr DJ. VEGF-A expression by HSV-1-infected cells drives corneal lymphangiogenesis. J Exp Med. 2009;207: Cursiefen C, Chen L, Dana MR, Streilein JW. Corneal lymphangiogenesis: evidence, mechanisms, and implications for corneal transplant immunology. Cornea. 2003;22: Chong EM, Dana MR. Graft failure, IV: immunologic mechanisms of corneal transplant rejection. Int Ophthalmol. 2008;28: Dietrich T, Bock F, Yuen D, et al. Cutting edge: lymphatic vessels, not blood vessels, primarily mediate immune rejections after transplantation. J Immunol. 2010;184: Chung ES, Saban DR, Chauhan SK, Dana R. Regulation of blood vessel versus lymphatic vessel growth in the cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50: Chen L, Hamrah P, Cursiefen C, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 mediates induction of corneal alloimmunity. Nat Med. 2004;10: He Y, Kozaki K, Karpanen T, et al. Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94: Jeltsch M, Kaipainen A, Joukov V, et al. Hyperplasia of lymphatic vessels in VEGF-C transgenic mice. Science. 1997;276: Kubo H, Cao R, Brakenhielm E, Makinen T, Cao Y, Alitalo K. Blockade of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 signaling inhibits fibroblast growth factor-2-induced lymphangiogenesis in mouse cornea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2002;99: Veikkola T, Jussila L, Makinen T, et al. Signalling via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 is sufficient for lymphangiogenesis in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 2001;20: Cao Y, Linden P, Farnebo J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95: Witzenbichler B, Asahara T, Murohara T, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-c (VEGF-C/VEGF-2) promotes angiogenesis in the setting of tissue ischemia. Am J Pathol. 1998;153: Miller DW, Vosseler S, Mirancea N, et al. Rapid vessel regression, protease inhibition, and stromal normalization upon short-term vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 inhibition in skin carcinoma heterotransplants. Am J Pathol. 2005;167: Prewett M, Huber J, Li Y, et al. Antivascular endothelial growth factor receptor (fetal liver kinase 1) monoclonal antibody inhibits tumor angiogenesis and growth of several mouse and human tumors. Cancer Res. 1999;59: Chung ES, Chauhan SK, Jin Y, et al. Contribution of macrophages to angiogenesis induced by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3-specific ligands. Am J Pathol. 2009;175: Albuquerque RJ, Hayashi T, Cho WG, et al. Alternatively spliced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 is an essential en-
5 IOVS, April 2011, Vol. 52, No. 5 Critical Time Window for Intervening Lymphangiogenesis 2597 dogenous inhibitor of lymphatic vessel growth. Nat Med. 2009; 15: Chen L, Cursiefen C, Barabino S, Zhang Q, Dana MR. Novel expression and characterization of lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronate receptor 1 (LYVE-1) by conjunctival cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46: Cursiefen C, Chen L, Borges LP, et al. VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment. J Clin Invest. 2004;113: Zhang H, Hu X, Tse J, Tilahun F, Qiu M, Chen L. Spontaneous lymphatic vessel formation and regression in the murine cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52: Chen L, Huq S, Gardner H, de Fougerolles AR, Barabino S, Dana MR. Very late antigen 1 blockade markedly promotes survival of corneal allografts. Arch Ophthalmol. 2007;125: Ecoiffier T, Yuen D, Chen L. Differential distribution of blood and lymphatic vessels in the murine cornea. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51: Dana MR, Streilein JW. Loss and restoration of immune privilege in eyes with corneal neovascularization. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1996;37: Cursiefen C, Maruyama K, Jackson DG, Streilein JW, Kruse FE. Time course of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis after brief corneal inflammation. Cornea. 2006;25:
Lymphatic research signifies a new field of discovery and. Spontaneous Lymphatic Vessel Formation and Regression in the Murine Cornea.
 Cornea Spontaneous Lymphatic Vessel Formation and Regression in the Murine Cornea Hui Zhang, 1 Xuemei Hu, 2 Julie Tse, 1 Firehiwott Tilahun, 1 Mengsheng Qiu, 2 and Lu Chen 1 PURPOSE. Lymphatic dysfunctions
Cornea Spontaneous Lymphatic Vessel Formation and Regression in the Murine Cornea Hui Zhang, 1 Xuemei Hu, 2 Julie Tse, 1 Firehiwott Tilahun, 1 Mengsheng Qiu, 2 and Lu Chen 1 PURPOSE. Lymphatic dysfunctions
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease. Sunali Goyal MD
 Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal MD Mentor: Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Claes Dohlman Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea & Refractive Surgery Massachusetts
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal MD Mentor: Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Claes Dohlman Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea & Refractive Surgery Massachusetts
Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts
 Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
NOVEL CHARACTERIZATION OF bend.3 CELLS THAT EXPRESS LYMPHATIC VESSEL ENDOTHELIAL HYALURONAN RECEPTOR-1
 73 Lymphology 47 (2014) 73-81 NOVEL CHARACTERIZATION OF bend.3 CELLS THAT EXPRESS LYMPHATIC VESSEL ENDOTHELIAL HYALURONAN RECEPTOR-1 D. Yuen, R. Leu, J. Tse, S. Wang, L.L. Chen 2, L. Chen 1 1 Center for
73 Lymphology 47 (2014) 73-81 NOVEL CHARACTERIZATION OF bend.3 CELLS THAT EXPRESS LYMPHATIC VESSEL ENDOTHELIAL HYALURONAN RECEPTOR-1 D. Yuen, R. Leu, J. Tse, S. Wang, L.L. Chen 2, L. Chen 1 1 Center for
Chapter 10 Lymphatic Vessels in the Development of Tissue and Organ Rejection
 Chapter 10 Lymphatic Vessels in the Development of Tissue and Organ Rejection Deniz Hos and Claus Cursiefen Abstract The lymphatic vascular system amongst other tasks is critically involved in the regulation
Chapter 10 Lymphatic Vessels in the Development of Tissue and Organ Rejection Deniz Hos and Claus Cursiefen Abstract The lymphatic vascular system amongst other tasks is critically involved in the regulation
An in Vivo Method for Visualizing Flow Dynamics of Cells within Corneal Lymphatics
 An in Vivo Method for Visualizing Flow Dynamics of Cells within Corneal Lymphatics Beatrice Bourghardt Peebo, Per Fagerholm and Neil Lagali Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work,
An in Vivo Method for Visualizing Flow Dynamics of Cells within Corneal Lymphatics Beatrice Bourghardt Peebo, Per Fagerholm and Neil Lagali Linköping University Post Print N.B.: When citing this work,
Blood and lymphatic vessels are critical to organ and tissue
 Cornea The Maintenance of Lymphatic Vessels in the Cornea Is Dependent on the Presence of Macrophages Kazuichi Maruyama, 1 3 Toru Nakazawa, 4 Claus Cursiefen, 5 Yuko Maruyama, 1 Nico Van Rooijen, 3 Patricia
Cornea The Maintenance of Lymphatic Vessels in the Cornea Is Dependent on the Presence of Macrophages Kazuichi Maruyama, 1 3 Toru Nakazawa, 4 Claus Cursiefen, 5 Yuko Maruyama, 1 Nico Van Rooijen, 3 Patricia
LABORATORY SCIENCES. Promotion of Graft Survival by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Neutralization After High-Risk Corneal Transplantation
 LAORATORY SCIENCES Promotion of Graft Survival by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Neutralization After High-Risk Corneal Transplantation joern O. achmann, MD; Felix ock, MSc; Stanley J. Wiegand, PhD;
LAORATORY SCIENCES Promotion of Graft Survival by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Neutralization After High-Risk Corneal Transplantation joern O. achmann, MD; Felix ock, MSc; Stanley J. Wiegand, PhD;
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease.
 Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Corneal Lymphatics: Role in Ocular Inflammation as Inducer and. Responder of Adaptive Immunity
 Corneal Lymphatics: Role in Ocular Inflammation as Inducer and Responder of Adaptive Immunity The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Corneal Lymphatics: Role in Ocular Inflammation as Inducer and Responder of Adaptive Immunity The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Allograft rejection is a leading cause of corneal graft failure
 Cornea Effects of Topical and Subconjunctival Bevacizumab in High-Risk Corneal Transplant Survival Mohammad H. Dastjerdi, 1,2,3,4 Daniel R. Saban, 1,2,4 Andre Okanobo, 1,2,3 Nambi Nallasamy, 1,2 Zahra
Cornea Effects of Topical and Subconjunctival Bevacizumab in High-Risk Corneal Transplant Survival Mohammad H. Dastjerdi, 1,2,3,4 Daniel R. Saban, 1,2,4 Andre Okanobo, 1,2,3 Nambi Nallasamy, 1,2 Zahra
Lymphatic and Blood Vessels in the Eye: Physiology, Health, and Disease
 Journal of Ophthalmology Lymphatic and Blood Vessels in the Eye: Physiology, Health, and Disease Guest Editors: Yasuaki Hata, Ofra Benny, Claus Cursiefen, and Shintaro Nakao Lymphatic and Blood Vessels
Journal of Ophthalmology Lymphatic and Blood Vessels in the Eye: Physiology, Health, and Disease Guest Editors: Yasuaki Hata, Ofra Benny, Claus Cursiefen, and Shintaro Nakao Lymphatic and Blood Vessels
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Evidence of Corneal Lymphangiogenesis in Dry Eye Disease
 INIA SIENES Evidence of orneal ymphangiogenesis in Dry Eye Disease A Potential ink to Adaptive Immunity? Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, PhD; Jaafar El Annan, MD; Nambi Nallasamy, AB; Qiang Zhang, MD;
INIA SIENES Evidence of orneal ymphangiogenesis in Dry Eye Disease A Potential ink to Adaptive Immunity? Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, PhD; Jaafar El Annan, MD; Nambi Nallasamy, AB; Qiang Zhang, MD;
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 COMPARISON OF TOPICAL INTERLEUKIN-1 VS TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR-ALPHA BLOCKADE WITH CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY ON MURINE CORNEAL INFLAMMATION, NEOVASCULARIZATION, AND TRANSPLANT SURVIVAL (AN AMERICAN OPHTHALMOLOGICAL
COMPARISON OF TOPICAL INTERLEUKIN-1 VS TUMOR NECROSIS FACTOR-ALPHA BLOCKADE WITH CORTICOSTEROID THERAPY ON MURINE CORNEAL INFLAMMATION, NEOVASCULARIZATION, AND TRANSPLANT SURVIVAL (AN AMERICAN OPHTHALMOLOGICAL
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells
 CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
Cellular-Level Characterization of Lymph Vessels in Live, Unlabeled Corneas by In Vivo. Confocal Microscopy
 Cellular-Level Characterization of Lymph Vessels in Live, Unlabeled Corneas by In Vivo Confocal Microscopy Beatrice Bourghardt Peebo, Per Fagerholm, Catharina Traneus-Röckert and Neil Lagali Linköping
Cellular-Level Characterization of Lymph Vessels in Live, Unlabeled Corneas by In Vivo Confocal Microscopy Beatrice Bourghardt Peebo, Per Fagerholm, Catharina Traneus-Röckert and Neil Lagali Linköping
VEGF-C shown to have major role in Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD)
 ASX and Media release 9 May 2013 VEGF-C shown to have major role in Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Data presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2013 conference
ASX and Media release 9 May 2013 VEGF-C shown to have major role in Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Data presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2013 conference
Murine Orthotopic Corneal Transplantation in High-Risk Eyes
 Murine Orthotopic Corneal Transplantation in High-Risk Eyes Rejection Is Dictated Primarily by Weak Rather Than Strong Alloantigens Yoichiro Sano, Bruce R. Ksander, and]. Wayne Streilein Purpose. Using
Murine Orthotopic Corneal Transplantation in High-Risk Eyes Rejection Is Dictated Primarily by Weak Rather Than Strong Alloantigens Yoichiro Sano, Bruce R. Ksander, and]. Wayne Streilein Purpose. Using
LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE EMERGENCE OF MOLECULAR AND TRANSGENIC LYMPHOLOGY: WHAT DO WE (REALLY) KNOW SO FAR?
 1 Lymphology 39 (2006) 1-7 LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE EMERGENCE OF MOLECULAR AND TRANSGENIC LYMPHOLOGY: WHAT DO WE (REALLY) KNOW SO FAR? C. Suri Independent Biotechnology Consultant,* Tarrytown, New
1 Lymphology 39 (2006) 1-7 LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE EMERGENCE OF MOLECULAR AND TRANSGENIC LYMPHOLOGY: WHAT DO WE (REALLY) KNOW SO FAR? C. Suri Independent Biotechnology Consultant,* Tarrytown, New
Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in conjunctival malignant melanoma
 BJO Online First, published on July 23, 2009 as 10.1136/bjo.2008.147355 Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in conjunctival malignant melanoma Paul Zimmermann* 1, Tina Dietrich* 1,2, Felix Bock 1, Folkert
BJO Online First, published on July 23, 2009 as 10.1136/bjo.2008.147355 Tumor-associated lymphangiogenesis in conjunctival malignant melanoma Paul Zimmermann* 1, Tina Dietrich* 1,2, Felix Bock 1, Folkert
Apart from the extraocular conjunctiva and corneal limbus, Invasion of Lymphatic Vessels into the Eye after Open Globe Injuries. Anatomy and Pathology
 Anatomy and Pathology Invasion of Lymphatic Vessels into the Eye after Open Globe Injuries Julia M. Wessel, 1 Carmen Hofmann-Rummelt, 1 Friedrich E. Kruse, 1 Claus Cursiefen, 1,2 and Ludwig M. Heindl 1,2
Anatomy and Pathology Invasion of Lymphatic Vessels into the Eye after Open Globe Injuries Julia M. Wessel, 1 Carmen Hofmann-Rummelt, 1 Friedrich E. Kruse, 1 Claus Cursiefen, 1,2 and Ludwig M. Heindl 1,2
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 Morpholino Increases Graft Survival in a Murine Penetrating Keratoplasty Model
 Cornea Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 Morpholino Increases Graft Survival in a Murine Penetrating Keratoplasty Model Yang Kyung Cho, 1,2 Xiaohui Zhang, 1 Hironori Uehara, 1 Jason R. Young,
Cornea Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 1 Morpholino Increases Graft Survival in a Murine Penetrating Keratoplasty Model Yang Kyung Cho, 1,2 Xiaohui Zhang, 1 Hironori Uehara, 1 Jason R. Young,
Role of Th17 cells in the immunopathogenesis of dry eye disease
 Role of Th17 cells in the immunopathogenesis of dry eye disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Chauhan,
Role of Th17 cells in the immunopathogenesis of dry eye disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Chauhan,
Diploma Thesis. Lymphangiogenesis in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome. Denise Traxler-Weidenauer. Advisor: Priv.-Doz. Dr. Konrad HOETZENECKER, PhD
 Diploma Thesis Lymphangiogenesis in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Denise Traxler-Weidenauer Advisor: Priv.-Doz. Dr. Konrad HOETZENECKER, PhD Co-advisor: Dr. med. univ. Thomas SCHWEIGER University Clinic
Diploma Thesis Lymphangiogenesis in Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome Denise Traxler-Weidenauer Advisor: Priv.-Doz. Dr. Konrad HOETZENECKER, PhD Co-advisor: Dr. med. univ. Thomas SCHWEIGER University Clinic
LABORATORY SCIENCES. Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease
 ONLINE FIRST LABORATORY SIENES Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, DVM, PhD; Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Objective: To determine
ONLINE FIRST LABORATORY SIENES Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, DVM, PhD; Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Objective: To determine
Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target
 Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target Lecture Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Prof. Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences University of
Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target Lecture Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Prof. Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences University of
Tumour-associated lymphangiogenesis in conjunctival malignant melanoma
 1 Department of Ophthalmology, University Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany; 2 Department of Ophthalmology, University Medical Center Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany Correspondence to: Dr C Cursiefen,
1 Department of Ophthalmology, University Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany; 2 Department of Ophthalmology, University Medical Center Regensburg, Regensburg, Germany Correspondence to: Dr C Cursiefen,
LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TUMORS AND THE LYMPHATICS: WHAT MORE IS THERE TO KNOW?
 62 Lymphology 39 (2006) 62-68 LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TUMORS AND THE LYMPHATICS: WHAT MORE IS THERE TO KNOW? J.P. Sleeman Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut für Toxikologie
62 Lymphology 39 (2006) 62-68 LYMPHANGIOGENESIS REVIEWS THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TUMORS AND THE LYMPHATICS: WHAT MORE IS THERE TO KNOW? J.P. Sleeman Forschungszentrum Karlsruhe, Institut für Toxikologie
For personal use only
 ASX and Media release 6 April 211 Circadian s Inhibits Tumour Growth in Models of Lung, Ovarian and Prostate Cancer Data demonstrates efficacy of with other therapeutic agents in mouse models of lung,
ASX and Media release 6 April 211 Circadian s Inhibits Tumour Growth in Models of Lung, Ovarian and Prostate Cancer Data demonstrates efficacy of with other therapeutic agents in mouse models of lung,
Fate of Orthotopic Corneal Allografts in Eyes That Cannot Support Anterior Chamber-Associated Immune Deviation Induction
 Fate of Orthotopic Corneal Allografts in Eyes That Cannot Support Anterior Chamber-Associated Immune Deviation Induction Yoichiro Sano, Bruce R. Ksander, and]. Wayne Streilein Purpose. Corneal allografts
Fate of Orthotopic Corneal Allografts in Eyes That Cannot Support Anterior Chamber-Associated Immune Deviation Induction Yoichiro Sano, Bruce R. Ksander, and]. Wayne Streilein Purpose. Corneal allografts
Corneal Antigen-Presenting Cells: Diversity, Plasticity, and Disguise The Cogan Lecture
 Corneal Antigen-Presenting Cells: Diversity, Plasticity, and Disguise The Cogan Lecture The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Corneal Antigen-Presenting Cells: Diversity, Plasticity, and Disguise The Cogan Lecture The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Lymphatics and Lymphangiogenesis in the Eye
 Lymphatics and Lymphangiogenesis in the Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
Lymphatics and Lymphangiogenesis in the Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
Report. Immune Privilege Extended to Allogeneic Tumor Cells in the Vitreous Covity
 Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32, No. 1, January 1991 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Report Immune Privilege Extended to Allogeneic Tumor Cells in the
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol. 32, No. 1, January 1991 Copyright Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology Report Immune Privilege Extended to Allogeneic Tumor Cells in the
Supplemental Material
 Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Supplemental Material Supplementary Fig. 1. EETs stimulate primary tumor growth. a) Schematic presentation of genetic and pharmacological tools used to manipulate endogenous EET levels. b) Endothelial
Except for the extraocular conjunctiva, 1,2 the human eye is
 Intraocular Lymphangiogenesis in Malignant Melanomas of the Ciliary Body with Extraocular Extension Ludwig M. Heindl, 1 Tanja N. Hofmann, 1 Harald L. J. Knorr, 1 Carmen Rummelt, 1 Falk Schrödl, 2 Ursula
Intraocular Lymphangiogenesis in Malignant Melanomas of the Ciliary Body with Extraocular Extension Ludwig M. Heindl, 1 Tanja N. Hofmann, 1 Harald L. J. Knorr, 1 Carmen Rummelt, 1 Falk Schrödl, 2 Ursula
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb. by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral
 Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Supplementary Information Downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor and nuclear factor-κb by sirtuin 1 contributes to renoprotection in unilateral ureteral obstruction Shao-Yu Yang 1,2, Shuei-Liong
Blockade of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Inhibits Corneal Lymphangiogenesis METHODS
 Cornea Blockade of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Inhibits Corneal Lymphangiogenesis Deniz Hos, 1,2 Birgit Regenfuss, 2 Felix Bock, 2 Jasmine Onderka, 2 and Claus Cursiefen 1,2 PURPOSE. To analyze whether
Cornea Blockade of Insulin Receptor Substrate-1 Inhibits Corneal Lymphangiogenesis Deniz Hos, 1,2 Birgit Regenfuss, 2 Felix Bock, 2 Jasmine Onderka, 2 and Claus Cursiefen 1,2 PURPOSE. To analyze whether
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis
 Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Effect of Photodynamic Therapy and Anti-VEGF Therapy in the Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization : (FTIR) Study
 2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section : Engineering and Technology Effect of Photodynamic Therapy and Anti-VEGF Therapy in the Treatment of Corneal
2017 IJSRSET Volume 3 Issue 5 Print ISSN: 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section : Engineering and Technology Effect of Photodynamic Therapy and Anti-VEGF Therapy in the Treatment of Corneal
The Critical Role of Lymph Nodes in Corneal Alloimmunization and Graft Rejection
 The Critical Role of Lymph Nodes in Corneal Alloimmunization and Graft Rejection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
The Critical Role of Lymph Nodes in Corneal Alloimmunization and Graft Rejection The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
PTERYGIUM IS AN INVASIVE OCUlar
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Increasing Lymphatic Microvessel Density in Primary Pterygia Shiqi Ling, MD; Lingyi Liang, MD; Haotian Lin, MD; Weihua Li, MD; Jiangang Xu, MD Objective: To examine lymphatic microvessel
CLINICAL SCIENCES Increasing Lymphatic Microvessel Density in Primary Pterygia Shiqi Ling, MD; Lingyi Liang, MD; Haotian Lin, MD; Weihua Li, MD; Jiangang Xu, MD Objective: To examine lymphatic microvessel
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology. Robin Lorenz
 Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
Mucosal Immunology Sophomore Dental and Optometry Microbiology Section I: Immunology Robin Lorenz rlorenz@uab.edu Why do we Need to Understand How the Mucosal Immune System Works? The mucosa is the major
TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis
 Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0304 TITLE: Notch in Pathological Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Minji Kim CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Columbia University New York, NY 10032 REPORT
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Simultaneous in vivo imaging of blood and lymphatic vessel growth in Prox1 GFP/Flk1::myr mcherry mice
 Simultaneous in vivo imaging of blood and lymphatic vessel growth in Prox1 GFP/Flk1::myr mcherry mice Jimmy Zhu 1,, Jennifer Dugas-Ford 1,, Michael Chang 1, Patryk Purta 1, Kyu-Yeon Han 1, Young- Kwon
Simultaneous in vivo imaging of blood and lymphatic vessel growth in Prox1 GFP/Flk1::myr mcherry mice Jimmy Zhu 1,, Jennifer Dugas-Ford 1,, Michael Chang 1, Patryk Purta 1, Kyu-Yeon Han 1, Young- Kwon
Chapter 7 Conclusions
 VII-1 Chapter 7 Conclusions VII-2 The development of cell-based therapies ranging from well-established practices such as bone marrow transplant to next-generation strategies such as adoptive T-cell therapy
VII-1 Chapter 7 Conclusions VII-2 The development of cell-based therapies ranging from well-established practices such as bone marrow transplant to next-generation strategies such as adoptive T-cell therapy
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Dellinger
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0052 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Dellinger CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX 75390 REPORT DATE: February 2013 TYPE OF REPORT: Annual
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0052 TITLE: PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Dellinger CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas, TX 75390 REPORT DATE: February 2013 TYPE OF REPORT: Annual
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis
 The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer
 Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Assistant Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, Rajindra Hospital, Patiala, Punjab, India 3
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-85, p-issn: 79-86.Volume 6, Issue 7 Ver. X (July. 7), PP 5-5 www.iosrjournals.org A Randomized Controlled Prospective Study To Assess
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 79-85, p-issn: 79-86.Volume 6, Issue 7 Ver. X (July. 7), PP 5-5 www.iosrjournals.org A Randomized Controlled Prospective Study To Assess
FUCH S DYSTROPHY & CATARACT SURGERY TREATMENT ALGORITHM
 FUCH S DYSTROPHY & CATARACT SURGERY TREATMENT ALGORITHM ΙΟΑΝΝΙS Α. MALLIAS, MD, PHD Director of the Dept. of Ophthalmology, Mediterraneo Hospital, Glyfada, Athens, Greece Clinical Fellow in Cornea and
FUCH S DYSTROPHY & CATARACT SURGERY TREATMENT ALGORITHM ΙΟΑΝΝΙS Α. MALLIAS, MD, PHD Director of the Dept. of Ophthalmology, Mediterraneo Hospital, Glyfada, Athens, Greece Clinical Fellow in Cornea and
Assessment of Keratitis Damage in an Age Dependent Mouse Model Using Analytical Software
 Assessment of Keratitis Damage in an Age Dependent Mouse Model Using Analytical Software Quincy C. Moore III, PhD, 1 Emmanuel B. Olorunyomi, 1 Miles E. DuBose, 2 and Cleveland O. Lane Jr, PhD 1 1 Prairie
Assessment of Keratitis Damage in an Age Dependent Mouse Model Using Analytical Software Quincy C. Moore III, PhD, 1 Emmanuel B. Olorunyomi, 1 Miles E. DuBose, 2 and Cleveland O. Lane Jr, PhD 1 1 Prairie
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis
 Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
CHAPTER 18: Immune System
 CHAPTER 18: Immune System 1. What are four characteristics of the specific immune system? a. b. c. d. 2. List the two main types of defense mechanisms and briefly describe features of each. 3. Give examples
CHAPTER 18: Immune System 1. What are four characteristics of the specific immune system? a. b. c. d. 2. List the two main types of defense mechanisms and briefly describe features of each. 3. Give examples
Review of relationship between vascular endothelial growth factor family & receptors and tumor angiogenesis
 16 1 2004 2 hinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 16, No. 1 Feb., 2004 1004-0374 (2004) 01-0019-05 1 201203 2 200025 (vascular endothelial growth factor, ) (vascular permeability factor, VPF), -A -B -
16 1 2004 2 hinese Bulletin of Life Sciences Vol. 16, No. 1 Feb., 2004 1004-0374 (2004) 01-0019-05 1 201203 2 200025 (vascular endothelial growth factor, ) (vascular permeability factor, VPF), -A -B -
Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration
 Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
Braun et al. Supplementary Information 1 Supplementary Information Afferent lymph-derived T cells and dendritic cells use different CCR7-dependent routes for lymph node entry and intranodal migration Asolina
PATIENT INFORMATION ON CORNEAL GRAFT
 PATIENT INFORMATION ON CORNEAL GRAFT (TRANSPLANT) SURGERY M ANANDAN What is the cornea? The clear window of the eye approximately 0.5mm thick and 12mm across. It lies in front of the fluid filled anterior
PATIENT INFORMATION ON CORNEAL GRAFT (TRANSPLANT) SURGERY M ANANDAN What is the cornea? The clear window of the eye approximately 0.5mm thick and 12mm across. It lies in front of the fluid filled anterior
Draining Lymph Nodes of Corneal. Hosts Exhibit Evidence for Donor Major Histocompatibility Complex
 Draining Lymph Nodes of Corneal Transplant Hosts Exhibit Evidence for Donor Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class II positive Dendritic Cells Derived from MHC Class II negative Grafts The Harvard
Draining Lymph Nodes of Corneal Transplant Hosts Exhibit Evidence for Donor Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class II positive Dendritic Cells Derived from MHC Class II negative Grafts The Harvard
Matrix metalloproteinase 14 participates in corneal lymphangiogenesis through the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling pathway
 2120 Matrix metalloproteinase 14 participates in corneal lymphangiogenesis through the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling pathway HAI TAO DU and PING LIU Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital
2120 Matrix metalloproteinase 14 participates in corneal lymphangiogenesis through the VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling pathway HAI TAO DU and PING LIU Department of Ophthalmology, The First Affiliated Hospital
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS. (A) Workflow for tumor cell line derivation and orthotopic implantation.
 SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r
 Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 516 HYPERPLASIA OF THE ANTERIOR LAYER OF THE IRIS STROMA*t BY MALCOLM N. LUXENBERG From the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Miami School
Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino
 Supplementary Materials Online: Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino synovitis grade and Mankin cartilage pathology scale Hemophilic synovitis was graded 0-10
Supplementary Materials Online: Supplemental Methods: Histopathology scoring of individual components of Valentino synovitis grade and Mankin cartilage pathology scale Hemophilic synovitis was graded 0-10
Intraocular Pressure Reconstitution and Maintenance for Cadaveric Porcine Eyes in Simulated Wet-Lab Experience
 Intraocular Pressure Reconstitution and Maintenance for Cadaveric Porcine Eyes in Simulated Wet-Lab Experience Francesca Marie Giliberti, MD Julia Marie Parisi Fullerton, MD Virginia Commonwealth University
Intraocular Pressure Reconstitution and Maintenance for Cadaveric Porcine Eyes in Simulated Wet-Lab Experience Francesca Marie Giliberti, MD Julia Marie Parisi Fullerton, MD Virginia Commonwealth University
Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
 Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
 Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Hiroki Fujita, Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, Soh Futagami and Takashi Tokoro Department of Visual Science, Tokyo Medical
Case Report: Indocyanine Green Dye Leakage from Retinal Artery in Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion Hiroki Fujita, Kyoko Ohno-Matsui, Soh Futagami and Takashi Tokoro Department of Visual Science, Tokyo Medical
Clinical Study Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization Using Anti-VEGF Bevacizumab
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2014, Article ID 178132, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/178132 Clinical Study Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization Using Anti-VEGF
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2014, Article ID 178132, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/178132 Clinical Study Treatment of Corneal Neovascularization Using Anti-VEGF
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty - Techniques
 Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty - Techniques SHERAZ DAYA MD FACP FACS FRCS(Ed) FRCOphth Financial Disclosure Company Code 1. Abbott Medical Optics Inc. S 2. Bausch + Lomb C,L 3. Carl Zeiss Meditec
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty - Techniques SHERAZ DAYA MD FACP FACS FRCS(Ed) FRCOphth Financial Disclosure Company Code 1. Abbott Medical Optics Inc. S 2. Bausch + Lomb C,L 3. Carl Zeiss Meditec
Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Cytological Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid on Wound Healing Following Extraction Gocmen Gokhan 1 *, Gonul O 1, Oktay NS 2, Pisiriciler R 2 and Goker
LYMPHANGIOGENESIS AND CANCER METASTASIS
 LYMPHANGIOGENESIS AND CANCER METASTASIS Steven A. Stacker*, Marc G. Achen*, Lotta Jussila, Megan E. Baldwin* and Kari Alitalo Lymphatic vessels are important for the spread of solid tumours, but the mechanisms
LYMPHANGIOGENESIS AND CANCER METASTASIS Steven A. Stacker*, Marc G. Achen*, Lotta Jussila, Megan E. Baldwin* and Kari Alitalo Lymphatic vessels are important for the spread of solid tumours, but the mechanisms
Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer
 Pathophysiology 17 (2010) 229 251 Review Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer Sophia Ran, Lisa Volk, Kelly Hall, Michael J. Flister Department of Medical Microbiology, Immunology
Pathophysiology 17 (2010) 229 251 Review Lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis in breast cancer Sophia Ran, Lisa Volk, Kelly Hall, Michael J. Flister Department of Medical Microbiology, Immunology
Therapeutic Efficacy of Topical Epigallocatechin Gallate in Murine Dry Eye
 Therapeutic Efficacy of Topical Epigallocatechin Gallate in Murine Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Therapeutic Efficacy of Topical Epigallocatechin Gallate in Murine Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
LABORATORY SCIENCES. Suppression of Inflammatory Corneal Lymphangiogenesis by Application of Topical Corticosteroids
 LABORATORY SCIENCES Suppression of Inflammatory Corneal Lymphangiogenesis by Application of Topical Corticosteroids Deniz Hos, MD; Daniel R. Saban, PhD; Felix Bock, PhD; Birgit Regenfuss, PhD; Jasmine
LABORATORY SCIENCES Suppression of Inflammatory Corneal Lymphangiogenesis by Application of Topical Corticosteroids Deniz Hos, MD; Daniel R. Saban, PhD; Felix Bock, PhD; Birgit Regenfuss, PhD; Jasmine
T cell development October 28, Dan Stetson
 T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
T cell development October 28, 2016 Dan Stetson stetson@uw.edu 441 Lecture #13 Slide 1 of 29 Three lectures on T cells (Chapters 8, 9) Part 1 (Today): T cell development in the thymus Chapter 8, pages
Ocular and periocular trauma
 Ocular and periocular trauma No financial disclosures. Tina Rutar M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Ophthalmology and Pediatrics Director, Visual Center for the Child University of California San Francisco
Ocular and periocular trauma No financial disclosures. Tina Rutar M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Ophthalmology and Pediatrics Director, Visual Center for the Child University of California San Francisco
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0367 TITLE: Regulatory role of the NF-kB pathway in lymphangiogenesis and breast cancer mestatasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Flister CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Southern
AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0367 TITLE: Regulatory role of the NF-kB pathway in lymphangiogenesis and breast cancer mestatasis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Michael Flister CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Southern
Sclerokeratoplasty David S. Chu, M.D. Cases
 Sclerokeratoplasty David S. Chu, M.D. Cases Case 1 40 year-old female from Peru presented to our Service with inflamed OS for 2 months duration. Her symptoms began as red painful OS, which progressively
Sclerokeratoplasty David S. Chu, M.D. Cases Case 1 40 year-old female from Peru presented to our Service with inflamed OS for 2 months duration. Her symptoms began as red painful OS, which progressively
Fuchs Dystrophy: A New Paradigm in Diagnosis and Treatment. Disclosure. Fuchs Dystrophy. David G. Hwang, MD, FACS. Genetics and Pathogenesis
 Fuchs Dystrophy: A New Paradigm in Diagnosis and Treatment David G. Hwang, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Kimura Endowed Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea Service and Refractive Surgery Services
Fuchs Dystrophy: A New Paradigm in Diagnosis and Treatment David G. Hwang, MD, FACS Professor and Vice Chair Kimura Endowed Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea Service and Refractive Surgery Services
Key Words: NSCLC, angiogenesis, b-fgf, FGF2, FGFR, stroma
 TITLE PAGE Prognostic Impact of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 in NSCLC: Co-Expression with VEGFR-3 and PDGF-B Predicts Poor Survival. Tom Donnem 1,2 Khalid Al-Shibli 3,4 Samer Al-Saad 3,5 Lill-Tove Busund
TITLE PAGE Prognostic Impact of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 in NSCLC: Co-Expression with VEGFR-3 and PDGF-B Predicts Poor Survival. Tom Donnem 1,2 Khalid Al-Shibli 3,4 Samer Al-Saad 3,5 Lill-Tove Busund
Case History. Slit lamp exam: Clinical Pearls in the Management of Iritis. 2- injection: Irregular SPK and staining AC: grade 3 cell & flare
 Clinical Pearls in the Management of Iritis Paul Karpecki, OD, FAAO Corneal Services and Ocular Disease Research Koffler Vision Group-Lexington, KY 68 y.o. Caucasian female Complains of photophobia and
Clinical Pearls in the Management of Iritis Paul Karpecki, OD, FAAO Corneal Services and Ocular Disease Research Koffler Vision Group-Lexington, KY 68 y.o. Caucasian female Complains of photophobia and
Lymphatic Network in Cancer and Some Chemical Observations
 Lymphatic Network in Cancer and Some Chemical Observations DORINA CORICOVAC 1, HORIA PLES 2, IULIA PINZARU 1, DANIELA IONESCU 1 * 1 Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy,
Lymphatic Network in Cancer and Some Chemical Observations DORINA CORICOVAC 1, HORIA PLES 2, IULIA PINZARU 1, DANIELA IONESCU 1 * 1 Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy,
Ocular Studies of EMF Exposure at the MMW M. Kojima 1,2,3), Y. Suzuki 4)
 Ocular Studies of EMF Exposure at the MMW M. Kojima 1,2,3), Y. Suzuki 4) 1. Division of Vision Research for Environmental Health, Medical Research Institute, Kanazawa Medical University 2. Department of
Ocular Studies of EMF Exposure at the MMW M. Kojima 1,2,3), Y. Suzuki 4) 1. Division of Vision Research for Environmental Health, Medical Research Institute, Kanazawa Medical University 2. Department of
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Impact of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Coexpression with VEGFR-3 and PDGF-B Predicts Poor Survival Tom Donnem, MD,* Khalid Al-Shibli, MD, Samer Al-Saad,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prognostic Impact of Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Coexpression with VEGFR-3 and PDGF-B Predicts Poor Survival Tom Donnem, MD,* Khalid Al-Shibli, MD, Samer Al-Saad,
The development of T cells in the thymus
 T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
T cells rearrange their receptors in the thymus whereas B cells do so in the bone marrow. The development of T cells in the thymus The lobular/cellular organization of the thymus Immature cells are called
Research Article Conjunctival Lymphangiogenesis Was Associated with the Degree of Aggression in Substantial Recurrent Pterygia
 Ophthalmology Volume 1, Article ID 1595, pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/1/1595 Research Article Conjunctival Lymphangiogenesis Was Associated with the Degree of Aggression in Substantial Recurrent Pterygia
Ophthalmology Volume 1, Article ID 1595, pages http://dx.doi.org/.1155/1/1595 Research Article Conjunctival Lymphangiogenesis Was Associated with the Degree of Aggression in Substantial Recurrent Pterygia
People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes
 People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes IMPERFECTLY MOVING TOWARDS & FAINTING GOATS Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 1 Review PARTNERING WITH SCIENCE: New Hope for the Effective Treatment
People Living with And Inspired by Diabetes IMPERFECTLY MOVING TOWARDS & FAINTING GOATS Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 Vol. 2 No. 2 Fall 2016 1 Review PARTNERING WITH SCIENCE: New Hope for the Effective Treatment
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A Case Report of Recurrent Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma M Zhao 1, W Lin 2 *, Z Liu 2 ABSTRACT
 A Case Report of Recurrent Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma M Zhao 1, W Lin 2 *, Z Liu 2 ABSTRACT A case of recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva is presented here. A 13-yearsold male
A Case Report of Recurrent Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma M Zhao 1, W Lin 2 *, Z Liu 2 ABSTRACT A case of recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva is presented here. A 13-yearsold male
Medicine HUMAN AMNIOTIC MEMBRANE FOR ACUTE SEVERE ALKALI BURN % VISUAL ACUITY RECOVERY
 Research and Science Today No. 2(10)/2015 Medicine HUMAN AMNIOTIC MEMBRANE FOR ACUTE SEVERE ALKALI BURN - 100 % VISUAL ACUITY RECOVERY Alina GHEORGHE * Monica Daniela POP 1 Calin- Petru TATARU 2 Constantin
Research and Science Today No. 2(10)/2015 Medicine HUMAN AMNIOTIC MEMBRANE FOR ACUTE SEVERE ALKALI BURN - 100 % VISUAL ACUITY RECOVERY Alina GHEORGHE * Monica Daniela POP 1 Calin- Petru TATARU 2 Constantin
Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid
 Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid Roland K. Herrmann,* W. Gerald Robison, Jr.,* and John G. Dieri-)- The effects of vitamin E and A deficiencies on the
Deficiencies of Vitamins E and A in the Rat: Lipofuscin Accumulation in the Choroid Roland K. Herrmann,* W. Gerald Robison, Jr.,* and John G. Dieri-)- The effects of vitamin E and A deficiencies on the
Transgenic Mouse Models of Corneal Neovascularization: New Perspectives for Angiogenesis Research
 Reviews Transgenic Mouse Models of Corneal Neovascularization: New Perspectives for Angiogenesis Research Jakob Nikolas Kather and Jens Kroll Department of Vascular Biology and Tumor Angiogenesis, Center
Reviews Transgenic Mouse Models of Corneal Neovascularization: New Perspectives for Angiogenesis Research Jakob Nikolas Kather and Jens Kroll Department of Vascular Biology and Tumor Angiogenesis, Center
HEM- AND LYMPH- ANGIOGENESIS IN CANCER METASTASIS
 From THE DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY, TUMOR AND CELL BIOLOGY Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden HEM- AND LYMPH- ANGIOGENESIS IN CANCER METASTASIS Hong Ji Stockholm 2013 All previously published papers
From THE DEPARTMENT OF MICROBIOLOGY, TUMOR AND CELL BIOLOGY Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden HEM- AND LYMPH- ANGIOGENESIS IN CANCER METASTASIS Hong Ji Stockholm 2013 All previously published papers
Effect of tear deficiency on the course of endotoxin-induced keratitis
 UDC 617.713-002.-092.9:617.764.1-008.811.4 Effect of tear deficiency on the course of endotoxin-induced keratitis T.B. Gaydamaka, 1 S.Ya. Rafalyuk 2 1 Filatov Eye Disease and Tissue Therapy Institute 2
UDC 617.713-002.-092.9:617.764.1-008.811.4 Effect of tear deficiency on the course of endotoxin-induced keratitis T.B. Gaydamaka, 1 S.Ya. Rafalyuk 2 1 Filatov Eye Disease and Tissue Therapy Institute 2
Lamellar Keratoplasty for the Treatment of Fungal Keratitis
 Cornea 21(1): 33 37, 2002. 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Lamellar Keratoplasty for the Treatment of Fungal Keratitis Lixin Xie, M.D., Weiyun Shi, M.D., Zhaosheng Liu, M.D., and
Cornea 21(1): 33 37, 2002. 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Lamellar Keratoplasty for the Treatment of Fungal Keratitis Lixin Xie, M.D., Weiyun Shi, M.D., Zhaosheng Liu, M.D., and
